|
ĂŠtapisme
Ătapisme ( French for ''gradualism'') is the term for a strategy for independence dominant in the Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois since 1974. It is associated with the figure of Claude Morin, who convinced Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois leader RenĂŠ LĂŠvesque and eventually a majority of party delegates to adopt its principles. Proponents of the strategy are called ''ĂŠtapistes''. It advocates a step-by-step approach to achieving independence. Before 1974, the Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois programme stipulated that independence would be declared upon electing a majority of Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois Members of the National Assembly of Quebec (MNAs), under Quebec's first-past-the-post electoral system and its British parliamentary system. Under ''ĂŠtapisme'', the Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois would promise a good government first and propose a referendum on independence second. At the first referendum of 1980, ''ĂŠtapisme'' was also implemented in the referendum process, since the question asked for a mandate to negotiate sovereignty-ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pur Et Dur
Pur et dur (; a common expression in French literally meaning "pure and hard") is a term used in Quebec politics to refer to hardliners of the Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois and the Quebec independence movement. It is most commonly used in the media, where it was popularized. It is also used to criticize some members of the Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois. Some within the party resent the use of the term by the media, but some have embraced it. It is similar to the term " SNP fundamentalist", used in Scottish politics for a faction of the Scottish National Party, another pro-independence party. Many of the first "purs et durs" came from the Rassemblement pour l'indĂŠpendance nationale who, through entryism, joined the Parti QuĂŠbĂŠcois in the early days of the 1960s. They are associated with strong opinions about independence (including the need to attain it quickly, the question of an eventual supranational union, or "sovereignty-association", and the question of the "ĂŠtapisme" approach) and language pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oĂŻlâlanguages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possibilism (politics)
The Possibilists (), also called Broussists (), were a faction of the French socialist movement led by Paul Brousse. BenoĂŽt Malon and others supported the faction although they did not always fully share its inspiring principles. It originated within the "Federation of the Socialist Workers' Party of France" (''FĂŠdĂŠration du parti des travailleurs socialistes de France''), a Marxist-inspired organisation founded by Paul Lafargue, Jules Guesde and others, in Marseille, in 1879. Brousse opposed Marxist tactics and proclaimed the reformist principle of directing everyday political activity towards achieving the goals that were concretely 'possible' time by time, while maintaining that socialists should keep always ready to jump at future revolutionary opportunities.Carl Landauer, "The Origin of Socialist Reformism in France"; ''International Review of Social History'', Volume 12 , Issue 1 , April 1967, pp. 81â107. The Possibilists soon won a majority within the Federation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformist Socialism
Reformism is a political tendency advocating the reform of an existing system or institution â often a political or religious establishment â as opposed to its abolition and replacement via revolution. Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can eventually lead to fundamental changes in a society's political and economic systems. Reformism as a political tendency and hypothesis of social change grew out of opposition to revolutionary socialism, which contends that revolutionary upheaval is a necessary precondition for the structural changes necessary to transform a capitalist system into a qualitatively different socialist system. Responding to a pejorative conception of reformism as non- transformational, philosopher AndrĂŠ Gorz conceived non-reformist reform in 1987 to prioritize human needs over capitalist needs. As a political doctrine, centre-left reformism is distinguished from centre-right or prag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
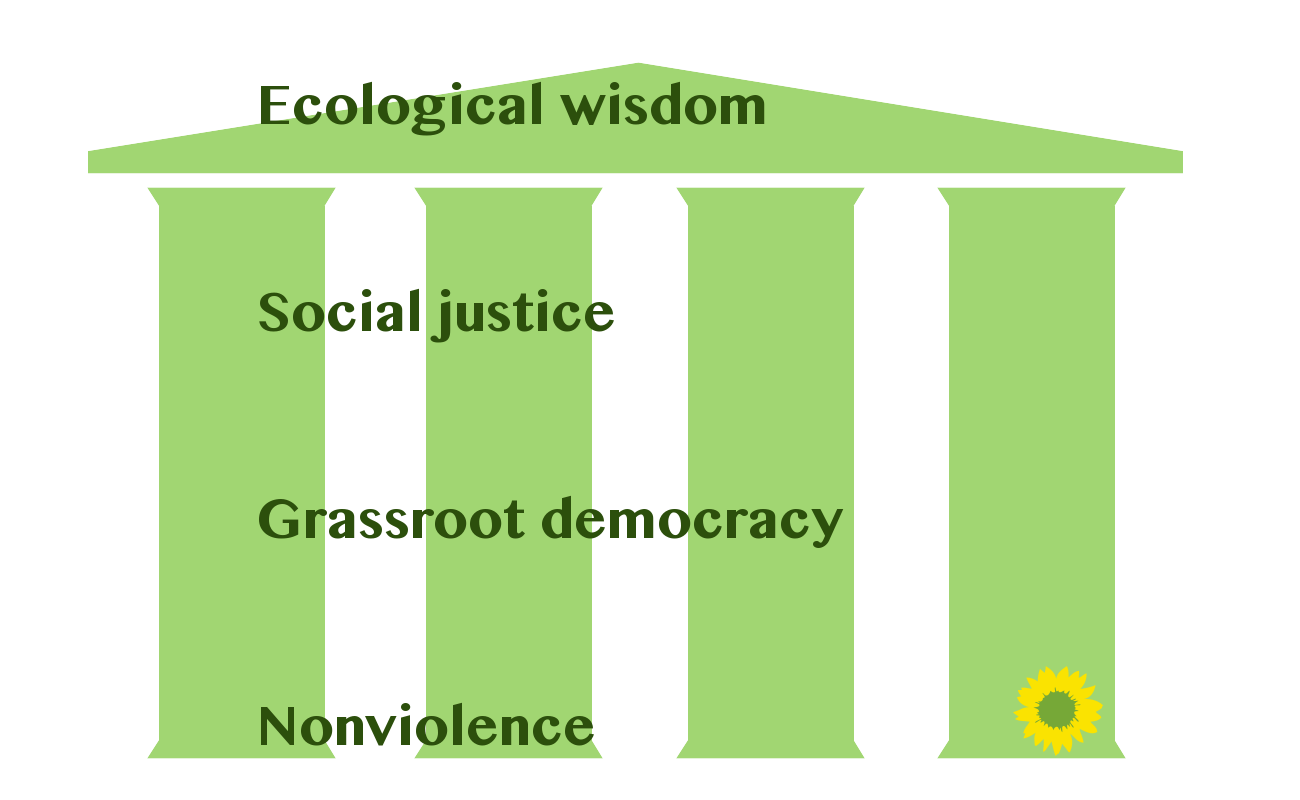
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the Western world in the 1970s; since then, green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term ''green'' was used initially in relation to ''Alliance 90/The Greens, die GrĂźnen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term ''political ecology'' is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realos
Fundis is short for fundamentalists. The term was used for a faction within the German Green Party. The faction was formed in conflict to the Realo-faction within their party. The term has also been applied to similar conflicts. General meaning The abbreviation Fundi is a label applied to members who tend towards a ''fundamentalist'' interpretation of its common ideology (e.g. 'green' values), as opposed to the more "pragmatic realism" of the Realo alternative. Other terms for green Fundis are wild greens or deep greens. They tend towards veganism, a strong animal rights approach and an aversion to traditional political methods, rejecting more centralized systems of governance. Many Fundis believe that economic growth and industrialism are the root of ecological problems, and therefore advocate for an end to modern industry, instead proposing a system of decentralized rural communities driven by post-industrial economics. German Greens In the 1980s and 1990s, a conflict betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec Sovereignty Movement
The Quebec sovereignty movement (French: ''mouvement souverainiste du QuĂŠbec'', ) is a political movement advocating for Quebec's independence from Canada. Proponents argue that Quebecers form a distinct nation with a unique culture, language, history, and set of values, and thus should exercise their right to self-determination. This principle includes the possibility of choosing between integration with a third state, political association with another state, or full independence, enabling Quebecers to establish a sovereign state with its own constitution. Supporters believe that an independent Quebec would be better positioned to promote its economic, social, environmental, and cultural development. They contend that self-governance would allow Quebec to manage its resources, such as its vast renewable natural assets and strategic geographic location, in alignment with its interests. Additionally, sovereignty would enable Quebec to establish its own fiscal policies, particip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incrementalism
:''In politics, the term "incrementalism" is also used as a synonym for Gradualism#Politics and society, Gradualism.'' Incrementalism is a method of working by adding to or subtracting from a project using many small wikt:incremental, incremental changes instead of a few (extensively planned) large jumps. Logical incrementalism implies that the steps in the process are sensible. Logical incrementalism focuses on "the Power-Behavioral Approach to planning rather than to the Formal Systems Planning Approach". In public policy, incrementalism is the method of change by which many small policy changes are enacted over time in order to create a larger broad based policy change. Political scientist Charles E. Lindblom developed this theoretical policy of rationality in the 1950s as a middle way between the rational actor model and bounded rationality, as both long term, goal-driven policy rationality and satisficing were not seen as adequate. Origin Most people use incrementalism witho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradualism
Gradualism, from the Latin ("step"), is a hypothesis, a theory or a tenet assuming that change comes about gradually or that variation is gradual in nature and happens over time as opposed to in large steps. Uniformitarianism, incrementalism, and reformism are similar concepts. Gradualism can also refer to desired, controlled change in society, institutions, or policies. For example, social democrats and democratic socialists see the socialist society as achieved through gradualism. Geology and biology In the natural sciences, gradualism is the theory which holds that profound change is the cumulative product of slow but continuous processes, often contrasted with catastrophism. The theory was proposed in 1795 by James Hutton, a Scottish geologist, and was later incorporated into Charles Lyell's theory of uniformitarianism. Tenets from both theories were applied to biology and formed the basis of early evolutionary theory. Charles Darwin was influenced by Lyell's ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNP Gradualist
The Scottish National Party (SNP; ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic party. The party holds 61 of the 129 seats in the Scottish Parliament, and holds 9 out of the 57 Scottish seats in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. It is represented by 419 of the 1,227 local councillors across Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from the United Kingdom and for Scotland's membership in the European Union, with a platform based on progressive social policies and civic nationalism. Founded in 1934 with the amalgamation of the National Party of Scotland and the Scottish Party, the party has had continuous parliamentary List of Scottish National Party MPs, representation in Westminster since Winnie Ewing won the 1967 Hamilton by-election. With the establishment of the devolved Scottish Parliament in 1999, the SNP became the second-largest party, serving two terms as the Opposition (parliamentary), opposition. The SNP gaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Parizeau
Jacques Parizeau (; August 9, 1930June 1, 2015) was a Canadian politician and economist who served as the 26th premier of Quebec from September 26, 1994, to January 29, 1996. Early life and career Parizeau was born in Montreal, Quebec, the son of Germaine ( Biron) and GĂŠrard Parizeau, from a family of wealth. GĂŠrard Parizeau built one of Quebecâs great fortunes and one of the provinceâs largest financial firms from a brokerage he established in the 1930s. Jacques' great-grandfather was a founder of the Montreal ''Chambre de Commerce'' and his grandfather was a doctor of renown and a ''Chevalier'' of the ''LĂŠgion dâhonneur.'' As a teenager, Parizeau had radical views and distributed leaflets for Communist Fred Rose (politician), Fred Rose's election campaigns. While sympathetic to the Labor-Progressive Party he never joined. His parents supported bilingualism and sent him to English summer camp. He attended Collège Stanislas (Quebec), Collège Stanislas, a Roman Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |