|
2011 Baden-Württemberg State Election
The 2011 Baden-Württemberg state election was held on 27 March 2011 to elect the members of the 14th Landtag of Baden-Württemberg. The incumbent coalition government of the Christian Democratic Union of Germany, Christian Democratic Union and Free Democratic Party (Germany), Free Democratic Party led by List of Ministers-President of Baden-Württemberg, Minister-President Stefan Mappus lost its majority. Alliance 90/The Greens, The Greens achieved their best result in a state election up to this point at 24%, and became the second largest party in the Landtag. They subsequently formed a coalition with the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD), and Greens leader Winfried Kretschmann was elected Minister-President. He became the first Green politician to serve as a state head of government in Germany. Campaign and issues The Baden-Württemberg election was considered to have significant ramifications for Chancellor Angela Merkel; the state had been a CD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag Of Baden-Württemberg
The Landtag of Baden-Württemberg is the diet (assembly), diet of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It convenes in Stuttgart and currently consists of 154 members of five political parties. The majority before the 2021 Baden-Württemberg state election, 2021 election was a coalition of the Alliance '90/The Greens, Alliance 90/The Greens and the Christian Democratic Union (Germany), Christian Democratic Union (CDU), supporting the cabinet Kretschmann II, cabinet of Green Minister-President Winfried Kretschmann. Current Composition After the elections of 14 March 2021, the composition of the Landtag is as follows: Elections are conducted using a Mixed-member proportional representation, mixed-member proportional representation system, with a minimum of 5% vote share to receive any seats. However, there are some exceptions, making the Baden-Württemberg election system one of the most complicated in Germany. The minimum size of the Landtag is 120 members, of which 70 memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Station
A train station, railroad station, or railway station is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight, or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track, and a station building providing such ancillary services as ticket sales, waiting rooms, and baggage/freight service. Stations on a single-track line often have a passing loop to accommodate trains travelling in the opposite direction. Locations at which passengers only occasionally board or leave a train, sometimes consisting of a short platform and a waiting area but sometimes indicated by no more than a sign, are variously referred to as "stops", " flag stops", " halts", or "provisional stopping places". The stations themselves may be at ground level, underground, or elevated. Connections may be available to intersecting rail lines or other transport modes such as buses, trams, or other rapid transit systems. Terminology ''Train station'' is the terminology typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 German Federal Election
The 2009 German federal election was held in Germany on 27 September 2009 to elect the members of the 17th Bundestag. The Christian Democratic Union (Germany), Christian Democratic Union (CDU), its Bavarian sister party, the Christian Social Union of Bavaria, Christian Social Union (CSU), and the Free Democratic Party (Germany), Free Democratic Party (FDP) won the election, and the three parties formed a new centre-right government with Angela Merkel as Chancellor of Germany, chancellor. While CDU/CSU's share of votes decreased slightly, it was more than compensated by the gains of their "desired coalition partner", the liberal FDP, that won the strongest result in its history. CDU and CSU's former partner in the "Grand coalition (Germany), Grand coalition", the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) led by Frank-Walter Steinmeier, conceded defeat after dropping by more than 11 percentage points, receiving its hitherto worst result since the end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Left (Germany)
Die Linke (; ), also known as the Left Party ( ), is a Democratic socialism, democratic socialist List of political parties in Germany, political party in Germany. The party was founded in 2007 as the result of the merger of the Party of Democratic Socialism (Germany), Party of Democratic Socialism (PDS) and Labour and Social Justice – The Electoral Alternative. Through the PDS, the party is the direct descendant of the Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist ruling party of former East Germany, the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED). Since October 2024, The Left's co-Chair (officer), chairpersons have been Ines Schwerdtner and Jan van Aken (politician), Jan van Aken. The party holds 64 seats out of 630 in the German federal parliament (the Bundestag), having won 8.8% of votes cast in the 2025 German federal election. Its parliamentary group is the second-smallest of seven in the Bundestag, and is headed by parliamentary co-leaders Heidi Reichinnek and Sören Pellmann. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
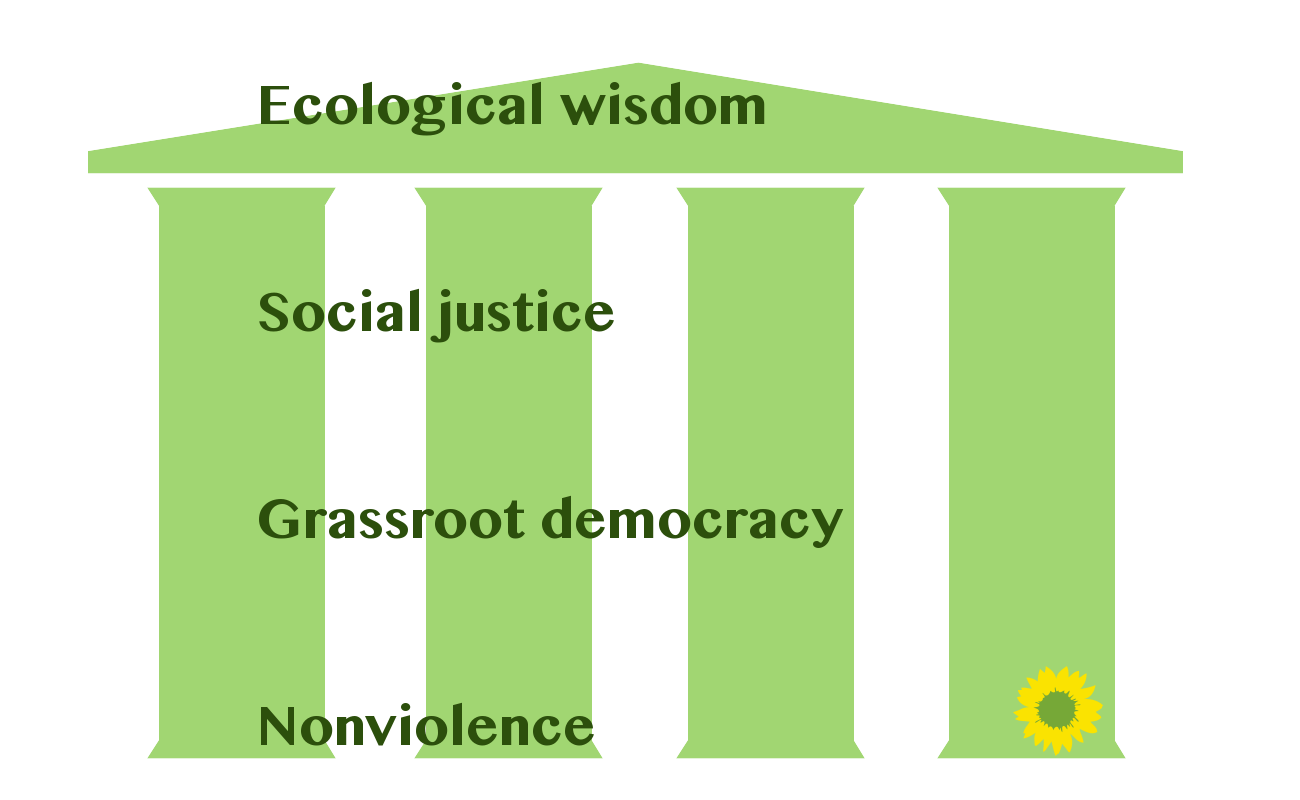
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the Western world in the 1970s; since then, green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term ''green'' was used initially in relation to ''Alliance 90/The Greens, die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term ''political ecology'' is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, economic freedom, political freedom and freedom of speech. Classical liberalism, contrary to progressive branches like social liberalism, looks more negatively on social policies, taxation and the state involvement in the lives of individuals, and it advocates deregulation. Until the Great Depression and the rise of social liberalism, classical liberalism was called economic liberalism. Later, the term was applied as a retronym, to distinguish earlier 19th-century liberalism from social liberalism. By modern standards, in the United States, the bare term ''liberalism'' often means social or progressive liberalism, but in Europe and Australia, the bare term ''liberalism'' often means classical liberalism. Classical liberalism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democracy
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, social democracy has taken the form of predominantly capitalist economies, a robust welfare state, policies promoting social justice, market regulation, and a more Redistribution of income and wealth, equitable distribution of income. Social democracy maintains a commitment to Representative democracy, representative and participatory democracy. Common aims include curbing Social inequality, inequality, eliminating the oppression of Social privilege, underprivileged groups, eradicating poverty, and upholding universally accessible public services such as child care, Universal education, education, elderly care, Universal health care, health care, and workers' compensation. Economically, it support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democracy
Christian democracy is an ideology inspired by Christian social teaching to respond to the challenges of contemporary society and politics. Christian democracy has drawn mainly from Catholic social teaching and neo-scholasticism, as well as the Neo-Calvinist tradition within Christianity; it later gained ground with Lutherans and Pentecostals, among other denominational traditions of Christianity in various parts of the world. During the nineteenth century, its principal concerns were to reconcile Catholicism with democracy, to answer the " social question" surrounding capitalism and the working class, and to resolve the tensions between church and state. In the twentieth century, Christian democrats led postwar Western and Southern Europe in building modern welfare states and constructing the European Union. Furthermore; in the late twentieth and early twenty-first century, Christian democracy has gained support in Eastern Europe among former communist states sufferi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster
The Fukushima nuclear accident was a major nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan, which began on 11 March 2011. The cause of the accident was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which resulted in electrical grid failure and damaged nearly all of the power plant's Emergency power system, backup energy sources. The subsequent inability to sufficiently cool reactors after shutdown compromised Primary containment, containment and resulted in the release of radioactive contamination, radioactive contaminants into the surrounding environment. The accident was rated seven (the maximum severity) on the International Nuclear Event Scale by Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency, following a report by the JNES (Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization). It is regarded as the worst nuclear incident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, which was also rated a seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale. According to the United Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both List of German states by area, area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and List of German states by population, population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). The List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Konstanz, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. Modern Baden-Württemberg includes the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either binding (resulting in the adoption of a new policy) or advisory (functioning like a large-scale opinion poll). Etymology 'Referendum' is the gerundive form of the Latin language, Latin verb , literally "to carry back" (from the verb , "to bear, bring, carry" plus the inseparable prefix , here meaning "back"Marchant & Charles, Cassell's Latin Dictionary, 1928, p. 469.). As a gerundive is an adjective,A gerundive is a verbal adjective (Kennedy's Shorter Latin Primer, 1962 edition, p. 91.) not a noun, it cannot be used alone in Latin, and must be contained within a context attached to a noun such as , "A proposal which must be carried back to the people". The addition of the verb (3rd person singular, ) to a gerundive, denotes the idea of nece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Disobedience
Civil disobedience is the active and professed refusal of a citizenship, citizen to obey certain laws, demands, orders, or commands of a government (or any other authority). By some definitions, civil disobedience has to be nonviolent to be called "civil". Hence, civil disobedience is sometimes equated with peaceful protests or nonviolent resistance. Henry David Thoreau's essay ''Resistance to Civil Government'', first published in 1849 and then published posthumously in 1866 as ''Civil Disobedience (Thoreau), Civil Disobedience'', popularized the term in the US, although the concept itself was practiced long before this work. Various forms of civil disobedience have been used by prominent activists, such as Women's suffrage in the United States, American women's suffrage leader Susan B. Anthony in the late 19th century, Egyptian nationalist Saad Zaghloul during the 1910s, and Indian nationalist Mahatma Gandhi in 1920s British Raj, British India as part of his leadership of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |