|
Matei Basarab
Matei Basarab (; 1588, Brâncoveni, Olt – 9 April 1654, Bucharest) was the voivode (prince) of Wallachia from 1632 to 1654. Reign Much of Matei's reign was spent fighting off incursions from Moldavia, which he successfully accomplished in 1637, 1639, and 1653 – see Battle of Finta. He was an enlightened ruler, and is noted for introducing the printing press to Wallachia (1634) and creating the first Wallachian code of laws as well as patronizing art and religion (founder of the first upper school in his Principality). He built more than 45 churches and monasteries, being compared to Stephen the Great, the famous ruler of Moldavia. His election in 1632 signified the first official exception to a rule set by custom. Basarab was merely a boyar (of the Craiovești family) and one not related to previous Princes (although it seems that a similar point can be made about such rulers as Michael the Brave). The reason for this choice has been explained as a reaction of indigeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
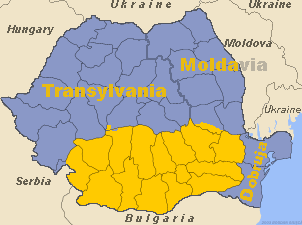
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was forced to accept the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire; this lasted until the 19th century. In 1859, Wallachia united with Moldavia to form the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Princes Of Wallachia
This is a list of princes of Wallachia, from the first mention of a medieval polity situated between the Southern Carpathians and the Danube until the union with Moldavia in 1859, which unification of Moldavia and Wallachia, led to the creation of Romania. Notes Dynastic rule is hard to ascribe, given the loose traditional definition of the ruling family. On principle, princes were chosen from any family branch, including a previous ruler's bastard sons, being defined as ''os de domn'', "of Voivode marrow", or as having ''heregie'', "heredity" (from the Latin ''hereditas''); the institutions charged with the Elective monarchy, election, dominated by the boyars, had fluctuating degrees of influence. The system itself was challenged by usurpers, and became obsolete with the Phanariotes, Phanariote epoch, when rulers were appointed by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans; between 1821 and 1878 (the date of Romania's independence), various systems combining election and appointment were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael The Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvania (1599–1600). He is considered one of Romania's greatest national heroes. Since the 19th century, Michael the Brave has been regarded by Romanian nationalism, Romanian nationalists as a symbol of Romanian unity, as his reign marked the first time in history all principalities inhabited by Romanians were under the same ruler. His rule over Wallachia began in the autumn of 1593. Two years later, Long Turkish War, war with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans began, a conflict in which the Prince fought the Battle of Călugăreni, resulting in a victory against an army nearly three times the size of the army of Michael the Brave, considered one of the most important battles of his reign. Although the Wallachians emerged victorious from the battle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian (language)
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called '' Daco-Romanian'' as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian. It is also spoken as a minority language by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Bulgaria, Hungary, Serbia and Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 25 million people as a first language. Romanian was also known as '' Moldovan'' in Moldova, although the Constitutional Court of Moldova ruled in 2013 that "the official language of Moldova is Romanian". On 16 March 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasile Lupu
Lupu Coci, known as Vasile Lupu (; 1595 – 1661), was the voivode of Moldavia between 1634 and 1653. He was of Albanian and Greek origin. Lupu had secured the Moldavian throne in 1634 after a series of complicated intrigues and managed to hold it for twenty years. Vasile was a capable administrator and a brilliant financier and was soon almost the richest man in the Christian East. His gifts to Ottoman leaders kept him on good terms with the Ottoman authorities. Early life The Coci family settled in Wallachia (Țara Rumânească) in the first half of the 16th century. His father, Nicolae (Neculai) Coci was an Albanian shopkeeper, the son of Constantin (Coce) and Ecaterina, who originated from Macedonia or Epirus. His mother was Greek. Nicolae entered Moldavian nobility in 1593. Nikolae was born in Arbanasi. According to different researchers it was a village in modern-day Bulgaria ( Arbanasi or Dolno Arbanasi - today a suburb of Razgrad), while some historians claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Moldavian Rulers
This is a list of monarchs of Moldavia, from the first mention of the medieval polity east of the Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians and until its disestablishment in 1862, when Unification of Moldavia and Wallachia, it united with Wallachia, the other Danubian Principalities, Danubian Principality, to form the modern-day state of Romania. Notes Dynastic rule is hard to ascribe, given the loose traditional definition of the ruling family (on principle, princes were chosen from any branch, including a previous monarch's bastard sons – being defined as ''os de domn'' – "of Hospodar, domn marrow", or as having ''hereghie'' – "heredity" (from the Latin ''hereditas''); the institutions charged with the Elective monarchy, election, dominated by the boyars, had fluctuating degrees of influence). The system itself was challenged by usurpers, and became obsolete with the Phanariotes, Phanariote epoch, when monarchs were appointed by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Ottoman Dynasty, Sultans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George II Rákóczi
George II Rákóczi (30 January 1621 – 7 June 1660), was a Hungarian nobleman, Prince of Transylvania (1648-1660), the eldest son of George I and Zsuzsanna Lorántffy. Early life He was elected Prince of Transylvania during his father's lifetime (19 February 1642). On 3 February 1643, he married Sophia Báthory, a granddaughter of Stephen Báthory IX. Their son was Francis I Rákóczi. War with the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Preparation On ascending the throne (October 1648), his first thought was to realize his father's ambitions in Poland. With this object in view, he allied himself, in the beginning of 1649, with the Cossack hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky, and the hospodars of Moldavia and Wallachia, ( Vasile Lupu and Matei Basarab), but took no action for several years. On 6 December 1656, by the Treaty of Radnot, he also allied with King Charles X Gustav of Sweden against King John II Casimir of Poland. Rákóczi was to seize the provinces of Lesser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Transylvanian Rulers
These are lists of political office-holders in Transylvania, from the 10th century, until 1867. * Count of the Székelys – royal officials appointed from the first half of the 13th century to the second half of the 15th century to lead the Székelys independently of the voivodes. ** List of counts of the Székelys * Duke of Transylvania – members of the royal family bearing the title duke in the 13th and 14th centuries ** List of dukes of Transylvania * Voivode of Transylvania – great officials of the realm appointed by the monarchs to administer parts of Transylvania (includes a list of the ''sovereigns appointing them'') ** List of voivodes of Transylvania (12th–16th century) * Prince of Transylvania – monarchs of the Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711) under Ottoman suzerainty ** List of princes of Transylvania (1570–1711) *** List of princesses consort of Transylvania (1570–1711) * During the (Grand) Principality of Transylvania (1711–1867), the tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border are the Carpathian Mountains and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Historical Transylvania also includes small parts of neighbouring Western Moldavia and even a small part of south-western neighbouring Bukovina to its north east (represented by Suceava County). Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history, coupled with its multi-cultural character. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other very well preserved medieval iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Bistrița, Alba Iuli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seimeni
Seimeni (plural of ''Seimen'') designates the group of flintlock-armed infantry mercenaries charged with guarding the ''hospodar'' (ruler) and his court in 17th and 18th century Wallachia and Moldavia. They were mostly of Serb and other Balkan origin. The term is of Turkish origin: ''seğmen'' means "young armed man". In modern transcriptions of Slavonic, it may also appear as ''simén'' (plural: ''siméni'') or ''siimén'' (''siiméni''). Menaced by the growing privileges of boyars and threatened to lose land grants or be turned into serfs, the Wallachian ''seimeni'' rebelled in 1655, being crushed after Prince Constantin Șerban enlisted the help of George II Rákóczi, Prince of Transylvania, as well as that of Moldavia's Voivode Gheorghe Ștefan. After exercising a rule of terror in Bucharest, capturing and executing several boyars A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |