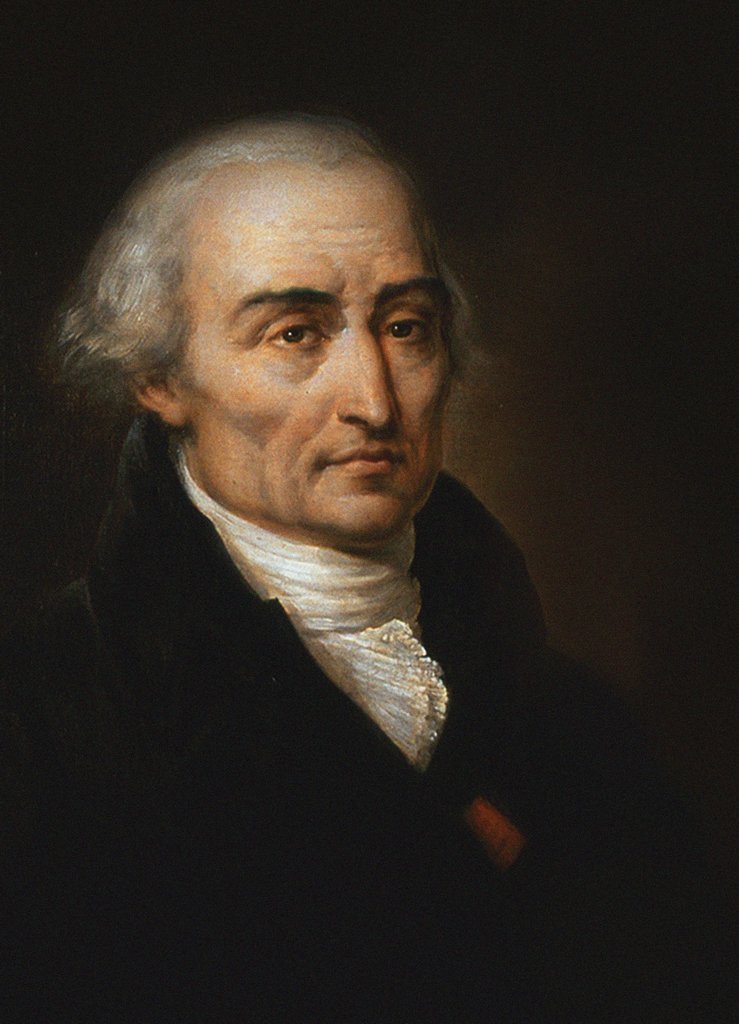|
Lagrange Duality
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an Italians, Italian mathematician and astronomer, later naturalized France, French. He made significant contributions to the fields of mathematical analysis, analysis, number theory, and both classical mechanics, classical and celestial mechanics. In 1766, on the recommendation of Swiss Leonhard Euler and French Jean le Rond d'Alembert, d'Alembert, Lagrange succeeded Euler as the director of mathematics at the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, Prussia, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is mainly on the western bank of the Po River, below its Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 847,287 (31 January 2022) while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million. The city used to be a major European political centre. From 1563, it was the capital of the Duchy of Savoy, then of the Kingdom of Sardinia ruled by the House of Savoy, and the first capital of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1865. Turin is sometimes called "the cradle of Italian liberty" for having been the political and intellectual centre of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |