|
List Of EC Numbers
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission number, Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) (Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NAD+ or Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase, Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase, Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** (R,R)-butanediol dehydrogenase, Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-xylulose Reductase
In enzymology, a D-xylulose reductase ( EC 1.1.1.9) is an enzyme that is classified as an Oxidoreductase (EC 1) specifically acting on the CH-OH group of donors (EC 1.1.1) that uses NAD+ or NADP+ as an acceptor (EC 1.1.1.9). This enzyme participates in pentose and glucuronate interconversions; a set of metabolic pathways that involve converting pentose sugars and glucuronate into other compounds. Nomenclature The systematic name of this enzyme class is xylitol:NAD+ 2-oxidoreductase (D-xylulose-forming). Other common names used include : * NAD+-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase * xylitol dehydrogenase* erythritol dehydrogenase (as this enzyme also acts as an L-erythrylose reductase) * 2,3-cis-polyol(DPN) dehydrogenase (C3-5) * pentitol-DPN dehydrogenase, and * xylitol-2-dehydrogenase EC number An Enzyme Commission (EC) number is a classification identifier given to all enzymes that helps identify their function and relationships to other enzymes. The EC number for D-xylulose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully Conjugated system, conjugated cyclic diketone, dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone" (thus the name of the class). Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (''ortho''-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone. The name is derived from that of quinic acid (with the suffix "-one" indicating a ketone), since it is one of the compounds obtained upon oxidation of quinic acid. Quinic acid, like quinine is obtained from cinchona bark, called quinaquina in the indigenous languages of Peruvian tribes. Properties Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups. In inorganic chemistry, the anion appears in a few rare minerals, but the functional group has tremendous importance in biochemistry. Disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Compounds of the form are usually called ''persulfides'' instead. Organic disulfides Structure Disulfides have a C–S–S–C dihedral angle approaching 90°. The S–S bond length is 2.03 Å in diphenyl disulfide, similar to that in elemental sulfur. Disulfides are usually symmetric but they can also be unsymmetric. Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organosulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
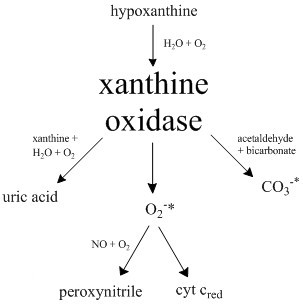
Xanthine Oxidase
Xanthine oxidase (XO or XAO) is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans. Xanthine oxidase is defined as an ''enzyme activity'' (EC 1.17.3.2). The same protein, which in humans has the HGNC approved gene symbol ''XDH'', can also have xanthine dehydrogenase activity (EC 1.17.1.4). Most of the protein in the liver exists in a form with xanthine dehydrogenase activity, but it can be converted to xanthine oxidase by reversible sulfhydryl oxidation or by irreversible proteolytic modification. "XDH xanthine dehydrogenase" Reaction The following chemical reactions are catalyzed by xanthine oxidase: * hypoxanthine + H2O + O2 xanthine + H2O2 * xanthine + H2O + O2 uric acid + H2O2 * Xanthine oxidase ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamine Oxidase
In enzymology, a thiamine oxidase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction ::thiamine + 2 O2 + H2O \rightleftharpoons thiamine acetic acid + 2 H2O2 The 3 substrates of this enzyme are thiamine, O2, and H2O, whereas its two products are thiamine acetic acid and H2O2. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with oxygen as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is thiamine:oxygen 5-oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include thiamin dehydrogenase, thiamine dehydrogenase, and thiamin:oxygen 5-oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in thiamine metabolism. It employs one cofactor, FAD A fad, trend, or craze is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation, or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short time period. Fads are objects or behaviors tha .... References * * * EC 1.1.3 Flavopr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-gulonolactone Oxidase
L-Gulonolactone oxidase ( ECbr>1.1.3.8 is an enzyme that produces vitamin C. It is expressed in most mammals, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini (a suborder of primates, including humans), in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone (2-keto-gulono-γ-lactone) and hydrogen peroxide. It uses FAD as a cofactor. The L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone then converts to ascorbic acid spontaneously, without enzymatic action. The structure of L-gulonolactone oxidase in rats helps identify characteristics of this enzyme. Gulonolactone oxidase deficiency The non-functional gulonolactone oxidase pseudogene (''GULOP'') was mapped to human chromosome 8p21, which corresponds to an evolutionarily conserved segment on either porcine chromosome 4 (SSC4) or 14 (SSC14). GULO produces the precursor to ascorbic acid, which spontaneously converts to the vitamin itself. The loss of activity of the gene encoding L-gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Oxidase
The glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx or GOD) also known as notatin (EC number 1.1.3.4) is an oxidoreductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present. Glucose oxidase is widely used for the determination of free glucose in body fluids (medical testing), in vegetal raw material, and in the food industry. It also has many applications in biotechnologies, typically enzyme assays for biochemistry including biosensors in nanotechnologies. It was first isolated by Detlev Müller in 1928 from ''Aspergillus niger''. Function Several species of fungi and insects synthesize glucose oxidase, which produces hydrogen peroxide, which kills bacteria. Notatin, extracted from antibacterial cultures of '' Penicillium notatum'', was originally named Penicillin A, but was renamed to avoid confusion with penicillin. Not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous (Fe(II)) to the ferric (Fe(III)) oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature. History Cytochromes were initially described in 1884 by Charles Alexander MacMunn as respiratory pigments (myohematin or histohematin). In the 1920s, Keilin rediscovered these respiratory pigments and na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia. HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and was long regarded as having seven transmembrane domains, with the active site located in a long carboxyl terminal domain in the cytosol. More recent evidence shows it to contain eight transmembrane domains. In humans, the gene for HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH) is located on the long arm of the fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) () and () is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate, producing alpha-ketoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) and CO2. This is a two-step process, which involves oxidation of isocitrate (a secondary alcohol) to oxalosuccinate (a ketone), followed by the decarboxylation of the carboxyl group beta to the ketone, forming alpha-ketoglutarate. In humans, IDH exists in three isoforms: IDH3 catalyzes the third step of the citric acid cycle while converting NAD+ to NADH in the mitochondria. The isoforms IDH1 and IDH2 catalyze the same reaction outside the context of the citric acid cycle and use NADP+ as a cofactor instead of NAD+. They localize to the cytosol as well as the mitochondrion and peroxisome. Structure The NAD-IDH is composed of three subunits, is allosterically regulated, and requires an integrated Mg2+ or Mn2+ ion. The closest homologue that has a known structure is the '' E. coli'' NADP-dependent IDH, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |