The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финляндская война́ 1939–1940) are often used in Russian
historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians hav ...
br>
В.Н. Барышников. От прохладного мира к Зимней войне. Восточная политика Финляндии в 1930–е годы. Санкт-Петербург, 1997.; О.Д. Дудорова. Неизвестные страницы Зимней войны. In: Военно-исторический журнал. 1991. №9.; Зимняя война 1939–1940. Книга первая. Политическая история. М., 1998. –
;
ttp://www.otvaga2004.narod.ru/photo/winterwar/wwar1.htm М. Коломиец. Танки в Зимней войне 1939–1940. In: «Фронтовая иллюстрация», 2001Александр Широкорад. Северные войны России. М., 2001.; Владимир Холодковский. Эта Зимняя война. In: Ленинская правда. 1990. 4 янв., c. 3. Russo–Finnish War 1939–1940 or Finno-Russian War 1939–1940 are used by the U.S.
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The librar ...
' catalogue (see authority control)., group="F" also known as the First Soviet-Finnish War, was a war between the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
. The war began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, and ended three and a half months later with the
Moscow Peace Treaty on 13 March 1940. Despite superior military strength, especially in tanks and aircraft, the Soviet Union suffered severe losses and initially made little headway. The
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
deemed the attack illegal and expelled the Soviet Union from the organisation.
The Soviets made several demands, including that Finland cede substantial border territories in exchange for land elsewhere, claiming security reasonsprimarily the protection of
Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, from the Finnish border. When Finland refused, the Soviets invaded. Most sources conclude that the Soviet Union had intended to conquer all of Finland, and use the establishment of the
puppet Finnish Communist government and the
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
's secret protocols as evidence of this, while other sources argue against the idea of a full Soviet conquest. Finland repelled Soviet attacks for more than two months and inflicted substantial losses on the invaders while temperatures ranged as low as . The battles focused mainly on
Taipale along the
Karelian Isthmus, on
Kollaa
The Kollaa (russian: Колласйоки, fi, Kollaanjoki or ') is a long river in the Republic of Karelia, Russia. It starts from Lake Kollasjärvi in the Suoyarvsky District and flows to Lake Tulmozero ( fi, Tulemajärvi) in the Pryazhin ...
in
Ladoga Karelia and on
Raate Road in
Kainuu, but there were also battles in
Salla and
Petsamo in
Lapland
Lapland may refer to:
Places
*Lapland or Sápmi, an ethno-cultural region stretching over northern Fennoscandia (parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia)
**Lapland (Finland) (''Lappi''/''Lappland''), a Finnish region
*** Lapland (former pr ...
. After the Soviet military reorganized and adopted different tactics, they renewed their offensive in February and overcame Finnish defences.
Hostilities ceased in March 1940 with the signing of the
Moscow Peace Treaty in which Finland ceded 9% of its territory to the Soviet Union. Soviet losses were heavy, and the country's international reputation suffered. Their gains exceeded their pre-war demands, and the Soviets received substantial territories along
Lake Ladoga and further north. Finland retained its
sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
and enhanced its international reputation. The poor performance of the
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
encouraged German Chancellor
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
to believe that an attack on the Soviet Union would be successful and confirmed negative Western opinions of the Soviet military. After 15 months of
Interim Peace, in June 1941,
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
commenced
Operation Barbarossa, and the
Continuation War between Finland and the Soviets began.
Background
Finnish-Soviet relations and politics

Until the early 19th century, Finland was the eastern part of the
Kingdom of Sweden
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country located on t ...
. From 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809, the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
waged the
Finnish War against the Kingdom of Sweden, ostensibly to protect the Russian capital,
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, and eventually led to the conquest and
annexation of Finland and its conversion into an
autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
.
[ Trotter 2002, pp. 3–5] The resulting
Grand Duchy of Finland enjoyed wide autonomy within Russia until the end of the 19th century, when Russia began attempts
to assimilate Finland as part of a general policy to strengthen the central government and unify the Empire by
Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
. Those attempts were aborted because of Russia's internal strife, but they ruined Russia's relations with Finland and increased support for Finnish self-determination movements.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 4–6]
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
led to the collapse of the Russian Empire during the
Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
of 1917 and to the
Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
. On 15 November 1917, the
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
Russian government
declared that national minorities possessed the right of self-determination, including the right to secede and form a separate state, which gave Finland a window of opportunity. On 6 December 1917, the
Senate of Finland declared the nation's independence.
Soviet Russia, later the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, recognised the new Finnish government just three weeks after the declaration.
Finland achieved full sovereignty in May 1918 after a
four-month civil war in which the conservative
Whites defeated the socialist
Reds with the help of the
Imperial German Army, pro-German
Jägers, and some Swedish troops, in addition to the expulsion of Bolshevik troops.
[ Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), p. 3]
Finland joined the League of Nations in 1920 and sought security guarantees, but Finland's primary goal was co-operation with the
Scandinavian countries, mainly Sweden, and it focused on the exchange of information and on defence planning (the joint defence of
Åland
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an Federacy, autonomous and Demilitarized zone, demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1 ...
, for example), rather than on
military exercises or on the stockpiling and the deployment of
materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the spec ...
. Nevertheless, Sweden carefully avoided committing itself to Finnish foreign policy.
[ Turtola (1999a), pp. 21–24] Finland's military policy included clandestine
defence co-operation with
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
.
[ Turtola (1999a), pp. 33–34]
The period after the Finnish Civil War until the early 1930s was a politically unstable time in Finland because of the continued rivalry between the conservatives and the socialists. The
Communist Party of Finland was declared illegal in 1931, and the nationalist
Lapua Movement organised
anticommunist violence, which culminated in a
failed coup attempt in 1932. The successor of the Lapua Movement, the
Patriotic People's Movement, had a minor presence in national politics and never had more than 14 seats of the 200 in the
Finnish Parliament.
[ Edwards (2006), pp. 26–27
] By the late 1930s, the export-oriented Finnish economy was growing and the nation's extreme political movements had diminished.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 18]

After Soviet involvement in the Finnish Civil War in 1918, no formal peace treaty was signed. In 1918 and 1919, Finnish volunteers conducted two unsuccessful military incursions across the Soviet border, the
Viena and
Aunus expeditions, to annex areas in
Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for ...
that according to the
Greater Finland ideology would combine all
Finnic peoples into a single state. In 1920, Finnish communists, based in Soviet Russia, attempted to assassinate the former Finnish
White Guard Commander-in-Chief, Marshal
Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim. On 14 October 1920, Finland and Soviet Russia signed the
Treaty of Tartu, confirming the old border between the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland and
Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. T ...
proper as the new Finnish–Soviet border. Finland also received
Petsamo, with its
ice-free harbour
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
on the Arctic Ocean. Despite the signing of the treaty, relations between the two countries remained strained. The Finnish government allowed volunteers to cross the border to support the
East Karelian uprising in Russia in 1921, and Finnish communists in the Soviet Union continued to prepare for revenge and staged a cross-border raid into Finland, the
Pork Mutiny
The pork mutiny ( fi, Läskikapina sv, Fläskrevolten) was an incident in Northern Finland in 1922. On February 2 a group of roughly armed Red Guard members crossed the Finnish-Soviet border near Kuolajärvi and Savukoski after disarming a comp ...
, in 1922.
[ Turtola (1999a), pp. 30–33] In 1932, the
Soviet–Finnish Non-Aggression Pact was signed between both countries, and it was reaffirmed for ten years in 1934.
Foreign trade in Finland was booming, but less than 1% of it was with the Soviet Union.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 31] In 1934, the Soviet Union joined the League of Nations.
Justification
Soviet General Secretary
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
regarded it a disappointment that the Soviet Union could not halt the Finnish Revolution. He thought that the pro-Finland movement in Karelia posed a direct threat to
Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and that the area and defences of Finland could be used to invade the Soviet Union or restrict fleet movements. Soviet propaganda then painted Finland's leadership as a "vicious and reactionary
fascist clique". Field Marshal Mannerheim and
Väinö Tanner, the leader of the
Finnish Social Democratic Party
The Social Democratic Party of Finland (SDP, fi, Suomen sosialidemokraattinen puolue ; sv, Finlands socialdemokratiska parti), shortened to the Social Democrats ( fi, link=no, Sosiaalidemokraatit; sv, link=no, Socialdemokrater) and commonly kno ...
, were targeted for particular scorn.
[ Edwards (2006), pp. 32–33] When Stalin gained absolute power through the
Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secreta ...
of 1938, the Soviets changed their foreign policy toward Finland and began to pursue the reconquest of the provinces of Tsarist Russia that had been lost during the chaos of the
October Revolution of 1917 and the Russian Civil War almost two decades earlier. Soviet leaders believed that the old empire's extended borders provided territorial security and wanted Leningrad, only from the Finnish border, to enjoy a similar level of security against the rising power of
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
.
[ Lightbody (2004), p. 52]
Negotiations

In April 1938,
NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
agent
Boris Yartsev
Boris Arkadyevich Rybkin (russian: Бори́с Арка́дьевич Ры́бкин)born Boruch Aronovich Rivkin russian: Борух Аронович Рывкин; 19 June 189927 November 1947) was a Soviet diplomat and a secret agent of the NK ...
contacted Finnish Foreign Minister
Rudolf Holsti and Finnish Prime Minister
Aimo Cajander, stating that the Soviets did not trust Germany and that war was considered possible between the two countries. The Red Army would not wait passively behind the border but would rather "advance to meet the enemy". Finnish representatives assured Yartsev that Finland was committed to a policy of neutrality and that the country would resist any armed incursion. Yartsev suggested that Finland cede or lease some islands in the
Gulf of Finland along the seaward approaches to Leningrad, but Finland refused.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 12–13][ Turtola (1999a), pp. 32–33]
Negotiations continued throughout 1938 without results. The Finnish reception of Soviet entreaties was decidedly cool, as the violent collectivisation and purges in Stalin's Soviet Union resulted in a poor opinion of the country. Most of the Finnish communist elite in the Soviet Union had been executed during the
Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secreta ...
, further tarnishing the Soviets' image in Finland. Meanwhile, Finland was attempting to negotiate a military co-operation plan with Sweden and hoping to jointly defend
Åland
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an Federacy, autonomous and Demilitarized zone, demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1 ...
.
[ Turtola (1999a), pp. 34–35]
The Soviet Union and Nazi Germany signed the
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
in August 1939. It was publicly a
non-aggression treaty, but it included a secret protocol in which eastern European countries were divided into
spheres of interest. Finland fell into the Soviet sphere. On 1 September 1939, Germany began its
invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
, and two days later, the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany. On 17 September, the Soviets
invaded Eastern Poland.
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
,
Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and
Lithuania were soon
forced to accept treaties that allowed the Soviets to establish military bases on their soil.
[ Engle and Paananen (1985), p. 6] Estonia accepted the
ultimatum by signing the agreement on 28 September. Latvia and Lithuania followed in October. Unlike the three Baltic countries, Finland started a gradual
mobilisation under the guise of "additional
refresher training".
[ Turtola (1999a), pp. 38–41] The Soviets had already started intensive mobilisation near the Finnish border in 1938–39. Assault troops thought to be necessary for the invasion did not begin deployment until October 1939. Operational plans made in September called for the invasion to start in November.
[ Ries (1988), pp. 55–56][ Manninen (1999a), pp. 141–148]

On 5 October 1939, the Soviets invited a Finnish delegation to Moscow for negotiations.
Juho Kusti Paasikivi, the Finnish envoy to Sweden, was sent to Moscow to represent the Finnish government.
The Soviet delegation demanded that the border between the USSR and Finland on the
Karelian Isthmus be moved westward to a point only east of
Viipuri () and that Finland destroy all existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus. Likewise, the delegation demanded the cession of islands in the Gulf of Finland as well as
Rybachy Peninsula ( fi, Kalastajasaarento). The Finns would also have to lease the
Hanko Peninsula for 30 years and to permit the Soviets to establish a
military base
A military base is a facility directly owned and operated by or for the military or one of its branches that shelters military equipment and personnel, and facilitates training and operations. A military base always provides accommodations for o ...
there. In exchange, the Soviet Union would cede
Repola and
Porajärvi from
Eastern Karelia
East Karelia ( fi, Itä-Karjala, Karelian: ''Idä-Karjala''), also rendered as Eastern Karelia or Russian Karelia, is a name for the part of Karelia that since the Treaty of Stolbova in 1617 has remained Eastern Orthodox under Russian supremacy. ...
, an area twice the size as that of the territory demanded from Finland.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 14–16]
The Soviet offer divided the Finnish government but was eventually rejected with respect to the opinion of the public and Parliament. On 31 October, Soviet Foreign Minister
Vyacheslav Molotov publicly announced Soviet demands in public to the
Supreme Soviet. The Finns made two counteroffers to cede the
Terijoki area to the Soviet Union. That would double the distance between Leningrad and the Finnish border but was far less than the Soviets had demanded.
[ Turtola (1999a), pp. 41–43] The Finns would also cede the islands in the Gulf of Finland. The Finnish delegation returned home on 13 November and took for granted that the negotiations would continue.
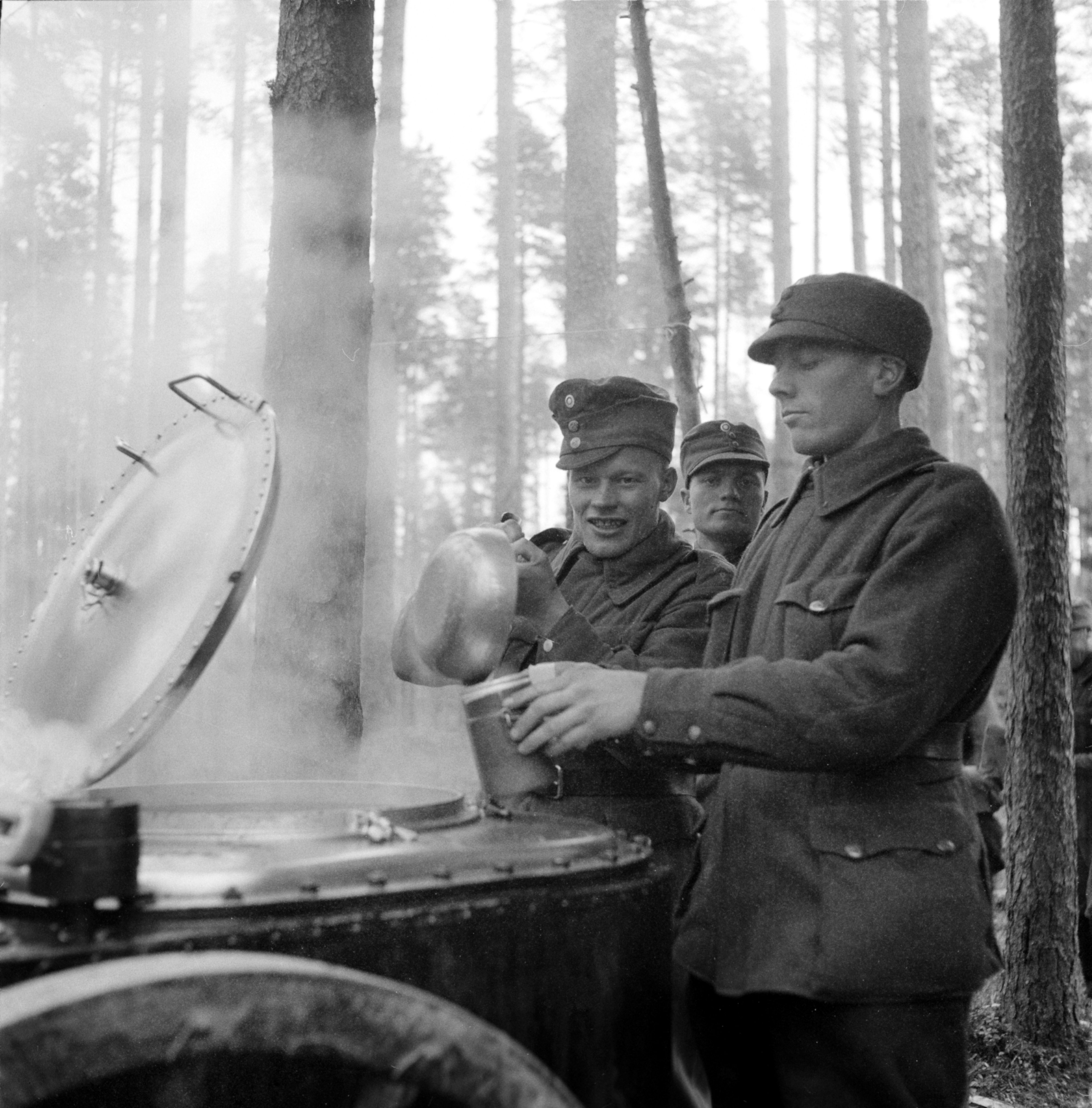
Shelling of Mainila and Soviet intentions
On 26 November 1939, an incident was reported near the Soviet village of
Mainila, near the border with Finland. A Soviet border guard post had been shelled by an unknown party resulting, according to Soviet reports, in the deaths of four and injuries of nine border guards. Research conducted by several Finnish and Russian historians later concluded that the shelling was a
false flag operation since there were no artillery units there, and it was carried out from the Soviet side of the border by an NKVD unit with the purpose of providing the Soviets with a ''
casus belli'' and a pretext to withdraw from the non-aggression pact.
[ Ries (1988), pp. 77–78] Soviet war games held in March 1938 and 1939 had been based on a scenario in which border incidents taking place at the village of Mainila would spark the war.

Molotov claimed that the incident was a Finnish artillery attack. He demanded that Finland apologise for the incident and to move its forces beyond a line from the border. Finland denied responsibility for the attack, rejected the demands and called for a joint Finnish–Soviet commission to examine the incident. In turn, the Soviet Union claimed that the Finnish response was hostile, renounced the non-aggression pact and severed diplomatic relations with Finland on 28 November. In the following years,
Soviet historiography described the incident as Finnish provocation. Doubt on the official Soviet version was cast only in the late 1980s, during the policy of ''
glasnost''. The issue has continued to divide Russian historiography even after the
end of the Soviet Union in 1991.
[ Kilin (2007a), pp. 99–100]
In 2013, Russian President
Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime m ...
stated at a meeting with military historians that the Soviets had launched the Winter War to "correct mistakes" made in determining the border with Finland after 1917. Opinion on the scale of the initial Soviet invasion decision is divided. The puppet Finnish communist government and the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact's secret protocols are used as proof by those who argue that the Soviet Union had intended to conquer all of Finland.
Hungarian historian István Ravasz wrote that the
Soviet Central Committee had set out in 1939 that the former borders of the Tsarist Empire were to be restored, including Finland.
American political scientist
Dan Reiter stated that the Soviets "sought to impose a
regime change" and thus "achieve absolute victory". He quoted Molotov, who had commented in November 1939 on the regime change plan to a Soviet ambassador that the new government "will not be Soviet, but one of a democratic republic. Nobody is going to set up Soviets over there, but we hope it will be a government we can come to terms with as to ensure the security of Leningrad".
According to Russian historian
Yuri Kilin, the Soviet terms encompassed the strongest fortified approaches of the Finnish defences for a reason. He claimed that Stalin had little hope for such a deal but would play for time for the ongoing mobilisation. He stated the objective as being to secure Finland from being used as a staging ground by means of regime change.

Others argue against the idea of a complete Soviet conquest. American historian
William R. Trotter asserted that Stalin's objective was to secure Leningrad's flank from a possible German invasion through Finland. He stated that "the strongest argument" against a Soviet intention of full conquest is that it did not happen in either 1939 or during the Continuation War in 1944 even though Stalin "could have done so with comparative ease".
Bradley Lightbody wrote that the "entire Soviet aim had been to make the Soviet border more secure".
In 2002, Russian historian A. Chubaryan stated that no documents had been found in Russian archives that support a Soviet plan to annex Finland. Rather, the objective was to gain Finnish territory and to reinforce Soviet influence in the region.
Opposing forces
Soviet military plan
Before the war, Soviet leadership had expected total victory within a few weeks. The Red Army had just completed the
invasion of eastern Poland at a cost of fewer than 4,000 casualties after Germany attacked Poland from the west. Stalin's expectations of a quick Soviet triumph were backed up by politician
Andrei Zhdanov and military strategist
Kliment Voroshilov, but other generals were more reserved. Red Army Chief of Staff
Boris Shaposhnikov advocated a fuller build-up, extensive
fire support
Fire support is defined by the United States Department of Defense as " Fires that directly support land, maritime, amphibious, and special operations forces to engage enemy forces, combat formations, and facilities in pursuit of tactical and o ...
and logistical preparations, a rational
order of battle and the deployment of the army's best units. Zhdanov's military commander,
Kirill Meretskov, reported, "The terrain of coming operations is split by lakes, rivers, swamps, and is almost entirely covered by forests.... The proper use of our forces will be difficult". These doubts were not reflected in Meretskov's troop deployments, and he publicly announced that the Finnish campaign would take two weeks at most. Soviet soldiers had even been warned not to cross the border mistakenly into Sweden.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 34] The leader of the Leningrad Military District,
Andrei Zhdanov, commissioned a celebratory piece from
Dmitri Shostakovich, ''
Suite on Finnish Themes'', intended to be performed as the marching bands of the Red Army paraded through Helsinki.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 98]
Stalin's purges in the 1930s had devastated the officer corps of the Red Army; those purged included three of its five marshals, 220 of its 264 division or higher-level commanders and 36,761 officers of all ranks. Fewer than half of all the officers remained.
[ Conquest (2007), p. 450] They were commonly replaced by soldiers who were less competent but more loyal to their superiors. Unit commanders were overseen by
political commissars, whose approval was needed to approve and ratify military decisions, which they evaluated based on their political merits. The dual system further complicated the Soviet chain of command
[ Ries (1988), p. 56] and annulled the independence of commanding officers.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 189]
After the Soviet success at the
Battles of Khalkhin Gol against Japan, on the USSR's eastern border, Soviet High Command had divided into two factions. One side was represented by the
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebeli ...
veterans General
Pavel Rychagov from the
Soviet Air Forces; the tank expert General
Dmitry Pavlov and Stalin's favourite general, Marshal
Grigory Kulik, the chief of artillery. The other faction was led by Khalkhin Gol veterans General
Georgy Zhukov of the Red Army and General
Grigory Kravchenko of the Soviet Air Forces. Under this divided command structure, the lessons of the Soviet Union's "first real war on a massive scale using tanks, artillery, and aircraft" at Khalkin Gol went unheeded.
[ Coox (1985), p. 997] As a result, Russian
BT tanks were less successful during the Winter War, and it took the Soviet Union three months and over a million men to accomplish what Zhukov had managed at Khalkhin Gol in ten days (albeit in completely different circumstances).
Soviet order of battle

Soviet generals were impressed by the success of German ''
Blitzkrieg''
tactics, but they had been tailored to conditions in
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
, with its dense well-mapped network of paved roads. Armies fighting there had recognised supply and communications centres, which could be easily targeted by armoured vehicle regiments. Finnish Army centres, in contrast, were deep inside the country. There were no paved roads, and even gravel or dirt roads were scarce. Most of the terrain consisted of trackless forests and swamps. The war correspondent
John Langdon-Davies observed the landscape: "Every acre of its surface was created to be the despair of an attacking military force". Waging ''Blitzkrieg'' in Finland was a highly-difficult proposition, and according to Trotter, the Red Army failed to meet the level of tactical co-ordination and local initiative that would be required to execute such tactics in Finland.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 35–36]
Commander of the
Leningrad Military District Kiril Meretskov initially ran the overall operation against the Finns.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 93] The command was passed on 9 December 1939 to the General Staff Supreme Command (later known as
Stavka), directly under Kliment Voroshilov (chairman),
Nikolai Kuznetsov,
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
and
Boris Shaposhnikov.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 125] In January 1940, the Leningrad Military District was reformed and renamed "North-Western Front". Semyon Timoshenko was chosen Army Commander to break the Mannerheim Line.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 204]
The Soviet forces were organised as follows:
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 38–39]
* The
7th Army, comprising nine divisions, a tank corps and three tank brigades, was located on the Karelian Isthmus. Its objective was the city of Viipuri. The force was later divided into the 7th and
13th Armies.
[ Kilin and Raunio (2007), p. 13]
* The
8th Army, comprising six divisions and a tank brigade, was north of Lake Ladoga. Its mission was to execute a flanking manoeuvre around the northern shore of Lake Ladoga to strike at the rear of the
Mannerheim Line.
* The
9th Army was positioned to strike into Central Finland through the
Kainuu region. It was composed of three divisions with one more on its way. Its mission was to thrust westward to cut Finland in half.
* The
14th Army Fourteenth Army or 14th Army may refer to:
* 14th Army (German Empire), a World War I field Army
* 14th Army (Wehrmacht), a World War II field army
* Italian Fourteenth Army
* Japanese Fourteenth Army, a World War II field army, in 1944 converted ...
, comprising three divisions, was based in
Murmansk. Its objectives were to capture the
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada ( Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm ( Greenland), Finland, Iceland ...
port of
Petsamo and then advance to the town of
Rovaniemi.
Finnish order of battle

The Finnish strategy was dictated by geography. The border with the Soviet Union was mostly impassable except along a handful of
unpaved road Unpaved roads may refer to:
* Dirt roads
* Gravel roads
A gravel road is a type of unpaved road surfaced with gravel that has been brought to the site from a quarry or stream bed. They are common in less-developed nations, and also in the ru ...
s. In prewar calculations, the Finnish
Defence Command, which had established its wartime headquarters at
Mikkeli,
had estimated seven Soviet divisions on the Karelian Isthmus and no more than five along the whole border north of Lake Ladoga. In the estimation, the manpower ratio would have favoured the attacker by three to one. The true ratio was much higher, however, since for example, 12 Soviet divisions were deployed north of Lake Ladoga.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 42–44]
Finland had a large force of reservists, which was trained in regular maneuvers, some of which had experience from the recent
Finnish Civil War. The soldiers were also almost universally trained in basic survival techniques, such as skiing. The Finnish Army was not able to equip all its soldiers with proper uniforms at the outbreak of war, but its reservists were equipped with warm civilian clothing. However, the sparsely-populated highly-agrarian Finland had to draft so many of its working men that the
Finnish economy
The economy of Finland is a highly industrialised, mixed economy with a per capita output similar to that of western European economies such as France, Germany and the United Kingdom. The largest sector of Finland's economy is services at 72.7 p ...
was massively strained because of a lack of workers. An even greater problem than lack of soldiers was the lack of
materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the spec ...
since foreign shipments of anti-tank weapons and aircraft were arriving only in small quantities. The ammunition situation was alarming, as stockpiles had cartridges, shells and fuel to last only 19 to 60 days. The ammunition shortage meant the Finns could seldom afford
counter-battery or
saturation fire. Finnish tank forces were operationally nonexistent.
The ammunition situation was alleviated somewhat since Finns were largely armed with
Mosin–Nagant
The Mosin–Nagant is a five-shot, bolt-action, internal magazine–fed military rifle. Known officially as the 3-line rifle M1891 and informally in Russia and former Soviet Union as Mosin's rifle ( ru , винтовка Мосина, ISO 9: ...
rifles dating from the Finnish Civil War, which used the same
7.62×54mmR cartridge that was used by Soviet forces. The situation was so severe that Finnish soldiers sometimes had to maintain their ammunition supply by looting the bodies of dead Soviet soldiers.
The Finnish forces were positioned as follows:
[ Trotter (2002), p. 47]
* The
Army of the Isthmus
The Army of the Isthmus ( fi, Kannaksen Armeija) was a formation of the Finnish Army during the Winter War. It was stationed on the Karelian Isthmus and was the largest formation of the Finnish Army, as it was charged to defend the important ist ...
was composed of six divisions under the command of
Hugo Österman. The
II Army Corps was positioned on its right flank and the
III Army Corps, on its left flank.
* The
IV Army Corps was located north of Lake Ladoga. It was composed of two divisions under
Juho Heiskanen
Juho Henrik Heiskanen (18 December 1889 Joensuu, Pielisensuu – 11 December 1950) was a Finland, Finnish major general during World War II.
Biography
Heiskanen joined the Finnish Jäger troops, Jaeger Movement in 1915 and trained and fought in th ...
, who was soon replaced by
Woldemar Hägglund.
* The
North Finland Group was a collection of White Guards,
border guards and drafted
reservist units under
Wiljo Tuompo.
Soviet invasion
Start of invasion and political operations

On 30 November 1939, Soviet forces invaded Finland with 21 divisions, totalling 450,000 men, and
bombed Helsinki,
[ Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), p. 6] killing about 100 citizens and destroying more than 50 buildings. In response to international criticism, Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov stated that the Soviet Air Force was not bombing Finnish cities but rather dropping humanitarian aid to the starving Finnish population; they were sarcastically dubbed
Molotov bread baskets by Finns. The Finnish statesman J. K. Paasikivi commented that the Soviet attack without a
declaration of war violated three separate non-aggression pacts: the Treaty of Tartu, which was signed in 1920, the non-aggression pact between Finland and the Soviet Union, which was signed in 1932 and again in 1934; and also the
Covenant of the League of Nations, which the Soviet Union signed in 1934.
Field Marshal C.G.E. Mannerheim was appointed Commander-in-Chief of the
Finnish Defence Forces after the Soviet attack. In a further reshuffling,
Aimo Cajander's caretaker cabinet was replaced by
Risto Ryti and
his cabinet, with
Väinö Tanner as foreign minister because of opposition to Cajander's prewar politics.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 48–51] Finland brought the matter of the Soviet invasion before the League of Nations. The League expelled the Soviet Union on 14 December 1939 and exhorted its members to aid Finland.

On 1 December 1939, the Soviet Union formed a
puppet government, named the
Finnish Democratic Republic, to govern Finland after Soviet conquest. Headed by
Otto Wille Kuusinen, the government operated in the parts of Finnish Karelia occupied by the Soviets, and was also referred to as the "Terijoki Government", after the village of
Terijoki, the first settlement captured by the advancing Red Army.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 58] After the war, the puppet government was reabsorbed into the Soviet Union. From the very outset of the war, working-class Finns stood behind the legitimate government in Helsinki.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 61] Finnish national unity against the Soviet invasion was later called the
spirit of the Winter War
The Spirit of the Winter War ( fi, Talvisodan henki, ) is the national unity that had been credited with having saved Finland from disintegrating along class and ideological lines under the invasion of the Soviet Union during the Winter War from No ...
.
[ Soikkanen (1999), p. 235]
First battles and Soviet advance to Mannerheim Line
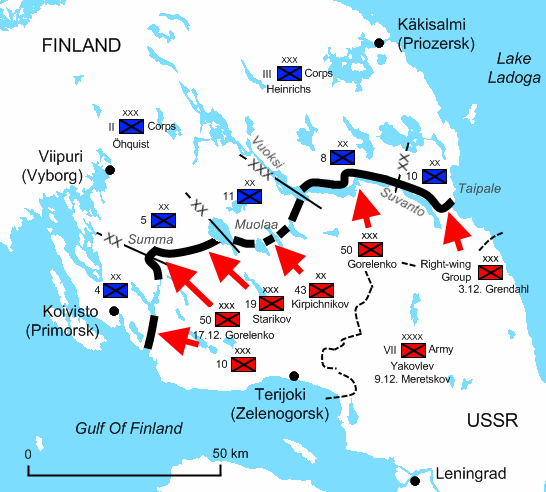
The array of Finnish defence structures that during the war started to be called the Mannerheim Line was located on the Karelian Isthmus approximately from the Soviet border. The Red Army soldiers on the Isthmus numbered 250,000, facing 130,000 Finns.
[ Geust; Uitto (2006), p. 54] The Finnish command deployed a
defence in depth of about 21,000 men in the area in front of the Mannerheim Line to delay and damage the Red Army before it reached the line.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 69] In combat, the most severe cause of confusion among Finnish soldiers was Soviet tanks. The Finns had few
anti-tank weapons and insufficient training in modern
anti-tank tactics. According to Trotter, the favoured Soviet armoured tactic was a simple frontal charge, the weaknesses of which could be exploited. The Finns learned that at close range, tanks could be dealt with in many ways; for example, logs and crowbars jammed into the
bogie wheels would often immobilise a tank. Soon, Finns fielded a better ad hoc weapon, the
Molotov cocktail, a glass bottle filled with
flammable liquids and with a simple hand-lit
fuse. Molotov cocktails were eventually mass-produced by the Finnish ''
Alko'' alcoholic-beverage corporation and bundled with matches with which to light them. 80 Soviet tanks were destroyed in the border zone engagements.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 72–73]
By 6 December, all of the Finnish covering forces had withdrawn to the Mannerheim Line. The Red Army began its first major attack against the Line in
Taipalethe area between the shore of Lake Ladoga, the
Taipale river and the
Suvanto waterway. Along the Suvanto sector, the Finns had a slight advantage of elevation and dry ground to dig into. The Finnish
artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieg ...
had scouted the area and made fire plans in advance, anticipating a Soviet assault. The
Battle of Taipale began with a forty-hour Soviet artillery preparation. After the
barrage, Soviet infantry attacked across open ground but was repulsed with heavy casualties. From 6 to 12 December, the Red Army continued to try to engage using only a single division. Next, the Red Army strengthened its artillery and deployed tanks and the
150th Rifle Division forward to the Taipale front. On 14 December, the bolstered Soviet forces launched a new attack but were pushed back again. A third Soviet division entered the fight but performed poorly and panicked under shell fire. The assaults continued without success, and the Red Army suffered heavy losses. One typical Soviet attack during the battle lasted just an hour but left 1,000 dead and 27 tanks strewn on the ice.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 76–78] North of Lake Ladoga on the
Ladoga Karelia front, the defending Finnish units relied on the terrain. Ladoga Karelia, a large forest wilderness, did not have road networks for the modern Red Army.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 51–55] The
Soviet 8th Army
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
had extended a new railroad line to the border, which could double the supply capability on the front. On 12 December, the advancing Soviet
139th Rifle Division, supported by the
56th Rifle Division The 56th Rifle Division () was an infantry division of the Red Army and later the Soviet Army of the Soviet Union, formed three times.
First formation
On 21 November 1919 the 56th Rifle Division ( :ru:56-я стрелковая дивизия ...
, was defeated by a much smaller Finnish force under
Paavo Talvela in
Tolvajärvi
Lake Tolvajärvi (russian: Толваярви; fi, Tolvajärvi) is a group of lakes in the Republic of Karelia, in the Ladoga Karelia. It is a part of the Vuoksi drainage basin. The group of lakes have flows through rivers to the Finnish Lake Pie ...
, the first Finnish victory of the war.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 121]
In Central and Northern Finland, roads were few and the terrain hostile. The Finns did not expect large-scale Soviet attacks, but the Soviets sent eight divisions, heavily supported by armour and artillery. The
155th Rifle Division
The 155th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army of the Soviet Union. It was established in Opotschka in 1939. In December 1939, it fought in the Winter War and attacked the town of Lieksa. In October 1941, it was destroyed i ...
attacked at
Lieksa, and further north the
44th attacked at
Kuhmo
Kuhmo (known as ''Kuhmoniemi'' until 1937) is a town and a municipality in Finland and is located at the south-eastern corner of the Kainuu region. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population ...
. The 163rd Rifle Division was deployed at
Suomussalmi and ordered to cut Finland in half by advancing on the Raate road. In
Finnish Lapland, the Soviet
88th and 122nd Rifle Divisions attacked at
Salla. The Arctic port of Petsamo was attacked by the 104th Mountain Rifle Division by sea and land, supported by
naval gunfire.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 53–54]
Operations from December to January
Weather conditions
The winter of 1939–40 was exceptionally cold with the Karelian Isthmus experiencing a record low temperature of on 16 January 1940.
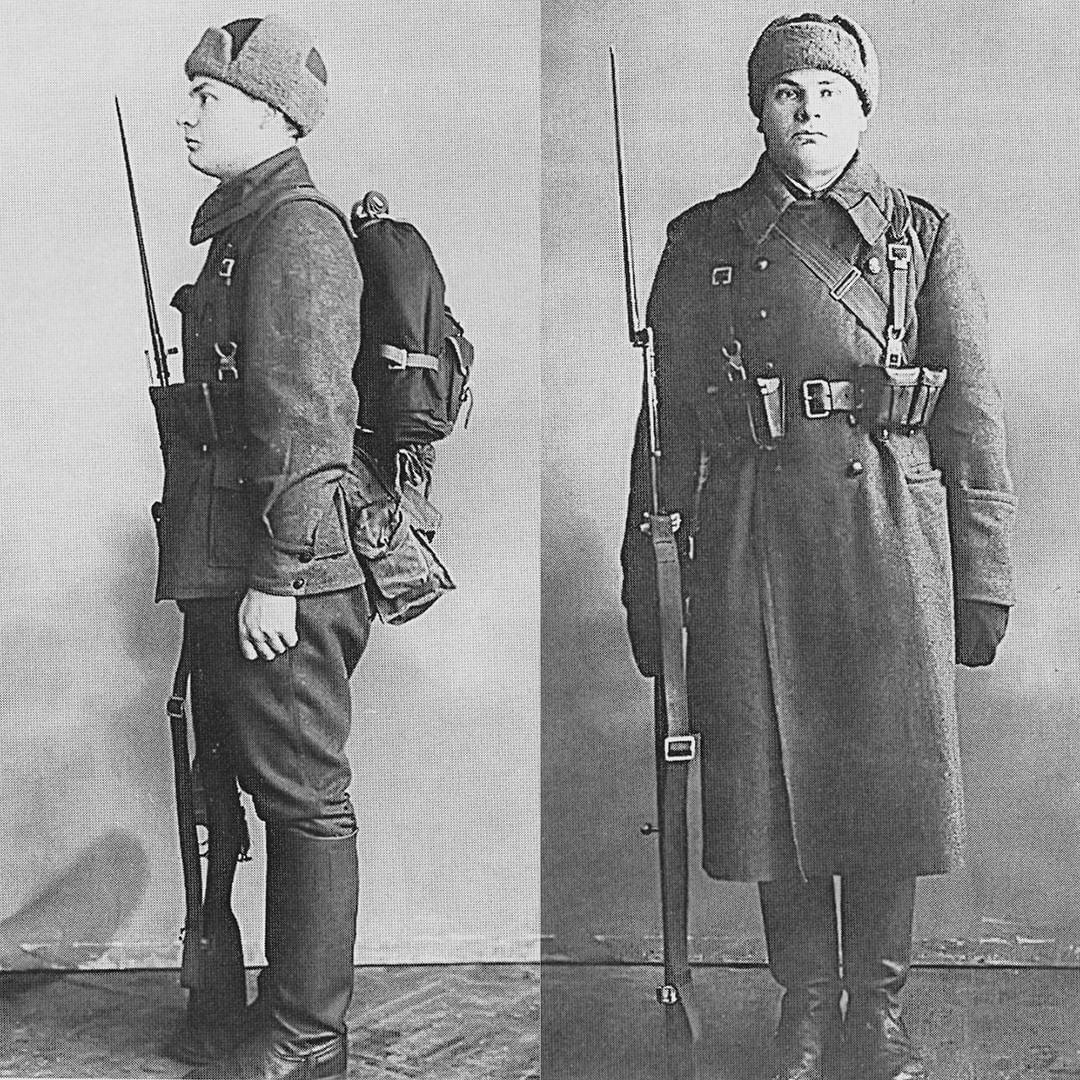
[ Paulaharju (1999), p. 292] At the beginning of the war, only those Finnish soldiers who were in
active service had
uniforms and
weapons. The rest had to make do with their own clothing, which for many soldiers was their normal winter clothing with a semblance of insignia added. Finnish soldiers were skilled in
cross-country skiing.
[ Paulaharju (1999), pp. 289–290] The cold, snow, forest, and long hours of darkness were factors that the Finns could use to their advantage. The Finns dressed in layers, and the
ski troopers wore a lightweight white snow cape. This snow-camouflage made the ski troopers almost invisible so that they could more easily execute
guerrilla attacks against Soviet columns. At the beginning of the war, Soviet tanks were painted in standard
olive drab and men dressed in regular
khaki uniforms. Not until late January 1940 did the Soviets paint their equipment white and issue
snowsuits to their infantry.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 145–146]
Most Soviet soldiers had proper winter clothes, but this was not the case with every unit. In the
Battle of Suomussalmi, thousands of Soviet soldiers died of
frostbite. The Soviet troops also lacked skill in skiing, so soldiers were restricted to movement by road and were forced to move in long columns. The Red Army lacked proper winter tents, and troops had to sleep in improvised shelters.
[ Paulaharju (1999), pp. 297–298] Some Soviet units incurred frostbite casualties as high as ten percent even before crossing the Finnish border.
However, the cold weather did give an advantage to Soviet tanks, as they could move over frozen terrain and bodies of water, rather than being immobilised in swamps and mud.
According to Krivosheev, at least 61,506 Soviet troops were sick or
frostbitten
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when exposed to extreme low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occurs in the hand ...
during the war.
Finnish guerrilla tactics

In battles from Ladoga Karelia to the Arctic port of
Petsamo, the Finns used
guerrilla tactics. The Red Army was superior in numbers and material, but Finns used the advantages of speed,
manoeuvre warfare and
economy of force. Particularly on the Ladoga Karelia front and during the
Battle of Raate Road, the Finns isolated smaller portions of numerically superior Soviet forces. With Soviet forces divided into smaller groups, the Finns dealt with them individually and attacked from all sides.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 131–132]
For many of the encircled Soviet troops in a
pocket (called a ''
motti'' in Finnish, originally meaning of firewood), staying alive was an ordeal comparable to combat. The men were freezing and starving and endured poor sanitary conditions. Historian
William R. Trotter described these conditions as follows: "The Soviet soldier had no choice. If he refused to fight, he would be shot. If he tried to sneak through the forest, he would freeze to death. And surrender was no option for him; Soviet propaganda had told him how the Finns would torture prisoners to death."
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 148–149] The problem however was that the Finns were mostly too weak to fully exploit their success. Some of the pockets of encircled Soviet soldiers held out for weeks and even months, binding a huge number of Finnish forces.
Battles of the Mannerheim Line
The terrain on the Karelian Isthmus did not allow guerrilla tactics, so the Finns were forced to resort to the more conventional Mannerheim Line, with its flanks protected by large bodies of water. Soviet propaganda claimed that it was as strong as or even stronger than the
Maginot Line. Finnish historians, for their part, have belittled the line's strength, insisting that it was mostly conventional trenches and log-covered
dugouts
Dugout may refer to:
* Dugout (shelter), an underground shelter
* Dugout (boat), a logboat
* Dugout (smoking), a marijuana container
Sports
* In bat-and-ball sports, a dugout is one of two areas where players of the home or opposing teams sit whe ...
.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 62–63] The Finns had built 221 strong-points along the Karelian Isthmus, mostly in the early 1920s. Many were extended in the late 1930s. Despite these defensive preparations, even the most fortified section of the Mannerheim Line had only one
reinforced-concrete bunker per kilometre. Overall, the line was weaker than similar lines in mainland Europe.
[ Vuorenmaa (1999), pp. 494–495] According to the Finns, the real strength of the line was the "stubborn defenders with a lot of ''
sisu''" – a Finnish idiom roughly translated as "
guts, fighting spirit".
On the eastern side of the Isthmus, the Red Army attempted to break through the Mannerheim Line at the battle of Taipale. On the western side, Soviet units faced the Finnish line at Summa, near the city of Viipuri, on 16 December. The Finns had built 41 reinforced-concrete bunkers in the Summa area, making the defensive line in this area stronger than anywhere else on the Karelian Isthmus. Because of a mistake in planning, the nearby Munasuo swamp had a -wide gap in the line.
[ Laaksonen (1999), p. 407] During the
First Battle of Summa, a number of Soviet tanks broke through the thin line on 19 December, but the Soviets could not benefit from the situation because of insufficient co-operation between branches of service. The Finns remained in their trenches, allowing the Soviet tanks to move freely behind the Finnish line, as the Finns had no proper anti-tank weapons. The Finns succeeded in repelling the main Soviet assault. The tanks, stranded behind enemy lines, attacked the strongpoints at random until they were eventually destroyed, 20 in all. By 22 December, the battle ended in a Finnish victory.
[ Laaksonen (1999), pp. 411–412]
The Soviet advance was stopped at the Mannerheim Line. Red Army troops suffered from poor morale and a shortage of supplies, eventually refusing to participate in more
suicidal frontal attacks. The Finns, led by General
Harald Öhquist, decided to launch a counter-attack and encircle three Soviet divisions into a ''motti'' near Viipuri on 23 December. Öhquist's plan was bold; however it failed. The Finns lost 1,300 men, and the Soviets were later estimated to have lost a similar number.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 87–89]
Battles in Ladoga Karelia

The strength of the Red Army north of Lake Ladoga in Ladoga Karelia surprised the Finnish Headquarters. Two Finnish divisions were deployed there, the 12th Division led by
Lauri Tiainen
Lauri Taavetti Tiainen (15 February 1891, Rantasalmi – 18 September 1958) was a Finnish colonel during World War II. Kilin and Raunio 2007, p. 71
Tiainen joined the Jaeger Movement in 1915 and trained and fought in the Royal Prussian 27th Jäge ...
and the 13th Division led by
Hannu Hannuksela. They also had a support group of three
brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division. ...
s, bringing their total strength to over 30,000. The Soviets deployed a
division for almost every road leading west to the Finnish border. The 8th Army was led by
Ivan Khabarov, who was replaced by
Grigory Shtern on 13 December.
[ Kilin and Raunio (2007), p. 113] The Soviets' mission was to destroy the Finnish troops in the area of Ladoga Karelia and advance into the area between
Sortavala and
Joensuu
Joensuu (; krl, Jovensuu; ) is a city and municipality in North Karelia, Finland, located on the northern shore of Lake Pyhäselkä (northern part of Lake Saimaa) at the mouth of the Pielinen River (''Pielisjoki''). It was founded in 1848. T ...
within 10 days. The Soviets had a 3:1 advantage in manpower and a 5:1 advantage in artillery, as well as
air supremacy.
[ Juutilainen (1999a), pp. 504–505]
Finnish forces panicked and retreated in front of the overwhelming Red Army. The commander of the Finnish IV Army Corps Juho Heiskanen was replaced by Woldemar Hägglund on 4 December.
[ Juutilainen (1999a), p. 506] On 7 December, in the middle of the Ladoga Karelian front, Finnish units retreated near the small stream of Kollaa. The waterway itself did not offer protection, but alongside it, there were
ridges up to high. The ensuing
battle of Kollaa
The Battle of Kollaa was fought from December 7, 1939, to March 13, 1940, in Ladoga's Karelia, Finland, as a part of the Soviet-Finnish Winter War.
Description and outcome
Despite having far fewer troops than the Soviets, the Finnish for ...
lasted until the end of the war. A memorable quote, "Kollaa holds" ( fi, Kollaa kestää) became a legendary motto among Finns.
[ Juutilainen (1999a), p. 520] Further contributing to the legend of Kollaa was the sniper
Simo Häyhä, dubbed "the White Death" by Soviets, and credited with over 500 kills. Captain
Aarne Juutilainen, dubbed "the Terror of Morocco", also became a living legend in the Battle of Kollaa. To the north, the Finns retreated from
Ägläjärvi to
Tolvajärvi
Lake Tolvajärvi (russian: Толваярви; fi, Tolvajärvi) is a group of lakes in the Republic of Karelia, in the Ladoga Karelia. It is a part of the Vuoksi drainage basin. The group of lakes have flows through rivers to the Finnish Lake Pie ...
on 5 December and then repelled a Soviet offensive in the battle of Tolvajärvi on 11 December.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 110]
In the south, two Soviet divisions were united on the northern side of the Lake Ladoga coastal road. As before, these divisions were trapped as the more mobile Finnish units counterattacked from the north to flank the Soviet columns. On 19 December, the Finns temporarily ceased their assaults due to exhaustion.
[ Juutilainen (1999a), pp. 510–511] It was not until the period of 6–16 January 1940 that the Finns resumed their offensive, dividing Soviet divisions into smaller ''mottis.''
[ Juutilainen (1999a), p. 514] Contrary to Finnish expectations, the encircled Soviet divisions did not try to break through to the east but instead entrenched. They were expecting reinforcements and supplies to
arrive by air. As the Finns lacked the necessary heavy artillery equipment and were short of men, they often did not directly attack the ''mottis'' they had created; instead, they worked to eliminate only the most dangerous threats. Often the ''motti'' tactic was not applied as a strategy, but as a Finnish adaptation to the behaviour of Soviet troops under fire.
[ Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), p. 44] In spite of the cold and hunger, the Soviet troops did not surrender easily but fought bravely, often entrenching their tanks to be used as
pillboxes and building timber dugouts. Some specialist Finnish soldiers were called in to attack the ''mottis''; the most famous of them was Major
Matti Aarnio
Matti Armas Aarnio, known as Motti-Matti (24 February 1901, Kouvola – 16 December 1984) was a Finnish military officer and a specialist in '' motti'' battles during World War II.
Career
Aarnio was a volunteer with the White Guards at the Savo ...
, or "Motti-Matti" as he became known.
[ Juutilainen (1999a), pp. 516–517]
In
North Karelia, Soviet forces were outmanoeuvred at
Ilomantsi and Lieksa. The Finns used effective guerrilla tactics, taking special advantage of their superior skiing skills and snow-white
layered clothing and executing surprise ambushes and raids. By the end of December, the Soviets decided to retreat and transfer resources to more critical fronts.
[ Vuorenmaa (1999), pp. 559–561]
Battles in Kainuu

The Suomussalmi–Raate engagement was a double operation
[ Vuorenmaa (1999), p. 550] which would later be used by
military academics as a classic example of what well-led troops and innovative tactics can do against a much larger adversary. Suomussalmi was a municipality of 4,000 with long lakes, wild forests and few roads. The Finnish command believed that the Soviets would not attack there, but the Red Army committed two divisions to the Kainuu area with orders to cross the wilderness, capture the city of
Oulu and effectively cut Finland in two. There were two roads leading to Suomussalmi from the frontier: the northern Juntusranta road and the southern Raate road.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 150]

The
Battle of Raate Road, which occurred during the month-long battle of Suomussalmi, resulted in one of the largest Soviet losses in the Winter War. The Soviet 44th and parts of the 163rd Rifle Division, comprising about 14,000 troops,
[ Kulju (2007), p. 230] were almost completely destroyed by a Finnish ambush as they marched along the forest road. A small unit blocked the Soviet advance while Finnish Colonel
Hjalmar Siilasvuo and his 9th Division cut off the retreat route, split the enemy force into smaller ''mottis'', and then proceeded to destroy the remnants
in detail as they retreated. The Soviets suffered 7,000–9,000 casualties;
[ Kulju (2007), p. 229] the Finnish units, 400.
[ Kantakoski (1998), p. 283] The Finnish troops captured dozens of tanks, artillery pieces, anti-tank guns, hundreds of trucks, almost 2,000 horses, thousands of rifles, and much-needed ammunition and medical supplies.
[ Kulju (2007), pp. 217–218] So sure of their victory had the Soviets been that a military band, complete with instruments, banners and notes, was traveling with the 44th Division to perform in a victory parade. The Finns found their instruments among the captured materiel.
Battles in Finnish Lapland

The Finnish area of
Lapland
Lapland may refer to:
Places
*Lapland or Sápmi, an ethno-cultural region stretching over northern Fennoscandia (parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia)
**Lapland (Finland) (''Lappi''/''Lappland''), a Finnish region
*** Lapland (former pr ...
, bestriding the
Arctic Circle, is sparsely developed, with little daylight and persistent snow-cover during winter; the Finns expected nothing more than raiding parties and reconnaissance patrols. Instead, the Soviets sent full divisions.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 171–174] On 11 December, the Finns rearranged the defence of Lapland and detached the
Lapland Group from the North Finland Group. The group was placed under the command of
Kurt Wallenius.
In southern Lapland, near the village of Salla, the Soviet 88th and 122nd Divisions, totaling 35,000 men, advanced. In the
Battle of Salla, the Soviets proceeded easily to Salla, where the road split. Further ahead was
Kemijärvi
Kemijärvi ( se, Giemajávri, smn, Kiemâjävri, sms, Ǩeeʹmmjäuʹrr) is a town and municipalities of Finland, municipality of Finland. It is located in the provinces of Finland, province of Lapland, Finland, Lapland.
History
The first pe ...
, while the fork to
Pelkosenniemi lead northwest. On 17 December, the Soviet northern group, comprising an infantry regiment, a
battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions are ...
, and a company of tanks, was outflanked by a Finnish battalion. The 122nd retreated, abandoning much of its heavy equipment and vehicles. Following this success, the Finns shuttled reinforcements to the defensive line in front of Kemijärvi. The Soviets hammered the defensive line without success. The Finns counter-attacked, and the Soviets retreated to a new defensive line where they stayed for the rest of the war.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 178–180][ Vuorenmaa (1999), pp. 545–549]

To the north was Finland's only ice-free port in the Arctic, Petsamo. The Finns lacked the manpower to defend it fully, as the main front was distant at the Karelian Isthmus. In the battle of Petsamo, the Soviet 104th Division attacked the Finnish 104th Independent Cover Company. The Finns abandoned Petsamo and concentrated on delaying actions. The area was treeless, windy, and relatively low, offering little defensible terrain. The
almost constant darkness and extreme temperatures of the Lapland winter benefited the Finns, who executed guerrilla attacks against Soviet supply lines and patrols. As a result, the Soviet movements were halted by the efforts of one-fifth as many Finns.
Aerial warfare
Soviet Air Force
The USSR enjoyed
air superiority throughout the war. The
Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
, supporting the Red Army's invasion with about 2,500 aircraft (the most common type being
Tupolev SB), was not as effective as the Soviets might have hoped. The material damage by the bomb raids was slight as Finland offered few valuable targets for
strategic bombing
Strategic bombing is a military strategy used in total war with the goal of defeating the enemy by destroying its morale, its economic ability to produce and transport materiel to the theatres of military operations, or both. It is a systemati ...
. For example, the city of
Tampere
Tampere ( , , ; sv, Tammerfors, ) is a city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclo ...
was one of the most important targets because it was an important railway junction, and also housed
State Aircraft Factory and the
Tampere Linen and Iron Industry premises, which manufactured
munition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weapo ...
s and weapons, including
grenade launchers. Often, targets were village depots with little value. The country had few modern highways in the interior, therefore making the railways the main targets for bombers.
Rail tracks were cut thousands of times but the Finns hastily repaired them and service resumed within a matter of hours.
The Soviet Air Force learned from its early mistakes, and by late February instituted more effective tactics.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 193]
The largest bombing raid against the capital of Finland,
Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
, occurred on the first day of the war. The capital was bombed only a few times thereafter. All in all, Soviet bombings cost Finland five percent of its total man-hour production. Nevertheless, Soviet air attacks affected thousands of civilians, killing 957.
The Soviets recorded 2,075 bombing attacks in 516 localities. The city of Viipuri, a major Soviet objective close to the Karelian Isthmus front, was almost levelled by nearly 12,000 bombs. No attacks on civilian targets were mentioned in Soviet radio or newspaper reports. In January 1940, the Soviet ''
Pravda'' newspaper continued to stress that no civilian targets in Finland had been struck, even accidentally.
[ Tillotson (1993), p. 157] It is estimated that the Soviet air force lost about 400 aircraft because of inclement weather, lack of fuel and tools, and during transport to the front. The Soviet Air Force flew approximately 44,000 sorties during the war.
Finnish Air Force

At the beginning of the war, Finland had a small air force, with only 114 combat planes fit for duty. Missions were limited, and
fighter aircraft were mainly used to repel Soviet bombers. Strategic bombings doubled as opportunities for military
reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops ( skirmishe ...
. Old-fashioned and few in number, aircraft offered little support for Finnish ground troops. In spite of losses, the number of planes in the
Finnish Air Force rose by over 50 percent by the end of the war.
[ Peltonen (1999), pp. 607–608] The Finns received shipments of British, French, Italian, Swedish and American aircraft.
Finnish fighter pilots often flew their motley collection of planes into Soviet formations that outnumbered them 10 or even 20 times. Finnish fighters shot down 200 Soviet aircraft, while losing 62 of their own on all causes.
[ Tillotson (1993), p. 160] Finnish anti-aircraft guns downed more than 300 enemy aircraft.
Often, a Finnish forward
air base consisted of a frozen lake, a
windsock, a telephone set and some tents. Air-raid warnings were given by Finnish women organised by the
Lotta Svärd. The top scoring fighter ace was
Jorma Sarvanto, with 12.83 victories. He would increase his tally during the
Continuation War.
Naval warfare
Naval activity
There was little naval activity during the Winter War. The
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
began to freeze over by the end of December, impeding the movement of
warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster a ...
s; by mid-winter, only
ice breakers and
submarines could still move. The other reason for low naval activity was the nature of
Soviet Navy forces in the area. The
Baltic Fleet was a coastal defence force which did not have the training, logistical structure, or
landing craft to undertake large-scale operations. The Baltic Fleet possessed two
battleships, one
heavy cruiser, almost 20
destroyers, 50
motor torpedo boats, 52 submarines, and other miscellaneous vessels. The Soviets used naval bases in
Paldiski
Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the Pakri Peninsula of northwestern Estonia. Since 2017, it's the administrative centre of Lääne-Harju Parish of Harju County. Previously a village of Estonia-Swedes known by the historical ...
,
Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju '' ...
and
Liepāja
Liepāja (; liv, Līepõ; see other names) is a state city in western Latvia, located on the Baltic Sea. It is the largest-city in the Kurzeme Region and the third-largest city in the country after Riga and Daugavpils. It is an important ice ...
for their operations.
[ Elfvegren (1999), p. 681]
The
Finnish Navy
The Finnish Navy ( fi, Merivoimat, sv, Marinen) is one of the branches of the Finnish Defence Forces. The navy employs 2,300 people and about 4,300 conscripts are trained each year. Finnish Navy vessels are given the ship prefix "FNS", short f ...
was a coastal defence force with two
coastal defence ships, five submarines, four
gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-ste ...
s, seven motor torpedo boats, one
minelayer and six
minesweepers and at least 5
icebreakers. The two coastal defence ships, and , were moved to harbour in
Turku where they were used to bolster the air defence. Their anti-aircraft guns shot down one or two planes over the city, and the ships remained there for the rest of the war.
At 18 January, Finnish armed icebreaker
''Tarmo'' was severely damaged at
Kotka, received 2 bombs from a Soviet bomber with 39 Finnish troops killed in action. As well as coastal defence, the Finnish Navy protected the Ålandish and Finnish
merchant vessels in the Baltic Sea.
[ Elfvegren (1999), p. 678]
Soviet aircraft bombed Finnish vessels and harbours and dropped
mines into Finnish
seaways. Still, only five merchant ships were lost to Soviet action. World War II, which had started before the Winter War, proved more costly for the Finnish merchant vessels, with 26 lost due to hostile action in 1939 and 1940.
[ Elfvegren (1999), p. 692]
Coastal artillery
Finnish coastal artillery batteries defended important harbours and naval bases. Most batteries were left over from the Imperial Russian period, with guns being the most numerous. Finland attempted to modernise its old guns and installed a number of new batteries, the largest of which featured a gun battery on the island of
Kuivasaari in front of Helsinki, originally intended to block the Gulf of Finland to Soviet ships with the help of batteries on the Estonian side.
[ Leskinen (1999), p. 130]
The first naval battle occurred in the Gulf of Finland on 1 December, near the island of
Russarö
Russarö is an island south of Hanko. The island is closed to the public as it is military area of the Finnish Defence Forces. The island hosts the five-storey Russarö Lighthouse built in 1863 and a Finnish Meteorological Institute weather stati ...
, south of
Hanko. That day, the weather was fair and visibility was excellent. The Finns spotted the Soviet cruiser and two destroyers. When the ships were at a range of , the Finns opened fire with four coastal guns. After five minutes of firing by the coastal guns, the cruiser had been damaged by near misses and retreated. The destroyers remained undamaged, but the ''Kirov'' suffered 17 dead and 30 wounded. The Soviets already knew the locations of the Finnish coastal batteries, but were surprised by their range.
[ Silvast (1999), pp. 694–696]
Coastal artillery had a greater effect on land by reinforcing defence in conjunction with army artillery. Two sets of fortress artillery made significant contributions to the early battles on the Karelian Isthmus and in Ladoga Karelia. These were located at
Kaarnajoki Gromovo (russian: Гро́мово; fi, Sakkola) is a settlement in Priozersky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located 18 km northwest of Sosnovo, and a station of the Saint Petersburg-Kuznechnoye railway. Gromovo is situated on the no ...
on the Eastern Isthmus and at
Mantsi on the northeastern shore of Lake Ladoga. The fortress of
Koivisto provided similar support from the southwestern coast of the Isthmus.
[ Tillotson (1993), pp. 152–153]
Soviet breakthrough in February
Red Army reforms and offensive preparations

Joseph Stalin was not pleased with the results of December in the Finnish campaign. The Red Army had been humiliated. By the third week of the war, Soviet propaganda was already working to explain the failures of the Soviet military to the populace: blaming bad terrain and harsh climate, and falsely claiming that the Mannerheim Line was stronger than the Maginot Line, and that the Americans had sent 1,000 of their best pilots to Finland. Chief of Staff
Boris Shaposhnikov was given full authority over operations in the Finnish theatre, and he ordered the suspension of frontal assaults in late December.
Kliment Voroshilov was replaced with
Semyon Timoshenko as the commander of the Soviet forces in the war on 7 January.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 203–204] The main focus of the Soviet attack was switched to the Karelian Isthmus. Timoshenko and Zhdanov reorganised and tightened control between different branches of service in the Red Army. They also changed tactical doctrines to meet the realities of the situation.
[ Laaksonen (1999), pp. 424–425]
The Soviet forces on the Karelian Isthmus were divided into two armies: the 7th and the 13th Army. The 7th Army, now under Kirill Meretskov, would concentrate 75 percent of its strength against the stretch of the Mannerheim Line between
Taipale and the Munasuo swamp. Tactics would be basic: an armoured wedge for the initial breakthrough, followed by the main infantry and vehicle assault force. The Red Army would prepare by pinpointing the Finnish frontline fortifications. The 123rd Rifle Division then rehearsed the assault on life-size
mock-ups. The Soviets shipped large numbers of new tanks and artillery pieces to the theatre. Troops were increased from ten divisions to 25–26 divisions with six or seven tank brigades and several independent tank platoons as support, totalling 600,000 soldiers.
On 1 February, the Red Army began a large offensive, firing 300,000 shells into the Finnish line in the first 24 hours of the
bombardment.
Soviet offensive on the Karelian Isthmus
Although the Karelian Isthmus front was less active in January than in December, the Soviets increased bombardments, wearing down the defenders and softening their fortifications. During daylight hours, the Finns took shelter inside their fortifications from the bombardments and repaired damage during the night. The situation led quickly to war exhaustion among the Finns, who lost over 3,000 soldiers in
trench warfare. The Soviets also made occasional small infantry assaults with one or two companies.
[ Laaksonen (1999), pp. 426–427] Because of the shortage of ammunition, Finnish artillery emplacements were under orders to fire only against directly threatening ground attacks. On 1 February, the Soviets further escalated their artillery and air bombardments.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 214–215]
Although the Soviets refined their tactics and morale improved, the generals were still willing to accept massive losses to reach their objectives. Attacks were screened by smoke, heavy artillery, and armour support, but the infantry charged in the open and in dense formations.
Unlike their tactics in December, Soviet tanks advanced in smaller numbers. The Finns could not easily eliminate tanks if infantry troops protected them.
[ Laaksonen (1999), p. 430] After 10 days of constant artillery barrage, the Soviets achieved a breakthrough on the Western Karelian Isthmus in the
Second Battle of Summa.
By 11 February, the Soviets had approximately 460,000 soldiers, 3,350 artillery pieces, 3,000 tanks and 1,300 aircraft deployed on the Karelian Isthmus. The Red Army was constantly receiving new recruits after the breakthrough.
[ Geust; Uitto (2006), p. 77] Opposing them, the Finns had eight divisions, totalling about 150,000 soldiers. One by one, the defenders' strongholds crumbled under the Soviet attacks and the Finns were forced to retreat. On 15 February, Mannerheim authorised a general retreat of the II Corps to a fallback line of defence. On the eastern side of the isthmus, the Finns continued to resist Soviet assaults, achieving a stalemate in the battle of Taipale.
[ Laaksonen (1999), p. 452]
Peace negotiations
Although the Finns attempted to re-open negotiations with Moscow by every means during the war, the Soviets did not respond. In early January, Finnish communist
Hella Wuolijoki contacted the Finnish Government. She offered to contact Moscow through the Soviet Union's ambassador to Sweden,
Alexandra Kollontai. Wuolijoki departed for
Stockholm and met Kollontai secretly at a hotel. On 29 January, Molotov put an end to the puppet
Terijoki Government and recognized the Ryti–Tanner government as the legal government of Finland, informing it that the USSR was willing to negotiate peace.
By mid-February, it became clear that the Finnish forces were rapidly approaching exhaustion. For the Soviets, casualties were high, the situation was a source of political embarrassment to the Soviet regime, and there was a risk of
Franco-British intervention (which was overestimated by Soviet intelligence in February and March 1940). With the spring thaw approaching, the Soviet forces risked becoming bogged down in the forests. Finnish Foreign Minister Väinö Tanner arrived in Stockholm on 12 February and negotiated the peace terms with the Soviets through the Swedes. German representatives, not aware that the negotiations were underway, suggested on 17 February that Finland negotiate with the Soviet Union.
Both Germany and Sweden were keen to see an end to the Winter War. The Germans feared losing the
iron ore fields in Northern Sweden and threatened to attack at once if the Swedes granted the Allied forces
right of passage. The German invasion plan, named ''Studie Nord'', was later implemented as
Operation Weserübung.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 261] Leon Trotsky opined after the war that Hitler would view a Soviet occupation of Finland as a threat to this plan. Any potential German plans for bases in Finland would also be thwarted if the Soviets occupied Finland, though Trotsky himself believed that Hitler was not interested in occupying Finland, but rather its role as a buffer between Germany and the USSR.
As the Finnish Cabinet hesitated in the face of harsh Soviet conditions, Sweden's King
Gustav V made a
public statement on 19 February in which he confirmed having declined Finnish pleas for support from Swedish troops. On 25 February, the Soviet peace terms were spelt out in detail. On 29 February, the Finnish Government accepted the Soviet terms in principle and was willing to enter into negotiations. Red Army commanders wished to continue the war, whereas the Communist Party pointed out that the war had been too costly and called for the signing of a peace treaty. The party believed that Finland could be taken over later by means of a revolution. The heated discussion that ensued failed to yield any clear result and the matter went to a vote, in which the party's opinion prevailed and the decision was taken to bring hostilities to an end.
End of war in March
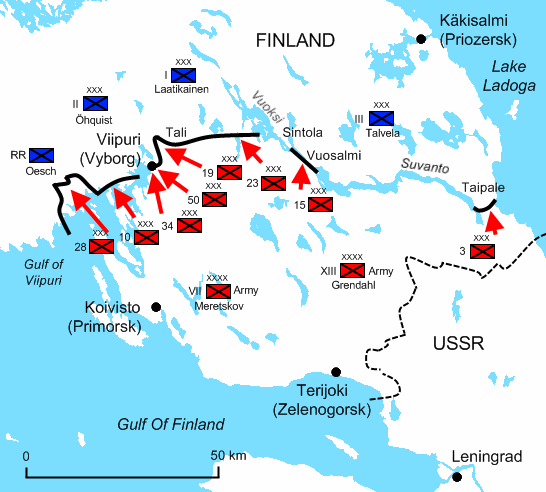
On 5 March, the Red Army advanced past the Mannerheim Line and entered the
suburbs of Viipuri. The same day, the Red Army established a beachhead on the Western
Gulf of Viipuri
Vyborg Bay (, , ) is a deep inlet running northeastward near the eastern end of Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea. The city of Vyborg is located near the head of the gulf.
The Monrepos Park is considered a jewel of the bay and a major draw for ...
. The Finns proposed an
armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the ...
on 6 March, but the Soviets, wanting to keep the pressure on the Finnish government, declined the offer. The Finnish peace delegation travelled to Moscow via Stockholm and arrived on 7 March. They were disappointed to find that Joseph Stalin was not present during peace negotiations, likely due to the Red Army's humiliation by the Finns.
The Soviets had further demands, as their military position was strong and improving. On 9 March, the Finnish military situation on the Karelian Isthmus was dire, as troops were experiencing heavy casualties. Artillery ammunition was exhausted and weapons were wearing out. The Finnish government, realizing that the hoped-for Franco-British military expedition would not arrive in time, as Norway and Sweden had not given the
Allies right of passage, had little choice but to accept the Soviet terms. Finnish President
Kyösti Kallio resisted the idea of giving up any territory to the Soviet Union, but was forced to agree to sign the Moscow Peace Treaty. When he signed the document, the tormented president uttered the well-known words:
Moscow Peace Treaty

The Moscow Peace Treaty was signed in Moscow on 12 March 1940. A
cease-fire took effect the next day at noon Leningrad time, 11 a.m. Helsinki time. With it, Finland ceded a portion of Karelia, the entire Karelian Isthmus and land north of Lake Ladoga. The area included Viipuri (Finland's second-largest city
opulation Registeror fourth-largest city
hurch and Civil Register depending on the census data), much of Finland's industrialised territory, and significant land still held by Finland's militaryall in all, nine percent of Finnish territory. The ceded territory included 13 percent of Finland's economic assets.
[ Kirby (2006), p. 215] 12 percent of Finland's population, 422,000 to 450,000 Karelians,
were evacuated and lost their homes.
[ Engle and Paananen (1985), pp. 142–143] Finland ceded a part of the region of
Salla, Rybachy Peninsula in the
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian ter ...
, and four islands in the Gulf of Finland. The Hanko peninsula was leased to the Soviet Union as a military base for 30 years. The region of Petsamo, captured by the Red Army during the war, was returned to Finland according to the treaty.
[ Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), p. 10]

Finnish concessions and territorial losses exceeded
Soviet pre-war demands. Before the war, the Soviet Union demanded for the frontier with Finland on the Karelian Isthmus to be moved westward to a point east of Viipuri to the line between Koivisto and
Lipola; for existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus to be demolished and for the islands of
Suursaari,
Tytärsaari, and
Koivisto in the Gulf of Finland and Rybachy Peninsula to be ceded. In exchange, the Soviet Union proposed to cede Repola and Porajärvi from Eastern Karelia, an area twice as large as the territories that were originally demanded from the Finns.
[ Van Dyke (1997), pp. 189–190][ Trotter 2002, pp. 14–16]
Foreign support
Foreign volunteers
World opinion largely supported the Finnish cause, and the Soviet aggression was generally deemed unjustified. World War II had not yet directly affected France, the United Kingdom or the United States; the Winter War was practically the only conflict in Europe at that time and thus held major world interest. Several foreign organisations sent material aid, and many countries granted credit and military materiel to Finland. Nazi Germany allowed arms to pass through its territory to Finland, but after a Swedish newspaper made this public, Adolf Hitler initiated a policy of silence towards Finland, as part of improved German–Soviet relations following the signing of the
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 194–202]
The largest foreign contingent came from neighboring Sweden, which provided nearly 8,760 volunteers during the war. The
Volunteer Corps was formed of predominantly Swedes, as well as 1,010 Danes and 727 Norwegians. They fought on the northern front at Salla during the last days of the war. A Swedish unit of
Gloster Gladiator fighters, named "the Flight Regiment 19" also participated. Swedish anti-air batteries with
Bofors guns were responsible for air defence in northern Finland and the city of Turku.
[ Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), pp. 21–22] Volunteers arrived from
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, Italy and Estonia. 350
American nationals of Finnish background volunteered, and 210 volunteers of other nationalities arrived in Finland before the war ended.
, a
Norwegian, fought in the Winter War before returning to
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and later achieved fame as a resistance fighter during the
German occupation of Norway. In total, Finland received 12,000 volunteers, 50 of whom died during the war.
[ Juutilainen (1999b), p. 776] The British actor
Christopher Lee volunteered in the war for two weeks, but did not face combat.
White émigrés and Russian prisoners-of-war
Finland officially refused overtures from the anti-Soviet
Russian All-Military Union (ROVS) for aid. Nevertheless, Mannerheim eventually agreed to establish a small Russian detachment (''Russkaya narodnaya armiya'', RNA) of 200 men after being introduced to
Boris Bazhanov, a high-ranking ROVS member, in person in January 1940. The project was deemed top secret, and was under the auspices of the intelligence division of the Finnish army headquarters.
The ranks of RNA were to be filled by prisoners-of-war, but it would be commanded by White émigrés instead of captured Soviet Army officers, who were deemed unreliable. Bazhanov's Finnish assistant Feodor Schulgin chose Captain Vladimir Kiseleff, Lieutenant Vladimir Lugovskoy, Anatoly Budyansky and brothers Nikolay and Vladimir Bastamov as officers for the unit. Of the five, the Bastamovs were not Finnish citizens, but had
Nansen passports. The prisoners-of-war were trained in
Huittinen, although it is possible that some were also trained in
Lempäälä
Lempäälä (; Swedish also ) is a municipality in the Pirkanmaa region of Finland with inhabitants (). Lempäälä is located south of the city of Tampere. The municipality covers an area of of which is water. The population density is .
The ...
.
RNA never participated in battle, despite Boris Bazhanov's later claims to the contrary in his memoirs. About 35 to 40 members of it were present during a battle in
Ruskeala in early March 1940, where they spread flyers and broadcast propaganda to encircled Soviet troops, but did not carry weapons. The men were subsequently detained by Finnish forces, who mistook them for Soviet infiltrators. After the war's end, Bazhanov was immediately asked to leave Finland, which he did. Finnish military historian
Carl Geust presumes that most members of the RNA were executed after they were returned to the Soviet Union after the war. Additionally, Vladimir Bastamov was later extradited into the Soviet Union as one of the
Leino prisoners in 1945, and was sentenced to 20 years of hard labour. He was released after Stalin's death and returned to Finland in 1956.
Franco-British intervention plans

France had been one of the earliest supporters of Finland during the Winter War. The French saw an opportunity to weaken Germany's resource imports via a Finnish counteroffensive, as both Sweden and the Soviet Union were strategic trading partners to Germany. France had another motive, preferring to have a major war in a remote part of Europe rather than on French soil. France planned to re‑arm the
Polish exile units and transport them to the Finnish Arctic port of Petsamo. Another proposal was a massive air strike with Turkish co-operation against the
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
oil fields.
The British, for their part, wanted to block the flow of iron ore from Swedish mines to Germany as the Swedes supplied up to 40 percent of Germany's iron demand.
[ Trotter (2002), pp. 235–236] The matter was raised by British Admiral
Reginald Plunkett on 18 September 1939, and the next day
Winston Churchill brought up the subject in the
Chamberlain War Cabinet.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 141] On 11 December, Churchill opined that the British should gain a foothold in Scandinavia with the objective to help the Finns, but without a war with the Soviet Union.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 145] Because of the heavy German reliance on Northern Sweden's iron ore, Hitler had made it clear to the Swedish government in December that any Allied troops on Swedish soil would immediately provoke a German invasion.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 237]
On 19 December, French Prime Minister
Édouard Daladier introduced his plan to the General Staff and the War Cabinet. In his plan, Daladier created linkage between the war in Finland and the iron ore in Sweden.
There was a danger of Finland's possible fall under Soviet hegemony. In turn, Nazi Germany could occupy both Norway and Sweden. These two powers could divide Scandinavia between them, as they had already done with Poland. The main motivation of the French and the British was to reduce the German war-making ability.
[ Edwards (2006), p. 146]
The Military Co-ordination Committee met on 20 December in London, and two days later the French plan was put forward.
The
Anglo-French Supreme War Council elected to send notes to Norway and Sweden on 27 December, urging the Norwegians and Swedes to help Finland and offer the Allies their support. Norway and Sweden rejected the offer on 5 January 1940.
The Allies came up with a new plan, in which they would demand that Norway and Sweden give them right of passage by citing a League of Nations resolution as justification. The expedition troops would disembark at the Norwegian port of Narvik and proceed by rail toward Finland, passing through the Swedish ore fields on the way. This demand was sent to Norway and Sweden on 6 January, but it was likewise rejected six days later.
Stymied but not yet dissuaded from the possibility of action, the Allies formulated a final plan on 29 January. First, the Finns would make a formal request for assistance. Then, the Allies would ask Norway and Sweden for permission to move the "volunteers" across their territory. Finally, to protect the supply line from German actions, the Allies would send units ashore at
Namsos,
Bergen, and
Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, an ...
. The operation would have required 100,000 British and 35,000 French soldiers with naval and air support. The supply convoys would sail on 12 March and the landings would begin on 20 March. The end of the war on 13 March cancelled Franco-British plans to send troops to Finland through Northern
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
.
[ Trotter (2002), p. 239]
Aftermath and casualties
Finland

The 105-day war had a profound and depressing effect in Finland. Meaningful international support was minimal and arrived late, and the German blockade had prevented most armament shipments.
[ Edwards (2006), pp. 272–273] The 15-month period between the Winter War and
Operation Barbarossa, part of which was
Continuation War, was later called the
Interim Peace.
After the end of the war, the situation of the Finnish Army on the Karelian Isthmus became a subject of debate in Finland. Orders had already been issued to prepare a retreat to the next line of defence in the Taipale sector. Estimates of how long the Red Army could have been delayed by retreat-and-stand operations varied from a few days to a few weeks, or to a couple of months at most.
Immediately after the war, Helsinki officially announced 19,576 dead. According to revised estimates in 2005 by Finnish historians, 25,904 people died or went missing and 43,557 were wounded on the Finnish side during the war. Finnish and Russian researchers have estimated that there were 800–1,100
Finnish prisoners of war, of whom between 10 and 20 percent died. The Soviet Union repatriated 847 Finns after the War.
Air raids killed 957 civilians.
Between 20 and 30 tanks were destroyed and 62 aircraft were lost.
Also, Finland had to cede all ships of the
Finnish Ladoga Naval Detachment to the Soviet Union by virtue of the
Moscow Peace Treaty.
During the
Interim Peace, Finland aimed to improve its defensive capabilities and conducted negotiations with Sweden on a military alliance, but negotiations ended once it became clear that both Germany and the Soviet Union opposed such an alliance.
[ Turtola (1999b), p. 863] On 31 July 1940, German Chancellor
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
gave the order to plan an assault on the Soviet Union and so Germany had to reassess its position regarding Finland. Until then, Germany had rejected Finnish appeals to purchase arms. However, the prospect of an invasion of the Soviet Union reversed the policy. In August, the secret sale of weapons to Finland was permitted.
Karelian evacuees established an interest group, the
Finnish Karelian League, to defend Karelian rights and interests and to find a way to
return ceded regions of Karelia to Finland.
[ Ahtiainen (2000)] Finland wished to re-enter the war mainly because of the Soviet invasion of Finland during the Winter War, which had taken place after Finland had failed by relying on the League of Nations and on Nordic neutrality. Finland aimed primarily to reverse its territorial losses from the Moscow Peace Treaty and, depending on the success of the German invasion of the Soviet Union, possibly to expand its borders, especially into
East Karelia. Some right-wing groups, such as the
Academic Karelia Society, supported a
Greater Finland ideology. The
Continuation War began in June 1941 and led to Finnish participation in the
Siege of Leningrad as well as the
Finnish occupation of East Karelia.

Soviet Union
The Soviet General Staff Supreme Command (''
Stavka'') met in April 1940, reviewed the lessons of the Finnish campaign and recommended reforms. The role of frontline political commissars was reduced, and old-fashioned ranks and forms of discipline were reintroduced. Clothing, equipment and tactics for winter operations were improved. Not all of the reforms had been completed when Germans initiated
Operation Barbarossa 14 months later.

Between the Winter War and ''
perestroika'' in the late 1980s, Soviet historiography relied solely on Molotov's speeches on the Winter War. In his radio speech of 29 November 1939, Molotov argued that the Soviet Union had tried to negotiate guarantees of security for
Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
for two months. The Finns had taken a hostile stance to "please foreign imperialists". Finland had undertaken military provocation, and the Soviet Union could no longer abide by the non-aggression pacts. According to Molotov, the Soviet Union did not want to occupy or annex Finland, but the goal was purely to secure Leningrad.
[ Vihavainen (1999), pp. 893–896]
The official Soviet figure, with reference to the command of the Leningrad Military District, was published at a session of the
Supreme Soviet on 26 March 1940, with 48,475 dead and 158,863 sick and wounded.
More recent Russian estimates vary: in 1990,
Mikhail Semiryaga claimed 53,522 dead, and
N. I. Baryshnikov
N is the fourteenth letter of the Latin alphabet.
N or n may also refer to:
Mathematics
* \mathbb, the set of natural numbers
* N, the field norm
* N for ''nullae'', a rare Roman numeral for zero
* n, the size of a statistical sample
Sci ...
, 53,500. In 1997,
Grigoriy Krivosheyev claimed 126,875 dead and missing and total casualties of 391,783, with 188,671 wounded.
In 1991,
Yuri Kilin claimed 63,990 dead and total casualties of 271,528. In 2007, he revised the estimate of dead to 134,000
and in 2012, he updated the estimate to 138,533. In 2013,
Pavel Petrov stated that the Russian State Military Archive has a database confirming 167,976 killed or missing along with the soldiers' names, dates of birth and ranks.
There were 5,572
Soviet prisoners of war in Finland.
After the Winter War, the Soviet prisoners were returned to the USSR in accordance with the Moscow Peace Treaty. Of these, 450 were released, 4,354 were sentenced to imprisonment in labour camps ranging from 3 to 10 years and 414 were exposed to be "active in traitorous activities while in captivity", with 334 criminal cases being transferred to the
Supreme Court of the Soviet Union; 232 of those cases ended in a death penalty.
Between 1,200 and 3,543 Soviet tanks were destroyed. The official figure was 611 tank casualties, but Yuri Kilin found a note received by the head of the Soviet General Staff, Boris Shaposhnikov, reporting 3,543 tank casualties and 316 tanks destroyed. According to the Finnish historian
Ohto Manninen
Ohto Heikki Sulevi Manninen (24 March 1943 in Helsinki), is a Finnish historian, PhD 1977. Manninen was 1984–95 associate professor at Helsinki University, 1995–98 professor of Finland's history at Tampere University. In 1998 he became p ...
, the 7th Soviet Army lost 1,244 tanks during the breakthrough battles of the Mannerheim Line in mid-winter. In the immediate aftermath of the war, the Finnish estimate of the number of lost Soviet tanks was 1,000 to 1,200.
The Soviet Air Forces lost around 1,000 aircraft, but fewer than half of them were combat casualties.
According Carl Fredrik Geust, based on the studies of Soviet air force units, Finnish anti-aircraft units shot down 119 and Finnish fighter pilots 131 Soviet aircraft, though all Soviet aircraft losses had been more than 900.
Germany
The Winter War was a political success for the Germans. Both the Red Army and the League of Nations were humiliated, and the Anglo-French Supreme War Council had been revealed to be chaotic and powerless. The German policy of neutrality was unpopular in the homeland, and relations with Italy had suffered. After the Moscow Peace Treaty, Germany improved its ties with Finland, and within two weeks,
Finnish-German relations were at the top of the agenda.
[ Edwards (2006), pp. 277–279] More importantly, the very poor performance of the Red Army convinced Hitler that an
invasion on the Soviet Union would be successful. In June 1941, Hitler declared, "we have only to kick in the door and the whole rotten structure will come crashing down".
[ Sedlar (2007), p. 8]
Allies
The Winter War laid bare the disorganisation and ineffectiveness of the Red Army and that of the Allies. The
Anglo-French Supreme War Council was unable to formulate a workable plan, revealing its unsuitability to make effective war in either Britain or France. This failure led to the collapse of the
Third Daladier Government in France and the nomination of
Paul Reynaud as the new
Prime Minister of France.
[ Edwards (2006), pp. 13–14]
See also
*
List of Finnish military equipment of World War II
*
List of Soviet Union military equipment of World War II
The following is a list of Soviet military equipment of World War II which includes firearms, artillery, vehicles, aircraft and warships. World War II was the deadliest war in history which started in 1939 and ended in 1945. Following political ...
*
Finnish Civil War
*
Continuation War
*
Lapland War
*
International relations (1919–1939)
*
Karelian question
*
List of Finnish corps in the Winter War
*
List of Finnish divisions in the Winter War
*
List of wars involving Finland
*
Mannerheim Line
*
Military history of Finland during World War II
*
Military history of the Soviet Union
The military history of the Soviet Union began in the days following the 1917 October Revolution that brought the Bolsheviks to power. In 1918 the new government formed the Red Army, which then defeated its various internal enemies in the Russian ...
*
Foreign interventions by the Soviet Union
*
Phoney War
*
Timeline of the Winter War
*
Winter War in popular culture
The Winter War in popular culture has had a deep and wide influence in Finland and elsewhere. The Winter War began three months after World War II had started and had full media attention, as the other European fronts had a calm period.
Films a ...
*
Simo Häyhä
*
Aarne Juutilainen
Notes
References
Sources
English
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Finnish, Russian and other languages
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* (Myth of the Mannerheim Line)
Further reading
*
* Chew, Allen F. ''The White Death: The Epic of the Soviet-Finnish Winter War'' ().
*
* Engle, Eloise and Paananen, Pauri. ''The Winter War: The Soviet Attack on Finland 1939–1940'' ().
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
(online review)*
*
* Trotter, William R.: ''A Frozen Hell: The Russo-Finnish Winter War of 1939–1940'' ().
*
*
* Weeks, Jessica L. 2014.
Dictators at War and Peace'' Ch. 4. Cornell University Press.
*
External links
Военный альбом(photographs of the Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940)
Finna(search service for information from Finnish archives, libraries and museums)
Finnish Wartime Photograph Archive(under
CC BY 4.0)
Fire and Ice: The Winter War of Finland and Russia(Winter War history from a documentary film's website)
National Archives of the United Kingdom
{{Authority control
Wars involving Finland
Wars involving the Soviet Union
1939 in Finland
1940 in Finland
1939 in the Soviet Union
1940 in the Soviet Union
Conflicts in 1939
Conflicts in 1940
Eastern European theatre of World War II
Finland in World War II
History of Karelia
Karelian Isthmus
League of Nations
Winter events
Winter in the Soviet Union
20th century in Finland
 Until the early 19th century, Finland was the eastern part of the
Until the early 19th century, Finland was the eastern part of the  After Soviet involvement in the Finnish Civil War in 1918, no formal peace treaty was signed. In 1918 and 1919, Finnish volunteers conducted two unsuccessful military incursions across the Soviet border, the Viena and Aunus expeditions, to annex areas in
After Soviet involvement in the Finnish Civil War in 1918, no formal peace treaty was signed. In 1918 and 1919, Finnish volunteers conducted two unsuccessful military incursions across the Soviet border, the Viena and Aunus expeditions, to annex areas in  In April 1938,
In April 1938,  On 5 October 1939, the Soviets invited a Finnish delegation to Moscow for negotiations. Juho Kusti Paasikivi, the Finnish envoy to Sweden, was sent to Moscow to represent the Finnish government. The Soviet delegation demanded that the border between the USSR and Finland on the Karelian Isthmus be moved westward to a point only east of Viipuri () and that Finland destroy all existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus. Likewise, the delegation demanded the cession of islands in the Gulf of Finland as well as Rybachy Peninsula ( fi, Kalastajasaarento). The Finns would also have to lease the Hanko Peninsula for 30 years and to permit the Soviets to establish a
On 5 October 1939, the Soviets invited a Finnish delegation to Moscow for negotiations. Juho Kusti Paasikivi, the Finnish envoy to Sweden, was sent to Moscow to represent the Finnish government. The Soviet delegation demanded that the border between the USSR and Finland on the Karelian Isthmus be moved westward to a point only east of Viipuri () and that Finland destroy all existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus. Likewise, the delegation demanded the cession of islands in the Gulf of Finland as well as Rybachy Peninsula ( fi, Kalastajasaarento). The Finns would also have to lease the Hanko Peninsula for 30 years and to permit the Soviets to establish a  Molotov claimed that the incident was a Finnish artillery attack. He demanded that Finland apologise for the incident and to move its forces beyond a line from the border. Finland denied responsibility for the attack, rejected the demands and called for a joint Finnish–Soviet commission to examine the incident. In turn, the Soviet Union claimed that the Finnish response was hostile, renounced the non-aggression pact and severed diplomatic relations with Finland on 28 November. In the following years, Soviet historiography described the incident as Finnish provocation. Doubt on the official Soviet version was cast only in the late 1980s, during the policy of '' glasnost''. The issue has continued to divide Russian historiography even after the end of the Soviet Union in 1991. Kilin (2007a), pp. 99–100
In 2013, Russian President
Molotov claimed that the incident was a Finnish artillery attack. He demanded that Finland apologise for the incident and to move its forces beyond a line from the border. Finland denied responsibility for the attack, rejected the demands and called for a joint Finnish–Soviet commission to examine the incident. In turn, the Soviet Union claimed that the Finnish response was hostile, renounced the non-aggression pact and severed diplomatic relations with Finland on 28 November. In the following years, Soviet historiography described the incident as Finnish provocation. Doubt on the official Soviet version was cast only in the late 1980s, during the policy of '' glasnost''. The issue has continued to divide Russian historiography even after the end of the Soviet Union in 1991. Kilin (2007a), pp. 99–100
In 2013, Russian President  Others argue against the idea of a complete Soviet conquest. American historian William R. Trotter asserted that Stalin's objective was to secure Leningrad's flank from a possible German invasion through Finland. He stated that "the strongest argument" against a Soviet intention of full conquest is that it did not happen in either 1939 or during the Continuation War in 1944 even though Stalin "could have done so with comparative ease". Bradley Lightbody wrote that the "entire Soviet aim had been to make the Soviet border more secure". In 2002, Russian historian A. Chubaryan stated that no documents had been found in Russian archives that support a Soviet plan to annex Finland. Rather, the objective was to gain Finnish territory and to reinforce Soviet influence in the region.
Others argue against the idea of a complete Soviet conquest. American historian William R. Trotter asserted that Stalin's objective was to secure Leningrad's flank from a possible German invasion through Finland. He stated that "the strongest argument" against a Soviet intention of full conquest is that it did not happen in either 1939 or during the Continuation War in 1944 even though Stalin "could have done so with comparative ease". Bradley Lightbody wrote that the "entire Soviet aim had been to make the Soviet border more secure". In 2002, Russian historian A. Chubaryan stated that no documents had been found in Russian archives that support a Soviet plan to annex Finland. Rather, the objective was to gain Finnish territory and to reinforce Soviet influence in the region.
 Soviet generals were impressed by the success of German '' Blitzkrieg'' tactics, but they had been tailored to conditions in
Soviet generals were impressed by the success of German '' Blitzkrieg'' tactics, but they had been tailored to conditions in  The Finnish strategy was dictated by geography. The border with the Soviet Union was mostly impassable except along a handful of
The Finnish strategy was dictated by geography. The border with the Soviet Union was mostly impassable except along a handful of  On 30 November 1939, Soviet forces invaded Finland with 21 divisions, totalling 450,000 men, and bombed Helsinki, Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), p. 6 killing about 100 citizens and destroying more than 50 buildings. In response to international criticism, Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov stated that the Soviet Air Force was not bombing Finnish cities but rather dropping humanitarian aid to the starving Finnish population; they were sarcastically dubbed Molotov bread baskets by Finns. The Finnish statesman J. K. Paasikivi commented that the Soviet attack without a declaration of war violated three separate non-aggression pacts: the Treaty of Tartu, which was signed in 1920, the non-aggression pact between Finland and the Soviet Union, which was signed in 1932 and again in 1934; and also the Covenant of the League of Nations, which the Soviet Union signed in 1934. Field Marshal C.G.E. Mannerheim was appointed Commander-in-Chief of the Finnish Defence Forces after the Soviet attack. In a further reshuffling, Aimo Cajander's caretaker cabinet was replaced by Risto Ryti and his cabinet, with Väinö Tanner as foreign minister because of opposition to Cajander's prewar politics. Trotter (2002), pp. 48–51 Finland brought the matter of the Soviet invasion before the League of Nations. The League expelled the Soviet Union on 14 December 1939 and exhorted its members to aid Finland.
On 30 November 1939, Soviet forces invaded Finland with 21 divisions, totalling 450,000 men, and bombed Helsinki, Jowett & Snodgrass (2006), p. 6 killing about 100 citizens and destroying more than 50 buildings. In response to international criticism, Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov stated that the Soviet Air Force was not bombing Finnish cities but rather dropping humanitarian aid to the starving Finnish population; they were sarcastically dubbed Molotov bread baskets by Finns. The Finnish statesman J. K. Paasikivi commented that the Soviet attack without a declaration of war violated three separate non-aggression pacts: the Treaty of Tartu, which was signed in 1920, the non-aggression pact between Finland and the Soviet Union, which was signed in 1932 and again in 1934; and also the Covenant of the League of Nations, which the Soviet Union signed in 1934. Field Marshal C.G.E. Mannerheim was appointed Commander-in-Chief of the Finnish Defence Forces after the Soviet attack. In a further reshuffling, Aimo Cajander's caretaker cabinet was replaced by Risto Ryti and his cabinet, with Väinö Tanner as foreign minister because of opposition to Cajander's prewar politics. Trotter (2002), pp. 48–51 Finland brought the matter of the Soviet invasion before the League of Nations. The League expelled the Soviet Union on 14 December 1939 and exhorted its members to aid Finland.
 On 1 December 1939, the Soviet Union formed a puppet government, named the Finnish Democratic Republic, to govern Finland after Soviet conquest. Headed by Otto Wille Kuusinen, the government operated in the parts of Finnish Karelia occupied by the Soviets, and was also referred to as the "Terijoki Government", after the village of Terijoki, the first settlement captured by the advancing Red Army. Trotter (2002), p. 58 After the war, the puppet government was reabsorbed into the Soviet Union. From the very outset of the war, working-class Finns stood behind the legitimate government in Helsinki. Trotter (2002), p. 61 Finnish national unity against the Soviet invasion was later called the
On 1 December 1939, the Soviet Union formed a puppet government, named the Finnish Democratic Republic, to govern Finland after Soviet conquest. Headed by Otto Wille Kuusinen, the government operated in the parts of Finnish Karelia occupied by the Soviets, and was also referred to as the "Terijoki Government", after the village of Terijoki, the first settlement captured by the advancing Red Army. Trotter (2002), p. 58 After the war, the puppet government was reabsorbed into the Soviet Union. From the very outset of the war, working-class Finns stood behind the legitimate government in Helsinki. Trotter (2002), p. 61 Finnish national unity against the Soviet invasion was later called the  The array of Finnish defence structures that during the war started to be called the Mannerheim Line was located on the Karelian Isthmus approximately from the Soviet border. The Red Army soldiers on the Isthmus numbered 250,000, facing 130,000 Finns. Geust; Uitto (2006), p. 54 The Finnish command deployed a defence in depth of about 21,000 men in the area in front of the Mannerheim Line to delay and damage the Red Army before it reached the line. Trotter (2002), p. 69 In combat, the most severe cause of confusion among Finnish soldiers was Soviet tanks. The Finns had few anti-tank weapons and insufficient training in modern anti-tank tactics. According to Trotter, the favoured Soviet armoured tactic was a simple frontal charge, the weaknesses of which could be exploited. The Finns learned that at close range, tanks could be dealt with in many ways; for example, logs and crowbars jammed into the bogie wheels would often immobilise a tank. Soon, Finns fielded a better ad hoc weapon, the Molotov cocktail, a glass bottle filled with flammable liquids and with a simple hand-lit fuse. Molotov cocktails were eventually mass-produced by the Finnish '' Alko'' alcoholic-beverage corporation and bundled with matches with which to light them. 80 Soviet tanks were destroyed in the border zone engagements. Trotter (2002), pp. 72–73
By 6 December, all of the Finnish covering forces had withdrawn to the Mannerheim Line. The Red Army began its first major attack against the Line in Taipalethe area between the shore of Lake Ladoga, the Taipale river and the Suvanto waterway. Along the Suvanto sector, the Finns had a slight advantage of elevation and dry ground to dig into. The Finnish
The array of Finnish defence structures that during the war started to be called the Mannerheim Line was located on the Karelian Isthmus approximately from the Soviet border. The Red Army soldiers on the Isthmus numbered 250,000, facing 130,000 Finns. Geust; Uitto (2006), p. 54 The Finnish command deployed a defence in depth of about 21,000 men in the area in front of the Mannerheim Line to delay and damage the Red Army before it reached the line. Trotter (2002), p. 69 In combat, the most severe cause of confusion among Finnish soldiers was Soviet tanks. The Finns had few anti-tank weapons and insufficient training in modern anti-tank tactics. According to Trotter, the favoured Soviet armoured tactic was a simple frontal charge, the weaknesses of which could be exploited. The Finns learned that at close range, tanks could be dealt with in many ways; for example, logs and crowbars jammed into the bogie wheels would often immobilise a tank. Soon, Finns fielded a better ad hoc weapon, the Molotov cocktail, a glass bottle filled with flammable liquids and with a simple hand-lit fuse. Molotov cocktails were eventually mass-produced by the Finnish '' Alko'' alcoholic-beverage corporation and bundled with matches with which to light them. 80 Soviet tanks were destroyed in the border zone engagements. Trotter (2002), pp. 72–73
By 6 December, all of the Finnish covering forces had withdrawn to the Mannerheim Line. The Red Army began its first major attack against the Line in Taipalethe area between the shore of Lake Ladoga, the Taipale river and the Suvanto waterway. Along the Suvanto sector, the Finns had a slight advantage of elevation and dry ground to dig into. The Finnish  In battles from Ladoga Karelia to the Arctic port of Petsamo, the Finns used guerrilla tactics. The Red Army was superior in numbers and material, but Finns used the advantages of speed, manoeuvre warfare and economy of force. Particularly on the Ladoga Karelia front and during the Battle of Raate Road, the Finns isolated smaller portions of numerically superior Soviet forces. With Soviet forces divided into smaller groups, the Finns dealt with them individually and attacked from all sides. Trotter (2002), pp. 131–132
For many of the encircled Soviet troops in a pocket (called a '' motti'' in Finnish, originally meaning of firewood), staying alive was an ordeal comparable to combat. The men were freezing and starving and endured poor sanitary conditions. Historian William R. Trotter described these conditions as follows: "The Soviet soldier had no choice. If he refused to fight, he would be shot. If he tried to sneak through the forest, he would freeze to death. And surrender was no option for him; Soviet propaganda had told him how the Finns would torture prisoners to death." Trotter (2002), pp. 148–149 The problem however was that the Finns were mostly too weak to fully exploit their success. Some of the pockets of encircled Soviet soldiers held out for weeks and even months, binding a huge number of Finnish forces.
In battles from Ladoga Karelia to the Arctic port of Petsamo, the Finns used guerrilla tactics. The Red Army was superior in numbers and material, but Finns used the advantages of speed, manoeuvre warfare and economy of force. Particularly on the Ladoga Karelia front and during the Battle of Raate Road, the Finns isolated smaller portions of numerically superior Soviet forces. With Soviet forces divided into smaller groups, the Finns dealt with them individually and attacked from all sides. Trotter (2002), pp. 131–132
For many of the encircled Soviet troops in a pocket (called a '' motti'' in Finnish, originally meaning of firewood), staying alive was an ordeal comparable to combat. The men were freezing and starving and endured poor sanitary conditions. Historian William R. Trotter described these conditions as follows: "The Soviet soldier had no choice. If he refused to fight, he would be shot. If he tried to sneak through the forest, he would freeze to death. And surrender was no option for him; Soviet propaganda had told him how the Finns would torture prisoners to death." Trotter (2002), pp. 148–149 The problem however was that the Finns were mostly too weak to fully exploit their success. Some of the pockets of encircled Soviet soldiers held out for weeks and even months, binding a huge number of Finnish forces.
 The strength of the Red Army north of Lake Ladoga in Ladoga Karelia surprised the Finnish Headquarters. Two Finnish divisions were deployed there, the 12th Division led by
The strength of the Red Army north of Lake Ladoga in Ladoga Karelia surprised the Finnish Headquarters. Two Finnish divisions were deployed there, the 12th Division led by  The Suomussalmi–Raate engagement was a double operation Vuorenmaa (1999), p. 550 which would later be used by military academics as a classic example of what well-led troops and innovative tactics can do against a much larger adversary. Suomussalmi was a municipality of 4,000 with long lakes, wild forests and few roads. The Finnish command believed that the Soviets would not attack there, but the Red Army committed two divisions to the Kainuu area with orders to cross the wilderness, capture the city of Oulu and effectively cut Finland in two. There were two roads leading to Suomussalmi from the frontier: the northern Juntusranta road and the southern Raate road. Trotter (2002), p. 150
The Suomussalmi–Raate engagement was a double operation Vuorenmaa (1999), p. 550 which would later be used by military academics as a classic example of what well-led troops and innovative tactics can do against a much larger adversary. Suomussalmi was a municipality of 4,000 with long lakes, wild forests and few roads. The Finnish command believed that the Soviets would not attack there, but the Red Army committed two divisions to the Kainuu area with orders to cross the wilderness, capture the city of Oulu and effectively cut Finland in two. There were two roads leading to Suomussalmi from the frontier: the northern Juntusranta road and the southern Raate road. Trotter (2002), p. 150
 The Battle of Raate Road, which occurred during the month-long battle of Suomussalmi, resulted in one of the largest Soviet losses in the Winter War. The Soviet 44th and parts of the 163rd Rifle Division, comprising about 14,000 troops, Kulju (2007), p. 230 were almost completely destroyed by a Finnish ambush as they marched along the forest road. A small unit blocked the Soviet advance while Finnish Colonel Hjalmar Siilasvuo and his 9th Division cut off the retreat route, split the enemy force into smaller ''mottis'', and then proceeded to destroy the remnants in detail as they retreated. The Soviets suffered 7,000–9,000 casualties; Kulju (2007), p. 229 the Finnish units, 400. Kantakoski (1998), p. 283 The Finnish troops captured dozens of tanks, artillery pieces, anti-tank guns, hundreds of trucks, almost 2,000 horses, thousands of rifles, and much-needed ammunition and medical supplies. Kulju (2007), pp. 217–218 So sure of their victory had the Soviets been that a military band, complete with instruments, banners and notes, was traveling with the 44th Division to perform in a victory parade. The Finns found their instruments among the captured materiel.
The Battle of Raate Road, which occurred during the month-long battle of Suomussalmi, resulted in one of the largest Soviet losses in the Winter War. The Soviet 44th and parts of the 163rd Rifle Division, comprising about 14,000 troops, Kulju (2007), p. 230 were almost completely destroyed by a Finnish ambush as they marched along the forest road. A small unit blocked the Soviet advance while Finnish Colonel Hjalmar Siilasvuo and his 9th Division cut off the retreat route, split the enemy force into smaller ''mottis'', and then proceeded to destroy the remnants in detail as they retreated. The Soviets suffered 7,000–9,000 casualties; Kulju (2007), p. 229 the Finnish units, 400. Kantakoski (1998), p. 283 The Finnish troops captured dozens of tanks, artillery pieces, anti-tank guns, hundreds of trucks, almost 2,000 horses, thousands of rifles, and much-needed ammunition and medical supplies. Kulju (2007), pp. 217–218 So sure of their victory had the Soviets been that a military band, complete with instruments, banners and notes, was traveling with the 44th Division to perform in a victory parade. The Finns found their instruments among the captured materiel.
 The Finnish area of
The Finnish area of  To the north was Finland's only ice-free port in the Arctic, Petsamo. The Finns lacked the manpower to defend it fully, as the main front was distant at the Karelian Isthmus. In the battle of Petsamo, the Soviet 104th Division attacked the Finnish 104th Independent Cover Company. The Finns abandoned Petsamo and concentrated on delaying actions. The area was treeless, windy, and relatively low, offering little defensible terrain. The almost constant darkness and extreme temperatures of the Lapland winter benefited the Finns, who executed guerrilla attacks against Soviet supply lines and patrols. As a result, the Soviet movements were halted by the efforts of one-fifth as many Finns.
To the north was Finland's only ice-free port in the Arctic, Petsamo. The Finns lacked the manpower to defend it fully, as the main front was distant at the Karelian Isthmus. In the battle of Petsamo, the Soviet 104th Division attacked the Finnish 104th Independent Cover Company. The Finns abandoned Petsamo and concentrated on delaying actions. The area was treeless, windy, and relatively low, offering little defensible terrain. The almost constant darkness and extreme temperatures of the Lapland winter benefited the Finns, who executed guerrilla attacks against Soviet supply lines and patrols. As a result, the Soviet movements were halted by the efforts of one-fifth as many Finns.
 At the beginning of the war, Finland had a small air force, with only 114 combat planes fit for duty. Missions were limited, and fighter aircraft were mainly used to repel Soviet bombers. Strategic bombings doubled as opportunities for military
At the beginning of the war, Finland had a small air force, with only 114 combat planes fit for duty. Missions were limited, and fighter aircraft were mainly used to repel Soviet bombers. Strategic bombings doubled as opportunities for military  Joseph Stalin was not pleased with the results of December in the Finnish campaign. The Red Army had been humiliated. By the third week of the war, Soviet propaganda was already working to explain the failures of the Soviet military to the populace: blaming bad terrain and harsh climate, and falsely claiming that the Mannerheim Line was stronger than the Maginot Line, and that the Americans had sent 1,000 of their best pilots to Finland. Chief of Staff Boris Shaposhnikov was given full authority over operations in the Finnish theatre, and he ordered the suspension of frontal assaults in late December. Kliment Voroshilov was replaced with Semyon Timoshenko as the commander of the Soviet forces in the war on 7 January. Trotter (2002), pp. 203–204 The main focus of the Soviet attack was switched to the Karelian Isthmus. Timoshenko and Zhdanov reorganised and tightened control between different branches of service in the Red Army. They also changed tactical doctrines to meet the realities of the situation. Laaksonen (1999), pp. 424–425
The Soviet forces on the Karelian Isthmus were divided into two armies: the 7th and the 13th Army. The 7th Army, now under Kirill Meretskov, would concentrate 75 percent of its strength against the stretch of the Mannerheim Line between Taipale and the Munasuo swamp. Tactics would be basic: an armoured wedge for the initial breakthrough, followed by the main infantry and vehicle assault force. The Red Army would prepare by pinpointing the Finnish frontline fortifications. The 123rd Rifle Division then rehearsed the assault on life-size mock-ups. The Soviets shipped large numbers of new tanks and artillery pieces to the theatre. Troops were increased from ten divisions to 25–26 divisions with six or seven tank brigades and several independent tank platoons as support, totalling 600,000 soldiers. On 1 February, the Red Army began a large offensive, firing 300,000 shells into the Finnish line in the first 24 hours of the bombardment.
Joseph Stalin was not pleased with the results of December in the Finnish campaign. The Red Army had been humiliated. By the third week of the war, Soviet propaganda was already working to explain the failures of the Soviet military to the populace: blaming bad terrain and harsh climate, and falsely claiming that the Mannerheim Line was stronger than the Maginot Line, and that the Americans had sent 1,000 of their best pilots to Finland. Chief of Staff Boris Shaposhnikov was given full authority over operations in the Finnish theatre, and he ordered the suspension of frontal assaults in late December. Kliment Voroshilov was replaced with Semyon Timoshenko as the commander of the Soviet forces in the war on 7 January. Trotter (2002), pp. 203–204 The main focus of the Soviet attack was switched to the Karelian Isthmus. Timoshenko and Zhdanov reorganised and tightened control between different branches of service in the Red Army. They also changed tactical doctrines to meet the realities of the situation. Laaksonen (1999), pp. 424–425
The Soviet forces on the Karelian Isthmus were divided into two armies: the 7th and the 13th Army. The 7th Army, now under Kirill Meretskov, would concentrate 75 percent of its strength against the stretch of the Mannerheim Line between Taipale and the Munasuo swamp. Tactics would be basic: an armoured wedge for the initial breakthrough, followed by the main infantry and vehicle assault force. The Red Army would prepare by pinpointing the Finnish frontline fortifications. The 123rd Rifle Division then rehearsed the assault on life-size mock-ups. The Soviets shipped large numbers of new tanks and artillery pieces to the theatre. Troops were increased from ten divisions to 25–26 divisions with six or seven tank brigades and several independent tank platoons as support, totalling 600,000 soldiers. On 1 February, the Red Army began a large offensive, firing 300,000 shells into the Finnish line in the first 24 hours of the bombardment.
 On 5 March, the Red Army advanced past the Mannerheim Line and entered the suburbs of Viipuri. The same day, the Red Army established a beachhead on the Western
On 5 March, the Red Army advanced past the Mannerheim Line and entered the suburbs of Viipuri. The same day, the Red Army established a beachhead on the Western  The Moscow Peace Treaty was signed in Moscow on 12 March 1940. A cease-fire took effect the next day at noon Leningrad time, 11 a.m. Helsinki time. With it, Finland ceded a portion of Karelia, the entire Karelian Isthmus and land north of Lake Ladoga. The area included Viipuri (Finland's second-largest city opulation Registeror fourth-largest city hurch and Civil Register depending on the census data), much of Finland's industrialised territory, and significant land still held by Finland's militaryall in all, nine percent of Finnish territory. The ceded territory included 13 percent of Finland's economic assets. Kirby (2006), p. 215 12 percent of Finland's population, 422,000 to 450,000 Karelians, were evacuated and lost their homes. Engle and Paananen (1985), pp. 142–143 Finland ceded a part of the region of Salla, Rybachy Peninsula in the
The Moscow Peace Treaty was signed in Moscow on 12 March 1940. A cease-fire took effect the next day at noon Leningrad time, 11 a.m. Helsinki time. With it, Finland ceded a portion of Karelia, the entire Karelian Isthmus and land north of Lake Ladoga. The area included Viipuri (Finland's second-largest city opulation Registeror fourth-largest city hurch and Civil Register depending on the census data), much of Finland's industrialised territory, and significant land still held by Finland's militaryall in all, nine percent of Finnish territory. The ceded territory included 13 percent of Finland's economic assets. Kirby (2006), p. 215 12 percent of Finland's population, 422,000 to 450,000 Karelians, were evacuated and lost their homes. Engle and Paananen (1985), pp. 142–143 Finland ceded a part of the region of Salla, Rybachy Peninsula in the  Finnish concessions and territorial losses exceeded Soviet pre-war demands. Before the war, the Soviet Union demanded for the frontier with Finland on the Karelian Isthmus to be moved westward to a point east of Viipuri to the line between Koivisto and Lipola; for existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus to be demolished and for the islands of Suursaari, Tytärsaari, and Koivisto in the Gulf of Finland and Rybachy Peninsula to be ceded. In exchange, the Soviet Union proposed to cede Repola and Porajärvi from Eastern Karelia, an area twice as large as the territories that were originally demanded from the Finns. Van Dyke (1997), pp. 189–190 Trotter 2002, pp. 14–16
Finnish concessions and territorial losses exceeded Soviet pre-war demands. Before the war, the Soviet Union demanded for the frontier with Finland on the Karelian Isthmus to be moved westward to a point east of Viipuri to the line between Koivisto and Lipola; for existing fortifications on the Karelian Isthmus to be demolished and for the islands of Suursaari, Tytärsaari, and Koivisto in the Gulf of Finland and Rybachy Peninsula to be ceded. In exchange, the Soviet Union proposed to cede Repola and Porajärvi from Eastern Karelia, an area twice as large as the territories that were originally demanded from the Finns. Van Dyke (1997), pp. 189–190 Trotter 2002, pp. 14–16
 France had been one of the earliest supporters of Finland during the Winter War. The French saw an opportunity to weaken Germany's resource imports via a Finnish counteroffensive, as both Sweden and the Soviet Union were strategic trading partners to Germany. France had another motive, preferring to have a major war in a remote part of Europe rather than on French soil. France planned to re‑arm the Polish exile units and transport them to the Finnish Arctic port of Petsamo. Another proposal was a massive air strike with Turkish co-operation against the
France had been one of the earliest supporters of Finland during the Winter War. The French saw an opportunity to weaken Germany's resource imports via a Finnish counteroffensive, as both Sweden and the Soviet Union were strategic trading partners to Germany. France had another motive, preferring to have a major war in a remote part of Europe rather than on French soil. France planned to re‑arm the Polish exile units and transport them to the Finnish Arctic port of Petsamo. Another proposal was a massive air strike with Turkish co-operation against the  The 105-day war had a profound and depressing effect in Finland. Meaningful international support was minimal and arrived late, and the German blockade had prevented most armament shipments. Edwards (2006), pp. 272–273 The 15-month period between the Winter War and Operation Barbarossa, part of which was Continuation War, was later called the Interim Peace. After the end of the war, the situation of the Finnish Army on the Karelian Isthmus became a subject of debate in Finland. Orders had already been issued to prepare a retreat to the next line of defence in the Taipale sector. Estimates of how long the Red Army could have been delayed by retreat-and-stand operations varied from a few days to a few weeks, or to a couple of months at most.
Immediately after the war, Helsinki officially announced 19,576 dead. According to revised estimates in 2005 by Finnish historians, 25,904 people died or went missing and 43,557 were wounded on the Finnish side during the war. Finnish and Russian researchers have estimated that there were 800–1,100 Finnish prisoners of war, of whom between 10 and 20 percent died. The Soviet Union repatriated 847 Finns after the War. Air raids killed 957 civilians. Between 20 and 30 tanks were destroyed and 62 aircraft were lost. Also, Finland had to cede all ships of the Finnish Ladoga Naval Detachment to the Soviet Union by virtue of the Moscow Peace Treaty.
During the Interim Peace, Finland aimed to improve its defensive capabilities and conducted negotiations with Sweden on a military alliance, but negotiations ended once it became clear that both Germany and the Soviet Union opposed such an alliance. Turtola (1999b), p. 863 On 31 July 1940, German Chancellor
The 105-day war had a profound and depressing effect in Finland. Meaningful international support was minimal and arrived late, and the German blockade had prevented most armament shipments. Edwards (2006), pp. 272–273 The 15-month period between the Winter War and Operation Barbarossa, part of which was Continuation War, was later called the Interim Peace. After the end of the war, the situation of the Finnish Army on the Karelian Isthmus became a subject of debate in Finland. Orders had already been issued to prepare a retreat to the next line of defence in the Taipale sector. Estimates of how long the Red Army could have been delayed by retreat-and-stand operations varied from a few days to a few weeks, or to a couple of months at most.
Immediately after the war, Helsinki officially announced 19,576 dead. According to revised estimates in 2005 by Finnish historians, 25,904 people died or went missing and 43,557 were wounded on the Finnish side during the war. Finnish and Russian researchers have estimated that there were 800–1,100 Finnish prisoners of war, of whom between 10 and 20 percent died. The Soviet Union repatriated 847 Finns after the War. Air raids killed 957 civilians. Between 20 and 30 tanks were destroyed and 62 aircraft were lost. Also, Finland had to cede all ships of the Finnish Ladoga Naval Detachment to the Soviet Union by virtue of the Moscow Peace Treaty.
During the Interim Peace, Finland aimed to improve its defensive capabilities and conducted negotiations with Sweden on a military alliance, but negotiations ended once it became clear that both Germany and the Soviet Union opposed such an alliance. Turtola (1999b), p. 863 On 31 July 1940, German Chancellor 
 Between the Winter War and '' perestroika'' in the late 1980s, Soviet historiography relied solely on Molotov's speeches on the Winter War. In his radio speech of 29 November 1939, Molotov argued that the Soviet Union had tried to negotiate guarantees of security for
Between the Winter War and '' perestroika'' in the late 1980s, Soviet historiography relied solely on Molotov's speeches on the Winter War. In his radio speech of 29 November 1939, Molotov argued that the Soviet Union had tried to negotiate guarantees of security for