|
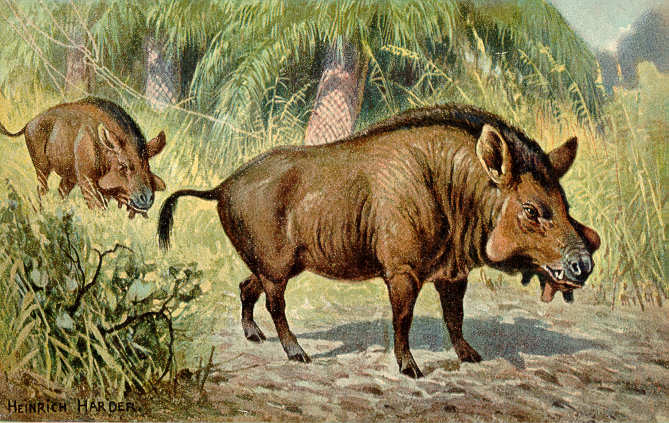
Microbunodontinae
The microbunodontines were an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that were predominately a Paleogene group of Eurasian artiodactyls. The group died out at the end of the Late Miocene. It comprised the genera '' Anthracokeryx'', '' Geniokeryx'', ''Microbunodon'', and possibly '' Etruscotherium''. They are different from the other anthracothere lineages by their smaller size, slenderer limbs and male specimens having laterally compressed, longer canines. They were originally classified as members of the other subfamily of anthracotheres, Anthracotheriinae The anthracotheriines are an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that comprised Paleogene to early Neogene North American and Eurasian artiodactyls. The group contained the genera '' Anthracotherium'', ''Heptacodon'', and ''Paenanthracotherium ... but recent phylogenetic studies have found them to be their own clade sister to Bothriodontinae. References Anthracotheres Mammal subfamilies Eocene first appearances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracotheriinae
The anthracotheriines are an extinct subfamily of anthracotheres that comprised Paleogene to early Neogene North American and Eurasian artiodactyls. The group contained the genera '' Anthracotherium'', ''Heptacodon'', and ''Paenanthracotherium ''Paenanthracotherium'' was a genus of anthracothere that lived in Europe and Asia during the Oligocene. Taxonomy The type species of the genus is ''Paenanthracotherium bergeri''. The species ''"Anthracotherium" hippoideum'' and ''"Brachyodus ...'', as well as possibly '' Myaingtherium'' and '' Siamotherium''. They were small to large sized anthracotheres, and when compared to the other two subfamilies, Microbunodontinae and Bothriodontinae, anthracotheriines are found to occupy a primitive, basal position in the family. References Anthracotheres Mammal subfamilies Eocene first appearances {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbunodon
''Microbunodon'' was a genus of extinct artiodactyl mammals in the family Anthracotheriidae. It lived between the upper Eocene and the lower Pliocene (about 35–5 million years ago). Its fossil remains have been found in Europe and Asia. Description ''Microbunodon'', unlike most of its close relatives, was small in size and with a slight build. Its weight did not exceed 20–25 kilograms and the skull was about 20–30 centimeters long. ''Microbunodon'' was slim with long legs and a short snout with long prominent canine teeth in males, similar to a saber-toothed cat. It was characterized by a fused mandibular symphysis, with a ventral ridge-like prominence. Classification The genus ''Microbunodon'' was established by Deperet in 1908 to accommodate a species previously described by Georges Cuvier in 1822 and attributed to the genus '' Anthracotherium'', as ''A. minimum'', from the Oligocene superior of France. The type species, ''Microbunodon minimum'', lived in the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracokeryx
''Anthracokeryx'' is a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammal belonging to Anthracotheriidae that lived in Asia during the middle to late Eocene. Taxonomy ''Anthracokeryx'' was treated as a junior synonym of ''Anthracotherium'' by Tsubamoto et al. (2002) based on similarities in dental morphology.Tsubamoto T, Takai M, Egi N, Shigehara N, Tun ST, Aung AK, Soe Aung Naing, Thein T. 2002. The Anthracotheriidae (Mammalia; Artiodactyla) from the Eocene Pondaung Formation (Myanmar) and comments on some other anthracotheres from the Eocene of Asia. Paleontological Research. 6:363–384. However, other authors have rejected the synonymy and recognized ''Anthracokeryx'' as a distinct form in the subfamily Microbunodontinae. Distribution Fossils of ''Anthracokeryx'' are known from China, Myanmar, and Vietnam Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracothere
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, '' Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, '' Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Potho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracotheres
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, '' Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, '' Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Pothohar Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Mya. It is the beginning of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognised as a formal stratigraphic term, 'Tertiary' is still widely found in earth science literature and remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg" (but the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation PE for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps). During the Paleogene, mammals diversified from relatively small, simple forms into a large group of diverse animals in the wake of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that ended the preceding C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million years ago) to 5.333 Ma. The evolution of life The gibbons (family Hylobatidae) and orangutans (genus ''Pongo'') are the first groups to split from the line leading to the hominins, including humans, then gorillas (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally, chimpanzees and bonobo The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the co ...s (genus '' Pan''). The splitting date between hominin and chimpanzee lineages is placed by some between 4 to 8 million years ago, that is, during the Late Miocene. References External links GeoWhen Database - Late Miocene .03 03 * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriodontinae
The bothriodontines are a paraphyletic assemblage of anthracotheres that originated from Eurasia in the late middle Eocene (Bartonian). The group can be distinguished from other anthracothere lineages by their upper molars with the mesostyle that is occupied by the transverse valley, selenodont cusps, ventrally concave symphysis, elongated muzzles, with presence of a diastema between the canine and first premolar. The size range of the group ranged from small, basal forms to larger and more derived forms. During their evolution, the bothriodontines undergone a trend from evolving from small basal forms such as '' Qatraniodon'' into larger taxa such as ''Libycosaurus'' and ''Merycopotamus ''Merycopotamus'' is an extinct genus of Asian anthracothere that appeared during the Middle Miocene The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is ...''. Some genera the snouts became even more e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |