|
Agricultural Pollution
Agricultural pollution refers to biotic and abiotic byproducts of farming practices that result in contamination or degradation of the environment and surrounding ecosystems, and/or cause injury to humans and their economic interests. The pollution may come from a variety of sources, ranging from point source water pollution (from a single discharge point) to more diffuse, landscape-level causes, also known as non-point source pollution and air pollution. Once in the environment these pollutants can have both direct effects in surrounding ecosystems, i.e. killing local wildlife or contaminating drinking water, and downstream effects such as dead zones caused by agricultural runoff is concentrated in large water bodies. Management practices, or ignorance of them, play a crucial role in the amount and impact of these pollutants. Management techniques range from animal management and housing to the spread of pesticides and fertilizers in global agricultural practices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Pollution In The Wairarapa
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Use Change
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: forest land, cropland (agricultural land), grassland, wetlands, settlements and other lands. The way humans use land, and how land use is changing, has many impacts on the environment. Effects of land use choices and changes by humans include, for example, urban sprawl, soil erosion, soil degradation, land degradation and desertification. Land use and land management practices have a major impact on natural resources including water, soil, nutrients, plants and animals. ''Land use change'' is "the change from one land-use category to another". Land-use change, together with use of fossil fuels, are the major anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide, a dominant greenhouse gas. Human activity is the most significant cause of land cover change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
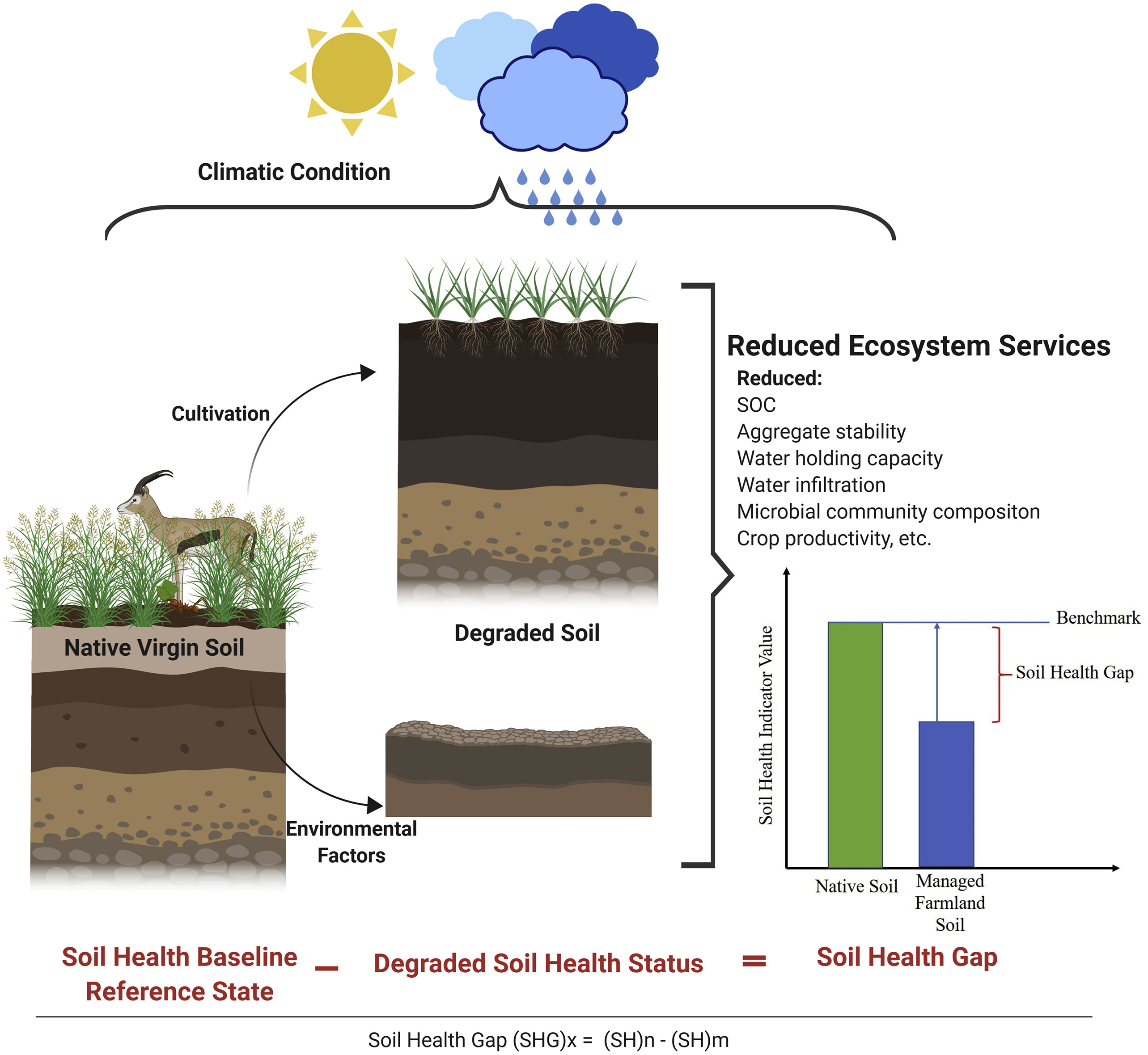
Soil Health
Soil health is a state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment. In more colloquial terms, the health of soil arises from favorable interactions of all soil components (living and non-living) that belong together, as in microbiota, plants and animals. It is possible that a soil can be healthy in terms of ecosystem functioning but not necessarily serve crop production or human nutrition directly, hence the scientific debate on terms and measurements. Soil health testing is pursued as an assessment of this status but tends to be confined largely to agronomic objectives. Soil health depends on soil biodiversity (with a robust soil biology, soil biota), and it can be improved via soil management, especially by care to keep protective living covers on the soil and by natural (carbon-containing) soil amendments. Inorganic fertilizers do not necessarily damage soil health if they are not used in excess, and if they bring about a general improveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeochemical Cycle
A biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the Earth's crust. Major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. In each cycle, the chemical element or molecule is transformed and cycled by living organisms and through various geological forms and reservoirs, including the atmosphere, the soil and the oceans. It can be thought of as the pathway by which a chemical substance Wiktionary:cycle, cycles (is turned over or moves through) the Biotic components, biotic compartment and the Abiotic, abiotic compartments of Earth. The biotic compartment is the biosphere and the abiotic compartments are the atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere. For example, in the carbon cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis, which converts it into organic compounds that are used by organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater Pollution
Groundwater pollution (also called groundwater contamination) occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and make their way into groundwater. This type of water pollution can also occur naturally due to the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent, contaminant, or impurity in the groundwater, in which case it is more likely referred to as contamination rather than pollution. Groundwater pollution can occur from on-site sanitation systems, landfill leachate, effluent from wastewater treatment plants, leaking sewers, petrol filling stations, hydraulic fracturing (fracking) or from over application of fertilizers in agriculture. Pollution (or contamination) can also occur from naturally occurring contaminants, such as arsenic contamination of groundwater, arsenic or fluoride. Using polluted groundwater causes hazards to public health through poisoning or the spread of disease (Waterborne diseases, water-borne diseases). The pollutant often produces a contaminant Plume (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the secretary of agriculture, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Brooke Rollins, who has served since February 13, 2025. Approximately 71% of the USDA's $213 billion budget goes towards nutrition assistance programs administered by the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS). The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (formerly known as the 'Food Stamp' program), which is the cornerstone of USDA's nutrition assistance. The United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Organic Program
The National Organic Program (NOP) is the federal regulatory framework in the United States, United States of America governing organic food. It is also the name of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) program responsible for administering and enforcing the regulatory framework. The core mission of the NOP is to protect the integrity of the USDA organic seal. The seal is used for products adhering to USDA standards that contain at least 95% Organic farming, organic ingredients. The Organic Foods Production Act of 1990 (OFPA) required that the USDA develop national standards for organic products, and the final rule establishing the NOP was first published in the Federal Register in 2000 and is codified in the Code of Federal Regulations at . Overview The NOP covers fresh and processed food, processed agricultural food products. The National Organic Program grew from fewer than twelve total employees in 2008 to approximately 37 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorption
Sorption is a physical and chemical process by which one substance becomes attached to another. Specific cases of sorption are treated in the following articles: ; Absorption: "the incorporation of a substance in one state into another of a different state" (e.g., liquids being absorbed by a solid or gases being absorbed by a liquid); ; Adsorption: The physical adherence or bonding of ions and molecules onto the surface of another phase (e.g., reagents adsorbed to a solid catalyst surface); ; Ion exchange: An exchange of ions between two electrolytes or between an electrolyte solution and a complex. The reverse of sorption is desorption. Sorption rate The adsorption and absorption rate of a diluted solute in gas or liquid solution to a surface or interface can be calculated using Fick's laws of diffusion Fick's laws of diffusion describe diffusion and were first posited by Adolf Fick in 1855 on the basis of largely experimental results. They can be used to solve for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Organic Pollutant
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are organic compounds that are resistant to degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes. They are toxic and adversely affect human health and the environment around the world. Because they can be transported by wind and water, most POPs generated in one country can and do affect people and wildlife far from where they are used and released. The effect of POPs on human and environmental health was discussed, with intention to eliminate or severely restrict their production, by the international community at the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001. Most POPs are pesticides or insecticides, and some are also solvents, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals. Although some POPs arise naturally (e.g. from volcanoes), most are man-made. The "dirty dozen" POPs identified by the Stockholm Convention include aldrin, chlordane, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, HCB, mirex, toxaphene, PCBs, DDT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cropduster Spraying Pesticides
Aerial application, or crop dusting, involves spraying crops with crop protection products from an agricultural aircraft. Planting certain types of seed are also included in aerial application. The specific spreading of fertilizer is also known as ''aerial topdressing ''in some countries. Many countries have severely limited aerial application of pesticides and other products because of environmental and public health hazards like Pesticide drift, spray drift; most notably, the European Union banned it outright with a few highly restricted exceptions in 2009, effectively ending the practice in all member states. Agricultural aircraft are highly specialized, purpose-built aircraft. Today's agricultural aircraft are often powered by turbine engines of up to and can carry as much as of crop protection product. Helicopters are sometimes used, and some aircraft serve double duty as water bombers in areas prone to wildfires. These aircraft are referred to as SEAT, or "single engine ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Food System
A sustainable food system is a type of food system that provides healthy diet, healthy food to people and creates sustainable environmental, economic, and social systems that surround food. Sustainable food systems start with the development of Sustainable agriculture, sustainable agricultural practices, development of more Food distribution, sustainable food distribution systems, creation of sustainable diets, and reduction of food waste throughout the system. Sustainable food systems have been argued to be central to many or all Sustainable Development Goals, 17 Sustainable Development Goals. Moving to sustainable food systems, including via Sustainable consumption#Sustainable food consumption, shifting consumption to sustainable diets, is an important component of climate change mitigation, addressing the causes of climate change and Climate change adaptation#Agriculture, adapting to it. A 2020 review conducted for the European Union found that up to 37% of global greenhouse gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |