|
169th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 169th Infantry Division () was a German infantry division during World War II. History The division was formed in 1939. It took part in Operation Fall Gelb and stayed in France until being transferred to Finnish Lapland in 1941. The division was part of the German XXXVI Corps which also included SS Division Nord and the Finnish 6th Division. On 1 July the corps began its attack which was aimed at Kandalaksha on the White Sea coast. The division crossed the Finnish-Soviet Border just north of Salla. During the heavy fighting against the Soviet 122nd Division the SS Division Nord broke and fled. On 8 July the 169th occupied Salla. With the help of the Finnish 6th Division the Soviets were pushed back beyond the pre-Winter War borders. In September the division had advanced to the River Verman (''Vermanjoki''), here the offensive finally stalled. During autumn 1941 AOK Norwegen decided to shifts its attack to the area held by the Finnish 3rd Division. The 169th Divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peace Treaty on 13 March 1940. Despite superior military strength, especially in tanks and aircraft, the Soviet Union suffered severe losses and initially made little headway. The League of Nations deemed the attack illegal and expelled the Soviet Union from its organization. The Soviets made several demands, including that Finland cede substantial border territories in exchange for land elsewhere, claiming security reasonsprimarily the protection of Leningrad, from the Finnish border. When Finland refused, the Soviets invaded. Most sources conclude that the Soviet Union had intended to conquer all of Finland, and cite the establishment of the Finnish Democratic Republic, puppet Finnish Communist government and the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
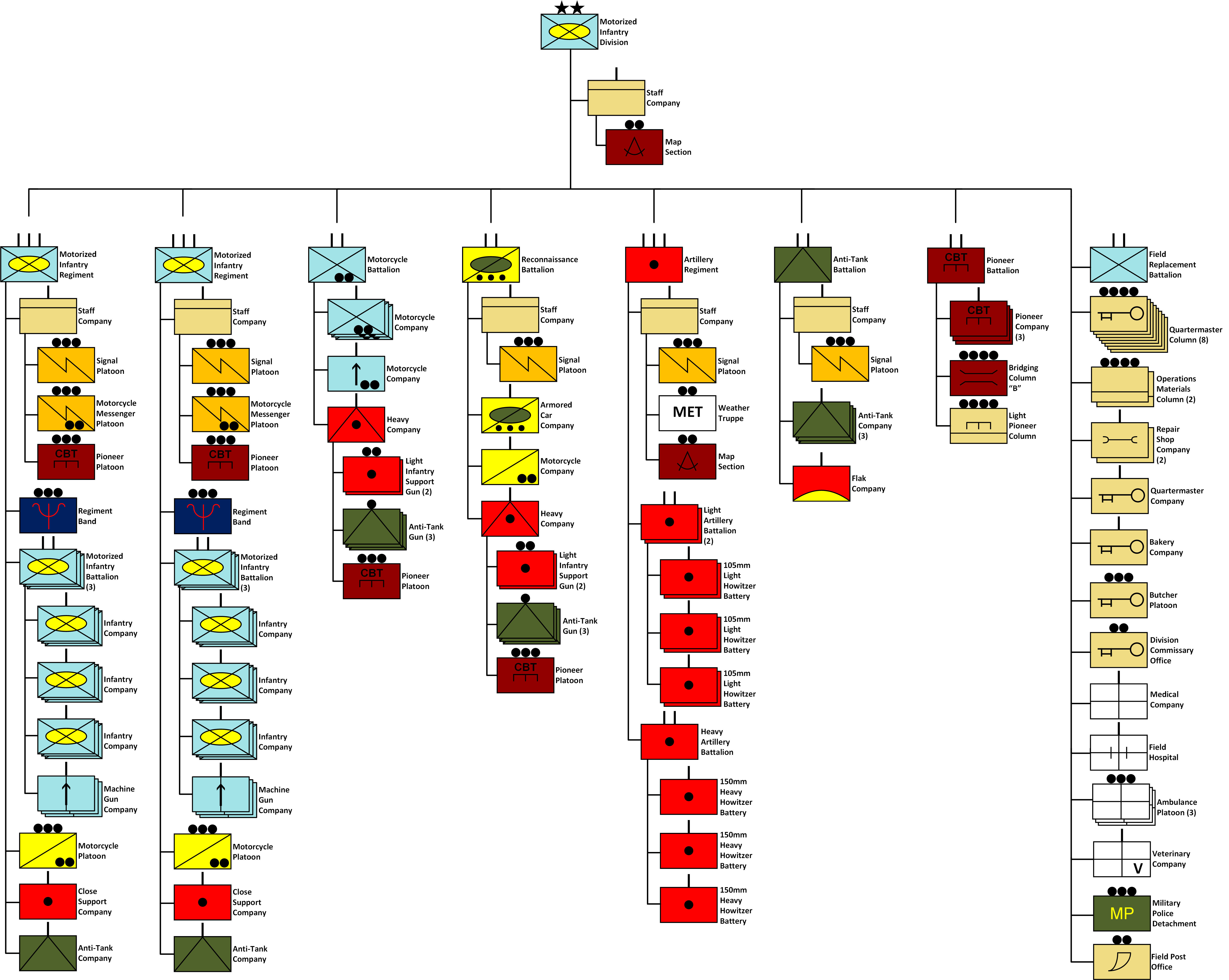
German Units In The Arctic
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) * German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term (''Reich Defence'') and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to German rearmament, rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and bellicose moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi regime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and Military budget, defence spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Divisions In World War II
This article lists Division (military), divisions of the Wehrmacht (German Armed Forces) and Waffen-SS active during World War II, including divisions of the German Army (1935–1945), Heer (army), Luftwaffe (air force), and the Kriegsmarine (navy). Upgrades and reorganizations are shown only to identify the variant names for what is notionally a single unit; other upgrades and reorganizations are deferred to the individual articles. Due to the scope of this list, pre-war changes are not shown. Most of these divisions trained in Berlin, which is also where new military technology was kept and tested. German unit designations These designations are normally not translated and used in the German form in the unit name or description. Army (Heer) Panzer divisions Numbered panzer divisions Named panzer divisions Light mechanized divisions The designation "Light" (''leichte in German'') had various meanings in the German Army of World War II. There were a series of 5 Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Unit
Military organization ( AE) or military organisation ( BE) is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer such military capability as a national defense policy may require. Formal military organization tends to use hierarchical forms (see Modern hierarchy for terminology and approximate troop strength per hierarchical unit). In some countries, paramilitary forces are included in a nation's armed forces, though not considered military. Armed forces that are not a part of military or paramilitary organizations, such as insurgent forces, often emulate military organizations, or use these structures. History The use of formalized ranks in a hierarchical structure came into widespread use with the Roman Army. The Roman Army was organized into legions, each comprising around 5000 soldiers and led by a legate. Each legion was further divided into centuries which were led by centurions. In modern times, executive control, management and administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet–Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union during World War II. It began with a Finnish declaration of war on 25 June 1941 and ended on 19 September 1944 with the Moscow Armistice. The Soviet Union and Finland had previously fought the Winter War from 1939 to 1940, which ended with the Soviet failure to conquer Finland and the Moscow Peace Treaty. Numerous reasons have been proposed for the Finnish decision to invade, with regaining territory lost during the Winter War regarded as the most common. Other justifications for the conflict include Finnish President Risto Ryti's vision of a Greater Finland and Commander-in-Chief Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim's desire to annex East Karelia. The following paragraph contains a bundle of cites for the Finnish participation in the siege of Leningrad, which is a commonly debated complex issue in the article (see talk).--> On 22 June 1941 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Radziej
__NOTOC__ Georg Radziej (7 January 1895 – 13 May 1972) was a German general during World War II. He may have been a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Awards and decorations * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 9 May 1945 as ''Generalleutnant () is the German-language variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries. Austria Generalleutnant is the second highest general officer rank in the Austrian Armed Forces (''Bundesheer''), roughly equivalent to the NATO ...'' and commander of the 169. Infanterie-DivisionFellgiebel 2000, p. 283. Notes References Citations Bibliography * * 1895 births 1972 deaths People from Pyskowice Military personnel from the Province of Silesia Lieutenant generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel of World War I Prussian Army personnel Recipients of the clasp to the Iron Cross, 1st class Recipients of the Gold German Cross Recipients of the Knight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Dittmar
Kurt Dittmar (January 5, 1891 in Magdeburg – April 26, 1959 in Stadtoldendorf) was a German general in World War II, who served as the Official Military Commentator of the German Armed Forces. Biography Dittmar entered the German Imperial Army as Officer candidate in March 1909. He was assigned to the 4th Engineer Battalion (''Magdeburgisches Pionier-Bataillon Nr.4.'') and commissioned a second lieutenant one year later. During World War I, Dittmar served with the rank of captain as a company commander and also as a temporary battalion commander. After the War, Dittmar entered the Reichswehr and continued to serve with engineers units, where he reached the rank of Colonel (''Oberst'') to the date of April 1, 1936. With the outbreak of the World War II, Dittmar served as a commander of the engineer school in Berlin-Karlshorst. He became a divisional commander in February 1941 and led the 169th Infantry Division, which was later stationed in Finland. In the summer of 1941, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Kirchheim
Heinrich Kirchheim (6 April 1882 – 14 December 1973) was a German generalleutnant who served in both World War I and World War II. He is also one of few German officers who were awarded the Pour le Mérite and the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. He also served as a deputy member on the "Court of Military Honour," a drumhead court-martial that expelled many of the officers involved in the 20 July Plot from the Army before handing them over to the People's Court. Early military career Kirchheim entered the Imperial Army as an officer candidate on 1 May 1899. He became a Leutnant with the Infanterie-Regiment Prinz Friedrich der Niederlande (2. Westfälisches) Nr. 15 in Minden on 18 October 1900. On 1 October 1904 he transferred to the Schutztruppe of German Southwest Africa, going on an eight-year tour of duty in the colony. In January 1904, the native Herero tribe of Southwest Africa rebelled against German colonial rule over the expropriation of their land and cattle. Late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Müller-Gebhard
__NOTOC__ Philipp Müller-Gebhard (15 October 1889 – 2 July 1970) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. Awards and decorations * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 3 September 1942 as ''Generalleutnant () is the German-language variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries. Austria Generalleutnant is the second highest general officer rank in the Austrian Armed Forces (''Bundesheer''), roughly equivalent to the NATO ...'' and commander of 72. Infanterie-DivisionFellgiebel 2000, p. 261. References Citations Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mueller-Gebhard, Philipp 1889 births 1970 deaths Military personnel from Heidelberg Lieutenant generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel of World War I Recipients of the clasp to the Iron Cross, 1st class Recipients of the Gold German Cross Recipients of the Knight's Cross of the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air force, air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-General, Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies, General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently grante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |