Karelia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Karelia (; Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the federal subjects of the
Karelia (; Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the federal subjects of the
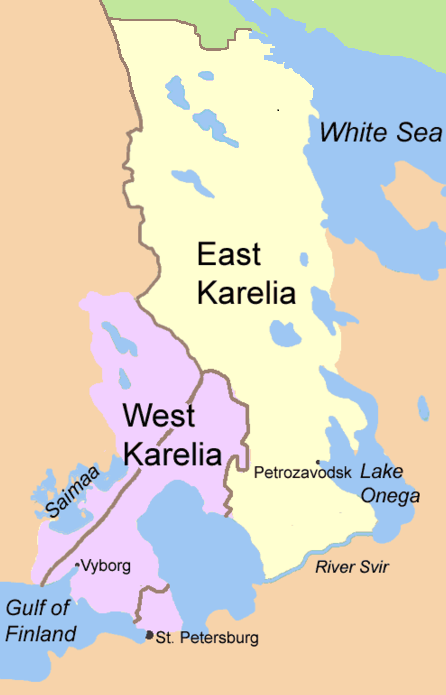 Karelia stretches from the
Karelia stretches from the 
 During the
During the  The Treaty of Nystad (Finnish: Uudenkaupungin rauha) in 1721 between
The Treaty of Nystad (Finnish: Uudenkaupungin rauha) in 1721 between  At the beginning of the
At the beginning of the
 On the Finnish side, the area is Finnish-speaking. The South Karelian dialects of the
On the Finnish side, the area is Finnish-speaking. The South Karelian dialects of the
"They Took My Father,"
by Mayme Sevander and Laurie Hertzel, a history of
Karelians
(The Peoples of the Red Book)
Tracing Finland's eastern border
– ThisisFINLAND
Saimaa Canal links two Karelia
– ThisisFINLAND
Visitkarelia.fi – Information about travel, tourism and other fields in North Karelia
Information about Southern Karelia travel
Pielis.ru – travel information about North Karelia region and City of Joensuu
Article about Karelia with photos and useful tourist information.
* [http://shop.migrationinstitute.fi/product/195/their-ideals-were-crushed-a-daughters-story-of-the-sade-commune-in-soviet-karelia Their Ideals Were Crushed. A Daughter's Story of the Säde Commune in Soviet Karelia.] {{Coord, 63, N, 32, E, display=title Fennoscandia Historical regions in Russia History of Karelia Historical geography of Finland Former disputed land areas
 Karelia (; Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the federal subjects of the
Karelia (; Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the federal subjects of the Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
and Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census ...
) and Finland (the regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
of South Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast).
Hist ...
, North Karelia, and the eastern portion of Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso (; ; "Kymi River, Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a Regions of Finland, region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, Southern Savonia, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means lit ...
).
Use of name
Various regions may be called Karelia. Finnish Karelia is a historical province of Finland and is now divided between Finland and Russia, often called just ''Karjala'' in Finnish. The eastern part of this chieflyLutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
area was ceded to Russia after the Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
of 1939–40.
The Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
is a Russian federal subject, including East Karelia, with a chiefly Russian Orthodox population.
Within present-day Finland, ''Karjala'' refers to the regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
of South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
and North Karelia, although parts of historical Karelia also lie within the region of Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso (; ; "Kymi River, Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a Regions of Finland, region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, Southern Savonia, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means lit ...
(east of the River Kymi), Northern Savonia ( Kaavi, Rautavaara and Säyneinen), and Southern Savonia
South Savo (or Southern Savonia; ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region in the south-east of Finland. It borders the regions of North Savo, North Karelia, South Karelia, Kymenlaakso, Päijät-Häme, and Central Finland. The total area of South Savo ...
( Mäntyharju).
Geography
 Karelia stretches from the
Karelia stretches from the White Sea
The White Sea (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; ) is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the nort ...
coast to the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
. It contains the two largest lakes in Europe, Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
and Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic ...
. The Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the we ...
is located between the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
and Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
. The highest point of Karelia, the high Nuorunen, is located on the Russian side of the Maanselkä hill region.
The border between Karelia and Ingria
Ingria (; ; ; ) is a historical region including, and adjacent to, what is now the city of Saint Petersburg in northwestern Russia. The region lies along the southeastern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordered by Lake Ladoga on the Karelian ...
, the land of the closely related Ingrian people, had originally been the Neva River
The Neva ( , ; , ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it is the fourth-l ...
itself but later on it was moved northward into the Karelian isthmus to follow the Sestra River (), today in the Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
metropolitan area, but in 1812–1940 the Russo-Finnish border.
On the other side of Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
, the River Svir is usually thought of as the traditional southern border of Karelian territory while Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic ...
and the White Sea
The White Sea (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; ) is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the nort ...
mark the Eastern border. The River Kymi marks the historic western border of Karelian territory as it served as the boundary between the Häme Finns and the Karelians during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. The River Kymi is also said to have formed a boundary between the eastern and western cultural spheres by the beginning of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
at the latest. In the North lived the nomadic
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
Samis, but there were no natural borders except for large wooded areas (taiga
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. In North A ...
) and the tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
.
In historical texts, Karelia is sometimes divided into ''East Karelia'' and ''West Karelia,'' which are also called Russian Karelia and Finnish Karelia respectively. The area to the north of Lake Ladoga which belonged to Finland before World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
is called Ladoga Karelia, and the parishes on the old pre-war border are sometimes called Border Karelia. White Karelia (sometimes the Finnish or Karelian term "Viena Karelia", or in some English-language sources, "White Sea Karelia", is used) is the northern part of East Karelia and Olonets Karelia is the southern part.
Tver Karelia denotes the villages in the Tver Oblast
Tver Oblast (, ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was known as Kalinin Oblast (). Population:
Tver Oblast is a region of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno. Much o ...
that are inhabited by Tver Karelians
Tver Karelians are a people who inhabit regions of Tver, Saint Petersburg, and Moscow. Their dialect is remarkable in that it does not borrow from other Balto-Finnic languages due to centuries of geographical isolation. Although the number of ...
.

Inhabited localities
*Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
**Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (, ; Karelian language, Karelian, Veps language, Vepsian and ) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city is 280,890 as of 2022.
...
(, ''Petroskoi'', from late 1941 to 1944 known to Finns as ''Äänislinna/Onegaborg'')
** Belomorsk (, ''Sorokka'')
** Medvežyegorsk (, ''Karhumäki'')
** Kalevala (, Uhtua)
** Kem (, ''Vienan Kemi'', compare with Kemi
Kemi (; ; ; ) is a cities of Finland, town and municipalities of Finland, municipality of Finland. It is located approximately from the city of Tornio and the Finland–Sweden border, Swedish border. The distance to Oulu is to the south and t ...
)
** Kostomukša (, ''Kostamus'')
** Kondopoga (, ''Kontupohja'')
** Sortavala (, ''Sortavala'', ''Sordavala'')
** Suojarvi (, ''Suojärvi'')
** Segeža (, ''Sekehe'')
** Pitkjaranta (, ''Pitkäranta'')
** Olonec (, ''Aunus'')
*Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the we ...
**Vyborg
Vyborg (; , ; , ; , ) is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital H ...
(, ''Viipuri'', ''Viborg'')
** Priozersk (, ''Käkisalmi, Kexholm'')
** Primorsk (Примо́рск, ''Koivisto'', ''Björkö)''
** Svetogorsk (, ''Enso'')
*South Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast).
Hist ...
**Imatra
Imatra is a city in Finland, located in the southeastern interior of the country. Imatra is located in the region of South Karelia, on Saima, Lake Saimaa and the River Vuoksi. The population of Imatra is approximately , while the Imatra sub-regi ...
** Joutseno
**Lappeenranta
Lappeenranta (; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of South Karelia. It is located in the southeastern interior of the country and in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Lappeenranta is approximately , while the Lappeenranta sub-r ...
(''Villmanstrand'')
* North Karelia
** Joensuu
** Ilomantsi (''Ilomants'')
** Kitee
** Kesälahti
**Kontiolahti
Kontiolahti (; literally meaning "bear bay") is a municipalities of Finland, municipality in Finland. It is located in the North Karelia regions of Finland, region, about north of Joensuu. The municipality has a population of () and covers an ar ...
** Lieksa
** Liperi
** Nurmes
** Outokumpu
History
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, settlers from western Finland mixed with the local population to form the Karelian ethnic group. Possible migration from elsewhere may also have contributed to the Karelian ethnic composition.
Archeological evidence indicates that Karelian inhabitation was highest along the western shore of Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
and the Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the we ...
, with multiple cemeteries and other archeological discoveries dating from AD 600 to AD 800. In South Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast).
Hist ...
, the number of archeological discoveries from this time period is lower, though permanent inhabitation was nonetheless present. Lappee, South Karelia has been continuously inhabited for approximately 2,000 years. In North Karelia, only one archeological discovery from this time period has been found, dating to the eighth century. The considerably higher number of archeological discoveries in these regions from AD 800 to AD 1050 indicates that the Karelian population grew and expanded rapidly during this time.
Karelia was bitterly fought over by Sweden and the Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic () was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries in northern Russia, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east. Its capital was the city of Novgorod. The ...
for a period starting in the 13th-century Swedish-Novgorodian Wars. The Treaty of Nöteborg
The Treaty of Nöteborg, also known as the Treaty of Orehovsk (; ; ), is a conventional name for the peace treaty signed at Shlisselburg Fortress, Oreshek (; ) on 12 August 1323. It was the first agreement between Sweden and the Novgorod Republic ...
(Finnish: Pähkinäsaaren rauha) in 1323 divided Karelia between the two. Sweden received the southern portion of the Karelian Isthmus and most of South Karelia. The province of Swedish Karelia would include this territory, plus the region east of the Kymi river, with Viborg (Finnish: Viipuri) becoming the capital of the province. Novgorod received the northern portion of the Karelian Isthmus. North Karelia, Ladoga Karelia, and the northern portion of South Karelia fell under Novgorodian control. Käkisalmi served as the main population center of this region.
In the Treaty of Stolbovo of 1617, large parts of Russian Karelia were ceded to Sweden. Conflicts between the new Swedish rulers and the indigenous population of these areas led to an exodus: thousands of Karelians, including the ancestors of the Tver Karelians
Tver Karelians are a people who inhabit regions of Tver, Saint Petersburg, and Moscow. Their dialect is remarkable in that it does not borrow from other Balto-Finnic languages due to centuries of geographical isolation. Although the number of ...
, emigrated to Russia.
 The Treaty of Nystad (Finnish: Uudenkaupungin rauha) in 1721 between
The Treaty of Nystad (Finnish: Uudenkaupungin rauha) in 1721 between Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
and Sweden ceded a portion of Karelia to Russia. The Treaty of Åbo
The Treaty of Åbo, or the Treaty of Turku, was a peace treaty signed between the Russian Empire and Sweden in Åbo (Turku) on in the end of the Russo-Swedish War of 1741–1743.
History
By the end of the war, the Imperial Russian Army had ...
in 1743 between Sweden and Russia then ceded South Karelia to Russia. After Finland had been occupied by Russia in the Finnish War
The Finnish War (; ; ) was fought between the Gustavian era, Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a result of the war, the eastern third of Sweden was established a ...
, parts of the ceded provinces ( Old Finland) were incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland was the predecessor state of modern Finland. It existed from 1809 to 1917 as an Autonomous region, autonomous state within the Russian Empire.
Originating in the 16th century as a titular grand duchy held by the Monarc ...
in 1812. In 1917, Finland became independent and the border was confirmed by the Treaty of Tartu in 1920.
Finnish partisans were involved in attempts to overthrow the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
in Russian Karelia ( East Karelia) in 1918–21, as in the failed Aunus expedition. They also wanted to incorporate the rest of Karelia into Finland and cooperated with the short-lived Republic of Uhtua. These mainly private expeditions ended after the signing of the Treaty of Tartu. After the end of the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
and the establishment of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in 1922, the Russian part of Karelia became the Karelian Autonomous republic of the Soviet Union (ASSR) in 1923.
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in 1939, the Soviet Union attacked Finland, thus starting the Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
. The Treaty of Moscow, signed in 1940, handed a large portion of Finnish Karelia to the Soviet Union, and over 400,000 people had to be relocated within Finland. During the Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet–Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union during World War II. It began with a Finnish declaration of war on 25 June 1941 and ended on 19 ...
of 1941-1944, Finland took back territory ceded in 1940, and also invaded and occupied much of East Karelia. Finland was forced out of these regions in 1944. After the war, Soviet expansion caused considerable bitterness in Finland, which lost its fourth biggest city, Viipuri, its industrial heartland along the river Vuoksi, the eastern portion of the Saimaa canal that connected central Finland to the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
, and access to the fishing waters of Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
(Finnish: Laatokka). One eighth of its citizens became refugees with no chance of return. The whole population from the areas ceded to the Soviet Union was evacuated and resettled in other parts of Finland. The present inhabitants of the former Finnish parts of Russia, including the city of Vyborg/Viipuri and the Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the we ...
– are post-war immigrants or their descendants.
The former Karelian ASSR was incorporated into a new Karelo-Finnish SSR
The Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic (Karelo-Finnish SSR), also called Soviet Karelia or simply known as Karelia, was a republic of the Soviet Union. It existed from 31 March 1940 until it was made part of the Russian SFSR on 16 July 1956 ...
from 1941 to 1956, but then it became an ASSR again. Karelia was the only Soviet republic that was "demoted" from an SSR to an ASSR within the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
. In 1991, with the collapse of the Soviet Union, the ASSR became the Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
.
The portion of Viipuri Province
Viipuri Province was a Historical provinces of Finland, historical province of Finland from 1812 to 1945.
History
The predecessor of the province was Vyborg Governorate, which was established in 1744 from territories ceded by the Swedish Empi ...
that remained within Finland following the Second World War was renamed Kymi Province, and kept this name from 1945 to 1997. The eastern part of this province is now the region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
of South Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast).
Hist ...
, while the western portion is part of Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso (; ; "Kymi River, Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a Regions of Finland, region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, Southern Savonia, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means lit ...
.
Politics
Karelia is politically divided between Finland and Russia. TheRepublic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
is a federal subject of Russia
The federal subjects of Russia, also referred to as the subjects of the Russian Federation () or simply as the subjects of the federation (), are the administrative division, constituent entities of Russia, its top-level political division ...
formed in 1991 from the Karelian ASSR. The Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the we ...
belongs to the Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census ...
. The Finnish side consists of parts of the regions (''maakunta'') of South Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast).
Hist ...
, North Karelia and Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso (; ; "Kymi River, Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a Regions of Finland, region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, Southern Savonia, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means lit ...
.
There are some small groups of Finns campaigning for closer ties between Finland and Karelia: for instance, in the Karjalan Liitto (Karelian League) and ProKarelia.
Demographics
 On the Finnish side, the area is Finnish-speaking. The South Karelian dialects of the
On the Finnish side, the area is Finnish-speaking. The South Karelian dialects of the Finnish language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Finnic languages, Finnic language of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official langu ...
(closely related to the Karelian language) are spoken in South Karelia. The eastern Savonian dialects are spoken in North Karelia, part of the group of dialects spoken in Eastern and Central Finland.
Ingrian Finnish dialects are spoken in Ingria, an area around St. Petersburg between the Estonian border and Lake Ladoga. Ingrian Finns settled in the region in the 17th century after the Swedish conquest of the area. The settlers spoke Karelian and Savonian dialects of Finnish. The older inhabitants of Ingria, the Ingrians, have their own language which is related to the Karelian language and the south-eastern dialects of Finnish.
Karelians
Karelians (; ; ; ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely ...
evacuated from the part of Finnish Karelia ceded to Russia were resettled all over Finland. Today about one million people in Finland can trace their roots in the area ceded to the Soviet Union after World War II. In Finland, about 5,000 people speak the Karelian language.
Culture
*'' Kalevala'' * Karelian Bear Dog * Karelian hot pot *Karelian language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some ...
* Karelian pasties
* Karelo-Finnish Laika
* Music of Karelia
Tourism
Russian Karelia is a regular destination for international tourism due to its unique architectural, cultural and historical sites such as Kizhi and Valaam. The region is visited by tourists in both summer and winter when possible activities include riding in a sled behind a dog team and running from the banya to an ice hole and back. Summer hikers can visit the Kivach waterfall or the Demon's Chair plateau. InSouth Karelia
South Karelia (or ''Southern Karelia'', ; ) is a Regions of Finland, region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, Southern Savonia, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia (Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast).
Hist ...
, Lappeenranta
Lappeenranta (; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of South Karelia. It is located in the southeastern interior of the country and in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Lappeenranta is approximately , while the Lappeenranta sub-r ...
is a popular destination for Russian tourists, with 1.5 million visiting annually. Imatrankoski in Imatra
Imatra is a city in Finland, located in the southeastern interior of the country. Imatra is located in the region of South Karelia, on Saima, Lake Saimaa and the River Vuoksi. The population of Imatra is approximately , while the Imatra sub-regi ...
has been a tourist attraction since the late 18th century, when the Empress of Russia Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
visited the site in 1772.
Koli National Park
Koli National Park () is a national park in the municipalities of Joensuu, Lieksa and Kontiolahti in the North Karelia region of Finland. It covers of forested hills on the western shore of Lake Pielinen. The park was established in 1991 a ...
in North Karelia began receiving tourists when Karelianism became a major trend. Koli was a source of inspiration for numerous painter
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with ...
s and composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and def ...
s such as Jean Sibelius
Jean Sibelius (; ; born Johan Julius Christian Sibelius; 8 December 186520 September 1957) was a Finnish composer of the late Romantic music, Romantic and 20th-century classical music, early modern periods. He is widely regarded as his countr ...
, Juhani Aho
Juhani Aho, originally Johannes Brofeldt (11 September 1861 – 8 August 1921), was a Finnish author and journalist. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature sixteen times.
Early life
Juhani Aho was born at Lapinlahti in 1861. His ...
and Eero Järnefelt
Erik "Eero" Nikolai Järnefelt (8 November 1863 – 15 November 1937) was a Finnish painter and art professor. He is best known for his portraits and landscapes of the area around Koli National Park, in the North Karelia region of Finland. He wa ...
, who in turn contributed to Karelianism through their work. Koli gained national park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
status in 1991.
See also
* Asbestos-ceramic, a type of pottery made in Karelia and the vicinity. * History of Finland * Karelianism, a cultural movement in theGrand Duchy of Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland was the predecessor state of modern Finland. It existed from 1809 to 1917 as an Autonomous region, autonomous state within the Russian Empire.
Originating in the 16th century as a titular grand duchy held by the Monarc ...
.
*'' Karelia Suite'', a collection of pieces by the composer Jean Sibelius
Jean Sibelius (; ; born Johan Julius Christian Sibelius; 8 December 186520 September 1957) was a Finnish composer of the late Romantic music, Romantic and 20th-century classical music, early modern periods. He is widely regarded as his countr ...
.
* Lauri Törni, born in Viipuri, a soldier and recipient of the Mannerheim Cross during the Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet–Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union during World War II. It began with a Finnish declaration of war on 25 June 1941 and ended on 19 ...
, who later served with the German and American armies.
* Karelian pony, horse breed native to Russia.
References
Bibliography
"They Took My Father,"
by Mayme Sevander and Laurie Hertzel, a history of
Finnish American
Finnish Americans (, ) comprise Americans with ancestral roots in Finland, or Finnish people who immigrated to and reside in the United States. The Finnish-American population is around 650,000. Many Finnish people historically immigrated to ...
s who emigrated to Soviet Karelia during the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
.
*
*
External links
Karelians
(The Peoples of the Red Book)
Tracing Finland's eastern border
– ThisisFINLAND
Saimaa Canal links two Karelia
– ThisisFINLAND
Visitkarelia.fi – Information about travel, tourism and other fields in North Karelia
Information about Southern Karelia travel
Pielis.ru – travel information about North Karelia region and City of Joensuu
Article about Karelia with photos and useful tourist information.
* [http://shop.migrationinstitute.fi/product/195/their-ideals-were-crushed-a-daughters-story-of-the-sade-commune-in-soviet-karelia Their Ideals Were Crushed. A Daughter's Story of the Säde Commune in Soviet Karelia.] {{Coord, 63, N, 32, E, display=title Fennoscandia Historical regions in Russia History of Karelia Historical geography of Finland Former disputed land areas