|
Acremonium
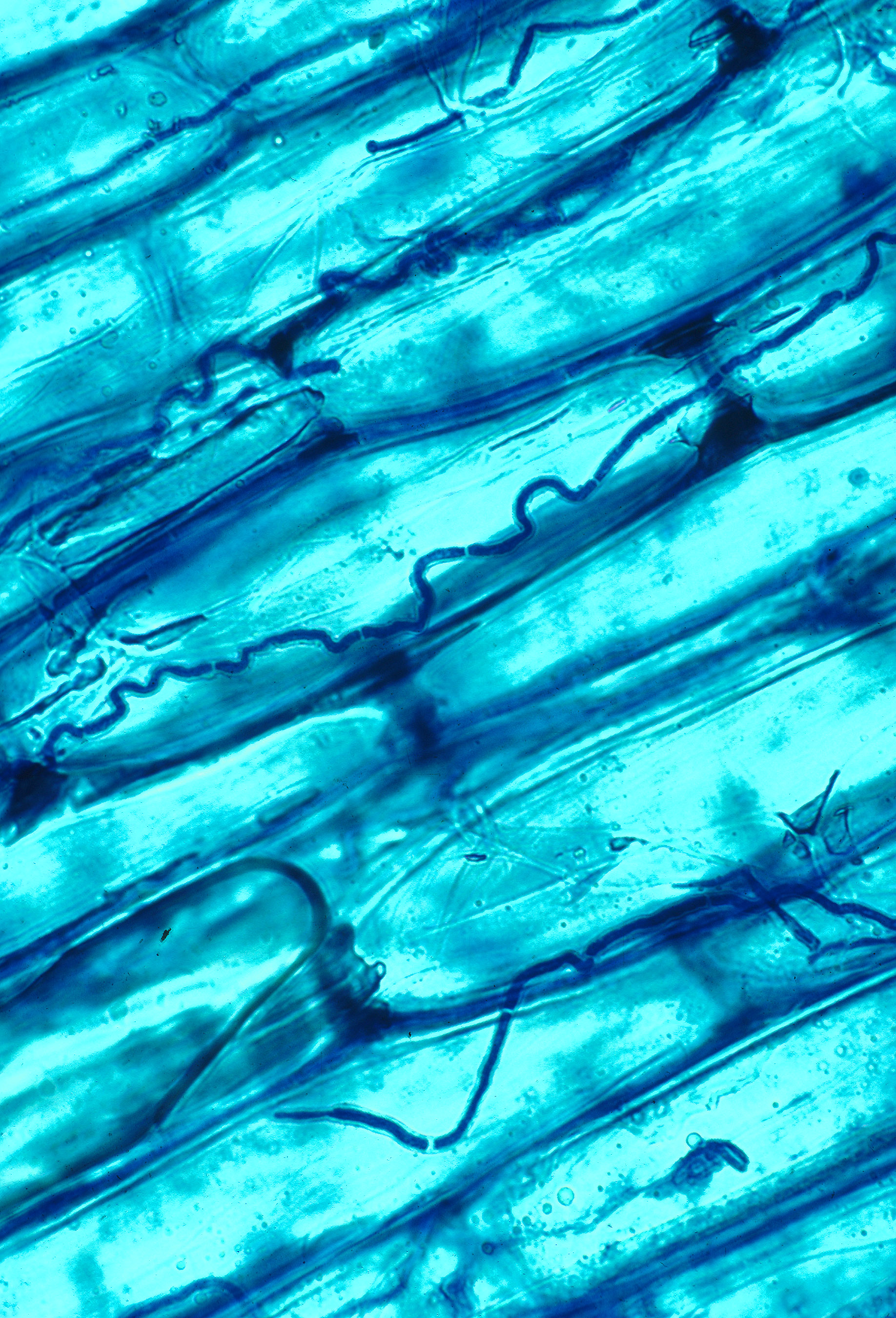
''Acremonium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae. It used to be known as ''Cephalosporium''. Description ''Acremonium'' species are usually slow-growing and are initially compact and moist. Their hyphae are fine and hyaline, and produce mostly simple phialides. Their conidia are usually one-celled (i.e. ameroconidia), hyaline or pigmented, globose to cylindrical, and mostly aggregated in slimy heads at the apex of each phialide. '' Epichloë'' species are closely related and were once included in ''Acremonium'', but were later split off into a new genus '' Neotyphodium'', which has now been restructured within the genus '' Epichloë''. Clinical significance The genus ''Acremonium'' contains about 100 species, of which most are saprophytic, being isolated from dead plant material and soil. Many species are recognized as opportunistic pathogens of man and animals, causing eumycetoma, onychomycosis, and hyalohyphomycosis. Infections of humans by fungi of this ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acremonium Alcalophilum
''Acremonium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae. It used to be known as ''Cephalosporium''. Description ''Acremonium'' species are usually slow-growing and are initially compact and moist. Their hyphae are fine and hyaline, and produce mostly simple phialides. Their conidia are usually one-celled (i.e. ameroconidia), hyaline or pigmented, globose to cylindrical, and mostly aggregated in slimy heads at the apex of each phialide. ''Epichloë'' species are closely related and were once included in ''Acremonium'', but were later split off into a new genus '' Neotyphodium'', which has now been restructured within the genus ''Epichloë''. Clinical significance The genus ''Acremonium'' contains about 100 species, of which most are saprophytic, being isolated from dead plant material and soil. Many species are recognized as opportunistic pathogens of man and animals, causing eumycetoma, onychomycosis, and hyalohyphomycosis. Infections of humans by fungi of this genus ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë
''Epichloë'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi forming an endophytic symbiosis with grasses. Grass choke disease is a symptom in grasses induced by some ''Epichloë'' species, which form spore-bearing mats (stromata) on tillers and suppress the development of their host plant's inflorescence. For most of their life cycle however, ''Epichloë'' grow in the intercellular space of stems, leaves, inflorescences, and seeds of the grass plant without incurring symptoms of disease. In fact, they provide several benefits to their host, including the production of different herbivore-deterring alkaloids, increased stress resistance, and growth promotion. Within the family Clavicipitaceae, ''Epichloë'' is embedded in a group of endophytic and plant pathogenic fungi, whose common ancestor probably derived from an animal pathogen. The genus includes both species with a sexually reproducing (teleomorphic) stage and asexual, anamorphic species. The latter were previously placed in the form g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
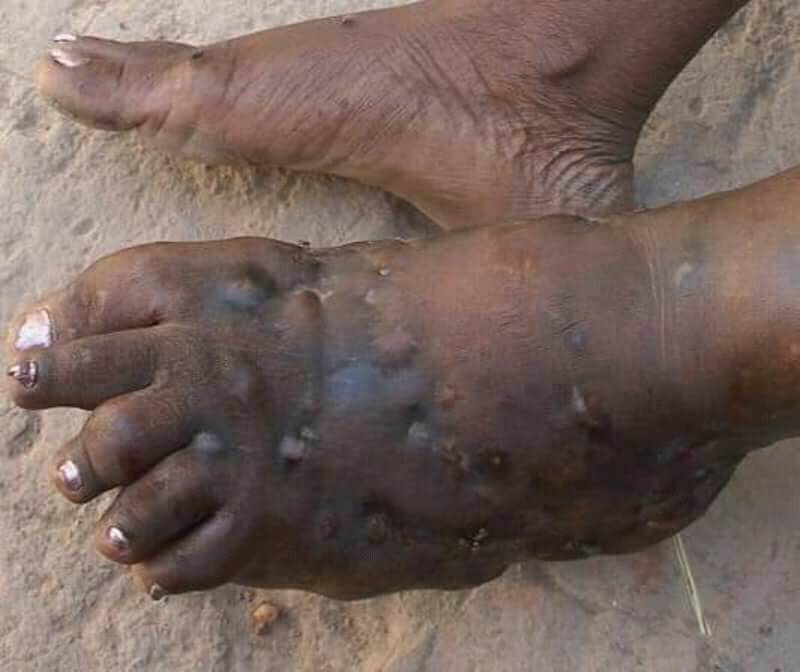
Eumycetoma
Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot, is a persistent fungal infection of the skin and the tissues just under the skin, affecting most commonly the feet, although it can occur in hands and other body parts. It starts as a painless wet nodule, which may be present for years before ulceration, swelling, grainy discharge and weeping from sinuses and fistulae, followed by bone deformity. Several fungi can cause eumycetoma, including: '' Madurella mycetomatis'', '' Madurella grisea'', ''Leptosphaeria senegalensis'', '' Curvularia lunata'', '' Scedosporium apiospermum'', ''Neotestudina rosatii'', and ''Acremonium'' and ''Fusarium'' species. Diagnosis is by biopsy, visualising the fungi under the microscope and culture. Medical imaging may reveal extent of bone involvement. Other tests include ELISA, immunodiffusion, and DNA Barcoding. Treatment includes surgical removal of affected tissue and antifungal medicines. After treatment, recurrence is common. Sometimes, amputation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalosporins
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus '' Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964. Discovery The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945. Structure Cephalosporin contains a 6-membered dihydrothiazine ring. Substitutions at position 3 generally affect pharmacology; substitutions at position 7 affect antibacterial activity, but these cases are not always true. Medical uses Cephalosporins can be indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominantly again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyalohyphomycosis
Hyalohyphomycosis is a group of opportunistic mycotic infections caused by nondematiaceous molds, and may be contrasted with phaeohyphomycosis. A hyalohyphomycetes example is '' Fusarium''. See also * '' Acremonium'' * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against t ... References Animal fungal diseases Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions {{Cutaneous-infection-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Brotzu
Giuseppe Brotzu (Cagliari, 24 January 1895 – Cagliari, 8 April 1976) was an Italian pharmacologist and politician. Biography Giuseppe Brotzu was born in Ghilarza, a town of the Province of Oristano, Sardinia. He graduated from the University of Cagliari, Sardinia in (1919) and later completed the specialization in Hygiene at University of Siena in 1922. He graduated in Medicine and Surgery at the University of Bologna in 1925. He became a professor at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia in 1932, and between 1939 and 1943 he was the director of University of Cagliari. Scientific research Brotzu is recognized as the discoverer of the cephalosporin-based antibiotics, that were first isolated from cultures of ''Cephalosporium'' (now known as ''Acremonium'') in 1948. He noticed that these cultures produced substances that were effective against ''Salmonella typhi'', the cause of typhoid fever, which had beta-lactamase. He was awarded the ''Laurea ad honorem'' at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotyphodium
''Neotyphodium'' is a genus of endophytic fungi symbiotic with grasses. It used to contain a number of asexually reproducing species that colonize the leaves of cool-season grasses, but most of them, including the type species '' N. coenophialum'', were merged into the genus '' Epichloë'' in 2014. Two species of unclear position were excluded from this treatment: *''Neotyphodium chilense'' from Chile should be treated as ''Acremonium chilense'' since the previous transfer to ''Neotyphodium'' is untested. *''Neotyphodium starrii'' is closely related to ''N. coenophialum'', but the taxonomic status within ''Epichloë'' (whether it is a distinct species or not) is unclear (''nomen dubium In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application. Zoology In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...''). References Hypocreales genera Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults. The cause is usually a bacterial infection, but rarely can be a fungal infection. It may occur by spread from the blood or from surrounding tissue. Risks for developing osteomyelitis include diabetes, intravenous drug use, prior removal of the spleen, and trauma to the area. Diagnosis is typically suspected based on symptoms and basic laboratory tests as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).This is because plain radiographs are unremarkable in the first few days following acute infection. Diagnosis is further confirmed by blood tests, medical imaging, or bone biopsy. Treatment of bacterial osteomyelitis often involves both antimicrobials and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypocreales
The Hypocreales are an order of fungi within the class Sordariomycetes. In 2008, it was estimated that it contained some 237 genera, and 2647 species in seven families. Since then, a considerable number of further taxa have been identified, including an additional family, the Stachybotryaceae. According to the Catalog of Life, the Hypocreales contains 6 families, 137 genera, and 1411 species. Species of Hypocreales are usually recognized by their brightly colored, perithecial ascomata, or spore-producing structures. These are often yellow, orange or red. Genera ''incertae sedis'' According to a 2020 review of fungal classification, the following genera within the Hypocreales have an uncertain taxonomic placement ('' incertae sedis''), and have not been assigned to any family: *'' Acremoniopsis'' – 1 sp. *''Berkelella'' – 2 spp. *''Bulbithecium'' – 1 sp. *'' Cephalosporiopsis'' – 10 spp. *'' Chondronectria'' – 1 sp. *'' Cylindronectria'' – 1 sp. *'' Diploo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypocreaceae
The Hypocreaceae are a family within the class Sordariomycetes. Species of Hypocreaceae are usually recognized by their brightly colored, perithecial ascomata, typically yellow, orange or red. The family was proposed by Giuseppe De Notaris in 1844. According to the ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008), the family has 22 genera and 454 species. Genera *'' Acrostalagmus'' *'' Aphysiostroma'' *'' Cladobotryum'' *''Gliocladium'' *'' Hypocrea'' *'' Hypocreopsis'' *''Hypomyces'' *'' Mycogone'' *'' Podostroma'' *'' Protocrea'' *'' Rogersonia'' *'' Sarawakus'' *'' Sepedonium'' *'' Sphaerostilbella'' *'' Sporophagomyces'' *'' Stephanoma'' *''Trichoderma ''Trichoderma'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae that is present in all soils, where they are the most prevalent culturable fungi. Many species in this genus can be characterized as opportunistic avirulent plant symbionts. This ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q3144255 Ascomycota families Taxa nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |