Romania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern and
 It is believed that the
It is believed that the
 The
The
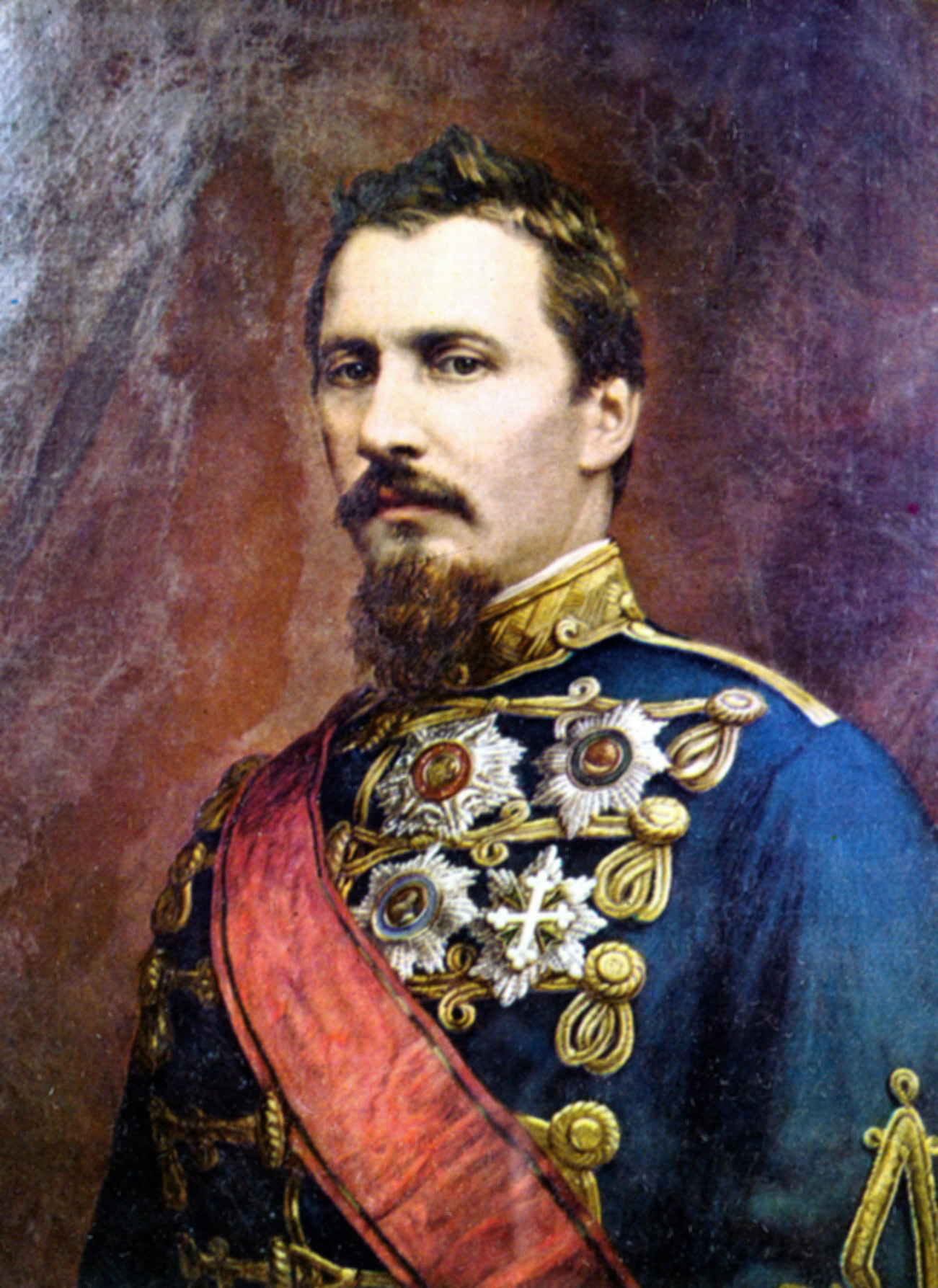

, 24 January 2009, ''Jurnalul Național'', accessed 6 July 2012 After carrying out numerous reforms that laid the foundations for the modernisation of the state, he was forced in 1866 by a broad coalition of the political parties of the time, also known as the "
History of Romania
”. Encarta. Accessed 14 March 2009.
Eugen Denize. Accessed 15 March 2009. Following Antonescu's outright refusal, King Mihai I ordered the dismissal and arrest of the marshal, and Romania switched sides to join the Allies.
Accessed 16 August 2010. In the early 1960s, the Romanian government began asserting a certain degree of independence from the
ICI. Accessed 15 March 2009. although it did not abandon its repressive policies (which it labeled "revolutionary conquests") in domestic affairs. In 1965, communist leader
''
 In the context of the fall of communism throughout Eastern Europe during the
In the context of the fall of communism throughout Eastern Europe during the
. Hdrstats.undp.org. Retrieved on 21 August 2010. However, Romania's development suffered a major setback during the late 2000s' recession leading to a large gross domestic product contraction and a budget deficit in 2009. This led to Romania borrowing from the International Monetary Fund. Worsening economic conditions led to unrest and triggered a political crisis in 2012. Since 2014, Romania launched an anti-corruption effort that led to the prosecution of medium- and high-level political, judicial and administrative offenses by the
Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
. It borders Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
to the north and east, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
to the west, Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
to the southwest, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
to the south, Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
to the east, and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typi ...
, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
, empties into the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta (, ; , ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. Occurring where the Danube, Danube River empties into the Black Sea, most of the Danube Delta lies in Romania ...
in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak
Moldoveanu Peak (, ; "Moldavian Peak"), at , is the highest mountain peak in Romania.Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
is the country's largest urban area and financial centre
A financial centre (financial center in American English) or financial hub is a location with a significant concentration of commerce in financial services.
The commercial activity that takes place in a financial centre may include banking, ...
. Other major urban areas
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
include Cluj-Napoca
Cluj-Napoca ( ; ), or simply Cluj ( , ), is a city in northwestern Romania. It is the second-most populous city in the country and the seat of Cluj County. Geographically, it is roughly equidistant from Bucharest (), Budapest () and Belgrade ( ...
, Timișoara
Timișoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of Timiș County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, Timișoara is consider ...
, Iași
Iași ( , , ; also known by other #Etymology and names, alternative names), also referred to mostly historically as Jassy ( , ), is the Cities in Romania, third largest city in Romania and the seat of Iași County. Located in the historical ...
, Constanța
Constanța (, , ) is a city in the Dobruja Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Romania. A port city, it is the capital of Constanța County and the country's Cities in Romania, fourth largest city and principal port on the Black ...
and Brașov
Brașov (, , ; , also ''Brasau''; ; ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the county seat (i.e. administrative centre) of Brașov County.
According to the 2021 Romanian census, ...
.
Settlement in the territory of modern Romania began in the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears ...
, later becoming the Dacian Kingdom
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
before Roman conquest and Romanisation
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, ...
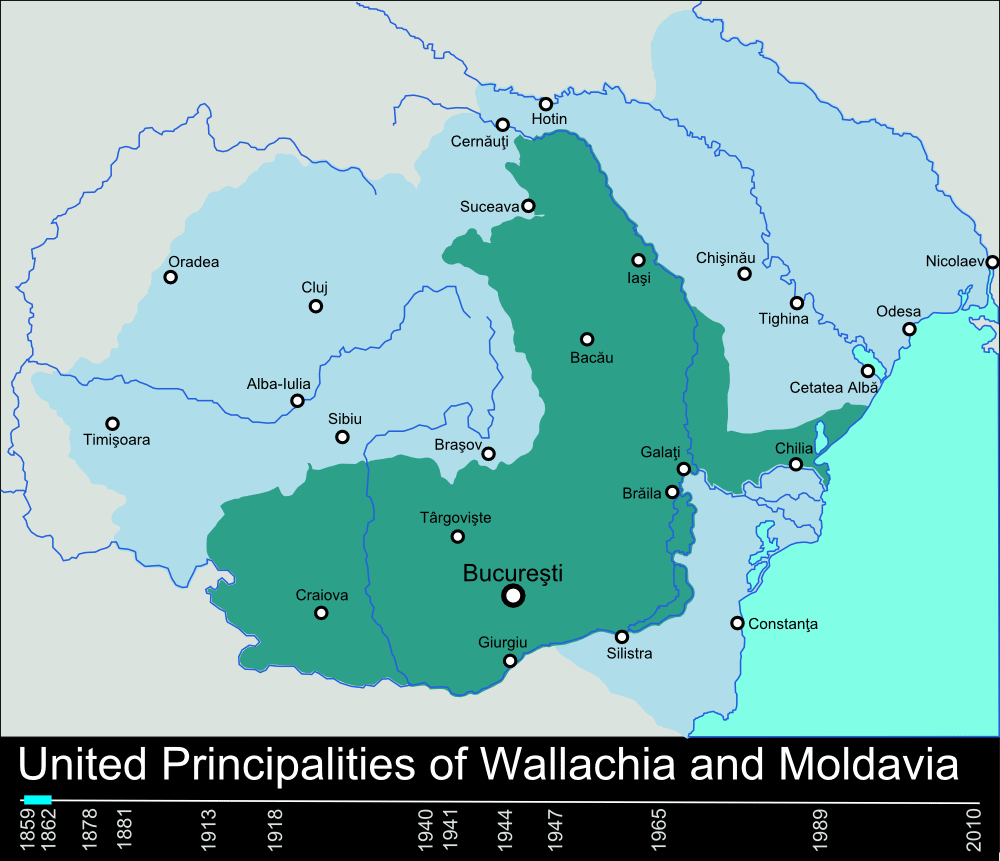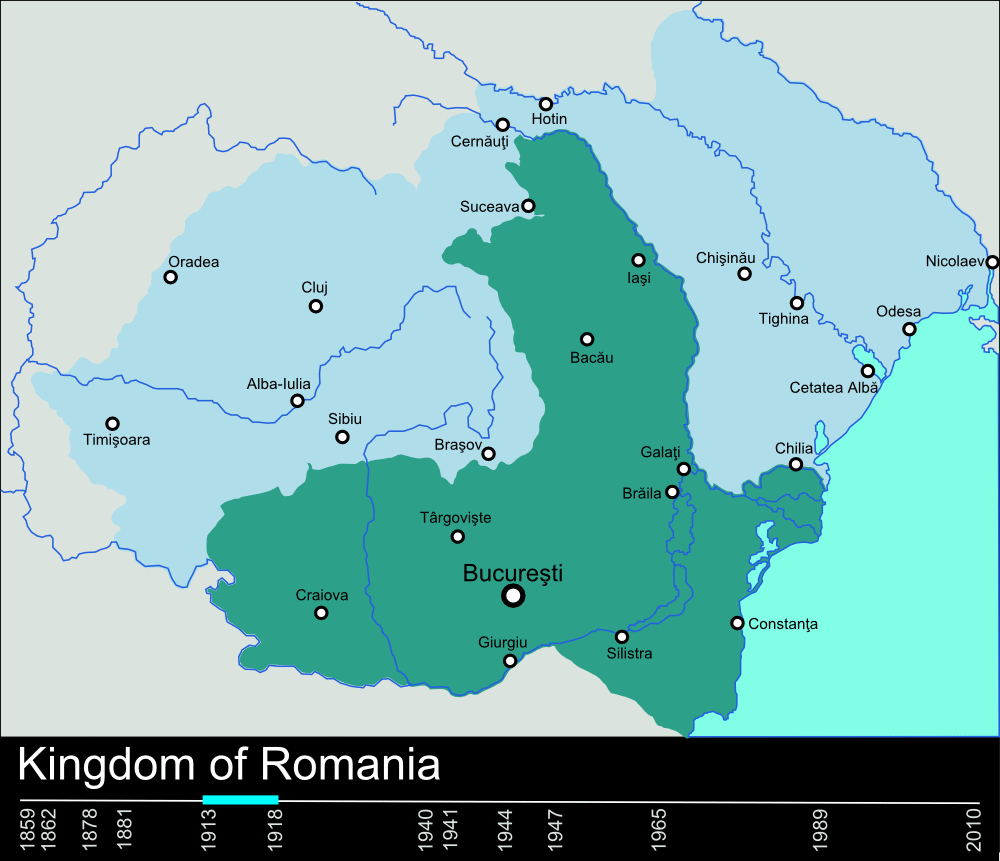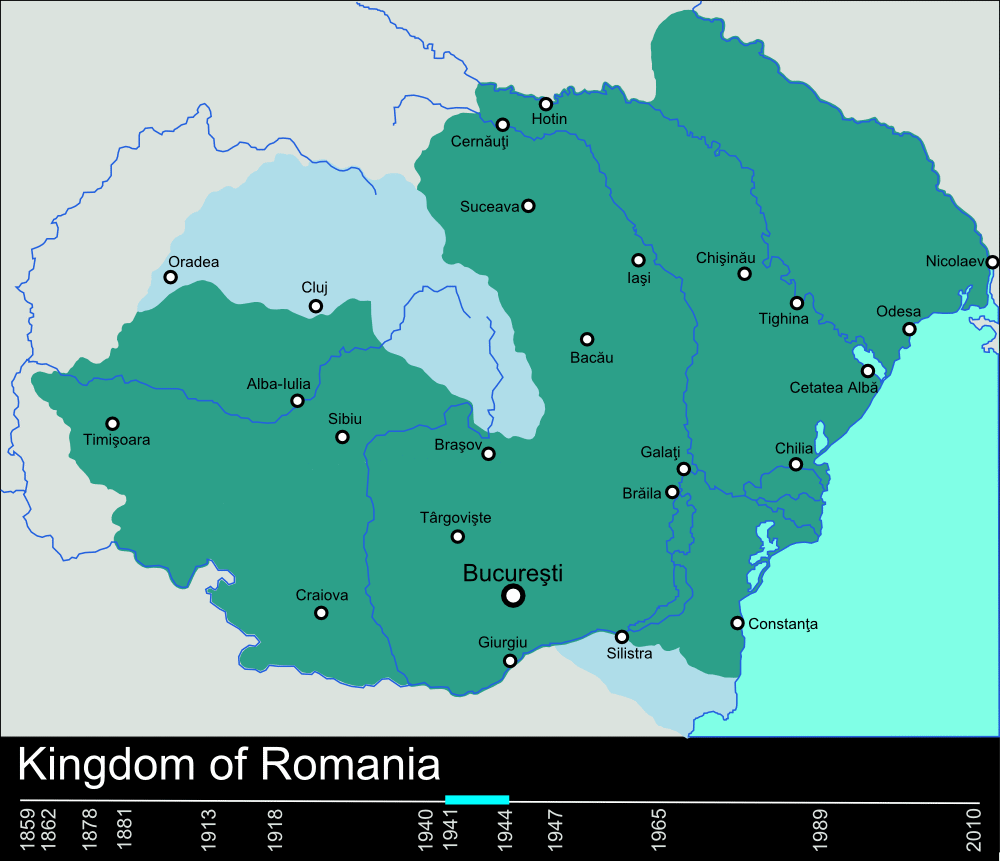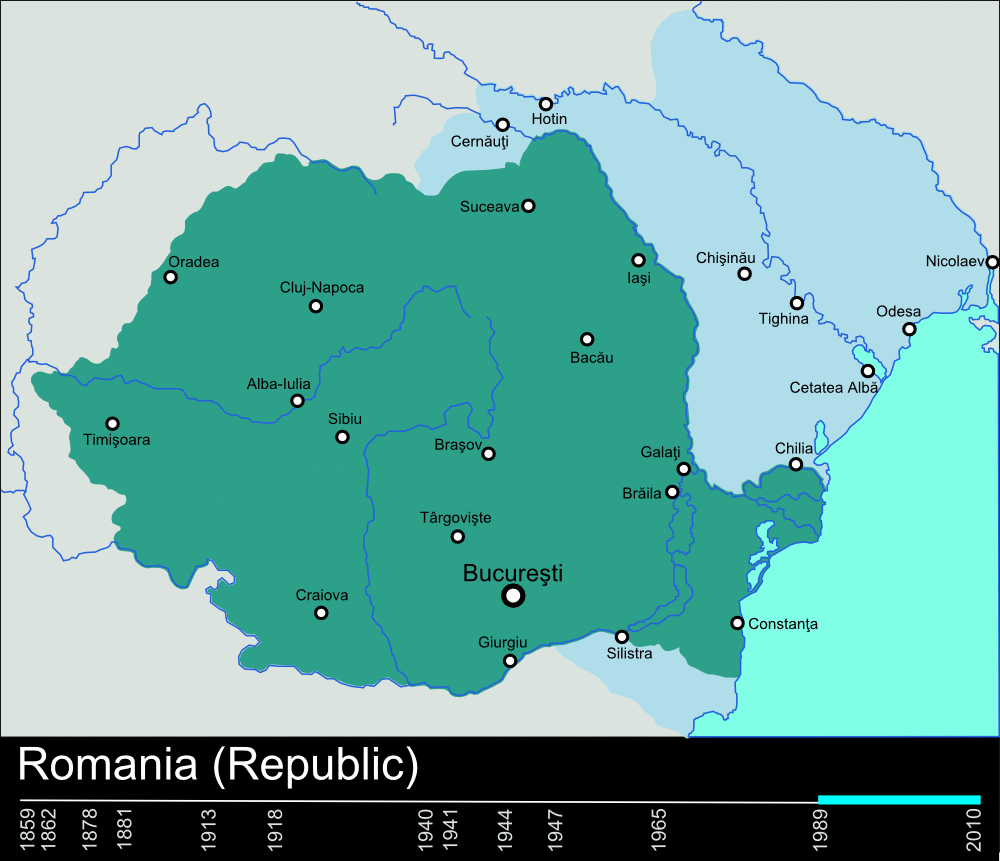
. The modern Romanian state formed in 1859 with the unification of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
under Alexandru Ioan Cuza
Alexandru Ioan Cuza (, or Alexandru Ioan I, also Anglicised as Alexander John Cuza; 20 March 1820 – 15 May 1873) was the first ''domnitor'' (prince) of the Romanian Principalities through his double election as List of monarchs of Moldavia ...
, becoming Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania () was a constitutional monarchy that existed from with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King of Romania, King Carol I of Romania, Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian royal family), until 1947 wit ...
in 1881 under Carol I
Carol I or Charles I of Romania (born Karl Eitel Friedrich Zephyrinus Ludwig von Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen; 20 April 1839 – ), was the monarch of Romania from 1866 to his death in 1914, ruling as Prince (''Domnitor'') from 1866 to 1881, and as ...
. Romania gained independence from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in 1877, formalised by the Treaty of Berlin. After World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
, and Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
joined the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynast ...
, forming Greater Romania
Greater Romania () is the Kingdom of Romania in the interwar period, achieved after the Great Union or the related pan-nationalist ideal of a nation-state which would incorporate all Romanian speakers.Irina LivezeanuCultural Politics in Greate ...
, which reached its largest territorial extent. In 1940, under Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
pressure, Romania lost territories to Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. Following the 1944 Romanian coup d'état
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 2 – WWII:
** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixt ...
, Romania switched sides to join the Allies. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, it regained Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania (, ) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary (1920-1946), Kingdom ...
through the Paris Peace Treaties. Under Soviet occupation
During World War II, the Soviet Union occupied and annexed several countries effectively handed over by Nazi Germany in the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of 1939. These included the eastern regions of Poland (incorporated into three differe ...
, King Michael I was forced to abdicate, and Romania became a socialist republic
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. This article is about states that refer to themselves as socialist states, and not specifically ab ...
and Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
member. After the 1989 Revolution, Romania began a transition to liberal democracy
Liberal democracy, also called Western-style democracy, or substantive democracy, is a form of government that combines the organization of a democracy with ideas of liberalism, liberal political philosophy. Common elements within a liberal dem ...
and a market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production, and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a mark ...
.
Romania is a developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
with a high-income economy
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a country with a gross national income per capita of US$14,005 or more in 2023, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" ...
, classified as a middle power
A middle power is a state that is not a superpower or a great power, but still exerts influence and plays a significant role in international relations. These countries often possess certain capabilities, such as strong economies, advanced tech ...
in international relations
International relations (IR, and also referred to as international studies, international politics, or international affairs) is an academic discipline. In a broader sense, the study of IR, in addition to multilateral relations, concerns al ...
. It is a unitary republic
A unitary state is a (sovereign) state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or sub-state units). Such units exer ...
with a multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
and a semi-presidential
A semi-presidential republic, or dual executive republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamen ...
representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy or electoral democracy, is a type of democracy where elected delegates represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies func ...
. It is home to 11 UNESCO World Heritage Sites
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
and has become an increasingly popular tourist destination, attracting 14 million foreign visitors in 2024. Romania is a net exporter of automotive and vehicle parts worldwide and has established a growing reputation as a technology centre, with some of the fastest internet speeds globally. Romania is a member of several international organisations
An international organization, also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is an organization that is established by a treaty or other type of instrument governed by international law and possesses its own leg ...
, including the European Union, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
, and the BSEC.
Etymology
''Romania'' derives from the local name forRomanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
(), which in turn derives from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''romanus'', meaning "Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
" or "of Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
". This ethnonym for Romanians is first attested in the 16th century by Italian humanists travelling in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
, and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
. The oldest known surviving document written in Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
that can be precisely dated, a 1521 letter known as the " Letter of Neacșu from Câmpulung", is notable for including the first documented occurrence of ''Romanian'' in a country name: Wallachia is mentioned as .
History
Dacia and the Roman Empire
 It is believed that the
It is believed that the tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ...
responsible for creating the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
culture on the territory of modern Romania belonged to the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
group of Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, in ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (, ''Geōgraphiká''; or , "Strabo's 17 Books on Geographical Topics") or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek in the late 1st century BC, or early 1st cen ...
'', notes that the Getae spoke the same language as the Thracians, and the Dacians the same language as the Getae. However, the earliest account of the Getae is attributed to Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
. The conquest of Dacia by the Romans led to the fusion of two cultures—the Daco-Romans became the ancestors of the Romanian people
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
. After Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
became a province of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, elements of Roman culture and civilisation—most notably Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
, which laid the foundation for the development of the Romanian language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved fr ...
—were introduced.
Based on information from the inscription at Dionysupolis
Dionysupolis or Dionysoupolis or Dionysopolis or Dionysou polis () was a town of ancient Thrace, later of Moesia, on the river Ziras. It was founded as a Thracian settlement in was founded in the 5th century BC, but was later colonised by the Ionia ...
and the account of Iordanes, it is known that under the rule of Burebista
Burebista () was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, ...
, assisted by the great priest Deceneu, the first Geto-Dacian state was formed. In 44 BC, Burebista was assassinated by one of his servants. After his death, the Geto-Dacian state fragmented into four, and later five, kingdoms. The core of the state remained in the area of the Șureanu Mountains
The Șureanu Mountains ( German: ''Mühlbacher Gebirge'', Hungarian: ''Kudzsiri-havasok''), belong to Romania's Parâng range in the Southern Carpathians, with peaks frequently exceeding .
The mountains are located north of Romania's Jiu Vall ...
, where successive rulers such as Deceneu, Comosicus
Comosicus was a Dacian king and high priest who lived in the 1st century BC. The only reference to Comosicus is a passage in the writings of the Roman historian Jordanes.
Sources
Jordanes refers to Burebista as king of Dacia, but then goes on to ...
, and Coryllus held power. The centralised Dacian state reached the peak of its development under Decebalus
Decebalus (; ), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a R ...
.Small Encyclopedia of Universal History, p. 284 – Marcel D. Popa, Horia C. Matei – Editura Politică, Bucharest, 1988. During this period, a series of conflicts with the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
continued, with part of the Dacian state being conquered in 106 AD by the Roman emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
. Between 271 and 275 AD, the Aurelian retreat took place.
Period of the Principalities and the Phanariot Era
In thefirst millennium
File:1st millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: Depiction of Jesus, the central figure in Christianity; The Colosseum, a landmark of the once-mighty Roman Empire; Kaaba, the Great Mosque of Mecca, the holiest site of Islam; Chess, a ne ...
, waves of nomads
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, Nomadic pastoralism, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and Merchant, trader nomads. In the twentieth century, ...
swept across the territory of Romania: the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
during the 3rd–4th centuries, the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
in the 4th century, the Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the G ...
in the 5th century, the Avars in the 6th century, the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
in the 7th century, the Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the ...
in the 9th century, the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
, the Cumans
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cumania, Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Ru ...
, the Uzes and the Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
during the 10th–12th centuries, and the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
in the 13th century. In 1054, a series of ecclesiastical differences and theological disputes between the in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Greek East and Latin West
Greek East and Latin West are terms used to distinguish between the two parts of the Greco-Roman world and of medieval Christendom, specifically the eastern regions where Greek was the ''lingua franca'' (Greece, Anatolia, the southern Balkans, ...
caused the Great Schism, eventually resulting in Romania adopting Orthodoxy.
In the 13th century
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar.
The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched ...
, the first bearers of the Slavic noble title Knyaz
A , also , ''knjaz'' or (), is a historical Slavs, Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times. It is usually translated into English language, English as 'prince', 'king' or 'duke', depending on specific historical c ...
south of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
are attested. Later, in the context of the crystallisation of feudal relations, as a result of the creation of favourable internal and external conditions (the weakening of Hungarian pressure and the diminishing of Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
domination), autonomous feudal states emerged south and east of the Carpathians – in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
in 1310, under Basarab I
Basarab I (), also known as Basarab the Founder (; – 1351/1352), was a ''voivode'' and later the first independent ruler of Wallachia who lived in the first half of the . Many details of his life are uncertain. According to two popular theo ...
, and Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
in 1359, under Bogdan I. Among the Romanian rulers who played a more important role can be mentioned: Alexander the Good
Alexander I, commonly known as Alexander the Good (; – 1 January 1432) was Voivode of Moldavia between 1400 and 1432. He was the son of Roman I and succeeded Iuga to the throne. As ruler he initiated a series of reforms while consolidating ...
, Stephen the Great
Stephen III, better known as Stephen the Great (; ; died 2 July 1504), was List of rulers of Moldavia, Voivode (or Prince) of Moldavia from 1457 to 1504. He was the son of and co-ruler with Bogdan II of Moldavia, Bogdan II, who was murdered in ...
, Petru Rareș
Petru Rareș (; – 3 September 1546) or Petru IV was twice voivode of Moldavia from 20 January 1527 to 18 September 1538 and from 19 February 1541 to 3 September 1546. He was an illegitimate child born (probably at Hârlău) to Stephen III of ...
, and Dimitrie Cantemir
Dimitrie or Demetrius; Cantemir (; ; 26 October 1673 – 21 August 1723), also known by other spellings, was a Moldavian prince, statesman, and man of letters. He twice served as voivode of Moldavia (March–April 1693 and 1710–1711). Durin ...
in Moldova; Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder (, ; 1355 – 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited the throne.
After the dea ...
, Vlad the Impaler
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ) or Vlad Dracula (; ; 1428/31 – 1476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most important rulers in Wallachian hi ...
, Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvani ...
, and Constantin Brâncoveanu
Constantin Brâncoveanu (; 1654 – August 15, 1714) was List of Wallachian rulers, Prince of Wallachia between 1688 and 1714.
Biography
Ascension
Constantin Brâncoveanu was the son of Pope Brâncoveanu (Matthew) and his wife, Stanca Can ...
in Wallachia; and John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi (; ; ; ; ; – 11 August 1456) was a leading Kingdom of Hungary, Hungarian military and political figure during the 15th century, who served as Regent of Hungary, regent of the Kingdom of Hungary (1301–1526), Kingdom of Hungary ...
in Transylvania.
Beginning in the late 15th century
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian calendar dates from 1 January 1401 (represented by the Roman numerals MCDI) to 31 December 1500 (MD).
In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Re ...
, the two principalities gradually came under the influence of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, which throughout the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
was part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, governed by voivodes, became a self-governing principality and a vassal of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
from 1526. At the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries, Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvani ...
for a very brief period ruled over a large part of the territory of present-day Romania.
Early modern times and national awakening
The Kingdom of Hungary collapsed, and the Ottomans occupied parts of Banat and Crișana in 1541. Transylvania andMaramureș
( ; ; ; ) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, along parts of the upper Tisza River drainage basin; it covers the Maramureș Depression and the ...
, along with the rest of Banat and Crișana developed into a new state under Ottoman suzerainty, the Principality of Transylvania. The Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, initiated in Germany by Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
in 1517, encouraged the rise of Protestantism and four denominations—Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyteri ...
, Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
, Unitarianism
Unitarianism () is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian sect of Christianity. Unitarian Christians affirm the wikt:unitary, unitary God in Christianity, nature of God as the singular and unique Creator deity, creator of the universe, believe that ...
, and Roman Catholicism—were officially acknowledged in 1568. The Romanians' Orthodox faith remained only tolerated, although they made up more than one-third of the population, according to 17th-century estimates.
The princes of Transylvania, Wallachia, and Moldavia joined the Holy League against the Ottoman Empire in 1594. The Wallachian prince, Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvani ...
, united the three principalities under his rule in May 1600. The neighbouring powers forced him to abdicate in September, but he became a symbol of the unification of the Romanian lands in the 19th century. Although the rulers of the three principalities continued to pay tribute to the Ottomans, the most talented princes—Gabriel Bethlen
Gabriel Bethlen (; 1580 – 15 November 1629) was Prince of Transylvania from 1613 to 1629 and Duke of Opole from 1622 to 1625. He was also King-elect of Hungary from 1620 to 1621, but he never took control of the whole kingdom. Bethlen, sup ...
of Transylvania, Matei Basarab
Matei Basarab (; 1588, Brâncoveni, Olt – 9 April 1654, Bucharest) was the voivode (prince) of Wallachia from 1632 to 1654.
Reign
Much of Matei's reign was spent fighting off incursions from Moldavia, which he successfully accomplished in 1 ...
of Wallachia, and Vasile Lupu
Lupu Coci, known as Vasile Lupu (; 1595 – 1661), was the voivode of Moldavia between 1634 and 1653. He was of Albanian and Greek origin. Lupu had secured the Moldavian throne in 1634 after a series of complicated intrigues and managed to h ...
of Moldavia—strengthened their autonomy.
The united armies of the Holy League expelled the Ottoman troops from Central Europe between 1684 and 1699, and the Principality of Transylvania was integrated into the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. The Habsburgs supported the Catholic clergy and persuaded the Orthodox Romanian prelates to accept the union with the Roman Catholic Church in 1699. In the 18th century
The 18th century lasted from 1 January 1701 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCI) to 31 December 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the Atlantic Revolutions. Revolutions began to ch ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
maintained their internal autonomy, but in 1711
In the Swedish calendar it was a common year starting on Sunday, one day ahead of the Julian and ten days behind the Gregorian calendar.
Events
January–March
* January – Cary's Rebellion: The Lords Proprietor appoint Edward ...
and 1716
Events
January–March
* January 16 – The application of the Nueva Planta decrees to Catalonia make it subject to the laws of the Crown of Castile, and abolishes the Principality of Catalonia as a political entity, conclud ...
, respectively, the period of the Phanariots
Phanariots, Phanariotes, or Fanariots (, , ) were members of prominent Greek families in Phanar (Φανάρι, modern ''Fener''), the chief Greek quarter of Constantinople where the Ecumenical Patriarchate is located, who traditionally occupie ...
began, with rulers appointed directly by the Porte from among the noble families of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
origin in Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. With the signing of the Ausgleich in 1867
There were only 354 days this year in the newly purchased territory of Alaska. When the territory transferred from the Russian Empire to the United States, the calendric transition from the Julian to the Gregorian Calendar was made with only 1 ...
, Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
quickly lost its remaining political autonomy, being politically and administratively incorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
. The Church Union strengthened the Romanian intellectuals' devotion to their Roman heritage. The Orthodox Church was restored in Transylvania only after Orthodox monks stirred up revolts in 1744 and 1759. The organisation of the Transylvanian Military Frontier
The Transylvanian Military Frontier (; ; ) was a territory in the Habsburg monarchy. It was a section of the Habsburg Military Frontier.
History
It was founded in 1762 from territories that had been part of the Habsburg Principality of Transyl ...
caused further disturbances, especially among the Székelys in 1764.
Princes Dimitrie Cantemir
Dimitrie or Demetrius; Cantemir (; ; 26 October 1673 – 21 August 1723), also known by other spellings, was a Moldavian prince, statesman, and man of letters. He twice served as voivode of Moldavia (March–April 1693 and 1710–1711). Durin ...
of Moldavia and Constantin Brâncoveanu
Constantin Brâncoveanu (; 1654 – August 15, 1714) was List of Wallachian rulers, Prince of Wallachia between 1688 and 1714.
Biography
Ascension
Constantin Brâncoveanu was the son of Pope Brâncoveanu (Matthew) and his wife, Stanca Can ...
of Wallachia concluded alliances with the Habsburg Monarchy and Russia against the Ottomans, but they were dethroned in 1711 and 1714, respectively. The sultans lost confidence in the native princes and appointed Orthodox merchants from the Phanar district of Istanbul to rule Moldova and Wallachia. The Phanariot
Phanariots, Phanariotes, or Fanariots (, , ) were members of prominent Greeks, Greek families in Fener, Phanar (Φανάρι, modern ''Fener''), the chief Greek quarter of Constantinople where the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Ecume ...
princes pursued oppressive fiscal policies and dissolved the army. The neighbouring powers took advantage of the situation: the Habsburg Monarchy annexed the northwestern part of Moldavia, or Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
, in 1775, and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
seized the eastern half of Moldavia, or Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
, in 1812.
A census revealed that the Romanians were more numerous than any other ethnic group in Transylvania in 1733, but legislation continued to use contemptuous adjectives (such as "tolerated" and "admitted") when referring to them. The Uniate bishop, Inocențiu Micu-Klein
Ioan Inocențiu Micu-Klein, also known by his lay name Ioan Micu (1692 – 22 September 1768), was a Bishop of Fogaras and Primate of the Romanian Greek Catholic Church from 1730 to his resignation in 1751. He played an instrumental role in the ...
who demanded recognition of the Romanians as the fourth privileged nation was forced into exile. Uniate and Orthodox clerics and laymen jointly signed a plea for the Transylvanian Romanians' emancipation in 1791, but the monarch and the local authorities refused to grant their requests.
 The
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (; ), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on , in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kaynardzha, Bulgaria and Cuiugiuc, Romania) between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, ending the R ...
authorised the Russian ambassador in Istanbul to defend the autonomy of Moldavia and Wallachia (known as the Danubian Principalities
The Danubian Principalities (, ) was a conventional name given to the Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, which emerged in the early 14th century. The term was coined in the Habsburg monarchy after the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (1774) ...
) in 1774. Taking advantage of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
, a Wallachian lesser nobleman, Tudor Vladimirescu, stirred up a revolt against the Ottomans in January 1821, but he was murdered in June by Phanariot Greeks. After a new Russo-Turkish War, the Treaty of Adrianople strengthened the autonomy of the Danubian Principalities in 1829, although it also acknowledged the sultan's right to confirm the election of the princes.
Mihail Kogălniceanu
Mihail Kogălniceanu (; also known as Mihail Cogâlniceanu, Michel de Kogalnitchan; September 6, 1817 – July 1, 1891) was a Romanian Liberalism, liberal statesman, lawyer, historian and publicist; he became Prime Minister of Romania on Octo ...
, Nicolae Bălcescu
Nicolae Bălcescu () (29 June 181929 November 1852) was a Romanian Wallachian soldier, historian, journalist, and leader of the 1848 Wallachian Revolution.
Early life
Born in Bucharest to a family of low-ranking nobility, he used his mother ...
and other leaders of the 1848 revolutions in Moldavia and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
demanded the emancipation of the peasants and the union of the two principalities, but Russian and Ottoman troops crushed their revolt. The Wallachian revolutionists were the first to adopt the blue, yellow and red tricolour
A triband is a vexillological style which consists of three stripes arranged to form a flag. These stripes may be two or three colours, and may be charged with an emblem in the middle stripe. Not all tribands are tricolour flags, which requires t ...
as the national flag
A national flag is a flag that represents and national symbol, symbolizes a given nation. It is Fly (flag), flown by the government of that nation, but can also be flown by its citizens. A national flag is typically designed with specific meanin ...
. In Transylvania, most Romanians supported the imperial government against the Hungarian revolutionaries Hungarian may refer to:
* Hungary, a country in Central Europe
* Kingdom of Hungary, state of Hungary, existing between 1000 and 1946
* Hungarians/Magyars, ethnic groups in Hungary
* Hungarian algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm for solving the ...
after the Diet passed a law concerning the union of Transylvania and Hungary. Bishop Andrei Șaguna
Andrei Șaguna (; 20 January 1808, Miskolc, Kingdom of Hungary (1526–1867), Hungary – 28 June 1873, Nagyszeben, Kingdom of Hungary (1867–1918), Hungary) was a Metropolitan bishop of the Romanian Orthodox Church in Transylvania, and one of ...
proposed the unification of the Romanians of the Habsburg Monarchy in a separate duchy, but the central government refused to change the internal borders.
Unification and the Kingdom of Romania

From the Little Union to the Great War
The modern Romanian state was created through the unification of the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, accepted as a federative structure by the Great Powers following the Paris Convention of 1858, and later cemented by the simultaneous election as ruler of both states of the unionistAlexandru Ioan Cuza
Alexandru Ioan Cuza (, or Alexandru Ioan I, also Anglicised as Alexander John Cuza; 20 March 1820 – 15 May 1873) was the first ''domnitor'' (prince) of the Romanian Principalities through his double election as List of monarchs of Moldavia ...
.150 de ani de la Unirea Principatelor Române, 24 January 2009, ''Jurnalul Național'', accessed 6 July 2012 After carrying out numerous reforms that laid the foundations for the modernisation of the state, he was forced in 1866 by a broad coalition of the political parties of the time, also known as the "
Monstrous coalition
"Monstrous coalition" () is the name that has remained in the collective consciousness of Romania to refer to the alliance between conservatives and radical liberals in order to obtain Alexandru Ioan Cuza's removal from power in 1866. This name was ...
", to abdicate and leave the country.Constantiniu, Florin: ''A Sincere History of the Romanian People'', Bucharest, Editura Univers Enciclopedic, 1997 – ISBN 973-9243-07-X
The union was at one time in peril, but the political leaders of the era succeeded in placing on the princely throne Carol I of Romania
Carol I or Charles I of Romania (born Karl Eitel Friedrich Zephyrinus Ludwig von Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen; 20 April 1839 – ), was the monarch of Romania from 1866 to his death in 1914, ruling as Prince (''Domnitor'') from 1866 to 1881, and as ...
, who accepted the Constitution and took the oath on 10 May 1866. Eleven years later, on 10 May 1877, Romania proclaimed its independence—achieved on the battlefield—and in 1881, on the same day of the year, Carol was crowned as King of Romania
The King of Romania () or King of the Romanians () was the title of the monarch of the Kingdom of Romania from 1881 until 1947, when the Romanian Workers' Party proclaimed the Romanian People's Republic following Michael I's forced abdication. ...
. In 1913, Romania entered the Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict that broke out when Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia and Kingdom of Greece, Greece, on 1 ...
against Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, at the end of which it obtained Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja or South Dobruja ( or simply , ; or , ), also the Quadrilateral (), is an area of north-eastern Bulgaria comprising Dobrich and Silistra provinces, part of the historical region of Dobruja. It has an area of 7,412 square km an ...
. In 1914, King Carol I
Carol I or Charles I of Romania (born Karl Eitel Friedrich Zephyrinus Ludwig von Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen; 20 April 1839 – ), was the monarch of Romania from 1866 to his death in 1914, ruling as Prince (''Domnitor'') from 1866 to 1881, and as ...
died, and his nephew, Ferdinand I, succeeded him on the throne.
World War I and the Great Union
In 1916, Romania enteredWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in Europe and th ...
on the side of the Entente Powers
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers ...
. Although the Romanian forces did not perform well militarily, by the end of the war the Austrian and Russian Empires had disintegrated; the National Assembly in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, and the Sfatul Țării
''Sfatul Țării'' ("Council of the Country"; ) was a council of political, public, cultural, and professional organizations in the guberniya, Governorate of Bessarabia in Russian Empire, Tsarist Russia. This became a legislative body which e ...
in Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
and Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
proclaimed their union with Romania, and King Ferdinand I and Queen Maria were crowned sovereign of all Romanians in Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; ; ) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the river Mureș (river), Mureș in the historical region of Transylvania, it has a ...
on 15 October 1922. The Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
recognised all the union proclamations in accordance with the right to self-determination established by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
’s ''Fourteen Points''.
Interwar period
After having left the country and renounced his claim to the throne in 1925,Carol II
Carol II (4 April 1953) was King of Romania from 8 June 1930, until his forced abdication on 6 September 1940. As the eldest son of Ferdinand I of Romania, King Ferdinand I, he became crown prince upon the death of his grand-uncle, King Carol I, ...
returned in 1930 and usurped his son’s throne; influenced by his inner circle—referred to by historians as the "Royal Camarilla"—he gradually undermined the democratic system, and in 1938 he assumed dictatorial powers. Although he was pro-Western (especially Anglophile), Carol attempted to appease extreme centrifugal forces by appointing nationalist governments that adopted anti-Semitic measures, such as the Goga cabinet and the one led by the Orthodox Patriarch Miron Cristea
Miron Cristea (; monastic name of Elie Cristea ; 20 July 1868 – 6 March 1939) was a Romanian cleric and politician.
A bishop in Hungarian-ruled Transylvania, Cristea was elected Metropolitan-Primate of the Orthodox Church of the newly unifie ...
.
World War II: Positions and territorial losses
Following theMolotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, officially the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and also known as the Hitler–Stalin Pact and the Nazi–Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Ge ...
of 1939, in June 1940 Romania accepted the loss of Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coa ...
, Northern Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
and the Hertsa
Hertsa or Hertza is a city located in Chernivtsi Raion, Chernivtsi Oblast in western Ukraine and has a population of
The city is located close to the border with Romania, southeast of Chernivtsi and north of Dorohoi. Until 2020, it was t ...
region in favour of the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(as stipulated in the Soviet ultimatum of 28 June 1940). Unaware of the details of the Soviet–German pact, Carol attempted to secure an alliance with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, and appointed Ion Gigurtu as President of the Council of Ministers, who declared that he would pursue a Nazi pro-Axis (Berlin–Rome) policy that was anti-Semitic and fascist-totalitarian in nature. Between 4 July and 4 September 1940, by accepting Hitler's arbitration over Transylvania (after Gigurtu declared on radio that Romania must make territorial sacrifices to justify its Nazi orientation and full adherence to the Berlin–Rome Axis), Romania ceded Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania (, ) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary (1920-1946), Kingdom ...
—including the city of Cluj
Cluj-Napoca ( ; ), or simply Cluj ( , ), is a city in northwestern Romania. It is the second-most populous city in the country and the seat of Cluj County. Geographically, it is roughly equidistant from Bucharest (), Budapest () and Belgrade ( ...
—to Hungary. The vast territories in Transylvania ceded by Ion Gigurtu to Hungary contained important natural resources, including gold mines. Ion Gigurtu also initiated negotiations to cede 8,000 km2 of Southern Dobruja to Bulgaria, these negotiations were interrupted by Antonescu's unconditional acceptance of the territorial cession.
In response to the chaotic withdrawal from Bessarabia, the territorial cessions, public discontent, and protests from political leaders, King Carol II suspended the 1938 Constitution of Romania
Events
January
* January 1 – State-owned railway networks are created by merger, in France (SNCF) and the Netherlands (Nederlandse Spoorwegen – NS).
* January 20 – King Farouk of Egypt marries Safinaz Zulficar, who beco ...
and appointed General Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu (; ; – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian military officer and Mareșal (Romania), marshal who presided over two successive Romania during World War II, wartime dictatorships as Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister and ''Conduc� ...
as Prime Minister. This measure, supported by the Iron Guard
The Iron Guard () was a Romanian militant revolutionary nationalism, revolutionary Clerical fascism, religious fascist Political movement, movement and political party founded in 1927 by Corneliu Zelea Codreanu as the Legion of the Archangel M ...
, demanded that the king abdicate in favour of his son, Mihai
Mihai () is a Romanian given name for males or a surname. It is equivalent to the English name Michael. A variant of the name is Mihail. Its female form is Mihaela. Notable people with these names include:
Given name
* Mihai Timofti (1948–2023 ...
. Subsequently, Antonescu assumed dictatorial powers and became President of the Council of Ministers, self-titling himself as the "Leader" of the state.Constantiniu, Florin: ''Hitler, Stalin and Romania – Romania and the Genesis of Operation “Barbarossa”'', Bucharest, Univers Enciclopedic, 2002�History of Romania
”. Encarta. Accessed 14 March 2009.
World War II
In 1941, as an ally ofNazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, Romania entered World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilisin ...
by declaring war on the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. A shift in fortunes only became discernible after the defeat at Stalingrad and the subsequent change of the USSR from a defensive to an offensive posture. On 23 August 1944, with the Soviet army having been present in northern Moldova since March, King Mihai I forcibly removed Marshal Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu (; ; – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian military officer and Mareșal (Romania), marshal who presided over two successive Romania during World War II, wartime dictatorships as Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister and ''Conduc� ...
from power, as he refused to sign an armistice with the Allies of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international Coalition#Military, military coalition formed during World War II (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers. Its principal members were the "Four Policeme ...
.''Memoria''Eugen Denize. Accessed 15 March 2009. Following Antonescu's outright refusal, King Mihai I ordered the dismissal and arrest of the marshal, and Romania switched sides to join the Allies.
Socialist Romania (1947–1989)
Less than three years after theSoviet occupation of Romania
The Soviet occupation of Romania refers to the period from 1944 to August 1958, during which the Soviet Union maintained a significant military presence in Socialist Republic of Romania, Romania. The fate of the territories held by Romania after 1 ...
, in 1947, King Michael I was forced to abdicate and the People's Republic of Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania (, RSR) was a Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist One-party state, one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989 (see Revolutions of 1989). From 1947 to 1965, the state was ...
—a state of "popular democracy"—was proclaimed. The newly established communist regime, led by the Romanian Workers' Party
The Romanian Communist Party ( ; PCR) was a communist party in Romania. The successor to the pro-Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave an ideological endorsement to a communist revolution that would replace the social syst ...
, consolidated its power through a Stalinist-type policy aimed at suppressing any political opposition and transforming the economic and social structures of the old bourgeois regime.Final Report of the Presidential Commission for the Analysis of the Communist Dictatorship in RomaniaAccessed 16 August 2010. In the early 1960s, the Romanian government began asserting a certain degree of independence from the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in its foreign policy,HistoryICI. Accessed 15 March 2009. although it did not abandon its repressive policies (which it labeled "revolutionary conquests") in domestic affairs. In 1965, communist leader
Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej
Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej (; 8 November 1901 – 19 March 1965) was a Romanian politician. He was the first Socialist Republic of Romania, Communist leader of Romania from 1947 to 1965, serving as first secretary of the Romanian Communist Party ...
died, ushering in a period of change in Romania."History » Communist Romania"''
Encyclopaedia Britannica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alp ...
''. Accessed 15 March 2009. After a brief power struggle, Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( ; ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian politician who was the second and last Communism, communist leader of Socialist Romania, Romania, serving as the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 u ...
emerged as the head of the communist party, becoming General Secretary of the Romanian Communist Party
The Romanian Communist Party ( ; PCR) was a communist party in Romania. The successor to the pro-Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave an ideological endorsement to a communist revolution that would replace the social system ...
in 1965, President of the State Council in 1967, and President of the Socialist Republic of Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania (, RSR) was a Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist One-party state, one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989 (see Revolutions of 1989). From 1947 to 1965, the state was ...
in 1974. Ceaușescu's rule from 1965 to 1989 grew increasingly authoritarian during the 1980s.
Romania since 1989
revolutions of 1989
The revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, were a revolutionary wave of liberal democracy movements that resulted in the collapse of most Communist state, Marxist–Leninist governments in the Eastern Bloc and other parts ...
, a protest in support of Reformed pastor László Tőkés that began in December 1989 in Timișoara
Timișoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of Timiș County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, Timișoara is consider ...
quickly escalated into a national uprising against the communist regime, ultimately resulting in the execution of Ceaușescu and his wife Elena on 25 December 1989.
An interim council composed of figures from civil society and former communist officials assumed control of the government, and Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu (; born 3 March 1930) is a Romanian politician and engineer who served as the second president of Romania from 1989 until 1996 and from 2000 until 2004. Between 1996 and 2000 and also from 2004 to 2008, the year in which he retired, ...
became the provisional president of the country. The new government reversed many of the authoritarian communist policies and dismissed several leaders of the former regime, although still influenced by members of the former regime (the basis for the Golaniad'','' and Mineriads
The mineriads () were a series of protests and often violent altercations by Jiu Valley miners in Bucharest during the 1990s, particularly 1990–91. The term "mineriad" is also used to refer to the most significant and violent of these encount ...
).
Return to democracy
In May 1990, the first free elections in Romania since1937
Events
January
* January 1 – Anastasio Somoza García becomes President of Nicaragua.
* January 5 – Water levels begin to rise in the Ohio River in the United States, leading to the Ohio River flood of 1937, which continues into Feb ...
elections were held, with Iliescu of the National Salvation Front winning the presidency with 85% of the vote. In 1992
1992 was designated as International Space Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1 – Boutros Boutros-Ghali of Egypt replaces Javier Pérez de Cuéllar of Peru as United Nations Secretary-General.
* January 6
** The Republ ...
, he was reelected in the first election after the adoption of a permanent constitution via a referendum held the previous year. Illiescu lost the 1996 election to Emil Constantinescu
Emil Constantinescu (; born 19 November 1939) is a Romanian professor and politician, who served as the President of Romania, from 1996 to 2000.
After the Romanian Revolution, Romanian Revolution of 1989, Constantinescu became a founding member ...
, but returned to power in 2000
2000 was designated as the International Year for the Culture of Peace and the World Mathematics, Mathematical Year.
Popular culture holds the year 2000 as the first year of the 21st century and the 3rd millennium, because of a tende ...
. Traian Băsescu
Traian Băsescu (; born 4 November 1951) is a Romanian politician who served as the president of Romania from 2004 to 2014. Prior to his presidency, Băsescu served as Romanian minister of transport on multiple occasions between 1991 and 2000, ...
was elected president in 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and Its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 60 ...
and 2009
2009 was designated as the International Year of Astronomy by the United Nations to coincide with the 400th anniversary of Galileo Galilei's first known astronomical studies with a telescope and the publication of Astronomia Nova by Joha ...
, serving until 2014
The year 2014 was marked by the surge of the Western African Ebola epidemic, West African Ebola epidemic, which began in 2013, becoming the List of Ebola outbreaks, most widespread outbreak of the Ebola, Ebola virus in human history, resul ...
at which point Klaus Iohannis
Klaus Werner Iohannis (; ; born 13 June 1959) is a Romanian politician, physicist, and former teacher who served as the fifth president of Romania from 2014 until his resignation in 2025. Prior to entering Politics of Romania, national politics, ...
succeeded him, being re-elected in 2019
This was the year in which the first known human case of COVID-19 was documented, preceding COVID-19 pandemic, the pandemic which was declared by the World Health Organization the following year.
Up to that point, 2019 had been described as ...
and serving until 2025
So far, the year has seen the continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudanese civil war, and the Gaza war. Internal crises in Bangladesh post-resignation v ...
. During these years several events occurred. In 2009, the country was bailed out by the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
as result of the Great Recession in Europe
The European recession is part of the Great Recession that began in mid-2007. The crisis spread rapidly and affected much of the region, with several countries already in recession as of February 2009, and most others suffering marked economic s ...
following the 2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
.
The post-1989 period has been characterised by the privatisation and closure of several former industrial and economic enterprises from the communist period were closed, while corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
has been a major issue in contemporary politics.
A National Anticorruption Directorate
The National Anticorruption Directorate (), formerly National Anticorruption Prosecution Office (), is the Romanian agency tasked with preventing, investigating and prosecuting Political corruption, corruption-related offenses (such as bribery, g ...
was formed in the country in 2002. During the 2000s, Romania had one of the highest economic growth rates in Europe and has been referred at times as "the Tiger of Eastern Europe". This has been accompanied by a significant improvement in living standards as the country successfully reduced domestic poverty and established a functional democratic state.Human Development Report 2009 – Country Fact Sheets – Romania. Hdrstats.undp.org. Retrieved on 21 August 2010. However, Romania's development suffered a major setback during the late 2000s' recession leading to a large gross domestic product contraction and a budget deficit in 2009. This led to Romania borrowing from the International Monetary Fund. Worsening economic conditions led to unrest and triggered a political crisis in 2012. Since 2014, Romania launched an anti-corruption effort that led to the prosecution of medium- and high-level political, judicial and administrative offenses by the
National Anticorruption Directorate
The National Anticorruption Directorate (), formerly National Anticorruption Prosecution Office (), is the Romanian agency tasked with preventing, investigating and prosecuting Political corruption, corruption-related offenses (such as bribery, g ...
. In 2015, massive anti-corruption protests which developed in the wake of the Colectiv nightclub fire
A nightclub fire which occurred in Bucharest, Romania, on 30 October 2015 killed 64 people (26 on site, 38 in hospitals) and injured 146. The fire was caused by a fireworks accident and is the deadliest such incident in Romanian history. It occ ...
led to the resignation of prime minister Victor Ponta
Victor Viorel Ponta (; born 20 September 1972) is a Romanian politician and jurist who served as Prime Minister of Romania from 2012 to 2015. He was president of the Social Democratic Party (Romania), Social Democratic Party (PSD) from 2010 to ...
. During 2017–2019, in response to measures which were perceived to weaken the fight against corruption, some of the biggest post-1989 protests took place in Romania, with over 500,000 people protesting nationwide.
The 2021 Romanian political crisis
A political crisis began on 1 September 2021 in Romania, engulfing both major coalition partners of the Cîțu Cabinet, namely the conservative-liberal National Liberal Party (PNL) and the progressive-liberal Save Romania Union (USR). The cri ...
led to the outsting of Florin Cîțu
Florin Vasile Cîțu (; born 1 April 1972) is a Romanian politician who served as Prime Minister of Romania between December 2020 and November 2021 (acting/ad interim between October and November 2021). Sometimes labeled as Romania's first liber ...
's incumbent government. The Ciucă Cabinet
The Ciucă Cabinet () was the 132nd government of Romania led by former Romanian Land Forces army general Nicolae Ciucă (PNL; also current PNL president) from 25 November 2021 to 12 June 2023.
The grand coalition forming the government, consi ...
then took power, with Romania since having experienced a shift towards authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in democracy, separation of powers, civil liberties, and ...
and illiberalism Historically, the adjective illiberal has been mostly applied to personal attitudes, behaviors and practices “unworthy of a free man”, such as lack of generosity, lack of sophisticated culture, intolerance, narrow-mindedness, meanness. Lord Ches ...
, as well as an increased corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
. Around this time, Romania was also hit by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. In the 2024 presidential election
This is a list of elections that were held in 2024. The National Democratic Institute also maintains a calendar of elections around the world.
*2024 United Nations Security Council election
*2024 national electoral calendar
*2024 local electoral ...
, Independent candidate Călin Georgescu
Călin Georgescu (; born 26 March 1962) is a Romanian far-right politician and agronomist. He has long worked in the field of sustainable development, and served as President of the European Research Centre for the Club of Rome (2013–2015).
G ...
achieved a surprise win in the first round. However, the Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ru ...
annulled the election results, citing Russian meddling. The cancellation led to far-right protests, criticism
Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative or positive qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. , ''the act of giving your opinion or judgment about the ...
by the Trump administration Presidency of Donald Trump may refer to:
* First presidency of Donald Trump, the United States presidential administration from 2017 to 2021
* Second presidency of Donald Trump, the United States presidential administration since 2025
See also
* ...
, and Ilie Bolojan
Ilie-Gavril Bolojan (; born 17 March 1969) is a Romanian politician serving as the president of the senate of Romania. He previously served as the acting president of Romania from February 2025, following the resignation of Klaus Iohannis, unti ...
becoming acting president in February 2025 as Iohannis resigned to political pressure. In the subsequent 2025 Romanian presidential election, Bucharest Mayor Nicușor Dan
Nicușor Daniel Dan (; born 20 December 1969) is a Romanian politician, mathematician, and civic activist serving as the sixth president of Romania since 2025. He previously served as the mayor of Bucharest from 2020 to 2025 and as a member of ...
was elected president.
Geography
Romania is the largest country inSoutheastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
and the twelfth-largest in Europe, having an area of . It lies between latitudes 43° and 49° N and longitudes 20° and 30° E. The terrain is distributed roughly equally between mountains, hills, and plains. The Carpathian Mountains dominate the centre of Romania, with 14 mountain ranges reaching above —the highest is Moldoveanu Peak
Moldoveanu Peak (, ; "Moldavian Peak"), at , is the highest mountain peak in Romania.Moldavian and
 Since December 1989, Romania has pursued a policy of strengthening relations with the West in general, more specifically with the United States and the EU, albeit with limited Romania–Russia relations, relations involving the Russian Federation. It joined NATO on 29 March 2004, the EU on 1 January 2007, while it joined the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in 1972, and is a founding member of the World Trade Organization. Romania is recognised as a
Since December 1989, Romania has pursued a policy of strengthening relations with the West in general, more specifically with the United States and the EU, albeit with limited Romania–Russia relations, relations involving the Russian Federation. It joined NATO on 29 March 2004, the EU on 1 January 2007, while it joined the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in 1972, and is a founding member of the World Trade Organization. Romania is recognised as a
 The Romanian Armed Forces consist of Romanian Land Forces, land, Romanian Air Force, air, and Romanian Naval Forces, naval forces led by a Chief of the Romanian General Staff, Commander-in-chief under the supervision of the Ministry of National Defence (Romania), Ministry of National Defence, and by the President of Romania, president as the Supreme Commander during wartime. The Armed Forces consist of approximately 55,000 reservists and 71,500 active military personnel—35,800 for land, 10,700 for air, 6,600 for naval forces, and 16,500 in other fields. Total defence spending in 2023 accounted for 2.44% of total national GDP, or approximately US$8.48 billion, with a total of $9 billion intended to be spent until 2026 for modernisation and acquisition of new equipment. Conscription stopped in 2007, when Romania switched to a volunteer army.
The Air Force operates General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon variants#F-16AM/BM Block 15 MLU, F-16AM/BM MLU fighters, C-27J Spartan and C-130 Hercules Military transport aircraft, transport aircraft, as well as IAR 330 and IAR 316 helicopters. A Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II procurement#Romania, procurement programme for F-35 fifth-generation fighters is also currently being carried out. The Naval Forces operate three frigates, of which two are Type 22 frigates acquired from the British Royal Navy, as well as four corvettes. The Romanian Danube Flotilla, River Flotilla operates Mihail Kogălniceanu-class river monitor, Mihail Kogălniceanu and Smârdan-class river monitors.
Romania contributed troops to the international coalition in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan beginning in 2002, with a peak deployment of 1,600 troops in 2010 (which was the 4th largest contribution according to the US). Its combat mission in the country concluded in 2014. Romanian troops participated in the History of Iraq (2003–2011), occupation of Iraq, reaching a peak of 730 soldiers before being slowly drawn down to 350 soldiers. Romania terminated its mission in Iraq and withdrew its last troops on 24 July 2009, among the last countries to do so. The frigate the ''Regele Ferdinand frigate, Regele Ferdinand'' participated in the 2011 military intervention in Libya.
In December 2011, the Romanian Senate unanimously adopted the draft law ratifying the Romania–United States relations, Romania-United States agreement signed in September of the same year that would allow the establishment and operation of a US land-based Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System, ballistic missile defence system in Romania as part of NATO's efforts to build a continental NATO missile defence system, missile shield. The Aegis Ashore missile system based at Deveselu Military Base, Deveslu became operational in 2016.
In 2024, construction work started on expanding the Mihail Kogălniceanu Air Base (RoAF 57th Air Base). The air base is set to become the largest NATO base in Europe after the implementation of a project spanning 20 years.
The Romanian Armed Forces consist of Romanian Land Forces, land, Romanian Air Force, air, and Romanian Naval Forces, naval forces led by a Chief of the Romanian General Staff, Commander-in-chief under the supervision of the Ministry of National Defence (Romania), Ministry of National Defence, and by the President of Romania, president as the Supreme Commander during wartime. The Armed Forces consist of approximately 55,000 reservists and 71,500 active military personnel—35,800 for land, 10,700 for air, 6,600 for naval forces, and 16,500 in other fields. Total defence spending in 2023 accounted for 2.44% of total national GDP, or approximately US$8.48 billion, with a total of $9 billion intended to be spent until 2026 for modernisation and acquisition of new equipment. Conscription stopped in 2007, when Romania switched to a volunteer army.
The Air Force operates General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon variants#F-16AM/BM Block 15 MLU, F-16AM/BM MLU fighters, C-27J Spartan and C-130 Hercules Military transport aircraft, transport aircraft, as well as IAR 330 and IAR 316 helicopters. A Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II procurement#Romania, procurement programme for F-35 fifth-generation fighters is also currently being carried out. The Naval Forces operate three frigates, of which two are Type 22 frigates acquired from the British Royal Navy, as well as four corvettes. The Romanian Danube Flotilla, River Flotilla operates Mihail Kogălniceanu-class river monitor, Mihail Kogălniceanu and Smârdan-class river monitors.
Romania contributed troops to the international coalition in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan beginning in 2002, with a peak deployment of 1,600 troops in 2010 (which was the 4th largest contribution according to the US). Its combat mission in the country concluded in 2014. Romanian troops participated in the History of Iraq (2003–2011), occupation of Iraq, reaching a peak of 730 soldiers before being slowly drawn down to 350 soldiers. Romania terminated its mission in Iraq and withdrew its last troops on 24 July 2009, among the last countries to do so. The frigate the ''Regele Ferdinand frigate, Regele Ferdinand'' participated in the 2011 military intervention in Libya.
In December 2011, the Romanian Senate unanimously adopted the draft law ratifying the Romania–United States relations, Romania-United States agreement signed in September of the same year that would allow the establishment and operation of a US land-based Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System, ballistic missile defence system in Romania as part of NATO's efforts to build a continental NATO missile defence system, missile shield. The Aegis Ashore missile system based at Deveselu Military Base, Deveslu became operational in 2016.
In 2024, construction work started on expanding the Mihail Kogălniceanu Air Base (RoAF 57th Air Base). The air base is set to become the largest NATO base in Europe after the implementation of a project spanning 20 years.
 In 2024, Romania has a GDP (PPP) of around $894 billion and a List of countries by GDP per capita (PPP), GDP per capita (purchasing power parity, PPP) of $47,203. According to the World Bank, Romania is a
In 2024, Romania has a GDP (PPP) of around $894 billion and a List of countries by GDP per capita (PPP), GDP per capita (purchasing power parity, PPP) of $47,203. According to the World Bank, Romania is a  Romania's main exports are vehicles, software, clothing and textiles, Machine industry, industrial machinery, Electrical device, electrical and Electronics, electronic equipment, Metallurgy, metallurgic products, raw materials, military equipment, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and Agriculture, agricultural products (fruits, vegetables, and flowers). Trade is mostly centred on the member states of the EU, with Germany, Italy and France being the country's single largest trading partners.
In 2005, the government replaced Romania's progressive tax system with a flat tax of 16% for both personal income and corporate profit, among the lowest rates in the EU. The economy is based predominantly on services, which account for 56.2% of the country's total GDP as of 2017, with industry and agriculture accounting for 30% and 4.4% respectively.
Approximately 25.8% of the Romanian workforce is employed in agriculture, one of the highest rates in Europe.
Romania has attracted increasing amounts of foreign investment following the end of Communism, with the stock of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Romania rising to €83.8 billion in June 2019. Romania's FDI outward stock (an external or foreign business either investing in or purchasing the stock of a local economy) amounted to $745 million in December 2018, the lowest value among the 28 EU member states.
Since 1867 the official currency has been the Romanian leu, Romanian ''leu'' ("lion") and following a denomination in 2005. After joining the EU in 2007, Romania plans to adopt the euro in 2029.
Romania's main exports are vehicles, software, clothing and textiles, Machine industry, industrial machinery, Electrical device, electrical and Electronics, electronic equipment, Metallurgy, metallurgic products, raw materials, military equipment, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and Agriculture, agricultural products (fruits, vegetables, and flowers). Trade is mostly centred on the member states of the EU, with Germany, Italy and France being the country's single largest trading partners.
In 2005, the government replaced Romania's progressive tax system with a flat tax of 16% for both personal income and corporate profit, among the lowest rates in the EU. The economy is based predominantly on services, which account for 56.2% of the country's total GDP as of 2017, with industry and agriculture accounting for 30% and 4.4% respectively.
Approximately 25.8% of the Romanian workforce is employed in agriculture, one of the highest rates in Europe.
Romania has attracted increasing amounts of foreign investment following the end of Communism, with the stock of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Romania rising to €83.8 billion in June 2019. Romania's FDI outward stock (an external or foreign business either investing in or purchasing the stock of a local economy) amounted to $745 million in December 2018, the lowest value among the 28 EU member states.
Since 1867 the official currency has been the Romanian leu, Romanian ''leu'' ("lion") and following a denomination in 2005. After joining the EU in 2007, Romania plans to adopt the euro in 2029.

 According to the Romania's National Institute of Statistics (INS), Romania's total road network was estimated in 2015 at . The World Bank estimates the railway network at of track, the fourth-largest railway network in Europe. Romania's Căile Ferate Române, rail transport experienced a dramatic decline after 1989 and was estimated at 99 million passenger journeys in 2004, but has experienced a recent (2013) revival due to infrastructure improvements and partial privatisation of lines, accounting for 45% of all passenger and freight movements in the country. Bucharest Metro, the only rapid transit, underground railway system, was opened in 1979 and measures with an average ridership in 2021 of 720,000 passengers during the workweek in the country. There are List of airports in Romania, sixteen international commercial airports in service today. Over 12.8 million passengers flew through Bucharest's Henri Coandă International Airport in 2017.
Romania is a net exporter of electrical energy and is 52nd worldwide in terms of consumption of electric energy. Around a third of the produced energy comes from renewable sources, mostly as hydroelectric power. It has one of the largest refining capacities in Eastern Europe, even though oil and natural gas production has been decreasing for more than a decade. With one of the largest reserves of crude oil and shale gas in Europe it is among the most energy-independent countries in the EU, and is looking to expand its nuclear power plant at Cernavodă Nuclear Power Plant, Cernavodă further.
There were almost 18.3 million connections to the Internet in June 2014. According to Bloomberg L.P., Bloomberg, in 2013 Romania ranked fifth in the world, and according to ''The Independent'', it ranks number one in Europe at Internet speeds, with
According to the Romania's National Institute of Statistics (INS), Romania's total road network was estimated in 2015 at . The World Bank estimates the railway network at of track, the fourth-largest railway network in Europe. Romania's Căile Ferate Române, rail transport experienced a dramatic decline after 1989 and was estimated at 99 million passenger journeys in 2004, but has experienced a recent (2013) revival due to infrastructure improvements and partial privatisation of lines, accounting for 45% of all passenger and freight movements in the country. Bucharest Metro, the only rapid transit, underground railway system, was opened in 1979 and measures with an average ridership in 2021 of 720,000 passengers during the workweek in the country. There are List of airports in Romania, sixteen international commercial airports in service today. Over 12.8 million passengers flew through Bucharest's Henri Coandă International Airport in 2017.
Romania is a net exporter of electrical energy and is 52nd worldwide in terms of consumption of electric energy. Around a third of the produced energy comes from renewable sources, mostly as hydroelectric power. It has one of the largest refining capacities in Eastern Europe, even though oil and natural gas production has been decreasing for more than a decade. With one of the largest reserves of crude oil and shale gas in Europe it is among the most energy-independent countries in the EU, and is looking to expand its nuclear power plant at Cernavodă Nuclear Power Plant, Cernavodă further.
There were almost 18.3 million connections to the Internet in June 2014. According to Bloomberg L.P., Bloomberg, in 2013 Romania ranked fifth in the world, and according to ''The Independent'', it ranks number one in Europe at Internet speeds, with
, 9 July 2010, jurnalul.ro, accessed on 21 August 2010 Most popular skiing resorts are along the Valea Prahovei and in Poiana Brașov. List of castles in Romania, Castles, fortifications, or strongholds as well as preserved medieval Transylvanian cities or towns such as
 The official language is Romanian, a Romance language (the most widely spoken of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance branch), which presents a consistent degree of similarity to Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, but shares many features equally with the rest of the Western Romance languages, specifically Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, and Catalan language, Catalan. The Romanian alphabet contains the same 26 letters of the standard Latin alphabet, as well as five additional ones (namely ''ă'', ''â'', ''î'', ''ț'', and ''ș''), totalling 31.
Romanian is spoken as a first language by 91.55% of the entire population, while Hungarian language, Hungarian and Vlax Romani are spoken by 6.28% and 1.20% of the population, respectively. There are also 40,861 native speakers of Ukrainian language, Ukrainian (concentrated in some compact regions near the border, where they form local majorities), 17,101 native speakers of Turkish language, Turkish, 15,943 native speakers of German language, German, and 14,414 native speakers of Russian language, Russian living in Romania.
According to the Constitution, local councils ensure linguistic rights to all minorities. In localities with ethnic minorities of over 20%, that minority's language can be used in the public administration, justice system, and education. Foreign citizens and stateless persons who live in Romania have access to justice and education in their own language. English and French are the main foreign languages taught in schools. In 2010, the identified 4,756,100 French speakers in the country. According to the 2012 Eurobarometer, English is spoken by 31% of Romanians, French is spoken by 17%, and Italian and German, each by 7%.
The official language is Romanian, a Romance language (the most widely spoken of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance branch), which presents a consistent degree of similarity to Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, but shares many features equally with the rest of the Western Romance languages, specifically Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, and Catalan language, Catalan. The Romanian alphabet contains the same 26 letters of the standard Latin alphabet, as well as five additional ones (namely ''ă'', ''â'', ''î'', ''ț'', and ''ș''), totalling 31.
Romanian is spoken as a first language by 91.55% of the entire population, while Hungarian language, Hungarian and Vlax Romani are spoken by 6.28% and 1.20% of the population, respectively. There are also 40,861 native speakers of Ukrainian language, Ukrainian (concentrated in some compact regions near the border, where they form local majorities), 17,101 native speakers of Turkish language, Turkish, 15,943 native speakers of German language, German, and 14,414 native speakers of Russian language, Russian living in Romania.
According to the Constitution, local councils ensure linguistic rights to all minorities. In localities with ethnic minorities of over 20%, that minority's language can be used in the public administration, justice system, and education. Foreign citizens and stateless persons who live in Romania have access to justice and education in their own language. English and French are the main foreign languages taught in schools. In 2010, the identified 4,756,100 French speakers in the country. According to the 2012 Eurobarometer, English is spoken by 31% of Romanians, French is spoken by 17%, and Italian and German, each by 7%.
 Since the Romanian Revolution of 1989, the Romanian educational system has been in a continuous process of reform that has received mixed criticism. In 2004, some 4.4 million individuals were enrolled in school. Of these, 650,000 were in kindergarten (three-six years), 3.11 million in primary and secondary level, and 650,000 in tertiary level (universities). In 2018, the adult literacy rate was 98.8%. Kindergarten is optional between three and five years. Since 2020, compulsory schooling starts at age 5 with the last year of kindergarten (grupa mare) and is compulsory until twelfth grade. Primary and secondary education is divided into 12 or 13 grades. There is also a semi-legal, informal Tutoring#Peer tutoring, private tutoring system used mostly during secondary school, which prospered during the Communist regime.
Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași, Babeș-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, University of Bucharest, and West University of Timișoara have been included in the QS World University Rankings' top 800.
Romania ranks fifth in the all-time medal count at the International Mathematical Olympiad with 316 total medals, dating back to 1959. Ciprian Manolescu managed to write a perfect paper (42 points) for a gold medal more times than anybody else in the history of the competition, in 1995, 1996 and 1997. Romania has achieved the highest team score in the competition, after China, Russia, the United States and Hungary. Romania also ranks sixth in the all-time medal count at the International Olympiad in Informatics with 107 total medals, dating back to 1989.
Since the Romanian Revolution of 1989, the Romanian educational system has been in a continuous process of reform that has received mixed criticism. In 2004, some 4.4 million individuals were enrolled in school. Of these, 650,000 were in kindergarten (three-six years), 3.11 million in primary and secondary level, and 650,000 in tertiary level (universities). In 2018, the adult literacy rate was 98.8%. Kindergarten is optional between three and five years. Since 2020, compulsory schooling starts at age 5 with the last year of kindergarten (grupa mare) and is compulsory until twelfth grade. Primary and secondary education is divided into 12 or 13 grades. There is also a semi-legal, informal Tutoring#Peer tutoring, private tutoring system used mostly during secondary school, which prospered during the Communist regime.
Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași, Babeș-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, University of Bucharest, and West University of Timișoara have been included in the QS World University Rankings' top 800.
Romania ranks fifth in the all-time medal count at the International Mathematical Olympiad with 316 total medals, dating back to 1959. Ciprian Manolescu managed to write a perfect paper (42 points) for a gold medal more times than anybody else in the history of the competition, in 1995, 1996 and 1997. Romania has achieved the highest team score in the competition, after China, Russia, the United States and Hungary. Romania also ranks sixth in the all-time medal count at the International Olympiad in Informatics with 107 total medals, dating back to 1989.
 The topic of the origin of Romanian culture began to be discussed by the end of the 18th century among the Transylvanian School scholars. Several writers rose to prominence in the 19th century, including: George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici,
The topic of the origin of Romanian culture began to be discussed by the end of the 18th century among the Transylvanian School scholars. Several writers rose to prominence in the 19th century, including: George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici,  Prominent Romanian painters include: Nicolae Grigorescu, Ștefan Luchian, Ion Andreescu Nicolae Tonitza, and Theodor Aman. Notable Romanian classical composers of the 19th and 20th centuries include: Ciprian Porumbescu, Anton Pann, Eduard Caudella, Mihail Jora, Dinu Lipatti, and especially George Enescu. The annual George Enescu Festival is held in Bucharest in honour of the 20th-century composer.
Contemporary musicians like Angela Gheorghiu, Gheorghe Zamfir, Inna, Alexandra Stan, and many others have achieved various levels of international acclaim. From the late 2000s through the early 2010s, the Romanian Popcorn (Romanian music style), popcorn music style had established itself in the international mainstream. At the Eurovision Song Contest Romanian singers achieved third place in 2005 and 2010.
In cinema, several movies of the Romanian New Wave have achieved international acclaim. At the Cannes Film Festival, ''The Death of Mr. Lazarescu'' by Cristi Puiu won the in 2005, while ''4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days'' by Cristian Mungiu won the festival's top prize, the , in 2007. At the Berlin International Film Festival, ''Child's Pose (film), Child's Pose'' by Călin Peter Netzer won the Golden Bear in 2013.
The list of World Heritage Sites includes List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, six cultural sites located within Romania, including eight painted churches of northern Moldavia, eight wooden churches of Maramureș, seven villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, the Horezu Monastery, and the Historic Centre of Sighișoara. The city of Sibiu, with its Brukenthal National Museum, was selected as the 2007 European Capital of Culture and the 2019 European Region of Gastronomy. Multiple castles exist in Romania, including the popular tourist attractions of Peleș Castle, Corvin Castle, and Bran Castle or "Dracula's Castle".
Prominent Romanian painters include: Nicolae Grigorescu, Ștefan Luchian, Ion Andreescu Nicolae Tonitza, and Theodor Aman. Notable Romanian classical composers of the 19th and 20th centuries include: Ciprian Porumbescu, Anton Pann, Eduard Caudella, Mihail Jora, Dinu Lipatti, and especially George Enescu. The annual George Enescu Festival is held in Bucharest in honour of the 20th-century composer.
Contemporary musicians like Angela Gheorghiu, Gheorghe Zamfir, Inna, Alexandra Stan, and many others have achieved various levels of international acclaim. From the late 2000s through the early 2010s, the Romanian Popcorn (Romanian music style), popcorn music style had established itself in the international mainstream. At the Eurovision Song Contest Romanian singers achieved third place in 2005 and 2010.
In cinema, several movies of the Romanian New Wave have achieved international acclaim. At the Cannes Film Festival, ''The Death of Mr. Lazarescu'' by Cristi Puiu won the in 2005, while ''4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days'' by Cristian Mungiu won the festival's top prize, the , in 2007. At the Berlin International Film Festival, ''Child's Pose (film), Child's Pose'' by Călin Peter Netzer won the Golden Bear in 2013.
The list of World Heritage Sites includes List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, six cultural sites located within Romania, including eight painted churches of northern Moldavia, eight wooden churches of Maramureș, seven villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, the Horezu Monastery, and the Historic Centre of Sighișoara. The city of Sibiu, with its Brukenthal National Museum, was selected as the 2007 European Capital of Culture and the 2019 European Region of Gastronomy. Multiple castles exist in Romania, including the popular tourist attractions of Peleș Castle, Corvin Castle, and Bran Castle or "Dracula's Castle".
 There are 12 non-working public holidays, including the Great Union Day, celebrated on 1 December in commemoration of the 1918 union of Transylvania with Romania. Winter holidays include the Christmas and New Year festivities during which various unique folklore dances and games are common: ''plugușorul'', ''sorcova'', ''ursul'', and ''capra''. The traditional Romanian dress that otherwise has largely fallen out of use during the 20th century, is a popular ceremonial vestment worn on these festivities, especially in rural areas. There are sacrifices of live pigs during Christmas and lambs during Easter that has required a special exemption from EU law after 2007. In the Easter, traditions such as Easter egg, painting the eggs are very common. On 1 March ' gifting is featured, which is a tradition whereby females are gifted with a type of talisman that is given for good luck.
Romanian cuisine has been influenced by Austrian cuisine, Austrian and German cuisine (especially in the historical regions that had been formerly administered by the
There are 12 non-working public holidays, including the Great Union Day, celebrated on 1 December in commemoration of the 1918 union of Transylvania with Romania. Winter holidays include the Christmas and New Year festivities during which various unique folklore dances and games are common: ''plugușorul'', ''sorcova'', ''ursul'', and ''capra''. The traditional Romanian dress that otherwise has largely fallen out of use during the 20th century, is a popular ceremonial vestment worn on these festivities, especially in rural areas. There are sacrifices of live pigs during Christmas and lambs during Easter that has required a special exemption from EU law after 2007. In the Easter, traditions such as Easter egg, painting the eggs are very common. On 1 March ' gifting is featured, which is a tradition whereby females are gifted with a type of talisman that is given for good luck.
Romanian cuisine has been influenced by Austrian cuisine, Austrian and German cuisine (especially in the historical regions that had been formerly administered by the
The Ancient History of Herodotus
' (Translated by William Beloe) (1859). Derby & Jackson. *
' (Translated by John Selby Watson) (1886). George Bell and Sons. * * * * * *
excerpt
* Hitchins, Keith. ''Rumania 1866-1947'' (1994) (Oxford History of Modern Europe
excerpt
* * * * * * * * * * * * * Stavrianos, L.S. '' The Balkans Since 1453'' (1958), major scholarly history
online free to borrow
* *
Country Profile
from BBC News.
Romania Article and Country Profile
from Encyclopædia Britannica
Romania Profile
from Balkan Insight.
România Un Secol de Istorie – statistical data
from National Institute of Statistics (Romania), INS
Romania
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. ;Government
Romanian Presidency
;Culture and history links
Treasures of the national library of Romania
Historic Houses of Romania
{{Coord, 46, N, 25, E, type:country, display=title Romania, 1859 establishments in Europe Balkan countries Countries in Europe Member states of the United Nations Member states of NATO Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the Three Seas Initiative Republics Countries and territories where Romanian is an official language States and territories established in 1859
Transylvanian
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
plateaus, the Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
and the Wallachian plains.
Romania is home to six terrestrial ecoregions: Balkan mixed forests
The Balkan mixed forests are a terrestrial ecoregion of southeastern Europe according to both the WWF and Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency. It belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests bio ...
, Central European mixed forests
The Central European mixed forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0412) is a temperate hardwood forest covering much of northeastern Europe, from Germany to Russia. The area is only about one-third forested, with pressure from human agriculture leaving the r ...
, East European forest steppe
The East European forest steppe ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0419) is a patchwork of broadleaf forest stands and grasslands (steppe) that stretches 2,100 km across Eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains in Ural (region), Ural, through Volga region, Povol ...
, Pannonian mixed forests
The Pannonian mixed forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in Europe. It covers an area of 307,720 km2 in all of Hungary, most of Slovakia, about half of Croatia and Slovenia, around a third of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Roman ...
, Carpathian montane conifer forests
The Carpathian montane conifer forests, also known as Carpathian montane forests, is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion in the Carpathian Mountains of the Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, Romania, and Ukraine.
Geography
The ecoregion cove ...
, and Pontic steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from n ...
. Natural and semi-natural ecosystems cover about 47% of the country's land area. There are almost (about 5% of the total area) of protected areas in Romania covering 13 national park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
s and three biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
reserves. The Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
river forms a large part of the border with Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, and flows into the Black Sea, forming the Danube Delta, which is the second-largest and best-preserved delta in Europe, and a biosphere reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, funga, or features of geologic ...
and a biodiversity World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. At , the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta (, ; , ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. Occurring where the Danube, Danube River empties into the Black Sea, most of the Danube Delta lies in Romania ...
is the largest continuous marshland in Europe, and supports 1,688 different plant species alone.
Romania has one of the largest areas of undisturbed forest in Europe, covering almost 27% of its territory. The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 47 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 5.95/10, ranking it 90th globally out of 172 countries. Some 3,700 plant species
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes ...
have been identified in the country, from which to date 23 have been declared natural monument
A natural monument is a natural or cultural feature of outstanding or unique value because of its inherent rarity, representative of aesthetic qualities, or cultural significance. They can be natural geological and geographical features such as w ...
s, 74 extinct, 39 endangered, 171 vulnerable, and 1,253 rare.
The fauna of Romania
The fauna of Romania comprises all the animal species inhabiting the country of Romania and its coastal territory in the Black Sea.
Invertebrates
Vertebrates
According to a systematic list of the Romanian vertebrate fauna, there are 732 ...
consists of 33,792 species of animals, 33,085 invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
and 707 vertebrate, with almost 400 unique species of mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians, including about 50% of Europe's (excluding Russia) brown bears and 20% of its wolf, wolves.
Climate
Owing to its distance from open sea and its position on the southeastern portion of the European continent, Romania has a climate that is continental climate, continental, with four distinct seasons. The average annual temperature is in the south and in the north. In summer, average maximum temperatures in Bucharest rise to , and temperatures over are fairly common in the lower-lying areas of the country. In winter, the average maximum temperature is below . Precipitation is average, with over per year only on the highest western mountains, while around Bucharest it drops to approximately . There are some regional differences: in western sections, such as Banat, the climate is milder and has some Mediterranean influences; the eastern part of the country has a more pronounced continental climate. In Dobruja, the Black Sea also exerts an influence over the region's climate.Politics
Romania is a Unitary state, unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential Representative democracy, representative democratic republic with a structured system of governance and an active civil society. The President of Romania, President, elected by popular vote, serves as the head of state, representing the country in Foreign relations of Romania, international affairs, safeguarding Constitution of Romania, constitutional order, and acting as Commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the Romanian Armed Forces. The Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister, appointed by the President and confirmed by the Parliament of Romania, Parliament, acts as the head of government, responsible for overseeing the Government of Romania, executive branch, implementing Foreign relations of Romania, domestic and foreign policies, and managing public administration. Legislative, Legislative authority is vested in a Bicameralism, bicameral Parliament, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies of Romania, Chamber of Deputies and the Senate of Romania, Senate, whose members are elected through a proportional representation system. The Judiciary of Romania, judiciary operates Judicial independence, independently, with the High Court of Cassation and Justice as the highest court of appeal.Government
Romania has a democratic,multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
, with Legislature, legislative power vested in the government and the Bicameralism, two chambers of the Parliament of Romania, Parliament, more specifically the Chamber of Deputies (Romania), Chamber of Deputies and the Senate of Romania, Senate. The judiciary is Judicial independence, independent of the executive and the legislature. The latter is elected by popular vote for a maximum of two terms of five years and appoints the prime minister who in turn appoints the Romanian Cabinet, Council of Ministers. The legislative branch of the government, collectively known as the Parliament of Romania, Parliament (residing at the Palace of the Parliament), consists of Bicameralism, two chambers (Senate of Romania, Senate and Chamber of Deputies (Romania), Chamber of Deputies) whose members are elected every four years by Plurality voting system, simple plurality.
The justice system is independent of the other branches of government and is made up of a hierarchical system of courts with the High Court of Cassation and Justice being the supreme court of Romania. There are also courts of appeal, county courts and local courts. The Romanian judicial system is strongly influenced by the French law, French model, is based on Civil law (legal system), civil law and is inquisitorial system, inquisitorial in nature. The Curtea Constituțională, Constitutional Court (''Curtea Constituțională'') is responsible for judging the compliance of laws and other state regulations with the constitution, which is the fundamental law of the country and can be amended only through a public referendum. Romania's 2007 entry into the EU has been a significant influence on its domestic policy, and including judicial reforms, increased judicial cooperation with other member states, and measures to combat corruption. The Economist Intelligence Unit rated Romania as a "hybrid regime" in 2024.
Foreign relations
middle power
A middle power is a state that is not a superpower or a great power, but still exerts influence and plays a significant role in international relations. These countries often possess certain capabilities, such as strong economies, advanced tech ...
for its military capabilities, as well as its active diplomatic engagement on the global stage.
In the past, recent governments have stated that one of their goals is to strengthen ties with and helping other countries (in particular Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, and Georgia (country), Georgia) and better integration with the rest of the West. Romania has also made clear since the late 1990s that it supports NATO and EU membership for the democratic former Soviet republics in Eastern Europe and the Caucasus.
Romania applied to join to the Schengen Area in 2007, acquiring full membership in 2025 along with Bulgaria. In December 2005, President Traian Băsescu and United States Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice signed an agreement that would allow a U.S. military presence at several Romanian facilities primarily in the eastern part of the country. In 2009, US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton referred to Romania as "one of the most trustworthy and respectable" US allies". However, by 2025, relations had worsen, with US vice president JD Vance in February 2025 JD Vance speech at the Munich Security Conference, scolding "Accusations of Russian interference in the 2024 Romanian presidential election, flimsy suspicions" and "enormous pressure from its continental neighbours" for causing the annulment of the 2024 Romanian presidential election, 2024 Romanian presidential election in which Călin Georgescu
Călin Georgescu (; born 26 March 1962) is a Romanian far-right politician and agronomist. He has long worked in the field of sustainable development, and served as President of the European Research Centre for the Club of Rome (2013–2015).
G ...
won the first round.
Romanian-Moldovan relations, Relations with Moldova are a special case given that the two countries share the same language and a History of Moldavia, common history. A Unification of Moldova and Romania, movement for unification of Moldova and Romania appeared in the early 1990s after both countries achieved emancipation from communist rule but lost ground in the mid-1990s when a new Moldovan government pursued an agenda towards preserving a Moldovan republic independent of Romania. After the 2009 Moldovan protests, 2009 protests in Moldova and the subsequent removal of Communists from power, relations between the two countries have improved considerably.
Military
 The Romanian Armed Forces consist of Romanian Land Forces, land, Romanian Air Force, air, and Romanian Naval Forces, naval forces led by a Chief of the Romanian General Staff, Commander-in-chief under the supervision of the Ministry of National Defence (Romania), Ministry of National Defence, and by the President of Romania, president as the Supreme Commander during wartime. The Armed Forces consist of approximately 55,000 reservists and 71,500 active military personnel—35,800 for land, 10,700 for air, 6,600 for naval forces, and 16,500 in other fields. Total defence spending in 2023 accounted for 2.44% of total national GDP, or approximately US$8.48 billion, with a total of $9 billion intended to be spent until 2026 for modernisation and acquisition of new equipment. Conscription stopped in 2007, when Romania switched to a volunteer army.
The Air Force operates General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon variants#F-16AM/BM Block 15 MLU, F-16AM/BM MLU fighters, C-27J Spartan and C-130 Hercules Military transport aircraft, transport aircraft, as well as IAR 330 and IAR 316 helicopters. A Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II procurement#Romania, procurement programme for F-35 fifth-generation fighters is also currently being carried out. The Naval Forces operate three frigates, of which two are Type 22 frigates acquired from the British Royal Navy, as well as four corvettes. The Romanian Danube Flotilla, River Flotilla operates Mihail Kogălniceanu-class river monitor, Mihail Kogălniceanu and Smârdan-class river monitors.
Romania contributed troops to the international coalition in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan beginning in 2002, with a peak deployment of 1,600 troops in 2010 (which was the 4th largest contribution according to the US). Its combat mission in the country concluded in 2014. Romanian troops participated in the History of Iraq (2003–2011), occupation of Iraq, reaching a peak of 730 soldiers before being slowly drawn down to 350 soldiers. Romania terminated its mission in Iraq and withdrew its last troops on 24 July 2009, among the last countries to do so. The frigate the ''Regele Ferdinand frigate, Regele Ferdinand'' participated in the 2011 military intervention in Libya.
In December 2011, the Romanian Senate unanimously adopted the draft law ratifying the Romania–United States relations, Romania-United States agreement signed in September of the same year that would allow the establishment and operation of a US land-based Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System, ballistic missile defence system in Romania as part of NATO's efforts to build a continental NATO missile defence system, missile shield. The Aegis Ashore missile system based at Deveselu Military Base, Deveslu became operational in 2016.
In 2024, construction work started on expanding the Mihail Kogălniceanu Air Base (RoAF 57th Air Base). The air base is set to become the largest NATO base in Europe after the implementation of a project spanning 20 years.
The Romanian Armed Forces consist of Romanian Land Forces, land, Romanian Air Force, air, and Romanian Naval Forces, naval forces led by a Chief of the Romanian General Staff, Commander-in-chief under the supervision of the Ministry of National Defence (Romania), Ministry of National Defence, and by the President of Romania, president as the Supreme Commander during wartime. The Armed Forces consist of approximately 55,000 reservists and 71,500 active military personnel—35,800 for land, 10,700 for air, 6,600 for naval forces, and 16,500 in other fields. Total defence spending in 2023 accounted for 2.44% of total national GDP, or approximately US$8.48 billion, with a total of $9 billion intended to be spent until 2026 for modernisation and acquisition of new equipment. Conscription stopped in 2007, when Romania switched to a volunteer army.
The Air Force operates General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon variants#F-16AM/BM Block 15 MLU, F-16AM/BM MLU fighters, C-27J Spartan and C-130 Hercules Military transport aircraft, transport aircraft, as well as IAR 330 and IAR 316 helicopters. A Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II procurement#Romania, procurement programme for F-35 fifth-generation fighters is also currently being carried out. The Naval Forces operate three frigates, of which two are Type 22 frigates acquired from the British Royal Navy, as well as four corvettes. The Romanian Danube Flotilla, River Flotilla operates Mihail Kogălniceanu-class river monitor, Mihail Kogălniceanu and Smârdan-class river monitors.
Romania contributed troops to the international coalition in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan beginning in 2002, with a peak deployment of 1,600 troops in 2010 (which was the 4th largest contribution according to the US). Its combat mission in the country concluded in 2014. Romanian troops participated in the History of Iraq (2003–2011), occupation of Iraq, reaching a peak of 730 soldiers before being slowly drawn down to 350 soldiers. Romania terminated its mission in Iraq and withdrew its last troops on 24 July 2009, among the last countries to do so. The frigate the ''Regele Ferdinand frigate, Regele Ferdinand'' participated in the 2011 military intervention in Libya.
In December 2011, the Romanian Senate unanimously adopted the draft law ratifying the Romania–United States relations, Romania-United States agreement signed in September of the same year that would allow the establishment and operation of a US land-based Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System, ballistic missile defence system in Romania as part of NATO's efforts to build a continental NATO missile defence system, missile shield. The Aegis Ashore missile system based at Deveselu Military Base, Deveslu became operational in 2016.
In 2024, construction work started on expanding the Mihail Kogălniceanu Air Base (RoAF 57th Air Base). The air base is set to become the largest NATO base in Europe after the implementation of a project spanning 20 years.
Administrative divisions
Romania is divided into 41 Counties of Romania, counties (''județe'') and the municipality ofBucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
. Each county is administered by a county council, responsible for local affairs, as well as a Prefect (Romania), prefect responsible for the administration of national affairs at the county level. The prefect is appointed by the central government but cannot be a member of any political party. Each county is subdivided further into cities of Romania, cities and Communes of Romania, communes, which have their own mayor and local council. There are a total of 320 cities and 2,861 communes in Romania. A total of 103 of the larger cities have Municipalities of Romania, municipality status, which gives them greater administrative power over local affairs. The municipality of Bucharest is a special case, as it enjoys a status on par to that of a county. It is further divided into six sectors of Bucharest, sectors and has a prefect, a general mayor (''primar general''), and a general city council.
The NUTS-3 (Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics) level divisions of the EU reflect Romania's administrative-territorial structure and correspond to the 41 counties plus Bucharest. The cities and communes correspond to the NUTS-5 level divisions, but there are no current NUTS-4 level divisions. The NUTS-1 (four macroregions of Romania, macroregions) and NUTS-2 (eight Development regions of Romania, development regions) divisions exist but have no administrative capacity and are used instead for coordinating regional development projects and statistical purposes.
Economy
 In 2024, Romania has a GDP (PPP) of around $894 billion and a List of countries by GDP per capita (PPP), GDP per capita (purchasing power parity, PPP) of $47,203. According to the World Bank, Romania is a
In 2024, Romania has a GDP (PPP) of around $894 billion and a List of countries by GDP per capita (PPP), GDP per capita (purchasing power parity, PPP) of $47,203. According to the World Bank, Romania is a high-income economy
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a country with a gross national income per capita of US$14,005 or more in 2023, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" ...
. According to Eurostat, Romania's GDP per capita (PPS) was 77% of the EU average (100%) in 2022, an increase from 44% in 2007 (the year of Romania's accession to the EU), making Romania one of the fastest growing economies in the EU.
The Bucharest Stock Exchange (BVB) is the stock exchange of Romania, located in Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
. In 2024, the BVB boasted a $74 billion market capitalization, market capitalisation and a trading volume of $7.2 billion. As of 2024, 86 companies were listed on the exchange. In September 2020, FTSE Russell upgraded the BVB from a Frontier market to a Emerging market, Secondary Emerging Market.
After 1989 the country experienced a decade of economic instability and decline, led in part by an obsolete industrial base and a lack of structural reform. From 2000 onwards, however, the Romanian economy was transformed into one of relative macroeconomic stability, characterised by high growth, low unemployment and declining inflation. In 2006, according to the National Institute of Statistics (Romania), Romanian Statistics Office, GDP growth in real terms was recorded at 7.7%, one of the highest rates in Europe. However, the Great Recession forced the government to borrow externally, including an IMF €20 billion bailout programme. According to The World Bank, GDP per capita in purchasing power parity grew from $13,703 in 2007 to $47,903 in 2023.
 Romania's main exports are vehicles, software, clothing and textiles, Machine industry, industrial machinery, Electrical device, electrical and Electronics, electronic equipment, Metallurgy, metallurgic products, raw materials, military equipment, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and Agriculture, agricultural products (fruits, vegetables, and flowers). Trade is mostly centred on the member states of the EU, with Germany, Italy and France being the country's single largest trading partners.
In 2005, the government replaced Romania's progressive tax system with a flat tax of 16% for both personal income and corporate profit, among the lowest rates in the EU. The economy is based predominantly on services, which account for 56.2% of the country's total GDP as of 2017, with industry and agriculture accounting for 30% and 4.4% respectively.
Approximately 25.8% of the Romanian workforce is employed in agriculture, one of the highest rates in Europe.
Romania has attracted increasing amounts of foreign investment following the end of Communism, with the stock of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Romania rising to €83.8 billion in June 2019. Romania's FDI outward stock (an external or foreign business either investing in or purchasing the stock of a local economy) amounted to $745 million in December 2018, the lowest value among the 28 EU member states.
Since 1867 the official currency has been the Romanian leu, Romanian ''leu'' ("lion") and following a denomination in 2005. After joining the EU in 2007, Romania plans to adopt the euro in 2029.
Romania's main exports are vehicles, software, clothing and textiles, Machine industry, industrial machinery, Electrical device, electrical and Electronics, electronic equipment, Metallurgy, metallurgic products, raw materials, military equipment, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and Agriculture, agricultural products (fruits, vegetables, and flowers). Trade is mostly centred on the member states of the EU, with Germany, Italy and France being the country's single largest trading partners.
In 2005, the government replaced Romania's progressive tax system with a flat tax of 16% for both personal income and corporate profit, among the lowest rates in the EU. The economy is based predominantly on services, which account for 56.2% of the country's total GDP as of 2017, with industry and agriculture accounting for 30% and 4.4% respectively.
Approximately 25.8% of the Romanian workforce is employed in agriculture, one of the highest rates in Europe.
Romania has attracted increasing amounts of foreign investment following the end of Communism, with the stock of foreign direct investment (FDI) in Romania rising to €83.8 billion in June 2019. Romania's FDI outward stock (an external or foreign business either investing in or purchasing the stock of a local economy) amounted to $745 million in December 2018, the lowest value among the 28 EU member states.
Since 1867 the official currency has been the Romanian leu, Romanian ''leu'' ("lion") and following a denomination in 2005. After joining the EU in 2007, Romania plans to adopt the euro in 2029.
Infrastructure
Timișoara
Timișoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of Timiș County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, Timișoara is consider ...
ranked among the highest in the world.
Tourism
Tourism is a significant contributor to the Romanian economy, generating around 5% of GDP. The number of tourists has been rising steadily, reaching 9.33 million foreign tourists in 2016, according to the Worldbank. Tourism in Romania attracted €400 million in investments in 2005. More than 60% of the foreign visitors in 2007 were from other EU countries. The popular summer attractions of Mamaia and other Romanian Black Sea resorts, Black Sea Resorts attracted 1.3 million tourists in 2009.Criza ne strică vacanța, 9 July 2010, jurnalul.ro, accessed on 21 August 2010 Most popular skiing resorts are along the Valea Prahovei and in Poiana Brașov. List of castles in Romania, Castles, fortifications, or strongholds as well as preserved medieval Transylvanian cities or towns such as
Cluj-Napoca
Cluj-Napoca ( ; ), or simply Cluj ( , ), is a city in northwestern Romania. It is the second-most populous city in the country and the seat of Cluj County. Geographically, it is roughly equidistant from Bucharest (), Budapest () and Belgrade ( ...
, Sibiu, Brașov
Brașov (, , ; , also ''Brasau''; ; ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the county seat (i.e. administrative centre) of Brașov County.
According to the 2021 Romanian census, ...
, Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; ; ) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the river Mureș (river), Mureș in the historical region of Transylvania, it has a ...
, Baia Mare, Bistrița, Mediaș, Cisnădie, Sebeș, or Sighișoara also attract a large number of tourists. Bran Castle, near Brașov, is one of the most famous attractions in Romania, drawing hundreds of thousands of tourists every year as it is often (falsely) advertised as being Dracula in popular culture, Dracula's Castle. Other attractions include the Danube Delta or the Sculptural Ensemble of Constantin Brâncuși at Târgu Jiu.
Rural tourism, focusing on getting visitors acquainted with local folklore and Tradition, customs, has become an important alternative, and is targeted to promote such sites as Bran, Brașov, Bran and its Dracula's Castle, the Churches of Moldavia, painted churches of northern Moldavia, and the wooden churches of Maramureș, or the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania. The Via Transilvanica long-distance hiking and cycling trail, which crosses 10 counties in the Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
and Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
regions of the country further promotes rural slow tourism.
In 2014, Romania had 32,500 companies active in the hotel and restaurant industry, with a total turnover of €2.6 billion. More than 1.9 million foreign tourists visited Romania in 2014, 12% more than in 2013. According to the country's National Statistics Institute, some 77% came from Europe (particularly from Germany, Italy, and France), 12% from Asia, and less than 7% from North America.
Science and technology
Historically, Romanian researchers and inventors have made notable contributions to several fields. In the history of flight, Traian Vuia built the first Airplane, aeroplane to take off under its own power and Aurel Vlaicu built and flew some of the earliest successful aircraft, while Henri Coandă discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics. Victor Babeș discovered more than 50 types of bacteria; biologist Nicolae Paulescu developed an extract of the pancreas and showed that it lowers blood sugar in diabetic dogs, thus being significant in the history of insulin; while Emil Palade received the Nobel Prize for his contributions to cell biology. Lazăr Edeleanu was the first chemist to synthesise amphetamine, and he also invented the procedure of separating valuable petroleum components with selective solvents. During the 1990s and 2000s, the development of research was hampered by several factors, including: corruption, low funding, and a considerable brain drain. In recent years, Romania has ranked the lowest or second-lowest in the EU by research and development spending as a percentage of GDP, standing at roughly 0.5% in 2016 and 2017, substantially below the EU average of just over 2%. The country joined the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2011, and CERN in 2016. In 2018, however, Romania lost its voting rights in the ESA due to a failure to pay €56.8 million in membership contributions to the agency. In the early 2010s, the situation for science in Romania was characterised as "rapidly improving" albeit from a low base. In January 2011, Parliament passed a law that enforces "strict quality control on universities and introduces tough rules for funding evaluation and peer review". Romania was ranked 48th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024. The nuclear physics facility of the EU's proposed Extreme Light Infrastructure (ELI) laser will be built in Romania. In early 2012, Romania launched its first Goliat, satellite from the Centre Spatial Guyanais in French Guiana. Starting in December 2014, Romania became a co-owner of the International Space Station.Demographics
According to the 2021 Romanian census, Romania's population was 19,053,815. Like other countries in the region, its population is expected to decline gradually as a result of sub-replacement fertility rates and negative net migration rate. According to the 2021 Romanian census, Romanians made up 89.33% of the population, Hungarian people, Hungarians 6.05% and the Romani people, Roma 3.44% of the population, but many ethnicities are not recorded, as they do not have ID cards. International sources give higher figures for Roma than the official census. According to the Council of Europe, the Romani people, Roma makes up 8.32% of the population. Hungarians constitute a majority in the counties of Harghita County, Harghita and Covasna County, Covasna. Other minorities include Ukrainians of Romania, Ukrainians, Germans of Romania, Germans, Turks of Romania, Turks, Lipovans, Aromanians in Romania, Aromanians, Tatars of Romania, Tatars, and Serbs of Romania, Serbs. In 1930, there were 745,421 Germans living in Romania, but only about 36,000 remained in the country to this day. , there were also approximately 133,000 immigrants living in Romania, primarily from Moldova and China. The total fertility rate (TFR) in 2018 was estimated at 1.36 children born per woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1, and one of the lowest in the world, it remains considerably below the high of 5.82 children born per woman in 1912. In 2014, 31.2% of births were to unmarried women. The birth rate (9.49‰, 2012) is much lower than the mortality rate (11.84‰, 2012), resulting in a shrinking (−0.26% per year, 2012) and aging population (median age: 41.6 years, 2018), one of the oldest populations in the world, with approximately 16.8% of total population aged 65 years and over. The life expectancy in 2015 was estimated at 74.92 years (71.46 years male, 78.59 years female). The number of Romanians and individuals with ancestors born in Romania living abroad is estimated at 12 million. After the Romanian Revolution of 1989, a significant number of Romanians emigrated to other European countries, North America or Australia. For example, in 1990, 96,919 Romanians permanently settled abroad.Languages
 The official language is Romanian, a Romance language (the most widely spoken of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance branch), which presents a consistent degree of similarity to Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, but shares many features equally with the rest of the Western Romance languages, specifically Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, and Catalan language, Catalan. The Romanian alphabet contains the same 26 letters of the standard Latin alphabet, as well as five additional ones (namely ''ă'', ''â'', ''î'', ''ț'', and ''ș''), totalling 31.
Romanian is spoken as a first language by 91.55% of the entire population, while Hungarian language, Hungarian and Vlax Romani are spoken by 6.28% and 1.20% of the population, respectively. There are also 40,861 native speakers of Ukrainian language, Ukrainian (concentrated in some compact regions near the border, where they form local majorities), 17,101 native speakers of Turkish language, Turkish, 15,943 native speakers of German language, German, and 14,414 native speakers of Russian language, Russian living in Romania.
According to the Constitution, local councils ensure linguistic rights to all minorities. In localities with ethnic minorities of over 20%, that minority's language can be used in the public administration, justice system, and education. Foreign citizens and stateless persons who live in Romania have access to justice and education in their own language. English and French are the main foreign languages taught in schools. In 2010, the identified 4,756,100 French speakers in the country. According to the 2012 Eurobarometer, English is spoken by 31% of Romanians, French is spoken by 17%, and Italian and German, each by 7%.
The official language is Romanian, a Romance language (the most widely spoken of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance branch), which presents a consistent degree of similarity to Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, but shares many features equally with the rest of the Western Romance languages, specifically Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, and Catalan language, Catalan. The Romanian alphabet contains the same 26 letters of the standard Latin alphabet, as well as five additional ones (namely ''ă'', ''â'', ''î'', ''ț'', and ''ș''), totalling 31.
Romanian is spoken as a first language by 91.55% of the entire population, while Hungarian language, Hungarian and Vlax Romani are spoken by 6.28% and 1.20% of the population, respectively. There are also 40,861 native speakers of Ukrainian language, Ukrainian (concentrated in some compact regions near the border, where they form local majorities), 17,101 native speakers of Turkish language, Turkish, 15,943 native speakers of German language, German, and 14,414 native speakers of Russian language, Russian living in Romania.
According to the Constitution, local councils ensure linguistic rights to all minorities. In localities with ethnic minorities of over 20%, that minority's language can be used in the public administration, justice system, and education. Foreign citizens and stateless persons who live in Romania have access to justice and education in their own language. English and French are the main foreign languages taught in schools. In 2010, the identified 4,756,100 French speakers in the country. According to the 2012 Eurobarometer, English is spoken by 31% of Romanians, French is spoken by 17%, and Italian and German, each by 7%.
Religion
Romania is a secular state and has no state religion. An overwhelming majority of the population identify themselves as Christians. At the country's 2021 census, 73.60% of respondents identified as Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christians, with 73.42% belonging to the Romanian Orthodox Church. Other denominations include Religion in Romania#Protestantism, Protestantism (6.22%), Roman Catholicism in Romania, Roman Catholicism (3.89%), and Romanian Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholicism (0.61%). From the remaining population 128,291 people belong to other Christian denominations or have another religion, which includes 58,347 Islam in Romania, Muslims (mostly of Turkish and Tatar ethnicity) and 2,708 History of the Jews in Romania, Jewish (Jews once constituted 4% of the Romanian population—728,115 persons in the 1930 census). Additionally, 71,430 people are Irreligion, irreligious, 57,229 are Atheism, atheist, 25,485 are Agnosticism, agnostic, and 2,658,165 people chose to not declare their religion. The Romanian Orthodox Church is an Autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church in full communion with other Orthodox churches, with a Patriarch of All Romania, Patriarch as its leader. It is the third-largest Eastern Orthodox Church in the world, and unlike other Orthodox churches, it functions within aLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
culture and uses a Romance languages, Romance liturgical language. Its canonical jurisdiction covers the territories of Romania and Moldova. Romania has the Eastern Orthodoxy by country, world's third-largest Eastern Orthodox population.
Urbanisation
Although 54.0% of the population lived in urban areas in 2011, this percentage has been declining since 1996. Counties with over urban population are Hunedoara County, Hunedoara, Brașov County, Brașov and Constanța County, Constanța, while those with less than a third are Dâmbovița County, Dâmbovița (30.06%) and Giurgiu County, Giurgiu and Teleorman County, Teleorman. Bucharest is the capital and the largest city in Romania, with a population of over 1.7 million in 2021. Its larger urban zone has a population of almost 2.2 million, which are planned to be included into a Bucharest metropolitan area, metropolitan area up to 20 times the area of the city proper. Another 17 cities have a population of over 100,000, with Cluj-Napoca, Iași, Constanța and Timișoara of more than 250,000 inhabitants, and Craiova, Brașov and Galați with over 200,000 inhabitants. Metropolitan areas in Romania, Metropolitan areas have been constituted for most of these cities.Education
 Since the Romanian Revolution of 1989, the Romanian educational system has been in a continuous process of reform that has received mixed criticism. In 2004, some 4.4 million individuals were enrolled in school. Of these, 650,000 were in kindergarten (three-six years), 3.11 million in primary and secondary level, and 650,000 in tertiary level (universities). In 2018, the adult literacy rate was 98.8%. Kindergarten is optional between three and five years. Since 2020, compulsory schooling starts at age 5 with the last year of kindergarten (grupa mare) and is compulsory until twelfth grade. Primary and secondary education is divided into 12 or 13 grades. There is also a semi-legal, informal Tutoring#Peer tutoring, private tutoring system used mostly during secondary school, which prospered during the Communist regime.
Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași, Babeș-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, University of Bucharest, and West University of Timișoara have been included in the QS World University Rankings' top 800.
Romania ranks fifth in the all-time medal count at the International Mathematical Olympiad with 316 total medals, dating back to 1959. Ciprian Manolescu managed to write a perfect paper (42 points) for a gold medal more times than anybody else in the history of the competition, in 1995, 1996 and 1997. Romania has achieved the highest team score in the competition, after China, Russia, the United States and Hungary. Romania also ranks sixth in the all-time medal count at the International Olympiad in Informatics with 107 total medals, dating back to 1989.
Since the Romanian Revolution of 1989, the Romanian educational system has been in a continuous process of reform that has received mixed criticism. In 2004, some 4.4 million individuals were enrolled in school. Of these, 650,000 were in kindergarten (three-six years), 3.11 million in primary and secondary level, and 650,000 in tertiary level (universities). In 2018, the adult literacy rate was 98.8%. Kindergarten is optional between three and five years. Since 2020, compulsory schooling starts at age 5 with the last year of kindergarten (grupa mare) and is compulsory until twelfth grade. Primary and secondary education is divided into 12 or 13 grades. There is also a semi-legal, informal Tutoring#Peer tutoring, private tutoring system used mostly during secondary school, which prospered during the Communist regime.
Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași, Babeș-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, University of Bucharest, and West University of Timișoara have been included in the QS World University Rankings' top 800.
Romania ranks fifth in the all-time medal count at the International Mathematical Olympiad with 316 total medals, dating back to 1959. Ciprian Manolescu managed to write a perfect paper (42 points) for a gold medal more times than anybody else in the history of the competition, in 1995, 1996 and 1997. Romania has achieved the highest team score in the competition, after China, Russia, the United States and Hungary. Romania also ranks sixth in the all-time medal count at the International Olympiad in Informatics with 107 total medals, dating back to 1989.
Healthcare
Healthcare in Romania is mainly provided by the public sector, which runs most hospitals and offers national health insurance to nearly all citizens. In 2021, healthcare costs were US$16. 7 billion, or US$2,385 per person, making up 5.69€ of GDP. Government spending is higher than in markets like Bulgaria but lower than Hungary. Spending is expected to rise by 7. US$5 billion (+37. 68%) from 2024 to 2028, reaching 27. US$3 billion by 2028. The Romanian National Institute of Statistics reports over 65,000 health units in Romania, with 53,000 in urban areas and 12,000 in rural areas. There are 543 hospitals, including 488 in urban and 55 in rural areas, along with 160 other hospital-like establishments. Nearly 50% of these are large facilities with over 100 beds, while 39% are small with fewer than 50 beds. The total number of inpatient beds is 135,085, allocated mainly to psychiatry, surgery, and internal medicine among other specialties.Culture
Arts and monuments
Architecture The topic of the origin of Romanian culture began to be discussed by the end of the 18th century among the Transylvanian School scholars. Several writers rose to prominence in the 19th century, including: George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici,
The topic of the origin of Romanian culture began to be discussed by the end of the 18th century among the Transylvanian School scholars. Several writers rose to prominence in the 19th century, including: George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici, Mihail Kogălniceanu
Mihail Kogălniceanu (; also known as Mihail Cogâlniceanu, Michel de Kogalnitchan; September 6, 1817 – July 1, 1891) was a Romanian Liberalism, liberal statesman, lawyer, historian and publicist; he became Prime Minister of Romania on Octo ...
, Vasile Alecsandri, Nicolae Bălcescu
Nicolae Bălcescu () (29 June 181929 November 1852) was a Romanian Wallachian soldier, historian, journalist, and leader of the 1848 Wallachian Revolution.
Early life
Born in Bucharest to a family of low-ranking nobility, he used his mother ...
, Ion Luca Caragiale, Ion Creangă, and Mihai Eminescu, the later being considered the greatest and most influential Romanian poet, particularly for the poem ''Luceafărul (poem), Luceafărul''.
In the 20th century, a number of Romanian artists and writers achieved international acclaim, including: Tristan Tzara, Marcel Janco, Mircea Eliade, Nicolae Grigorescu, Marin Preda, Liviu Rebreanu, Eugène Ionesco, Emil Cioran, and Constantin Brâncuși. Brâncuși has a sculptural ensemble in Târgu Jiu, while his sculpture ''Bird in Space'', was auctioned in 2005 for $27.5 million. Romanian-born Holocaust survivor Elie Wiesel received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1986, while Banat Swabians, Banat Swabian writer Herta Müller received the 2009 Nobel Prize in Literature.
 Prominent Romanian painters include: Nicolae Grigorescu, Ștefan Luchian, Ion Andreescu Nicolae Tonitza, and Theodor Aman. Notable Romanian classical composers of the 19th and 20th centuries include: Ciprian Porumbescu, Anton Pann, Eduard Caudella, Mihail Jora, Dinu Lipatti, and especially George Enescu. The annual George Enescu Festival is held in Bucharest in honour of the 20th-century composer.
Contemporary musicians like Angela Gheorghiu, Gheorghe Zamfir, Inna, Alexandra Stan, and many others have achieved various levels of international acclaim. From the late 2000s through the early 2010s, the Romanian Popcorn (Romanian music style), popcorn music style had established itself in the international mainstream. At the Eurovision Song Contest Romanian singers achieved third place in 2005 and 2010.
In cinema, several movies of the Romanian New Wave have achieved international acclaim. At the Cannes Film Festival, ''The Death of Mr. Lazarescu'' by Cristi Puiu won the in 2005, while ''4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days'' by Cristian Mungiu won the festival's top prize, the , in 2007. At the Berlin International Film Festival, ''Child's Pose (film), Child's Pose'' by Călin Peter Netzer won the Golden Bear in 2013.
The list of World Heritage Sites includes List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, six cultural sites located within Romania, including eight painted churches of northern Moldavia, eight wooden churches of Maramureș, seven villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, the Horezu Monastery, and the Historic Centre of Sighișoara. The city of Sibiu, with its Brukenthal National Museum, was selected as the 2007 European Capital of Culture and the 2019 European Region of Gastronomy. Multiple castles exist in Romania, including the popular tourist attractions of Peleș Castle, Corvin Castle, and Bran Castle or "Dracula's Castle".
Prominent Romanian painters include: Nicolae Grigorescu, Ștefan Luchian, Ion Andreescu Nicolae Tonitza, and Theodor Aman. Notable Romanian classical composers of the 19th and 20th centuries include: Ciprian Porumbescu, Anton Pann, Eduard Caudella, Mihail Jora, Dinu Lipatti, and especially George Enescu. The annual George Enescu Festival is held in Bucharest in honour of the 20th-century composer.
Contemporary musicians like Angela Gheorghiu, Gheorghe Zamfir, Inna, Alexandra Stan, and many others have achieved various levels of international acclaim. From the late 2000s through the early 2010s, the Romanian Popcorn (Romanian music style), popcorn music style had established itself in the international mainstream. At the Eurovision Song Contest Romanian singers achieved third place in 2005 and 2010.
In cinema, several movies of the Romanian New Wave have achieved international acclaim. At the Cannes Film Festival, ''The Death of Mr. Lazarescu'' by Cristi Puiu won the in 2005, while ''4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days'' by Cristian Mungiu won the festival's top prize, the , in 2007. At the Berlin International Film Festival, ''Child's Pose (film), Child's Pose'' by Călin Peter Netzer won the Golden Bear in 2013.
The list of World Heritage Sites includes List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, six cultural sites located within Romania, including eight painted churches of northern Moldavia, eight wooden churches of Maramureș, seven villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, the Horezu Monastery, and the Historic Centre of Sighișoara. The city of Sibiu, with its Brukenthal National Museum, was selected as the 2007 European Capital of Culture and the 2019 European Region of Gastronomy. Multiple castles exist in Romania, including the popular tourist attractions of Peleș Castle, Corvin Castle, and Bran Castle or "Dracula's Castle".
Holidays, traditions, and cuisine
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
), but also shares some similarities with other cuisines in the Balkans, Balkan region such as the Greek cuisine, Greek, Bulgarian cuisine, Bulgarian, or Serbian cuisine. ''Ciorbă'' includes a wide range of sour soups, while ', ' (similar to polenta), and ''Sarma (food), sarmale'' are featured commonly in main courses.
Pork, chicken, and beef are the preferred types of meat, but lamb and fish are also quite popular. Certain traditional recipes are made in direct connection with the holidays: ', ' and ' at Christmas; ', ' and ' at Easter and other Romanian holidays. ''Țuică'' is a strong plum brandy reaching a 70% alcohol content which is the country's traditional alcoholic beverage, taking as much as 75% of the national crop (Romania is one of the List of countries by plum production, largest plum producers in the world). Traditional alcoholic beverages also include Romanian wine, wine, ''rakia, rachiu'', ''Pálinka, palincă'' and ''vișinată'', but Beer in Romania, beer consumption has increased dramatically over recent years.
Media
Sports
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Romania with over 219,000 registered players . The market for professional football in Romania is roughly €740 million according to UEFA. The governing body is the Romanian Football Federation, which belongs to UEFA. The Romania national football team played its first match in 1922 and is one of only four national teams to have taken part in the first three FIFA World Cups, the other three being Brazil, France, and Belgium. Overall, it has played in seven World Cups and had its most successful period during the 1990s, when it finished 6th at the 1994 FIFA World Cup, eventually being ranked 3rd by FIFA in 1997. The most successful club is CSA Steaua București (football), Steaua București, who were the first Eastern European team to win the UEFA Champions League in 1986, and were runners-up in 1989. FC Dinamo București, Dinamo București reached the UEFA Champions League semi-final in 1984 and the UEFA Cup Winners' Cup semi-final in 1989–90 European Cup Winners' Cup, 1990. Other important Romanian football clubs are FC Rapid București, Rapid București, FC UTA Arad, UTA Arad, CS Universitatea Craiova, Universitatea Craiova, FC Petrolul Ploiești, Petrolul Ploiești, CFR Cluj, FC Astra Giurgiu, Astra Giurgiu, and FC Viitorul Constanța, Viitorul Constanța (the latter having recently merged with FCV Farul Constanța). Tennis is the second most popular sport. Romania reached the Davis Cup finals three times in 1969, 1971 and 1972. The second most popular team sport is team handball, handball. The Romania men's national handball team, men's team won the World Men's Handball Championship, handball world championship in 1961 World Men's Handball Championship, 1961, 1964 World Men's Handball Championship, 1964, 1970 World Men's Handball Championship, 1970, 1974 World Men's Handball Championship, 1974 making them the third most successful nation ever in the tournament. The Romania women's national handball team, women's team won the IHF World Women's Handball Championship, world championship in 1962 World Women's Handball Championship, 1962 and have enjoyed more success than their male counterparts in recent years. In the club competition Romanian teams have won the EHF Champions League a total of three times, CSA Steaua București (handball), Steaua București won in 1967–68 European Cup (handball), 1968 as well as 1976–77 European Cup (handball), 1977 and CS Dinamo București (men's handball), Dinamo București won in 1964–65 European Cup (handball), 1965. In women's handball, powerhouse CSM București (women's handball), CSM București lifted the Women's EHF Champions League, EHF Champions League trophy in 2016. Popular individual sports include combat sports, martial arts, and swimming. In professional boxing, Romania has produced many world champions across the weight divisions internationally recognised by governing bodies. Another popular combat sport is kickboxing, professional kickboxing, which has produced prominent practitioners including. Romania's 306 All-time Olympic Games medal table, all-time Summer Olympics medals would rank 12th most among all countries, while its 89 gold medals would be 14th most. The 1984 Summer Olympics was their most successful run, where they won 53 medals in total, 20 of them gold, ultimately placing 2nd to the hosts United States in the 1984 Summer Olympics medal table, medal rankings. Amongst countries who have never hosted the event themselves, they are second in the total number of medals earned. Artistic gymnastics, Gymnastics is the country's major medal-producing sport,See also
* Outline of RomaniaNotes
References
Sources
*The Ancient History of Herodotus
' (Translated by William Beloe) (1859). Derby & Jackson. *
' (Translated by John Selby Watson) (1886). George Bell and Sons. * * * * * *
excerpt
* Hitchins, Keith. ''Rumania 1866-1947'' (1994) (Oxford History of Modern Europe
excerpt
* * * * * * * * * * * * * Stavrianos, L.S. '' The Balkans Since 1453'' (1958), major scholarly history
online free to borrow
* *
External links
Country Profile
from BBC News.
Romania Article and Country Profile
from Encyclopædia Britannica
Romania Profile
from Balkan Insight.
România Un Secol de Istorie – statistical data
from National Institute of Statistics (Romania), INS
Romania
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. ;Government
Romanian Presidency
;Culture and history links
Treasures of the national library of Romania
Historic Houses of Romania
{{Coord, 46, N, 25, E, type:country, display=title Romania, 1859 establishments in Europe Balkan countries Countries in Europe Member states of the United Nations Member states of NATO Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the Three Seas Initiative Republics Countries and territories where Romanian is an official language States and territories established in 1859