XDNA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
xDNA (also known as expanded DNA or benzo-homologated DNA) is a size-expanded
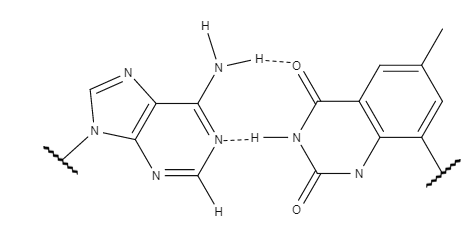 The success and implications of xDNA prompted research to examine other factors which could alter
The success and implications of xDNA prompted research to examine other factors which could alter 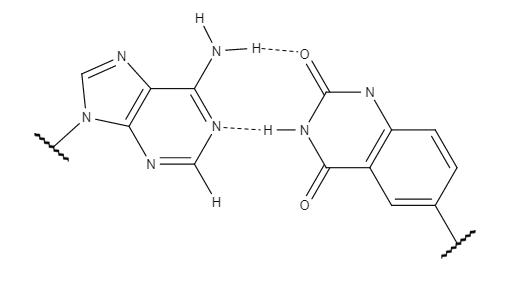 While xDNA and yDNA are quite similar in most properties, including their increased stacking interactions, yDNA shows superior mismatch recognition. y-pyrimidines display slightly stronger stacking interactions than x-pyrimidines as a result of the distance between the two
While xDNA and yDNA are quite similar in most properties, including their increased stacking interactions, yDNA shows superior mismatch recognition. y-pyrimidines display slightly stronger stacking interactions than x-pyrimidines as a result of the distance between the two
 Doubly-expanded (or ''naphtho-homologated'') nucleobases incorporate a
Doubly-expanded (or ''naphtho-homologated'') nucleobases incorporate a
nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
system synthesized from the fusion of a benzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
and one of the four natural bases: adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
, guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
, cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
, and thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
. This size expansion produces an 8 letter alphabet which has a larger information storage capacity than natural DNA's (often referred to as B-DNA in literature) 4 letter alphabet. As with normal base-pairing
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
, A pairs with xT, C pairs with xG, G pairs with xC, and T pairs with xA. The double helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by base pair, double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double Helix, helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its Nuclei ...
is thus 2.4 Å wider than a natural double helix. While similar in structure to B-DNA, xDNA has unique absorption, fluorescence, and stacking properties.
Initially synthesized as an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
probe by Nelson J. Leonard's group, benzo-homologated adenine was the first base synthesized. Later, Eric T. Kool's group finished synthesizing the remaining three expanded bases, eventually followed by yDNA ("wide" DNA), another benzo-homologated nucleotide system, and naphtho-homologated xxDNA and yyDNA. xDNA is more stable when compared to regular DNA when subjected to higher temperature, and while entire strands of xDNA, yDNA, xxDNA and yyDNA exist, they are currently difficult to synthesize and maintain. Experiments with xDNA provide new insight into the behavior of natural B-DNA. The extended bases xA, xC, xG, and xT are naturally fluorescent
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with color ...
, and single strands composed of only extended bases can recognize and bind to single strands of natural DNA, making them useful tools for studying biological systems. xDNA is most commonly formed with base pairs between a natural and expanded nucleobase
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
, however x-nucleobases can also be paired together. Current research supports xDNA as a viable genetic encoding system in the near future.
Origins
The firstnucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
to be expanded was the purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted puri ...
adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
. Nelson J. Leonard and colleagues synthesized this original x-nucleotide, which was referred to as "expanded adenine". xA was used as a probe in the investigation of active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding s ...
s of ATP-dependent enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s, more specifically what modifications the substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
could take while still being functional. Almost two decades later, the other three bases were successfully expanded and later integrated into a double helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by base pair, double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double Helix, helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its Nuclei ...
by Eric T. Kool and colleagues. Their goal was to create a synthetic genetic system which mimics and surpasses the functions of the natural genetic system, and to broaden the applications of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
both in living cells and in experimental biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
. Once the expanded base set was created, the goal shifted to identifying or developing faithful replication enzymes and further optimizing the expanded DNA alphabet.
Synthesis
In benzo-homologated purines (xA and xG), thebenzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
is bound to the nitrogenous base
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
through nitrogen-carbon (N-C) bonds. Benzo-homologated pyrimidines are formed through carbon-carbon (C-C) bonds between the base and the benzene. Thus far, x-nucleobases have been added to strands of DNA using phosphoramidite
A phosphoramidite (RO)2PNR2 is a monoamide of a phosphite diester. The key feature of phosphoramidites is their markedly high reactivity towards nucleophiles catalyzed by weak acids ''e.c''., triethylammonium chloride or 1''H''-tetrazole. In these ...
derivatives, as traditional polymerases
In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme ( EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by copying a DNA template s ...
have been unsuccessful in synthesizing strands of xDNA. X-nucleotides are poor candidates as substrates for B-DNA polymerases as their size interferes with binding at the catalytic domain
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding si ...
. Attempts at using template-independent enzymes have been successful as they have a reduced geometric constraint for substrates. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphom ...
(TdT) has been used previously to synthesize strands of bases which have been bound to fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with se ...
s. Using TdT, up to 30 monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
s can be combined to form a double-helix of xDNA, however this oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
ic xDNA appears to inhibit its own extension beyond this length due to the overwhelming hydrogen bonding. In order to minimize inhibition, xDNA can be hybridized into a regular helix.
Replication
For xDNA to be used as a substitute structure for information storage, it requires a reliable replication mechanism. Research into xDNA replication using aKlenow fragment
The Klenow fragment is a large protein fragment produced when DNA polymerase I from '' E. coli'' is enzymatically cleaved by the protease subtilisin. First reported in 1970, it retains the 5' → 3' polymerase activity and the 3’ → 5’ ...
from DNA polymerase I
DNA polymerase I (or Pol I) is an enzyme that participates in the process of prokaryotic DNA replication. Discovered by Arthur Kornberg in 1956, it was the first known DNA polymerase (and the first known of any kind of polymerase). It was init ...
shows that a natural base partner is selectively added in instances of single-nucleotide insertion. However, DNA polymerase IV
DNA polymerase IV is a prokaryotic polymerase that is involved in mutagenesis and is encoded by the ''dinB'' gene. It exhibits no 3′→5′ exonuclease (proofreading) activity and hence is error prone. In ''E. coli'', DNA polymerase IV (Pol 4) ...
(Dpo4) has been able to successfully use xDNA for these types of insertions with high fidelity, making it a promising candidate for future research in extending replicates of xDNA. xDNA's mismatch sensitivity is similar to that of B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
.
Structure
Similar to natural bases, x-nucleotides selectively assemble into a duplex-structure resembling B-DNA. xDNA was originally synthesized by incorporating a benzene ring into the nitrogenous base. However, other expanded bases have been able to incorporatethiophene
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reacti ...
and benzo hiophene as well. xDNA and yDNA use benzene rings to widen the bases and are thus termed "benzo-homologated". Another form of expanded nucleobases known as yyDNA incorporate naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation ...
into the base and are "naptho-homologated". xDNA has a rise of 3.2 Å and a twist of 32°, significantly smaller than B-DNA, which has a rise of 3.3 Å and a twist of 34.2° xDNA nucleotides can occur on both strands—either alone (known as "doubly expanded DNA") or mixed with natural bases—or exclusively on one strand or the other. Similar to B-DNA, xDNA can recognize and bind complementary single-stranded DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
or RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
sequences.
Duplexes formed from xDNA are similar to natural duplexes aside from the distance between the two sugar-phosphate backbones. xDNA helices have a greater number of base pairs per turn of the helix as a result of a reduced distance between neighbour nucleotides. NMR spectra report that xDNA helices are anti-parallel, right-handed
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to and causing it to be stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dext ...
and take an ''anti'' conformation around the glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of ether bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group o ...
, with a C2'-endo sugar pucker. Helices created from xDNA are more likely to take a B-helix over an A-helix conformation, and have an increased major groove width by 6.5 Å (where the backbones are farthest apart) and decreased minor groove width by 5.5 Å (where the backbones are closest together) compared to B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
. Altering groove width affects the xDNA's ability to associate with DNA-binding protein
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, becau ...
s, but as long as the expanded nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s are exclusive to one strand, recognition sites are sufficiently similar to B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
to allow bonding of transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s and small polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made throug ...
molecules. Mixed helices present the possibility of recognizing the four expanded bases using other DNA-binding molecules.
Properties
Expanded nucleotides and their oligomeric helices share many properties with their naturalB-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
counterparts, including their pairing preference: A with T, C with G. The various differences in chemical properties between xDNA and B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
support the hypothesis that the benzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
which expands x-nucleobases is not, in fact, chemically inert. xDNA is more hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
than B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
, and also has a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap (distance between the highest occupied molecular orbital and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) as a result of modified saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
*Saturated and unsaturated compounds, a classification of compounds related to their ability to resist addition reactions
** Degree of unsaturation
**Saturated fat or satu ...
. xDNA has higher melting temperatures than B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
(a mixed decamer of xA and T has a melting temperature of 55.6 °C, 34.3 °C higher than the same decamer of A and T), and exhibits an "all-or-nothing" melting behaviour.
Conformation
Under lab conditions, xDNA orients itself in the ''syn'' conformation. This unfortunately does not expose the binding face of the xDNA nucleotides to face the neighbouring strand for binding, meaning that extra measures must be applied to alter the conformation of xDNA before attempting to form helices. However, the ''anti'' and ''syn'' orientations are practically identical energetically in expanded bases. This conformational preference is seen primarily inpyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The oth ...
s, and purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted puri ...
s display minimal preference for orientation.
Enhanced stacking
Stacking of thenucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s in a double helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by base pair, double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double Helix, helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its Nuclei ...
is a major determinant of the helix's stability. With the added surface area
The surface area (symbol ''A'') of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the d ...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
available for bonding, stacking potential for the nucleobases increases with the addition of a benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
spacer. By increasing the separation between the nitrogenous base
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
s and either sugar-phosphate backbone, the helix's stacking energy is less variable and therefore more stable. The energies for natural nucleobase pairs vary from 18 to 52 kJ/mol. This variance is only 14–40 kJ/mol for xDNA.
Due to an increased overlap between and expanded strand of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and its neighbouring strand, there are greater interstrand interactions in expanded and mixed helices, resulting in a significant increase in the helix's stability. xDNA has enhanced stacking abilities resultant from changes in inter- and intrastrand hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
ing that arise from the addition of a benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
spacer, but expanding the bases does not alter hydrogen's contribution to the stability of the duplex. These stacking abilities are exploited by helices consisting of both xDNA and B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
in order to optimize the strength of the helix. Increased stacking is seen most prominently in strands consisting only of A and xA and T and xT, as T-xA has stronger stacking interactions than T- A.
The energy resultant from pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The oth ...
s ranges from 30 to 49 kJ/mol. The range for purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted puri ...
s is between 40-58kJ/mol. By replacing one nucleotide in a double-helix with an expanded nucleotide, the strength of the stacking interactions increases by 50%. Expanding both nucleotides results in a 90% increase in stacking strength. While xG has an overall negative effect on the binding strength of the helix, the other three expanded bases outweigh this with their positive effects. The change in energy caused by expanding the bases is mostly dependent on the rotation of the bond about the nucleobases' centers of mass, and center of mass stacking interactions improve the stacking potential of the helix. Because the size-expanded bases widen the helix, it is more thermally stable with a higher melting temperature.
Absorption
The addition of abenzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
spacer in x-nucleobase
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
s affects the bases' optical absorption
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy—and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy).
A ...
spectra. Time-dependent density functional theory
Time-dependent density-functional theory (TDDFT) is a quantum mechanical theory used in physics and chemistry to investigate the properties and dynamics of many-body systems in the presence of time-dependent potentials, such as electric or magne ...
(TDDFT) applied to xDNA revealed that the benzene component of the highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
) in the x-bases pins the absorption onset at an earlier point than natural bases. Another unusual feature of xDNA absorption spectra is the red-shifted excimer
An excimer (originally short for excited dimer) is a short-lived polyatomic molecule formed from two species that do not form a stable molecule in the ground state. In this case, formation of molecules is possible only if such atom is in an elec ...
s of xA in the low range. In terms of stacking fingerprints, there is a more pronounced hypochromicity seen in consecutive xA- T base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s.
Implications of xDNA's altered absorption include applications in nanoelectronic technology and nanobiotechnology
Nanobiotechnology, bionanotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blank ...
. The reduced spacing between x-nucleotides makes the helix
A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is for ...
stiffer, thus it is not as easily affected by substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
, electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
, and functional nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
forces. Other alterations to natural nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s resulting in different absorption spectra will broaden these applications in the future.
Fluorescence
One unique property of xDNA is its inherentfluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
. Natural bases can be bound directly to fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with se ...
s for use in microarrays
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of biological interactions. It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silicon thin-film cell� ...
, ''in situ'' hybridization, and polymorphism analysis. However, these fluorescent natural bases often fail as a result of self-quenching, which diminishes their fluorescent intensity and reduces their applicability as visual DNA tags. The pi interaction
In chemistry, π-effects or π-interactions are a type of non-covalent interaction that involves π systems. Just like in an electrostatic interaction where a region of negative charge interacts with a positive charge, the electron-rich π system ...
s between the rings in x-nucleobases result in an inherent fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
in the violet-blue range, with a Stokes shift between 50 and 80 nm. They also have a quantum yield
In particle physics, the quantum yield (denoted ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system.
\Phi(\lambda)=\frac
Applications
Fluorescence spectroscopy
The fluorescence ...
in the range of 0.3–0.6. xC has the greatest fluorescent emission.
Other expanded bases
After the creation of and successful research surrounding xDNA, more forms of expanded nucleotides were investigated. yDNA is a second, similar system of nucleotides which uses abenzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
to expand the four natural bases. xxDNA and yyDNA use naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation ...
, a polycyclic molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
consisting of two hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
rings. The two rings expand the base even wider, further altering its chemical properties.
yDNA
 The success and implications of xDNA prompted research to examine other factors which could alter
The success and implications of xDNA prompted research to examine other factors which could alter B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
's chemical properties and create a new system for information storage with broader applications. yDNA also uses a benzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
, similar to xDNA, with the only difference being the site of addition of the aromatic ring
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The e ...
. The location of the benzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
changes the preferred structure of the expanded helix. The altered conformation makes yDNA more similar to B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
in its orientation by changing the interstrand hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
s. Stability is highly dependent on the bases' rotation about the link between the base and the sugar of the backbone. yDNA's altered preference for this orientation makes it more stable overall than xDNA. The location of the benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
spacer also affects the bases' groove geometry, altering neighbour interactions. The base pairs between y-nucleotides and natural nucleotides is planar, rather than slightly twisted as with xDNA. This decreases the rise of the helix
A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is for ...
even further than achieved by xDNA.
 While xDNA and yDNA are quite similar in most properties, including their increased stacking interactions, yDNA shows superior mismatch recognition. y-pyrimidines display slightly stronger stacking interactions than x-pyrimidines as a result of the distance between the two
While xDNA and yDNA are quite similar in most properties, including their increased stacking interactions, yDNA shows superior mismatch recognition. y-pyrimidines display slightly stronger stacking interactions than x-pyrimidines as a result of the distance between the two anomer
In carbohydrate chemistry, a pair of anomers () is a pair of near-identical stereoisomers or diastereomers that differ at only the anomeric carbon, the carbon atom that bears the aldehyde or ketone functional group in the sugar's open-chain for ...
ic carbons, which is slightly larger in yDNA. xDNA still has stronger stacking interactions in model helices, but adding either x- or y-pyrimidines to a natural double helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by base pair, double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double Helix, helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its Nuclei ...
strengthens the intra- and interstrand interactions, increasing overall helix stability. In the end, which of the two has the strongest overall stacking interactions is dependent on the sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
; xT and yT bind A with similar strength, but the stacking energy of yC bound to G is stronger than xC by 4kJ/mol. yDNA and other expanded bases are part of a very young field which is highly understudied. Research suggest that the ideal conformation still remains to be discovered, but knowing that the benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
location affects the orientation and structure of expanded nucleobases adds information to their future design.
yyDNA and xxDNA
 Doubly-expanded (or ''naphtho-homologated'') nucleobases incorporate a
Doubly-expanded (or ''naphtho-homologated'') nucleobases incorporate a naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation ...
spacer instead of a benzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
, widening the base twice as much with its two-ringed structure. These structures (known as xxDNA and yyDNA) are 4.8 Å wider than natural bases and were once again created as a result of Leonard's research on expanded adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
in ATP-dependent enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s in 1984. No literature was published on these doubly-expanded bases for nearly three decades until 2013 when the first xxG was produced by Sharma, Lait, and Wetmore and incorporated along with xxA into a natural helix. Although very little research has been performed on xxDNA, xx-purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted puri ...
neighbours have already been shown to increase intrastrand stacking energy by up to 119% (as opposed to 62% in x-purines). xx-purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted puri ...
and pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The oth ...
interactions show an overall decrease in stacking energies, but the overall stability of duplexes including pyrimidines and xx-purines increases by 22%, more than twofold that of pyrimidines and x-purines.
Uses
xDNA has many applications in chemical and biological research, including expanding upon applications of naturalDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, such as scaffolding. In order to create self-assembling nanostructures, a scaffold is needed as a sort of trellis to support the growth. DNA has been used as a means to this end in the past, but expanded scaffolds make larger scaffolds for more complex self-assembly an option. xDNA's electrical conduction
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity i ...
properties also make it a prime candidate as a molecular wire
Molecular wires (or sometimes called molecular nanowires) are molecular chains that conduct electric current. They are the proposed building blocks for molecular
electronic devices. Their typical diameters are less than three nanometers, while th ...
, as its π-π interactions help it efficiently conduct electricity. Its 8-letter alphabet ( A, T, C, G, xA, xT, xC, xG) gives it the potential to store 2n times more states per sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
than DNA, where ''n'' is the number of bases in the sequence. For example, combining 6 nucleotides of with B-DNA
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, a ...
yields 4096 possible sequences, whereas a combination of the same number of nucleotides created with xDNA yields 262,144 possible sequences. Additionally, xDNA can be used as a fluorescent probe at enzyme active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding s ...
s, as was its original application by Leonard et al.
xDNA has also been applied to the study of protein-DNA interactions. Due to xDNA's natural fluorescing properties, it can easily be visualized in both lab and living conditions. xDNA is becoming more easy to create and oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
ize, and its high-affinity binding to complementary
Complement may refer to:
The arts
* Complement (music), an interval that, when added to another, spans an octave
** Aggregate complementation, the separation of pitch-class collections into complementary sets
* Complementary color, in the visu ...
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
sequences means that it can not only help locate these sequences floating around in the cell, but also when they are already interacting with other structures within the cell. xDNA also has potential applications in assays that employ TdT as it may improve reporters, and can be used as an affinity tag
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Part ...
for interstrand bonding.
See also
*DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
* RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
* DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
* Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of Genetic engineering techniques, technologies used to change the genet ...
* Nanobiotechnology
Nanobiotechnology, bionanotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blank ...
* Nucleobase
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
* Hachimoji DNA
* Artificially Expanded Genetic Information System
Artificially Expanded Genetic Information System (AEGIS) is a Nucleic acid analogue, synthetic DNA analog experiment that uses some Base pair#Unnatural base pair (UBP), unnatural base pairs from the laboratories of the Foundation for Applied Molec ...
(AEGIS)
References
{{Reflist Biochemistry methods DNA Genetics techniques Molecular biology