|
Apterygota
The name Apterygota is sometimes applied to a subclass of small, agile insects, distinguished from other insects by their lack of wings in the present and in their evolutionary history; notable examples are the silverfish, the firebrat, and the jumping bristletails. Their first known occurrence in the fossil record is during the Devonian period, 417–354 million years ago. The group Apterygota is not a clade; it is paraphyletic, and not universally recognized. As defined, the group contains two separate clades of wingless insects: Archaeognatha comprises jumping bristletails, while Zygentoma comprises silverfish and firebrats. The Zygentoma are in the clade Dicondylia with winged insects, a clade that includes all other insects, while Archaeognatha is sister to this lineage.A. Blanke, M. Koch, B. Wipfler, F. Wilde, B. Misof (2014) Head morphology of ''Tricholepidion gertschi'' indicates monophyletic Zygentoma. Frontiers in Zoology 11:16 doi:10.1186/1742-9994-11-16 The nymphs (y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
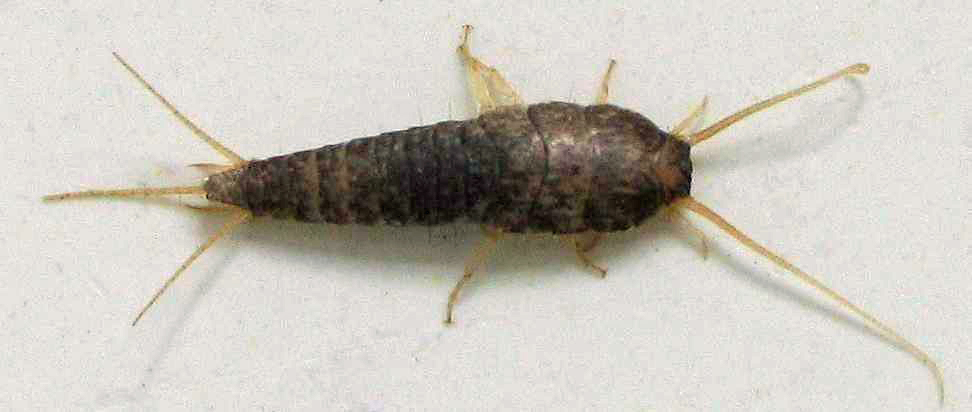
Silverfish
The silverfish (''Lepisma saccharinum'') is a species of small, primitive, wingless insect in the order Zygentoma (formerly Thysanura). Its common name derives from the insect's silvery light grey colour, combined with the fish-like appearance of its movements. The scientific name (''L. saccharinum'') indicates that the silverfish's diet consists of carbohydrates such as sugar or starches. While the common name ''silverfish'' is used throughout the global literature to refer to various species of Zygentoma, the Entomological Society of America restricts use of the term solely for ''Lepisma saccharinum''. Description The silverfish is a nocturnal insect typically long. Its abdomen tapers at the end, giving it a fish-like appearance. The newly hatched are whitish, but develop a greyish hue and metallic shine as they get older. It has two long cerci and one terminal filament at the tip of the abdomen between the cerci. It also has two small compound eyes, although other mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
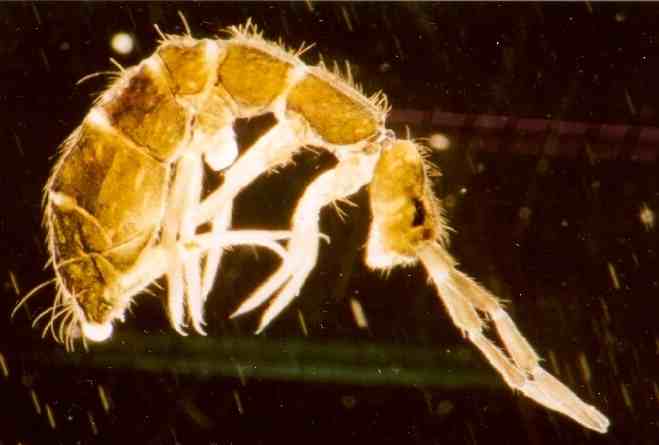
Archaeognatha
The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the same time as the arachnids. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils (the latter including body imprints and trackways) in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia. Until the late 20th century the suborders Zygentoma and Archaeognatha comprised the order Thysanura; both orders possess three-pronged tails comprising two lateral cerci and a medial epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. Of the three organs, the appendix dorsalis is considerably longer than the two cerci; in this the Archaeognatha differ from the Zygentoma, in which the three organs are subequal in length. In the late 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thysanura
Thysanura is the now deprecated name of what was, for over a century, recognised as an order in the class Insecta. The two constituent groups within the former order, the Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and the Zygentoma (silverfish and firebrats), share several characteristics, such as of having three long caudal filaments, the lateral ones being the cerci, while the one between (telson) is a medial cerciform appendage, specifically an epiproct. They are also both wingless, and have bodies covered with fine scales, rather like the scales of the practically unrelated Lepidoptera. In the late 20th century, it was recognized that the two suborders were not sister taxa, therefore Thysanura was paraphyletic, and the two suborders were each raised to the status of an independent monophyletic order, with Archaeognatha sister taxon to the Dicondylia, including the Zygentoma. Although the group Thysanura is no longer recognized, the name still appears in some published material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygentoma
Zygentoma are an order in the class Insecta, and consist of about 550 known species. The Zygentoma include the so-called silverfish or fishmoths, and the firebrats. A conspicuous feature of the order are the three long caudal filaments. The two lateral filaments are cerci, and the medial one is an epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. In this they resemble the Archaeognatha, although the cerci of Zygentoma, unlike in the latter order, are nearly as long as the epiproct. Until the late twentieth century the Zygentoma were regarded as a suborder of the Thysanura, until it was recognized that the order Thysanura was paraphyletic, thus raising the two suborders to the status of independent monophyletic orders, with Archaeognatha as sister group to the Dicondylia, including the Zygentoma. Etymology The name "Zygentoma" is derived from the Greek ('), in context meaning "yoke" or "bridge"; and ('), "insects", literally "cut into" because of the segmented anatomy of typical insects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entognatha
The Entognatha are a class of wingless and ametabolous arthropods, which, together with the insects, makes up the subphylum Hexapoda. Their mouthparts are entognathous, meaning that they are retracted within the head, unlike the insects. Entognatha are apterous, meaning that they lack wings. The class contains three orders: Collembola (springtails, 9000 species), Diplura (“two-tail”, 1000 species) and Protura (“first-tail”, 800 species). These three groups were historically united with the now-obsolete order Thysanura to form the class Apterygota, but it has since been recognized that the hexapodous condition of these animals has evolved independently from that of insects, and independently ''within'' each order. The orders may not be closely related, and Entognatha is now considered to be a polyphyletic group. Morphology These minute arthropods are apterous, unlike some orders of insects that have lost their wings secondarily (but are derived from winged ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics (synapomorphies'')'' that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a ' grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplura
The order Diplura ("two-pronged bristletails") is one of three orders of non-insect hexapods within the class Entognatha (alongside Collembola (springtails) and Protura). The name "diplura", or "two tails", refers to the characteristic pair of caudal appendages or filaments at the terminal end of the body. Around 800 species of diplurans have been described, of which around 170 occur in North America and 12 in Great Britain. Anatomy Diplurans are typically long, with most falling between . However, some species of '' Japyx'' may reach . They have no eyes and, apart from the darkened cerci in some species, they are unpigmented. Diplurans have long antennae with 10 or more bead-like segments projecting forward from the head. The abdomens of diplurans bear eversible vesicles, which seem to absorb moisture from the environment and help with the animal's water balance. The body segments themselves may display several types of setae, or scales and setae. Diplurans possess a cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protura
The Protura, or proturans, and sometimes nicknamed coneheads, are very small (0.6-1.5mm long), soil-dwelling animals, so inconspicuous they were not noticed until the 20th century. The Protura constitute an order of hexapods that were previously regarded as insects, and sometimes treated as a class in their own right. Some evidence indicates the Protura are basal to all other hexapods, although not all researchers consider them Hexapoda, rendering the monophyly of Hexapoda unsettled. Uniquely among hexapods, proturans show anamorphic development, whereby body segments are added during moults. There are close to 800 species, described in seven families. Nearly 300 species are contained in a single genus, '' Eosentomon''. Morphology Proturans have no eyes, wings, or antennae, and, lacking pigmentation, are usually white or pale brown. The sensory function of the antennae is fulfilled by the first of three pairs of five-segmented legs, which are held up, pointing forward and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores may additionally contain nourishment for the female, in which case it is called a nuptial gift, as in the instance of bush crickets. In the case of the toxic moth '' Utetheisa ornatrix'', the spermatophore includes sperm, nutrients, and pyrrolizidine alkaloids which prevent predation because it is poisonous to most organisms. However, in some species such as the Edith's checkerspot butterfly, the "gift" provides little nutrient value. The weight of the spermatophore transferred at mating has little effect on female reproductive output. Arthropods Spermatophores are the norm in arachnids and several soil arthropods. In various insects, such as bush crickets, the spermatophore is often surrounded by a proteinaceous spermatophyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collembola
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to all insects, which have external mouthparts. Collembolans are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from the ancient Greek "glue" and "peg"; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Some DNA sequence studies suggest that Collembola represent a separate evolutionary line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercus
Cerci (singular cercus) are paired appendages on the rear-most segments of many arthropods, including insects and symphylans. Many forms of cerci serve as sensory organs, but some serve as pinching weapons or as organs of copulation. In many insects, they simply may be functionless vestigial structures. In basal arthropods, such as silverfish, the cerci originate from the eleventh abdominal segment. As segment eleven is reduced or absent in the majority of arthropods, in such cases, the cerci emerge from the tenth abdominal segment. It is not clear that other structures so named are homologous. In the Symphyla they are associated with spinnerets. Morphology and functions Most cerci are segmented and jointed, or filiform (threadlike), but some take very different forms. Some Diplura, in particular ''Japyx'' species, have large, stout forcipate (pincer-like) cerci that they use in capturing their prey. The Dermaptera, or earwigs, are well known for the forcipate cerci that mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)

_(10353381334).jpg)

.jpg)