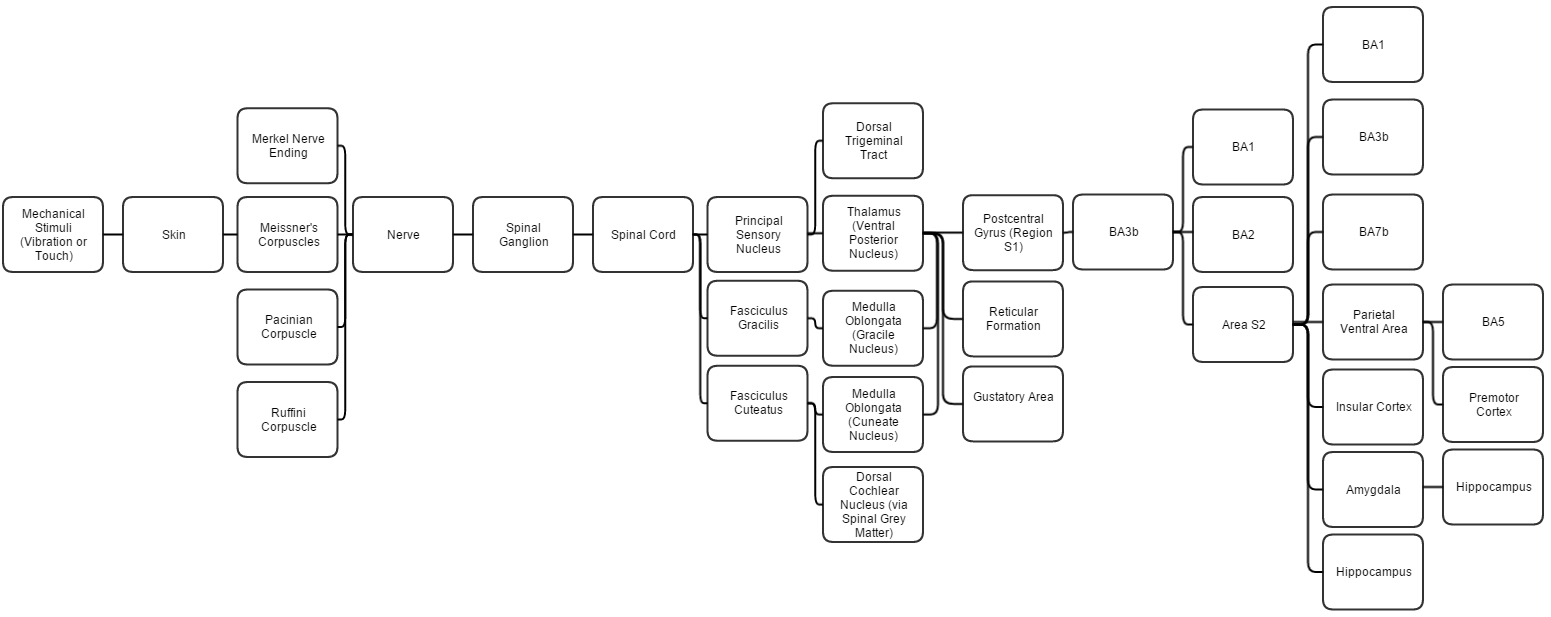
|
Touch
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of body position and balance ( proprioception). It is believed to act as a pathway between the different sensory modalities within the body. As of 2024 debate continued on the underlying mechanisms, correctness and validity of the somatosensory system model, and whether it impacts emotions in the body. The somatosensory system has been thought of as having two subdivisions; *one for the detection of mechanosensory information related to touch. Mechanosensory information includes that of light touch, vibration, pressure and tension in the skin. Much of this information belongs to the sense of touch which is a general somatic sense in contrast to the special senses of sight, smell, taste, hearing, and balance. * one for the nociception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Somatosensory Cortex
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of body position and balance (proprioception). It is believed to act as a pathway between the different sensory modalities within the body. As of 2024 debate continued on the underlying mechanisms, correctness and validity of the somatosensory system model, and whether it impacts emotions in the body. The somatosensory system has been thought of as having two subdivisions; *one for the detection of mechanosensory information related to touch. Mechanosensory information includes that of light touch, vibration, pressure and tension in the skin. Much of this information belongs to the sense of touch which is a general somatic sense in contrast to the special senses of sight, smell, taste, hearing, and balance. * one for the nociception detect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trigeminal Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (literal translation, lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for Sense, sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name (''trigeminal'', ) derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V), the maxillary nerve (V), and the mandibular nerve (V). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that Autonomic nervous system, autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve derives from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic pons, and the sensory division originates in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium, multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of Epithelium#Cell types, columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the Sole (foot), sole of the foot with most being roughly 90μm. Thickness does not vary between the sexes but becomes thinner with age. The human epidermis is an example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tactile Corpuscle
Tactile corpuscles or Meissner's corpuscles are a type of mechanoreceptor discovered by anatomist Georg Meissner (1829–1905) and Rudolf Wagner. This corpuscle is a type of nerve ending in the skin that is responsible for sensitivity to pressure. In particular, they have their highest sensitivity (lowest threshold) when sensing vibrations between 10 and 50 hertz. They are rapidly adaptive receptors. They are most concentrated in thick hairless skin, especially at the finger pads. Structure Tactile corpuscles are encapsulated myelinated nerve endings, surrounded by Schwann cells. The encapsulation consists of flattened supportive cells arranged as horizontal lamellae surrounded by a connective tissue capsule. The corpuscle is 30–140 μm in length and 40–60 μm in diameter. A single nerve fiber meanders between the lamellae and throughout the corpuscle. Location They are distributed on various areas of the skin, but concentrated in areas especially sensitive to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Special Senses
In medicine and anatomy, the special senses are the senses that have specialized organs devoted to them: * vision (the eye) * hearing and balance (the ear, which includes the auditory system and vestibular system) * smell (the nose) * taste (the tongue) The distinction between special and general senses is used to classify nerve fibers running to and from the central nervous system – information from special senses is carried in special somatic afferents and special visceral afferents. In contrast, the other sense, touch, is a somatic sense which does not have a specialized organ but comes from all over the body, most noticeably the skin but also the internal organs (viscera). Touch includes mechanoreception (pressure, vibration and proprioception), pain (nociception) and heat (thermoception), and such information is carried in general somatic afferents and general visceral afferents. Vision Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glabrous Skin
Glabrousness () is the technical term for a lack of hair, down hair, down, setae, trichomes, or other such covering. A glabrous surface may be a natural characteristic of all or part of a plant or animal, or be due to loss because of a physical condition, such as alopecia universalis in humans, which causes hair to fall out or not regrow. In botany Glabrousness or otherwise, of leaves, stems, and fruit is a feature commonly mentioned in plant Identification key, keys; in botany and mycology, a ''glabrous'' morphology (biology), morphological feature is one that is smooth and may be glossy. It has no bristles or hair-like structures such as trichomes. In anything like the zoological sense, no plants or fungi have hair or wool, although some structures may resemble such materials. The term "glabrous" strictly applies only to features that lack trichomes at all times. When an organ bears trichomes at first, but loses them with age, the term used is ''glabrescent''. In the model p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cutaneous Receptor
A cutaneous receptor is a sensory receptor found in the skin that provides information about temperature, touch (including vibration and pain), spatial orientation,pressure (stretching or squeezing), and metabolic circumstances (including those induced by external chemical substances). The main four types of cutaneous receptors are tactile corpuscles, bulbous corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, and Merkel nerve endings, although the latter do not qualify as sensory corpuscles in the narrow sense. Types The sensory receptors in the skin are: *Mechanoreceptors **Bulbous corpuscles (skin stretch) ** Bulboid corpuscles (Cold) **Tactile corpuscles (changes in texture, slow vibrations) ** Pacinian corpuscles (deep pressure, fast vibrations) ** Merkel nerve endings (sustained touch and pressure) ** Free nerve endings *thermoreceptor * nociceptors *chemoreceptors Modalities With the above-mentioned receptor types the skin can sense the modalities touch, pressure, vibration, temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sensory Nervous System
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sense, sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception and interoception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for Vision (sense), vision, Auditory system, hearing, somatic sensation, touch, taste, olfaction, smell, Vestibular system, balance and visceral sensation. Sense organs are transducers that convert data from the outer physical world to the realm of the mind where people interpret the information, creating their perception of the world around them. The receptive field is the area of the body or environment to which a receptor organ and receptor cells respond. For instance, the part of the world an eye can see, is its receptive field; the light that each Rod cell, rod or Cone cell, cone can see, is its receptive field. Receptive fields have been ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different things which can interfere with a normal sense of smell, including damage to the nose or smell receptors, anosmia, upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of Eleanor Gamble, published in 1898, which compared olfactory to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tactile Signing
Tactile signing is a common means of communication used by people with deafblindness. It is based on a sign language or another system of manual communication. "Tactile signing" refers to the mode or medium, i.e. signing (using some form of signed language or code), using ''touch''. It does not indicate whether the signer is using a tactile form of a natural language (e.g. American Sign Language), a modified form of such a visual sign language, a modified form of a manually coded language, or something else. Kinds Until the 1970s, most people who were deaf and blind lived lives of isolation. As professionals became aware of this population, attempts were made to serve deafblind people by creating manual alphabets or modifying sign languages used by deaf-sighted people. See for example Helen Keller National Center, LightHouse for the Blind and Visually Impaired and Alabama Institute for the Deaf and Blind. Several methods of deafblind communication have been developed, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |