|
Akseli Anttila
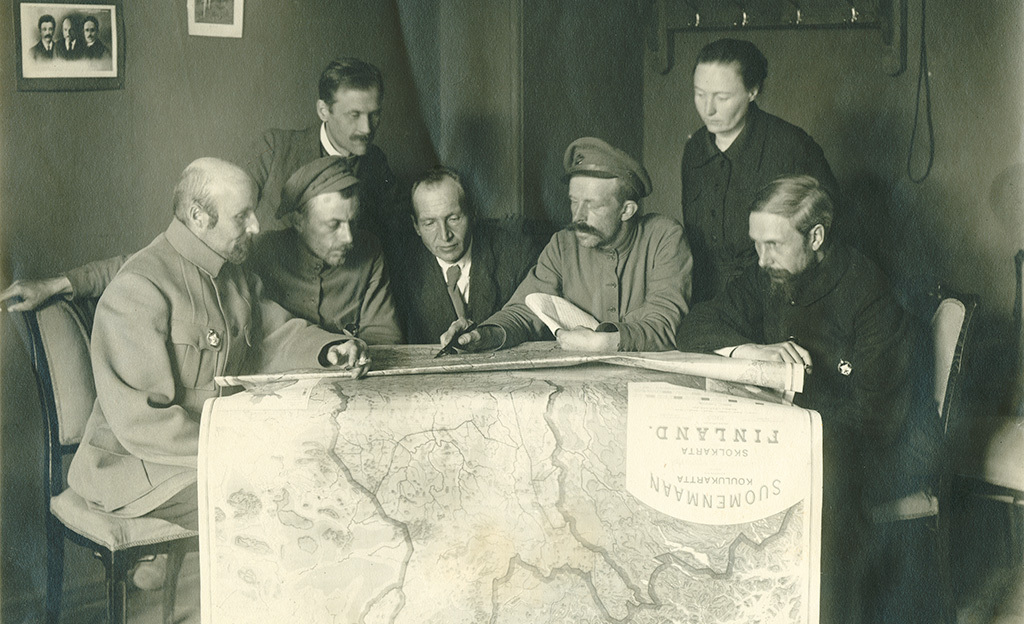
Akseli Anttila (; March 26, 1897 – March 11, 1953) was a Finnish-born Soviet major general of the Red Army. Life Akseli Anttila was born to a family of peasants in Ruovesi. After graduating from an agricultural college, Anttila worked in the railroads. He fought for the Red Guards in the 1918 Finnish Civil War and was captured by the Whites after the Battle of Tampere in 6 April in Pispala. Anttila was detained at the Tampere camp but managed to escape in August. He fled to Sweden and moved to the Soviet Russia in 1919. Anttila joined the exile Communist Party of Finland in Saint Petersburg and took an officer course in the international class of the Bolshevik military academy. He fought in the Russian Civil War, took part of the repression of the 1921 Kronstadt rebellion and was wounded in East Karelia in January 1922. After working as a teacher in the Bolshevik military academy, Anttila joined the Frunze Military Academy in 1930 and graduated 1933. He served in the Red A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruovesi
Ruovesi is a municipality in the Pirkanmaa region of Finland. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . Neighbouring municipalities are Juupajoki, Mänttä-Vilppula, Orivesi, Tampere, Virrat and Ylöjärvi. The municipality is unilingually Finnish. Helvetinjärvi National Park is located in Ruovesi. The biggest lake in the area of the municipality, Lake Ruovesi, is a part of the Kokemäki River basin. The educational department takes part in Lifelong Learning Programme 2007–2013 in Finland. File:Iso Helvetinjarvi.jpg, Helvetinjärvi National Park File:Ruovesi Church 2021.jpg, Ruovesi Church File:Ruovesi Forest.jpg, Birch forest near Ruovesi People born in Ruovesi * Väinö Nyström (1857 – 1918) * Verner Järvinen (1870 – 1941) * Kalle Häkkinen (1878 – 1919) * Akseli Anttila (1897 – 1953) * Jorma Gallen-Kallela (1898 – 1939) * Eila Eskola-Kyröläinen (1931 – 2015) * Kimmo Latvamäki ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pispala
Pispala is a city area 2.5 km from the centre of Tampere, Finland. It is located on the northern slope of Pispalanharju, the highest esker in Finland. Together with Pyynikki, Pispala is widely considered the most beautiful area of Tampere and tourists are often guided there for the view and the unique urban design features of the area. A monument to the Finnish poet Lauri Viita is located near the highest point of the ridge and there is a famous landmark in the area called the Shot tower (). History Pispala is named after the ''House of Pispa'', which had the obligation to house the bishops during their travel. It was first mentioned in 1492. Pispala was a rural area until as recently as 1869, at the time there were only two farms in the area: Pispala and Provasti. As Tampere was industrialised, Pispala grew without a unified local development plan, resulting in unique building styles and solutions. Specifically factory and construction workers resided there with most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peace Treaty on 13 March 1940. Despite superior military strength, especially in tanks and aircraft, the Soviet Union suffered severe losses and initially made little headway. The League of Nations deemed the attack illegal and expelled the Soviet Union from its organization. The Soviets made several demands, including that Finland cede substantial border territories in exchange for land elsewhere, claiming security reasonsprimarily the protection of Leningrad, from the Finnish border. When Finland refused, the Soviets invaded. Most sources conclude that the Soviet Union had intended to conquer all of Finland, and cite the establishment of the Finnish Democratic Republic, puppet Finnish Communist government and the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrid Front
The siege of Madrid was a two-and-a-half-year siege of the Republican-controlled Spanish capital city of Madrid by the Nationalist armies, under General Francisco Franco, during the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939). The city, besieged from October 1936, fell to the Nationalist armies on 28 March 1939. The Battle of Madrid in November 1936 saw the most intense fighting in and around the city when the Nationalists made their most determined attempt to take the Republican capital. The highest military awards of the Spanish Republic, the Laureate Plate of Madrid (), and the Madrid Distinction (), established by the Republican government to reward courage, were named after the capital of Spain because the city symbolised valour and Republican resistance during the long siege throughout the war. Uprising: Madrid held for the Republic (July 1936) The Spanish Civil War began with a failed ''coup d'état'' against the Popular Front Government of the Spanish Republic by Spanish A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Pavlov (general)
Dmitry Grigoryevich Pavlov (; 22 July 1941) was a Soviet general who commanded the key Soviet Western Front during the initial stage of the German invasion of the Soviet Union (Operation Barbarossa) in June 1941. After his forces were heavily defeated within the first few days of the campaign, he was relieved of his command, arrested, charged with military incompetence, and executed. Military career Pavlov was a veteran of the First World War, as well as the Russian Civil War, serving in the Red Army since 1919. He graduated from the Frunze Military Academy in 1928. He then commanded various mechanised and cavalry units. As one of the Soviet military advisers, in 1936–37 he took part in the Spanish Civil War on the Republican side (using the nom de guerre ''Pablo'') and commanded a brigade of Soviet tanks, for which he was made a Hero of the Soviet Union. In contrast to many other officers who took part in that war, he was not purged after his return to the Soviet Union,Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelia
Karelia (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast) and Finland (the Regions of Finland, regions of South Karelia, North Karelia, and the eastern portion of Kymenlaakso). Use of name Various regions may be called Karelia. Finnish Karelia is a historical province of Finland and is now divided between Finland and Russia, often called just ''Karjala'' in Finnish. The eastern part of this chiefly Lutheran area was ceded to Russia after the Winter War of 1939–40. The Republic of Karelia is a Russian federal subject, including East Karelia, with a chiefly Russian Orthodox population. Within present-day Finland, ''Karjala'' refers to the Regions of Finland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frunze Military Academy
The M. V. Frunze Military Academy (), or in full the Military Order of Lenin and the October Revolution, Red Banner, Order of Suvorov Academy in the name of M. V. Frunze (), was a military academy of the Soviet and later the Russian Armed Forces. Established in 1918 to train officers for the newly formed Red Army, the academy was one of the most prestigious military educational institutions in the Soviet Union. At first titled the General Staff Academy of the Red Army, taking on a similar role to its pre-revolutionary predecessor, the Imperial Nicholas Military Academy, it was renamed the Military Academy in 1921 and then the M. V. Frunze Military Academy in 1925, honouring Mikhail Frunze, who had been a commandant of the academy. It became a higher staff college with the addition of courses for senior command officers in the 1930s, before these were transferred in 1936 to the newly formed Military Academy of the General Staff. By this time many of the Red Army's most senior c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
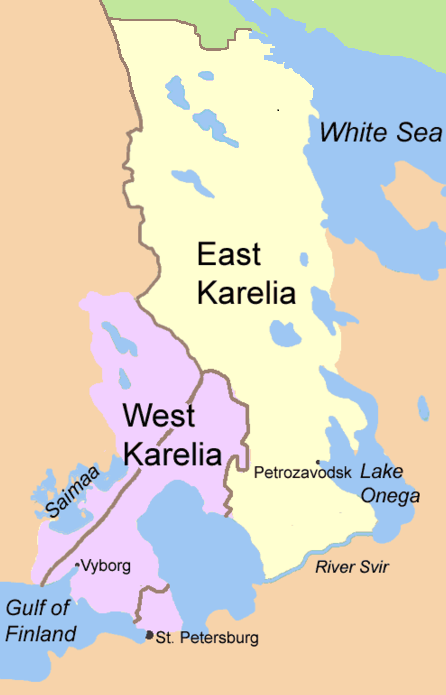
East Karelia
East Karelia (, ), also rendered as Eastern Karelia or Russian Karelia, is a name for the part of Karelia that is beyond the eastern border of Finland and since the Treaty of Stolbovo in 1617 has remained Eastern Orthodox and a part of Russia. It is separate from the western part of Karelia, called '' Finnish Karelia'' or historically ''Swedish Karelia'' (before 1808). Most of East Karelia has become part of the Republic of Karelia within the Russian Federation. It consists mainly of the old historical regions of Viena Karjala ( English: White Karelia) and Aunus Karjala ( English: Olonets Karelia). Culture and ideology 19th-century ethnic-nationalist Fennomans saw East Karelia as the ancient home of Finnic culture, "un-contaminated" by either Scandinavians or Slavs. In the sparsely populated East Karelian backwoods, mainly in White Karelia, Elias Lönnrot (1802–1884) collected the folk tales that ultimately would become Finland's national epic, the Kalevala (published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kronstadt Rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion () was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors, Marines, naval infantry, and civilians against the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik government in the Russian port city of Kronstadt. Located on Kotlin Island in the Gulf of Finland, Kronstadt defended the former capital city, Saint Petersburg, Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg), as the base of the Baltic Fleet. For sixteen days in March 1921, rebels in Kronstadt's naval fortress rose in opposition to the Soviet government which they had helped to consolidate. Led by Stepan Petrichenko, it was the last major revolt against Bolshevik rule on Russian territory during the Russian Civil War. Disappointed in the direction of the Bolshevik government, the rebels—whom Leon Trotsky himself had praised earlier as the "adornment and pride of the revolution"—demanded a series of reforms: reduction in Bolshevik power, newly elected Soviet (council), ''soviets'' (councils) to include libertarian socialism, socialist and anarchist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601,911 residents as of 2021, with more than 6.4 million people living in the Saint Petersburg metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As the former capital of the Russian Empire, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Finland
The Communist Party of Finland (, SKP; ) was a communist political party in Finland. The SKP was a section of Comintern and illegal in Finland until 1944. The SKP was banned by the state from its founding and did not participate in any elections with its own name. Instead, front organisations were used. In the 1920s, the communists took part in the Socialist Workers' Party of Finland (1920–1923) and the Socialist Electoral Organisation of Workers and Smallholders (1924–1930). Both of them were also banned. In 1944, a new front, the Finnish People's Democratic League was formed. The SKP controlled these fronts but they always had a prominent minority of non-communist socialists. History Early stages In 1918, the Reds lost the Finnish Civil War. The Social Democratic Party of Finland had supported the losing side, and several of its leaders were exiled in Soviet Russia. Some of these exiles founded the Communist Party of Finland in Moscow. The SKP was illegal in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |