|
Tavastians
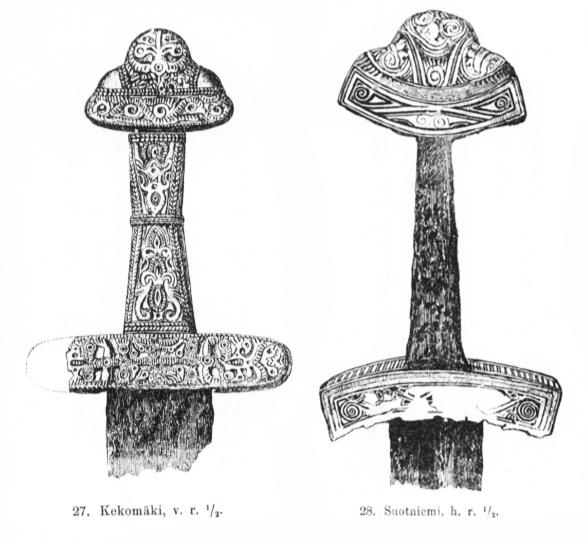
The Tavastians (; ) were an ancient Finnish tribes, Finnish tribe that inhabited the historical province of Tavastia (historical province), Tavastia (). In Russian sources, they are called ''Yem'' (Емь) or ''Yam'' (Ямь), but the term later disappeared from the Russian language after Finland was incorporated into the Swedish realm. The Tavastians are often noted for Finnish–Novgorodian wars, their conflicts with Novgorod. The Tavastians are also a modern subgroup of the Finnish people, distinguished by their use of Finnish language#Dialects, Tavastian dialects. History Tavastia (historical province), Tavastia () has been inhabited since the early Stone Age. The core area of ancient Tavastia was formed around Vanajavesi, Lake Vanajavesi. Example of organized cooperation of iron age Tavastians are the hillforts that form a clear line in south-north direction around Hämeenlinna. Most remarkable from these hillforts is the Rapola Castle which is the biggest hillfort found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish–Novgorodian Wars
The Finnish–Novgorodian wars were a series of conflicts between Finnic tribes in eastern Fennoscandia and the Republic of Novgorod from the 11th or 12th century to the early 13th century. The terms used in Russian chronicles to refer to Novgorod's enemy, the ''Yem'' (Емь, also transcribed as ''Em'') or ''Yam'' (Ямь), are unclear and probably referred to several different groups. Etymologically, they derive from the Finnish word ''Häme'', which means Tavastia. Some of the groups identified as Yem may have been the inhabitants of Tavastland in south-central Finland, the West Finns in general, or a sub-group of Karelians on the northern coast of the Ladoga who descended from western Finns who had moved to the area earlier. Sources The only known written sources on the Yem–Novgorodian wars are contained in Russian chronicles, especially the ''Novgorod First Chronicle'' (NPL). The Synod Scroll, the earliest surviving copy of the ''Novgorod First Chronicle'', mentions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Finns
The Baltic Finnic peoples, often simply referred to as the Finnic peoples, are the peoples inhabiting the Baltic Sea region in Northern and Eastern Europe who speak Finnic languages. They include the Finns, Estonians (including Võros and Setos), Karelians (including Ludes and Livvi), Veps, Izhorians, Votes, and Livonians. In some cases the Kvens, Ingrians, Tornedalians and speakers of Meänkieli are considered separate from the Finns. The bulk of the Finnic peoples (more than 98%) are ethnic Finns and Estonians, who reside in the two independent Finnic nation states—Finland and Estonia. Finnic peoples are also significant minority groups in neighbouring countries of Sweden, Norway and Russia, especially Karelia. Theories of origin According to the "Migration Theory" that was based primarily on comparative linguistics, the proto-Finns migrated from an ancient homeland somewhere in north-western Siberia or western Russia to the shores of the Baltic Sea around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelia (historical Province Of Finland)
Karelia (: ) is a historical province of Finland, consisting of the modern-day Finnish regions of South Karelia and North Karelia plus the historical regions of Ladoga Karelia and the Karelian Isthmus, which are now in Russia. Historical Karelia also extends to the regions of Kymenlaakso (east of the River Kymi), Northern Savonia ( Kaavi, Rautavaara and Säyneinen) and Southern Savonia (Mäntyharju). Karelia may also refer to the region as a whole, including the portion of Karelia within Russia. The term "Finnish Karelia" refers specifically to the historical Finnish province, while East Karelia or "Russian Karelia" refers to the portion of Karelia within Russia. Finland ceded a portion of Finnish Karelia to the Soviet Union after the Winter War of 1939–40. More than 400,000 evacuees from the ceded territories re-settled in various parts of Finland. Finnish Karelians include the present-day inhabitants of South Karelia and North Karelia, as well as the still-surviving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, opposite Estonia. Finland has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Helsinki. The majority of the population are Finns, ethnic Finns. The official languages are Finnish language, Finnish and Swedish language, Swedish; 84.1 percent of the population speak the first as their mother tongue and 5.1 percent the latter. Finland's climate varies from humid continental climate, humid continental in the south to boreal climate, boreal in the north. The land cover is predominantly boreal forest biome, with List of lakes of Finland, more than 180,000 recorded lakes. Finland was first settled around 9000 BC after the Last Glacial Period, last Ice Age. During the Stone Age, various cultures emerged, distinguished by differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish People
Finns or Finnish people (, ) are a Baltic Finns, Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these countries as well as those who have resettled. Some of these may be classified as separate ethnic groups, rather than subgroups of Finns. These include the Kvens and Forest Finns in Norway, the Tornedalians in Sweden, and the Ingrian Finns in Russia. Finnish language, Finnish, the language spoken by Finns, is closely related to other Balto-Finnic languages such as Estonian language, Estonian and Karelian language, Karelian. The Finnic languages are a subgroup of the larger Uralic languages, Uralic family of languages, which also includes Hungarian language, Hungarian. These languages are markedly different from most other languages spoken in Europe, which belong to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family of languages. Native Finns c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavastia (historical Province)
Tavastia (; ; ; also called ''Yam'' (Ямь) or ''Yem'' (Емь) in Russian sources) is a historical province in the south of Finland. It borders Finland Proper, Satakunta, Ostrobothnia, Savonia and Uusimaa. History The province has been inhabited since the Stone Age. Northern Tavastia was for a long time a wilderness inhabited by Sami hunter-gatherers and frequented also by Finnish hunters. Only during the late Middle Ages was agriculture slowly introduced to the northern parts of the province. Tavastia is first mentioned in an 11th-century Viking Age runestone ( Gs 13) located in present-day Gävle, Sweden, where it is referred to as '. At that time, Tavastia was said to stretch "from salt sea to salt sea," encompassing what would later become the provinces of Uusimaa and Satakunta, and including the inhabited regions of Southwest Finland within its arc. Numerous prehistoric weapons, like Ulfberht swords, and hillforts have been unearthed in the Tavastia region, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hämeen Härkätie
Hämeen Härkätie (Oxen Road of Tavastia) is an ancient road in Finland, connecting Turku in Finland Proper to Hämeenlinna in Tavastia Proper. The 162 kilometers long road has been in use at the latest in the 9th century and in many parts it has been in use since. Today, fulfills the same purpose as the connection between Turku and Hämeenlinna, but it follows the original route only near Turku. History The Oxen Road links two major Iron Age settlement areas in Finland, the valley of the Aurajoki river and the Lake Vanaja region of Häme. Vanaja region was one of the main areas in Finland in prehistoric times to acquire articles for export, such as furs and hides. The Aurajoki river valley was the region where these exports passed through to the Baltic sea. The road was a joint institution of several ancient parishes in Western Finland. The road passes through two ancient provinces, Lieto in Turku and ancient Vanaja in Häme which has probably required some kind of agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapola Castle
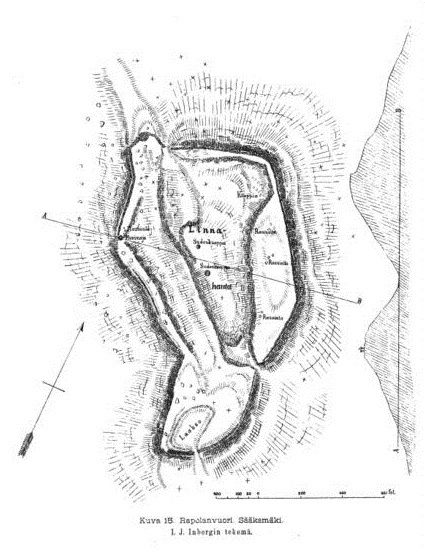
Rapola Hill Fort () is a hill fort in Sääksmäki in the municipality of Valkeakoski, Finland. Its walls have circled an area of 58 000 square meters and it is the biggest hill fort found in Finland. In 1921 senator and archaeologist Julius Ailio raised the question in his article if the fort had been the main fort of Tavastians. This view has also faced criticism later. According to excavations, the fort seems to have been in operation at least during the 13th and 15th centuries. This timing gives the postulation that it was built by the inhabitants in their struggles against invading Novgorodians and Swedes. Parts of it may be even earlier, since the area has been inhabited already in the 7th century. In excavations there have been found 80 depressions that have been interpreted as a place of residence and 13 places of hearths. Only one percent of the area of the hill fort has been excavated. A Papal Bull from 1340 mentions a person named ''Cuningas de Rapalum'' (King of Rap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hämeenlinna
Hämeenlinna (; ; ; or ''Croneburgum'') is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Kanta-Häme. It is located in the southern interior of the country and on the shores of Vanajavesi, Lake Vanajavesi. The population of Hämeenlinna is approximately , while the Hämeenlinna sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is the most populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality in Finland, and the 14th most populous List of urban areas in Finland by population, urban area in the country. Hämeenlinna is the oldest inland city in Finland and was one of the most important Finnish cities until the 19th century. Hämeenlinna was located in the heart of the historic province of Tavastia (historical province), Tavastia. Since then, Hämeenlinna has remained an important regional centre. The medieval Häme Castle (also known as ''Tavastia Castle'') is located in the town. Hämeenlinna is known as the birthplace of the Finnish national composer Jean Sibelius. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Häme
Tavastia (; ; ; also called ''Yam'' (Ямь) or ''Yem'' (Емь) in Russian sources) is a historical province in the south of Finland. It borders Finland Proper, Satakunta, Ostrobothnia, Savonia and Uusimaa. History The province has been inhabited since the Stone Age. Northern Tavastia was for a long time a wilderness inhabited by Sami hunter-gatherers and frequented also by Finnish hunters. Only during the late Middle Ages was agriculture slowly introduced to the northern parts of the province. Tavastia is first mentioned in an 11th-century Viking Age runestone ( Gs 13) located in present-day Gävle, Sweden, where it is referred to as '. At that time, Tavastia was said to stretch "from salt sea to salt sea," encompassing what would later become the provinces of Uusimaa and Satakunta, and including the inhabited regions of Southwest Finland within its arc. Numerous prehistoric weapons, like Ulfberht swords, and hillforts have been unearthed in the Tavastia region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kymenlaakso
Kymenlaakso (; ; "Kymi River, Kymi/Kymmene Valley") is a Regions of Finland, region in Finland. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Päijät-Häme, Southern Savonia, South Savo and South Karelia and Russia (Leningrad Oblast). Its name means literally ''The Valley of River Kymijoki, Kymi''. Kymijoki is one of the biggest rivers in Finland with a drainage basin with 11% of the area of Finland. The city of Kotka with 51,000 inhabitants is located at the delta of River Kymi and has the most important import harbour in Finland. Other cities are Kouvola further in the inland which has after a municipal merger 81,000 inhabitants and the old bastion town Hamina. Kymenlaakso was one of the first industrialization, industrialized regions of Finland. It became the most important region for paper industry, paper and pulp industry in Finland. Since the late 1900s many plants have closed, which has caused some deindustrialization, unemployment and population decline in Kymenlaakso, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavastian Dialects
Tavastian dialects (), or Häme dialects, are Western Finnish dialects spoken in Pirkanmaa, Päijät-Häme, Kanta-Häme, and in parts of Satakunta, Uusimaa and Kymenlaakso. The dialect spoken in the city of Tampere is part of the Tavastian dialects. The Tavastian dialects have influenced other Finnish dialects (especially the Southwest Finnish dialects). Dialectal features Pronunciation of D Where Standard Finnish has /d/, the Tavastian dialects have either /r/ or /l/ in its place. The ''r''-pronunciation is the more common one. The ''l''-pronunciation is encountered on two separate areas: in the eastern boundary of the dialect area as well as in a smaller area which includes Akaa and Tammela to name a few. Therefore, ''lehdet'' (leaves) can be pronounced as ''lehret'' or ''lehlet''. However, the plural of ''vesi'' (water, standard plural ''vedet'') can be pronounced as ''veset'' in the ''r''-dialects, in order to not cause confusion with ''veret'' (bloods, plural of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |