|
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a " trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support conducting edge states. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Insulator Informal Phase Diagram-en
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such as Stretch factor, stretching, Torsion (mechanics), twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a Set (mathematics), set endowed with a structure, called a ''Topology (structure), topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of List of continuity-related mathematical topics, continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of topological spaces, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and Homotopy, homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry In Quantum Mechanics
Symmetries in quantum mechanics describe features of spacetime and particles which are unchanged under some transformation, in the context of quantum mechanics, relativistic quantum mechanics and quantum field theory, and with applications in the mathematical formulation of the standard model and condensed matter physics. In general, symmetry in physics, invariance, and conservation laws, are fundamentally important constraints for formulating physical theories and models. In practice, they are powerful methods for solving problems and predicting what can happen. While conservation laws do not always give the answer to the problem directly, they form the correct constraints and the first steps to solving a multitude of problems. In application, understanding symmetries can also provide insights on the eigenstates that can be expected. For example, the existence of degenerate states can be inferred by the presence of non commuting symmetry operators or that the non degenerate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CdTe
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with cadmium sulfide to form a p–n junction solar PV cell. Applications CdTe is used to make thin film solar cells, accounting for about 8% of all solar cells installed in 2011. They are among the lowest-cost types of solar cell, although a comparison of total installed cost depends on installation size and many other factors, and has changed rapidly from year to year. The CdTe solar cell market is dominated by First Solar. In 2011, around 2 GWp of CdTe solar cells were produced; For more details and discussion see cadmium telluride photovoltaics. CdTe can be alloyed with mercury to make a versatile infrared detector material (HgCdTe). CdTe alloyed with a small amount of zinc makes an excellent solid-state X-ray and gamma ray detector (Cd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HgTe
Mercury telluride (HgTe) is a binary chemical compound of mercury and tellurium. It is a semi-metal related to the II-VI group of semiconductor materials. Alternative names are mercuric telluride and mercury(II) telluride. HgTe occurs in nature as the mineral form coloradoite. Physical properties All properties are at standard temperature and pressure unless stated otherwise. The lattice parameter is about 0.646 nm in the cubic crystalline form. The bulk modulus is about 42.1 GPa. The thermal expansion coefficient is about 5.2×10−6/K. The static and dynamic dielectric constants are 20.8 and 15.1, respectively. The thermal conductivity is low at 2.7 W·m2/(m·K). HgTe bonds are weak leading to low hardness values. The hardness is 2.7×107 kg/m2. Doping N-type doping can be achieved with elements such as boron, aluminium, gallium, or indium. Iodine and iron will also dope n-type. HgTe is naturally p-type due to mercury vacancies. P-type doping is also achieved by introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SnTe
Tin telluride is a compound of tin and tellurium (SnTe); is a IV-VI narrow band gap semiconductor and has direct band gap of 0.18 eV. It is often alloyed with lead to make lead tin telluride, which is used as an infrared detector material. Tin telluride normally forms p-type semiconductor (Extrinsic semiconductor) due to tin vacancies and is a low temperature superconductor. SnTe exists in three crystal phases. At Low temperatures, where the concentration of hole carriers is less than 1.5x1020 cm−3 , Tin Telluride exists in rhombohedral phase also known as α-SnTe. At room temperature and atmospheric pressure, Tin Telluride exists in NaCl-like cubic crystal phase, known as β-SnTe. While at 18 kbar pressure, β-SnTe transforms to γ-SnTe, orthorhombic phase, space group Pnma. This phase change is characterized by 11 percent increase in density and 360 percent increase in resistance for γ-SnTe. Tin telluride is a thermoelectric material. Theoretical studies imply that the n- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
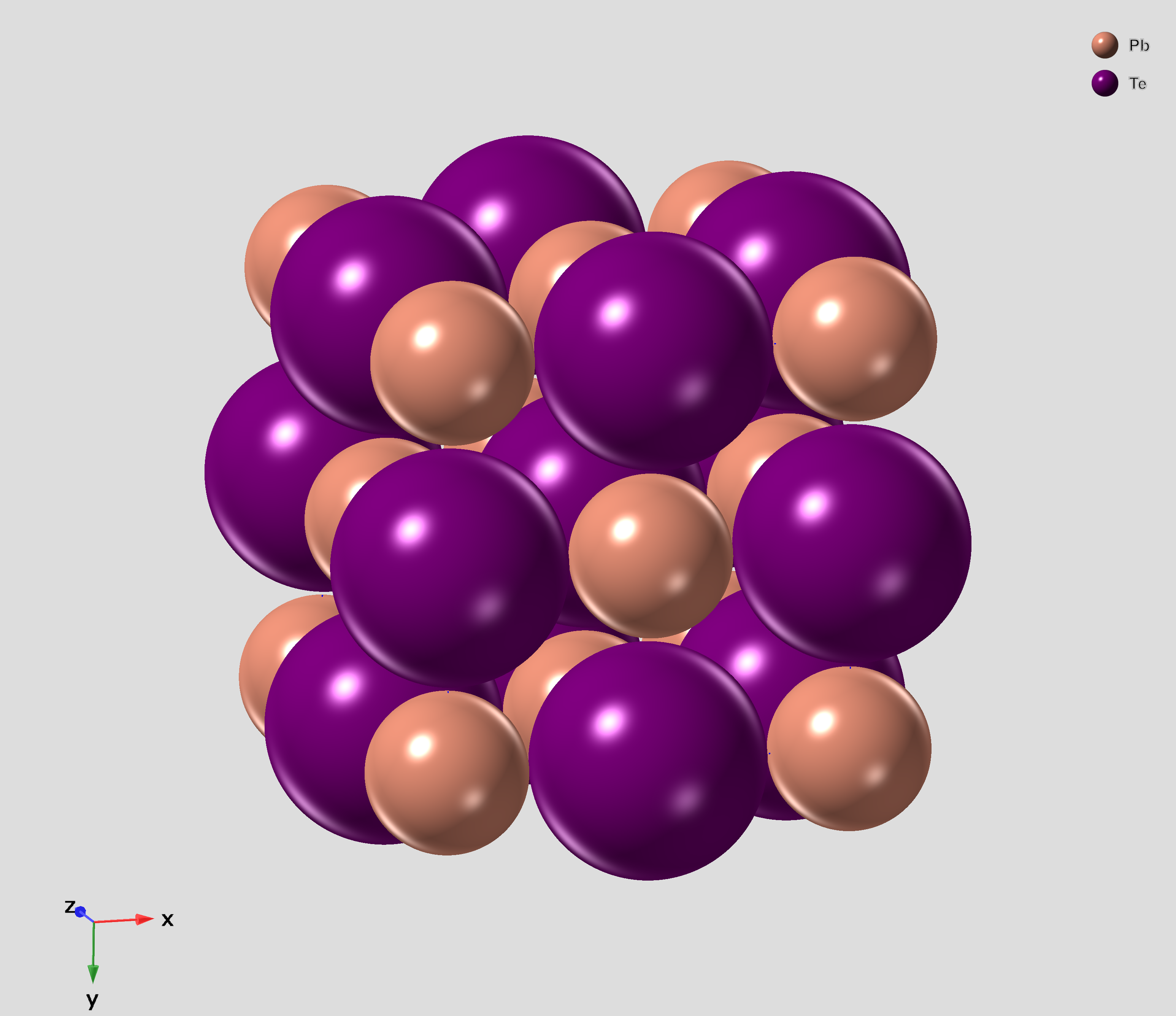
PbTe
Lead telluride is a compound of lead and tellurium (PbTe). It crystallizes in the NaCl crystal structure with Pb atoms occupying the cation and Te forming the anionic lattice. It is a narrow gap semiconductor with a band gap of 0.32 eV. It occurs naturally as the mineral altaite. Properties * Dielectric constant ~1000. * Electron Effective mass ~ 0.01 ''m''e * Hole mobility, μp = 600 cm2 V−1 s−1 (0 K); 4000 cm2 V−1 s−1 (300 K) * Seebeck coefficient: ~326 μV/K (undoped, at 300K), ~200 μV/K (Ag-doped) Applications PbTe has proven to be a very important intermediate thermoelectric material. The performance of thermoelectric materials can be evaluated by the figure of merit, ZT=S^2\sigma T/\kappa, in which S is the Seebeck coefficient, \sigma is the electrical conductivity and \kappa is the thermal conductivity. In order to improve the thermoelectric performance of materials, the power factor (S^2\sigma) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an Acoustical engineering, acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing (sense), Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Topological Insulators
In physics, magnetic topological insulators are three dimensional magnetic materials with a non-trivial topological index protected by a symmetry other than time-reversal. This type of material conducts electricity on its outer surface, but its volume behaves like an insulator. In contrast with a non-magnetic topological insulator, a magnetic topological insulator can have naturally gapped surface states as long as the quantizing symmetry is broken at the surface. These gapped surfaces exhibit a topologically protected half-quantized surface anomalous Hall conductivity (e^2/2h) perpendicular to the surface. The sign of the half-quantized surface anomalous Hall conductivity depends on the specific surface termination. Theory Axion coupling The \mathbb_2 classification of a 3D crystalline topological insulator can be understood in terms of the axion coupling \theta. A scalar quantity that is determined from the ground state wavefunction :\theta = -\frac\int_ d^3k \, \epsil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photonic Topological Insulator
Photonic topological insulators are artificial electromagnetic materials that support topologically non-trivial, unidirectional states of light. Photonic topological phases are classical electromagnetic wave analogues of electronic topological phases studied in condensed matter physics. Similar to their electronic counterparts, they, can provide robust unidirectional channels for light propagation. The field that studies these phases of light is referred to as topological photonics. History Topological order in solid state systems has been studied in condensed matter physics since the discovery of integer quantum Hall effect. But topological matter attracted considerable interest from the physics community after the proposals for possible observation of symmetry-protected topological phases (or the so-called ''topological insulators'') in graphene, and experimental observation of a 2D topological insulator in CdTe/HgTe/CdTe quantum wells in 2007. In 2008, Haldane and Raghu propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umklapp Scattering
In crystalline materials, Umklapp scattering (also U-process or Umklapp process) is a scattering process that results in a wave vector (usually written ''k'') which falls outside the first Brillouin zone. If a material is periodic, it has a Brillouin zone, and any point outside the first Brillouin zone can also be expressed as a point inside the zone. So, the wave vector is then mathematically transformed to a point inside the first Brillouin zone. This transformation allows for scattering processes which would otherwise violate the conservation of momentum: two wave vectors pointing to the right can combine to create a wave vector that points to the left. This non-conservation is why crystal momentum is not a true momentum. Examples include electron-lattice potential scattering or an anharmonic phonon-phonon (or electron-phonon) scattering process, reflecting an electronic state or creating a phonon with a momentum ''k''-vector outside the first Brillouin zone. Umklapp scatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Quantum Number
In physics and chemistry, the spin quantum number is a quantum number (designated ) that describes the intrinsic angular momentum (or spin angular momentum, or simply ''spin'') of an electron or other particle. It has the same value for all particles of the same type, such as = for all electrons. It is an integer for all bosons, such as photons, and a half-odd-integer for all fermions, such as electrons and protons. The component of the spin along a specified axis is given by the spin magnetic quantum number, conventionally written . The value of is the component of spin angular momentum, in units of the reduced Planck constant , parallel to a given direction (conventionally labelled the –axis). It can take values ranging from + to − in integer increments. For an electron, can be either or . Nomenclature The phrase ''spin quantum number'' refers to quantized spin angular momentum. The symbol is used for the spin quantum number, and is described as the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry-protected Topological Order
Symmetry-protected topological (SPT) order is a kind of order in absolute zero, zero-temperature quantum-mechanical states of matter that have a symmetry and a finite energy gap. To derive the results in a most-invariant way, renormalization group, renormalization group methods are used (leading to equivalence classes corresponding to certain fixed points). The SPT order has the following defining properties: (a) ''distinct SPT states with a given symmetry cannot be smoothly deformed into each other without a phase transition, if the deformation preserves the symmetry''. (b) ''however, they all can be smoothly deformed into the same trivial product state without a phase transition, if the symmetry is broken during the deformation''. The above definition works for both bosonic systems and fermionic systems, which leads to the notions of bosonic SPT order and fermionic SPT order. Using the notion of quantum entanglement, we can say that SPT states are short-range entanglement, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |