|
Neural Radiance Field
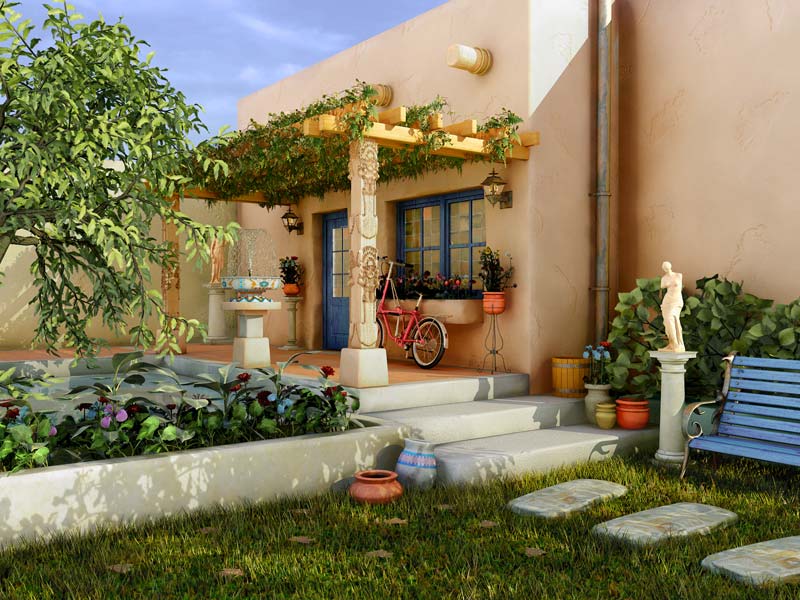
A neural radiance field (NeRF) is a method based on deep learning for reconstructing a three-dimensional representation of a scene from two-dimensional images. The NeRF model enables downstream applications of novel view synthesis, scene geometry reconstruction, and obtaining the reflectance properties of the scene. Additional scene properties such as camera poses may also be jointly learned. First introduced in 2020, it has since gained significant attention for its potential applications in computer graphics and content creation. Algorithm The NeRF algorithm represents a scene as a radiance field parametrized by a deep neural network (DNN). The network predicts a volume density and view-dependent emitted radiance given the spatial location (x,y,z) and viewing direction in Euler angles (\theta, \Phi) of the camera. By sampling many points along camera rays, traditional volume rendering techniques can produce an image. Data collection A NeRF needs to be retrained for each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function (mathematics), function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real number, real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a function, graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric "Normal distribution, bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian Root mean square, RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normal distribution, normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena. While the invention of the method is attributed to Aimé Laussedat, the term "photogrammetry" was coined by the German architect , which appeared in his 1867 article "Die Photometrographie." There are many variants of photogrammetry. One example is the extraction of three-dimensional measurements from two-dimensional data (i.e. images); for example, the distance between two points that lie on a plane parallel to the photographic image plane can be determined by measuring their distance on the image, if the scale (map), scale of the image is known. Another is the extraction of accurate color ranges and values representing such quantities as albedo, specular reflection, Metallicity#Photometric colors, metallicity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Structure From Motion
Structure from motion (SfM) is a photogrammetric range imaging technique for estimating three-dimensional structures from two-dimensional image sequences that may be coupled with local motion signals. It is a classic problem studied in the fields of computer vision and visual perception. In computer vision, the problem of SfM is to design an algorithm to perform this task. In visual perception, the problem of SfM is to find an algorithm by which biological creatures perform this task. Principle Humans perceive a great deal of information about the three-dimensional structure in their environment by moving around it. When the observer moves, objects around them move different amounts depending on their distance from the observer. This is known as motion parallax, and this depth information can be used to generate an accurate 3D representation of the world around them. Finding structure from motion presents a similar problem to finding structure from stereo vision. In both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaussian Splatting
Gaussian splatting is a volume rendering technique that deals with the direct rendering of volume data without converting the data into surface or line Geometric primitive, primitives. The technique was originally introduced as splatting by Lee Westover in the early 1990s. This technique was revitalized and exploded in popularity in 2023, when a research group from Inria proposed the seminal 3D Gaussian splatting that offers Real-time computer graphics, real-time radiance field rendering. Like other radiance field methods, it can convert multiple images into a representation of 3D space, then use the representation to create images as seen from new angles. Multiple works soon followed, such as 3D temporal Gaussian splatting that offers real-time dynamic scene rendering. 3D Gaussian splatting 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) is a technique used in the field of Real-time computer graphics, real-time radiance field rendering. It enables the creation of high-quality real-time nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graphics Processing Unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. GPUs were later found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. The ability of GPUs to rapidly perform vast numbers of calculations has led to their adoption in diverse fields including artificial intelligence (AI) where they excel at handling data-intensive and computationally demanding tasks. Other non-graphical uses include the training of neural networks and cryptocurrency mining. History 1970s Arcade system boards have used specialized graphics circuits since the 1970s. In early video game hardware, RAM for frame buffers was expensive, so video chips composited data together as the display was being scann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hash Function
A hash function is any Function (mathematics), function that can be used to map data (computing), data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values, though there are some hash functions that support variable-length output. The values returned by a hash function are called ''hash values'', ''hash codes'', (''hash/message'') ''digests'', or simply ''hashes''. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a ''hash table''. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called ''hashing'' or ''scatter-storage addressing''. Hash functions and their associated hash tables are used in data storage and retrieval applications to access data in a small and nearly constant time per retrieval. They require an amount of storage space only fractionally greater than the total space required for the data or records themselves. Hashing is a computationally- and storage-space-efficient form of data access that avoids the non-constant access time of ordered and unordered lists and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Voxel
In computing, a voxel is a representation of a value on a three-dimensional regular grid, akin to the two-dimensional pixel. Voxels are frequently used in the Data visualization, visualization and analysis of medical imaging, medical and scientific data (e.g. geographic information systems (GIS)). Voxels also have technical and artistic applications in video games, largely originating with surface rendering in ''Outcast (video game), Outcast'' (1999). ''Minecraft'' (2011) makes use of an entirely voxelated world to allow for a fully destructable and constructable environment. Voxel art, of the sort used in ''Minecraft'' and elsewhere, is a style and format of 3D art analogous to pixel art. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Instead, Rendering (computer graphics), rendering systems infer the position of a voxel based upon its position relative to other voxels (i.e., its pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Octree
An octree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly eight child node, children. Octrees are most often used to partition a three-dimensional space by recursive subdivision, recursively subdividing it into eight Octant (geometry), octants. Octrees are the three-dimensional analog of quadtrees. The word is derived from ''oct'' (Greek root meaning "eight") + ''tree''. Octrees are often used in 3D graphics and 3D game engines. For spatial representation Each node in an octree subdivides the space it represents into eight octant (solid geometry), octants. In a point region (PR) octree (analogous to a point quadtree), the node stores an explicit Point (geometry), three-dimensional point, which is the "center" of the subdivision for that node; the point defines one of the corners for each of the eight children. In a matrix-based (MX) octree (analogous to a region quadtree), the subdivision point is implicitly the center of the space the node represents. The root n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR), also known as mixed reality (MR), is a technology that overlays real-time 3D computer graphics, 3D-rendered computer graphics onto a portion of the real world through a display, such as a handheld device or head-mounted display. This experience is seamlessly interwoven with the physical world such that it is perceived as an immersion (virtual reality), immersive aspect of the real environment. In this way, augmented reality alters one's ongoing perception of a real-world environment, compared to virtual reality, which aims to completely replace the user's real-world environment with a simulated one. Augmented reality is typically visual, but can span multiple sensory Modality (human–computer interaction), modalities, including Hearing, auditory, haptic perception, haptic, and Somatosensory system, somatosensory. The primary value of augmented reality is the manner in which components of a digital world blend into a person's perception of the real world, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a Simulation, simulated experience that employs 3D near-eye displays and pose tracking to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), education (such as medical, safety, or military training) and business (such as virtual meetings). VR is one of the key technologies in the Reality–virtuality continuum, reality-virtuality continuum. As such, it is different from other digital visualization solutions, such as augmented virtuality and augmented reality. Currently, standard virtual reality systems use either virtual reality headsets or multi-projected environments to generate some realistic images, sounds, and other sensations that simulate a user's physical presence in a virtual environment. A person using virtual reality equipment is able to look around the artificial world, move around in it, and interact with virtual features or items. The effect is commonly creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Global Illumination
Global illumination (GI), or indirect illumination, is a group of algorithms used in 3D computer graphics that are meant to add more realistic lighting Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. ... to 3D scenes. Such algorithms take into account not only the light that comes directly from a light source (''direct illumination''), but also subsequent cases in which light rays from the same source are reflected by other surfaces in the scene, whether reflective or not (''indirect illumination''). Theoretically, reflections, refractions, and shadows are all examples of global illumination, because when simulating them, one object affects the rendering of another (as opposed to an object being affected only by a direct source of light). In practice, however, only the simulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |