|
931st Air Refueling Wing
The 931st Air Refueling Wing (931 ARW) is an Air Reserve Component (ARC) of the United States Air Force. It is assigned to the Fourth Air Force, Air Force Reserve Command, stationed at McConnell Air Force Base, Kansas. The 931st ARW is an associate unit with the 22d Air Refueling Wing, Air Mobility Command (AMC) and if mobilized the wing is gained by AMC. Overview The 931st ARW is an associate unit with the active-duty 22d Air Refueling Wing and currently has about 485 personnel. The host unit and the 931st ARW share responsibilities for maintenance, with flying operations conducted by both units, using the inventory of 24 KC-135R Stratotankers and Boeing KC-46 Pegasus. The group consists of the following units: 931st Operations Group * 18th Air Refueling Squadron * 905th Air Refueling Squadron * 924th Air Refueling Squadron *931st Operations Support Squadron 931st Maintenance Group * 931st Aircraft Maintenance Squadron * 931st Maintenance Squadron * 931st Maintenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing KC-135R Stratotanker
The Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker is an American military aerial refueling tanker aircraft that was developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype, alongside the Boeing 707 airliner. It has a narrower fuselage and is shorter than the 707. Boeing gave the aircraft the internal designation of Model 717 (number later assigned to a different Boeing aircraft). The KC-135 was the United States Air Force (USAF)'s first jet-powered refueling tanker and replaced the KC-97 Stratofreighter. The KC-135 was initially tasked with refueling strategic bombers, but it was used extensively in the Vietnam War and later conflicts such as Operation Desert Storm to extend the range and endurance of US tactical fighters and bombers. The KC-135 entered service with the USAF in 1957; it is one of nine military fixed-wing aircraft (six American, three Russian) with over 60 years of continuous serviceThe nine military fixed-wing aircraft with over 60 years of continuous service are Boeing B-52 Stratofortress bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KC-135
The Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker is an American military aerial refueling tanker aircraft that was developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype, alongside the Boeing 707 airliner. It has a narrower fuselage and is shorter than the 707. Boeing gave the aircraft the internal designation of Model 717 (number later assigned to a different Boeing aircraft). The KC-135 was the United States Air Force (USAF)'s first jet-powered refueling tanker and replaced the KC-97 Stratofreighter. The KC-135 was initially tasked with refueling strategic bombers, but it was used extensively in the Vietnam War and later conflicts such as Operation Desert Storm to extend the range and endurance of US tactical fighters and bombers. The KC-135 entered service with the USAF in 1957; it is one of nine military fixed-wing aircraft (six American, three Russian) with over 60 years of continuous serviceThe nine military fixed-wing aircraft with over 60 years of continuous service are Boeing B-52 Stratofortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airlift
An airlift is the organized delivery of Materiel, supplies or personnel primarily via military transport aircraft. Airlifting consists of two distinct types: strategic and tactical. Typically, strategic airlifting involves moving material long distances (such as across or off the continent or theater), whereas a tactical airlift focuses on deploying resources and material into a specific location with high precision. Depending on the situation, airlifted supplies can be delivered by a variety of means. When the destination and surrounding airspace is considered secure, the aircraft will land at an appropriate airport or airbase to have its cargo unloaded on the ground. When landing the craft or distributing the supplies to a certain area from a landing zone by surface transportation is not an option, the cargo aircraft can drop them in mid-flight using parachutes attached to the supply containers in question. When there is a broad area available where the intended receiver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
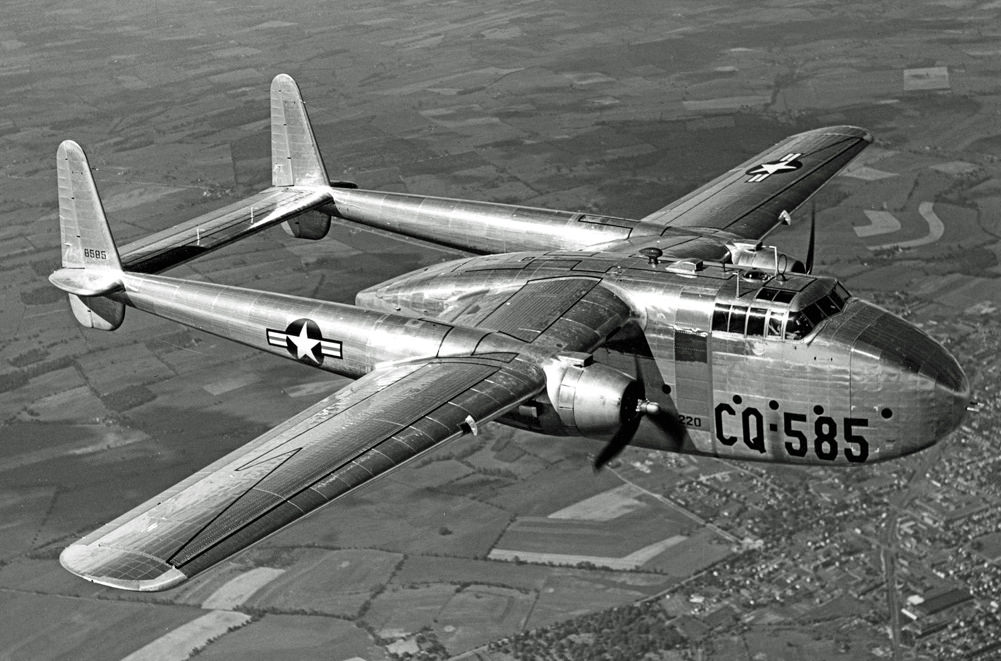
Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar
The Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar (Navy and Marine Corps designation R4Q) is an American military transport aircraft developed from the World War II-era Fairchild C-82 Packet, designed to carry cargo, personnel, Litter (rescue basket), litter patients, and mechanized equipment, and to drop cargo and troops by parachute. The first C-119 made its Maiden flight, initial flight in November 1947, and by the time production ceased in 1955, more than 1,100 had been built. Development The Air Force C-119 and Navy R4Q was initially a redesign of the earlier Fairchild C-82 Packet, C-82 Packet, built between 1945 and 1948. The Packet had provided limited service to the Air Force's Tactical Air Command and Military Air Transport Service before its design was found to have several serious problems. Though it continued in service until replaced, all of these were addressed in the C-119, which had its first test flight already in 1947. To improve pilot visibility, enlarge the cargo area, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tactical Air Command
Tactical Air Command (TAC) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, Major Command of the United States Air Force, established on 21 March 1946 and headquartered at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia. It was inactivated on 1 June 1992 and its personnel and equipment absorbed by Air Combat Command (ACC). Tactical Air Command was established to provide a balance between strategic, air defense, and tactical forces of the post–World War II U.S. Army Air Forces followed by, in 1947, the U.S. Air Force. In 1948, the Continental Air Command assumed control over air defense, tactical air, and air reserve forces. After two years in a subordinate role, Tactical Air Command (TAC) was established as a major command. In 1992, after assessing the mission of TAC and to accommodate a decision made regarding Strategic Air Command (SAC), Headquarters United States Air Force inactivated TAC and incorporated its resources i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
72d Troop Carrier Squadron
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. 7 is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Evolution of the Arabic digit For early Brahmi numerals, 7 was written more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted (ᒉ). The western Arab peoples' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arab peoples developed the digit from a form that looked something like 6 to one that looked like an uppercase V. Both modern Arab forms influenced the European form, a two-stroke form consisting of a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atterbury Air Force Base
Bakalar Air Force Base is a former U.S. Air Force base located northeast of Columbus, Indiana. During World War II, the base was known as Atterbury Air Field and Atterbury Army Air Base (named in memory of Brigadier General William Wallace Atterbury), but it was renamed Bakalar Air Force Base in 1954 in honor of First Lieutenant John Edmond Bakalar, USAAF. Established in 1942, the airfield served as a training base for medium-range C-46 Commando and C-47 Skytrain troop carrier planes and glider pilots. It also was used for training B-25 Mitchell and B-26 Marauder bomber crews. Reactivated during the Cold War, it was used as an Air Force Reserve training base for troop carrier, tactical airlift, and special operations flying units. The military base was closed in 1970. The present-day facility operates as the Columbus Municipal Airport. Initial construction In June 1942 it was announced that a new airfield would be established near Camp Atterbury, a military training camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Air Command
Continental Air Command (ConAC) (1948–1968) was a Major Command of the United States Air Force (USAF) responsible primarily for administering the Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve. During the Korean War, ConAC provided the necessary augmentation to the regular Air Force while it rebuilt itself under wartime conditions. Later, during the 1950s, it was a training force for reservists with no prior military service. ConAC provided peacetime airlift missions for the Air Force. It was mobilized twice in 1961 and 1962 by president Kennedy for the Berlin and Cuban Missile Crisis. Lastly, it was used by president Lyndon B. Johnson for airlift operations into the Dominican Republic and South Vietnam. It was inactivated in 1968 and replaced by Headquarters, Air Force Reserve (AFRES). History Origins After the end of World War II, the Harry S. Truman, Truman Administration was determined to bring the Federal budget back into balance. An enormous Government budget deficit, defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Crisis Of 1961
The Berlin Crisis of 1961 () was the last major European political and military incident of the Cold War concerning the status of the German capital city, Berlin, and of History of Germany (1945–90), post–World War II Germany. The crisis culminated in the city's ''de facto'' Partition (politics), partition with the East Germany, East German erection of the Berlin Wall. The Berlin Crisis of 1961 was the second attempt by Premier of the Soviet Union, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev to change the status of Berlin by demanding the withdrawal of all armed forces from the city and stopping the mass exodus of East Germans fleeing to the West. After the failure of his first Berlin Crisis of 1958–1959, ultimatum in 1958, Khrushchev renewed his demands at the 1961 Vienna summit, this time challenging the newly inaugurated U.S. President John F. Kennedy, John F. Kennedy. When talks broke down and no agreement was reached, in August 1961 East German leader Walter Ulbricht, with Khru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
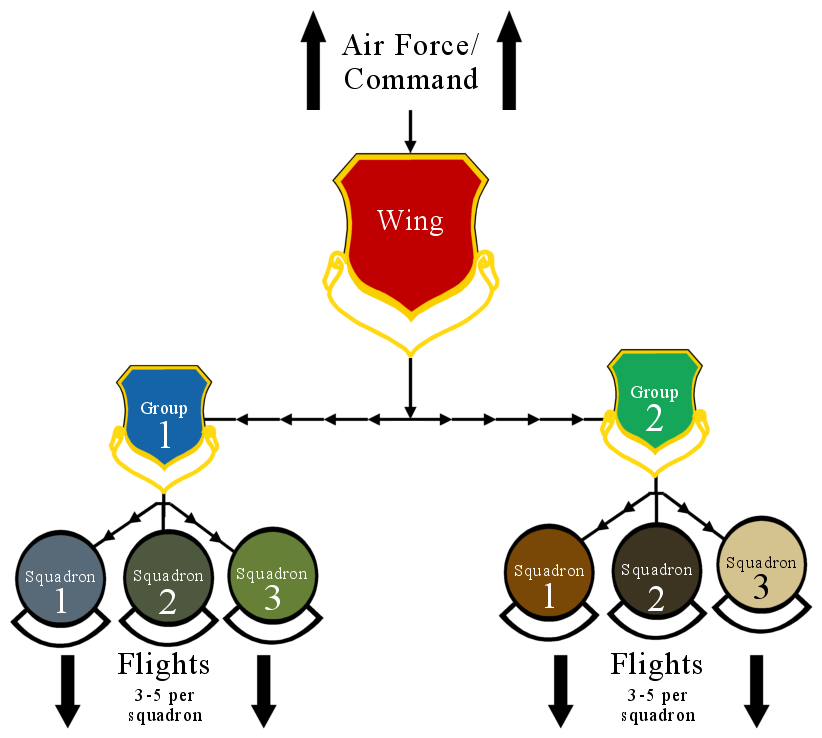
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squadron (aviation)
A squadron in an air force, or naval or army aviation service, is a unit comprising a number of military aircraft and their aircrews, usually of the same type, typically with 12 to 24 aircraft, sometimes divided into three or four flights, depending on aircraft type and air force. In most armed forces, two or more squadrons will form a group or a wing. Some military forces (including the United States Air Force, United States Space Force, French Air and Space Force, Royal Air Force, German Air Force, Royal Netherlands Air Force, Belgian Air Component and Republic of Singapore Air Force) also use the term "squadron" for non-flying ground units (e.g. radar squadrons, missile squadrons, air defense squadrons, aircraft maintenance squadrons, security forces squadrons, civil engineering squadrons, range operations squadrons, range management squadrons, weather squadrons, medical squadrons, etc.). Comparative organization Germany In World War I, the Imperial Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
924th Air Refueling Squadron
The 924th Air Refueling Squadron is an active United States Air Force associate unit. It is assigned to the 931st Operations Group at McConnell Air Force Base, Kansas. The squadron is the first Air Force Reserve Command unit dedicated to flying the Boeing KC-46 Pegasus. The earliest predecessor of the squadron was the 24th Transport Squadron which was activated at Morrison Field, Florida in 1942. The squadron supported the South Atlantic air ferrying route of Air Transport Command in World War II until it was disbanded in 1943. The 924th Air Refueling Squadron was activated at Castle in 1959. Through most of its existence it served as the tactical refueling component of the 93d Bombardment Wing, while its companion 93d Air Refueling Squadron was the "schoolhouse" for Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker aircrews, although in the 1980s, these roles were reversed. In 1985 the 24th and 924th squadrons were consolidated into a single unit. The unit was inactivated in 1992, shortly be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |