|
Ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biology and Evolution addresses th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminantia
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biology and Evolution addresses the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, the roe deer, and the moose. Male deer of all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. In this they differ from permanently horned antelope, which are part of a different family ( Bovidae) within the same order of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). The musk deer (Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains ( Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in herald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, the roe deer, and the moose. Male deer of all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. In this they differ from permanently horned antelope, which are part of a different family ( Bovidae) within the same order of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). The musk deer (Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains ( Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in herald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
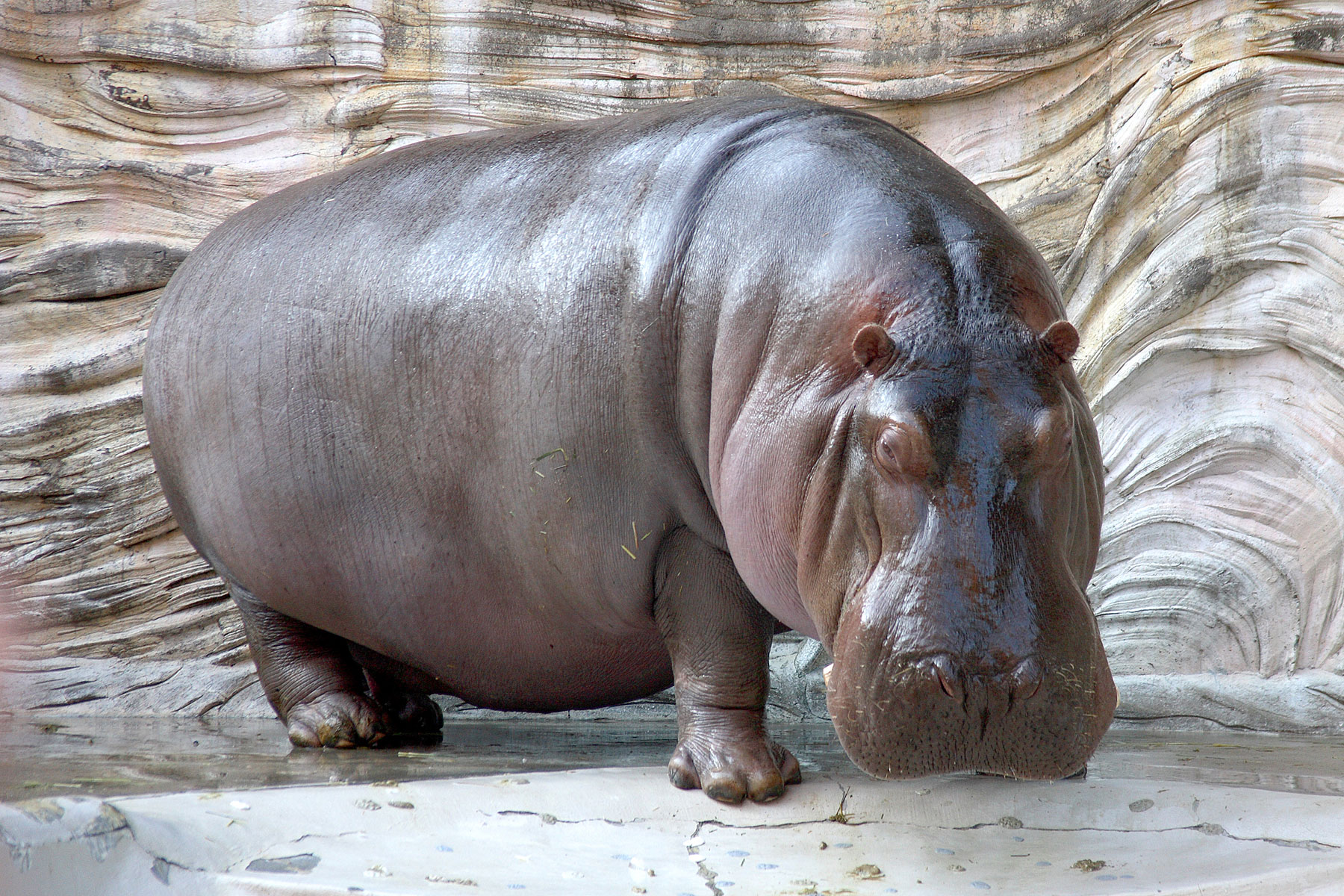
Pseudoruminant
Pseudoruminant is a classification of animals based on their digestive tract differing from the ruminants. Hippopotami and camels are ungulate mammals with a three-chambered stomach (ruminants have a four-chambered stomach) while equids (horses, asses, zebras) and rhinoceroses are monogastric herbivores. Anatomy Like ruminants, some pseudoruminants may use foregut fermentation to break down cellulose in fibrous plant species (while most others are hindgut fermenters with a large cecum The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, to which it is joined). The wo ...). But they have three-chambered stomachs (while others are monogastric) as opposed to ruminant stomachs which have four compartments. Species See also * Traditional ruminant References {{reflist Mammal taxonomy Animal anatomy Herb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteric Fermentation
Enteric fermentation is a digestive process by which carbohydrates are broken down by microorganisms into simple molecules for absorption into the bloodstream of an animal. Because of human agricultural reliance in many parts of the world on animals which digest by enteric fermentation, it is one of the factors in increased methane emissions. Ruminants Ruminant animals are those that have a rumen. A rumen is a multichambered stomach found almost exclusively among some artiodactyl mammals, such as cattle, sheep, and deer, enabling them to eat cellulose-enhanced tough plants and grains that monogastric (i.e., "single-chambered stomached") animals, such as humans, dogs, and cats, cannot digest. Although camels are thought to be ruminants they are not true ruminants. Enteric fermentation occurs when methane (CH4) is produced in the rumen as microbial fermentation takes place. Over 200 species of microorganisms are present in the rumen, although only about 10% of these play an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffidae
The Giraffidae are a family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a common ancestor with deer and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe (one or more species of '' Giraffa'', depending on taxonomic interpretation) and the okapi (the only known species of ''Okapia''). Both are confined to sub-Saharan Africa: the giraffe to the open savannas, and the okapi to the dense rainforest of the Congo. The two genera look very different on first sight, but share a number of common features, including a long, dark-coloured tongue, lobed canine teeth, and horns covered in skin, called ossicones. Taxonomy Evolutionary background The giraffids are ruminants of the clade Pecora. Other extant pecorans are the families Antilocapridae ( pronghorns), Cervidae (deer), Moschidae ( musk deer), and Bovidae ( cattle, goats and sheep, wildebeests and allies, and antelopes). The exact in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pecora
Pecora is an infraorder of even-toed hoofed mammals with ruminant digestion. Most members of Pecora have cranial appendages projecting from their frontal bones; only two extant genera lack them, ''Hydropotes'' and '' Moschus''. The name “Pecora” comes from the Latin word ''pecus'', which means “horned livestock”.Bubenik, A. Epigenetical, Morphological, Physiological, and Behavioral Aspects of Evolution of Horns, Pronghorns, and Antlers. in ''Horns, Pronghorns, and Antlers''. G. Bubenik and A. Bubenik eds. Springer-Verlag. New York. 1990 Although most pecorans have cranial appendages, only some of these are properly called “horns”, and many scientists agree that these appendages did not arise from a common ancestor, but instead evolved independently on at least two occasions.Janis, C., K. Scott. The Interrelationships of Higher Ruminant Families with Special Emphasis on the Members of the Cervoidea. ''American Museum Novitates''. 2893: 1-85. 1987. http://digitallibr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antilocapridae
The Antilocapridae are a family of artiodactyls endemic to North America. Their closest extant relatives are the giraffids with which they comprise the superfamily Giraffoidea. Only one species, the pronghorn (''Antilocapra americana''), is living today; all other members of the family are extinct. The living pronghorn is a small ruminant mammal resembling an antelope. Description In most respects, antilocaprids resemble other ruminants. They have a complex, four-chambered stomach for digesting tough plant matter, cloven hooves, and small, forked horns. Their horns resemble those of the bovids, in that they have a true horny sheath, but, uniquely, they are shed outside the breeding season, and subsequently regrown. Their lateral toes are even further diminished than in bovids, with the digits themselves being entirely lost, and only the cannon bones remaining. Antilocaprids have the same dental formula as most other ruminants: . Classification The antilocaprids are rum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, '' Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into up to eight extant species due to new research into their mitochondrial and nuclear DNA, as well as morphological measurements. Seven other extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil record. The giraffe's chief distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, its horn-like ossicones, and its spotted coat patterns. It is classified under the family Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Its scattered range extends from Chad in the north to South Africa in the south, and from Niger in the west to Somalia in the east. Giraffes usually inhabit savannahs and woodlands. Their food source is leaves, fru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
.jpg)




