|
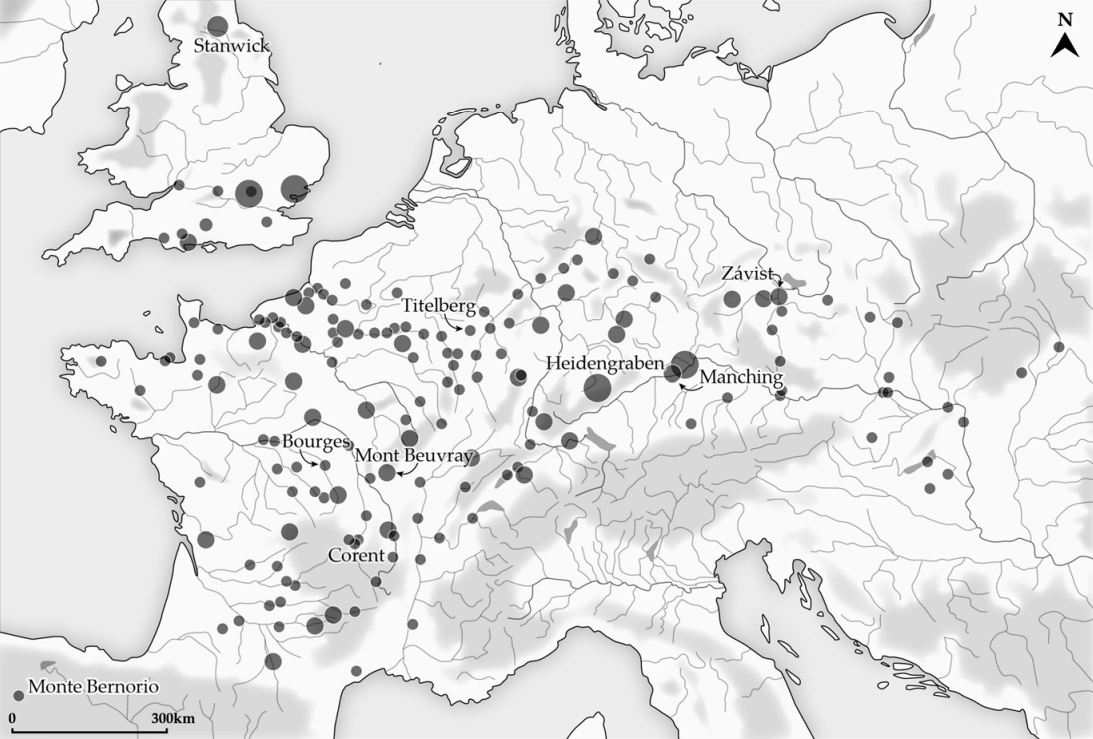
Glauberg
The Glauberg is a Celtic hillfort or oppidum in Hesse, Germany consisting of a fortified settlement and several burial mounds, "a princely seat of the late Hallstatt and early La Tène periods." Archaeological discoveries in the 1990s place the site among the most important early Celtic centres in Europe. It provides unprecedented evidence on Celtic burial, sculpture and monumental architecture. Location and topography Geologically, the Glauberg, a ridge (271 m asl) on the east edge of the Wetterau plain, is a basalt spur of the Vogelsberg range. Rising about 150 m above the surrounding areas, it is located between the rivers Nidder and Seeme and belongs to the community of Glauburg. The hilltop forms a nearly horizontal plateau of 800 by 80–200m. Its southwest promontory is known as Enzheimer Köpfchen. To the northwest, the Glauberg slopes steeply down towards the Nidder valley and, in the south, it is connected with undulating uplands. The plateau contained a small pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glauberg Digitales Geländemodell
The Glauberg is a Celts, Celtic hillfort or oppidum in Hesse, Germany consisting of a fortified settlement and several burial mounds, "a princely seat of the late Hallstatt culture, Hallstatt and early La Tène culture, La Tène periods." Archaeological discoveries in the 1990s place the site among the most important early Celtic centres in Europe. It provides unprecedented evidence on Celtic burial, sculpture and monumental architecture. Location and topography Geologically, the Glauberg, a ridge (271 m asl) on the east edge of the Wetterau plain, is a basalt spur of the Vogelsberg Mountains, Vogelsberg range. Rising about 150 m above the surrounding areas, it is located between the rivers Nidder and Seeme and belongs to the community of Glauburg. The hilltop forms a nearly horizontal plateau of 800 by 80–200m. Its southwest promontory is known as Enzheimer Köpfchen. To the northwest, the Glauberg slopes steeply down towards the Nidder valley and, in the south, it is connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallstatt Culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallstatt C, Hallstatt D) from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC (Bronze Age Europe, Late Bronze Age) and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations. It is named for its type site, Hallstatt, a lakeside village in the Austrian Salzkammergut southeast of Salzburg, Austria, Salzburg, where there was a rich salt mine, and some 1,300 burials are known, many with fine artifacts. Material from Hallstatt has been classified into four periods, designated "Hallstatt A" to "D". Hallstatt A and B are regarded as Late Bronze Age and the terms used for wider areas, such as "Hallstatt culture", or "period", "style" and so on, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glauburg
Glauburg is a municipality in the Wetteraukreis, in Hesse, Germany. It is located approximately 33 kilometers northeast of Frankfurt am Main. Glauburg is a municipality of Glauberg and Stockheim. The city hall of Glauburg is in Stockheim. The municipality was created in the municipal reform in 1971 from the districts of Glauberg and Stockheim. It is not far from the Bundesautobahn 45, A 45 autobahn (Giessen-Hanau). Glauburg-Stockheim station is at the junction of the Nidda Valley Railway, Frankfurt–Stockheim and the Gießen–Gelnhausen railway, Gießen–Gelnhausen lines. The valley in the neighborhood Nidder Glauburg has 3300 inhabitants and a good infrastructure, leading to a high standard of living and quality of life. Mountain birds are present in several protected areas around Glauberg, which has a number of hiking trails. History Documented Stockheim first appears 1198; Glauberg is mentioned in the year 802 the first time. Glauburg Upper Hesse is situated at the foot of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and the Culture of Golasecca, Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now Prehistory of France#The Iron Age, France, History of Belgium#Celtic and Roman periods, Belgium, Early history of Switzerland#Iron Age, Switzerland, History of Austria#Iron Age, Austria, History of England#Later Prehistory, England, History of Germany#Iron Age, Southern Germany, the History of the Czech lands#Iron Age, Czech Republic, Prehistoric Italy#Iron Age, Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
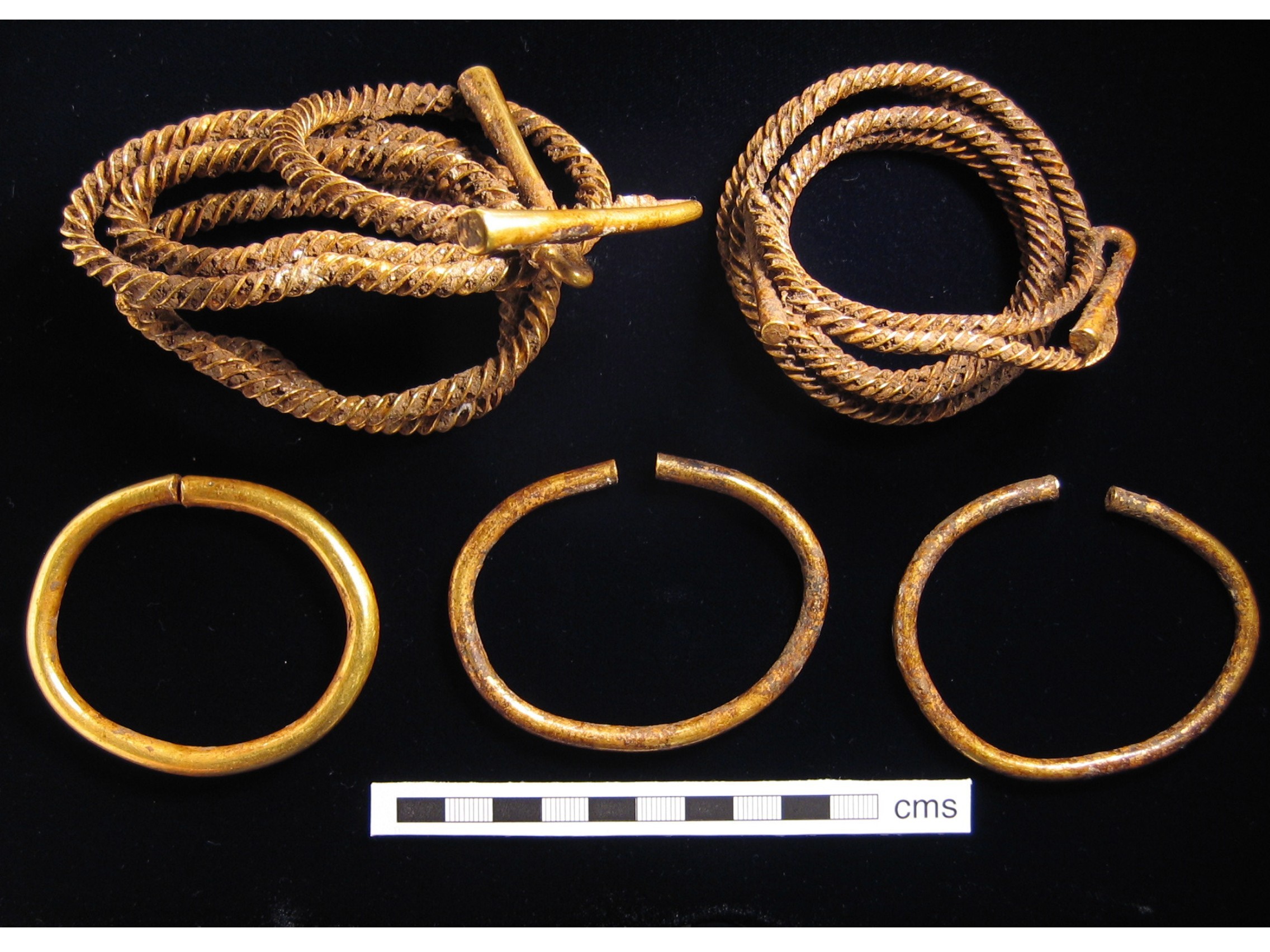
Torc
A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some have hook and ring closures and a few have mortice and tenon locking catches to close them. Many seem designed for near-permanent wear and would have been difficult to remove. Torcs have been found in Scythian, Illyrian, Thracian, Celtic, and other cultures of the European Iron Age from around the 8th century BC to the 3rd century AD. For Iron Age Celts, the gold torc seems to have been a key object. It identified the wearer—apparently usually female until the 3rd century BC, thereafter usually but not exclusively male—as a person of high rank, and many of the finest works of ancient Celtic art are torcs. Celtic torcs disappeared in the Migration Period, but during the Viking Age torc-style metal necklaces, mainly in silver, came back into fashion. Similar ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetterau
The Wetterau (, ) is a fertile undulating tract, watered by the Wetter (river), Wetter, a tributary of the Nidda (river), Nidda River, in the western German state of Hesse, between the hilly province Oberhessen and the north-western Taunus mountains. Bettina von Arnim writes of Wetterau in her text ''Diary of a Child'' in the chapter "Journey to the Wetterau". Geography The Wetterau is located north of Frankfurt am Main, on the eastern side of the Taunus and south-west of the Vogelsberg_Mountains, Vogelsberg. The main part of the region is taken up by the political region Wetteraukreis. The region got its name from the small creek Wetter (river), Wetter, but the region is crossed by several other creeks and rivers - for example, the Nidda (river), Nidda, Nidder, Horloff and Usa (Germany), Usa. History The Wetterau has a long history and is one of the oldest cultural landscapes in Germany. It was always a very fertile region and was populous from as early as the Neolithic Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesse
Hesse or Hessen ( ), officially the State of Hesse (), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major historic cities are Darmstadt and Kassel. With an area of 21,114.73 square kilometers and a population of over six million, it ranks seventh and fifth, respectively, among the sixteen German states. Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Germany's second-largest metropolitan area (after Rhine-Ruhr), is mainly located in Hesse. As a cultural region, Hesse also includes the area known as Rhenish Hesse (Rheinhessen) in the neighboring state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Etymology The German name , like the names of other German regions ( "Swabia", "Franconia", "Bavaria", "Saxony"), derives from the dative plural form of the name of the inhabitants or German tribes, eponymous tribe, the Hessians (, singular ). The geographical name represents a short equivalent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213 CE, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, which by the eighth century were collectively referred to as '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by the Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, however, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes Germanicus
The (Latin for ''Germanic frontier''), or 'Germanic Limes', is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier () fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubdued Germanic tribes from the years 83 to about 260 AD. The frontier used either a natural boundary such as a river or typically an earth bank and ditch with a wooden palisade and watchtowers at intervals, and a system of linked forts was built behind them. The path of the limes changed over time following advances and retreats due to pressure from external threats. At its height, the Limes Germanicus stretched from the North Sea outlet of the Rhine to near Regensburg (Castra Regina) on the Danube. These two major rivers afforded natural protection from mass incursions into imperial territory, with the exception of a gap stretching roughly from Roman Mogontiacum, Mogontiacum (now Mainz) on the Rhine to Castra Regina. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |