|
1749
Events January–March * January 3 ** Benning Wentworth issues the first of the New Hampshire Grants, leading to the establishment of Vermont. ** The first issue of ''Berlingske'', Denmark's oldest continually operating newspaper, is published. * January 21 – The Teatro Filarmonico, the main opera theater in Verona, Italy, is destroyed by fire. It is rebuilt in 1754. * February – The second part of John Cleland's erotic novel ''Fanny Hill'' (''Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure'') is published in London. The author is released from debtors' prison in March. * February 28 – Henry Fielding's comic novel ''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'' is published in London. Also this year, Fielding becomes magistrate at Bow Street, and first enlists the help of the Bow Street Runners, an early police force (eight men at first). * March 6 – A "corpse riot" breaks out in Glasgow after a body disappears from a churchyard in the Gorbals district. Suspicion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The History Of Tom Jones, A Foundling
''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'', often known simply as ''Tom Jones'', is a comic novel by English playwright and novelist Henry Fielding. It is a ''Bildungsroman'' and a picaresque novel. It was first published on 28 February 1749 in London and is among the earliest English works to be classified as a novel. It is the earliest novel mentioned by W. Somerset Maugham in his 1948 book ''Ten Novels and Their Authors, Great Novelists and Their Novels,'' in which Maugham ranks the ten best novels of the world. The novel is highly organised despite its length. Samuel Taylor Coleridge argued that it has one of the "three most perfect plots ever planned", alongside ''Oedipus Rex, Oedipus Tyrannus'' by Sophocles and ''The Alchemist (play), The Alchemist'' by Ben Jonson. It became a best-seller, with four editions published in its first year alone. It is generally regarded as Fielding's greatest book and as an influential English novel. Plot The wealthy Squire Allworthy and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
January 3
Events Pre-1600 *AD 69, 69 – The Roman legions on the Rhine refuse to declare their allegiance to Galba, instead proclaiming their legate, Aulus Vitellius, as emperor. * 250 – Emperor Decius orders everyone in the Roman Empire (except Jews) Decian persecution, to make sacrifices to the Roman gods. *1521 – Pope Leo X excommunicates Martin Luther in the papal bull ''Decet Romanum Pontificem''. 1601–1900 *1653 – By the Coonan Cross Oath, the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Church in India cuts itself off from colonial Portuguese tutelage. *1749 – Benning Wentworth issues the first of the New Hampshire Grants, leading to the establishment of Vermont. * 1749 – The first issue of ''Berlingske'', Denmark's oldest continually operating newspaper, is published. *1777 – American Revolutionary War: American forces under General George Washington defeat British forces at the Battle of Princeton, helping boost Patriot (American Revolution), patri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow Street Runners
The Bow Street Runners were the law enforcement officers of the Bow Street Magistrates' Court in the City of Westminster. They have been called London's first professional police force. The force originally numbered six men and was founded in 1749 by Magistrate (England and Wales), magistrate Henry Fielding, who was also well known as an author. His assistant, brother, and successor as magistrate, John Fielding, moulded the constables into a professional and effective force. ''Bow Street Runners'' was the public's nickname for the officers although the officers did not use the term themselves and considered it derogatory. The group was disbanded in 1839 and its personnel merged with the Metropolitan Police, which had been formed ten years earlier but the London metropolitan detective bureau trace their origins back from there. Policing before 1749 The Bow Street Runners are considered the first British police force. Before the force was founded, the law enforcing system was in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
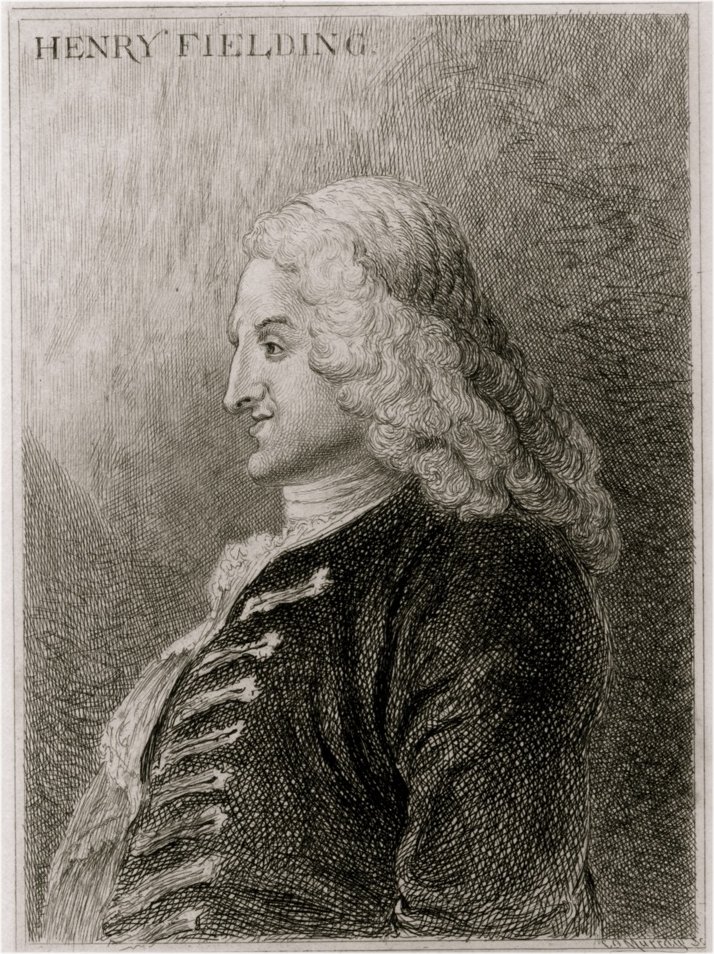
Henry Fielding
Henry Fielding (22 April 1707 – 8 October 1754) was an English writer and magistrate known for the use of humour and satire in his works. His 1749 comic novel ''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'' was a seminal work in the genre. Along with Samuel Richardson, Fielding is seen as the founder of the traditional English novel. He also played an important role in the history of law enforcement in the United Kingdom, using his authority as a magistrate to found the Bow Street Runners, London's first professional Police, police force. Early life Henry Fielding was born on 22 April 1707 at Sharpham Park, the seat of his mother's family in Sharpham, Somerset. He was the son of Lt.-Gen. Edmund Fielding and Sarah Gould, daughter of Sir Henry Gould. A scion of the Earl of Denbigh, his father was nephew of William Fielding, 3rd Earl of Denbigh. Educated at Eton College, Fielding began a lifelong friendship with William Pitt the Elder. His mother died when he was 11. A suit for custod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlingske
''Berlingske'', previously known as ''Berlingske Tidende'' (, 'Berling's Times'), is a Danish national daily newspaper based in Copenhagen. It is considered a newspaper of record for Denmark. First published on 3 January 1749, ''Berlingske'' is Denmark's oldest continually operating newspaper and among the oldest newspapers in the world. History and profile ''Berlingske'' was founded by Denmark's Royal Book Printer Ernst Henrich Berling and originally titled ''Kjøbenhavnske Danske Post-Tidender'', then the ''Berlingskes Politiske og Avertissements Tidende.'' The paper was supported by the Conservative Party. Until 1903 it had the official right to publish news about the government. In 1936, the newspaper's title was shortened to ''Berlingske Tidende''. Mendel Levin Nathanson twice served as the editor-in-chief of the paper: between 1838 and 1858 and between 1866 and 1868. The publisher is Det Berlingske Officin. The paper has a conservative stance and has no political parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanny Hill
''Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure'' – popularly known as ''Fanny Hill'' – is an erotic novel by the English novelist John Cleland first published in London in 1748 and 1749. Written while the author was in debtors' prison in London,Wagner, "Introduction", in Cleland, ''Fanny Hill'', 1985, p. 7. it is considered "the first original English prose pornography, and the first pornography to use the form of the novel". It is one of the most prosecuted and banned books in history. The book exemplifies the use of euphemism. The text has no swearing or explicit scientific terms for body parts, but uses many literary devices to describe genitalia. For example, the vagina is sometimes referred to as "the nethermouth". A critical edition by Peter Sabor includes a bibliography and explanatory notes. The collection ''Launching "Fanny Hill"'' contains several essays on the historical, social and economic themes underlying the novel. Publishing history The novel was published in two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cleland
John Cleland (24 September 1709 – 23 January 1789) was an English novelist best known for his fictional '' Fanny Hill: or, the Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure'', whose eroticism led to his arrest. James Boswell called him "a sly, old malcontent". Publication of ''Fanny Hill'' John Cleland began courting the Portuguese in a vain attempt to reestablish the Portuguese East India Company. In 1748, Cleland was arrested for an £840 debt (equivalent to a purchasing power of about £100,000 in 2005) and committed to Fleet Prison, where he remained for over a year. It was while he was in prison that Cleland finalised ''Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure.'' The text probably existed in manuscript for a number of years before Cleland developed it for publication. The novel was published in two instalments, in November 1748 and February 1749. In March of that year, he was released from prison. However, Cleland was arrested again in November 1749, along with the publishers and printer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hampshire Grants
The New Hampshire Grants or Benning Wentworth Grants were land grants made between 1749 and 1764 by the colonial governor of the Province of New Hampshire, Benning Wentworth. The land grants, totaling about 135 (including 131 towns), were made on land claimed by New Hampshire west of the Connecticut River, territory that was also claimed by the Province of New York. The resulting dispute led to the eventual establishment of the Vermont Republic, which later became the U.S. state of Vermont. Background The territory of what is now Vermont was first permanently settled by European settlers when William Dummer, acting governor of the Province of Massachusetts Bay, ordered the construction of a fort roughly where Brattleboro is located. Massachusetts laid claim to the territory west of the Merrimack River at the time, and it had settlers on the Connecticut River who were prepared to move further north. The border between Massachusetts and the neighboring Province of New Hamp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti. Born in Halle, Germany, Handel spent his early life in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712, where he spent the bulk of his career and became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the middle-German polyphonic choral tradition and by composers of the Italian Baroque. In turn, Handel's music forms one of the peaks of the "high baroque" style, bringing Italian opera to its highest development, creating the genres of English oratorio and organ concerto, and introducing a new style into English church music. He is consistently recognized as one of the greatest composers of his age. Handel started three commercial opera companies to supply the English nobility with Italian opera. In 1737, he had a physical breakdown, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon (Handel)
''Solomon'', Händel-Werke-Verzeichnis, HWV 67, is an oratorio by George Frideric Handel. The anonymous libretto – currently thought to have been penned by the English Jewish poet/playwright Moses Mendes (d.1758) – is based on the biblical stories of the wise king Solomon from Books of Kings, the First Book of Kings and Books of Chronicles, the Second Book of Chronicles, with additional material from ''Antiquities of the Jews'' by ancient historian Josephus, Flavius Josephus. The music was composed between 5 May and 13 June 1748 in music, 1748. The first performance took place on 17 March 1749 in music, 1749, with Caterina Galli in the title role at the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden Theatre in London, where it had two further performances. Handel revived the work in 1759. The oratorio contains a short and lively instrumental passage for two oboes and strings in Act Three, known as "The Arrival of the Queen of Sheba", which has become famous outside the context of the compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Arrival Of The Queen Of Sheba
"The Arrival of the Queen of Sheba", also known as "The Entrance of the Queen of Sheba" and "The Entry of the Queen of Sheba", is the sinfonia that opens Act III of George Frideric Handel's 1749 oratorio ''Solomon''. It is marked ''allegro'' and scored for two oboes and strings. It is now usually performed separately as a concert piece, and as such has become one of Handel's most famous works. Description "The Arrival of the Queen of Sheba" is one of two instrumental movements in ''Solomon'', an oratorio by George Frideric Handel written in May and June 1748 and premiered on 17 March 1749. Scored for two oboes, strings and continuo, it is the sinfonia which opens Act III, the only act in which Sheba appears, and it depicts the bustling preparations for her arrival rather than that entry itself. It is marked ''allegro'', and features lively violin passages and contrasting solos from the two oboes. Its modern title was apparently bestowed on it by Sir Thomas Beecham; certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Namur (1697)
HMS ''Namur'' was a 90-gun second rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Woolwich Dockyard in 1697. On 11 June 1723 she was ordered to be taken to pieces at Portsmouth and her timbers transferred to Deptford Dockyard. In 1729 the timbers were used to rebuild the ship according to the 1719 Establishment.Baugh 1965, p. 247 She was rebuilt by Richard Stacey at Deptford Dockyard and relaunched on 13 September 1729. In 1745, she was razeed to 74 guns. In February 1744 she took part in the Battle of Toulon (1744), Battle of Toulon. ''Namur'' was wrecked on 14 April 1749 in a storm near Fort St David on the east coast of India. In total, 520 of her crew were drowned, though Captain Marshal survived.Ships of the Old Navy, ''Namur''. Commanders of Note *Edward Falkingham 1731/2 *George Clinton (Royal Navy officer), George Clinton 1732 to 1734 *John Barnsley *Thomas Whitney *Samuel Faulknor *Sir Samuel Cornish, 1st Baronet, Samuel Cornish *George Berkeley Flagship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |