|
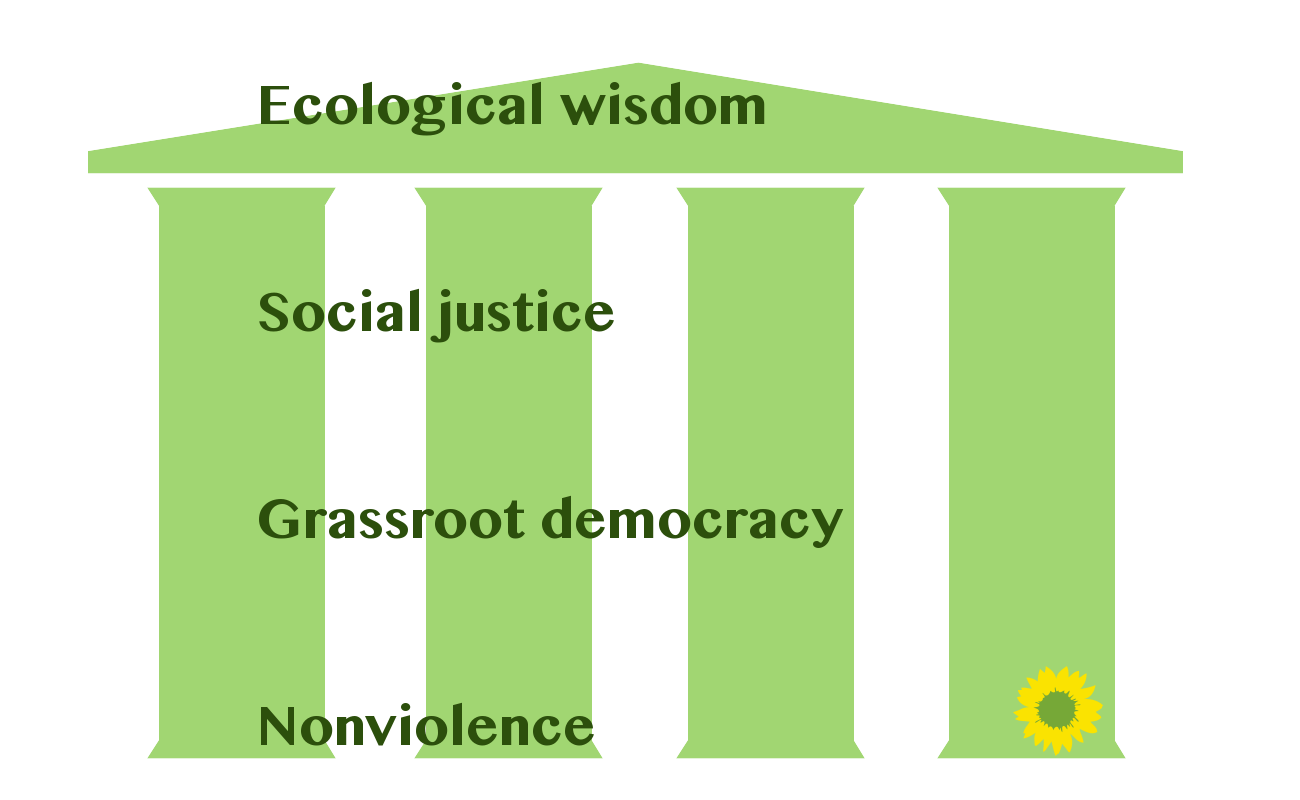
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the Western world in the 1970s; since then, green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term ''green'' was used initially in relation to ''Alliance 90/The Greens, die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term ''political ecology'' is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or values attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely about belief in certain knowledge, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones". Formerly applied primarily to Economy, economic, Political philosophy, political, or Religion, religious theories and policies, in a tradition going back to Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, more recent use treats the term as mainly condemnatory. The term was coined by Antoine Destutt de Tracy, a French Enlightenment aristocrat and philosopher, who conceived it in 1796 as the "science of ideas" to develop a rational system of ideas to oppose the irrational impulses of the mob. In political science, the term is used in a Linguistic description, descriptive sense to refer to List of political ideologies, political belief systems. Etymology The term ''ideology'' originates from French language, French , itself coined from combining (; close to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Progressivism
Progressivism is a left-leaning political philosophy and reform movement that seeks to advance the human condition through social reform. Adherents hold that progressivism has universal application and endeavor to spread this idea to human societies everywhere. Progressivism arose during the Age of Enlightenment out of the belief that civility in Europe was improving due to the application of new empirical knowledge.Harold Mah''Enlightenment Phantasies: Cultural Identity in France and Germany, 1750–1914'' Cornell University. (2003). p. 157. In modern political discourse, progressivism is often associated with social liberalism, a left-leaning type of liberalism, and social democracy. Within economic progressivism, there is some ideological variety on the social liberal to social democrat continuum, as well as occasionally some variance on cultural issues; examples of this include some Christian democrat and conservative-leaning communitarian movements. While many ideol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territory, and an experience of subjugation and discrimination under a dominant cultural model. Estimates of the population of Indigenous peoples range from 250 million to 600 million. There are some 5,000 distinct Indigenous peoples spread across every inhabited climate zone and inhabited continent of the world. Most Indigenous peoples are in a minority in the state or traditional territory they inhabit and have experienced domination by other groups, especially non-Indigenous peoples. Although many Indigenous peoples have experienced colonization by settlers from European nations, Indigenous identity is not determined by Western colonization. The rights of Indigenous peoples are outlined in national legislation, treaties and international law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walden
''Walden'' (; first published as ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods'') is an 1854 book by American transcendentalism, transcendentalist writer Henry David Thoreau. The text is a reflection upon the author's simple living in natural surroundings. The work is part personal declaration of independence, social experiment, voyage of spiritual discovery, satire, and—to some degree—a manual for Self-sustainability, self-reliance. ''Walden'' details Thoreau's experiences over the course of two years, two months, and two days in a cabin he built near Walden Pond amidst woodland owned by his friend and mentor Ralph Waldo Emerson, near Concord, Massachusetts, Concord, Massachusetts. Thoreau makes precise scientific observations of nature as well as metaphorical and poetic uses of natural Phenomenon, phenomena. He identifies many plants and animals by both their popular and scientific names, records in detail the color and clarity of different bodies of water, precisely dates and describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (born David Henry Thoreau; July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading Transcendentalism, transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and his essay "Civil Disobedience (Thoreau), Civil Disobedience" (originally published as "Resistance to Civil Government"), an argument in favor of citizen disobedience against an unjust state. Thoreau's books, articles, essays, journals, and poetry amount to more than 20 volumes. Among his lasting contributions are his nature writing, writings on natural history and philosophy, in which he anticipated the methods and findings of ecology and environmental history, two sources of modern-day environmentalism. His literary language, literary style interweaves close observation of nature, personal experience, pointed rhetoric, symbolic meanings, and historical lore, while displaying a poetic sensibility, ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
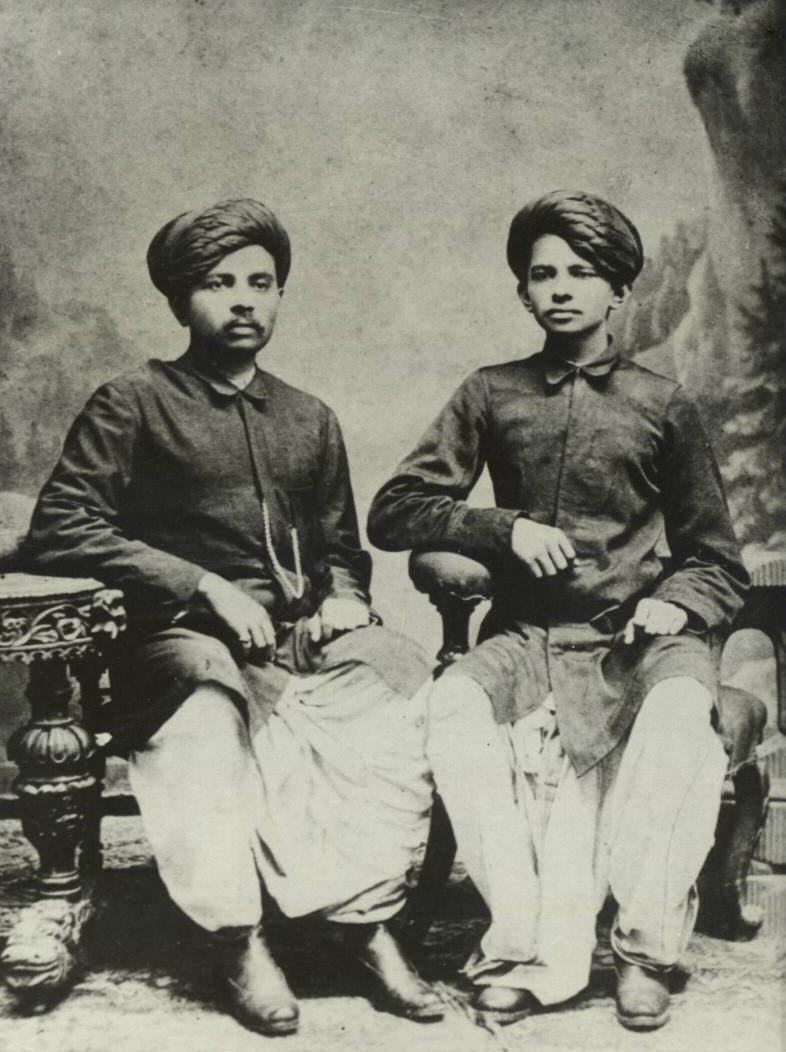
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (2October 186930January 1948) was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalism, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethics, political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful Indian independence movement, campaign for India's independence from British Raj, British rule. He inspired movements for Civil rights movements, civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (from Sanskrit, meaning great-souled, or venerable), first applied to him in Union of South Africa, South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world. Born and raised in a Hindu family in coastal Gujarat, Gandhi trained in the law at the Inner Temple in London and was called to the bar at the age of 22. After two uncertain years in India, where he was unable to start a successful law practice, Gandhi moved to South Africa in 1893 to represent an Indian merchant in a lawsuit. He went on to live in South Africa for 21 years. Here, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Conservatism
Green conservatism is a combination of conservatism with environmentalism. Environmental concern has been voiced by both conservative politicians and philosophers throughout the history of conservatism. The distinguishing feature of green conservatism is the adherence to market-based policies to address environmental concerns, rather than centralised planning. Individual and local empowerment is preferred over top down control. Where solutions to problems are global, such as climate change, green conservatives believe the government's role "is to empower individuals, entrepreneurs, and philanthropists to collaborate and come up with innovations that will solve climate change." Variants Americas Brazil The National Ecologic Party had ties to the Assemblies of God, the largest evangelical denomination present in Brazil, and upheld green conservatism but it has now changed its name to Patriota and renounced its green and pro-ecologist policies in favor of its conservative a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eco-capitalism
Eco-capitalism, also known as environmental capitalism or (sometimes) green capitalism, is the view that capital exists in nature as " natural capital" (ecosystems that have ecological yield) on which all wealth depends. Therefore, governments should use market-based policy-instruments (such as a carbon tax) to resolve environmental problems. The term "Blue Greens" is often applied to those who espouse eco-capitalism. Eco-capitalism can be thought of as the right-wing equivalent to Red Greens. Critics of eco-capitalism, such as eco-socialists, view continued economic growth and commodification of nature as an inevitability in capitalism, and thus criticize bright-green environmentalism. History The roots of eco-capitalism can be traced back to the late 1960s. The " Tragedy of the Commons", an essay published in 1968 in ''Science'' by Garrett Hardin, claimed the inevitability of malthusian catastrophe due to liberal or democratic government's policies to leave fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-wing
Right-wing politics is the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position based on natural law, economics, authority, property, religion, or tradition. Hierarchy and inequality may be seen as natural results of traditional social differences or competition in market economies. Right-wing politics are considered the counterpart to left-wing politics, and the left–right political spectrum is the most common political spectrum. The right includes social conservatives and fiscal conservatives, as well as right-libertarians. "Right" and "right-wing" have been variously used as compliments and pejoratives describing neoliberal, conservative, and fascist economic and social ideas. Positions The following positions are typically associated with right-wing politics. Anti-communism Early communists used the term "right-wing" in reference to conservatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social hierarchies. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in society whom its adherents perceive as disadvantaged relative to others as well as a belief that there are unjustified inequalities that need to be reduced or abolished, through radical means that change the nature of the society they are implemented in. According to emeritus professor of economics Barry Clark, supporters of left-wing politics "claim that human development flourishes when individuals engage in cooperative, mutually respectful relations that can thrive only when excessive differences in status, power, and wealth are eliminated." Within the left–right political spectrum, ''Left'' and ''right-wing politics, Right'' were coined during the French Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Anarchism
Green anarchism, also known as ecological anarchism or eco-anarchism, is an anarchist school of thought that focuses on ecology and environmental issues. It is an anti-capitalist and anti-authoritarian form of radical environmentalism, which emphasises social organization, freedom and self-fulfillment. Ecological approaches to anarchism were first formulated during the 19th century, as the rise of capitalism and colonialism caused environmental degradation. Drawing from the ecology of Charles Darwin, the anarchist Mikhail Bakunin elaborated a naturalist philosophy that rejected the dualistic separation of humanity from nature. This was developed into an ecological philosophy by Peter Kropotkin and Élisée Reclus, who advocated for the decentralisation and degrowth of industry as a means to advance both social justice and environmental protection. Green anarchism was first developed into a distinct political theory by sections of the New Left, as a revival in anarchism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrowth
Degrowth is an Academic research, academic and social Social movement, movement critical of the concept of economic growth, growth in Real gross domestic product, gross domestic product as a measure of Human development (economics), human and economic development. The idea of degrowth is based on ideas and research from economic anthropology, ecological economics, environmental sciences, and development studies. It argues that modern capitalism's unitary focus on growth causes widespread Environmental degradation, ecological damage and is unnecessary for the further increase of Standard of living, human living standards. Degrowth theory has been met with both academic acclaim and considerable criticism. Degrowth's main argument is that an infinite expansion of the economy is fundamentally contradictory to the Resource depletion, finiteness of material resources on Earth. It argues that economic growth measured by GDP should be abandoned as a policy objective. Policy should instead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |