Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. Its capital city is
Wiesbaden, and the largest
urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities ...
is
Frankfurt
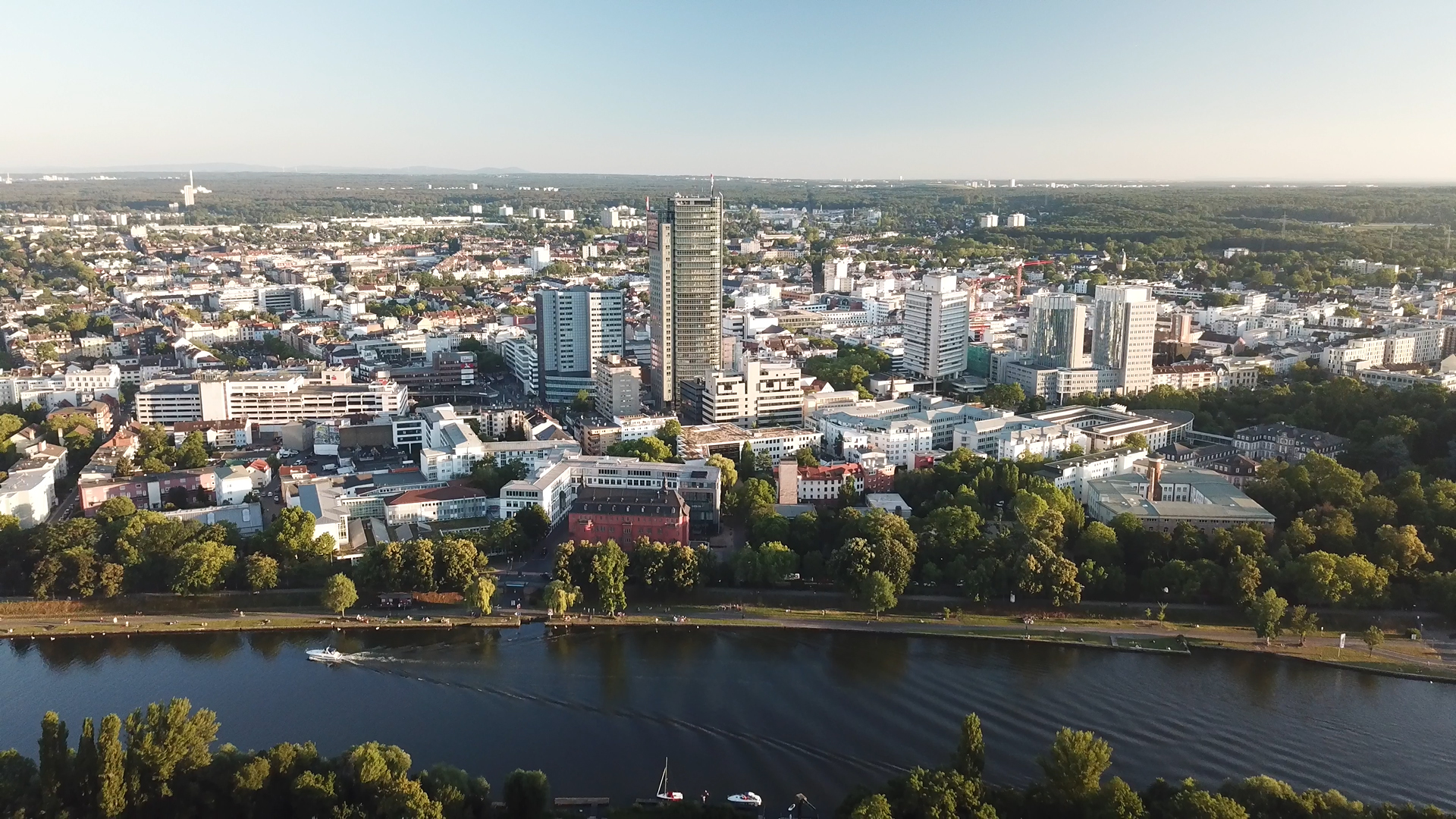
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
. Two other major historic cities are
Darmstadt and
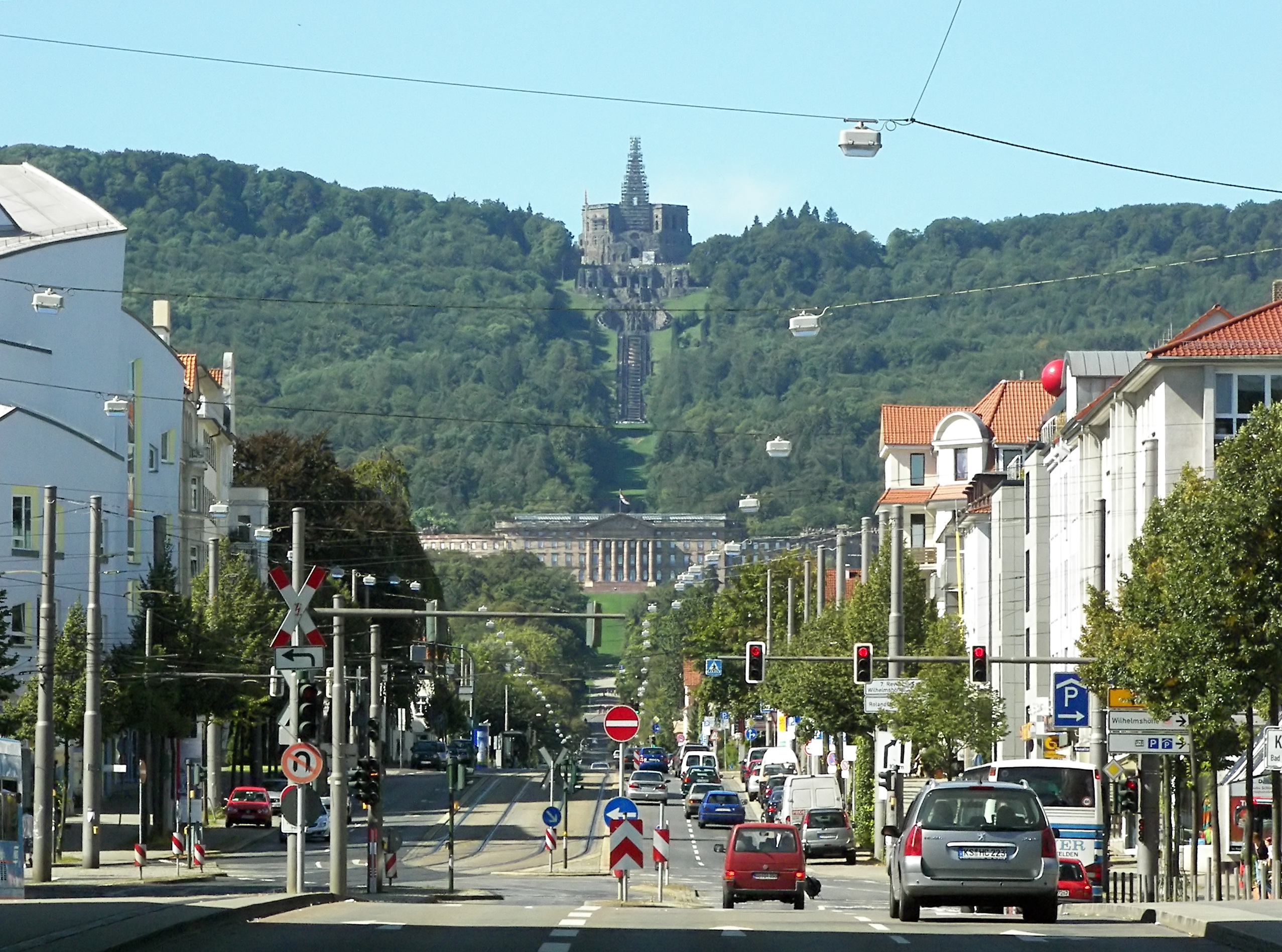
Kassel. With an area of 21,114.73 square kilometers and a population of just over six million, it ranks seventh and fifth, respectively, among the sixteen German states.
Frankfurt Rhine-Main
The Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region, often simply referred to as Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Frankfurt Rhine-Main area or Rhine-Main area (German: ''Rhein-Main-Gebiet'' or ''Frankfurt/Rhein-Main'', abbreviated FRM), is the second-largest metropolitan re ...
, Germany's second-largest metropolitan area (after
Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region (german: Metropolregion Rhein-Ruhr) is the largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the region covers ...
), is mainly located in Hesse.
As a
cultural region
In anthropology and geography, a cultural region, cultural sphere, cultural area or culture area refers to a geography with one relatively homogeneous human activity or complex of activities (culture). Such activities are often associated ...
, Hesse also includes the area known as
Rhenish Hesse
Rhenish Hesse or Rhine HesseDickinson, Robert E (1964). ''Germany: A regional and economic geography'' (2nd ed.). London: Methuen, p. 542. . (german: Rheinhessen) is a region and a former government district () in the German state of Rhineland- ...
(Rheinhessen) in the neighbouring state of
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
.
Name
The German name ''
Hessen
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Darms ...
'', like the names of other German regions (''Schwaben'' "Swabia", ''Franken'' "Franconia", ''Bayern'' "Bavaria", ''Sachsen'' "Saxony"), derives from the dative plural form of the name of the inhabitants or
eponymous tribe, the Hessians (''Hessen'', singular ''Hesse''). The geographical name represents a short equivalent of the older compound name ''Hessenland'' ("land of the Hessians"). The
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
form of the name is recorded as ''Hessun'' (dative plural of ''Hessi''); in
Middle Latin it appears as ''Hassia'', ''Hessia'', ''Hassonia''. The name of the Hessians ultimately continues the tribal name of the ''
Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the va ...
''.
The ancient name ''Chatti'' by the 7th century is recorded as ''Chassi'', and from the 8th century as ''Hassi'' or ''Hessi''.
An inhabitant of Hesse is called a "Hessian" (German: ''
Hesse'' (masculine), plural ''Hessen'', or ''Hessin'' (feminine), plural ''Hessinnen'').
The
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances i ...
term
"Hessian" for 18th-century British auxiliary troops originates with Landgrave
Frederick II of
Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the Lan ...
hiring out regular army units to the government of Great Britain to fight in the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
.
The English form ''Hesse'' was in common use by the 18th century, first in the hyphenated names of the states of ''Hesse-Cassel'' and ''Hesse-Darmstadt'', but the latinate form ''Hessia'' remained in common English usage well into the 19th century.
The
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
uses the German form ''Hessen'', even in English-language contexts, due to the policy of leaving regional names untranslated.
The
synthetic element
A synthetic element is one of 24 known chemical elements that do not occur naturally on Earth: they have been created by human manipulation of fundamental particles in a nuclear reactor, a particle accelerator, or the explosion of an atomic bomb; ...
hassium
Hassium is a chemical element with the symbol Hs and the atomic number 108. Hassium is highly radioactive; its most stable known isotopes have half-lives of approximately ten seconds. One of its isotopes, 270Hs, has magic numbers of both protons ...
, number 108 on the
periodic table, was named after the state of Hesse in 1997, following a proposal of 1992.
History
The territory of Hesse was delineated only in 1945, as
Greater Hesse, under
American occupation. It corresponds only loosely to the medieval
Landgraviate of Hesse
The Landgraviate of Hesse (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen) was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire. It existed as a single entity from 1264 to 1567, when it was divided among the sons of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse.
History
In the early Midd ...
.
In the 19th century, prior to the
unification of Germany, the territory of what is now Hesse comprised the territories of
Grand Duchy of Hesse, the
Duchy of Nassau
The Duchy of Nassau (German: ''Herzogtum Nassau'') was an independent state between 1806 and 1866, located in what is now the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse. It was a member of the Confederation of the Rhine and later of the G ...
, the free city of
Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
and the
Electorate of Hesse
The Electorate of Hesse (german: Kurfürstentum Hessen), also known as Hesse-Kassel or Kurhessen, was a landgraviate whose prince was given the right to elect the Emperor by Napoleon. When the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, its p ...
(also known as Hesse-Cassel).
Early history
The Central Hessian region was inhabited in the
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
.
Finds of tools in southern Hesse in Rüsselsheim suggest the presence of Pleistocene hunters about 13,000 years ago. A
fossil hominid skull that was found in northern Hesse, just outside the village of Rhünda, has been dated at 12,000 years ago.
The
Züschen tomb (German: Steinkammergrab von Züschen, sometimes also Lohne-Züschen) is a prehistoric burial monument, located between
Lohne and
Züschen, near
Fritzlar, Hesse, Germany. Classified as a gallery grave or a Hessian-Westphalian stone
cist
A cist ( or ; also kist ;
from grc-gre, κίστη, Middle Welsh ''Kist'' or Germanic ''Kiste'') is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Examples can be found across Europe and in the Middle Ea ...
(''hessisch-westfälische Steinkiste''), it is one of the most important
megalithic monuments in Central Europe. Dating to c. 3000 BC, it belongs to the Late
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Wartberg culture
The Wartberg culture (german: Wartbergkultur), sometimes: Wartberg group (''Wartberggruppe'') or Collared bottle culture (''Kragenflaschenkultur'') is a prehistoric culture from 3,600 -2,800 BC of the later Central European Neolithic. It is named ...
.
An early
Celtic presence in what is now Hesse is indicated by a mid-5th-century BC
La Tène-style burial uncovered at
Glauberg
The Glauberg is a Celtic oppidum in Hesse, Germany consisting of a fortified settlement and several burial mounds, "a princely seat of the late Hallstatt and early La Tène periods." Archaeological discoveries in the 1990s place the site among ...
. The region was later settled by the
Germanic Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the va ...
tribe around the 1st century BC, and the name ''Hesse'' is a continuation of that tribal name.
The
ancient Romans
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 ...
had a military camp in Dorlar, and in Waldgirmes directly on the eastern outskirts of Wetzlar was a civil settlement under construction. Presumably, the provincial government for the occupied territories of the right bank of Germania was planned at this location. The governor of Germania, at least temporarily, likely had resided here. The settlement appears to have been abandoned by the Romans after the devastating
Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius Quinctilius ...
failed in the year AD 9. The Chatti were also involved in the
Revolt of the Batavi in AD 69.
Hessia, from the early 7th century on, served as a buffer between areas dominated by the
Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
(to the north) and the
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, who brought the area to the south under their control in the early sixth century and occupied
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
(to the east) in 531. Hessia occupies the northwestern part of the modern German state of Hesse; its borders were not clearly delineated. Its geographic center is
Fritzlar; it extends in the southeast to
Hersfeld on the river Fulda, in the north to past
Kassel and up to the rivers Diemel and Weser. To the west, it occupies the valleys of the rivers Eder and Lahn (the latter until it turns south). It measured roughly 90 kilometers north–south, and 80 north-west.
The area around Fritzlar shows evidence of significant pagan belief from the 1st century on. Geismar was a particular focus of such activity; it was continuously occupied from the Roman period on, with a settlement from the Roman period, which itself had a predecessor from the 5th century BC. Excavations have produced a
horse burial
Horse burial is the practice of burying a horse as part of the ritual of human burial, and is found among many Indo-European speaking peoples and others, including Chinese and Turkic peoples. The act indicates the high value placed on horses in ...
and bronze artifacts. A possible religious cult may have centered on a natural spring in Geismar, called ''Heilgenbron''; the name "Geismar" (possibly "energetic pool") itself may be derived from that spring.
The village of , now a part of
Gudensberg
Gudensberg () is a small town in northern Hesse, Germany. Since the municipal reform in 1974, the nearby villages of Deute, Dissen, Dorla, Gleichen, Maden and Obervorschütz have become parts of the municipality.
Geography
Gudensberg is situated ...
near Fritzlar and less than ten miles from Geismar, was likely an ancient religious center; the basaltic outcrop of Gudensberg is named after Wodan, and a two-meter tall
quartzite megalith called the ''
Wotanstein'' is at the center of the village.
By the mid-7th century, the Franks had established themselves as overlords, which is suggested by archeological evidence of burials, and they built fortifications in various places, including
Christenberg. By 690, they took direct control over Hessia, apparently to counteract expansion by the Saxons, who built fortifications in
Gaulskopf and
Eresburg across the river Diemel, the northern boundary of Hessia. The
Büraburg
The Büraburg was a prominent hill castle with historic significance, on the Büraberg hill overlooking the Eder river near the town of Fritzlar in northern Hesse (Germany). Only foundation walls remain, and a church dedicated to St. Brigida.
...
(which already had a Frankish settlement in the sixth century) was one of the places the Franks fortified to resist the Saxon pressure, and according to John-Henry Clay, the Büraburg was "probably the largest man-made construction seen in Hessia for at least seven hundred years". Walls and trenches totaling one kilometer in length were made, and they enclosed "8 hectares of a spur that offered a commanding view over Fritzlar and the densely-populated heart of Hessia".
Following Saxon incursions into Chattish territory in the 7th century, two ''
gaue'' had been established; a Frankish one, comprising an area around
Fritzlar and
Kassel, and a Saxonian one. In the 9th century, the Saxon
Hessengau also came under the rule of the Franconians.
Holy Roman Empire

From 962 the land which would become Hesse was part of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
. In the 10th and 11th centuries it was mostly encompassed by the
Western or Rhenish part of the
stem duchy of
Franconia.
In the 12th century,
Hessengau passed to the
Landgraviate of Thuringia. As a result of the
War of the Thuringian Succession (1247–1264) the former Thuringian lands were partitioned between the
Wettin Margraviate of Meissen, which gained Thuringia proper, and the new
Landgraviate of Hesse
The Landgraviate of Hesse (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen) was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire. It existed as a single entity from 1264 to 1567, when it was divided among the sons of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse.
History
In the early Midd ...
, which remained with the
Ludovingians
The Ludovingians or Ludowingians (german: Ludowinger) were the ruling dynasty of Thuringia and Hesse during the 11th to 13th centuries.
Their progenitor was Louis the Bearded who was descended from a noble family whose genealogy cannot be pre ...
. From that point on the Ludovingian coat of arms came to represent both Thuringia and Hesse.
It rose to prominence under Landgrave
Philip the Magnanimous, who was one of the leaders of German
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. After Philip's death in 1567, the territory was divided among his four sons from his first marriage (Philip was a
bigamist
In cultures where monogamy is mandated, bigamy is the act of entering into a marriage with one person while still legally married to another. A legal or de facto separation of the couple does not alter their marital status as married persons. I ...
) into four lines:
Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the Lan ...
(or Hesse-Cassel),
Hesse-Darmstadt
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Darmstadt) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a younger branch of the House of Hesse. It was formed in 1567 following the division of the Landgraviate of Hesse betwee ...
,
Hesse-Rheinfels Hesse-Rheinfels was created as a cadet line of Hesse for Philip II, Landgrave of Hesse-Rheinfels (1541–1583), landgrave from 1567 until 1583, and as a cadet line of Hesse-Kassel for Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Rheinfels (1623–1693), landgrave ...
, and the also previously existing
Hesse-Marburg. As the latter two lines died out quite quickly (1583 and 1605, respectively), Hesse-Kassel and Hesse-Darmstadt were the two core states within the Hessian lands. Several collateral lines split off during the centuries, such as in 1622, when
Hesse-Homburg
Hesse-Homburg was formed into a separate landgraviate in 1622 by the landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt; it was to be ruled by his son, although it did not become independent of Hesse-Darmstadt until 1668. It was briefly divided into Hesse-Homburg and ...
split off from Hesse-Darmstadt, and in 1760 when
Hesse-Hanau
Hesse-Hanau was a territory in the Holy Roman Empire. It emerged when the former county of Hanau-Münzenberg became a secundogeniture of Hesse-Cassel in 1760. When the reigning count, William IX, also became landgrave of Hesse-Cassel in 1785, th ...
split off from Hesse-Kassel. In the late 16th century, Kassel adopted
Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
, while Darmstadt remained
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
and consequently the two lines often found themselves on opposing sides of conflicts, most notably in the disputes over Hesse-Marburg and in the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
, when Darmstadt fought on the side of the Emperor, while Kassel sided with
Sweden and
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
.

The Landgrave
Frederick II (1720–1785) ruled Hesse-Kassel as a benevolent despot, from 1760 to 1785. He combined
Enlightenment ideas with Christian values,
cameralist plans for central control of the economy, and a militaristic approach toward diplomacy. He funded the depleted treasury of the poor government by loaning 19,000 soldiers in complete military formations to
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
to fight in North America during the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, 1776–1783. These soldiers, commonly known as
Hessians, fought under the British flag. The British used the Hessians in several conflicts, including in the
Irish Rebellion of 1798
The Irish Rebellion of 1798 ( ga, Éirí Amach 1798; Ulster-Scots: ''The Hurries'') was a major uprising against British rule in Ireland. The main organising force was the Society of United Irishmen, a republican revolutionary group influenced ...
. For further revenue, the soldiers were loaned to other places as well. Most were conscripted, with their pay going to the Landgrave.
Modern history

French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars
In 1789 the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
began and in 1794, during the
War of the First Coalition, the
French Republic occupied the
Left Bank of the Rhine, including part of Lower Katzenelnbogen (, Hesse-Kassel's part of the former
County of Katzenelnbogen which was held by the
appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; french: apanage ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a sovereign, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture. It was common in much o ...
Hesse-Rotenburg
Hesse-Rotenburg is a former German landgraviate created from the landgraviate of Hesse-Cassel in 1627. Its independence ended in 1834 when the estates not bequeathed to princes Victor and Chlodwig of Hohenlohe-Waldenburg-Schillingsfürst were reu ...
).
Emperor Francis II
Francis II (german: Franz II.; 12 February 1768 – 2 March 1835) was the last Holy Roman Emperor (from 1792 to 1806) and the founder and Emperor of the Austrian Empire, from 1804 to 1835. He assumed the title of Emperor of Austria in response ...
formally recognised the annexation of the Left Bank in the 1801
Treaty of Lunéville. This led in 1803 to the , a substantial reorganisation (
mediatisation Mediatization or mediatisation may refer to:
* German mediatisation
German mediatisation (; german: deutsche Mediatisierung) was the major territorial restructuring that took place between 1802 and 1814 in Germany and the surrounding region by ...
) of the states and territories of the Empire. Several
exclaves of
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
were mediatised to
Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the Lan ...
and
Hesse-Darmstadt
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Darmstadt) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a younger branch of the House of Hesse. It was formed in 1567 following the division of the Landgraviate of Hesse betwee ...
, and Hesse-Darmstadt also gained the
Duchy of Westphalia from
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
, the parts of
Worms on the right-bank of the Rhine, and the former
Free City of
Friedberg.
Nassau-Weilburg
The House of Nassau-Weilburg, a branch of the House of Nassau, ruled a division of the County of Nassau, which was a state in what is now Germany, then part of the Holy Roman Empire, from 1344 to 1806.
On 17 July 1806, upon the dissolution of t ...
gained the right-bank territories of
Trier among other territories.
Orange-Nassau gained the
Prince-Bishopric of Fulda (as the
Principality of Nassau-Orange-Fulda). The
Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel was also elevated to the status of
Prince-Elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prin ...
(), with his state thereby becoming the
Electorate of Hesse
The Electorate of Hesse (german: Kurfürstentum Hessen), also known as Hesse-Kassel or Kurhessen, was a landgraviate whose prince was given the right to elect the Emperor by Napoleon. When the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, its p ...
or Electoral Hesse (german: Kurhessen, link=no, being the German-language term for the Empire's
College of Electors
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prince ...
).
In July 1806 Hesse-Darmstadt, Nassau-Weilburg,
Nassau-Usingen, and the newly-merged
Principality of Isenburg became founding members of
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
. Hesse-Darmstadt expanded further in the resulting mediatisation, absorbing numerous small states (including
Hesse-Homburg
Hesse-Homburg was formed into a separate landgraviate in 1622 by the landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt; it was to be ruled by his son, although it did not become independent of Hesse-Darmstadt until 1668. It was briefly divided into Hesse-Homburg and ...
and much of the territory of the Houses of , and
Sayn-Wittgenstein). It was also elevated by Napoleon to the status of
Grand Duchy, becoming the
Grand Duchy of Hesse. Orange-Nassau, which refused to join the Confederation, lost
Siegen,
Dillenburg
Dillenburg, officially Oranienstadt Dillenburg, is a town in Hesse's Gießen region in Germany. The town was formerly the seat of the old Dillkreis district, which is now part of the Lahn-Dill-Kreis.
The town lies on the German- Dutch holiday road ...
,
Hadamar
Hadamar is a small town in Limburg-Weilburg district in Hesse, Germany.
Hadamar is known for its Clinic for Forensic Psychiatry/Centre for Social Psychiatry, lying at the edge of town, in whose outlying buildings is also found the Hadamar Mem ...
and
Beilstein to
Berg Berg may refer to:
People
*Berg (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name)
*Berg Ng (born 1960), Hong Kong actor
* Berg (footballer) (born 1989), Brazilian footballer
Former states
* Berg (state), county and duchy of the Hol ...
and Fulda to the
Prince-Primate of the Confederation (and former Elector of Mainz)
Karl Theodor von Dalberg; the remainder of its territory was merged with that of Nassau-Usingen and Nassau-Weilburg in August 1806 to form the
Duchy of Nassau
The Duchy of Nassau (German: ''Herzogtum Nassau'') was an independent state between 1806 and 1866, located in what is now the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse. It was a member of the Confederation of the Rhine and later of the G ...
.
Waldeck also joined the Confederation in 1807.
The Holy Roman Empire was dissolved in August 1806, rendering Hesse-Kassel's electoral privilege meaningless. Hesse-Kassel was occupied by the French in October 1806 and the remainder of Lower Katzenelnbogen was annexed to the
French Empire as . The rest of its territory was annexed to the
Kingdom of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a kingdom in Germany, with a population of 2.6 million, that existed from 1807 to 1813. It included territory in Hesse and other parts of present-day Germany. While formally independent, it was a vassal state of the ...
in 1807;
Hesse-Hanau
Hesse-Hanau was a territory in the Holy Roman Empire. It emerged when the former county of Hanau-Münzenberg became a secundogeniture of Hesse-Cassel in 1760. When the reigning count, William IX, also became landgrave of Hesse-Cassel in 1785, th ...
(a
secundogeniture of Hesse-Kassel) was annexed to the
Grand Duchy of Frankfurt in 1810 along with the other territories held by the Prince-primate: Frankfurt, Fulda,
Aschaffenburg
Aschaffenburg (; South Franconian German, South Franconian: ''Aschebersch'') is a town in northwest Bavaria, Germany. The town of Aschaffenburg is not part of the Aschaffenburg (district), district of Aschaffenburg, but is its administrative sea ...
and
Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
.
As a result of the
German campaign of 1813
The German campaign (german: Befreiungskriege , lit=Wars of Liberation ) was fought in 1813. Members of the Sixth Coalition, including the German states of Austria and Prussia, plus Russia and Sweden, fought a series of battles in Germany ag ...
the Kingdom of Westphalia and the Grand Duchy of Frankfurt were dissolved and Hesse-Kassel and Hesse-Hanau were restored; Orange-Nassau was also restored in its territories previously lost to Berg.
As a result of the 1815
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
Hesse-Kassel gained Fulda (roughly the western third of the former Prince-Bishopric, the rest of which went to
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
and
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was a historical German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was ra ...
) from Frankfurt and part of Isenburg, while several of its small northern
exclaves were absorbed into
Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
, some small eastern areas were ceded to Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach and Lower Katzenelnbogen was ceded to Nassau. Hesse-Darmstadt lost the Duchy of Westphalia and the Sayn-Wittgensteiner lands to the
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n
Province of Westphalia but gained territory on the left bank of the Rhine centred on Mainz, which became known as
Rhenish Hesse
Rhenish Hesse or Rhine HesseDickinson, Robert E (1964). ''Germany: A regional and economic geography'' (2nd ed.). London: Methuen, p. 542. . (german: Rheinhessen) is a region and a former government district () in the German state of Rhineland- ...
(), and the remainder of Isenburg. Orange-Nassau, whose ruler was now also King
William I of
the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Grand Duke of Luxembourg, was ceded to Prussia but most of its territory aside from Siegen was then ceded on to Nassau. Hesse-Homburg and the
Free City of Frankfurt were also restored.
While the other former Electors had gained other titles, becoming either Kings or
Grand Dukes, the Elector of Hesse-Kassel alone retained the anachronistic title of Prince-Elector; a request to be recognised as "King of the
Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the va ...
" () was rejected by the Congress.
Following the mediatisations and the Congress of Vienna significantly fewer states remained in the region that is now Hesse: the Hessian states, Nassau, Waldeck and Frankfurt. The Kingdoms of Prussia and Bavaria also held some territory in the region. The Congress also established the
German Confederation, of which they all became members. Hesse-Hanau was (re-)absorbed into Hesse-Kassel in 1821.
German Empire
In the 1866
Austro-Prussian War the states of the region allied with
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
were defeated during the
Campaign of the Main. Following Prussia's victory and dissolution of the German Confederation, Prussia annexed Electoral Hesse, Frankfurt, Hesse-Homburg, Nassau and small parts of Bavaria and the Grand Duchy of Hesse, which were then combined into the
Province of Hesse-Nassau. The name survived, denoting the region around Kassel. The Grand Duchy of Hesse retained its autonomy in defeat because a greater part of the country was situated south of the river
Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
and it was feared that Prussian expansion beyond the Main might provoke France. However,
Upper Hesse
The term Upper Hesse (german: Provinz Oberhessen) originally referred to the southern possessions of the Landgraviate of Hesse, which were initially geographically separated from the more northerly Lower Hesse by the .
Later, it became the name o ...
(german: Oberhessen, link=no: the parts of Hesse-Darmstadt north of the Main around the town of
Gießen
Giessen, spelled Gießen in German (), is a town in the German state (''Bundesland'') of Hesse, capital of both the district of Giessen and the administrative region of Giessen. The population is approximately 90,000, with roughly 37,000 univers ...
) was incorporated into the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated st ...
(), a tight federation of German states established by Prussia in 1867, while also remaining part of the Grand Duchy. In 1871, after France's defeat in the
Franco-Prussian War, the whole of the Grand Duchy joined the
German Empire.
Around the turn of the 20th century, Darmstadt was one of the centres of the
Jugendstil
''Jugendstil'' ("Youth Style") was an artistic movement, particularly in the decorative arts, that was influential primarily in Germany and elsewhere in Europe to a lesser extent from about 1895 until about 1910. It was the German counterpart of ...
. Until 1907, the Grand Duchy of Hesse used the Hessian red and white lion ''barry'' as its coat-of-arms.
Weimar and Nazi periods
The
revolution of 1918 following the German defeat in
WWI
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
transformed Hesse-Darmstadt from a monarchy to a republic, which officially renamed itself the
People's State of Hesse
The People's State of Hesse (german: Volksstaat Hessen) was one of the constituent states of Germany from 1918 to 1945, as the successor to the Grand Duchy of Hesse (german: Großherzogtum Hessen) after the defeat of the German Empire in World W ...
(). The parts of Hesse-Darmstadt on the left bank of the Rhine (Rhenish Hesse), as well as those right-bank areas of Hesse-Darmstadt and Hesse-Nassau within of Koblenz or Mainz
were occupied by French troops until 1930 under the terms of the
Versailles peace treaty
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 19 ...
that officially ended World War I in 1919. The Kingdom of Prussia became the
Free State of Prussia
The Free State of Prussia (german: Freistaat Preußen, ) was one of the constituent states of Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it continued to be the domina ...
, of which Hesse-Nassau remained a province.
In 1929 the
Free State of Waldeck was dissolved and incorporated into Hesse-Nassau. In 1932
Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
(), formerly an exclave of the Prussian
Rhine Province situated between Hesse-Nassau and the Grand Duchy's Upper Hesse, was transferred to Hesse-Nassau. The former Hessian exclave of
Rinteln
Rinteln () is a small town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located on the banks of the Weser river above the Porta Westfalica. The town of Rinteln is in the broad valley between the hills of the Weserbergland and the North Lippe Bergland. In rela ...
(, the Hessian part of the former
County of Schaumburg) was also detached and transferred to the
Province of Hanover
The Province of Hanover (german: Provinz Hannover) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.
During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position ...
.
On 1 July 1944 the Prussian Province of Hesse-Nassau was formally divided into the provinces of
Kurhessen
The Electorate of Hesse (german: Kurfürstentum Hessen), also known as Hesse-Kassel or Kurhessen, was a landgraviate whose prince was given the right to elect the Emperor by Napoleon. When the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, its pri ...
and
Nassau. At the same time the former Hessian
Schmalkalden exclaves (), together with the of the
Province of Saxony, were transferred to
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
. The territories of the new provinces did not directly correspond with their pre-1866 namesakes but rather with the associated NSDAP :
Gau Electoral Hesse and
Gau Hesse-Nassau (excluding the areas which were part of the People's State of Hesse).
Post-World War II
After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the Hessian territory west of the Rhine
was again occupied by France, while the rest of the region was part of the
US occupation zone. On 17 September 1945 the
Wanfried agreement adjusted the border between American-occupied Kurhessen and
Soviet-occupied Thuringia. The United States proclaimed the state of
Greater Hesse () on 19 September 1945, out of the People's State of Hesse and most of what had been the Prussian Provinces of Kurhessen and Nassau. The French incorporated their parts of Hesse (Rhenish Hesse) and Nassau (as ) into the newly founded state of
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
() on 30 August 1946.
On 4 December 1946, Greater Hesse was officially renamed .
Hesse in the 1940s received more than a million
displaced ethnic Germans.
Due to its proximity to the
Inner German border, Hesse became an important location of
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
installations in the 1950s, especially military bases of the US
V Corps and
United States Army Europe
United States Army Europe and Africa (USAREUR-AF) is an Army Service Component Command (ASCC) /Theater Army responsible for directing United States Army operations throughout the U.S. European Command (EUCOM) and U.S. Africa Command (AFRICO ...
.
The first elected minister president of Hesse was
Christian Stock, followed by
Georg-August Zinn (both
Social Democrats
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote so ...
). The German Social Democrats gained an absolute majority in 1962 and pursued progressive policies with the so-called . The
CDU gained a relative majority in the 1974 elections, but the Social Democrats continued to govern in a coalition with the
FDP. Hesse was first governed by the CDU under
Walter Wallmann during 1987–1991, replaced by a SPD-Greens coalition under
Hans Eichel during 1991–1999. From 1999, Hesse was governed by the CDU under
Roland Koch
Roland Koch (born 24 March 1958) is a German jurist and former conservative politician of the CDU. He was the 7th Minister President of Hesse from 7 April 1999, immediately becoming the 53rd President of the Bundesrat, completing the term beg ...
(retired 2010) and
Volker Bouffier (incumbent as of 2020).
Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
during the 1960s to 1990s developed into one of the major cities of West Germany. As of 2016, 12% of the total population of Hesse lived in the city of Frankfurt.
Geography
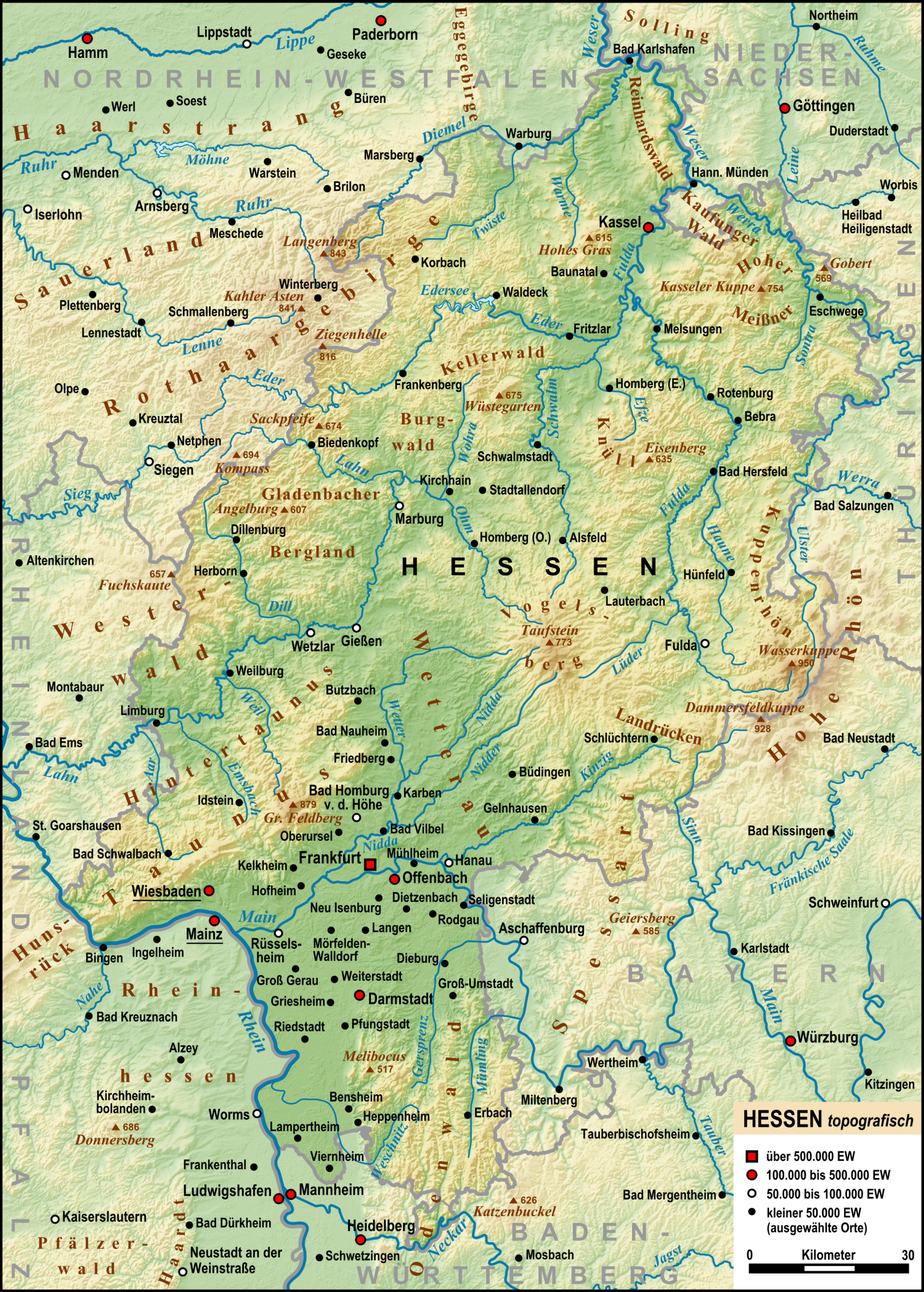
Situated in west-central Germany, the state of Hesse borders the German states of
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
,
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
,
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
,
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
,
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
, and
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inha ...
(starting in the north and proceeding clockwise).
Most of the population of Hesse lives in the southern part, in the
Rhine Main Area. The principal cities of the area include
Frankfurt am Main,
Wiesbaden,
Darmstadt,
Offenbach,
Hanau,
Giessen,
Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
, and
Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
. Other major towns in Hesse are
Fulda in the
east
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
, and
Kassel and
Marburg an der Lahn in the
north
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
. The densely populated Rhine-Main region is much better developed than the rural areas in the middle and northern parts of Hesse.
The most important rivers in Hesse are the
Fulda and
Eder in the north, the
Lahn in the central part of Hesse, and the
Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
and
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
in the south. The countryside is hilly and the numerous mountain ranges include the
Rhön, the
Westerwald
The Westerwald (; literally 'Western forest') is a low mountain range on the right bank of the river Rhine in the German federal states of Rhineland-Palatinate, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia. It is a part of the Rhenish Massif ( or Rhenish ...
, the
Taunus, the
Vogelsberg
The is a large volcanic mountain range in the German Central Uplands in the state of Hesse, separated from the Rhön Mountains by the Fulda river valley.
Emerging approximately 19 million years ago, the Vogelsberg is Central Europe's largest ...
, the
Knüll and the
Spessart
Spessart is a '' Mittelgebirge'', a range of low wooded mountains, in the States of Bavaria and Hesse in Germany. It is bordered by the Vogelsberg, Rhön and Odenwald. The highest elevation is the Geiersberg at 586 metres above sea level.
Ety ...
.
The Rhine borders Hesse on the southwest without running through the state. Only one
oxbow lake—the so-called
Stockstadt-Erfelder Altrhein—runs through Hesse. The mountain range between the rivers Main and the Neckar is called the
Odenwald. The plain between the rivers Main, Rhine, and Neckar, and the Odenwald Mountains is called the Ried.
Hesse is the greenest state in Germany, as forest covers 42% of the state.
Administration
Hesse is a
unitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only ...
governed directly by the
Hessian government in the capital city Wiesbaden, partially through regional vicarious authorities called ''Regierungspräsidien''. Municipal parliaments are, however, elected independently from the state government by the Hessian people. Local municipalities enjoy a considerable degree of
home rule.
Districts
The state is divided into three administrative provinces (''Regierungsbezirke''):
Kassel in the north and east,
Gießen
Giessen, spelled Gießen in German (), is a town in the German state (''Bundesland'') of Hesse, capital of both the district of Giessen and the administrative region of Giessen. The population is approximately 90,000, with roughly 37,000 univers ...
in the centre, and
Darmstadt in the south, the latter being the most populous region with the
Frankfurt Rhine-Main
The Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region, often simply referred to as Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Frankfurt Rhine-Main area or Rhine-Main area (German: ''Rhein-Main-Gebiet'' or ''Frankfurt/Rhein-Main'', abbreviated FRM), is the second-largest metropolitan re ...
agglomeration in its central area. The administrative regions have no legislature of their own, but are executive agencies of the state government.






Hesse is divided into 21 districts (Kreise) and five independent cities, each with their own local governments. They are, shown with abbreviations as used on vehicle number plates:
#
Bergstraße (Heppenheim
Heppenheim (Bergstraße) is the seat of Bergstraße district in Hesse, Germany, lying on the Bergstraße on the edge of the Odenwald. It is best known for being the birthplace of 4-time Formula One World Champion Sebastian Vettel.
Geography
...
) (HP)
#
Darmstadt-Dieburg
Darmstadt-Dieburg is a Kreis (district) in the south of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Offenbach, Aschaffenburg, Miltenberg, Odenwaldkreis, Bergstraße, Groß-Gerau, and the district-free city of Darmstadt, which it surrounds.
Histor ...
( Darmstadt) (DA, DI)
#
Groß-Gerau ( Groß-Gerau) (GG)
#
Hochtaunuskreis ( Bad Homburg) (HG, USI)
#
Main-Kinzig-Kreis
Main-Kinzig-Kreis is a Kreis (district) in the east of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Wetteraukreis, Vogelsbergkreis, Fulda, Bad Kissingen, Main-Spessart, Aschaffenburg, Offenbach and the district-free cities of Offenbach and Frankfur ...
(Gelnhausen
Gelnhausen () is a town, and the capital of the Main-Kinzig-Kreis, in Hesse, Germany. It is located approximately 40 kilometers east of Frankfurt am Main, between the Vogelsberg mountains and the Spessart range at the river Kinzig. It is one o ...
) (MKK, GN, HU, SLÜ)
#
Main-Taunus-Kreis ( Hofheim am Taunus) (MTK)
#
Odenwaldkreis
The Odenwaldkreis is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the south of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Darmstadt-Dieburg, Miltenberg, Neckar-Odenwald-Kreis, Rhein-Neckar-Kreis and Kreis Bergstraße. ''Odenwaldkreis'' belongs to the Rhine Neckar Are ...
( Erbach) (ERB)
#
Offenbach (Dietzenbach
Dietzenbach is the seat of Offenbach district in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' of Darmstadt in Hesse, Germany and lies roughly 12 km southeast of Frankfurt am Main on the waterstream Bieber. Before the Second World War, the current town was ...
) (OF)
#
Rheingau-Taunus-Kreis
Rheingau-Taunus is a Kreis (district) in the west of Hesse, Germany. Rheingau-Taunus-Kreis is part of the Darmstadt region; its main administrative seat is Bad Schwalbach. Outposted sections of the local administration are located in Idstein and R ...
( Bad Schwalbach) (RÜD, SWA)
#
Wetteraukreis
The Wetteraukreis is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the middle of Hesse, Germany. Neighbouring districts are Landkreis Gießen, Vogelsbergkreis, Main-Kinzig-Kreis, district-free Stadt Frankfurt, Hochtaunuskreis and Lahn-Dill-Kreis.
History
The distri ...
( Friedberg) (FB, BÜD)
#
Gießen
Giessen, spelled Gießen in German (), is a town in the German state (''Bundesland'') of Hesse, capital of both the district of Giessen and the administrative region of Giessen. The population is approximately 90,000, with roughly 37,000 univers ...
(Gießen
Giessen, spelled Gießen in German (), is a town in the German state (''Bundesland'') of Hesse, capital of both the district of Giessen and the administrative region of Giessen. The population is approximately 90,000, with roughly 37,000 univers ...
) (GI)
#
Lahn-Dill-Kreis
Lahn-Dill is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the west of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Siegen-Wittgenstein, Marburg-Biedenkopf, Gießen, Wetteraukreis, Hochtaunuskreis, Limburg-Weilburg, Westerwaldkreis.
History
The southern district b ...
(Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
) (LDK, DIL, WZ)
#
Limburg-Weilburg (Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
) (LM, WEL)
#
Marburg-Biedenkopf ( Marburg) (MR, BID)
#
Vogelsbergkreis
The Vogelsbergkreis is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the middle of Hesse, Germany. Neighbouring districts are Schwalm-Eder, Hersfeld-Rotenburg, Fulda, Main-Kinzig, Wetteraukreis, Gießen and Marburg-Biedenkopf.
History
The district was created in ...
( Lauterbach) (VB)
#
Fulda ( Fulda) (FD)
#
Hersfeld-Rotenburg
Hersfeld-Rotenburg is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Werra-Meißner, Wartburgkreis, Fulda, Vogelsbergkreis, Schwalm-Eder.
History
In 1821, districts were created in Hesse, including the districts H ...
(Bad Hersfeld
The festival and spa town of Bad Hersfeld (''Bad'' is "spa" in German; the Old High German name of the city was ''Herolfisfeld'') is the district seat of the Hersfeld-Rotenburg district in northeastern Hesse, Germany, roughly 50 km southe ...
) (HEF, ROF)
#
Kassel ( Kassel) (KS, HOG, WOH)
#
Schwalm-Eder-Kreis
Schwalm-Eder-Kreis is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the north of Hesse, Germany. Neighbouring districts are Kassel, Werra-Meißner, Hersfeld-Rotenburg, Vogelsberg, Marburg-Biedenkopf, and Waldeck-Frankenberg.
History
In 1821 districts were create ...
(Homberg (Efze)
Homberg () is a small town in the northern part of Hesse, a state in central Germany, with about 15,000 inhabitants. It is the seat of the Schwalm-Eder district. In 2008, the town hosted the 48th Hessentag state festival.
Geography
Homberg lies in ...
) (HR, ZIG, FZ)
#
Werra-Meißner-Kreis (Eschwege
Eschwege (), the district seat of the Werra-Meißner-Kreis, is a town in northeastern Hesse, Germany. In 1971, the town hosted the eleventh '' Hessentag'' state festival.
Geography
Location
The town lies on a broad plain tract of the river W ...
) (ESW, WIZ)
#
Waldeck-Frankenberg (Korbach
Korbach (pronunciation: ˈkoːɐˌbax), officially the Hanseatic City of Korbach (German: Hansestadt Korbach), is the district seat of Waldeck-Frankenberg in northern Hesse, Germany. It is over a thousand years old and is located on the German Tim ...
) (KB, FKB, WA)
Independent cities:
#
Darmstadt (DA)
#
Frankfurt am Main (F)
#
Kassel (KS)
#
Offenbach am Main (OF)
#
Wiesbaden (WI)
Rhenish Hesse
The term "Rhenish Hesse" (german: Rheinhessen) refers to the part of the former Grand Duchy of
Hesse-Darmstadt
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Darmstadt) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a younger branch of the House of Hesse. It was formed in 1567 following the division of the Landgraviate of Hesse betwee ...
located west of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
. It has not been part of the State of Hesse since 1946 due to divisions in the aftermath of World War II. This province is now part of the State of
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
. It is a hilly countryside largely devoted to vineyards; therefore, it is also called the "land of the thousand hills". Its larger towns include
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
,
Worms,
Bingen,
Alzey,
Nieder-Olm
Nieder-Olm is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Until 5 November 2006 it was an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – but it was raised to ...
, and
Ingelheim
Ingelheim (), officially Ingelheim am Rhein ( en, Ingelheim upon Rhine), is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's west bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat ...
. Many inhabitants commute to work in Mainz, Wiesbaden, or Frankfurt.
State symbols and politics
Hesse has been a parliamentary republic since 1918, except during
Nazi rule (1933–1945). The German federal system has elements of exclusive federal competences, shared competences, and exclusive competences of the states. Hesse is famous for having a rather brisk style in its politics with the ruling parties being either the center-right
Christian Democratic Union (CDU) or the center-left
Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). Due to the Hessian electoral laws, the biggest party normally needs a smaller coalition partner.
Head of state
As Hesse is a partly sovereign
federated state, its constitution combines the offices of the
head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and
head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
in one office called the
Minister-President (German: ''Ministerpräsident'') which is comparable to the office of a
prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
.
Most recent state election
In the
2018 state elections the two leading parties, CDU and SPD, lost 11.3% (7 seats) and 10.9% (8 seats) of the vote respectively. The Green party, a member of Hesse's previous governing coalition with CDU, gained 8.7% (16 seats). The largest gains during the election were made by
Alternative for Germany (AfD) at 13.1%. As AfD had not passed the 5% threshold in the
2013 state election, this marked its first entry into the
Hessian parliament (''Hessischer Landtag''). The two other parties also made gains. The major losses of the two leading parties (whose
coalition made up the federal cabinet during the election) closely mirrors the results of the
2018 state elections in Bavaria. In the current parliament the conservative CDU holds 40 seats, the centre-left SPD and the leftist Green party each hold 29 seats, the right-wing AfD holds 19 seats, the liberal
FDP party holds 11 seats and the socialist party
Die Linke holds 9 seats.

Foreign affairs
As a member state of the German federation, Hesse does not have a diplomatic service of its own. However, Hesse operates representation offices in such foreign countries as the United States, China, Hungary, Cuba, Russia, Poland, and Iran. These offices are mostly used to represent Hessian interests in cultural and economic affairs. Hesse has also permanent representation offices in Berlin at the
federal government of Germany
The Federal Cabinet or Federal Government (german: link=no, Bundeskabinett or ') is the chief executive body of the Federal Republic of Germany. It consists of the Federal Chancellor and cabinet ministers. The fundamentals of the cabinet's or ...
and in
Brussels at the
institutions of the European Union.
Flag and anthem
The flag colors of Hesse are red and white, which are printed on a Hessian sack. The
Hessian coat of arms shows a lion rampant striped with red and white. The official anthem of Hesse is called "''
Hessenlied
The Hessenlied (''Song of Hesse'') is the official anthem of the German federal state of Hesse. The text was written by Carl Preser (1828-1910), the melody was composed by Albrecht Brede
Albrecht ("noble", "bright") is a given name or surnam ...
''" ("Song of Hesse") and was written by Albrecht Brede (music) and Carl Preser (lyrics).
Demographics
Hesse has a population of over 6 million, nearly 4 million of which is concentrated in the Rhein-Main region (German: ''Rhein-Main Gebiet'') in the south of the state, an area that includes the most populous city,
Frankfurt am Main, the capital
Wiesbaden, and
Darmstadt and
Offenbach. The population of Hesse is predicted to shrink by 4.3% by 2030, with the biggest falls in the north of the state, especially in the area around the city of
Kassel. Frankfurt is the fastest growing city with a predicted rise in population of 4.8% by 2030. Frankfurt's growth is driven by its importance as a financial centre and it receives immigrants from all over the world: in 2015 over half of the city's population had an immigrant background.
Vital statistics
Source:
*Births January–March 2017 = 14,537
*Births January–March 2018 = 14,202
*Deaths January–March 2017 = 19,289
*Deaths January–March 2018 = 18,831
*Natural growth January–March 2017 = −4,752
*Natural growth January–March 2018 = −4,629
Language
Three different languages or dialect groups are spoken in Hesse: The Far North is part of the
Low Saxon language area, divided into a tiny
Eastphalian and a larger
Westphalian dialect area. Most of Hesse belongs to the
West Middle German dialect zone. There is some disagreement as to whether all Hessian dialects south of the
Benrath line may be subsumed under one dialect group: Rhine Franconian, or whether most dialects should be regarded as a dialect group of its own: Hessian, whereas only South Hessian is part of Rhine Franconian. Hessian proper can be split into Lower Hessian in the north, East Hessian in the East around
Fulda and Central Hessian, which covers the largest area of all dialects in Hesse. In the extreme Northeast, the
Thuringian
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon sp ...
dialect zone extends into Hesse, whereas in the Southeast, the state border to
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
is not fully identical to the dialect border between
East Franconian
East Franconian (german: Ostfränkisch) or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian (') in German, is a dialect which is spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, ...
and East Hessian.
Since approximately World War II, a spoken variety of
Standard German with dialect substrate has been superseding the traditional dialects mentioned so far. This development knows a north-to-south movement, the north being early to supplant the traditional language, whereas in the south, there is still a considerable part of the population that communicates in South Hessian. In most of the areas, however, the traditional language is close to extinction, whereas until the first half of the 20th century, almost the entire population spoke dialect in almost all situations. The Upper Class started to speak Standard German beginning in the late 19th century, so for decades, the traditional language served as a sociolect.
The prominent written language in Hesse has been Standard German since the 16th century. Before, the Low Saxon part used
Middle Low German, the rest of the Land
Early Modern German
Early New High German (ENHG) is a term for the period in the history of the German language generally defined, following Wilhelm Scherer, as the period 1350 to 1650.
The term is the standard translation of the German (Fnhd., Frnhd.), introduce ...
as prominent written languages. These had supplanted
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
in the
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
.
Religion

In 2016
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
was the most widespread religion in the state (63%).
40% of Hessians belonged to the
Protestant Church in Hesse and Nassau or
Evangelical Church of Hesse Electorate-Waldeck (members of the
Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
), 25% adhered to the
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, while other Christians constituted some 3%, the third most common religion of the Hessian population is
Islam with 7% of the population.
Education and Research
Higher education
The Hessian government has overall responsibility for the education within the state.
Hesse has follow universities:
*
Goethe University Frankfurt (43,972 students; Budget: € 666,4 Mio.)
*
Technical University of Darmstadt
Technical may refer to:
* Technical (vehicle), an improvised fighting vehicle
* Technical analysis, a discipline for forecasting the future direction of prices through the study of past market data
* Technical drawing, showing how something is co ...
(25,355 students; Budget: € 482,8 Mio.)
*
Justus Liebig University Giessen (28,480 students; Budget: € 425,4 Mio.)
*
Philipps University of Marburg (24,394 students; Budget: € 374,3 Mio.)
*
University of Kassel
The University of Kassel (german: link=no, Universität Kassel) is a university founded in 1971 located in Kassel, Hessen, in central Germany. As of February 2022 it had about 25,000 students and about 3300 staff, including more than 300 profe ...
(25,103 students; Budget: € 291,5 Mio.)
No any Hesse's university belongs to
German Excellence Universities.
Goethe_University_Frankfurt_Poelzig_Building.jpeg, Goethe University Frankfurt, Campus Westend
Karo5_Eingangsgebaeude_Verwaltungsgebaeude_TU_Darmstadt.jpg, Technical University of Darmstadt, Main Entrance
2004-JLU_Gießen_Sicherlich.jpg, Justus Liebig University Giessen
MarburgLahnbergeBMFZ.jpg, Philipps University of Marburg, Biomedical Research Center
Uni Kassel Eingang Holländischer Platz.jpg, University of Kassel, Entrance Holländischer Platz
There are many international schools in Hesse, primarily centred in and around Frankfurt.
Hesse is the only state in Germany where students have to study all three stanzas of the Das
Deutschlandlied.
Research
Big Science
A single existing
big science facility in Hesse is
GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research
The GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research (german: GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung) is a federally and state co-funded heavy ion () research center in the Wixhausen suburb of Darmstadt, Germany. It was founded in 1969 as th ...
in
Darmstadt-Wixhausen
Wixhausen is northernmost borough of the City of Darmstadt in southern Hesse, Germany. Covering an area of 23.247 km2, in 2006 it had 5,772 inhabitants and 1,310 houses. Its main claim to fame is the GSI heavy-ion research laboratory located ...
with 1,520 employees. The second one
Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research
The Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research (FAIR) is an international accelerator facility under construction which will use antiprotons and ions to perform research in the fields of: nuclear, hadron and particle physics, atomic and anti-matt ...
is in construction till 2025.
In space research there are 2 European organization
European Space Operations Center and
European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites in
Darmstadt.
Health & Medicine
*
Max Planck Institue for Heart and Lung Research,
Bad Nauheim
Bad Nauheim is a town in the Wetteraukreis district of Hesse state of Germany.
As of 2020, Bad Nauheim has a population of 32,493. The town is approximately north of Frankfurt am Main, on the east edge of the Taunus mountain range. It is a wor ...
*
Max Planck Institute for Brain Research,
Frankfurt-am-Main
*
Max Planck Institute of Biophysics,
Frankfurt-am-Main
* ,
Frankfurt-am-Main
* Fraunhofer Institute for Translational Medicine and Pharmacology,
Frankfurt-am-Main
*
Paul Ehrlich Institute (vaccines),
Langen
*
Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology
The Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology (german: Max-Planck-Institut für terrestrische Mikrobiologie, links=https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Max-Planck-Institut_f%C3%BCr_terrestrische_Mikrobiologie) is a research institute for terrestr ...
,
Marburg
* (researh of
Ebolavirus and
Marburgvirus;
Parasitology) with
BSL4-Labor,
Marburg
* ,
Marburg
* ,
Marburg
*
Sigmund Freud Institute (
psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek: + . is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might b ...
),
Frankfurt-am-Main
Informatics & Software
*
Hessian Centre for Artificial Intelligence, HQ in
Darmstadt, more locations in Hesse
*
German Research Centre for Artificial Intelligence,
Darmstadt
*
Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt
The Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) was a center for IT security research and development with an interdisciplinary and cross-organizational approach. It was founded in July 2008 by TU Darmstadt, the Fraunhofer Institu ...
,
Darmstadt
* ,
Darmstadt
* ,
Darmstadt
Others
* ,
Darmstadt
* , HQ in
Kassel, other location in
Rothwesten and
Bad Hersfeld
The festival and spa town of Bad Hersfeld (''Bad'' is "spa" in German; the Old High German name of the city was ''Herolfisfeld'') is the district seat of the Hersfeld-Rotenburg district in northeastern Hesse, Germany, roughly 50 km southe ...
* ,
Hanau
*
Max-Planck-Institut für europäische Rechtsgeschichte,
Frankfurt-am-Main
*
Institut für Sozialforschung at Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität
Frankfurt-am-Main
* Leibniz-Institut für Bildungsforschung und Bildungsinformation,
Frankfurt-am-Main
* Forschungsinstitut für Deutsche Sprache – Deutscher Sprachatlas – at Philipps-Universität Marburg
*
Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, * Forschungsinstitut und Naturmuseum Senckenberg, Frankfurt am Main
*
Peace Research Institute Frankfurt,
Frankfurt-am-Main
* Institut für sozial-ökologische Forschung,
Frankfurt-am-Main
*
Athene (research center),
Darmstadt
Culture
Hesse has a rich and varied cultural history, with many important cultural and historical centres and several UNESCO world-heritage sites.
Architecture, art, literature and music
Darmstadt has a rich cultural heritage as the former seat of the
Landgraves and
Grand Dukes of Hesse. It is known as centre of the
art nouveau Jugendstil
''Jugendstil'' ("Youth Style") was an artistic movement, particularly in the decorative arts, that was influential primarily in Germany and elsewhere in Europe to a lesser extent from about 1895 until about 1910. It was the German counterpart of ...
and modern architecture and there are also several important examples of 19th century architecture influenced by British and Russian imperial architecture due to close family ties of the Grand Duke's family to the reigning dynasties in
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
in the
Grand Duchy period. Darmstadt is an important centre for music, home of the
Darmstädter Ferienkurse for
contemporary music and the Jazz Institute Darmstadt, Europe's largest public jazz archive.
Frankfurt am Main is a major international cultural centre. Over 2 million people visit the city's approximately 60 exhibition centres every year. Amongst its most famous art galleries are the
Schirn Kunsthalle, a major centre for international modern art, and the
Städel, whose large collections include over 3000 paintings, 4000 photographs, and 100,000 drawings including works by
Picasso,
Monet,
Rembrandt and
Dürer.
Goethe was born in Frankfurt and there is a museum in his
birthplace
The place of birth (POB) or birthplace is the place where a person was born. This place is often used in legal documents, together with name and date of birth, to uniquely identify a person. Practice regarding whether this place should be a cou ...
. Frankfurt has many music venues, including an award-winning
opera house
An opera house is a theatre building used for performances of opera. It usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, and backstage facilities for costumes and building sets.
While some venues are constructed specifically fo ...
, the
Alte Oper
Alte Oper (Old Opera) is a concert hall in Frankfurt am Main, Hesse, Germany. It is located in the inner city, Innenstadt, within the banking district Bankenviertel. Today's Alte Oper was built in 1880 as the city's opera house, which was destr ...
, and the
Jahrhunderthalle. Its several theatres include the English Theatre, the largest English-speaking theatre on the European continent.
Kassel has many palaces and parks, including
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is , making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the ''Bergpark'', or "mountain park", bega ...
, a Baroque landscape park and UNESCO World Heritage site. The
Brothers Grimm lived and worked in Kassel for 30 years and the recently opened Grimmwelt museum explores their lives, works and influence and features their personal copies of the
Children's and Household Tales
''Grimms' Fairy Tales'', originally known as the ''Children's and Household Tales'' (german: Kinder- und Hausmärchen, lead=yes, ), is a German collection of fairy tales by the Grimm brothers or "Brothers Grimm", Jacob and Wilhelm, first publis ...
, which are on the UNESCO World Heritage "Memory of the World" Document register. The
Fridericianum
The Fridericianum is a museum in Kassel, Germany. Built in 1779, it is one of the oldest public museums in Europe. , built in 1779, is one of the oldest public museums in Europe. Kassel is also home to the ''
documenta'', a large modern art exhibition that has taken place every five years since the 1950s.
The Hessian Ministry of the Arts supports numerous independent cultural initiatives, organisations, and associations as well as artists from many fields including music, literature, theatre and dance, cinema and the new media, graphic art, and exhibitions. International cultural projects aim to further relations with European partners.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
Hesse has several UNESCO World Heritage sites. These include:
*
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is , making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the ''Bergpark'', or "mountain park", bega ...
in Kassel
*
Kellerwald-Edersee National Park
The Kellerwald-Edersee National Park (german: Nationalpark Kellerwald-Edersee), CDDA-No. 318077) in the North Hessian county of Waldeck-Frankenberg is a national park, 57.38 km² in area, that lies south of the Edersee lake in the nor ...
in North Hesse
*
Lorsch Abbey
Lorsch Abbey, otherwise the Imperial Abbey of Lorsch (german: Reichsabtei Lorsch; la, Laureshamense Monasterium or ''Laurissa''), is a former Imperial abbey in Lorsch, Germany, about east of Worms. It was one of the most renowned monasteries ...
* The
Messel Fossil Pit. Exhibits from the Messel Pit can be seen in Messel town museum, the Museum of Hessen in Darmstadt, and the
Senckenberg Museum
The Naturmuseum Senckenberg is a museum of natural history, located in Frankfurt am Main. It is the second-largest of its type in Germany. The museum contains a large and diverse collection of birds with 90,000 bird skins, 5,050 egg sets, 17,0 ...
in Frankfurt.
* The
Saalburg
The Saalburg is a Roman fort located on the main ridge of the Taunus, northwest of Bad Homburg, Hesse, Germany. It is a cohort fort, part of the Limes Germanicus, the Roman linear border fortification of the German provinces. The Saalburg, ...
, part of the
Roman Limes.
*
Darmstadt Artists' Colony
The Darmstadt Artists’ Colony refers both to a group of Jugendstil artists as well as to the buildings in Mathildenhöhe in Darmstadt in which these artists lived and worked in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The artists were largely fi ...
Sports

Frankfurt hosts the following professional sports teams or clubs:
*
1. FFC Frankfurt (1998–2020),
football (women)
*
Eintracht Frankfurt,
football (men, women)
*
FSV Frankfurt,
football (men)
*
Rot-Weiss Frankfurt
SG Rot-Weiss Frankfurt 01 is a German association football club from Frankfurt am Main. The association was founded on 11 November 1901 as FV Amicitia 1901 Bockenheim in what is today the city district of Bockenheim.
History Early years
The Fr ...
,
football
*
Frankfurter FC Germania 1894,
football
*
Skyliners Frankfurt,
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
*
Frankfurt Galaxy (1991–2007),
American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
*
Frankfurt Universe (2007–present),
American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
*
Frankfurter Löwen
The Frankfurter Löwen ( en, Frankfurt Lions) were an American football team from Frankfurt, Germany.
The ''Löwen'' were the first American football club to be formed in Germany.[American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...]
*
Frankfurt Sarsfields GAA
Frankfurt Sarsfields is a Frankfurt based Gaelic football team. The team competes in European wide tournaments and have been Shield runners-up in their first two seasons.
The aim of the club is to give Gaelic football players in Germany a chanc ...
,
Gaelic football
*
Frankfurt Lions (until 2010),
ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
*
Löwen Frankfurt (since 2010),
ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
*
SC 1880 Frankfurt,
rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
Frankfurt is host to the
classic cycle race
Eschborn-Frankfurt City Loop (known as ''Rund um den Henninger-Turm'' from 1961 to 2008). The city hosts also the annual
Frankfurt Marathon
The Frankfurt Marathon (official name as of 2016: Mainova Frankfurt Marathon, until 2015: BMW Frankfurt Marathon, until 2010: Commerzbank Frankfurt Marathon) is a marathon which has taken place every year in Frankfurt am Main since its inception i ...
and the
Ironman Germany.
Outside Frankfurt, notable professional sports teams include
Kickers Offenbach
Offenbacher Kickers, also known as Kickers Offenbach, is a German association football club in Offenbach am Main, Hesse. The club was founded on 27 May 1901 in the Rheinischer Hof restaurant by footballers who had left established local clubs ...
,
SV Darmstadt 98,
Marburg Mercenaries
The Marburg Mercenaries are an American football team from Marburg, Germany.
Internationally, the club's greatest success came in 2005, when it won the EFAF Cup, followed by a losing appearance in the Eurobowl in 2007. Domestically, the team's ...
,
Gießen 46ers
The JobStairs GIESSEN 46ers (formerly GIESSEN 46ers) is a professional basketball club based in Gießen, Germany, that plays in the Basketball Bundesliga. Their home arena is Sporthalle Gießen-Ost, with a capacity of 4,003 people.
History
The ...
,
MT Melsungen,
VfB Friedberg
The VfB Friedberg is a German association football club from the town of Friedberg, Hesse.
In pre-Second World War football the club has played at times at highest level, most notable the six seasons spend in the Gauliga Hessen from 1933 to 193 ...
, and the
Kassel Huskies
The EC Kassel Huskies are a professional ice hockey club based in Kassel, Hessen, Germany. The club currently competes in DEL2, the second level of ice hockey in Germany. The Huskies were founded in 1977 and have competed in the top five levels ...
.
TV and radio stations
The Hessian state broadcasting corporation is called HR (
Hessischer Rundfunk). HR is a member of the federal
ARD broadcasting association. HR provides a statewide TV channel as well as a range of regional radio stations (HR 1, HR 2, HR 3, HR 4, you fm and HR info). Besides the state run HR, privately run TV stations exist and are an important line of commerce. Among the commercial radio stations that are active in Hesse, Hit Radio FFH, Planet Radio, Harmony FM, Radio BOB and Antenne Frankfurt are the most popular.
Economy
Financial
With Hesse's largest city
Frankfurt am Main being home of the
European Central Bank (ECB), the
German Bundesbank and the
Frankfurt Stock Exchange, Hesse is home to the financial capital of mainland Europe. Furthermore, Hesse has always been one of the largest and healthiest economies in Germany. Its
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
in 2013 exceeded €236 billion (about US$316 billion). This makes Hesse itself one of the largest economies in Europe and the 38th largest in the world. According to GDP-per-capita figures, Hesse is the wealthiest state (after the
city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
and
Bremen) in Germany with approx. US$52,500.
Frankfurt is crucial as a
financial center, with both the
European Central Bank and the
Deutsche Bundesbank's headquarters located there. Numerous smaller banks and
Deutsche Bank,
DZ Bank
DZ Bank AG () is the second largest bank in Germany by asset size and the central institution for around 800 cooperative banks and their around 8,500 branch offices. Within the German Cooperative Financial Group, which is one of Germany's la ...
,
KfW Bank,
Commerzbank are also headquartered in Frankfurt, with the offices of several international banks also being housed there. Frankfurt is also the location of the most important German stock exchange, the Frankfurt Stock Exchange.
Insurance companies have settled mostly in
Wiesbaden. The city's largest private employer is the
R+V Versicherung, with about 3,900 employees, other major employers are
DBV-Winterthur, the
SV SparkassenVersicherung
SV, Sv, sv, etc. may refer to:
Places and language
* El Salvador, ISO 3166-1 country code SV
* South Vietnam, an extinct state
* Svalbard, Norway, FIPS country code SV
* Swedish language, ISO 639-1 language code sv
* Silicon Valley, a region in n ...
and the
Delta Lloyd Group.
ECB_Frankfurt_at_Sunset.jpg, European Central Bank
Deutsche_Bank_Taunusanlage.jpg, Deutsche Bank
Frankfurt_Commerzbank_vom_Schaumainkai.jpg, Commerzbank
Chemical & Pharma
The
Rhine-Main Region has the second largest industrial density in Germany after the
Ruhr area
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
. The main economic fields of importance are the
chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
and
pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
industries with
Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
,
Merck,
Heraeus,
Stada,
Messer Griesheim,
Bayer Crop Science
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutica ...
,
SGL Carbon
SGL Carbon SE is a European company based in Germany. It is one of the world's leading manufacturers of products from carbon.
With 31 production sites around the globe (17 in Europe, 9 in North America and 5 in Asia), and a service network in ov ...
,
Celanese,
Cabot,
Clariant,
Akzo Nobel
Akzo Nobel N.V., stylized as AkzoNobel, is a Dutch multinational company which creates paints and performance coatings for both industry and consumers worldwide. Headquartered in Amsterdam, the company has activities in more than 80 countrie ...
,
Kuraray,
Ineos,
LyondellBasell, and
Evonik Industries
Evonik Industries AG is a stock-listed German specialty chemicals company headquartered in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the second largest chemicals company in Germany, and one of the largest specialty chemicals companies in the ...
. But also other consumer goods are produced by
Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/consumer he ...
,
Coty and
Colgate Palmolive. The Rhine-Main Region is not restricted only to Hesse, smaller part is in
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
. There situated 2 important pharma companies:
BioNTech
BioNTech SE ( ; or short for Biopharmaceutical New Technologies) is a German biotechnology company based in Mainz that develops and manufactures active immunotherapies for patient-specific approaches to the treatment of diseases. It develop ...
(HQ), which found the first mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 in the world (licensed to
Pfizer), and
Boehringer Ingelheim, close to Hesse's border in
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
and
Ingelheim
Ingelheim (), officially Ingelheim am Rhein ( en, Ingelheim upon Rhine), is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's west bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat ...
respectively. It supports from
Max Planck Institue for Heart and Lung Research,
Max Planck Institute for Brain Research and
Paul Ehrlich Institute.
Also in other part of Hesse there is important pharma and medical manufacturers, especially in
Marburg where there is industry park based on ex-Behring Werke:
BioNTech
BioNTech SE ( ; or short for Biopharmaceutical New Technologies) is a German biotechnology company based in Mainz that develops and manufactures active immunotherapies for patient-specific approaches to the treatment of diseases. It develop ...
(mRNA vaccines),
CSL Behring
CSL Behring is a biopharmaceutical company, manufacturing plasma-derived, and recombination therapeutic products. Its line of therapies includes products for the treatment of bleeding disorders such as hemophilia and von Willebrand Disease; prim ...
,
Temmler and
Melsungen
Melsungen () is a small climatic spa town in the Schwalm-Eder district in northern Hesse, Germany. In 1987, the town hosted the 27th ''Hessentag'' state festival.
Geography
Melsungen lies on the river Fulda in the North Hesse Highlands. The str ...
with
B. Braun. Pharma activity in
Marburg is also supported from research facilities:
Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology
The Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology (german: Max-Planck-Institut für terrestrische Mikrobiologie, links=https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Max-Planck-Institut_f%C3%BCr_terrestrische_Mikrobiologie) is a research institute for terrestr ...
, , (researh of
Ebolavirus and
Marburgvirus;
Parasitology) with
BSL4-Labor, .
Merck controls ca. 60% of world's
liquid crystal market.
Heraeus,
Umicore
Umicore N.V.. formerly '' Union Minière'', is a multinational materials technology company headquartered in Brussels, Belgium.
Formed in 1989 by the merger of four companies in the mining and smelting industries, Umicore has since reshaped ...
and
Evonik Industries
Evonik Industries AG is a stock-listed German specialty chemicals company headquartered in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the second largest chemicals company in Germany, and one of the largest specialty chemicals companies in the ...
manufacture different type of catalysts from
Platinum metals,
Vanadium,
Neodymium,
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
,
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and etc.
In east
Fulda there is the tire plant (
Fulda Reifen). 2 other tire plants are in
Korbach
Korbach (pronunciation: ˈkoːɐˌbax), officially the Hanseatic City of Korbach (German: Hansestadt Korbach), is the district seat of Waldeck-Frankenberg in northern Hesse, Germany. It is over a thousand years old and is located on the German Tim ...
from
Continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
and
Hanau from
Goodyear.
Sanofi_Frankfurt_IPH.jpg, Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
in Inustrial Park " Höchst"
Merck_KGaA_Pyramide_Gruener_Turm.jpg, Merck in Darmstadt
Marburg,_Marbach_Behringwerk.jpg, Industrial Park "Behringwerke"
Metallurgy & Nuclear
Specialised metallurgical industry focused on
platinum metals has been represented by
Heraeus and
Umicore
Umicore N.V.. formerly '' Union Minière'', is a multinational materials technology company headquartered in Brussels, Belgium.
Formed in 1989 by the merger of four companies in the mining and smelting industries, Umicore has since reshaped ...
and magnetic materials have been a focus of
Vacuumschmelze based in
Hanau. Also in
Hanau there used to be a plant produing nuclear fuel (classical uranium, but also
MOX fuel
Mixed oxide fuel, commonly referred to as MOX fuel, is nuclear fuel that contains more than one oxide of fissile material, usually consisting of plutonium blended with natural uranium, reprocessed uranium, or depleted uranium. MOX fuel is an al ...
), but the production has stopped and the facility has been mothballed.
Heraeus continues to manufacture irradiation sources from
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
and
Iridium.
Engineering
In the mechanical and automotive engineering field
Opel in Rüsselsheim is worth mentioning. After acquisition Opel by
Stellantis, it is in rapid decline of production and employment. Which has also negative effect on automotive parts supplier,
Continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
will close a plant in
Karben and cut jobs at other location in Hesse. In northern Hesse, in
Baunatal,
Volkswagen AG has a large factory that manufactures spare parts, not far-away from it there is also a
Daimler Truck
Daimler Truck AG (holding company legal name Daimler Truck Holding AG) is one of the world's largest commercial vehicle manufacturers, with over 35 main locations worldwide and approximately 100,000 employees. Daimler Truck AG is headquartered in ...
plant, which produces an axes.
Alstom, after takeover of
Bombardier, has a large plant that manufactures
Traxx locomotives in
Kassel. Industrial printers (
Manroland
Manroland AG manufactures newspaper web offset presses, commercial web offset presses, and sheetfed offset presses for commercial, publications and packaging printing.
The company has production facilities in Offenbach am Main and Augsburg. Ma ...
,
Gallus Holding), x-ray airport check equipment (
Smiths), handling and loading equipment (
Dematic), chemical equipment (
Air Liquide Global E&C Solutions), vacuum pumps (
Pfeiffer Vacuum), vacuum industrial furnace (ALD Vacuum Technologies), textile machines (Karl Mayer), shavers (
Braun), medical (
Fresenius,
Sirona
In Celtic polytheism, Sirona was a goddess worshipped predominantly in East Central Gaul and along the Danubian limes. A healing deity, she was associated with healing springs; her attributes were snakes and eggs. She was sometimes depicted with A ...
) and industrial (Schenck Process,
Samson
Samson (; , '' he, Šīmšōn, label= none'', "man of the sun") was the last of the judges of the ancient Israelites mentioned in the Book of Judges (chapters 13 to 16) and one of the last leaders who "judged" Israel before the institution o ...
) apparatuses are produced in Rhine-Main Region.
Manufacturing of
heating boilers and
heat pumps
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing h ...
are typical for Hesse and represented with and
Viessmann.
Vistec produces
electron-beam lithography systems for semiconductor industry in
Weilburg
Weilburg is, with just under 13,000 inhabitants, the third biggest town in Limburg-Weilburg district in Hesse, Germany, after Limburg an der Lahn and Bad Camberg.
Geography
Location
The community lies in the Lahn valley between the Wester ...
, also there is manufacturing of inspection, testing and measurement equipment for semiconductor fabrication process from
KLA-Tencor.
Leica Microsystems
Leica Microsystems GmbH is a German microscope manufacturing company. It is a manufacturer of optical microscopes, equipment for the preparation of microscopic specimens and related products. There are ten plants in eight countries with distribu ...
manufactures different types of microscopes, inclusive they with special light microscopic optics, which are used in wafer and photo mask testing. PVA TePla from
Wettenberg is specialist for crystal growing process (Si, Ge, GaAs, GaP, InP) with
Czochralski Process,
Float-Zone Process,
High-Temperature Chemical Vapor Deposition, Vertical Gradient Freeze equipment, quality inspection apparatus, plasma and vacuum machine.
ABB
ABB Ltd. is a Swedish- Swiss multinational corporation headquartered in Zürich, Switzerland. The company was formed in 1988 when Sweden's Allmänna Svenska Elektriska Aktiebolaget (ASEA) and Switzerland's Brown, Boveri & Cie merged to crea ...
Robotics is in
Friedberg. Satisloh is a machine manufacturer in
Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
for the production of lenses and components for the optical industry.
Aerospace
The company operating
Frankfurt Airport is one of the largest employers in Hesse with nearly 22,000 employees. Aerospace cluster contains also
Rolls-Royce's aviation engine work in
Oberursel and
APU manufacturing plant and service center of
Honeywell in
Raunheim.
Optics & Electronics
Companies with an international reputation are located outside the Rhine-Main region in
Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
. There is the center of the optical, electrical and precision engineering industries,
Leitz Leitz may refer to several German companies:
*Esselte Leitz GmbH & Co KG, founded by Louis Leitz in 1896, a German manufacturer of office products
**Louis Leitz (1846–1918), German inventor and founder of Esselte Leitz GmbH & Co KG
* Leitz GmbH & ...
,
Leica,
Minox
Minox (pronounced ) is a manufacturer of cameras, known especially for its subminiature camera.
The first product to carry the Minox name was a subminiature camera, conceived in 1922, and finally invented and produced in 1936, by Baltic German ...
, Hensoldt (
Zeiss) and
Brita with several plants in central Hesse.
Oculus Optikgeräte manufactures
Scheimpflug tomographs for examining the anterior segment of the eye, topographers for measuring the anterior surface of the cornea, tonometers for assessing the biomechanical properties of the cornea, a wide-angle observation system for vitreous body surgery, universal trial goggles for subjective refraction, various perimeters for visual field testing and vision testing devices for testing eyesight.
Electrical transformers are produced by Hitachi ABB Power Grids in
Hanau and
Siemens Energy in
Frankfurt-am-Main.
SMA Solar Technology manufactures an inverters for photovoltaic systems.
Rittal is specialized on
electrical enclosure
An electrical enclosure is a cabinet for electrical or electronic equipment to mount switches, knobs and displays and to prevent electrical shock to equipment users and protect the contents from the environment. The enclosure is the only pa ...
situated in
Herborn and
Eschenburg
Eschenburg is a municipality in the Lahn-Dill-Kreis in Hesse, Germany. The community inherited its name from nearby Eschenburg mountain.
Geography
About 20 km², or 43.8%, of the municipal area is wooded, 9.85 km² of this being munic ...
. Power semiconductors from
IXYS in
Lampertheim
Lampertheim is a town in the Bergstraße district in Hesse, Germany. In 1984, the town hosted the 24th ''Hessentag'' state festival.
Geography
Location
Lampertheim lies in the southwest corner of Hesse in the Rhine rift at the Biedensand Cons ...
and UV and infrared lamps from
Heraeus.
IT & Telecom
Many IT and telecommunications companies are located in Hesse, many of them in Frankfurt and Darmstadt, like
Software AG
Founded in 1969, Software AG is an enterprise software company with over 10,000 enterprise customers in over 70 countries. The company is the second largest software vendor in Germany, and the seventh largest in Europe. Software AG is traded on t ...
(Darmstadt),
T-Systems
T-Systems International GmbH (T-Systems) is an internationally operating service provider for information technologies and digital transformation. The company is part of Deutsche Telekom AG and is headquartered in Frankfurt am Main.
As of 2012, T ...
(Frankfurt and Darmstadt),
Deutsche Telekom (laboratories in Darmstadt),
DB Systel (Frankfurt),
Lufthansa Systems (Raunheim near Frankfurt) and
DE-CIX
DE-CIX (Deutsche Commercial Internet Exchange) is an operator of carrier- and data-center-neutral Internet Exchanges, with operations in Europe, North America, Africa, the Middle East, India and Southeast Asia. All DE-CIX activities and companies ...
(Frankfurt).
Food & Beverage
Sweet making is typical, there are 2 big factories:
Ferrero,
Stadtallendorf
Stadtallendorf is a town in the district of Marburg-Biedenkopf, Hesse, Germany. It lies about east of Marburg. In 2010, the town hosted the 50th Hessentag state festival.
Geography
Location
Under the German system of ''Naturräume'', Stad ...
and Baronie (Sarotti),
Hattersheim am Main
Hattersheim am Main () is a town in the Main-Taunus district, Hesse (Germany) and part of the Frankfurt Rhein-Main urban area.
Geography
Neighbouring towns
Hattersheim borders the city of Frankfurt in the northeast, in the southeast with Kels ...
.
Frankfurter Sausage is famous, but there is also other sorts like
Frankfurter Rindswurst,
Ahle Wurst.
Beverage industry is well-developed and manufactures sparkling wine (
Sekt
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, European Union countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne regi ...
), white wine (
Riesling
Riesling (, ; ) is a white grape variety that originated in the Rhine region. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet, and sparkling wh ...
), mineral waters (
Selters), beers (
Radeberger) and
cider.
Gruene-Sauce-Denkmal.jpg, Green Sauce Monument
In
Frankfurt-Oberrad exists growing of wild herbs for
green sauce and monument.
Defunct Industries
The leather industry was predominantly based in
Offenbach, but is now extinct, existing only in museums. The same happened with Frankfurt's fur industry and Hanau's jewelry industry.
Typical Hesse's Products
Opel Insignia B FL IMG 4300.jpg, Opel Insignia
The Opel Insignia is a large family car (D-segment in Europe) developed and produced by the German car manufacturer Opel since 2008. Taking its name from a 2003 concept car, the model line serves as the flagship Opel car line, slotted above the ...
Braun_Shaver_-_Austin_Calhoon_Photograph.jpg, Braun Shaver
Leica_Q2_(L1000042).jpg, Leica Q2
Bombardier_TRAXX_187_002-1,_100_years_of_the_Lötschberg,_Lalden.jpg, Locomotive TRAXX
Hochleistungs-Kettenwirkautomat.jpg, Warp knitting machine (Karl Mayer)
DNEX-Tryckeriet,_interiör,_2017a.jpg, Printing machine (MAN Roland Colorman)
Apfelwein_Geripptes_Bembel.jpg, Apfelwein(Cider)
Riesling_Kabinett_1975_in_glass.jpg, Riesling
Riesling (, ; ) is a white grape variety that originated in the Rhine region. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet, and sparkling wh ...
wine
Unemployment
The
Hochtaunuskreis has the lowest unemployment rate at 3.8% while the independent city of Kassel has the highest rate nationally at 12.1%. In October 2018 the unemployment rate stood at 4.4% and was lower than the national average.
Traffic and public transportation
Road transport
Hesse has a dense highway network with a total of 24 motorways. The internationally important motorway routes through Hesse are the A3, A5, and A7. Close to Frankfurt Airport is the
Frankfurter Kreuz, Germany's busiest and one of Europe's busiest motorway junctions, where the motorways
A3 (Arnhem-Cologne-Frankfurt-Nuremberg-Passau) and
A5 (Hattenbach-Frankfurt-Karlsruhe-Basel) intersect. The A5 becomes as wide as four lanes in each direction near the city of Frankfurt am Main, and during the rush-hour, it is possible to use the emergency lanes on the A3 and A5 motorway in the
Rhine-Main Region, adding additional lanes. Other major leading Hesse highways are the
A4, the
A44 A44 may refer to :
* A44 road (Great Britain), a road connecting Oxford, England and Aberystwyth, Wales
* A44 motorway (Germany), a road connecting Aachen at the German-Belgian border and Kassel
* A44 motorway (Netherlands), a motorway in the Nethe ...
, the
A45, the Federal Highway
A66 and the
A67. There are also a number of smaller motorways and major trunk roads, some of which are
dual carriageways.
Railway transport
Hesse is accessed by many major rail lines, including the high-speed lines
Cologne–Frankfurt(op.speed 300 km/h) and
Hanover–Würzburg. Other north-south connections traverse major east–west routes from Wiesbaden and Mainz to Frankfurt and from Hanau and Aschaffenburg to Fulda and Kassel. The Frankfurt Central Station is the most important hub for German trains, with over 1,100 trains per day.
The region around Frankfurt has an extensive
S-Bahn network, the
S-Bahn Rhein-Main, which is complemented by many regional train connections. In the rest of the country, the rail network is less extensive. Since 2007, the region around Kassel has been served by the
RegioTram
The Bogotá suburban rail ('' Spanish: Tren de cercanías de Bogotá''), also known as RegioTram, is a transportation project to create a mass and rapid transport system to connect Bogotá with surrounding cities. The railways of the former Bogot ...
, a
tram-train-concept similar to the
Karlsruhe model.
Air transport
Frankfurt Airport is by far the largest airport in Germany with more than 57 million passengers each year, is and among the world's ten largest.
Frankfurt Egelsbach Airport
Frankfurt Egelsbach Airport (german: Flugplatz Frankfurt-Egelsbach) is a general aviation airport located near Egelsbach, a town in the German state of Hesse. It is located southeast of Frankfurt Airport.
History
The airport was opened in 1 ...
lies to the south, and is frequented by
general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
and private planes.
Kassel Airport offers a few flights to holiday destinations, but has struggled to compete. There are also a number of sports airfields.
Low-cost airline
A low-cost carrier or low-cost airline (occasionally referred to as '' no-frills'', ''budget'' or '' discount carrier'' or ''airline'', and abbreviated as ''LCC'') is an airline that is operated with an especially high emphasis on minimizing op ...
s, especially
Ryanair, use
Frankfurt-Hahn Airport as a major base, although the airport is actually located about 100 km from Frankfurt in the neighbouring state of
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
. The DFS (
German air traffic control) has its headquarters in
Langen.
References
Notes
Bibliography
* Ingrao, Charles W. The ''Hessian mercenary state: ideas, institutions, and reform under Frederick II, 1760–1785'' (Cambridge University Press, 2003).
* Ingrao, Charles. "" Barbarous Strangers": Hessian State and Society during the American Revolution." ''
American Historical Review
''The American Historical Review'' is a quarterly academic history journal and the official publication of the American Historical Association. It targets readers interested in all periods and facets of history and has often been described as the ...
'' 87.4 (1982): 954–976
online* Wegert, Karl H. "Contention with Civility: The State and Social Control in the German Southwest, 1760–1850." ''
Historical Journal'' 34.2 (1991): 349–369
online* Wilder, Colin F. "" THE RIGOR OF THE LAW OF EXCHANGE": How People Changed Commercial Law and Commercial Law Changed People (Hesse-Cassel, 1654–1776)." ''Zeitschrift für Historische Forschung'' (2015): 629–659
online*
*
External links
Official government portal (English version)
Wiki about Hesse in Hessian language*
*
{{Authority control
NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union
States of Germany
 Situated in west-central Germany, the state of Hesse borders the German states of
Situated in west-central Germany, the state of Hesse borders the German states of 



 Hesse is divided into 21 districts (Kreise) and five independent cities, each with their own local governments. They are, shown with abbreviations as used on vehicle number plates:
# Bergstraße (
Hesse is divided into 21 districts (Kreise) and five independent cities, each with their own local governments. They are, shown with abbreviations as used on vehicle number plates:
# Bergstraße ( In 2016
In 2016  Frankfurt hosts the following professional sports teams or clubs:
* 1. FFC Frankfurt (1998–2020), football (women)
* Eintracht Frankfurt, football (men, women)
* FSV Frankfurt, football (men)
*
Frankfurt hosts the following professional sports teams or clubs:
* 1. FFC Frankfurt (1998–2020), football (women)
* Eintracht Frankfurt, football (men, women)
* FSV Frankfurt, football (men)
*