|
Syrigma
The whistling heron (''Syrigma sibilatrix'') is a medium-sized, often terrestrial heron of South America. There are two subspecies, the southern ''S. s. sibilatrix'' and the northern ''S. s. fostersmithi''. Description The whistling heron measures 53 to 64 cm in length and weighs 521 to 546 g. The southern subspecies is bigger but has a shorter bill in proportion to the body. The overall impression of standing birds is gray, with flying birds showing conspicuous white rear parts (lower back, belly, and tail). In both subspecies, adults' upperparts except the lower back are blue-gray. The feathers of the sides of head, sides of the neck, breast, and scapular area are basically white but are stained gold to buff, perhaps by the powder down typical of herons or by secretions of the preen gland; the color varies from bird to bird. In the nominate subspecies, the crown and crest (separate plumes up to 4 cm long on the nape) are black and the upper wing coverts are cinn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychus'' are referred to as bitterns, and, together with the zigzag heron, or zigzag bittern, in the monotypic genus ''Zebrilus'', form a monophyletic group within the Ardeidae. Egrets do not form a biologically distinct group from herons, and tend to be named differently because they are mainly white or have decorative plumes in breeding plumage. Herons, by evolutionary adaptation, have long beaks. The classification of the individual heron/egret species is fraught with difficulty, and no clear consensus exists about the correct placement of many species into either of the two major genera, '' Ardea'' and '' Egretta''. Similarly, the relationships of the genera in the family are not completely resolved. However, one species formerly consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantanal
The Pantanal () is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay. It sprawls over an area estimated at between . Various subregional ecosystems exist, each with distinct hydrological, geological and ecological characteristics; up to 12 of them have been defined.Susan Mcgrath, photos by Joel Sartore, ''Brazil's Wild Wet'', National Geographic Magazine, August 2005 Roughly 80% of the Pantanal floodplains are submerged during the rainy seasons, nurturing a biologically diverse collection of aquatic plants and helping to support a dense array of animal species. Etymology The name "Pantanal" comes from the Portuguese word ''pântano'' that means "big wetland", "big bog", "big swamp", "big quagmire" or "big marsh" plus the suffix ''-al'', that means "abundance, agglome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by humans, and is driven primarily by the availability of food. It occurs mainly in the northern hemisphere, where birds are funneled onto specific routes by natural barriers such as the Mediterranean Sea or the Caribbean Sea. Migration of species such as storks, turtle doves, and swallows was recorded as many as 3,000 years ago by Ancient Greek authors, including Homer and Aristotle, and in the Book of Job. More recently, Johannes Leche began recording dates of arrivals of spring migrants in Finland in 1749, and modern scientific studies have used techniques including bird ringing and satellite tracking to trace migrants. Threats to migratory birds have grown with habitat destruction, especially of stopover and wintering sites, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus ''Eucalyptus'' have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard or stringy, leaves with oil glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut". Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are native to Australia, and every state and territory has representative species. About three-quarters of Australian forests are eucalypt forests. Wildfire is a feature of the Australian landscape and many eucalypt species are adapted to fire, and resprout after fire or have seeds which survive fire. A few species are native to islands north of Australia and a smaller number are only found outside the continent. Eucalypts have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araucaria
''Araucaria'' (; original pronunciation: .ɾawˈka. ɾja is a genus of evergreen coniferous trees in the family Araucariaceae. There are 20 extant species in New Caledonia (where 14 species are endemic, see New Caledonian ''Araucaria''), Norfolk Island, eastern Australia, New Guinea, East Argentina, South Brazil, Chile and Paraguay. They are still common in the South Pacific rejoin and Eastern Australia. Description ''Araucaria'' are mainly large trees with a massive erect stem, reaching a height of . The horizontal, spreading branches grow in whorls and are covered with leathery or needle-like leaves. In some species, the leaves are narrow, awl-shaped and lanceolate, barely overlapping each other; in others they are broad and flat, and overlap broadly. The trees are mostly dioecious, with male and female cones found on separate trees, though occasional individuals are monoecious or change sex with time. The female cones, usually high on the top of the tree, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragonfly
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threatens dragonfly populations around the world. Adult dragonflies are characterized by a pair of large, multifaceted compound eyes, two pairs of strong, transparent wings, sometimes with coloured patches, and an elongated body. Many dragonflies have brilliant iridescent or metallic colours produced by structural colouration, making them conspicuous in flight. An adult dragonfly's compound eyes have nearly 24,000 ommatidia each. Dragonflies can be mistaken for the closely related damselflies, which make up the other odonatan infraorder ( Zygoptera) and are similar in body plan though usually lighter in build; however, the wings of most dragonflies are held flat and away from the body, while damselflies hold their wings folded at rest, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplomado Falcon
The aplomado falcon (''Falco femoralis'') is a medium-sized falcon of the Americas. The species' largest contiguous range is in South America, but not in the deep interior Amazon Basin. It was long known as ''Falco fusco-coerulescens'' or ''Falco fuscocaerulescens'', but these names are now believed to refer to the bat falcon (''F. rufigularis''). Its resemblance in shape to the hobbies accounts for its old name orange-chested hobby. ''Aplomado'' is an unusual Spanish word for " lead-colored", referring to the blue-grey areas of the plumage – an approximate English translation would be "plumbeous falcon". Spanish names for the species include ''halcón aplomado'' and ''halcón fajado'' (roughly "banded falcon" in reference to the characteristic pattern); in Brazil it is known as ''falcão-de-coleira''. Description The aplomado falcon is very slender, long-winged, and long-tailed, the size of a small peregrine falcon (''F. peregrinus''), at 12–16 in (30–40 cm) l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleptoparasitism
Kleptoparasitism (etymologically, parasitism by theft) is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is evolutionarily stable when stealing is less costly than direct feeding, which can mean when food is scarce or when victims are abundant. Many kleptoparasites are arthropods, especially bees and wasps, but including some true flies, dung beetles, bugs, and spiders. Cuckoo bees are specialized kleptoparasites which lay their eggs either on the pollen masses made by other bees, or on the insect hosts of parasitoid wasps. They are an instance of Emery's rule, which states that insect social parasites tend to be closely related to their hosts. The behavior occurs, too, in vertebrates including birds such as skuas, which persistently chase other seabirds until they disgorge their food, and carnivorous mammals such as spotted hyenas and lions. Other species opportunistically indulge in kleptoparasitism. Strategy Kleptoparasitism is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-headed Heron
The black-headed heron (''Ardea melanocephala'') is a wading bird of the heron family Ardeidae, common throughout much of sub-Saharan Africa and Madagascar. It is mainly resident, but some west African birds move further north in the rainy season. This species usually breeds in the wet season in colonies in trees, reedbeds or cliffs. It builds a bulky stick nest, and lays 2–4 eggs. It often feeds in shallow water, spearing fish or frogs with its long, sharp bill. It will also hunt well away from water, taking large insects, small mammals, and birds. It will wait motionless for its prey, or slowly stalk its victim. The black-headed heron is a large bird, standing 85 cm tall, and it has a 150 cm wingspan. It is nearly as large as the grey heron, which it resembles in appearance, although it is generally darker. Its plumage is largely grey above, and paler grey below. It has a powerful dusky bill. The flight is slow, with the neck retracted. This is characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
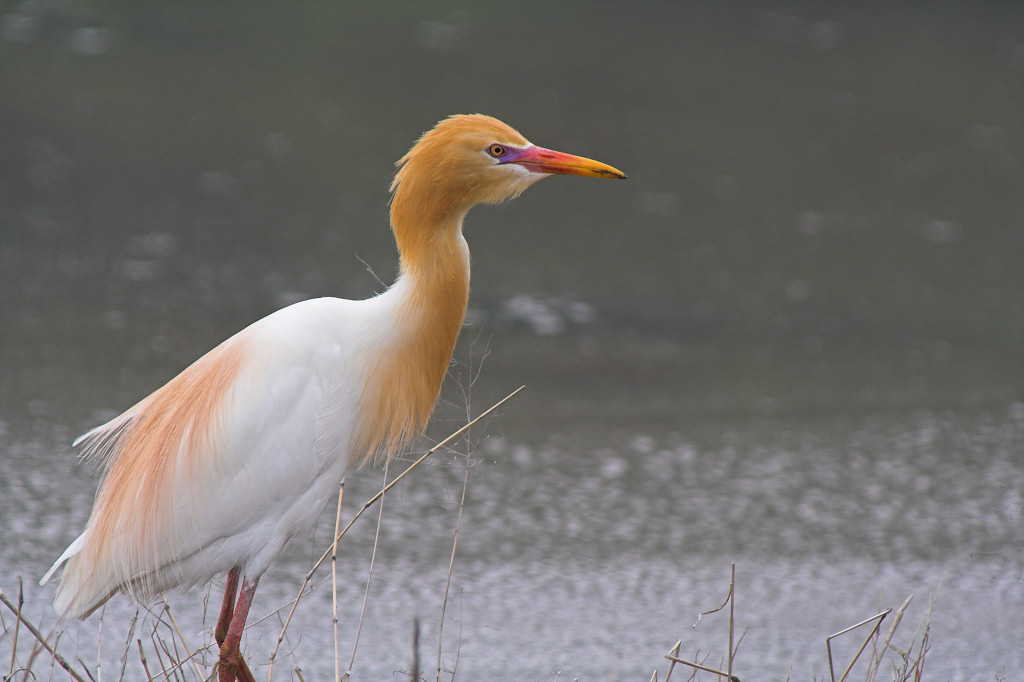
Cattle Egret
The cattle egret (''Bubulcus ibis'') is a cosmopolitan species of heron (family Ardeidae) found in the tropics, subtropics, and warm-temperate zones. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Bubulcus'', although some authorities regard its two subspecies as full species, the western cattle egret and the eastern cattle egret. Despite the similarities in plumage to the egrets of the genus '' Egretta'', it is more closely related to the herons of '' Ardea''. Originally native to parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe, it has undergone a rapid expansion in its distribution and successfully colonised much of the rest of the world in the last century. It is a white bird adorned with buff plumes in the breeding season. It nests in colonies, usually near bodies of water and often with other wading birds. The nest is a platform of sticks in trees or shrubs. Cattle egrets exploit drier and open habitats more than other heron species. Their feeding habitats include seasonally inunda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
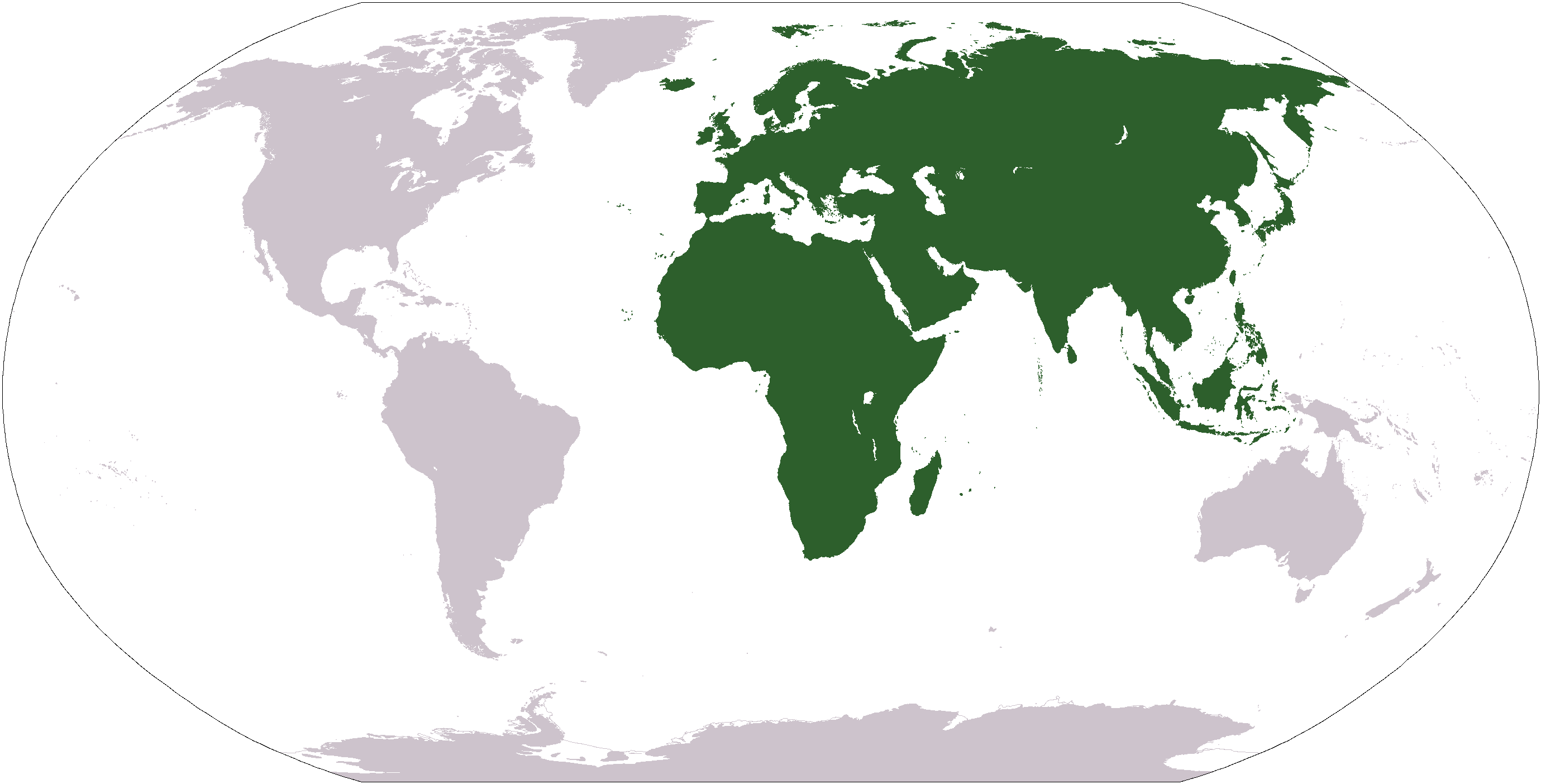
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they have a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |