Graphics processing unit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized
 The Atari 2600 in 1977 used a video shifter called the Television Interface Adaptor. Atari 8-bit computers (1979) had ANTIC, a video processor which interpreted instructions describing a " display list"—the way the scan lines map to specific bitmapped or character modes and where the memory is stored (so there did not need to be a contiguous frame buffer). 6502 machine code subroutines could be triggered on scan lines by setting a bit on a display list instruction. ANTIC also supported smooth vertical and horizontal scrolling independent of the CPU.
The Atari 2600 in 1977 used a video shifter called the Television Interface Adaptor. Atari 8-bit computers (1979) had ANTIC, a video processor which interpreted instructions describing a " display list"—the way the scan lines map to specific bitmapped or character modes and where the memory is stored (so there did not need to be a contiguous frame buffer). 6502 machine code subroutines could be triggered on scan lines by setting a bit on a display list instruction. ANTIC also supported smooth vertical and horizontal scrolling independent of the CPU.
 The NEC μPD7220 was the first implementation of a
The NEC μPD7220 was the first implementation of a 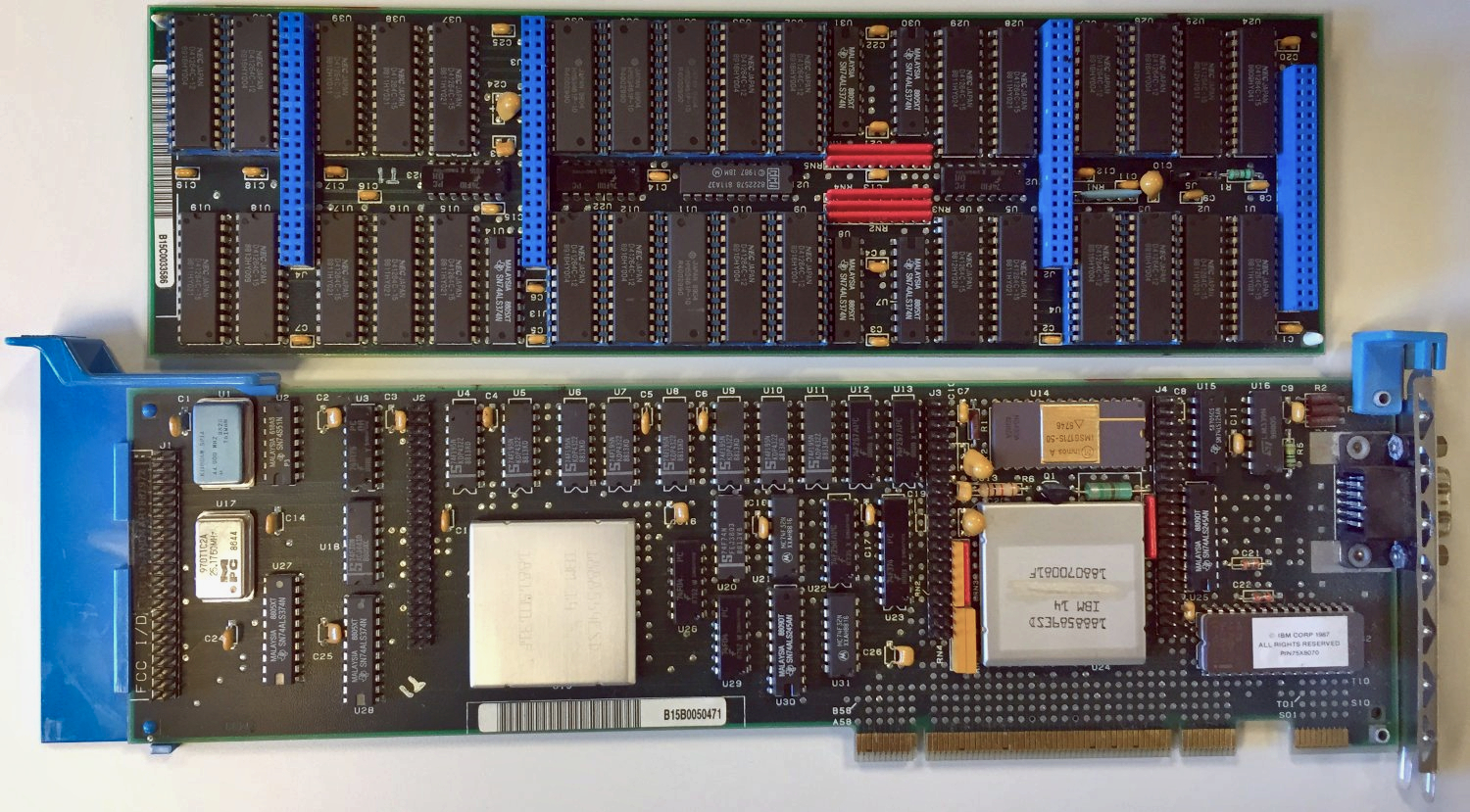 In 1987, the
In 1987, the 


 In 1991, S3 Graphics introduced the '' S3 86C911'', which its designers named after the Porsche 911 as an indication of the performance increase it promised. The 86C911 spawned a variety of imitators: by 1995, all major PC graphics chip makers had added 2D acceleration support to their chips. Fixed-function ''Windows accelerators'' surpassed expensive general-purpose graphics coprocessors in Windows performance, and such coprocessors faded from the PC market.
Throughout the 1990s, 2D GUI acceleration evolved. As manufacturing capabilities improved, so did the level of integration of graphics chips. Additional
In 1991, S3 Graphics introduced the '' S3 86C911'', which its designers named after the Porsche 911 as an indication of the performance increase it promised. The 86C911 spawned a variety of imitators: by 1995, all major PC graphics chip makers had added 2D acceleration support to their chips. Fixed-function ''Windows accelerators'' surpassed expensive general-purpose graphics coprocessors in Windows performance, and such coprocessors faded from the PC market.
Throughout the 1990s, 2D GUI acceleration evolved. As manufacturing capabilities improved, so did the level of integration of graphics chips. Additional
transition from Unix to the forthcoming Windows NT OS
the deal which was signed in 1995 was not announced publicly until 1998. In the intervening period, Microsoft worked closely with SGI to port OpenGL to Windows NT. In that era, OpenGL had no standard driver model for competing hardware accelerators to compete on the basis of support for higher level 3D texturing and lighting functionality. In 1994 Microsoft announced DirectX 1.0 and support for gaming in the forthcoming Windows 95 consumer OS. In 199
Microsoft announced the acquisition of UK based Rendermorphics Ltd
and the Direct3D driver model for the acceleration of consumer 3D graphics. The Direct3D driver model shipped with DirectX 2.0 in 1996. It included standards and specifications for 3D chip makers to compete to support 3D texture, lighting and Z-buffering. ATI, which was later to be acquired by AMD, began development on the first Direct3D GPUs. Nvidia quickly pivoted from
failed deal with Sega
in 1996 to aggressively embracing support for Direct3D. In this era Microsoft merged their internal Direct3D and OpenGL teams and worked closely with SGI to unify driver standards for both industrial and consumer 3D graphics hardware accelerators. Microsoft ran annual events for 3D chip makers called "Meltdowns" to test their 3D hardware and drivers to work both with Direct3D and OpenGL. It was during this period of strong Microsoft influence over 3D standards that 3D accelerator cards moved beyond being simple rasterizers to become more powerful general purpose processors as support for hardware accelerated texture mapping, lighting, Z-buffering and compute created the modern GPU. During this period the same Microsoft team responsible for Direct3D and OpenGL driver standardization introduced their own Microsoft 3D chip design called Talisman. Details of this era are documented extensively in the books
Game of X
v.1 and v.2 by Russel Demaria,
Renegades of the Empire
by Mike Drummond,
Opening the Xbox
by Dean Takahashi and
Masters of Doom
by David Kushner. The Nvidia '' GeForce 256'' (also known as NV10) was the first consumer-level card with hardware-accelerated T&L. While the OpenGL API provided software support for texture mapping and lighting, the first 3D hardware acceleration for these features arrived with the first Direct3D accelerated consumer GPU's.

 ''Integrated graphics processing units'' (IGPU), ''integrated graphics'', ''shared graphics solutions'', ''integrated graphics processors'' (IGP), or ''unified memory architectures'' (UMA) use a portion of a computer's system RAM rather than dedicated graphics memory. IGPs can be integrated onto a motherboard as part of its northbridge chipset, or on the same die (integrated circuit) with the CPU (like AMD APU or Intel HD Graphics). On certain motherboards, AMD's IGPs can use dedicated sideport memory: a separate fixed block of high performance memory that is dedicated for use by the GPU. computers with integrated graphics account for about 90% of all PC shipments. They are less costly to implement than dedicated graphics processing, but tend to be less capable. Historically, integrated processing was considered unfit for 3D games or graphically intensive programs but could run less intensive programs such as Adobe Flash. Examples of such IGPs would be offerings from SiS and VIA circa 2004. However, modern integrated graphics processors such as AMD Accelerated Processing Unit and Intel Graphics Technology (HD, UHD, Iris, Iris Pro, Iris Plus, and Xe-LP) can handle 2D graphics or low-stress 3D graphics.
Since GPU computations are memory-intensive, integrated processing may compete with the CPU for relatively slow system RAM, as it has minimal or no dedicated video memory. IGPs use system memory with bandwidth up to a current maximum of 128 GB/s, whereas a discrete graphics card may have a bandwidth of more than 1000 GB/s between its VRAM and GPU core. This memory bus bandwidth can limit the performance of the GPU, though multi-channel memory can mitigate this deficiency. Older integrated graphics chipsets lacked hardware
''Integrated graphics processing units'' (IGPU), ''integrated graphics'', ''shared graphics solutions'', ''integrated graphics processors'' (IGP), or ''unified memory architectures'' (UMA) use a portion of a computer's system RAM rather than dedicated graphics memory. IGPs can be integrated onto a motherboard as part of its northbridge chipset, or on the same die (integrated circuit) with the CPU (like AMD APU or Intel HD Graphics). On certain motherboards, AMD's IGPs can use dedicated sideport memory: a separate fixed block of high performance memory that is dedicated for use by the GPU. computers with integrated graphics account for about 90% of all PC shipments. They are less costly to implement than dedicated graphics processing, but tend to be less capable. Historically, integrated processing was considered unfit for 3D games or graphically intensive programs but could run less intensive programs such as Adobe Flash. Examples of such IGPs would be offerings from SiS and VIA circa 2004. However, modern integrated graphics processors such as AMD Accelerated Processing Unit and Intel Graphics Technology (HD, UHD, Iris, Iris Pro, Iris Plus, and Xe-LP) can handle 2D graphics or low-stress 3D graphics.
Since GPU computations are memory-intensive, integrated processing may compete with the CPU for relatively slow system RAM, as it has minimal or no dedicated video memory. IGPs use system memory with bandwidth up to a current maximum of 128 GB/s, whereas a discrete graphics card may have a bandwidth of more than 1000 GB/s between its VRAM and GPU core. This memory bus bandwidth can limit the performance of the GPU, though multi-channel memory can mitigate this deficiency. Older integrated graphics chipsets lacked hardware
NVIDIA – What is GPU computing?
* Th
''GPU Gems'' book series
How GPUs work
GPU Caps Viewer – Video card information utility
ARM Mali GPUs Overview
{{DEFAULTSORT:Graphics Processing Unit Graphics processing units, GPGPU Graphics hardware Virtual reality OpenCL compute devices Artificial intelligence Application-specific integrated circuits Hardware acceleration Digital electronics Electronic design Electronic design automation
electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or Conductive trace, traces through which electric current can flow. It is a t ...
designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
s, mobile phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This rad ...
s, personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s, workstations, and game consoles. GPUs were later found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. The ability of GPUs to rapidly perform vast numbers of calculations has led to their adoption in diverse fields including artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
(AI) where they excel at handling data-intensive and computationally demanding tasks. Other non-graphical uses include the training of neural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
and cryptocurrency mining.
History
1970s
Arcade system board
An arcade video game is an arcade game that takes player input from its controls, processes it through electrical or computerized components, and displays output to an electronic monitor or similar display. All arcade video games are coin-opera ...
s have used specialized graphics circuits since the 1970s. In early video game hardware, RAM for frame buffers was expensive, so video chips composited data together as the display was being scanned out on the monitor.
A specialized barrel shifter circuit helped the CPU animate the framebuffer graphics for various 1970s arcade video games from Midway and Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
, such as '' Gun Fight'' (1975), '' Sea Wolf'' (1976), and ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978). The Namco Galaxian arcade system in 1979 used specialized graphics hardware that supported RGB color, multi-colored sprites, and tilemap backgrounds. The Galaxian hardware was widely used during the golden age of arcade video games, by game companies such as Namco, Centuri, Gremlin, Irem, Konami
, commonly known as Konami, , is a Japanese multinational entertainment company and video game developer and video game publisher, publisher headquartered in Chūō, Tokyo, Chūō, Tokyo. The company also produces and distributes trading card ...
, Midway, Nichibutsu, Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
, and Taito.
 The Atari 2600 in 1977 used a video shifter called the Television Interface Adaptor. Atari 8-bit computers (1979) had ANTIC, a video processor which interpreted instructions describing a " display list"—the way the scan lines map to specific bitmapped or character modes and where the memory is stored (so there did not need to be a contiguous frame buffer). 6502 machine code subroutines could be triggered on scan lines by setting a bit on a display list instruction. ANTIC also supported smooth vertical and horizontal scrolling independent of the CPU.
The Atari 2600 in 1977 used a video shifter called the Television Interface Adaptor. Atari 8-bit computers (1979) had ANTIC, a video processor which interpreted instructions describing a " display list"—the way the scan lines map to specific bitmapped or character modes and where the memory is stored (so there did not need to be a contiguous frame buffer). 6502 machine code subroutines could be triggered on scan lines by setting a bit on a display list instruction. ANTIC also supported smooth vertical and horizontal scrolling independent of the CPU.
1980s
 The NEC μPD7220 was the first implementation of a
The NEC μPD7220 was the first implementation of a personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
graphics display processor as a single large-scale integration
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(LSI) integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
chip. This enabled the design of low-cost, high-performance video graphics cards such as those from Number Nine Visual Technology. It became the best-known GPU until the mid-1980s. It was the first fully integrated VLSI (very large-scale integration) metal–oxide–semiconductor ( NMOS) graphics display processor for PCs, supported up to 1024×1024 resolution, and laid the foundations for the PC graphics market. It was used in a number of graphics cards and was licensed for clones such as the Intel 82720, the first of Intel's graphics processing units. The Williams Electronics arcade games '' Robotron 2084'', '' Joust'', ''Sinistar
''Sinistar'' is a 1983 multidirectional shooter arcade video game developed and manufactured by Williams Electronics. It was created by Sam Dicker, Jack Haeger, Noah Falstein, RJ Mical, Python Anghelo, and Richard Witt. Players control a sp ...
'', and '' Bubbles'', all released in 1982, contain custom blitter chips for operating on 16-color bitmaps.
In 1984, Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
released the ARTC HD63484, the first major CMOS graphics processor for personal computers. The ARTC could display up to 4K resolution when in monochrome mode. It was used in a number of graphics cards and terminals during the late 1980s. In 1985, the Amiga was released with a custom graphics chip including a blitter for bitmap manipulation, line drawing, and area fill. It also included a coprocessor with its own simple instruction set, that was capable of manipulating graphics hardware registers in sync with the video beam (e.g. for per-scanline palette switches, sprite multiplexing, and hardware windowing), or driving the blitter. In 1986, Texas Instruments released the TMS34010, the first fully programmable graphics processor. It could run general-purpose code but also had a graphics-oriented instruction set. During 1990–1992, this chip became the basis of the Texas Instruments Graphics Architecture ("TIGA") Windows accelerator cards.
 In 1987, the
In 1987, the IBM 8514
IBM 8514 is a graphics card manufactured by IBM and introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of personal computers in 1987. It supports a display resolution of pixels with 256 colors at 43.5 Hz ( interlaced), or at 60 Hz ( non-interlaced ...
graphics system was released. It was one of the first video cards for IBM PC compatibles that implemented fixed-function 2D primitives in electronic hardware. Sharp's X68000, released in 1987, used a custom graphics chipset with a 65,536 color palette and hardware support for sprites, scrolling, and multiple playfields. It served as a development machine for Capcom
is a Japanese video game company. It has created a number of critically acclaimed and List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises, with its most commercially successful being ''Resident Evil'', ''Monster ...
's CP System arcade board. Fujitsu's FM Towns computer, released in 1989, had support for a 16,777,216 color palette. In 1988, the first dedicated polygonal 3D graphics boards were introduced in arcades with the Namco System 21 and Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
Air System.

IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
introduced its proprietary Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the IBM PC compatible industry within three years. T ...
(VGA) display standard in 1987, with a maximum resolution of 640×480 pixels. In November 1988, NEC Home Electronics announced its creation of the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) to develop and promote a Super VGA (SVGA) computer display standard as a successor to VGA. Super VGA enabled graphics display resolutions up to 800×600 pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s, a 56% increase.
1990s

 In 1991, S3 Graphics introduced the '' S3 86C911'', which its designers named after the Porsche 911 as an indication of the performance increase it promised. The 86C911 spawned a variety of imitators: by 1995, all major PC graphics chip makers had added 2D acceleration support to their chips. Fixed-function ''Windows accelerators'' surpassed expensive general-purpose graphics coprocessors in Windows performance, and such coprocessors faded from the PC market.
Throughout the 1990s, 2D GUI acceleration evolved. As manufacturing capabilities improved, so did the level of integration of graphics chips. Additional
In 1991, S3 Graphics introduced the '' S3 86C911'', which its designers named after the Porsche 911 as an indication of the performance increase it promised. The 86C911 spawned a variety of imitators: by 1995, all major PC graphics chip makers had added 2D acceleration support to their chips. Fixed-function ''Windows accelerators'' surpassed expensive general-purpose graphics coprocessors in Windows performance, and such coprocessors faded from the PC market.
Throughout the 1990s, 2D GUI acceleration evolved. As manufacturing capabilities improved, so did the level of integration of graphics chips. Additional application programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that des ...
s (APIs) arrived for a variety of tasks, such as Microsoft's WinG
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-d ...
graphics library for Windows 3.x, and their later DirectDraw interface for hardware acceleration of 2D games in Windows 95 and later.
In the early- and mid-1990s, real-time 3D graphics became increasingly common in arcade, computer, and console games, which led to increasing public demand for hardware-accelerated 3D graphics. Early examples of mass-market 3D graphics hardware can be found in arcade system boards such as the Sega Model 1, Namco System 22, and Sega Model 2, and the fifth-generation video game consoles such as the Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
, PlayStation, and Nintendo 64. Arcade systems such as the Sega Model 2 and SGI Onyx-based Namco Magic Edge Hornet Simulator in 1993 were capable of hardware T&L ( transform, clipping, and lighting) years before appearing in consumer graphics cards. Another early example is the Super FX chip, a RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
-based on-cartridge graphics chip used in some SNES games, notably '' Doom'' and '' Star Fox''. Some systems used DSPs to accelerate transformations. Fujitsu, which worked on the Sega Model 2 arcade system, began working on integrating T&L into a single LSI solution for use in home computers in 1995; the Fujitsu Pinolite, the first 3D geometry processor for personal computers, released in 1997. The first hardware T&L GPU on home
A home, or domicile, is a space used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for one or more human occupants, and sometimes various companion animals. Homes provide sheltered spaces, for instance rooms, where domestic activity can be p ...
video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s was the Nintendo 64's Reality Coprocessor, released in 1996. In 1997, Mitsubishi released the 3Dpro/2MP, a GPU capable of transformation and lighting, for workstations and Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
desktops; ATi used it for its FireGL 4000 graphics card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics accelerator, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or colloquially GPU) is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a displa ...
, released in 1997.
The term "GPU" was coined by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
in reference to the 32-bit Sony GPU (designed by Toshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
) in the PlayStation video game console, released in 1994.
In the PC world, notable failed attempts for low-cost 3D graphics chips included the S3 '' ViRGE'', ATI Rage, and Matrox ''Mystique''. These chips were essentially previous-generation 2D accelerators with 3D features bolted on. Many were pin-compatible with the earlier-generation chips for ease of implementation and minimal cost. Initially, 3D graphics were possible only with discrete boards dedicated to accelerating 3D functions (and lacking 2D graphical user interface (GUI) acceleration entirely) such as the PowerVR and the 3dfx ''Voodoo''. However, as manufacturing technology continued to progress, video, 2D GUI acceleration, and 3D functionality were all integrated into one chip. Rendition's ''Verite'' chipsets were among the first to do this well. In 1997, Rendition collaborated with Hercules and Fujitsu on a "Thriller Conspiracy" project which combined a Fujitsu FXG-1 Pinolite geometry processor with a Vérité V2200 core to create a graphics card with a full T&L engine years before Nvidia's GeForce 256; This card, designed to reduce the load placed upon the system's CPU, never made it to market. NVIDIA RIVA 128 was one of the first consumer-facing GPU integrated 3D processing unit and 2D processing unit on a chip.
OpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a Language-independent specification, cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D computer graphics, 2D and 3D computer graphics, 3D vector graphics. The API is typic ...
was introduced in the early 1990s by Silicon Graphics as a professional graphics API, with proprietary hardware support for 3D rasterization. In 1994, Microsoft acquired Softimage, the dominant CGI movie production tool used for early CGI movie hits like ''Jurassic Park'', ''Terminator 2'' and ''Titanic''. With that deal came a strategic relationship with SGI and a commercial license of their OpenGL libraries, enabling Microsoft to port the API to the Windows NT OS but not to the upcoming release of Windows 95. Although it was little known at the time, SGI had contracted with Microsoft ttransition from Unix to the forthcoming Windows NT OS
the deal which was signed in 1995 was not announced publicly until 1998. In the intervening period, Microsoft worked closely with SGI to port OpenGL to Windows NT. In that era, OpenGL had no standard driver model for competing hardware accelerators to compete on the basis of support for higher level 3D texturing and lighting functionality. In 1994 Microsoft announced DirectX 1.0 and support for gaming in the forthcoming Windows 95 consumer OS. In 199
Microsoft announced the acquisition of UK based Rendermorphics Ltd
and the Direct3D driver model for the acceleration of consumer 3D graphics. The Direct3D driver model shipped with DirectX 2.0 in 1996. It included standards and specifications for 3D chip makers to compete to support 3D texture, lighting and Z-buffering. ATI, which was later to be acquired by AMD, began development on the first Direct3D GPUs. Nvidia quickly pivoted from
failed deal with Sega
in 1996 to aggressively embracing support for Direct3D. In this era Microsoft merged their internal Direct3D and OpenGL teams and worked closely with SGI to unify driver standards for both industrial and consumer 3D graphics hardware accelerators. Microsoft ran annual events for 3D chip makers called "Meltdowns" to test their 3D hardware and drivers to work both with Direct3D and OpenGL. It was during this period of strong Microsoft influence over 3D standards that 3D accelerator cards moved beyond being simple rasterizers to become more powerful general purpose processors as support for hardware accelerated texture mapping, lighting, Z-buffering and compute created the modern GPU. During this period the same Microsoft team responsible for Direct3D and OpenGL driver standardization introduced their own Microsoft 3D chip design called Talisman. Details of this era are documented extensively in the books
Game of X
v.1 and v.2 by Russel Demaria,
Renegades of the Empire
by Mike Drummond,
Opening the Xbox
by Dean Takahashi and
Masters of Doom
by David Kushner. The Nvidia '' GeForce 256'' (also known as NV10) was the first consumer-level card with hardware-accelerated T&L. While the OpenGL API provided software support for texture mapping and lighting, the first 3D hardware acceleration for these features arrived with the first Direct3D accelerated consumer GPU's.
2000s
NVIDIA released the GeForce 256, marketed as the world's first GPU, integrating transform and lighting engines for advanced 3D graphics rendering. Nvidia was first to produce a chip capable of programmable shading: the '' GeForce 3''. Each pixel could now be processed by a short program that could include additional image textures as inputs, and each geometric vertex could likewise be processed by a short program before it was projected onto the screen. Used in the Xbox console, this chip competed with the one in thePlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October, in Europe on 24 Novembe ...
, which used a custom vector unit for hardware-accelerated vertex processing (commonly referred to as VU0/VU1). The earliest incarnations of shader execution engines used in Xbox were not general-purpose and could not execute arbitrary pixel code. Vertices and pixels were processed by different units, which had their resources, with pixel shaders having tighter constraints (because they execute at higher frequencies than vertices). Pixel shading engines were more akin to a highly customizable function block and did not "run" a program. Many of these disparities between vertex and pixel shading were not addressed until the Unified Shader Model.
In October 2002, with the introduction of the ATI '' Radeon 9700'' (also known as R300), the world's first Direct3D 9.0 accelerator, pixel and vertex shaders could implement looping and lengthy floating point math, and were quickly becoming as flexible as CPUs, yet orders of magnitude faster for image-array operations. Pixel shading is often used for bump mapping, which adds texture to make an object look shiny, dull, rough, or even round or extruded.
With the introduction of the Nvidia GeForce 8 series and new generic stream processing units, GPUs became more generalized computing devices. Parallel GPUs are making computational inroads against the CPU, and a subfield of research, dubbed GPU computing or GPGPU for ''general purpose computing on GPU'', has found applications in fields as diverse as machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
, oil exploration, scientific image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
, linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathemat ...
, statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
, 3D reconstruction, and stock options pricing. GPGPU was the precursor to what is now called a compute shader (e.g. CUDA, OpenCL, DirectCompute) and actually abused the hardware to a degree by treating the data passed to algorithms as texture maps and executing algorithms by drawing a triangle or quad with an appropriate pixel shader. This entails some overheads since units like the scan converter are involved where they are not needed (nor are triangle manipulations even a concern—except to invoke the pixel shader).
Nvidia's CUDA platform, first introduced in 2007, was the earliest widely adopted programming model for GPU computing. OpenCL
OpenCL (Open Computing Language) is a software framework, framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous computing, heterogeneous platforms consisting of central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), di ...
is an open standard defined by the Khronos Group that allows for the development of code for both GPUs and CPUs with an emphasis on portability. OpenCL solutions are supported by Intel, AMD, Nvidia, and ARM, and according to a report in 2011 by Evans Data, OpenCL had become the second most popular HPC tool.
2010s
In 2010, Nvidia partnered withAudi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. A subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The origins of the compa ...
to power their cars' dashboards, using the Tegra GPU to provide increased functionality to cars' navigation and entertainment systems. Advances in GPU technology in cars helped advance self-driving technology. AMD's Radeon HD 6000 series cards were released in 2010, and in 2011 AMD released its 6000M Series discrete GPUs for mobile devices. The Kepler line of graphics cards by Nvidia were released in 2012 and were used in the Nvidia's 600 and 700 series cards. A feature in this GPU microarchitecture included GPU boost, a technology that adjusts the clock-speed of a video card to increase or decrease it according to its power draw. The Kepler microarchitecture was manufactured.
The PS4 and Xbox One
The Xbox One is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. Announced in May 2013, it is the successor to Xbox 360 and the third console in the Xbox#Consoles, Xbox series. It was first released in North America, parts of Europe, Austra ...
were released in 2013; they both use GPUs based on AMD's Radeon HD 7850 and 7790. Nvidia's Kepler line of GPUs was followed by the Maxwell
Maxwell may refer to:
People
* Maxwell (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
** James Clerk Maxwell, mathematician and physicist
* Justice Maxwell (disambiguation)
* Maxwell baronets, in the Baronetage of N ...
line, manufactured on the same process. Nvidia's 28 nm chips were manufactured by TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC or Taiwan Semiconductor) is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is one of the world's most valuable semiconductor companies, the world' ...
in Taiwan using the 28 nm process. Compared to the 40 nm technology from the past, this manufacturing process allowed a 20 percent boost in performance while drawing less power. Virtual reality headsets have high system requirements; manufacturers recommended the GTX 970 and the R9 290X or better at the time of their release. Cards based on the Pascal microarchitecture were released in 2016. The GeForce 10 series of cards are of this generation of graphics cards. They are made using the 16 nm manufacturing process which improves upon previous microarchitectures. Nvidia released one non-consumer card under the new Volta architecture, the Titan V. Changes from the Titan XP, Pascal's high-end card, include an increase in the number of CUDA cores, the addition of tensor cores, and HBM2. Tensor cores are designed for deep learning, while high-bandwidth memory is on-die, stacked, lower-clocked memory that offers an extremely wide memory bus. To emphasize that the Titan V is not a gaming card, Nvidia removed the "GeForce GTX" suffix it adds to consumer gaming cards.
In 2018, Nvidia launched the RTX 20 series GPUs that added ray-tracing cores to GPUs, improving their performance on lighting effects. Polaris 11 and Polaris 10 GPUs from AMD are fabricated by a 14 nm process. Their release resulted in a substantial increase in the performance per watt of AMD video cards. AMD also released the Vega GPU series for the high end market as a competitor to Nvidia's high end Pascal cards, also featuring HBM2 like the Titan V.
In 2019, AMD released the successor to their Graphics Core Next (GCN) microarchitecture/instruction set. Dubbed RDNA, the first product featuring it was the Radeon RX 5000 series of video cards.AMD press release: The company announced that the successor to the RDNA microarchitecture would be incremental (a "refresh"). AMD unveiled the Radeon RX 6000 series, its RDNA 2 graphics cards with support for hardware-accelerated ray tracing. The product series, launched in late 2020, consisted of the RX 6800, RX 6800 XT, and RX 6900 XT. The RX 6700 XT, which is based on Navi 22, was launched in early 2021.
The PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X and Series S were released in 2020; they both use GPUs based on the RDNA 2 microarchitecture with incremental improvements and different GPU configurations in each system's implementation.
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
first entered the GPU market in the late 1990s, but produced lackluster 3D accelerators compared to the competition at the time. Rather than attempting to compete with the high-end manufacturers Nvidia and ATI/AMD, they began integrating Intel Graphics Technology GPUs into motherboard chipsets, beginning with the Intel 810 for the Pentium III, and later into CPUs. They began with the Intel Atom 'Pineview' laptop processor in 2009, continuing in 2010 with desktop processors in the first generation of the Intel Core line and with contemporary Pentiums and Celerons. This resulted in a large nominal market share, as the majority of computers with an Intel CPU also featured this embedded graphics processor. These generally lagged behind discrete processors in performance. Intel re-entered the discrete GPU market in 2022 with its Arc series, which competed with the then-current GeForce 30 series and Radeon 6000 series cards at competitive prices.
2020s
In the 2020s, GPUs have been increasingly used for calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems, such as training ofneural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
on enormous datasets that are needed for large language models. Specialized processing cores on some modern workstation's GPUs are dedicated for deep learning since they have significant FLOPS performance increases, using 4×4 matrix multiplication and division, resulting in hardware performance up to 128 TFLOPS in some applications. These tensor cores are expected to appear in consumer cards, as well.
GPU companies
Many companies have produced GPUs under a number of brand names. In 2009,Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
, Nvidia, and AMD/ ATI were the market share leaders, with 49.4%, 27.8%, and 20.6% market share respectively. In addition, Matrox produces GPUs. Chinese companies such as Jingjia Micro have also produced GPUs for the domestic market although in terms of worldwide sales, they still lag behind market leaders.
Modern smartphones use mostly Adreno GPUs from Qualcomm
Qualcomm Incorporated () is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software and services related to wireless techn ...
, PowerVR GPUs from Imagination Technologies, and Mali GPUs from ARM.
Computational functions
Modern GPUs have traditionally used most of theirtransistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s to do calculations related to 3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
. In addition to the 3D hardware, today's GPUs include basic 2D acceleration and framebuffer capabilities (usually with a VGA compatibility mode). Newer cards such as AMD/ATI HD5000–HD7000 lack dedicated 2D acceleration; it is emulated by 3D hardware. GPUs were initially used to accelerate the memory-intensive work of texture mapping and rendering polygons. Later, dedicated hardware was added to accelerate geometric calculations such as the rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
and translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
of vertices into different coordinate systems. Recent developments in GPUs include support for programmable shaders which can manipulate vertices and textures with many of the same operations that are supported by CPUs, oversampling and interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
techniques to reduce aliasing, and very high-precision color spaces.
Several factors of GPU construction affect the performance of the card for real-time rendering, such as the size of the connector pathways in the semiconductor device fabrication, the clock signal frequency, and the number and size of various on-chip memory caches. Performance is also affected by the number of streaming multiprocessors (SM) for NVidia GPUs, or compute units (CU) for AMD GPUs, or Xe cores for Intel discrete GPUs, which describe the number of on-silicon processor core units within the GPU chip that perform the core calculations, typically working in parallel with other SM/CUs on the GPU. GPU performance is typically measured in floating point operations per second ( FLOPS); GPUs in the 2010s and 2020s typically deliver performance measured in teraflops (TFLOPS). This is an estimated performance measure, as other factors can affect the actual display rate.
GPU accelerated video decoding and encoding
Most GPUs made since 1995 support the YUV color space and hardware overlays, important for digital video playback, and many GPUs made since 2000 also supportMPEG
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by International Organization for Standardization, ISO and International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC that sets standards for media coding, includ ...
primitives such as motion compensation and iDCT. This hardware-accelerated video decoding, in which portions of the video decoding process and video post-processing are offloaded to the GPU hardware, is commonly referred to as "GPU accelerated video decoding", "GPU assisted video decoding", "GPU hardware accelerated video decoding", or "GPU hardware assisted video decoding".
Recent graphics cards decode high-definition video on the card, offloading the central processing unit. The most common APIs for GPU accelerated video decoding are DxVA for Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
operating systems and VDPAU, VAAPI, XvMC, and XvBA for Linux-based and UNIX-like operating systems. All except XvMC are capable of decoding videos encoded with MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 ASP (MPEG-4 Part 2), MPEG-4 AVC (H.264 / DivX 6), VC-1, WMV3/ WMV9, Xvid / OpenDivX (DivX 4), and DivX 5 codecs, while XvMC is only capable of decoding MPEG-1 and MPEG-2.
There are several dedicated hardware video decoding and encoding solutions.
Video decoding processes that can be accelerated
Video decoding processes that can be accelerated by modern GPU hardware are: * Motion compensation (mocomp) * Inverse discrete cosine transform (iDCT) ** Inverse telecine 3:2 and 2:2 pull-down correction * Inverse modified discrete cosine transform (iMDCT) * In-loop deblocking filter * Intra-frame prediction * Inverse quantization (IQ) * Variable-length decoding (VLD), more commonly known as slice-level acceleration * Spatial-temporal deinterlacing and automatic interlace/ progressive source detection * Bitstream processing ( Context-adaptive variable-length coding/ Context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding) and perfect pixel positioning These operations also have applications in video editing, encoding, and transcoding.2D graphics APIs
An earlier GPU may support one or more 2D graphics API for 2D acceleration, such as GDI and DirectDraw.3D graphics APIs
A GPU can support one or more 3D graphics API, such asDirectX
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct" ...
, Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
, OpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a Language-independent specification, cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D computer graphics, 2D and 3D computer graphics, 3D vector graphics. The API is typic ...
, OpenGL ES
OpenGL for Embedded Systems (OpenGL ES or GLES) is a subset of the OpenGL computer graphics rendering application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D computer graphics such as those used by video games, typically hardware-accelerate ...
, Vulkan.
GPU forms
Terminology
In the 1970s, the term "GPU" originally stood for ''graphics processor unit'' and described a programmable processing unit working independently from the CPU that was responsible for graphics manipulation and output. In 1994,Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
used the term (now standing for ''graphics processing unit'') in reference to the PlayStation console's Toshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
-designed Sony GPU. The term was popularized by Nvidia in 1999, who marketed the GeForce 256 as "the world's first GPU". It was presented as a "single-chip processor with integrated transform, lighting, triangle setup/clipping, and rendering engines". Rival ATI Technologies coined the term "visual processing unit" or VPU with the release of the Radeon 9700 in 2002. The AMD Alveo MA35D features dual VPU’s, each using the 5 nm process
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems defines the "5 nm" process as the MOSFET technology node following the 7 nm process, "7 nm" node. In 2020, Samsung Electronics, Samsung and TSMC entered volume ...
in 2023.
In personal computers, there are two main forms of GPUs. Each has many synonyms:
* '' Dedicated graphics'' also called ''discrete graphics''.
* '' Integrated graphics'' also called ''shared graphics solutions'', ''integrated graphics processors'' (IGP), or ''unified memory architecture'' (UMA).
Usage-specific GPU
Most GPUs are designed for a specific use, real-time 3D graphics, or other mass calculations: # Gaming #* GeForce GTX, RTX #* Nvidia Titan #* Radeon HD, R5, R7, R9, RX, Vega and Navi series #* Radeon VII #* Intel Arc # Cloud Gaming #* Nvidia GRID #* Radeon Sky # Workstation #* Nvidia Quadro #* Nvidia RTX #* AMD FirePro #* AMD Radeon Pro #* Intel Arc Pro # Cloud Workstation #* Nvidia Tesla #* AMD FireStream # Artificial Intelligence training and Cloud #* Nvidia Tesla #* AMD Radeon Instinct # Automated/Driverless car #* Nvidia Drive PXDedicated graphics processing unit
''Dedicated graphics processing units'' uses RAM that is dedicated to the GPU rather than relying on the computer’s main system memory. This RAM is usually specially selected for the expected serial workload of the graphics card (seeGDDR
Graphics DDR SDRAM (GDDR SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) specifically designed for applications requiring high bandwidth, e.g. graphics processing units (GPUs). GDDR SDRAM is distinct from the more widely kno ...
). Sometimes systems with dedicated ''discrete'' GPUs were called "DIS" systems as opposed to "UMA" systems (see next section).
Dedicated GPUs are not necessarily removable, nor does it necessarily interface with the motherboard in a standard fashion. The term "dedicated" refers to the fact that graphics card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics accelerator, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or colloquially GPU) is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a displa ...
s have RAM that is dedicated to the card's use, not to the fact that ''most'' dedicated GPUs are removable. Dedicated GPUs for portable computers are most commonly interfaced through a non-standard and often proprietary slot due to size and weight constraints. Such ports may still be considered PCIe or AGP in terms of their logical host interface, even if they are not physically interchangeable with their counterparts.
Graphics cards with dedicated GPUs typically interface with the motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
by means of an expansion slot
Expansion may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''L'Expansion'', a French monthly business magazine
* Expansion (album), ''Expansion'' (album), by American jazz pianist Dave Burrell, released in 2004
* Expansions (McCoy Tyner album), ''Ex ...
such as PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripher ...
(PCIe) or Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP). They can usually be replaced or upgraded with relative ease, assuming the motherboard is capable of supporting the upgrade. A few graphics cards still use Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots, but their bandwidth is so limited that they are generally used only when a PCIe or AGP slot is not available.
Technologies such as Scan-Line Interleave by 3dfx, SLI and NVLink
NVLink is a wire-based serial multi-lane near-range communications protocol, communications link developed by Nvidia. Unlike PCI Express, a device can consist of multiple NVLinks, and devices use mesh networking to communicate instead of a central ...
by Nvidia and CrossFire by AMD allow multiple GPUs to draw images simultaneously for a single screen, increasing the processing power available for graphics. These technologies, however, are increasingly uncommon; most games do not fully use multiple GPUs, as most users cannot afford them. Multiple GPUs are still used on supercomputers (like in Summit
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous.
The term (mountain top) is generally used only for ...
), on workstations to accelerate video (processing multiple videos at once) and 3D rendering, for VFX, GPGPU workloads and for simulations, and in AI to expedite training, as is the case with Nvidia's lineup of DGX workstations and servers, Tesla GPUs, and Intel's Ponte Vecchio GPUs.
Integrated graphics processing unit
 ''Integrated graphics processing units'' (IGPU), ''integrated graphics'', ''shared graphics solutions'', ''integrated graphics processors'' (IGP), or ''unified memory architectures'' (UMA) use a portion of a computer's system RAM rather than dedicated graphics memory. IGPs can be integrated onto a motherboard as part of its northbridge chipset, or on the same die (integrated circuit) with the CPU (like AMD APU or Intel HD Graphics). On certain motherboards, AMD's IGPs can use dedicated sideport memory: a separate fixed block of high performance memory that is dedicated for use by the GPU. computers with integrated graphics account for about 90% of all PC shipments. They are less costly to implement than dedicated graphics processing, but tend to be less capable. Historically, integrated processing was considered unfit for 3D games or graphically intensive programs but could run less intensive programs such as Adobe Flash. Examples of such IGPs would be offerings from SiS and VIA circa 2004. However, modern integrated graphics processors such as AMD Accelerated Processing Unit and Intel Graphics Technology (HD, UHD, Iris, Iris Pro, Iris Plus, and Xe-LP) can handle 2D graphics or low-stress 3D graphics.
Since GPU computations are memory-intensive, integrated processing may compete with the CPU for relatively slow system RAM, as it has minimal or no dedicated video memory. IGPs use system memory with bandwidth up to a current maximum of 128 GB/s, whereas a discrete graphics card may have a bandwidth of more than 1000 GB/s between its VRAM and GPU core. This memory bus bandwidth can limit the performance of the GPU, though multi-channel memory can mitigate this deficiency. Older integrated graphics chipsets lacked hardware
''Integrated graphics processing units'' (IGPU), ''integrated graphics'', ''shared graphics solutions'', ''integrated graphics processors'' (IGP), or ''unified memory architectures'' (UMA) use a portion of a computer's system RAM rather than dedicated graphics memory. IGPs can be integrated onto a motherboard as part of its northbridge chipset, or on the same die (integrated circuit) with the CPU (like AMD APU or Intel HD Graphics). On certain motherboards, AMD's IGPs can use dedicated sideport memory: a separate fixed block of high performance memory that is dedicated for use by the GPU. computers with integrated graphics account for about 90% of all PC shipments. They are less costly to implement than dedicated graphics processing, but tend to be less capable. Historically, integrated processing was considered unfit for 3D games or graphically intensive programs but could run less intensive programs such as Adobe Flash. Examples of such IGPs would be offerings from SiS and VIA circa 2004. However, modern integrated graphics processors such as AMD Accelerated Processing Unit and Intel Graphics Technology (HD, UHD, Iris, Iris Pro, Iris Plus, and Xe-LP) can handle 2D graphics or low-stress 3D graphics.
Since GPU computations are memory-intensive, integrated processing may compete with the CPU for relatively slow system RAM, as it has minimal or no dedicated video memory. IGPs use system memory with bandwidth up to a current maximum of 128 GB/s, whereas a discrete graphics card may have a bandwidth of more than 1000 GB/s between its VRAM and GPU core. This memory bus bandwidth can limit the performance of the GPU, though multi-channel memory can mitigate this deficiency. Older integrated graphics chipsets lacked hardware transform and lighting
Transform, clipping, and lighting (T&L or TCL) is a term used in computer graphics.
Overview
Transformation is the task of producing a two-dimensional view of a 3D computer graphics, three-dimensional scene. Clipping (computer graphics), Clipp ...
, but newer ones include it.
On systems with "Unified Memory Architecture" (UMA), including modern AMD processors with integrated graphics, modern Intel processors with integrated graphics, Apple processors, the PS5 and Xbox Series (among others), the CPU cores and the GPU block share the same pool of RAM and memory address space. This allows the system to dynamically allocate memory between the CPU cores and the GPU block based on memory needs (without needing a large static split of the RAM) and thanks to zero copy transfers, removes the need for either copying data over a bus between physically separate RAM pools or copying between separate address spaces on a single physical pool of RAM, allowing more efficient transfer of data.
Hybrid graphics processing
Hybrid GPUs compete with integrated graphics in the low-end desktop and notebook markets. The most common implementations of this are ATI's HyperMemory and Nvidia's TurboCache. Hybrid graphics cards are somewhat more expensive than integrated graphics, but much less expensive than dedicated graphics cards. They share memory with the system and have a small dedicated memory cache, to make up for the high latency of the system RAM. Technologies within PCI Express make this possible. While these solutions are sometimes advertised as having as much as 768 MB of RAM, this refers to how much can be shared with the system memory.Stream processing and general purpose GPUs (GPGPU)
It is common to use a general purpose graphics processing unit (GPGPU) as a modified form of stream processor (or a vector processor), running compute kernels. This turns the massive computational power of a modern graphics accelerator's shader pipeline into general-purpose computing power. In certain applications requiring massive vector operations, this can yield several orders of magnitude higher performance than a conventional CPU. The two largest discrete (see " Dedicated graphics processing unit" above) GPU designers, AMD and Nvidia, are pursuing this approach with an array of applications. Both Nvidia and AMD teamed withStanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
to create a GPU-based client for the Folding@home distributed computing project for protein folding calculations. In certain circumstances, the GPU calculates forty times faster than the CPUs traditionally used by such applications.
GPGPUs can be used for many types of embarrassingly parallel tasks including ray tracing. They are generally suited to high-throughput computations that exhibit data-parallelism to exploit the wide vector width SIMD architecture of the GPU.
GPU-based high performance computers play a significant role in large-scale modelling. Three of the ten most powerful supercomputers in the world take advantage of GPU acceleration.
GPUs support API extensions to the C programming language such as OpenCL
OpenCL (Open Computing Language) is a software framework, framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous computing, heterogeneous platforms consisting of central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), di ...
and OpenMP. Furthermore, each GPU vendor introduced its own API which only works with their cards: AMD APP SDK from AMD, and CUDA from Nvidia. These allow functions called compute kernels to run on the GPU's stream processors. This makes it possible for C programs to take advantage of a GPU's ability to operate on large buffers in parallel, while still using the CPU when appropriate. CUDA was the first API to allow CPU-based applications to directly access the resources of a GPU for more general purpose computing without the limitations of using a graphics API.
Since 2005 there has been interest in using the performance offered by GPUs for evolutionary computation
Evolutionary computation from computer science is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms ...
in general, and for accelerating the fitness evaluation in genetic programming in particular. Most approaches compile linear
In mathematics, the term ''linear'' is used in two distinct senses for two different properties:
* linearity of a '' function'' (or '' mapping'');
* linearity of a '' polynomial''.
An example of a linear function is the function defined by f(x) ...
or tree programs on the host PC and transfer the executable to the GPU to be run. Typically a performance advantage is only obtained by running the single active program simultaneously on many example problems in parallel, using the GPU's SIMD architecture. However, substantial acceleration can also be obtained by not compiling the programs, and instead transferring them to the GPU, to be interpreted there. Acceleration can then be obtained by either interpreting multiple programs simultaneously, simultaneously running multiple example problems, or combinations of both. A modern GPU can simultaneously interpret hundreds of thousands of very small programs.
External GPU (eGPU)
An external GPU is a graphics processor located outside of the housing of the computer, similar to a large external hard drive. External graphics processors are sometimes used with laptop computers. Laptops might have a substantial amount of RAM and a sufficiently powerful central processing unit (CPU), but often lack a powerful graphics processor, and instead have a less powerful but more energy-efficient on-board graphics chip. On-board graphics chips are often not powerful enough for playing video games, or for other graphically intensive tasks, such as editing video or 3D animation/rendering. Therefore, it is desirable to attach a GPU to some external bus of a notebook.PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripher ...
is the only bus used for this purpose. The port may be, for example, an ExpressCard or mPCIe port (PCIe ×1, up to 5 or 2.5 Gbit/s respectively), a Thunderbolt 1, 2, or 3 port (PCIe ×4, up to 10, 20, or 40 Gbit/s respectively), a USB4 port with Thunderbolt compatibility, or an OCuLink port. Those ports are only available on certain notebook systems. eGPU enclosures include their own power supply (PSU), because powerful GPUs can consume hundreds of watts.
Energy efficiency
Sales
In 2013, 438.3 million GPUs were shipped globally and the forecast for 2014 was 414.2 million. However, by the third quarter of 2022, shipments of PC GPUs totaled around 75.5 million units, down 19% year-over-year.See also
* UALink * Texture mapping unit (TMU) * Render output unit (ROP) * Brute force attack *Computer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), random-access memory (RAM), motherboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, and computer case. It includes external devices ...
* Computer monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a electronic visual display, visual display, support electronics, power supply, Housing (engineering), housing, electri ...
* GPU cache
* GPU virtualization
* Manycore processor
* Physics processing unit (PPU)
* Tensor processing unit (TPU)
* Ray-tracing hardware
* Software rendering
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th cen ...
* Vision processing unit (VPU)
* Vector processor
* Video card
* Video display controller
* Video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
* AI accelerator
* GPU Vector Processor internal features
Hardware
* List of AMD graphics processing units * List of Nvidia graphics processing units *List of Intel graphics processing units
This article contains information about Intel's GPUs (see Intel Graphics Technology) and motherboard graphics chipsets in table form. In 1982, Intel licensed the NEC μPD7220 and announced it as the Intel 82720 Graphics Display Controller.
...
* List of discrete and integrated graphics processing units
* Intel GMA
The Intel Graphics Media Accelerator (GMA) is a series of integrated graphics processors introduced in 2004 by Intel, replacing the earlier Intel Extreme Graphics series and being succeeded by the Intel HD and Iris Graphics series.
This serie ...
* Larrabee
* Nvidia PureVideo – the bit-stream technology from Nvidia used in their graphics chips to accelerate video decoding on hardware GPU with DXVA.
* SoC
* UVD (Unified Video Decoder) – the video decoding bit-stream technology from ATI to support hardware (GPU) decode with DXVA
APIs
* OpenGL API * DirectX Video Acceleration (DxVA) API forMicrosoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
operating-system.
* Mantle (API)
* Vulkan (API)
* Video Acceleration API (VA API)
* VDPAU (Video Decode and Presentation API for Unix)
* X-Video Bitstream Acceleration (XvBA), the X11 equivalent of DXVA for MPEG-2, H.264, and VC-1
* X-Video Motion Compensation – the X11 equivalent for MPEG-2 video codec only
Applications
* GPU cluster * Mathematica – includes built-in support for CUDA and OpenCL GPU execution * Molecular modeling on GPU * Deeplearning4j – open-source, distributed deep learning for JavaReferences
Sources
*External links
NVIDIA – What is GPU computing?
* Th
''GPU Gems'' book series
How GPUs work
GPU Caps Viewer – Video card information utility
ARM Mali GPUs Overview
{{DEFAULTSORT:Graphics Processing Unit Graphics processing units, GPGPU Graphics hardware Virtual reality OpenCL compute devices Artificial intelligence Application-specific integrated circuits Hardware acceleration Digital electronics Electronic design Electronic design automation