|
Smacker Video
Smacker video is a video file format (with the ''.SMK'' file extension) developed by Epic Games Tools, and primarily used for full-motion video in video games. Smacker uses an adaptive 8-bit RGB palette. RAD's format for video at higher color depths is Bink Video. The Smacker format specifies a container format, a video compression format, and an audio compression format. Since its release in 1994, Smacker has been used in over 2300 games. Blizzard used this format for the cinematic videos seen in its games '' Warcraft II'', ''StarCraft'' and '' Diablo I''. The format has been reverse engineered and implemented in libavcodec. A non-commercial SourceForge project ''libsmacker'' released an open source decoder in 2013.SourceForge projeclibsmacker/ref> Technical details File format (container) Smacker defines its own container format. A Smacker file can contain a Smacker video track and up to seven audio tracks. Each audio track can have either one channel (mono) or two channels ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bink Smacker Video Logo , a hip-hop producer
{{disambig ...
Bink may refer to: * Bink (conjunction), a Mexican Asian; a mix of the slurs beaner and chink * Bink Video, a video format popular in many video games * Bink (The Magicians of Xanth), a character of the Xanth series by Piers Anthony * Bink (producer) Roosevelt Harrell III (born February 20, 1972), known professionally as Bink, is an American hip hop producer from Norfolk, Virginia, who is noted for his work with Roc-A-Fella Records artists. His most high-profile work has been Jay-Z's critic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palette (computing)
In computer graphics, a palette is the set of available colors from which an image can be made. In some systems, the palette is fixed by the hardware design, and in others it is dynamic, typically implemented via a color lookup table (CLUT), a correspondence table in which selected colors from a certain color space's color reproduction range are assigned an index, by which they can be referenced. By referencing the colors via an index, which takes less information than needed to describe the actual colors in the color space, this technique aims to reduce data usage, including processing, transfer bandwidth, RAM usage, and storage. Images in which colors are indicated by references to a CLUT are called indexed color images. Description As of 2019, the most common image colorspace in graphics cards is the RGB color model with 8 bits per pixel color depth. Using this technique, 8 bits per pixel are used to describe the luminance level in each of the RGB channels, therefore 24 bit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S3 Texture Compression
S3 Texture Compression (S3TC) (sometimes also called DXTn, DXTC, or BCn) is a group of related lossy texture compression algorithms originally developed by Iourcha et al. of S3 Graphics, Ltd. for use in their Savage 3D computer graphics accelerator. The method of compression is strikingly similar to the previously published Color Cell Compression, which is in turn an adaptation of Block Truncation Coding published in the late 1970s. Unlike some image compression algorithms (e.g. JPEG), S3TC's fixed-rate data compression coupled with the single memory access (cf. Color Cell Compression and some VQ-based schemes) made it well-suited for use in compressing textures in hardware-accelerated 3D computer graphics. Its subsequent inclusion in Microsoft's DirectX 6.0 and OpenGL 1.3 (via the GL_EXT_texture_compression_s3tc extension) led to widespread adoption of the technology among hardware and software makers. While S3 Graphics is no longer a competitor in the graphics accelerator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickTime Graphics
QuickTime Graphics is a lossy video compression and decompression algorithm (codec) developed by Apple Inc. and first released as part of QuickTime 1.x in the early 1990s. The codec is also known by the name Apple Graphics and its FourCC SMC. The codec operates on 8-bit palettized RGB data. The bit-stream format of QuickTime Graphics has been reverse-engineered and a decoder has been implemented in the projects XAnim and libavcodec. Technical Details The input video that the codec operates on is in an 8-bit palettized RGB colorspace. Compression is achieved by conditional replenishment and by reducing the palette from 256 colors to a per-4×4 block adaptive palette of 1-16 colors. Because Apple Video operates in the image domain without motion compensation, decoding is much faster than MPEG-style codecs which use motion compensation and perform coding in a transform domain. As a tradeoff, the compression performance of Apple Graphics is lower. The decoding complexity is app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Video 1
Microsoft Video 1 or MS-CRAM is an early lossy video compression and decompression algorithm (codec) that was released with version 1.0 of Microsoft's Video for Windows in November 1992. It is based on MotiVE, a vector quantization codec which Microsoft licensed from Media Vision. In 1993, Media Vision marketed the Pro Movie Spectrum, an ISA board that captured video in both raw and MSV1 formats (the MSV1 processing was done in hardware on the board). Compression algorithm Microsoft Video 1 operates either in an 8-bit palettized color space or in a 15-bit RGB color space. Each frame is split into 4×4 pixel blocks. Each 4×4 pixel block can be coded in one of three modes: skip, 2-color or 8-color. In skip mode, the content from the previous frame is copied to the current frame in a conditional replenishment fashion. In 2-color mode, two colors per 4×4 block are transmitted, and 1 bit per pixel is used to select between the two colors. In 8-color mode, the same scheme applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Video
Apple Video is a lossy video compression and decompression algorithm (codec) developed by Apple Inc. and first released as part of QuickTime 1.0 in 1991. The codec is also known as QuickTime Video, by its FourCC RPZA and the name Road Pizza. (The codename "Road Pizza" is a reference to the idea that "when you run over an animal, you're basically compressing it on the freeway".) When used in the AVI container, the FourCC AZPR is also used. The bit-stream format of Apple Video has been reverse-engineered and a decoder has been implemented in the projects XAnim and Libavcodec. Technical Details The codec operates on 4×4 blocks of pixels in the RGB colorspace. Each frame is segmented into 4×4 blocks in raster-scan order. Each block is coded in one of four coding modes: skip, single color, four color, or 16 color. Colors are represented by 16 bits with a bit-depth of 5 bit for each of the three components red, green, and blue, a format known as RGB555. Because Apple Video op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Quantization
In computer graphics, color quantization or color image quantization is quantization applied to color spaces; it is a process that reduces the number of distinct colors used in an image, usually with the intention that the new image should be as visually similar as possible to the original image. Computer algorithms to perform color quantization on bitmaps have been studied since the 1970s. Color quantization is critical for displaying images with many colors on devices that can only display a limited number of colors, usually due to memory limitations, and enables efficient compression of certain types of images. The name "color quantization" is primarily used in computer graphics research literature; in applications, terms such as ''optimized palette generation'', ''optimal palette generation'', or ''decreasing color depth'' are used. Some of these are misleading, as the palettes generated by standard algorithms are not necessarily the best possible. Algorithms Most standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indexed Color
In computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer computer data storage, memory and Hard disk drive, file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers. It is a form of Vector quantization#Use in data compression, vector quantization compression. When an image is encoding, encoded in this way, color information is not directly carried by the image pixel data, but is stored in a separate piece of data called a color lookup table (CLUT) or Palette (computing), palette: an array of color specifications. Every element in the array represents a color, indexed by its position within the array. Each image pixel does not contain the full specification of its color, but only its index into the ''palette''. This technique is sometimes referred as pseudocolor or indirect color, as colors are addressed indirectly. History Early graphics display systems that used 8-bit indexed color with frame buffers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Pulse Code Modulation
Differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) is a signal encoder that uses the baseline of pulse-code modulation (PCM) but adds some functionalities based on the prediction of the samples of the signal. The input can be an analog signal or a digital signal. If the input is a continuous-time analog signal, it needs to be sampled first so that a discrete-time signal is the input to the DPCM encoder. * Option 1: take the values of two consecutive samples; if they are analog samples, quantize them; calculate the difference between the first one and the next; the output is the difference. * Option 2: instead of taking a difference relative to a previous input sample, take the difference relative to the output of a local model of the decoder process; in this option, the difference can be quantized, which allows a good way to incorporate a controlled loss in the encoding. Applying one of these two processes, short-term redundancy (positive correlation of nearby values) of the signal is eli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
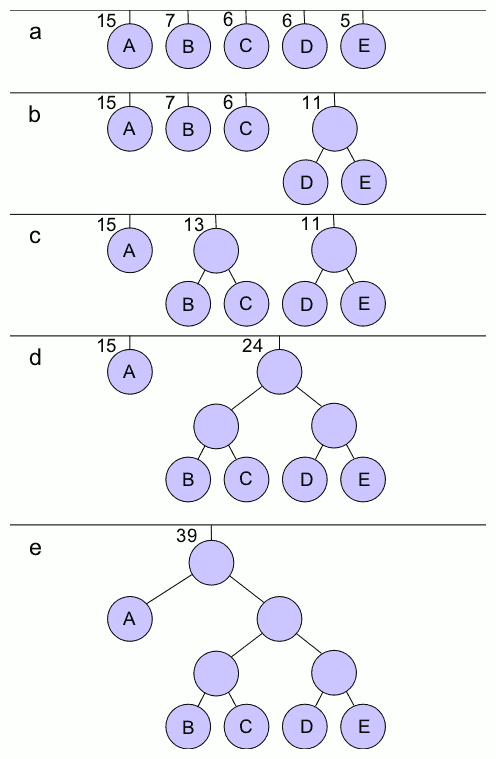
Huffman Coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Doctor of Science, Sc.D. student at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes". The output from Huffman's algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (''weight'') for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman's method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear time, linear to the number of input weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Coding
In information theory, an entropy coding (or entropy encoding) is any lossless data compression method that attempts to approach the lower bound declared by Shannon's source coding theorem, which states that any lossless data compression method must have an expected code length greater than or equal to the entropy of the source. More precisely, the source coding theorem states that for any source distribution, the expected code length satisfies \operatorname E_ ell(d(x))\geq \operatorname E_ \log_b(P(x))/math>, where \ell is the function specifying the number of symbols in a code word, d is the coding function, b is the number of symbols used to make output codes and P is the probability of the source symbol. An entropy coding attempts to approach this lower bound. Two of the most common entropy coding techniques are Huffman coding and arithmetic coding. If the approximate entropy characteristics of a data stream are known in advance (especially for signal compression), a simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Quantization
In computer graphics, color quantization or color image quantization is quantization applied to color spaces; it is a process that reduces the number of distinct colors used in an image, usually with the intention that the new image should be as visually similar as possible to the original image. Computer algorithms to perform color quantization on bitmaps have been studied since the 1970s. Color quantization is critical for displaying images with many colors on devices that can only display a limited number of colors, usually due to memory limitations, and enables efficient compression of certain types of images. The name "color quantization" is primarily used in computer graphics research literature; in applications, terms such as ''optimized palette generation'', ''optimal palette generation'', or ''decreasing color depth'' are used. Some of these are misleading, as the palettes generated by standard algorithms are not necessarily the best possible. Algorithms Most standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |