Archaeognatha on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various
 Further unusual features are that the abdominal sternites are each composed of three
Further unusual features are that the abdominal sternites are each composed of three
9th Dresden Meeting on Insect Phylogeny 2019
/ref> After fertilization she lays a batch of around 30 eggs in a suitable crevice. The young resemble the adults, and take up to two years to reach sexual maturity, depending on the species and conditions such as temperature and available food. Unlike most insects, the adults continue to moult after reaching adulthood, and typically mate once at each
Archaeognatha
- Tree of Life Web Project
Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State College Department of Entomology {{DEFAULTSORT:Archaeognatha Insect orders Insects of the Arctic Middle Devonian first appearances
common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often con ...
s such as jumping bristletails. Among extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
period at about the same time as the arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, wh ...
s. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils
A trace fossil, also called an ichnofossil (; ), is a fossil record of biological activity by lifeforms, but not the preserved remains of the organism itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, which are the fossilized remains of part ...
(the latter including body imprints and trackways) in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia.
Until the late 20th century the suborders Zygentoma
Zygentoma are an order in the class Insecta, and consist of about 550 known species. The Zygentoma include the so-called silverfish or fishmoths, and the firebrats. A conspicuous feature of the order are the three long caudal filaments. The t ...
and Archaeognatha comprised the order Thysanura; both orders possess three-pronged tails comprising two lateral cerci and a medial epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. Of the three organs, the appendix dorsalis is considerably longer than the two cerci; in this the Archaeognatha differ from the Zygentoma, in which the three organs are subequal in length. In the late 20th century, it was recognized that the order Thysanura was paraphyletic, thus the two suborders were each raised to the status of an independent monophyletic order, with Archaeognatha sister taxon to the Dicondylia, including the Zygentoma.
The order Archaeognatha is cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitan may refer to:
Internationalism
* World citizen, one who eschews traditional geopolitical divisions derived from national citizenship
* Cosmopolitanism, the idea that all of humanity belongs to a single moral community
* Cosmopolitan ...
; it includes roughly 500 species in two families. No species is currently evaluated as being at conservation risk.
Description
Archaeognatha are small insects with elongated bodies and backs that are arched, especially over thethorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
. Their abdomen ends in three long tail-like structures, of which the lateral two are cerci, while the medial filament, which is longest, is an epiproct. The tenth abdominal segment is reduced. The antennae are flexible. The two large compound eye
A compound eye is a Eye, visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidium, ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens (anatomy), lens, and p ...
s meet at the top of the head, and there are three ocelli
A simple eye or ocellus (sometimes called a pigment pit) is a form of eye or an optical arrangement which has a single lens without the sort of elaborate retina that occurs in most vertebrates. These eyes are called "simple" to distinguish the ...
. The mouthparts are partly retractable, with simple chewing mandibles and seven-segmented maxillary palps which are commonly longer than the legs.
Unlike other insect orders, they do not have olfactory receptor-coreceptors ( Orco), which have either been lost or were never present in the first place.
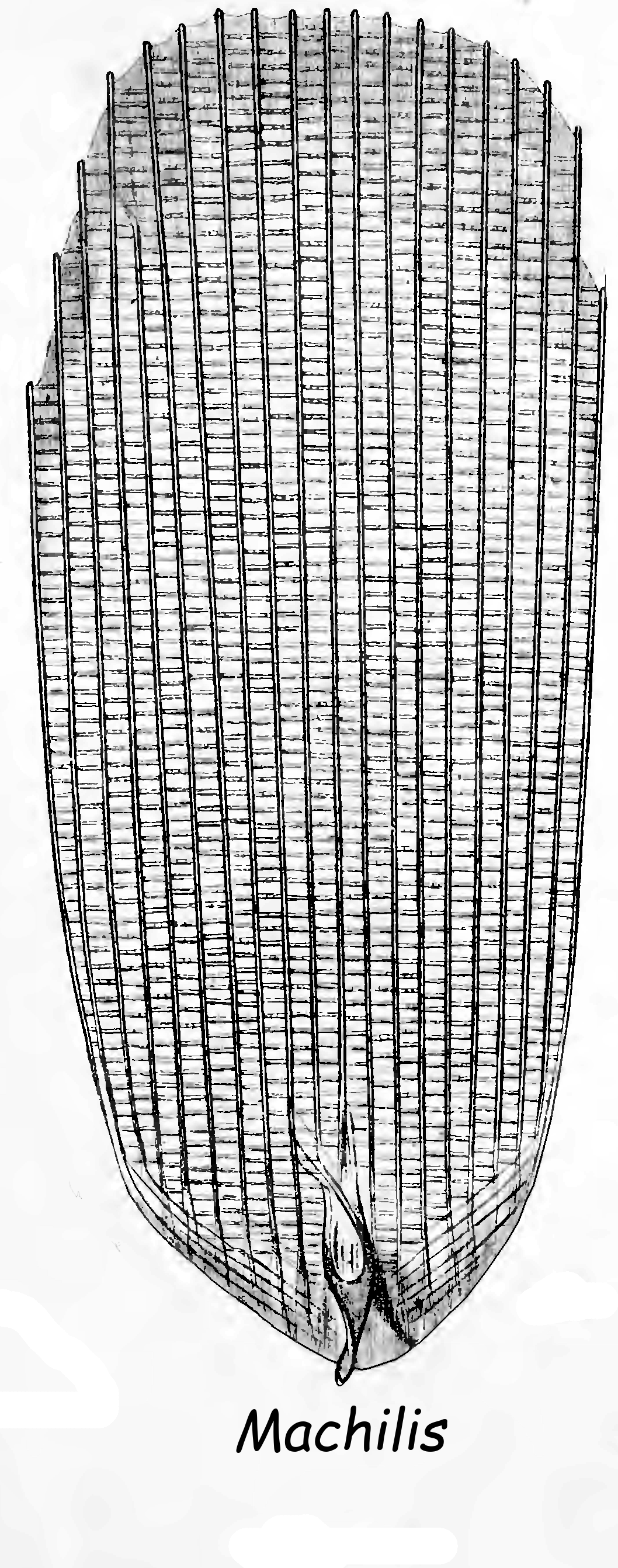
Archaeognatha differ from Zygentoma in various ways, such as their relatively small head, their bodies being compressed laterally (from side to side) instead of flattened dorsiventrally, and in their being able to use their tails to spring up to into the air if disturbed. They have eight pairs of short appendages called styli on abdominal segments 2 to 9. Family Machilidae is also unique among insects in possessing small muscleless styli on the second and third thoracic legs, but are absent on the second pair of thoracic legs in some genera. Similar stylets on the legs are absent in family Meinertellidae. They have one or two pairs of eversible membranous vesicles on the underside of abdominal segments 1 to 7, which are used to absorb water and assisting with molting. There are nine pairs of spiracles; two pairs on the thorax, and seven pairs on abdominal segments 2 to 8. The pair of spiracles on the first abdominal segment has been lost.
 Further unusual features are that the abdominal sternites are each composed of three
Further unusual features are that the abdominal sternites are each composed of three sclerite
A sclerite (Greek language, Greek , ', meaning "hardness, hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instea ...
s, and they cement themselves to the substrate before molting, often using their own feces as glue. The body is covered with readily detached scales, that make the animals difficult to grip and also may protect the exoskeleton from abrasion. The thin exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
offers little protection against dehydration, and they accordingly must remain in moist air, such as in cool, damp situations under stones or bark.
Etymology
The name Archaeognatha is derived from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, meaning 'ancient', and , meaning ' jaw'. This refers to the articulation of the mandibles, which are different from those of other insects. It was originally believed that Archaeognatha possessed a single phylogenetically primitive condyle each (thus the name "Monocondylia"), where all more derived insects have two, but this has since been shown to be incorrect; all insects, including Archaeognatha, have dicondylic mandibles, but archaeognaths possess two articulations that are homologous to those in other insects, though slightly different.
An alternative name, Microcoryphia, comes from the Greek , and , which in context means 'head'.
Taxonomy
Biology
Archaeognatha occur in a wide range ofhabitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
s. While most species live in moist soil, others have adapted to chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant plant community, community found primarily in California, southern Oregon, and northern Baja California. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intens ...
, and even sandy deserts. They feed primarily on algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
, but also lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
s, moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
es, or decaying organic detritus
In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Reminera ...
.
Three types of mating behavior are known. In some species the male spins a silk thread (carrier thread) stretched out on the ground. On the thread there are droplets of sperm which the female will take up when her ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
makes contact. In others a packet of sperm (spermatophore
A spermatophore, from Ancient Greek σπέρμα (''spérma''), meaning "seed", and -φόρος (''-phóros''), meaning "bearing", or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especiall ...
) is deposited on the top of a short stalk. If a female takes up the sperm or not is often random, but in many species the male will try to lead the female's genitals over the sperm during courtship. A more direct way of fertilization occurs in species of the genus Petrobius, where the male place a droplet of sperm directly on the female's ovipositor. One hypothesis is that the external genitals of insects started as structures specialized for water-uptake, which could reach deeper crevices than the coxal vesicles, and over time the female would use it to take up sperm from the ground instead of water./ref> After fertilization she lays a batch of around 30 eggs in a suitable crevice. The young resemble the adults, and take up to two years to reach sexual maturity, depending on the species and conditions such as temperature and available food. Unlike most insects, the adults continue to moult after reaching adulthood, and typically mate once at each
instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'' 'form, likeness') is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, which occurs between each moult (''ecdysis'') until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to ...
. Archaeognaths may have a total lifespan of up to four years, longer than most larger insects.
References
External links
Archaeognatha
- Tree of Life Web Project
Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State College Department of Entomology {{DEFAULTSORT:Archaeognatha Insect orders Insects of the Arctic Middle Devonian first appearances