Visual Pollution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The visual system is the physiological basis of

 * The eye, especially the retina
* The optic nerve
* The optic chiasma
* The optic tract
* The lateral geniculate body
* The optic radiation
* The visual cortex
* The visual association cortex.
These are components of the visual pathway, also called the optic pathway, that can be divided into anterior and posterior visual pathways. The anterior visual pathway refers to structures involved in vision before the lateral geniculate nucleus. The posterior visual pathway refers to structures after this point.
* The eye, especially the retina
* The optic nerve
* The optic chiasma
* The optic tract
* The lateral geniculate body
* The optic radiation
* The visual cortex
* The visual association cortex.
These are components of the visual pathway, also called the optic pathway, that can be divided into anterior and posterior visual pathways. The anterior visual pathway refers to structures involved in vision before the lateral geniculate nucleus. The posterior visual pathway refers to structures after this point.

 The visual cortex is responsible for processing the visual image. It lies at the rear of the brain (highlighted in the image), above the cerebellum. The region that receives information directly from the LGN is called the primary visual cortex (also called V1 and striate cortex). It creates a bottom-up saliency map of the visual field to guide attention or eye gaze to salient visual locations. Hence selection of visual input information by attention starts at V1 along the visual pathway.
Visual information then flows through a cortical hierarchy. These areas include V2, V3, V4 and area V5/MT. (The exact connectivity depends on the species of the animal.) These secondary visual areas (collectively termed the extrastriate visual cortex) process a wide variety of visual primitives. Neurons in V1 and V2 respond selectively to bars of specific orientations, or combinations of bars. These are believed to support edge and corner detection. Similarly, basic information about color and motion is processed here.
Heider, et al. (2002) found that neurons involving V1, V2, and V3 can detect stereoscopic illusory contours; they found that stereoscopic stimuli subtending up to 8° can activate these neurons.
The visual cortex is responsible for processing the visual image. It lies at the rear of the brain (highlighted in the image), above the cerebellum. The region that receives information directly from the LGN is called the primary visual cortex (also called V1 and striate cortex). It creates a bottom-up saliency map of the visual field to guide attention or eye gaze to salient visual locations. Hence selection of visual input information by attention starts at V1 along the visual pathway.
Visual information then flows through a cortical hierarchy. These areas include V2, V3, V4 and area V5/MT. (The exact connectivity depends on the species of the animal.) These secondary visual areas (collectively termed the extrastriate visual cortex) process a wide variety of visual primitives. Neurons in V1 and V2 respond selectively to bars of specific orientations, or combinations of bars. These are believed to support edge and corner detection. Similarly, basic information about color and motion is processed here.
Heider, et al. (2002) found that neurons involving V1, V2, and V3 can detect stereoscopic illusory contours; they found that stereoscopic stimuli subtending up to 8° can activate these neurons.
 However, there is still much debate about the degree of specialization within these two pathways, since they are in fact heavily interconnected.
Horace Barlow proposed the '' efficient coding hypothesis'' in 1961 as a theoretical model of sensory coding in the
However, there is still much debate about the degree of specialization within these two pathways, since they are in fact heavily interconnected.
Horace Barlow proposed the '' efficient coding hypothesis'' in 1961 as a theoretical model of sensory coding in the
primary visual cortex (V1)
motivated the V1 Saliency Hypothesis that V1 creates a bottom-up saliency map to guide attention exogenously. With attentional selection as a center stage, vision is seen as composed of encoding, selection, and decoding stages. The default mode network is a network of brain regions that are active when an individual is awake and at rest. The visual system's default mode can be monitored during resting state fMRI: Fox, et al. (2005) found that
the human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks"
in which the visual system switches from resting state to attention. In the parietal lobe, the lateral and ventral intraparietal cortex are involved in visual attention and saccadic eye movements. These regions are in the intraparietal sulcus (marked in red in the adjacent image).
 Proper function of the visual system is required for sensing, processing, and understanding the surrounding environment. Difficulty in sensing, processing and understanding light input has the potential to adversely impact an individual's ability to communicate, learn and effectively complete routine tasks on a daily basis.
In children, early diagnosis and treatment of impaired visual system function is an important factor in ensuring that key social, academic and speech/language developmental milestones are met.
Cataract is clouding of the lens, which in turn affects vision. Although it may be accompanied by yellowing, clouding and yellowing can occur separately. This is typically a result of ageing, disease, or drug use.
Presbyopia is a visual condition that causes farsightedness. The eye's lens becomes too inflexible to accommodate to normal reading distance, focus tending to remain fixed at long distance.
Glaucoma is a type of blindness that begins at the edge of the visual field and progresses inward. It may result in tunnel vision. This typically involves the outer layers of the optic nerve, sometimes as a result of buildup of fluid and excessive pressure in the eye.
Scotoma is a type of blindness that produces a small blind spot in the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Homonymous hemianopia is a type of blindness that destroys one entire side of the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Quadrantanopia is a type of blindness that destroys only a part of the visual field typically caused by partial injury in the primary visual cortex. This is very similar to homonymous hemianopia, but to a lesser degree.
Prosopagnosia, or face blindness, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize faces. This disorder often arises after damage to the fusiform face area.
Visual agnosia, or visual-form agnosia, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize objects. This disorder often arises after damage to the ventral stream.
Proper function of the visual system is required for sensing, processing, and understanding the surrounding environment. Difficulty in sensing, processing and understanding light input has the potential to adversely impact an individual's ability to communicate, learn and effectively complete routine tasks on a daily basis.
In children, early diagnosis and treatment of impaired visual system function is an important factor in ensuring that key social, academic and speech/language developmental milestones are met.
Cataract is clouding of the lens, which in turn affects vision. Although it may be accompanied by yellowing, clouding and yellowing can occur separately. This is typically a result of ageing, disease, or drug use.
Presbyopia is a visual condition that causes farsightedness. The eye's lens becomes too inflexible to accommodate to normal reading distance, focus tending to remain fixed at long distance.
Glaucoma is a type of blindness that begins at the edge of the visual field and progresses inward. It may result in tunnel vision. This typically involves the outer layers of the optic nerve, sometimes as a result of buildup of fluid and excessive pressure in the eye.
Scotoma is a type of blindness that produces a small blind spot in the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Homonymous hemianopia is a type of blindness that destroys one entire side of the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Quadrantanopia is a type of blindness that destroys only a part of the visual field typically caused by partial injury in the primary visual cortex. This is very similar to homonymous hemianopia, but to a lesser degree.
Prosopagnosia, or face blindness, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize faces. This disorder often arises after damage to the fusiform face area.
Visual agnosia, or visual-form agnosia, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize objects. This disorder often arises after damage to the ventral stream.
Evolution of fan worm eyes (August 1, 2017) Phys.org
/ref> Only higher primate Old World (African)
"Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System"
– John Moran Eye Center at University of Utah
VisionScience.com
– An online resource for researchers in vision science.
Journal of Vision
– An online, open access journal of vision science.
i-Perception
– An online, open access journal of perception science.
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Visual System Sensory systems
visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ...
(the ability to detect and process light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
). The system detects, transduces and interprets information concerning light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
within the visible range to construct an image
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ...
and build a mental model of the surrounding environment. The visual system is associated with the eye and functionally divided into the optical system (including cornea and lens) and the neural system (including the retina and visual cortex).
The visual system performs a number of complex tasks based on the ''image forming'' functionality of the eye, including the formation of monocular images, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis
Binocular vision is seeing with two eyes, which increases the size of the Visual field, visual field. If the visual fields of the two eyes overlap, binocular #Depth, depth can be seen. This allows objects to be recognized more quickly, camouflage ...
and assessment of distances to ( depth perception) and between objects, motion perception, pattern recognition
Pattern recognition is the task of assigning a class to an observation based on patterns extracted from data. While similar, pattern recognition (PR) is not to be confused with pattern machines (PM) which may possess PR capabilities but their p ...
, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and colour vision. Together, these facilitate higher order tasks, such as object identification. The neuropsychological side of visual information processing is known as visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ...
, an abnormality of which is called visual impairment, and a complete absence of which is called blindness. The visual system also has several non-image forming visual functions, independent of visual perception, including the pupillary light reflex and circadian photoentrainment.
This article describes the human visual system, which is representative of mammalian vision, and to a lesser extent the vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
visual system.
System overview


Optical
Together, the cornea and lens refract light into a small image and shine it on the retina. The retina transduces this image into electrical pulses using rods and cones. The optic nerve then carries these pulses through the optic canal. Upon reaching the optic chiasm the nerve fibers decussate (left becomes right). The fibers then branch and terminate in three places.Neural
Most of the optic nerve fibers end in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). Before the LGN forwards the pulses to V1 of the visual cortex (primary) it gauges the range of objects and tags every major object with a velocity tag. These tags predict object movement. The LGN also sends some fibers to V2 and V3. V1 performs edge-detection to understand spatial organization (initially, 40 milliseconds in, focusing on even small spatial and color changes. Then, 100 milliseconds in, upon receiving the translated LGN, V2, and V3 info, also begins focusing on global organization). V1 also creates a bottom-up saliency map to guide attention or gaze shift. V2 both forwards (direct and via pulvinar) pulses to V1 and receives them. Pulvinar is responsible for saccade and visual attention. V2 serves much the same function as V1, however, it also handles illusory contours, determining depth by comparing left and right pulses (2D images), and foreground distinguishment. V2 connects to V1 - V5. V3 helps process ' global motion' (direction and speed) of objects. V3 connects to V1 (weak), V2, and the inferior temporal cortex. V4 recognizes simple shapes, and gets input from V1 (strong), V2, V3, LGN, and pulvinar. V5's outputs include V4 and its surrounding area, and eye-movement motor cortices ( frontal eye-field and lateral intraparietal area). V5's functionality is similar to that of the other V's, however, it integrates local object motion into global motion on a complex level. V6 works in conjunction with V5 on motion analysis. V5 analyzes self-motion, whereas V6 analyzes motion of objects relative to the background. V6's primary input is V1, with V5 additions. V6 houses the topographical map for vision. V6 outputs to the region directly around it (V6A). V6A has direct connections to arm-moving cortices, including the premotor cortex. The inferior temporal gyrus recognizes complex shapes, objects, and faces or, in conjunction with thehippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
, creates new memories. The pretectal area is seven unique nuclei. Anterior, posterior and medial pretectal nuclei inhibit pain (indirectly), aid in REM, and aid the accommodation reflex, respectively. The Edinger-Westphal nucleus moderates pupil dilation and aids (since it provides parasympathetic fibers) in convergence of the eyes and lens adjustment. Nuclei of the optic tract are involved in smooth pursuit eye movement and the accommodation reflex, as well as REM.
The suprachiasmatic nucleus is the region of the hypothalamus that halts production of melatonin (indirectly) at first light.
Structure
Eye
Light entering the eye is refracted as it passes through the cornea. It then passes through the pupil (controlled by the iris) and is further refracted by the lens. The cornea and lens act together as a compound lens to project an inverted image onto the retina.
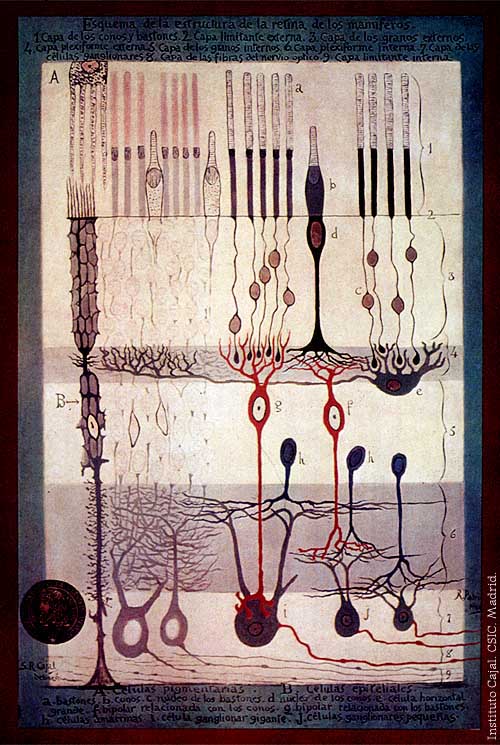
Retina
The retina consists of many photoreceptor cells which contain particularprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s called opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most pro ...
s. In humans, two types of opsins are involved in conscious vision: rod opsins and cone opsins. (A third type, melanopsin in some retinal ganglion cells (RGC), part of the body clock mechanism, is probably not involved in conscious vision, as these RGC do not project to the lateral geniculate nucleus but to the pretectal olivary nucleus.) An opsin absorbs a photon (a particle of light) and transmits a signal to the cell through a signal transduction pathway, resulting in hyper-polarization of the photoreceptor.
Rods and cones differ in function. Rods are found primarily in the periphery of the retina and are used to see at low levels of light. Each human eye contains 120 million rods. Cones are found primarily in the center (or fovea) of the retina. There are three types of cones that differ in the wavelengths of light they absorb; they are usually called short or blue, middle or green, and long or red. Cones mediate day vision and can distinguish color
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though co ...
and other features of the visual world at medium and high light levels. Cones are larger and much less numerous than rods (there are 6-7 million of them in each human eye).
In the retina, the photoreceptors synapse directly onto bipolar cells, which in turn synapse onto ganglion cells of the outermost layer, which then conduct action potentials to the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
. A significant amount of visual processing arises from the patterns of communication between neurons in the retina. About 130 million photo-receptors absorb light, yet roughly 1.2 million axons of ganglion cells transmit information from the retina to the brain. The processing in the retina includes the formation of center-surround receptive fields of bipolar and ganglion cells in the retina, as well as convergence and divergence from photoreceptor to bipolar cell. In addition, other neurons in the retina, particularly horizontal and amacrine cells, transmit information laterally (from a neuron in one layer to an adjacent neuron in the same layer), resulting in more complex receptive fields that can be either indifferent to color and sensitive to motion
In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and frame of reference to an o ...
or sensitive to color and indifferent to motion.
= Mechanism of generating visual signals
= The retina adapts to change in light through the use of the rods. In the dark, the chromophore retinal has a bent shape called cis-retinal (referring to a ''cis'' conformation in one of the double bonds). When light interacts with the retinal, it changes conformation to a straight form called trans-retinal and breaks away from the opsin. This is called bleaching because the purified rhodopsin changes from violet to colorless in the light. At baseline in the dark, the rhodopsin absorbs no light and releasesglutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
, which inhibits the bipolar cell. This inhibits the release of neurotransmitters from the bipolar cells to the ganglion cell. When there is light present, glutamate secretion ceases, thus no longer inhibiting the bipolar cell from releasing neurotransmitters to the ganglion cell and therefore an image can be detected.
The final result of all this processing is five different populations of ganglion cells that send visual (image-forming and non-image-forming) information to the brain:
#M cells, with large center-surround receptive fields that are sensitive to depth, indifferent to color, and rapidly adapt to a stimulus;
#P cells, with smaller center-surround receptive fields that are sensitive to color and shape
A shape is a graphics, graphical representation of an object's form or its external boundary, outline, or external Surface (mathematics), surface. It is distinct from other object properties, such as color, Surface texture, texture, or material ...
;
#K cells, with very large center-only receptive fields that are sensitive to color and indifferent to shape or depth;
# another population that is intrinsically photosensitive; and
#a final population that is used for eye movements.
A 2006 University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f ...
study calculated the approximate bandwidth of human retinas to be about 8,960 kilobits per second, whereas guinea pig retinas transfer at about 875 kilobits.
In 2007 Zaidi and co-researchers on both sides of the Atlantic studying patients without rods and cones, discovered that the novel photoreceptive ganglion cell in humans also has a role in conscious and unconscious visual perception. The peak spectral sensitivity was 481 nm. This shows that there are two pathways for vision in the retina – one based on classic photoreceptors (rods and cones) and the other, newly discovered, based on photo-receptive ganglion cells which act as rudimentary visual brightness detectors.
Photochemistry
The functioning of a camera is often compared with the workings of the eye, mostly since both focus light from external objects in the field of view onto a light-sensitive medium. In the case of the camera, this medium is film or an electronic sensor; in the case of the eye, it is an array of visual receptors. With this simple geometrical similarity, based on the laws of optics, the eye functions as a transducer, as does a CCD camera. In the visual system, retinal, technically called ''retinene
The retinenes (retinene1 and retinene2) are derivative (chemistry), chemical derivatives of vitamin A (see retinol) formed through oxidation reactions.
Retinene1 is better known as retinal and is fundamental in the transduction of light into visua ...
''1 or "retinaldehyde", is a light-sensitive molecule found in the rods and cones of the retina. Retinal is the fundamental structure involved in the transduction of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
into visual signals, i.e. nerve impulses in the ocular system of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. In the presence of light, the retinal molecule changes configuration and as a result, a nerve impulse is generated.
Optic nerve
The information about the image via the eye is transmitted to the brain along the optic nerve. Different populations of ganglion cells in the retina send information to the brain through the optic nerve. About 90% of the axons in the optic nerve go to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus. These axons originate from the M, P, and K ganglion cells in the retina, see above. This parallel processing is important for reconstructing the visual world; each type of information will go through a different route toperception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
. Another population sends information to the superior colliculus in the midbrain, which assists in controlling eye movements ( saccades) as well as other motor responses.
A final population of photosensitive ganglion cells, containing melanopsin for photosensitivity, sends information via the retinohypothalamic tract to the pretectum ( pupillary reflex), to several structures involved in the control of circadian rhythms and sleep such as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (the biological clock), and to the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (a region involved in sleep regulation). A recently discovered role for photoreceptive ganglion cells is that they mediate conscious and unconscious vision – acting as rudimentary visual brightness detectors as shown in rodless coneless eyes.
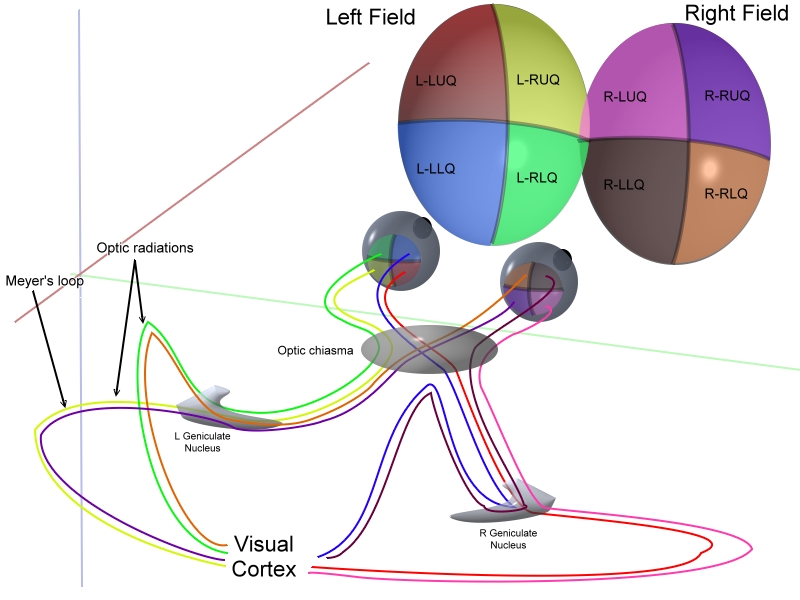
Optic chiasm
The optic nerves from both eyes meet and cross at the optic chiasm, at the base of the hypothalamus of the brain. At this point, the information coming from both eyes is combined and then splits according to the visual field. The corresponding halves of the field of view (right and left) are sent to the left and right halves of the brain, respectively, to be processed. That is, the right side of primary visual cortex deals with the left half of the ''field of view'' from both eyes, and similarly for the left brain. A small region in the center of the field of view is processed redundantly by both halves of the brain.Optic tract
Information from the right ''visual field'' (now on the left side of the brain) travels in the left optic tract. Information from the left ''visual field'' travels in the right optic tract. Each optic tract terminates in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) in the thalamus.
Lateral geniculate nucleus
: The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is a sensory relay nucleus in the thalamus of the brain. The LGN consists of six layers inhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s and other primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s starting from catarrhines, including cercopithecidae and apes. Layers 1, 4, and 6 correspond to information from the contralateral (crossed) fibers of the nasal retina (temporal visual field); layers 2, 3, and 5 correspond to information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
from the ipsilateral (uncrossed) fibers of the temporal retina (nasal visual field).
Layer one contains M cells, which correspond to the M ( magnocellular) cells of the optic nerve of the opposite eye and are concerned with depth or motion. Layers four and six of the LGN also connect to the opposite eye, but to the P cells (color and edges) of the optic nerve. By contrast, layers two, three and five of the LGN connect to the M cells and P ( parvocellular) cells of the optic nerve for the same side of the brain as its respective LGN.
Spread out, the six layers of the LGN are the area of a credit card and about three times its thickness. The LGN is rolled up into two ellipsoids about the size and shape of two small birds' eggs. In between the six layers are smaller cells that receive information from the K cells (color) in the retina. The neurons of the LGN then relay the visual image to the primary visual cortex (V1) which is located at the back of the brain ( posterior end) in the occipital lobe in and close to the calcarine sulcus. The LGN is not just a simple relay station, but it is also a center for processing; it receives reciprocal input from the cortical and subcortical layers and reciprocal innervation
René Descartes (1596–1650) was one of the first to conceive a model of reciprocal innervation (in 1626) as the principle that provides for the control of agonist and antagonist muscles. Reciprocal innervation describes skeletal muscles as ...
from the visual cortex.

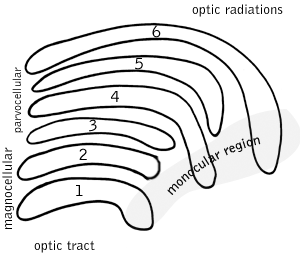
Optic radiation
The optic radiations, one on each side of the brain, carry information from the thalamic lateral geniculate nucleus to layer 4 of the visual cortex. The P layer neurons of the LGN relay to V1 layer 4C β. The M layer neurons relay to V1 layer 4C α. The K layer neurons in the LGN relay to large neurons called blobs in layers 2 and 3 of V1. There is a direct correspondence from an angular position in the visual field of the eye, all the way through the optic tract to a nerve position in V1 up to V4, i.e. the primary visual areas. After that, the visual pathway is roughly separated into a ventral and dorsal pathway.Visual cortex
 The visual cortex is responsible for processing the visual image. It lies at the rear of the brain (highlighted in the image), above the cerebellum. The region that receives information directly from the LGN is called the primary visual cortex (also called V1 and striate cortex). It creates a bottom-up saliency map of the visual field to guide attention or eye gaze to salient visual locations. Hence selection of visual input information by attention starts at V1 along the visual pathway.
Visual information then flows through a cortical hierarchy. These areas include V2, V3, V4 and area V5/MT. (The exact connectivity depends on the species of the animal.) These secondary visual areas (collectively termed the extrastriate visual cortex) process a wide variety of visual primitives. Neurons in V1 and V2 respond selectively to bars of specific orientations, or combinations of bars. These are believed to support edge and corner detection. Similarly, basic information about color and motion is processed here.
Heider, et al. (2002) found that neurons involving V1, V2, and V3 can detect stereoscopic illusory contours; they found that stereoscopic stimuli subtending up to 8° can activate these neurons.
The visual cortex is responsible for processing the visual image. It lies at the rear of the brain (highlighted in the image), above the cerebellum. The region that receives information directly from the LGN is called the primary visual cortex (also called V1 and striate cortex). It creates a bottom-up saliency map of the visual field to guide attention or eye gaze to salient visual locations. Hence selection of visual input information by attention starts at V1 along the visual pathway.
Visual information then flows through a cortical hierarchy. These areas include V2, V3, V4 and area V5/MT. (The exact connectivity depends on the species of the animal.) These secondary visual areas (collectively termed the extrastriate visual cortex) process a wide variety of visual primitives. Neurons in V1 and V2 respond selectively to bars of specific orientations, or combinations of bars. These are believed to support edge and corner detection. Similarly, basic information about color and motion is processed here.
Heider, et al. (2002) found that neurons involving V1, V2, and V3 can detect stereoscopic illusory contours; they found that stereoscopic stimuli subtending up to 8° can activate these neurons.
Visual association cortex
As visual information passes forward through the visual hierarchy, the complexity of the neural representations increases. Whereas a V1 neuron may respond selectively to a line segment of a particular orientation in a particular retinotopic location, neurons in the lateral occipital complex respond selectively to a complete object (e.g., a figure drawing), and neurons in the visual association cortex may respond selectively to human faces, or to a particular object. Along with this increasing complexity of neural representation may come a level of specialization of processing into two distinct pathways: the dorsal stream and the ventral stream (the Two Streams hypothesis, first proposed by Ungerleider and Mishkin in 1982). The dorsal stream, commonly referred to as the "where" stream, is involved in spatial attention (covert and overt), and communicates with regions that control eye movements and hand movements. More recently, this area has been called the "how" stream to emphasize its role in guiding behaviors to spatial locations. The ventral stream, commonly referred to as the "what" stream, is involved in the recognition, identification and categorization of visual stimuli.brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
. Limitations in the applicability of this theory in thprimary visual cortex (V1)
motivated the V1 Saliency Hypothesis that V1 creates a bottom-up saliency map to guide attention exogenously. With attentional selection as a center stage, vision is seen as composed of encoding, selection, and decoding stages. The default mode network is a network of brain regions that are active when an individual is awake and at rest. The visual system's default mode can be monitored during resting state fMRI: Fox, et al. (2005) found that
the human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks"
in which the visual system switches from resting state to attention. In the parietal lobe, the lateral and ventral intraparietal cortex are involved in visual attention and saccadic eye movements. These regions are in the intraparietal sulcus (marked in red in the adjacent image).
Development
Infancy
Newborn infants have limited color perception. One study found that 74% of newborns can distinguish red, 36% green, 25% yellow, and 14% blue. After one month, performance "improved somewhat." Infant's eyes do not have the ability to accommodate. Pediatricians are able to perform non-verbal testing to assess visual acuity of a newborn, detect nearsightedness and astigmatism, and evaluate the eye teaming and alignment. Visual acuity improves from about 20/400 at birth to approximately 20/25 at 6 months of age. This happens because the nerve cells in the retina and brain that control vision are not fully developed.Childhood and adolescence
Depth perception, focus, tracking and other aspects of vision continue to develop throughout early and middle childhood. From recent studies in theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
there is some evidence that the amount of time school aged children spend outdoors, in natural light, may have some impact on whether they develop myopia. The condition tends to get somewhat worse through childhood and adolescence, but stabilizes in adulthood. More prominent myopia (nearsightedness) and astigmatism are thought to be inherited. Children with this condition may need to wear glasses.
Adulthood
Vision is often one of the first senses affected by aging. A number of changes occur with aging: * Over time, the lens becomes yellowed and may eventually become brown, a condition known as brunescence or brunescent cataract. Although many factors contribute to yellowing, lifetime exposure to ultraviolet light and aging are two main causes. * The lens becomes less flexible, diminishing the ability to accommodate ( presbyopia). * While a healthy adult pupil typically has a size range of 2–8 mm, with age the range gets smaller, trending towards a moderately small diameter. * On average tear production declines with age. However, there are a number of age-related conditions that can cause excessive tearing.Other functions
Balance
Along withproprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position.
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of propri ...
and vestibular function, the visual system plays an important role in the ability of an individual to control balance and maintain an upright posture. When these three conditions are isolated and balance is tested, it has been found that vision is the most significant contributor to balance, playing a bigger role than either of the two other intrinsic mechanisms. The clarity with which an individual can see his environment, as well as the size of the visual field, the susceptibility of the individual to light and glare, and poor depth perception play important roles in providing a feedback loop to the brain on the body's movement through the environment. Anything that affects any of these variables can have a negative effect on balance and maintaining posture. This effect has been seen in research involving elderly subjects when compared to young controls, in glaucoma patients compared to age matched controls, cataract patients pre and post surgery, and even something as simple as wearing safety goggles. Monocular vision (one eyed vision) has also been shown to negatively impact balance, which was seen in the previously referenced cataract and glaucoma studies, as well as in healthy children and adults.
According to Pollock et al. (2010) stroke is the main cause of specific visual impairment, most frequently visual field loss ( homonymous hemianopia, a visual field defect). Nevertheless, evidence for the efficacy of cost-effective interventions aimed at these visual field defects is still inconsistent.
Clinical significance
 Proper function of the visual system is required for sensing, processing, and understanding the surrounding environment. Difficulty in sensing, processing and understanding light input has the potential to adversely impact an individual's ability to communicate, learn and effectively complete routine tasks on a daily basis.
In children, early diagnosis and treatment of impaired visual system function is an important factor in ensuring that key social, academic and speech/language developmental milestones are met.
Cataract is clouding of the lens, which in turn affects vision. Although it may be accompanied by yellowing, clouding and yellowing can occur separately. This is typically a result of ageing, disease, or drug use.
Presbyopia is a visual condition that causes farsightedness. The eye's lens becomes too inflexible to accommodate to normal reading distance, focus tending to remain fixed at long distance.
Glaucoma is a type of blindness that begins at the edge of the visual field and progresses inward. It may result in tunnel vision. This typically involves the outer layers of the optic nerve, sometimes as a result of buildup of fluid and excessive pressure in the eye.
Scotoma is a type of blindness that produces a small blind spot in the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Homonymous hemianopia is a type of blindness that destroys one entire side of the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Quadrantanopia is a type of blindness that destroys only a part of the visual field typically caused by partial injury in the primary visual cortex. This is very similar to homonymous hemianopia, but to a lesser degree.
Prosopagnosia, or face blindness, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize faces. This disorder often arises after damage to the fusiform face area.
Visual agnosia, or visual-form agnosia, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize objects. This disorder often arises after damage to the ventral stream.
Proper function of the visual system is required for sensing, processing, and understanding the surrounding environment. Difficulty in sensing, processing and understanding light input has the potential to adversely impact an individual's ability to communicate, learn and effectively complete routine tasks on a daily basis.
In children, early diagnosis and treatment of impaired visual system function is an important factor in ensuring that key social, academic and speech/language developmental milestones are met.
Cataract is clouding of the lens, which in turn affects vision. Although it may be accompanied by yellowing, clouding and yellowing can occur separately. This is typically a result of ageing, disease, or drug use.
Presbyopia is a visual condition that causes farsightedness. The eye's lens becomes too inflexible to accommodate to normal reading distance, focus tending to remain fixed at long distance.
Glaucoma is a type of blindness that begins at the edge of the visual field and progresses inward. It may result in tunnel vision. This typically involves the outer layers of the optic nerve, sometimes as a result of buildup of fluid and excessive pressure in the eye.
Scotoma is a type of blindness that produces a small blind spot in the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Homonymous hemianopia is a type of blindness that destroys one entire side of the visual field typically caused by injury in the primary visual cortex.
Quadrantanopia is a type of blindness that destroys only a part of the visual field typically caused by partial injury in the primary visual cortex. This is very similar to homonymous hemianopia, but to a lesser degree.
Prosopagnosia, or face blindness, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize faces. This disorder often arises after damage to the fusiform face area.
Visual agnosia, or visual-form agnosia, is a brain disorder that produces an inability to recognize objects. This disorder often arises after damage to the ventral stream.
Other animals
Differentspecies
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
are able to see different parts of the light spectrum; for example, bees can see into the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
, while pit vipers can accurately target prey with their pit organs, which are sensitive to infrared radiation. The mantis shrimp possesses arguably the most complex visual system of any species. The eye of the mantis shrimp holds 16 color receptive cones, whereas humans only have three. The variety of cones enables them to perceive an enhanced array of colors as a mechanism for mate selection, avoidance of predators, and detection of prey. Swordfish also possess an impressive visual system. The eye of a swordfish can generate heat to better cope with detecting their prey at depths of 2000 feet. Certain one-celled microorganisms, the warnowiid dinoflagellates have eye-like ocelloids, with analogous structures for the lens and retina of the multi-cellular eye. The armored shell of the chiton '' Acanthopleura granulata'' is also covered with hundreds of aragonite crystalline eyes, named ocelli, which can form image
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ...
s.
Many fan worms, such as '' Acromegalomma interruptum'' which live in tubes on the sea floor of the Great Barrier Reef, have evolved compound eyes on their tentacles, which they use to detect encroaching movement. If movement is detected, the fan worms will rapidly withdraw their tentacles. Bok, et al., have discovered opsins and G proteins in the fan worm's eyes, which were previously only seen in simple ciliary photoreceptors in the brains of some invertebrates, as opposed to the rhabdomeric receptors in the eyes of most invertebrates. cited bEvolution of fan worm eyes (August 1, 2017) Phys.org
/ref> Only higher primate Old World (African)
monkeys
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes. Thus monkeys, in that sense, co ...
and apes ( macaques, apes, orangutans) have the same kind of three-cone photoreceptor color vision humans have, while lower primate New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
(South American) monkeys ( spider monkeys, squirrel monkeys, cebus monkeys) have a two-cone photoreceptor kind of color vision.
Biologists have determined that humans have extremely good vision compared to the overwhelming majority of animals, particularly in daylight, surpassed only by a few large species of predatory birds. Other animals such as dogs are thought to rely more on senses other than vision, which in turn may be better developed than in humans.
History
In the second half of the 19th century, many motifs of the nervous system were identified such as the neuron doctrine and brain localization, which related to the neuron being the basic unit of the nervous system and functional localisation in the brain, respectively. These would become tenets of the fledgling neuroscience and would support further understanding of the visual system. The notion that the cerebral cortex is divided into functionally distinct cortices now known to be responsible for capacities such as touch ( somatosensory cortex), movement ( motor cortex), and vision ( visual cortex), was first proposed by Franz Joseph Gall in 1810. Evidence for functionally distinct areas of the brain (and, specifically, of the cerebral cortex) mounted throughout the 19th century with discoveries by Paul Broca of the language center (1861), and Gustav Fritsch and Eduard Hitzig of the motor cortex (1871). Based on selective damage to parts of the brain and the functional effects of the resulting lesions, David Ferrier proposed that visual function was localized to the parietal lobe of the brain in 1876. In 1881, Hermann Munk more accurately located vision in the occipital lobe, where the primary visual cortex is now known to be. In 2014, a textbook "Understanding vision: theory, models, and data" illustrates how to link neurobiological data and visual behavior/psychological data through theoretical principles and computational models.See also
References
Further reading
* * * Heiting, G., (2011). Your infant's vision Development. Retrieved February 27, 2012 from http://www.allaboutvision.com/parents/infants.htm * * * * . (H.D. Steklis and J. Erwin, editors.) pp. 203–278. * * The Aging Eye; See into Your future. (2009). Retrieved February 27, 2012 from https://web.archive.org/web/20111117045917/http://www.realage.com/check-your-health/eye-health/aging-eye * * * .External links
"Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System"
– John Moran Eye Center at University of Utah
VisionScience.com
– An online resource for researchers in vision science.
Journal of Vision
– An online, open access journal of vision science.
i-Perception
– An online, open access journal of perception science.
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Visual System Sensory systems