|
Anthracotheriinae
The anthracotheriines are an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that comprised Paleogene to early Neogene North American and Eurasian artiodactyls. The group contained the genera '' Anthracotherium'', ''Heptacodon'', and ''Paenanthracotherium ''Paenanthracotherium'' was a genus of anthracothere that lived in Europe and Asia during the Oligocene. Taxonomy The type species of the genus is ''Paenanthracotherium bergeri''. The species ''"Anthracotherium" hippoideum'' and ''"Brachyodus ...'', as well as possibly '' Myaingtherium'' and '' Siamotherium''. They were small to large sized anthracotheres, and when compared to the other two subfamilies, Microbunodontinae and Bothriodontinae, anthracotheriines are found to occupy a primitive, basal position in the family. References Anthracotheres Mammal subfamilies Eocene first appearances {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptacodon
''Heptacodon'' is an extinct genus of anthracothere endemic to North America during the Paleogene (from the middle Eocene to the early Oligocene). They were medium to large-sized anthracotheres with a distinct facial features such short heavy rostrums and robust but simple molars. ''Heptacodon'' is a member of the anthracothere subfamily Anthracotheriinae The anthracotheriines are an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that comprised Paleogene to early Neogene North American and Eurasian artiodactyls. The group contained the genera ''Anthracotherium'', '' Heptacodon'', and '' Paenanthracotherium ..., whose distribution as a whole are in North America and Eurasia. However ''Heptacodon'' has only been found in North America, with the species ''H. yeguaensis'' from Texas representing the oldest known anthracotheres to be found in North America dating to the middle Eocene. Fossils of this genus have been found in the states of North Dakota, Oregon, South Dakota, Texas, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracotheres
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, '' Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, '' Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Pothohar Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paenanthracotherium
''Paenanthracotherium'' was a genus of anthracothere that lived in Europe and Asia during the Oligocene. Taxonomy The type species of the genus is ''Paenanthracotherium bergeri''. The species ''"Anthracotherium" hippoideum'' and ''"Brachyodus ''Brachyodus'' was a genus of anthracothere that lived in Europe during the Early Miocene. Taxonomy The type and only species of this genus is ''B. onoideus''. The nominal species ''"Brachyodus" strategus'' has been reassigned to '' Paenanthraco ..." strategus'' have been reassigned to this genus based on similarities with ''P. bergeri''.Laureline Scherler; Fabrice Lihoreau; Damien Becker (2018). "To split or not to split Anthracotherium? A phylogeny of Anthracotheriinae (Cetartiodactyla: Hippopotamoidea) and its palaeobiogeographical implications". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. Online edition. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zly052. Distribution Fossils of ''Paenanthracotherium'' are known from France, Germany, Pakistan, Romania, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbunodontinae
The microbunodontines were an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that were predominately a Paleogene group of Eurasian artiodactyls. The group died out at the end of the Late Miocene. It comprised the genera '' Anthracokeryx'', '' Geniokeryx'', ''Microbunodon'', and possibly '' Etruscotherium''. They are different from the other anthracothere lineages by their smaller size, slenderer limbs and male specimens having laterally compressed, longer canines. They were originally classified as members of the other subfamily of anthracotheres, Anthracotheriinae The anthracotheriines are an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that comprised Paleogene to early Neogene North American and Eurasian artiodactyls. The group contained the genera '' Anthracotherium'', ''Heptacodon'', and ''Paenanthracotherium ... but recent phylogenetic studies have found them to be their own clade sister to Bothriodontinae. References Anthracotheres Mammal subfamilies Eocene first appearances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracothere
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, '' Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, '' Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Potho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
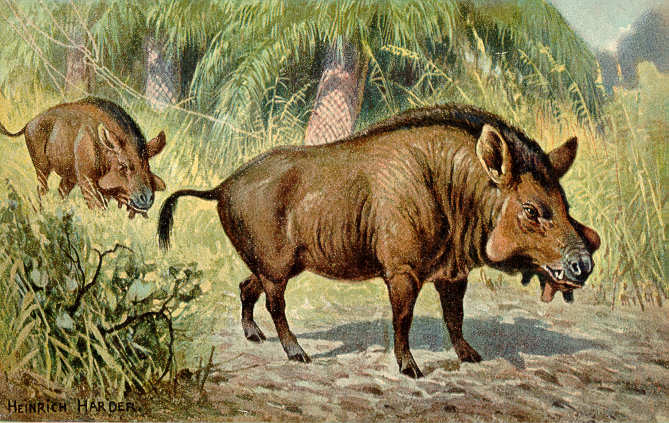
Anthracotherium
''Anthracotherium'' (from el, ἄνθραξ , 'coal' and el, θηρίον 'beast') was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals, characterized by having 44 teeth, with five semi-crescentic cusps on the crowns of the upper molars. The genus ranged from the middle Eocene period until the early Miocene, having a distribution throughout Eurasia. Material subjectively assigned to ''Anthracotherium'' from Pakistan suggests the last species died out soon after the start of the Miocene. Description The genus typifies the family Anthracotheriidae, if only because it is the most thoroughly studied. In many respects, especially the anatomy of the lower jaw, ''Anthracotherium'', as with the other members of the family, is allied to the hippopotamus, of which it is probably an ancestral form. Anthracotheres, together with hippos, are grouped with cetaceans in the clade Whippomorpha. Etymology The genus name stems from the fact that the holotype and other first specimens were ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriodontinae
The bothriodontines are a paraphyletic assemblage of anthracotheres that originated from Eurasia in the late middle Eocene (Bartonian). The group can be distinguished from other anthracothere lineages by their upper molars with the mesostyle that is occupied by the transverse valley, selenodont cusps, ventrally concave symphysis, elongated muzzles, with presence of a diastema between the canine and first premolar. The size range of the group ranged from small, basal forms to larger and more derived forms. During their evolution, the bothriodontines undergone a trend from evolving from small basal forms such as '' Qatraniodon'' into larger taxa such as ''Libycosaurus'' and ''Merycopotamus ''Merycopotamus'' is an extinct genus of Asian anthracothere that appeared during the Middle Miocene The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is ...''. Some genera the snouts became even more e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Mya. It is the beginning of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognised as a formal stratigraphic term, 'Tertiary' is still widely found in earth science literature and remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg" (but the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation PE for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps). During the Paleogene, mammals diversified from relatively small, simple forms into a large group of diverse animals in the wake of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that ended the preceding C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography and in the English-speaking world outside the United States, particularly in Canada, "North America" and "North American" can refer to just Canada and the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans ('' Homo habilis'') appeared in Africa near the end of the period. Some continental movements took place, the most significant event being the connection of North and South America at the Isthmus of Panama, late in the Pliocene. This cut off the warm ocean currents from the Pacific t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)