Money on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as
 The use of barter-like methods may date back to at least 100,000 years ago, though there is no evidence of a society or economy that relied primarily on barter. Instead, non-monetary societies operated largely along the principles of gift economy and
The use of barter-like methods may date back to at least 100,000 years ago, though there is no evidence of a society or economy that relied primarily on barter. Instead, non-monetary societies operated largely along the principles of gift economy and 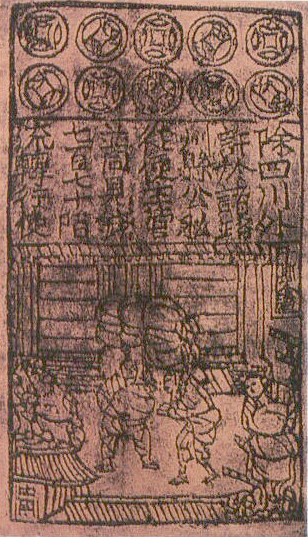 The system of commodity money eventually evolved into a system of representative money. This occurred because gold and silver merchants or banks would issue receipts to their depositors, redeemable for the commodity money deposited. Eventually, these receipts became generally accepted as a means of payment and were used as money. Paper money or banknotes were first used in China during the
The system of commodity money eventually evolved into a system of representative money. This occurred because gold and silver merchants or banks would issue receipts to their depositors, redeemable for the commodity money deposited. Eventually, these receipts became generally accepted as a means of payment and were used as money. Paper money or banknotes were first used in China during the
 In economics, money is any
In economics, money is any
 Many items have been used as commodity money such as naturally scarce
Many items have been used as commodity money such as naturally scarce
 Fiat money or fiat currency is money whose value is not derived from any intrinsic value or guarantee that it can be converted into a valuable commodity (such as gold). Instead, it has value only by government order (fiat). Usually, the government declares the fiat currency (typically notes and coins from a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve System in the U.S.) to be legal tender, making it unlawful not to accept the fiat currency as a means of repayment for all debts, public and private.Black, Henry Campbell (1910). ''A Law Dictionary Containing Definitions Of The Terms And Phrases Of American And English Jurisprudence, Ancient And Modern'', p. 494. West Publishing Co. Black's Law Dictionary defines the word "fiat" to mean "a short order or warrant of a Judge or magistrate directing some act to be done; an authority issuing from some competent source for the doing of some legal act"
Some bullion coins such as the Australian Gold Nugget and American Eagle are legal tender, however, they trade based on the market price of the metal content as a
Fiat money or fiat currency is money whose value is not derived from any intrinsic value or guarantee that it can be converted into a valuable commodity (such as gold). Instead, it has value only by government order (fiat). Usually, the government declares the fiat currency (typically notes and coins from a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve System in the U.S.) to be legal tender, making it unlawful not to accept the fiat currency as a means of repayment for all debts, public and private.Black, Henry Campbell (1910). ''A Law Dictionary Containing Definitions Of The Terms And Phrases Of American And English Jurisprudence, Ancient And Modern'', p. 494. West Publishing Co. Black's Law Dictionary defines the word "fiat" to mean "a short order or warrant of a Judge or magistrate directing some act to be done; an authority issuing from some competent source for the doing of some legal act"
Some bullion coins such as the Australian Gold Nugget and American Eagle are legal tender, however, they trade based on the market price of the metal content as a
. Retrieved July-18-09. Fiat money, if physically represented in the form of currency (paper or coins), can be accidentally damaged or destroyed. However, fiat money has an advantage over representative or commodity money, in that the same laws that created the money can also define rules for its replacement in case of damage or destruction. For example, the U.S. government will replace mutilated Federal Reserve Notes (U.S. fiat money) if at least half of the physical note can be reconstructed, or if it can be otherwise proven to have been destroyed. By contrast, commodity money that has been lost or destroyed cannot be recovered.
 In premodern China, the need for credit and for circulating a medium that was less of a burden than exchanging thousands of copper coins led to the introduction of paper money. This economic phenomenon was a slow and gradual process that took place from the late
In premodern China, the need for credit and for circulating a medium that was less of a burden than exchanging thousands of copper coins led to the introduction of paper money. This economic phenomenon was a slow and gradual process that took place from the late  At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world, a vigorous monetary economy was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar). Innovations introduced by economists, traders and merchants of the Muslim world include the earliest uses of credit, cheques, savings accounts, transactional accounts, loaning, trusts,
At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world, a vigorous monetary economy was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar). Innovations introduced by economists, traders and merchants of the Muslim world include the earliest uses of credit, cheques, savings accounts, transactional accounts, loaning, trusts,  By 1900, most of the industrializing nations were on some form of a gold standard, with paper notes and silver coins constituting the circulating medium. Private banks and governments across the world followed Gresham's law: keeping gold and silver paid but paying out in notes. This did not happen all around the world at the same time, but occurred sporadically, generally in times of war or financial crisis, beginning in the early part of the 20th century and continuing across the world until the late 20th century, when the regime of floating fiat currencies came into force. One of the last countries to break away from the
By 1900, most of the industrializing nations were on some form of a gold standard, with paper notes and silver coins constituting the circulating medium. Private banks and governments across the world followed Gresham's law: keeping gold and silver paid but paying out in notes. This did not happen all around the world at the same time, but occurred sporadically, generally in times of war or financial crisis, beginning in the early part of the 20th century and continuing across the world until the late 20th century, when the regime of floating fiat currencies came into force. One of the last countries to break away from the
 Commercial bank money or demand deposits are claims against financial institutions that can be used for the purchase of goods and services. A demand deposit account is an account from which funds can be withdrawn at any time by check or cash withdrawal without giving the bank or financial institution any prior notice. Banks have the legal obligation to return funds held in demand deposits immediately upon demand (or 'at call'). Demand deposit withdrawals can be performed in person, via checks or bank drafts, using automatic teller machines (ATMs), or through online banking.
Commercial bank money is created by commercial banks whose reserves (held as cash and other highly liquid assets) typically constitute only a fraction of their deposits, while the banks maintain an obligation to redeem all these deposits upon demand - a practise known as fractional-reserve banking. Commercial bank money differs from commodity and fiat money in two ways: firstly it is non-physical, as its existence is only reflected in the account ledgers of banks and other financial institutions, and secondly, there is some element of risk that the claim will not be fulfilled if the financial institution becomes insolvent.
The money multiplier theory presents the process of creating commercial bank money as a multiple (greater than 1) of the amount of base money created by the country's
Commercial bank money or demand deposits are claims against financial institutions that can be used for the purchase of goods and services. A demand deposit account is an account from which funds can be withdrawn at any time by check or cash withdrawal without giving the bank or financial institution any prior notice. Banks have the legal obligation to return funds held in demand deposits immediately upon demand (or 'at call'). Demand deposit withdrawals can be performed in person, via checks or bank drafts, using automatic teller machines (ATMs), or through online banking.
Commercial bank money is created by commercial banks whose reserves (held as cash and other highly liquid assets) typically constitute only a fraction of their deposits, while the banks maintain an obligation to redeem all these deposits upon demand - a practise known as fractional-reserve banking. Commercial bank money differs from commodity and fiat money in two ways: firstly it is non-physical, as its existence is only reflected in the account ledgers of banks and other financial institutions, and secondly, there is some element of risk that the claim will not be fulfilled if the financial institution becomes insolvent.
The money multiplier theory presents the process of creating commercial bank money as a multiple (greater than 1) of the amount of base money created by the country's
 When gold and silver were used as money, the money supply could grow only if the supply of these metals was increased by mining. This rate of increase would accelerate during periods of
When gold and silver were used as money, the money supply could grow only if the supply of these metals was increased by mining. This rate of increase would accelerate during periods of
 The definition of money says it is money only "in a particular country or socio-economic context". In general, communities only use a single measure of value, which can be identified in the prices of goods listed for sale. There might be multiple media of exchange, which can be observed by what is given to purchase goods ("medium of exchange"), etc. In most countries, the government acts to encourage a particular forms of money, such as requiring it for taxes and punishing
The definition of money says it is money only "in a particular country or socio-economic context". In general, communities only use a single measure of value, which can be identified in the prices of goods listed for sale. There might be multiple media of exchange, which can be observed by what is given to purchase goods ("medium of exchange"), etc. In most countries, the government acts to encourage a particular forms of money, such as requiring it for taxes and punishing
excerpt
. * Ferguson, Niall. ''The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World'' (2009
excerpt
* Keen, Steve (February 2015)
"What Is Money and How Is It Created?"
argues, "Banks create money by issuing a loan to a borrower; they record the loan as an asset, and the money they deposit in the borrower's account as a liability. This, in one way, is no different to the way the Federal Reserve creates money ... money is simply a third party's promise to pay which we accept as full payment in exchange for goods. The two main third parties whose promises we accept are the government and the banks ... money ... is not backed by anything physical, and instead relies on trust. Of course, that trust can be abused ... we continue to ignore the main game: what the banks do (for good and for ill) that really drives the economy." ''
excerpt
* * Lanchester, John, "The Invention of Money: How the heresies of two bankers became the basis of our modern economy", ''
PDF
* Weatherford, Jack. ''The history of money'' (2009). by a cultural anthropologist
excerpt
"Money"
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Niall Ferguson, Richard J. Evans and Jane Humphries (''In Our Time'', Mar. 1, 2001) * {{Authority control Currency Economic anthropology Trade
payment
A payment is the tender of something of value, such as money or its equivalent, by one party (such as a person or company) to another in exchange for goods or services provided by them, or to fulfill a legal obligation or philanthropy desir ...
for goods and services
Goods are items that are usually (but not always) tangible, such as pens or Apple, apples. Services are activities provided by other people, such as teachers or barbers. Taken together, it is the Production (economics), production, distributio ...
and repayment of debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Co ...
s, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are: medium of exchange, a unit of account, a store of value and sometimes, a standard of deferred payment.
Money was historically an emergent market phenomenon that possessed intrinsic value as a commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic goods, good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the Market (economics), market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to w ...
; nearly all contemporary money systems are based on unbacked fiat money
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tende ...
without use value. Its value is consequently derived by social convention, having been declared by a government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
or regulatory entity to be legal tender; that is, it must be accepted as a form of payment within the boundaries of the country, for "all debts, public and private", in the case of the United States dollar
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
.
The money supply of a country comprises all currency in circulation (banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
s and coin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
s currently issued) and, depending on the particular definition used, one or more types of bank money (the balances held in checking accounts, savings accounts, and other types of bank accounts). Bank money, whose value exists on the books of financial institutions and can be converted into physical notes or used for cashless payment, forms by far the largest part of broad money in developed countries.
Etymology
The word money derives from the Latin word with the meaning "coin" via French . The Latin word is believed to originate from a temple of Juno, on Capitoline, one of Rome's seven hills. In the ancient world, Juno was often associated with money. The temple of Juno Moneta at Rome was the place where the mint of Ancient Rome was located. The name "Juno" may have derived from the Etruscan goddess Uni and "Moneta" either from the Latin word "monere" (remind, warn, or instruct) or the Greek word "moneres" (alone, unique). In the Western world, a prevalent term for coin-money has been '' specie'', stemming from Latin , meaning "in kind".History
 The use of barter-like methods may date back to at least 100,000 years ago, though there is no evidence of a society or economy that relied primarily on barter. Instead, non-monetary societies operated largely along the principles of gift economy and
The use of barter-like methods may date back to at least 100,000 years ago, though there is no evidence of a society or economy that relied primarily on barter. Instead, non-monetary societies operated largely along the principles of gift economy and debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Co ...
. When barter did in fact occur, it was usually between either complete strangers or potential enemies.
Many cultures around the world eventually developed the use of commodity money. The Mesopotamian shekel was a unit of weight, and relied on the mass of something like 160 grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
of barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
. The first usage of the term came from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
circa 3000 BC. Societies in the Americas, Asia, Africa and Australia used shell money—often, the shells of the cowry (''Cypraea moneta L.'' or ''C. annulus L.''). According to Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
, the Lydians were the first people to introduce the use of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver coins. It is thought by modern scholars that these first stamped coins
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
were minted around 650 to 600 BC.
 The system of commodity money eventually evolved into a system of representative money. This occurred because gold and silver merchants or banks would issue receipts to their depositors, redeemable for the commodity money deposited. Eventually, these receipts became generally accepted as a means of payment and were used as money. Paper money or banknotes were first used in China during the
The system of commodity money eventually evolved into a system of representative money. This occurred because gold and silver merchants or banks would issue receipts to their depositors, redeemable for the commodity money deposited. Eventually, these receipts became generally accepted as a means of payment and were used as money. Paper money or banknotes were first used in China during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
. These banknotes, known as " jiaozi", evolved from promissory notes that had been used since the 7th century. However, they did not displace commodity money and were used alongside coins. In the 13th century, paper money became known in Europe through the accounts of travellers, such as Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
and William of Rubruck. Marco Polo's account of paper money during the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
is the subject of a chapter of his book, '' The Travels of Marco Polo'', titled " How the Great Kaan Causeth the Bark of Trees, Made Into Something Like Paper, to Pass for Money All Over his Country." Banknotes were first issued in Europe by Stockholms Banco in 1661 and were again also used alongside coins. The gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
, a monetary system where the medium of exchange are paper notes that are convertible into pre-set, fixed quantities of gold, replaced the use of gold coins as currency in the 17th–19th centuries in Europe. These gold standard notes were made legal tender, and redemption into gold coins was discouraged. By the beginning of the 20th century, almost all countries had adopted the gold standard, backing their legal tender notes with fixed amounts of gold.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and the Bretton Woods Conference, most countries adopted fiat currencies that were fixed to the U.S. dollar. The U.S. dollar was in turn fixed to gold. In 1971 the U.S. government suspended the convertibility of the dollar to gold. After this many countries de-pegged their currencies from the U.S. dollar, and most of the world's currencies became unbacked by anything except the governments' fiat of legal tender and the ability to convert the money into goods via payment. According to proponents of modern money theory, fiat money is also backed by taxes. By imposing taxes, states create demand for the currency they issue.
Functions
In ''Money and the Mechanism of Exchange (1875)'', William Stanley Jevons famously analyzed money in terms of four functions: a '' medium of exchange'', a ''common measure of value'' (or unit of account), a ''standard of value'' (or standard of deferred payment), and a '' store of value''. By 1919, Jevons's four functions of money were summarized in the couplet: :Money's a matter of functions four, :A Medium, a Measure, a Standard, a Store. This couplet would later become widely popular in macroeconomics textbooks. Most modern textbooks now list only three functions, that of medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value, not considering a standard of deferred payment as a distinguished function, but rather subsuming it in the others.Krugman, Paul & Wells, Robin, ''Economics'', Worth Publishers, New York (2006) There have been many historical disputes regarding the combination of money's functions, some arguing that they need more separation and that a single unit is insufficient to deal with them all. One of these arguments is that the role of money as a medium of exchange conflicts with its role as a store of value: its role as a store of value requires holding it without spending, whereas its role as a medium of exchange requires it to circulate. T.H. Greco. ''Money: Understanding and Creating Alternatives to Legal Tender'', White River Junction, Vt: Chelsea Green Publishing (2001). Others argue that storing of value is just deferral of the exchange, but does not diminish the fact that money is a medium of exchange that can be transported both across space and time. The term "financial capital" is a more general and inclusive term for all liquid instruments, whether or not they are a uniformly recognized tender.Medium of exchange
When money is used to intermediate the exchange of goods and services, it is performing a function as a ''medium of exchange''. It thereby avoids the inefficiencies of a barter system, such as the inability to permanently ensure " coincidence of wants". For example, between two parties in a barter system, one party may not have or make the item that the other wants, indicating the non-existence of the coincidence of wants. Having a medium of exchange can alleviate this issue because the former can have the freedom to spend time on other items, instead of being burdened to only serve the needs of the latter. Meanwhile, the latter can use the medium of exchange to seek for a party that can provide them with the item they want.Measure of value
A ''unit of account'' (in economics) is a standard numerical monetary unit of measurement of the market value of goods, services, and other transactions. Also known as a "measure" or "standard" of relative worth and deferred payment, a unit of account is a necessary prerequisite for the formulation of commercial agreements that involve debt. Money acts as a standard measure and a common denomination of trade. It is thus a basis for quoting and bargaining of prices. It is necessary for developing efficient accounting systems like double-entry bookkeeping.Standard of deferred payment
While ''standard of deferred payment'' is distinguished by some texts, particularly older ones, other texts subsume this under other functions. A "standard of deferred payment" is an accepted way to settle adebt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Co ...
—a unit in which debts are denominated, and the status of money as legal tender, in those jurisdictions which have this concept, states that it may function for the discharge of debts. When debts are denominated in money, the real value of debts may change due to inflation and deflation, and for sovereign and international debts via debasement
A debasement of coinage is the practice of lowering the intrinsic value of coins, especially when used in connection with commodity money, such as gold or silver coins, while continuing to circulate it at face value. A coin is said to be debased ...
and devaluation.
Store of value
To act as a ''store of value'', money must be able to be reliably saved, stored, and retrieved—and be predictably usable as a medium of exchange when it is retrieved. The value of the money must also remain stable over time. Some have argued that inflation, by reducing the value of money, diminishes the ability of the money to function as a store of value.Properties
The functions of money are that it is a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. To fulfill these various functions, money must be: * Fungible: its individual units must be capable of mutual substitution (i.e., interchangeability). * Durable: able to withstand repeated use. * Divisible: divisible to small units. * Portable: easily carried and transported. * Acceptable: most people must accept the money as payment * Scarce: its supply in circulation must be limited.Money supply
 In economics, money is any
In economics, money is any financial instrument
Financial instruments are monetary contracts between parties. They can be created, traded, modified and settled. They can be cash (currency), evidence of an ownership, interest in an entity or a contractual right to receive or deliver in the form ...
that can fulfill the functions of money (detailed above). These financial instruments together are collectively referred to as the money supply of an economy. In other words, the money supply is the number of financial instruments within a specific economy available for purchasing goods or services. Since the money supply consists of various financial instruments (usually currency, demand deposits, and various other types of deposits), the amount of money in an economy is measured by adding together these financial instruments creating a ''monetary aggregate''.
Economists employ different ways to measure the stock of money or money supply, reflected in different types of monetary aggregates, using a categorization system that focuses on the liquidity of the financial instrument used as money. The most commonly used monetary aggregates (or types of money) are conventionally designated M1, M2, and M3. These are successively larger aggregate categories: M1 is currency (coins and bills) plus demand deposits (such as checking accounts); M2 is M1 plus savings accounts and time deposits under $100,000; M3 is M2 plus larger time deposits and similar institutional accounts. M1 includes only the most liquid financial instruments, and M3 relatively illiquid instruments. The precise definition of M1, M2, etc. may be different in different countries.
Another measure of money, M0, is also used. M0 is base money, or the amount of money actually issued by the central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
of a country. It is measured as currency plus deposits of banks and other institutions at the central bank. M0 is also the only money that can satisfy the reserve requirements of commercial banks.
Creation of money
In current economic systems, money is created by two procedures: Legal tender, or narrow money (M0) is the cash created by a Central Bank by minting coins and printing banknotes. Bank money, or broad money (M1/M2) is the money created by private banks through the recording of loans as deposits of borrowing clients, with partial support indicated by the ''cash ratio''. Currently, bank money is created as electronic money. Bank money, whose value exists on the books of financial institutions and can be converted into physical notes or used for cashless payment, forms by far the largest part of broad money in developed countries. In most countries, the majority of money is mostly created as M1/M2 by commercial banks making loans. Contrary to some popular misconceptions, banks do not act simply as intermediaries, lending out deposits that savers place with them, and do not depend on central bank money (M0) to create new loans and deposits.Market liquidity
"Market liquidity" describes how easily an item can be traded for another item, or into the common currency within an economy. Money is the most liquid asset because it is universally recognized and accepted as a common currency. In this way, money gives consumers thefreedom
Freedom is the power or right to speak, act, and change as one wants without hindrance or restraint. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving oneself one's own laws".
In one definition, something is "free" i ...
to trade goods and services easily without having to barter.
Liquid financial instruments are easily tradable and have low transaction costs. There should be no (or minimal) spread between the prices to buy and sell the instrument being used as money.
Types
Commodity
 Many items have been used as commodity money such as naturally scarce
Many items have been used as commodity money such as naturally scarce precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high Value (economics), economic value. Precious metals, particularly the noble metals, are more corrosion resistant and less reactivity (chemistry), chemically reac ...
s, conch shells, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, beads, etc., as well as many other things that are thought of as having value. Commodity money value comes from the commodity out of which it is made. The commodity itself constitutes the money, and the money is the commodity.Mises, Ludwig von. '' The Theory of Money and Credit'', (Indianapolis, IN: Liberty Fund, Inc., 1981), trans. H. E. Batson. Ch.3 Part One: The Nature of Money, Chapter 3: The Various Kinds of Money, Section 3: Commodity Money, Credit Money, and Fiat Money, Paragraph 25. Examples of commodities that have been used as mediums of exchange include gold, silver, copper, rice, Wampum, salt, peppercorns, large stones, decorated belts, shells, alcohol, cigarettes, cannabis, candy, etc. These items were sometimes used in a metric of perceived value in conjunction with one another, in various commodity valuation or price system economies. The use of commodity money is similar to barter, but a commodity money provides a simple and automatic unit of account for the commodity which is being used as money. Although some gold coins such as the Krugerrand are considered legal tender, there is no record of their face value on either side of the coin. The rationale for this is that emphasis is laid on their direct link to the prevailing value of their fine gold content. American Eagles are imprinted with their gold content and legal tender face value.
Representative
In 1875, the British economist William Stanley Jevons described the money used at the time as " representative money". Representative money is money that consists of token coins, paper money or other physical tokens such as certificates, that can be reliably exchanged for a fixed quantity of a commodity such as gold or silver. The value of representative money stands in direct and fixed relation to the commodity that backs it, while not itself being composed of that commodity.Fiat
 Fiat money or fiat currency is money whose value is not derived from any intrinsic value or guarantee that it can be converted into a valuable commodity (such as gold). Instead, it has value only by government order (fiat). Usually, the government declares the fiat currency (typically notes and coins from a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve System in the U.S.) to be legal tender, making it unlawful not to accept the fiat currency as a means of repayment for all debts, public and private.Black, Henry Campbell (1910). ''A Law Dictionary Containing Definitions Of The Terms And Phrases Of American And English Jurisprudence, Ancient And Modern'', p. 494. West Publishing Co. Black's Law Dictionary defines the word "fiat" to mean "a short order or warrant of a Judge or magistrate directing some act to be done; an authority issuing from some competent source for the doing of some legal act"
Some bullion coins such as the Australian Gold Nugget and American Eagle are legal tender, however, they trade based on the market price of the metal content as a
Fiat money or fiat currency is money whose value is not derived from any intrinsic value or guarantee that it can be converted into a valuable commodity (such as gold). Instead, it has value only by government order (fiat). Usually, the government declares the fiat currency (typically notes and coins from a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve System in the U.S.) to be legal tender, making it unlawful not to accept the fiat currency as a means of repayment for all debts, public and private.Black, Henry Campbell (1910). ''A Law Dictionary Containing Definitions Of The Terms And Phrases Of American And English Jurisprudence, Ancient And Modern'', p. 494. West Publishing Co. Black's Law Dictionary defines the word "fiat" to mean "a short order or warrant of a Judge or magistrate directing some act to be done; an authority issuing from some competent source for the doing of some legal act"
Some bullion coins such as the Australian Gold Nugget and American Eagle are legal tender, however, they trade based on the market price of the metal content as a commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic goods, good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the Market (economics), market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to w ...
, rather than their legal tender face value (which is usually only a small fraction of their bullion value).usmiNT.gov. Retrieved July-18-09. Fiat money, if physically represented in the form of currency (paper or coins), can be accidentally damaged or destroyed. However, fiat money has an advantage over representative or commodity money, in that the same laws that created the money can also define rules for its replacement in case of damage or destruction. For example, the U.S. government will replace mutilated Federal Reserve Notes (U.S. fiat money) if at least half of the physical note can be reconstructed, or if it can be otherwise proven to have been destroyed. By contrast, commodity money that has been lost or destroyed cannot be recovered.
Demurrage
Coinage
These factors led to the shift of the store of value being the metal itself: at first silver, then both silver and gold, and at one point there was bronze as well. Now we have copper coins and other non-precious metals as coins. Metals were mined, weighed, and stamped into coins. This was to assure the individual taking the coin that he was getting a certain known weight of precious metal. Coins could be counterfeited, but they also created a new unit of account, which helped lead to banking. Archimedes' principle provided the next link: coins could now be easily tested for their fine weight of the metal, and thus the value of a coin could be determined, even if it had been shaved, debased or otherwise tampered with (seeNumismatics
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, medals, and related objects.
Specialists, known as numismatists, are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, but the discipline also inclu ...
).
In most major economies using coinage, copper, silver, and gold formed three tiers of coins. Gold coins were used for large purchases, payment of the military, and backing of state activities. Silver coins were used for midsized transactions, and as a unit of account for taxes, dues, contracts, and fealty, while copper coins represented the coinage of common transaction. This system had been used in ancient India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
since the time of the Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas were sixteen Realm, kingdoms and aristocracy, aristocratic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE, during the History of India#Second urbanisation (c. 600 – 200 BCE), second urbanis ...
. In Europe, this system worked through the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
period because there was virtually no new gold, silver, or copper introduced through mining or conquest. Thus the overall ratios of the three coinages remained roughly equivalent.
Paper
 In premodern China, the need for credit and for circulating a medium that was less of a burden than exchanging thousands of copper coins led to the introduction of paper money. This economic phenomenon was a slow and gradual process that took place from the late
In premodern China, the need for credit and for circulating a medium that was less of a burden than exchanging thousands of copper coins led to the introduction of paper money. This economic phenomenon was a slow and gradual process that took place from the late Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
(618–907) into the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
(960–1279). It began as a means for merchants to exchange heavy coinage for receipt
A receipt (also known as a packing list, packing slip, packaging slip, (delivery) docket, shipping list, delivery list, bill of the parcel, Manifest (transportation), manifest, or customer receipt) is a document acknowledging that something h ...
s of deposit issued as promissory notes from shops of wholesalers, notes that were valid for temporary use in a small regional territory. In the 10th century, the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
government began circulating these notes amongst the traders in their monopolized salt industry. The Song government granted several shops the sole right to issue banknotes, and in the early 12th century the government finally took over these shops to produce state-issued currency. Yet the banknotes issued were still regionally valid and temporary; it was not until the mid 13th century that a standard and uniform government issue of paper money was made into an acceptable nationwide currency. The already widespread methods of woodblock printing and then Pi Sheng's movable type
Movable type (US English; moveable type in British English) is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable Sort (typesetting), components to reproduce the elements of a document (usually individual alphanumeric charac ...
printing by the 11th century was the impetus for the massive production of paper money in premodern China.
exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
s, the transfer of credit and debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Co ...
, and banking institutions for loans and deposits.
In Europe, paper money was first introduced in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
in 1661. Sweden was rich in copper, thus, because of copper's low value, extraordinarily big coins (often weighing several kilograms) had to be made. The advantages of paper currency were numerous: it reduced transport of gold and silver, and thus lowered the risks; it made loaning gold or silver at interest easier since the specie (gold or silver) never left the possession of the lender until someone else redeemed the note; and it allowed for a division of currency into credit and specie backed forms. It enabled the sale of stock
Stocks (also capital stock, or sometimes interchangeably, shares) consist of all the Share (finance), shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporatio ...
in joint stock companies, and the redemption of those shares in the paper.
However, these advantages are held within their disadvantages. First, since a note has no intrinsic value, there was nothing to stop issuing authorities from printing more of it than they had specie to back it with. Second, because it increased the money supply, it increased inflationary pressures, a fact observed by David Hume in the 18th century. The result is that paper money would often lead to an inflationary bubble, which could collapse if people began demanding hard money, causing the demand for paper notes to fall to zero. The printing of paper money was also associated with wars, and financing of wars, and therefore regarded as part of maintaining a standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars ...
. For these reasons, paper currency was held in suspicion and hostility in Europe and America. It was also addictive since the speculative profits of trade and capital creation were quite large. Major nations established mints to print money and mint coins, and branches of their treasury to collect taxes and hold gold and silver stock.
At this time both silver and gold were considered legal tender, and accepted by governments for taxes. However, the instability in the ratio between the two grew over the 19th century, with the increase both in the supply of these metals, particularly silver, and of trade. This is called bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed Exchange rate, rate of ...
and the attempt to create a bimetallic standard where both gold and silver backed currency remained in circulation occupied the efforts of inflationists. Governments at this point could use currency as an instrument of policy, printing paper currency such as the United States greenback, to pay for military expenditures. They could also set the terms at which they would redeem notes for specie, by limiting the amount of purchase, or the minimum amount that could be redeemed.
 By 1900, most of the industrializing nations were on some form of a gold standard, with paper notes and silver coins constituting the circulating medium. Private banks and governments across the world followed Gresham's law: keeping gold and silver paid but paying out in notes. This did not happen all around the world at the same time, but occurred sporadically, generally in times of war or financial crisis, beginning in the early part of the 20th century and continuing across the world until the late 20th century, when the regime of floating fiat currencies came into force. One of the last countries to break away from the
By 1900, most of the industrializing nations were on some form of a gold standard, with paper notes and silver coins constituting the circulating medium. Private banks and governments across the world followed Gresham's law: keeping gold and silver paid but paying out in notes. This did not happen all around the world at the same time, but occurred sporadically, generally in times of war or financial crisis, beginning in the early part of the 20th century and continuing across the world until the late 20th century, when the regime of floating fiat currencies came into force. One of the last countries to break away from the gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
was the United States in 1971.
No country anywhere in the world today has an enforceable gold standard or silver standard currency system.
Commercial bank
 Commercial bank money or demand deposits are claims against financial institutions that can be used for the purchase of goods and services. A demand deposit account is an account from which funds can be withdrawn at any time by check or cash withdrawal without giving the bank or financial institution any prior notice. Banks have the legal obligation to return funds held in demand deposits immediately upon demand (or 'at call'). Demand deposit withdrawals can be performed in person, via checks or bank drafts, using automatic teller machines (ATMs), or through online banking.
Commercial bank money is created by commercial banks whose reserves (held as cash and other highly liquid assets) typically constitute only a fraction of their deposits, while the banks maintain an obligation to redeem all these deposits upon demand - a practise known as fractional-reserve banking. Commercial bank money differs from commodity and fiat money in two ways: firstly it is non-physical, as its existence is only reflected in the account ledgers of banks and other financial institutions, and secondly, there is some element of risk that the claim will not be fulfilled if the financial institution becomes insolvent.
The money multiplier theory presents the process of creating commercial bank money as a multiple (greater than 1) of the amount of base money created by the country's
Commercial bank money or demand deposits are claims against financial institutions that can be used for the purchase of goods and services. A demand deposit account is an account from which funds can be withdrawn at any time by check or cash withdrawal without giving the bank or financial institution any prior notice. Banks have the legal obligation to return funds held in demand deposits immediately upon demand (or 'at call'). Demand deposit withdrawals can be performed in person, via checks or bank drafts, using automatic teller machines (ATMs), or through online banking.
Commercial bank money is created by commercial banks whose reserves (held as cash and other highly liquid assets) typically constitute only a fraction of their deposits, while the banks maintain an obligation to redeem all these deposits upon demand - a practise known as fractional-reserve banking. Commercial bank money differs from commodity and fiat money in two ways: firstly it is non-physical, as its existence is only reflected in the account ledgers of banks and other financial institutions, and secondly, there is some element of risk that the claim will not be fulfilled if the financial institution becomes insolvent.
The money multiplier theory presents the process of creating commercial bank money as a multiple (greater than 1) of the amount of base money created by the country's central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
, the multiple itself being a function of the legal regulation of banks imposed by financial regulators (e.g., potential reserve requirements) beside the business policies of commercial banks and the preferences of households - factors which the central bank can influence, but not control completely. Contemporary central banks generally do not control the creation of money, nor do they try to, though their interest rate-setting monetary policies naturally affect the amount of loans and deposits that commercial banks create.
Digital or electronic
The development of computer technology in the second part of the twentieth century allowed money to be represented digitally. By 1990, in the United States all money transferred between its central bank and commercial banks was in electronic form. By the 2000s most money existed as digital currency in bank databases. In 2012, by number of transaction, 20 to 58 percent of transactions were electronic (dependent on country). Anonymous digital currencies were developed in the early 2000s. Early examples include Ecash, bit gold, RPOW, and b-money. Not much innovation occurred until the conception ofBitcoin
Bitcoin (abbreviation: BTC; Currency symbol, sign: ₿) is the first Decentralized application, decentralized cryptocurrency. Based on a free-market ideology, bitcoin was invented in 2008 when an unknown entity published a white paper under ...
in 2008, which introduced the concept of a decentralised currency that requires no trusted third party.
Monetary policy
 When gold and silver were used as money, the money supply could grow only if the supply of these metals was increased by mining. This rate of increase would accelerate during periods of
When gold and silver were used as money, the money supply could grow only if the supply of these metals was increased by mining. This rate of increase would accelerate during periods of gold rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, ...
es and discoveries, such as when Columbus traveled to the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
and brought back gold and silver to Spain, or when gold was discovered in California in 1848. This caused inflation, as the value of gold went down. However, if the rate of gold mining could not keep up with the growth of the economy, gold became relatively more valuable, and prices (denominated in gold) would drop, causing deflation. Deflation was the more typical situation for over a century when gold and paper money backed by gold were used as money in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Modern-day monetary systems are based on fiat money and are no longer tied to the value of gold. The amount of money in the economy is influenced by monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
, which is the process by which a central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
influences the economy to achieve specific goals. Often, the goal of monetary policy is to maintain low and stable inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
, directly via an inflation targeting strategy, or indirectly via a fixed exchange rate system against a major currency with a stable inflation rate. In some cases, the central bank may pursue various supplementary goals. For example, it is clearly stated in the Federal Reserve Act
The Federal Reserve Act was passed by the 63rd United States Congress and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson on December 23, 1913. The law created the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States.
After Dem ...
that the Board of Governors
A board of directors is a governing body that supervises the activities of a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government agency.
The powers, duties, and responsibilities of a board of directors are determined by government regulations ...
and the Federal Open Market Committee should seek "to promote effectively the goals of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates."
A failed monetary policy can have significant detrimental effects on an economy and the society that depends on it. These include hyperinflation, stagflation, recession, high unemployment, shortages of imported goods, inability to export goods, and even total monetary collapse and the adoption of a much less efficient barter economy. This happened in Russia, for instance, after the fall of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of Nationalities, Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. :s: ...
.
Monetary policy strategies have changed over time. Some of the tools used to conduct contemporary monetary policy include:
* changing the interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
at which the central bank loans money to (or borrows money from) the commercial banks
* open market operations including currency purchases or sales
* forward guidance, i.e. publishing forecasts to communicate the likely future course of monetary policy
* raising or lowering bank reserve requirements
In the U.S., the Federal Reserve is responsible for conducting monetary policy, while in the eurozone the respective institution is the European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International ...
. Other central banks with a significant impact on global finances are the Bank of Japan, People's Bank of China and the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
.
During the 1970s and 1980s monetary policy in several countries was influenced by an economic theory known as monetarism. Monetarism argued that management of the money supply should be the primary means of regulating economic activity. The stability of the demand for money prior to the 1980s was a key finding of Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz supported by the work of David Laidler, and many others. It turned out, however, that maintaining a monetary policy strategy of targeting the money supply did not work very well: The relation between money growth and inflation was not as tight as expected by monetarist theory, and the short-run relation between the money supply and the interest rate, which is the chief instrument through which the central bank can influence output and inflation, was unreliable. Both problems were due to unpredictable shifts in the demand for money. Consequently, starting in the early 1990s a fundamental reorientation took place in most major central banks, starting to target inflation directly instead of the money supply and using the interest rate as their main instrument.
Locality
 The definition of money says it is money only "in a particular country or socio-economic context". In general, communities only use a single measure of value, which can be identified in the prices of goods listed for sale. There might be multiple media of exchange, which can be observed by what is given to purchase goods ("medium of exchange"), etc. In most countries, the government acts to encourage a particular forms of money, such as requiring it for taxes and punishing
The definition of money says it is money only "in a particular country or socio-economic context". In general, communities only use a single measure of value, which can be identified in the prices of goods listed for sale. There might be multiple media of exchange, which can be observed by what is given to purchase goods ("medium of exchange"), etc. In most countries, the government acts to encourage a particular forms of money, such as requiring it for taxes and punishing fraud
In law, fraud is intent (law), intentional deception to deprive a victim of a legal right or to gain from a victim unlawfully or unfairly. Fraud can violate Civil law (common law), civil law (e.g., a fraud victim may sue the fraud perpetrato ...
.
Some places do maintain two or more currencies, particularly in border towns or high-travel areas. Shops in these locations might list prices and accept payment in multiple currencies. Otherwise, foreign currency is treated as a financial asset in the local market. Foreign currency is commonly bought or sold on foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
s by travelers and traders.
Communities can change the money they use, which is known as currency substitution. This can happen intentionally, when a government issues a new currency. For example, when Brazil moved from the Brazilian cruzeiro to the Brazilian real. It can also happen spontaneously, when the people refuse to accept a currency experiencing hyperinflation (even if its use is encouraged by the government).
The money used by a community can change on a smaller scale. This can come through innovation, such as the adoption of cheques (checks). Gresham's law says that "bad money drives out good". That is, when buying a good, a person is more likely to pass on less-desirable items that qualify as "money" and hold on to more valuable ones. For example, coins with less silver in them (but which are still valid coins) are more likely to circulate in the community. This may effectively change the money used by a community.
The money used by a community does not have to be a currency issued by a government. A famous example of community adopting a new form of money is prisoners-of-war using cigarettes to trade.
Financial crimes
Counterfeiting
Counterfeit money is imitation currency produced without the legal sanction of the state or government. Producing or using counterfeit money is a form of fraud or forgery. Counterfeiting is almost as old as money itself. Plated copies (known as Fourrées) have been found of Lydian coins which are thought to be among the first western coins. Historically, objects that were difficult to counterfeit (e.g. shells, rare stones, precious metals) were often chosen as money. Before the introduction of paper money, the most prevalent method of counterfeiting involved mixing base metals with pure gold or silver. A form of counterfeiting is the production of documents by legitimate printers in response to fraudulent instructions. DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
forged British pounds and American dollars. Today some of the finest counterfeit banknotes are called '' Superdollars'' because of their high quality and likeness to the real U.S. dollar. There has been significant counterfeiting of Euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
banknotes and coins since the launch of the currency in 2002, but considerably less than for the U.S. dollar.
Money laundering
Money laundering is the process in which the proceeds of crime are transformed into ostensibly legitimate money or other assets. However, in several legal and regulatory systems the term money laundering has become conflated with other forms of financial crime, and sometimes used more generally to include misuse of the financial system (involving things such as securities, digital currencies, credit cards, and traditional currency), including terrorism financing,tax evasion
Tax evasion or tax fraud is an illegal attempt to defeat the imposition of taxes by individuals, corporations, trusts, and others. Tax evasion often entails the deliberate misrepresentation of the taxpayer's affairs to the tax authorities to red ...
, and evading of international sanctions.
See also
* Calculation in kind * Coin of account * Commons-based peer production * Counterfeit money * Digital currency *Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
* Foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
* Free Money Day
* Gift economy
* Intelligent banknote neutralisation system
* Labour voucher
* Leprosy colony money
* Local exchange trading system
* Monetary economics
* Money bag
* Money management
Investment management (sometimes referred to more generally as financial asset management) is the professional asset management of various securities, including shareholdings, bonds, and other assets, such as real estate, to meet specified ...
* Non-monetary economy
* Seigniorage
* Slang terms for money
* Social capital
* Universal basic income
* Velocity of Money
* World currency
Notes
References
Further reading
* Brzezinski, Adam; Palma, Nuno; Velde, François R. (2024). " Understanding Money Using Historical Evidence". ''Annual Review of Economics''. * Chown, John F. ''A History of Money: from AD 800'' (Psychology Press, 1994). * Davies, Glyn, and Duncan Connors. ''A History of Money'' (4th ed. U of Wales Press, 2016excerpt
. * Ferguson, Niall. ''The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World'' (2009
excerpt
* Keen, Steve (February 2015)
"What Is Money and How Is It Created?"
argues, "Banks create money by issuing a loan to a borrower; they record the loan as an asset, and the money they deposit in the borrower's account as a liability. This, in one way, is no different to the way the Federal Reserve creates money ... money is simply a third party's promise to pay which we accept as full payment in exchange for goods. The two main third parties whose promises we accept are the government and the banks ... money ... is not backed by anything physical, and instead relies on trust. Of course, that trust can be abused ... we continue to ignore the main game: what the banks do (for good and for ill) that really drives the economy." ''
Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine founded by B. C. Forbes in 1917. It has been owned by the Hong Kong–based investment group Integrated Whale Media Investments since 2014. Its chairman and editor-in-chief is Steve Forbes. The co ...
''
* Kuroda, Akinobu. ''A Global History of Money'' (Routledge, 2020)excerpt
* * Lanchester, John, "The Invention of Money: How the heresies of two bankers became the basis of our modern economy", ''
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. It was founded on February 21, 1925, by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a reporter for ''The New York T ...
'', 5 & 12 August 2019, pp. 28–31.
* Schurtz, Heinrich. ''An Outline of the Origins of Money'' (University of Chicago Press, 2024). Translated and annotated, with an introduction by Enrique Martino and Mario Schmidt. Foreword by Michael Hudson* Weatherford, Jack. ''The history of money'' (2009). by a cultural anthropologist
excerpt
External links
* * * *"Money"
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Niall Ferguson, Richard J. Evans and Jane Humphries (''In Our Time'', Mar. 1, 2001) * {{Authority control Currency Economic anthropology Trade