Upper Michigan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan—also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. or Yoop—is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of
 The first known inhabitants of the Upper Peninsula were tribes speaking
The first known inhabitants of the Upper Peninsula were tribes speaking 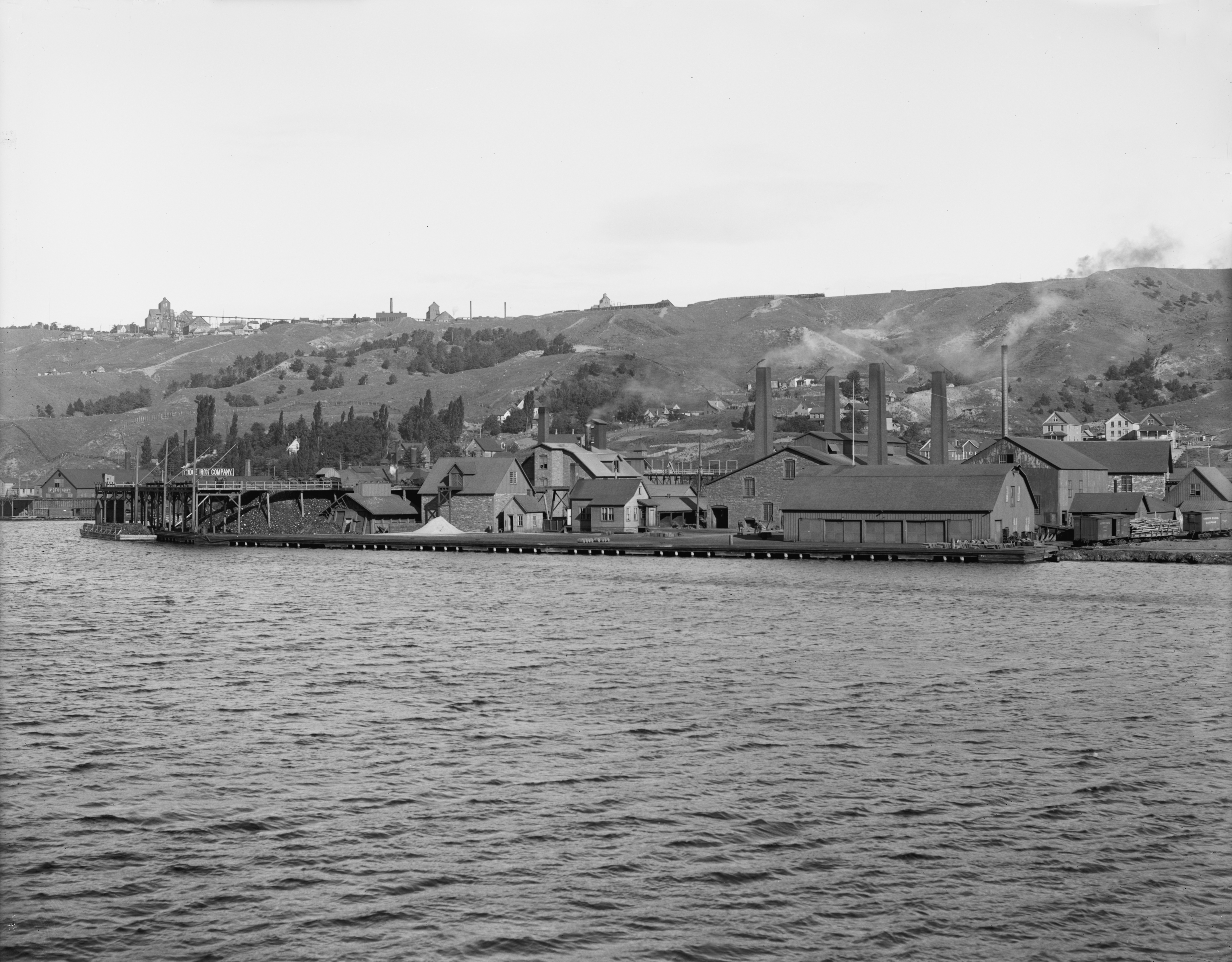 At the time, Michigan was considered the losing party in the compromise. The land in the Upper Peninsula was described in a federal report as a "sterile region on the shores of Lake Superior destined by soil and climate to remain forever a wilderness." This belief changed when rich mineral deposits (primarily copper and iron) were discovered in the 1840s. The Upper Peninsula's mines produced more mineral wealth than the
At the time, Michigan was considered the losing party in the compromise. The land in the Upper Peninsula was described in a federal report as a "sterile region on the shores of Lake Superior destined by soil and climate to remain forever a wilderness." This belief changed when rich mineral deposits (primarily copper and iron) were discovered in the 1840s. The Upper Peninsula's mines produced more mineral wealth than the

 Including extensive parts of the Great Lakes, the Upper Peninsula contains about of total area. Of that, about is its land area, about 29% of the state. It is bounded on the north by
Including extensive parts of the Great Lakes, the Upper Peninsula contains about of total area. Of that, about is its land area, about 29% of the state. It is bounded on the north by
/ref> The
 The Upper Peninsula has a
The Upper Peninsula has a
 Federal censuses indicate that the population of the Upper Peninsula grew throughout the 19th century as European settlers moved into the region, then boomed around the turn of the century, and experienced gradual decline overall during most of the 20th century. The decline was uneven, however: the population in the largest cities – Marquette, Sault Ste Marie, and Escanaba – grew somewhat, while smaller cities and non-urban areas have generally declined in population. The six westernmost counties experienced the largest decrease, from a 1920 population of 153,674 to a 2020 population of 79,392. Many ghost towns exist in the region.
A "" indicates an increase in population from the previous census, and a "" indicates a decrease in population from the previous census.
Federal censuses indicate that the population of the Upper Peninsula grew throughout the 19th century as European settlers moved into the region, then boomed around the turn of the century, and experienced gradual decline overall during most of the 20th century. The decline was uneven, however: the population in the largest cities – Marquette, Sault Ste Marie, and Escanaba – grew somewhat, while smaller cities and non-urban areas have generally declined in population. The six westernmost counties experienced the largest decrease, from a 1920 population of 153,674 to a 2020 population of 79,392. Many ghost towns exist in the region.
A "" indicates an increase in population from the previous census, and a "" indicates a decrease in population from the previous census.

 The Upper Peninsula of Michigan has three state universities ( Lake Superior State University in Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan Technological University in Houghton, and
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan has three state universities ( Lake Superior State University in Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan Technological University in Houghton, and
 Early settlers included multiple waves of people from
Early settlers included multiple waves of people from
 The Upper Peninsula is rich in mineral deposits, including iron, copper, nickel, and silver. Small amounts of gold have also been discovered and mined. In the 19th century, mining dominated the economy, and the UP became home to many isolated
The Upper Peninsula is rich in mineral deposits, including iron, copper, nickel, and silver. Small amounts of gold have also been discovered and mined. In the 19th century, mining dominated the economy, and the UP became home to many isolated

 There are 15 counties in the Upper Peninsula.
State prisons are located in Baraga, Marquette, Munising, Newberry, and Kincheloe.
There are 15 counties in the Upper Peninsula.
State prisons are located in Baraga, Marquette, Munising, Newberry, and Kincheloe.
 The Upper Peninsula is separated from the Lower by the
The Upper Peninsula is separated from the Lower by the
 The Eastern Upper Peninsula Transportation Authority operates car ferries in its area. These include ferries for Sugar Island, Neebish Island, and Drummond Island. Two ferry companies run passenger ferries from St. Ignace to Mackinac Island.
The three major bridges in the Upper Peninsula are:
*
The Eastern Upper Peninsula Transportation Authority operates car ferries in its area. These include ferries for Sugar Island, Neebish Island, and Drummond Island. Two ferry companies run passenger ferries from St. Ignace to Mackinac Island.
The three major bridges in the Upper Peninsula are:
*
Upper Peninsula of Michigan Travel
Western Upper Peninsula of Michigan
{{DEFAULTSORT:Upper Peninsula Of Michigan Regions of Michigan Cultural regions of the United States
Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac
The Straits of Mackinac ( ; ) are the short waterways between the U.S. state of Michigan's Upper and Lower Peninsulas, traversed by the Mackinac Bridge. The main strait is wide with a maximum depth of , and connects the Great Lakes of Lake M ...
. It is bounded primarily by Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. Lake Michigan–Huron has a larger combined surface area than Superior, but is normally considered tw ...
to the north, separated from the Canadian province of Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
at the east end by the St. Marys River, and flanked by Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is shared on the north and east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the south and west by the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the lake is derived from early French ex ...
and Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and depth () after Lake Superior and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the ...
along much of its south. Although the peninsula extends as a geographic feature into the state of Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, the state boundary follows the Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and Menominee
The Menominee ( ; meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recognized tribe of Na ...
rivers and a line connecting them.
First inhabited by Algonquian-speaking native American tribes, the area was explored by French colonists, then occupied by British forces, before being ceded to the newly established United States in the late 18th century. After being assigned to various territorial jurisdictions, it was granted to the newly formed state of Michigan as part of the settlement of a dispute with Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
over the city of Toledo. The region's exploitable timber resources and the discovery of iron and copper deposits in the 19th century brought immigrants, especially Finnish, French Canadian
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an ethnic group descended from French people, French colonists first arriving in Canada (New France), France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of ...
, Swedish, Norwegian, Cornish, and Italian (the peninsula includes the only counties in the United States where a plurality of residents claim Finnish ancestry). With the exhaustion of readily available minerals, the area's economy declined in the 20th century, largely becoming dependent on logging and tourism.
The Upper Peninsula contains 29% of the land area of Michigan but only 3% of its total population; at the height of the mining and timber era in the early 20th century it had as much as 11% of the state's population. Residents are nicknamed '' Yoopers'' (derived from "UP-ers") and have a strong regional identity, enhanced by the perception that the rest of the state neglects them. Proposals have been made to establish the Upper Peninsula as a separate state but have failed to gain traction. Its largest cities are Marquette, Sault Ste. Marie, Escanaba
Escanaba ( ), commonly shortened to Esky, is a port city and the county seat of Delta County, Michigan, Delta County in the U.S. state of Michigan, located on Little Bay de Noc in the state's Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula. The popu ...
, Menominee
The Menominee ( ; meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recognized tribe of Na ...
, Houghton, and Iron Mountain. Because of the surrounding waters and northern latitude, it receives more snow than most of the eastern U.S. The heavily forested land, soil types, short growing season, and logistical factors (e.g. long distance to market, lack of infrastructure) make the Upper Peninsula poorly suited for agriculture. The region is home to a variety of wildlife, including moose, wolves, coyotes, deer, foxes, bears, mountain lions, bobcats, eagles, hawks, and owls.
History
 The first known inhabitants of the Upper Peninsula were tribes speaking
The first known inhabitants of the Upper Peninsula were tribes speaking Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( ; also Algonkian) are a family of Indigenous languages of the Americas and most of the languages in the Algic language family are included in the group. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from ...
, specifically the Algonquian branches of Ojibwe
The Ojibwe (; Ojibwe writing systems#Ojibwe syllabics, syll.: ᐅᒋᐺ; plural: ''Ojibweg'' ᐅᒋᐺᒃ) are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland (''Ojibwewaki'' ᐅᒋᐺᐘᑭ) covers much of the Great Lakes region and the Great Plains, n ...
and Menominee
The Menominee ( ; meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recognized tribe of Na ...
. They arrived roughly around 800 C.E. and subsisted chiefly from fishing. Early tribes included the Menominee
The Menominee ( ; meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recognized tribe of Na ...
, Odawa
The Odawa (also Ottawa or Odaawaa ) are an Indigenous North American people who primarily inhabit land in the Eastern Woodlands region, now in jurisdictions of the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. Their territory long prec ...
, Ojibwe
The Ojibwe (; Ojibwe writing systems#Ojibwe syllabics, syll.: ᐅᒋᐺ; plural: ''Ojibweg'' ᐅᒋᐺᒃ) are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland (''Ojibwewaki'' ᐅᒋᐺᐘᑭ) covers much of the Great Lakes region and the Great Plains, n ...
, Nocquet, and Potawatomi
The Potawatomi (), also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, ...
. Étienne Brûlé
Étienne Brûlé (; – c. June 1633) was the first European colonization of the Americas, European explorer to journey beyond the St. Lawrence River into what is now known as Canada. He spent much of his early adult life among the Wyandot peop ...
of France was probably the first European to visit the peninsula, crossing the St. Marys River around 1620 in search of a route to the Far East. French colonists laid claim to the land in the 17th century, establishing missions and fur trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
posts such as Sault Ste. Marie and St. Ignace. Following the end of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
(part of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
) in 1763, the territory was ceded to Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
. Sault Ste. Marie is the oldest European settlement in Michigan and the site of Native American settlements for centuries.
American Indian tribes formerly allied with the French were dissatisfied with the British occupation, which brought new territorial policies. Whereas the French cultivated alliances among the Indians, the British postwar approach was to treat the tribes as conquered peoples. In 1763, tribes united in Pontiac's Rebellion to try to drive the British from the area. American Indians captured Fort Michilimackinac, at present-day Mackinaw City, then the principal fort of the British in the Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
region, as well as others and killed hundreds of British. In 1764, they began negotiations with the British, resulting in temporary peace and changes in objectionable British policies.
Although the Upper Peninsula nominally became United States territory with the 1783 Treaty of Paris, the British did not give up control until 1797 under terms of the Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
. As an American territory, the Upper Peninsula was still dominated by the fur trade. John Jacob Astor
John Jacob Astor (born Johann Jakob Astor; July 17, 1763 – March 29, 1848) was a German-born American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor. Astor made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by exporting History of opiu ...
founded the American Fur Company on Mackinac Island
Mackinac Island ( , ; ; ; ) is an island and resort area, covering in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac and "Mitchimakinak" in Ojibwemowin, meaning "Great Turtle". It is located in ...
in 1808; however, the industry began to decline in the 1830s as beaver and other game were overhunted.
When the Michigan Territory
The Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan. Detroit ...
was first established in 1805, it included only the Lower Peninsula and the eastern portion of the Upper Peninsula. In 1819, the territory was expanded to include the remainder of the Upper Peninsula, all of what later became Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, and part of Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
(previously included in the Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
and Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
Territories). When Michigan applied for statehood in the 1830s, the proposal corresponded to the original territorial boundaries. However, there was an armed conflict known as the Toledo War with the state of Ohio over the location of their mutual border. Meanwhile, the people of Michigan approved a constitution in May 1835 and elected state officials in late autumn 1835. Although the state government was not yet recognized by the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
, the territorial government effectively ceased to exist. President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
's government offered the remainder of the Upper Peninsula to Michigan if it would cede the Toledo Strip to Ohio. A constitutional convention of the state legislature refused, but a second convention, hastily convened by Governor Stevens Thomson Mason, consisting primarily of his supporters, agreed in December 1836 to the deal. In January 1837, the U.S. Congress admitted Michigan as a state of the Union.
 At the time, Michigan was considered the losing party in the compromise. The land in the Upper Peninsula was described in a federal report as a "sterile region on the shores of Lake Superior destined by soil and climate to remain forever a wilderness." This belief changed when rich mineral deposits (primarily copper and iron) were discovered in the 1840s. The Upper Peninsula's mines produced more mineral wealth than the
At the time, Michigan was considered the losing party in the compromise. The land in the Upper Peninsula was described in a federal report as a "sterile region on the shores of Lake Superior destined by soil and climate to remain forever a wilderness." This belief changed when rich mineral deposits (primarily copper and iron) were discovered in the 1840s. The Upper Peninsula's mines produced more mineral wealth than the California Gold Rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the U ...
, especially after shipping was improved by the opening of the Soo Locks in 1855 and docks in Marquette in 1859. The Upper Peninsula supplied 90% of America's copper by the 1860s. It was the nation's largest supplier of iron ore by the 1890s, and production continued to a peak in the 1920s but sharply declined shortly afterward. The last copper mine closed in 1995, although the majority of mines had closed decades before. Some iron mining continues near Marquette. The Eagle Mine, a nickel-copper mine, opened in 2014.
Thousands of Americans and immigrants moved to the area during the mining boom, prompting the federal government to create Fort Wilkins near Copper Harbor to maintain order. The first wave were the Cornish from Great Britain, with centuries of mining experience; followed by Irish, Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, and French Canadian
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an ethnic group descended from French people, French colonists first arriving in Canada (New France), France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of ...
s. During the 1890s, Finnish immigrants began settling there in large numbers, forming the population plurality in the northwestern portion of the peninsula. In the early 20th century, 75% of the population was foreign-born.
From 1861 to 1865, 90,000 Michigan men fought in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, including 1,209 from the Upper Peninsula. Houghton County contributed 460 soldiers, while Marquette County sent 265.
Geography
 Including extensive parts of the Great Lakes, the Upper Peninsula contains about of total area. Of that, about is its land area, about 29% of the state. It is bounded on the north by
Including extensive parts of the Great Lakes, the Upper Peninsula contains about of total area. Of that, about is its land area, about 29% of the state. It is bounded on the north by Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. Lake Michigan–Huron has a larger combined surface area than Superior, but is normally considered tw ...
, on the east by St. Marys River, on the south by the Niagara Escarpment, Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and depth () after Lake Superior and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the ...
and Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is shared on the north and east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the south and west by the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the lake is derived from early French ex ...
, and on the west by Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
and (counting the water border on Lake Superior) by Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
. It has about of continuous shoreline with the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
. There are about 4,300 inland lakes, the largest of which is Lake Gogebic, and of streams. Its lowest elevation is along the shoreline of Lake Huron and Lake Michigan, averaging above sea level. Its highest elevation is Mount Arvon
Mount Arvon ( ) at , is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Michigan. Located in L'Anse Township, Baraga County, Mount Arvon is part of the Huron Mountains. It rises about south of Lake Superior (elevation ). On the list of highes ...
, at .
Michigan's Upper Peninsula is bounded on land by Wisconsin to the southwest and west; and in territorial waters by Minnesota to the west, Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
to the west, north and east, and the Door Peninsula of Wisconsin extends into Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and depth () after Lake Superior and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the ...
east of the western Upper Peninsula.
Five Michigan Upper Peninsula counties include nearby major islands: Mackinac Island
Mackinac Island ( , ; ; ; ) is an island and resort area, covering in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac and "Mitchimakinak" in Ojibwemowin, meaning "Great Turtle". It is located in ...
, Round Island and Bois Blanc Island in Lake Huron are in Mackinac County
Mackinac County ( , ) is a County (United States), county in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 10,834. The county seat is St. Ignace, Michigan, St. Ignace. F ...
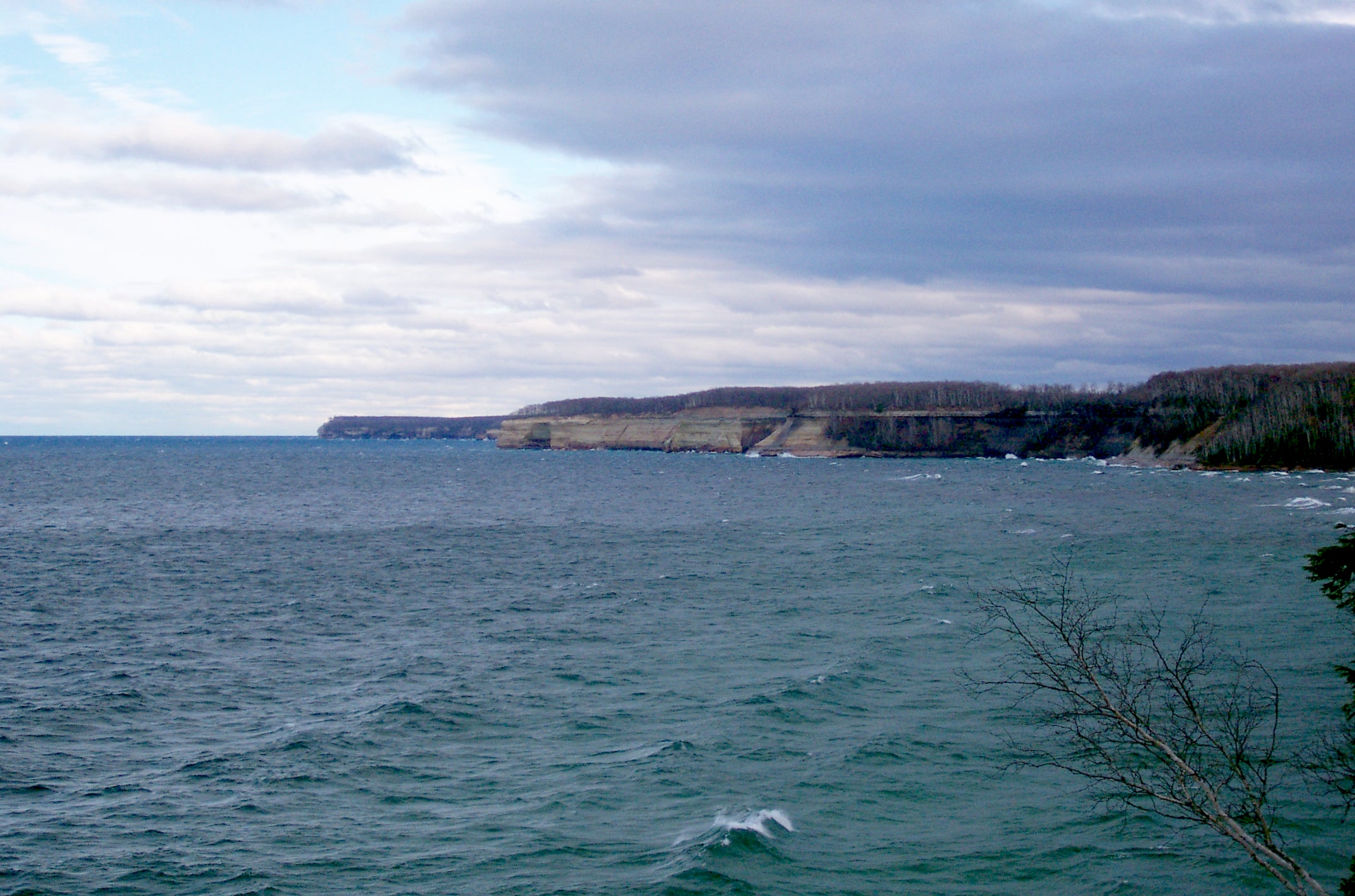
; Sugar Island and Neebish Island in the St. Marys River, and Drummond Island in Lake Huron are in Chippewa County; Grand Island is in Alger County; Summer Island is Delta County; and Isle Royale is part of Keweenaw County.The peninsula is divided between the flat, swampy areas in the east, part of the Great Lakes Plain, and the steeper, more rugged western half, called the Superior Upland, part of the Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield ( ), also called the Laurentian Shield or the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), th ...
. The rock in the western portion is the result of volcanic eruptions and is estimated to be at least 3.5 billion years old (much older than the eastern portion) and contains the region's ore resources. Banded-iron formations were deposited 2 billion years ago; this is the Marquette Range Supergroup. A considerable amount of bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid rock that lies under loose material ( regolith) within the crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface material. An exposed portion of bed ...
is visible. Mount Arvon is within the Huron Mountains
The Huron Mountains are located in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan, mostly in Marquette County, Michigan, Marquette County, and extending into Baraga County, Michigan, Baraga County, overlooking Lake ...
, located in Marquette and Baraga counties. The Porcupine Mountains are located in the extreme northwest of the peninsula. All of the higher areas are the remnants of ancient peaks, worn down over millions of years by erosion and glaciers./ref> The
Keweenaw Peninsula
The Keweenaw Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. Part of the greater landmass of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula, the Keweenaw Peninsula projects about northeasterly into Lake Superior, forming Keweena ...
is the northernmost part of the peninsula (not counting Isle Royale, which is politically part of the UP). It projects into Lake Superior and was the site of the first copper boom in the United States, part of a larger region of the peninsula called the Copper Country. Copper Island is its northernmost section. About one-third of the peninsula is government-owned recreational forest land today, including the Ottawa National Forest and Hiawatha National Forest. Although heavily logged in the 19th century, the majority of the land was forested with mature trees by the 1970s.
There was a boundary dispute over the border with Wisconsin. The northwesternmost portion of the border follows a line from Lac Vieux Desert
Lac Vieux Desert is a lake in the United States divided between Gogebic County, Michigan, and Vilas County, Wisconsin. Fed primarily by springs in the surrounding swamps, it is the source of the Wisconsin River, which flows out of its southwest co ...
to the headwaters of the Montreal River. An 1847 survey established the east branch of the Montreal River as the border. However, the 1908 revision of the Constitution of Michigan specified that the west branch of the Montreal River was the proper border, which would have placed an additional 360 square miles of land on the Michigan side of the border. A 1926 Supreme Court decision awarded this tract of land to Wisconsin.
Wildlife
The Upper Peninsula contains a large variety of wildlife. Some of the mammals found in the UP includeshrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to dif ...
s, moles, mice, white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known Common name, commonly as the whitetail and the Virginia deer, is a medium-sized species of deer native to North America, North, Central America, Central and South America. It is the ...
, moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
, black bears, cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') (, ''Help:Pronunciation respelling key, KOO-gər''), also called puma, mountain lion, catamount and panther is a large small cat native to the Americas. It inhabits North America, North, Central America, Cent ...
, gray and red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
es, wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
, river otters, martens, fishers, muskrat
The muskrat or common muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America.
The muskrat is found in wetlands over various climates ...
s, bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the wildcat, bay lynx, or red lynx, is one of the four extant species within the medium-sized wild cat genus '' Lynx''. Native to North America, it ranges from southern Canada through most of the c ...
s, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the Wolf, gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the c ...
s, snowshoe hare
The snowshoe hare (''Lepus americanus''), also called the varying hare or snowshoe rabbit, is a species of hare found in North America. It has the name "snowshoe" because of the large size of its hind feet. The animal's feet prevent it from sink ...
s, cotton-tail rabbits, porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp Spine (zoology), spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two Family (biology), families of animals: the Old World porcupines of the family Hystricidae, and the New ...
s, chipmunks, squirrels, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
s, opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 126 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North A ...
and bats. There is a large variety of birds, including hawks, osprey, owls, gulls, hummingbirds, chickadees, robins (the state bird), woodpeckers, warblers, and bald eagles. In terms of reptiles and amphibians
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
, the UP has common garter snakes, red bellied snakes, pine snakes, northern water snakes, brown snakes, eastern garter snakes, eastern fox snakes, eastern ribbon back snakes, green snakes, northern ringneck snakes, eastern milk snakes (Mackinac and Marquette counties) and eastern hognose snakes (Menominee County only), plus snapping turtles, wood turtles, and painted turtle
The painted turtle (''Chrysemys picta'') is the most widespread native turtle of North America. It lives in relatively slow-moving fresh waters, from southern Canada to northern Mexico, and from the Atlantic to the Pacific. They have been shown ...
s (the state reptile), green frogs, bullfrogs, northern leopard frog
''Lithobates pipiens''Integrated Taxonomic Information System nternet2012''Lithobates pipiens'' pdated 2012 Sept; cited 2012 Dec 26Available from: www.itis.gov/ formerly ''Rana pipiens'', commonly known as the northern leopard frog, is a s ...
s, and salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s. Lakes and rivers contain many fish such as walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', Synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the walleyed pike, yellow pike, yellow pikeperch or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern ...
, muskie, northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (pikes). They are commonly found in brackish water, moderately salty and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). T ...
, trout
Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the ...
, salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
, bullhead catfish, and bass. Invasive species like the alewife and sea lamprey can be found in the Great Lakes. The UP also contains many shellfish, such as clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
s, aquatic snails, and crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
. The American Bird Conservancy and the National Audubon Society
The National Audubon Society (Audubon; ) is an American non-profit environmental organization dedicated to conservation of birds and their habitats. Located in the United States and incorporated in 1905, Audubon is one of the oldest of such orga ...
have designated several locations as internationally Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
s.
After being nearly extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
from the conterminous United States, gray wolves survived in the remote northeastern corner of Minnesota and Ontario. The repopulation of wolves in this region has occurred naturally as they have expanded their territory after they were protected under the federal Endangered Species Act
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting and conserving imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of e ...
in 1978. Michigan Department of Natural Resources's principal goals set in 2008 included maintaining a viable wolf population, facilitating wolf-related benefits, minimizing wolf-related conflicts and conducting "science-based and socially acceptable management of wolves". Michigan removed wolves from the state's list of threatened and endangered species in 2009 having reached the recovery goal of 200 for five consecutive years in 2004. In 2012, FWS issued a rule that classified and delisted a sub-species called the Western Great Lakes wolves under the federal Endangered Species Act. Michigan had a legal wolf hunt in 2013. Wolves were returned to the list of federally threatened species in December 2014 as a result of a court ruling. The Department of Natural Resources found that an equilibrium has been achieved between the available habitat and the number of this predators the region can support. The department supports delisting as wolves have met and exceeded the biological recovery goals that would necessitate protection.
There is significant discussion and studies over the presence of eastern cougars in the UP. Historically, the last of the species, or subspecies, was extirpated near Newberry in 1906, although there have been sightings of the creatures over the years since. These reports increased in number over the first decade of the 21st century. The Michigan Department of Natural Resources and Environment (DNRE) formed a four-person team to investigate sightings in the state. The biologists with the DNRE currently do not believe that there is a breeding population anywhere in the state, rather that the sighted animals are visitors to the state. As late as January 2007, the DNRE's official position was that no cougars lived in Michigan. Several residents in the state disagree with both current and previous positions on the part of the DNRE. Researchers at Central Michigan University
Central Michigan University (CMU) is a Public university, public research university in Mount Pleasant, Michigan, United States. It was established in 1892 as a private normal school and became a state institution in 1895. CMU is one of the eigh ...
and the Michigan Wildlife Conservancy in 2006 published the findings of a study using DNA analysis of fecal samples taken in the Upper and Lower peninsulas that showed the presence of cougars at the time. These results were disputed in a second journal article in 2007 by other researchers from Eastern Michigan University
Eastern Michigan University (EMU, EMich, Eastern Michigan or simply Eastern) is a public university, public research university in Ypsilanti, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1849 as the Michigan State Normal School, it was the fourth normal ...
and the U.S. Forest Service. A citizen's group, the Michigan Citizens for Cougar Recognition (MCCR), independently tracked sightings and in 2009 listed Delta County as the location with the greatest number of reports in the state. The DNRE verified five sets of tracks and two trail camera photos in Delta, Chippewa, Marquette, and Menominee counties since 2008. DNRE officials acknowledge that there are cougars in the UP, but not elsewhere in the state. Critics of the DNRE's position on the species, including the founder of the MCCR, say that the department is attempting to "avoid paying for a cougar management program". In March 2025 the DNR released a statement that two cougar cubs were verified to be living in an undisclosed area of Ontonagon County, the first time cougar cubs have been verified the Western Great Lakes in over 100 years. The presence of the cubs, estimated via photographic evidence to be around seven weeks old, is in contrast to previous sightings which are thought to be transient adult animals and not representative of resident or breeding populations.
There also many invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
that are primarily brought in the ballast
Ballast is dense material used as a weight to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within ...
water of foreign ships, usually from the ocean bordering northeastern Asia. This water is dumped directly into the Great Lakes, depositing a variety of fresh and salt water fish and invertebrates, most notably the zebra mussel
The zebra mussel (''Dreissena polymorpha'') is a small freshwater mussel, an Aquatic animal, aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Dreissenidae. The species originates from the lakes of southern Russia and Ukraine, but has been accidentally Intro ...
, ''Dreissena polymorpha''. There are also many plant species that have been transported to the Great Lakes, including purple loosestrife, '' Lythrum salicaria'' and '' Phragmites australis'', both of which are considered to be a threat to native hydrophyte wetland plants. The emerald ash borer was first reported in the UP at Brimley State Park and is considered to be a serious ecological threat to the habitat and economy.
Climate
 The Upper Peninsula has a
The Upper Peninsula has a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(''Dfb'' in the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
system). The Great Lakes have a great effect on the larger part of the peninsula. Winters tend to be long, cold, and snowy for most of the peninsula, and because of its northern latitude, the daylight hours are short—around 8 hours between sunrise and sunset in the winter. Lake Superior has the greatest effect on the area, especially the northern and western parts. Lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises through colde ...
causes many areas to get in excess of of snow per year—especially in the Keweenaw Peninsula and Gogebic County, and to a lesser extent Baraga, Marquette and Alger counties, making the western UP a prominent part of the midwestern
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
snowbelt.
Records of of snow or more have been set in many communities in this area. The Keweenaw Peninsula averages more snowfall than any other location east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
. Because of the howling storms across Lake Superior, which cause dramatic amounts of precipitation, it has been said that the lake-effect snow makes the Keweenaw Peninsula the snowiest place east of the Rockies. Herman averages of snow every year. Lake-effect snow can cause blinding whiteouts in just minutes, and some storms can last for days. Hancock is found frequently on lists of the snowiest cities in America.
The banana belt along the Wisconsin border has a more continental climate since most of its weather does not arrive from the lakes. Summers tend to be warmer and winter nights much colder. Coastal communities have temperatures tempered by the Great Lakes. In summer, it might be cooler at lakeside than it is inland, and the opposite effect is seen in winter. The area of the Upper Peninsula north of Green Bay through Menominee and Escanaba (and extending west to Iron River) does not have the extreme weather and precipitation found to the north. The coldest temperature officially recorded in the Upper Peninsula was in Humboldt in January 1915.
Time zones
Like the entire Lower Peninsula, most of the Upper Peninsula is within theEastern Time Zone
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 U.S. states, states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico.
* Eastern Standard Time (EST) is five ...
. However, the four counties bordering Wisconsin are in the Central Time Zone
The North American Central Time Zone (CT) is a time zone in parts of Canada, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It ...
. In 1967, when the Uniform Time Act
The Uniform Time Act of 1966, , was a Law of the United States to "promote the adoption and observance of uniform time within the standard time zones" prescribed by the Standard Time Act of 1918. Its intended effect was to simplify the officia ...
came into effect, the Upper Peninsula went under year-round Central Standard Time, with no daylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time, daylight time (Daylight saving time in the United States, United States and Daylight saving time in Canada, Canada), or summer time (British Summer Time, United Kingdom, ...
. In 1973, the majority of the peninsula switched to Eastern Standard Time; only the four western border counties of Gogebic, Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, Dickinson, and Menominee
The Menominee ( ; meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recognized tribe of Na ...
continue to observe Central Standard Time. Daylight saving time is observed peninsula-wide.
Demographics
The Upper Peninsula remains a predominantly rural region. As of the 2020 census the region had a population of 301,608, just more than 3% of Michigan's total population and a decline of 3.2% from 2010. According to the 2010 census, 103,211 people live in the 12 towns of at least 4,000 people, covering . A total of 116,548 people live in the 18 towns and villages of at least 2,000 people, which cover —less than 1% of the peninsula's land area. Federal censuses indicate that the population of the Upper Peninsula grew throughout the 19th century as European settlers moved into the region, then boomed around the turn of the century, and experienced gradual decline overall during most of the 20th century. The decline was uneven, however: the population in the largest cities – Marquette, Sault Ste Marie, and Escanaba – grew somewhat, while smaller cities and non-urban areas have generally declined in population. The six westernmost counties experienced the largest decrease, from a 1920 population of 153,674 to a 2020 population of 79,392. Many ghost towns exist in the region.
A "" indicates an increase in population from the previous census, and a "" indicates a decrease in population from the previous census.
Federal censuses indicate that the population of the Upper Peninsula grew throughout the 19th century as European settlers moved into the region, then boomed around the turn of the century, and experienced gradual decline overall during most of the 20th century. The decline was uneven, however: the population in the largest cities – Marquette, Sault Ste Marie, and Escanaba – grew somewhat, while smaller cities and non-urban areas have generally declined in population. The six westernmost counties experienced the largest decrease, from a 1920 population of 153,674 to a 2020 population of 79,392. Many ghost towns exist in the region.
A "" indicates an increase in population from the previous census, and a "" indicates a decrease in population from the previous census.
Education

Northern Michigan University
Northern Michigan University (Northern Michigan, Northern or NMU) is a public university in Marquette, Michigan, United States. It was established in 1899 by the Michigan Legislature as Northern State Normal School. In 1963, the state designa ...
in Marquette) and five community colleges ( Bay Mills Community College in Brimley, Bay de Noc Community College in Escanaba and Iron Mountain, Gogebic Community College in Ironwood, and Keweenaw Bay Ojibwa Community College in Baraga).
Culture
 Early settlers included multiple waves of people from
Early settlers included multiple waves of people from Nordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; ) are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe, as well as the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic oceans. It includes the sovereign states of Denm ...
, and people of Finnish ancestry make up 16% of the peninsula's population. The Finnish sauna
The Finnish sauna (, ) is a substantial part of Culture of Finland, Finnish and Culture of Estonia, Estonian culture.
It was inscribed on the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists at the 17 December 2020 meeting of the UNESCO Intergovernmen ...
and the concept of ''sisu
is a Finnish word variously translated as stoic determination, tenacity of purpose, grit, bravery, resilience, and hardiness. It is held by Finns to express their national character. It is generally considered not to have a single-word ...
'' have been adopted widely by residents of the Upper Peninsula. The television program '' Finland Calling'' was for a long period the only Finnish-language television broadcast in the United States; it aired on Marquette station WLUC-TV from March 25, 1962, until March 29, 2015. Finlandia University, America's only college with Finnish roots, was located in Hancock, but has shut down as of spring 2023. Street signs in Hancock appear in English and Finnish to celebrate this heritage.
Other sizable ethnic communities in the Upper Peninsula include French-Canadian
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an ethnic group descended from French colonists first arriving in France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of French Canadians live in the prov ...
, German, Cornish, Italian, and Ojibwe
The Ojibwe (; Ojibwe writing systems#Ojibwe syllabics, syll.: ᐅᒋᐺ; plural: ''Ojibweg'' ᐅᒋᐺᒃ) are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland (''Ojibwewaki'' ᐅᒋᐺᐘᑭ) covers much of the Great Lakes region and the Great Plains, n ...
ancestry.
People from the Upper Peninsula speak a dialect influenced by Scandinavian and French-Canadian speech. A popular bumper sticker, a parody of the "Say YES to Michigan" slogan promoted by state tourism officials, shows an outline of the Upper Peninsula and the slogan, "Say ya to da UP, eh!" The dialect and culture are captured in many songs by Da Yoopers, a comedy music and skit troupe from Ishpeming.
The Keweenaw Peninsula is home to several ski areas. Mont Ripley, just outside Houghton, is popular among students of Michigan Technological University (the university actually owns the ski hill). Further up the peninsula in the small town of Lac La Belle is Mt. Bohemia. A skiing purist's resort, Bohemia is a self-proclaimed "experts only" mountain, and it does not groom
A bridegroom (often shortened to groom) is a man who is about to be married or who is newlywed.
When marrying, the bridegroom's future spouse is usually referred to as the bride. A bridegroom is typically attended by a best man and Groomsman, ...
its heavily gladed slopes. Other ski areas are Pine Mountain located in Iron Mountain, Norway Mountain in the town of the same name, and the Porcupine Mountains Ski Area located in Ontonagon.
Houghton is where professional ice hockey was first started in 1904.
Regional identity
As of 2018, the western Upper Peninsula is home to about 173,887 people, while the eastern Upper Peninsula is home to about 133,499 people, a total of 307,386—only about 3% of the state's population—living in almost one-third of the state's land area. Residents are known as Yoopers (from "UP-ers"), and many consider themselves Yoopers before they consider themselves Michiganders. (People living in the Lower Peninsula are commonly called "troll
A troll is a being in Nordic folklore, including Norse mythology. In Old Norse sources, beings described as trolls dwell in isolated areas of rocks, mountains, or caves, live together in small family units, and are rarely helpful to human bei ...
s" by Upper Peninsula residents, as they live " Under the Bridge".) This regionalism is not only a result of the physical separation of the two peninsulas, but also the history of the state.
Residents of the western Upper Peninsula take on some of the cultural identities of both Wisconsin and Michigan. In terms of sports fandom, residents may support Detroit professional teams or those of Wisconsin—particularly the Green Bay Packers
The Green Bay Packers are a professional American football team based in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The Packers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC North, North division. They ar ...
. This is a result of both proximity and the broadcast and print media of the area. The four counties that border Wisconsin are also in the Central Time Zone, unlike the rest of Michigan, which is on Eastern time. In some cases, commercial cartographers draw incorrect maps that inadvertently annex the Upper Peninsula into Wisconsin.
Cuisine
The Upper Peninsula has a distinctive local cuisine. The pasty (pronounced "pass-tee"), a kind of meat turnover originally brought to the region by Cornish miners, is popular among locals and tourists alike. Pasty varieties include chicken, venison, pork, hamburger, and pizza, all of which many restaurants serve. Many restaurants serve potato sausage and '' cudighi'', a spicy Italian meat. Finnish immigrants contributed '' nisu'', acardamom
Cardamom (), sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genus (biology), genera ''Elettaria'' and ''Amomum'' in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indon ...
-flavored sweet bread; '' limppu'', an Eastern Finnish rye bread; '' pannukakku'', a variant on the pancake with a custard flavor; '' viili'' (sometimes spelled "fellia"), a stretchy, fermented Finnish milk; and '' korppu'', hard slices of toasted cinnamon bread, traditionally dipped in coffee. Some Finnish foods such as ''juusto'' (squeaky cheese, essentially a cheese curd, like Leipäjuusto) and ''saunamakkara'' (a ring-bologna sausage) have become so ubiquitous in Upper Peninsula cuisine that they are now commonly found in most grocery stores and supermarkets.
Maple syrup
Maple syrup is a sweet syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Ma ...
is a highly prized local delicacy. Fresh Great Lakes fish, such as the lake trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater Salvelinus, char living mainly in lakes in Northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, laker, and grey trout. In Lake Sup ...
, whitefish, and (in the spring) smelt are widely eaten. There is minimal concern about contamination of fish from Lake Superior waters. Smoked fish is also popular. Thimbleberry jam and chokecherry jelly are a treat.
Economy
Industries
 The Upper Peninsula is rich in mineral deposits, including iron, copper, nickel, and silver. Small amounts of gold have also been discovered and mined. In the 19th century, mining dominated the economy, and the UP became home to many isolated
The Upper Peninsula is rich in mineral deposits, including iron, copper, nickel, and silver. Small amounts of gold have also been discovered and mined. In the 19th century, mining dominated the economy, and the UP became home to many isolated company town
A company town is a place where all or most of the stores and housing in the town are owned by the same company that is also the main employer. Company towns are often planned with a suite of amenities such as stores, houses of worship, schoo ...
s. For many years, mines in the Keweenaw Peninsula were the world's largest producers of copper. The mines began declining as early as 1913, with most closing temporarily during the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
. Mines reopened during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, but almost all quickly closed after the war ended. The last copper mine in the Copper Country was the White Pine mine, which closed in 1995. Marquette County sits along the Marquette Iron Range, which sent out a significant portion of the iron ore mined in the United States for many years. , Marquette County is home to one remaining iron ore mine and one nickel and copper mine.
From approximately 1870 to 1915, about 32 quarries mined Jacobsville Sandstone in the Upper Peninsula, particularly near Marquette and the community of Jacobsville. The sandstone was used in many buildings, both locally and around the United States.
Since logging of white pine began in the 1880s, timber has been an important industry. Stands of hemlock and hardwood
Hardwood is wood from Flowering plant, angiosperm trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostl ...
in the western reaches of the forest experienced larger scale selection-cutting beginning in the mid-20th century. Because of the highly seasonal climate and the short growing season, agriculture is limited in the Upper Peninsula, though potatoes, strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit is appreciated f ...
and a few other small fruits are grown.
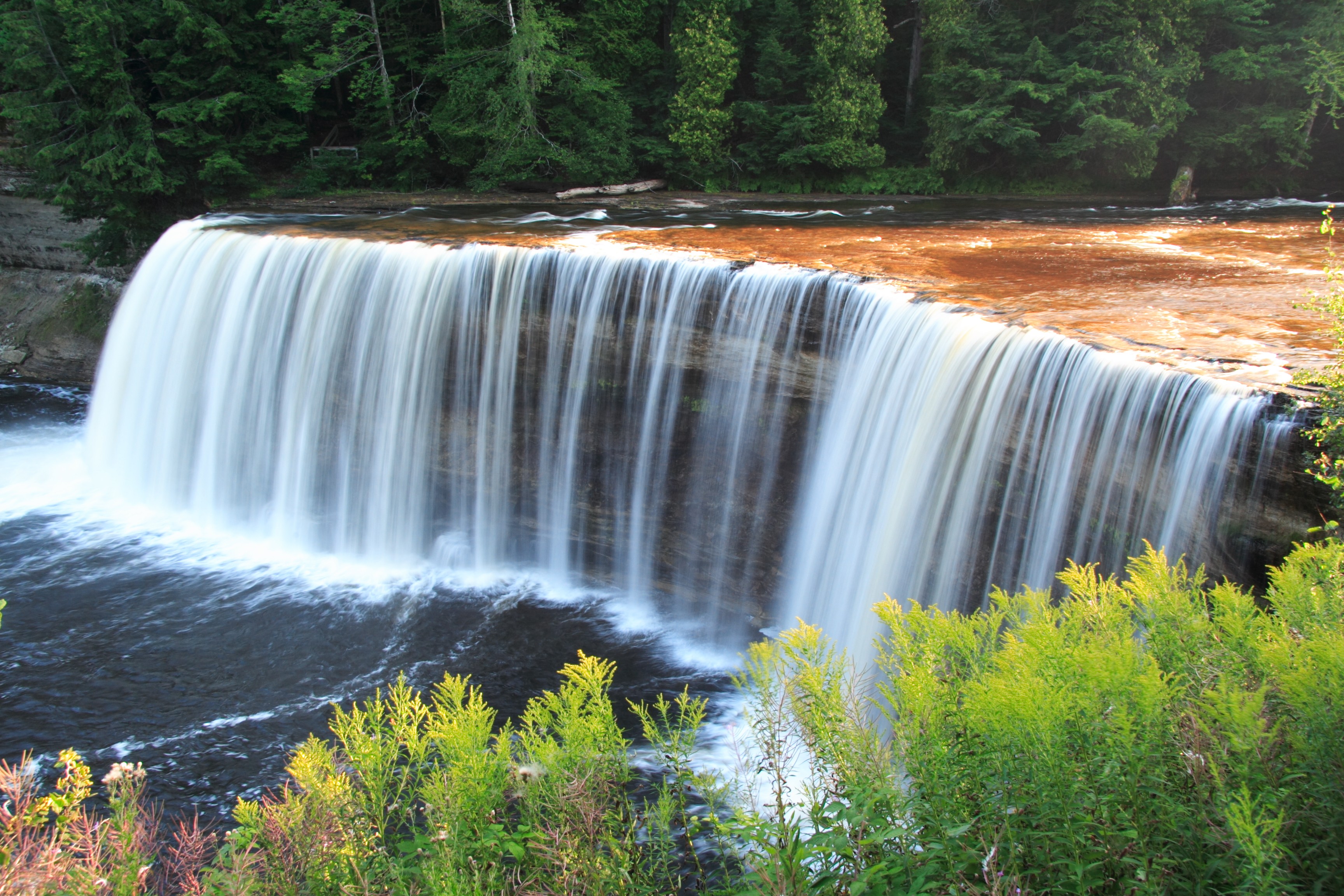
Tourism has become the main industry in recent decades. In 2005, ShermanTravel, LLC listed the Upper Peninsula as #10 in its assessment of all travel destinations worldwide. The peninsula has extensive coastline on the Great Lakes, large tracts of state and national forests, cedar swamps, more than 150 waterfalls, and low population densities. Because of the skiing, camping, boating, fishing, snowmobiling, hunting, and hiking opportunities, many Lower Peninsula and Wisconsin families spend their vacations in the UP, and tourists visit from Detroit, Chicago, Grand Rapids
Grand Rapids is the largest city and county seat of Kent County, Michigan, United States. With a population of 198,917 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census and estimated at 200,117 in 2024, Grand Rapids is the List of municipalities ...
, Milwaukee
Milwaukee is the List of cities in Wisconsin, most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the List of United States cities by population, 31st-most populous city in the United States ...
, and other metropolitan areas. The opening of the Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ; also referred to as the Mighty Mac or Big Mac) is a suspension bridge that connects the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper and Lower Peninsula of Michigan, Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. It spans the Str ...
in 1957 (see below) has made the Upper Peninsula easily accessible to tourists from the Lower Peninsula and southeast of Michigan, and has helped make the UP a year-round tourist destination.
During the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, the U.P. was home to two U.S. Air Force bases, Kincheloe south of Sault Ste. Marie, and K.I. Sawyer, south of Marquette. Both were bases of the Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile compon ...
(SAC), with B-52H bombers
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes
air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles.
There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is ...
; Kincheloe closed in 1977, and Sawyer in 1995.
In 2004, microbreweries began opening across the Upper Peninsula; 14 opened by 2014, and 23 by 2019. In 2019, their annual economic impact totaled $346 million. , three of Michigan's fifty largest breweries were in the Upper Peninsula: Keweenaw Brewing Company, Blackrocks Brewery, and the Ore Dock Brewing Company.
Media
There are five dailynewspapers
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ...
published in the Upper Peninsula, '' The Mining Journal'' in Marquette, '' The Daily Mining Gazette'' in Houghton, ''The Daily News'' in Iron Mountain, the ''Daily Press'' in Escanaba
Escanaba ( ), commonly shortened to Esky, is a port city and the county seat of Delta County, Michigan, Delta County in the U.S. state of Michigan, located on Little Bay de Noc in the state's Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula. The popu ...
, and ''The Evening News'' in Sault Ste. Marine. All but ''The Evening News'' are owned by Ogden Newspapers, with the former being owned by Gannett
Gannett Co., Inc. ( ) is an American mass media holding company headquartered in New York City. It is the largest U.S. newspaper publisher as measured by total daily circulation.
It owns the national newspaper ''USA Today'', as well as several ...
. ''The Mining Journal'', is the only daily newspaper that publishes a Sunday edition, which is distributed, with the exception of Chippewa and eastern Mackinac counties, across the entire UP (the other six days are distributed in its local area only). Additional, there are monlthly and student publications serving the region.
The Upper Peninsula is home to eight television stations
A television station is a set of equipment managed by a business, organisation or other entity such as an amateur television (ATV) operator, that transmits video content and audio content via radio waves directly from a transmitter on the earth's s ...
, 15 AM broadcasting
AM broadcasting is radio broadcasting using amplitude modulation (AM) transmissions. It was the first method developed for making audio radio transmissions, and is still used worldwide, primarily for medium wave (also known as "AM band") transm ...
stations, and 90 FM broadcasting
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting that uses frequency modulation (FM) of the radio broadcast carrier wave. Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to transmit high fidelity, high-f ...
stations. Most of the UP lies within the Marquette media market
A media market, broadcast market, media region, designated market area (DMA), television market area, or simply market is a region where the population can receive the same (or similar) television station, television and radio broadcasting, ra ...
. The eastern three counties of the peninsula are in the Cadillac-Traverse City market, while Gogebic County in the western UP is served by stations in the Duluth
Duluth ( ) is a Port, port city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of St. Louis County, Minnesota, St. Louis County. Located on Lake Superior in Minnesota's Arrowhead Region, the city is a hub for cargo shipping. The population ...
market, and Menominee County in the southern UP is served by stations from the Green Bay region. The peninsula's oldest television station is WLUC-TV in Negaunee Township, while the UP's longest continually operated radio station is WCCY in Houghton. Most of the region's radio signals originate from the population centers of Sault Ste. Marie, Escanaba, Marquette, or Houghton. Due to the vast and sparsely populated geography of the UP, many of the FM stations operate at maximum effective radiated power
Effective radiated power (ERP), synonymous with equivalent radiated power, is an IEEE standardized definition of directional radio frequency (RF) power, such as that emitted by a radio transmitter. It is the total power in watts that would ha ...
.
Government

Politics
During most of the " System of 1896", the Upper Peninsula was overwhelmingly Republican even by the standards of Michigan during this era. Some of its counties would often vote for the Republican candidate by among the widest margins in the nation. However, the region's politics began shifting in 1924, when the Upper Peninsula was the strongest region in Michigan for the insurgent candidacy of Progressive Robert M. La Follette. After theGreat Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
and as the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
era progressed, the Upper Peninsula became more Democratic than the state as a whole, voting that way when the state did not in 1940
A calendar from 1940 according to the Gregorian calendar, factoring in the dates of Easter and related holidays, cannot be used again until the year 5280.
Events
Below, events related to World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
*Janu ...
, 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The current Constitutions of Constitution of Italy, Italy and of Constitution of New Jersey, New Jersey (both later subject to amendment) ...
, 1976
Events January
* January 2 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 18 – Full diplomatic ...
, and 1988. However, the region would move back to Republicans in the 21st century, voting for the GOP candidate every time except in 2008
2008 was designated as:
*International Year of Languages
*International Year of Planet Earth
*International Year of the Potato
*International Year of Sanitation
The Great Recession, a worldwide recession which began in 2007, continued throu ...
, when Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
was able to carry it in his landslide victory in Michigan, though by much less than the state as a whole. The UP did not vote for his re-election in 2012
2012 was designated as:
*International Year of Cooperatives
*International Year of Sustainable Energy for All
Events January
*January 4 – The Cicada 3301 internet hunt begins.
* January 12 – Peaceful protests begin in the R ...
while the state did, and it further shifted to the Republican Party during the ascendancy of Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
, where his victory in the UP was vital in flipping the state red in 2016
2016 was designated as:
* International Year of Pulses by the sixty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly.
* International Year of Global Understanding (IYGU) by the International Council for Science (ICSU), the Internationa ...
. It voted Republican once more in 2020
The year 2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of even ...
and 2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
, Trump had the best performance for a Republican there in nearly a century in where Michigan flipped red again in 2024.
All counties in the UP are part of Michigan's 1st congressional district. Jack Bergman, a Republican, has been the U.S. representative for this district since January 2017.
In Michigan's 2010 gubernatorial election Republican Rick Snyder
Richard Dale Snyder (born August 19, 1958) is an American business executive, venture capitalist, attorney, accountant, and politician who served as the 48th governor of Michigan from 2011 to 2019. Snyder, who was born in Battle Creek, Michigan, ...
carried every UP county but one, Gogebic, on his way to victory over his Democratic opponent, Virg Bernero.
Proposed statehood
Due to the geographic separation and perceived cultural and political differences from the Lower Peninsula, at various times there have been proposals for the Upper Peninsula to secede from Michigan as a 51st state named ''Superior'', sometimes including portions of northern Wisconsin and/or the northern Lower Peninsula. Several prominent legislators, including the region's long-serving state representative Dominic Jacobetti, attempted unsuccessfully to gain passage of such a bill in the 1970s. It would be the least populous state in the union, and as stronger connections to the rest of Michigan have developed since completion of theMackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ; also referred to as the Mighty Mac or Big Mac) is a suspension bridge that connects the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper and Lower Peninsula of Michigan, Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. It spans the Str ...
in the 1950s, the proposal has remained largely dormant since the 1970s.
Notable attractions
* Adventure Mine * Agate Falls * Au Sable Light Station * Black River National Forest Scenic Byway *Bond Falls
Bond Falls is a waterfall on the middle branch of the Ontonagon River, a few miles east of Paulding in Haight Township in southern Ontonagon County, Michigan. The site is near U.S. Highway 45 in the western portion of the Upper Peninsula of ...
* Brockway Mountain Drive
* Calumet Theatre
* Calumet Downtown Historic District
* Castle Rock
* Copper Harbor
* Copper Peak, Ironwood Township
* DeYoung Family Zoo
* Fayette Historic State Park
* Fort Mackinac
* Fort Wilkins Historic State Park
* Garlyn Zoo
* Grand Hotel (Mackinac Island)
* Grand Island National Recreation Area
* Grand Sable Dunes
* The Great Lakes Shipwreck Museum
* Iron Mountain Iron Mine – Vulcan
* Isle Royale National Park
Isle Royale National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States consisting of Isle Royale, along with more than 400 small adjacent islands and the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in Michigan.
...
* Keweenaw National Historical Park
Keweenaw National Historical Park is a unit of the U.S. National Park Service. Established in 1992, the park celebrates the life and history of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is a federal-local ...
* Keweenaw Waterway and Portage Lake Lift Bridge
* Kitch-iti-kipi
* Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. Lake Michigan–Huron has a larger combined surface area than Superior, but is normally considered tw ...
* Lake Superior State University, Lakers
* Laughing Whitefish Falls
* Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ; also referred to as the Mighty Mac or Big Mac) is a suspension bridge that connects the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper and Lower Peninsula of Michigan, Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. It spans the Str ...
* Mackinac Island
Mackinac Island ( , ; ; ; ) is an island and resort area, covering in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac and "Mitchimakinak" in Ojibwemowin, meaning "Great Turtle". It is located in ...
* The Marquette Lighthouse
* Marquette Mountain Ski Resort
* Michigan Iron Industry Museum – Negaunee
* Michigan Technological University
* Mount Bohemia ski center (with the highest vertical drop, , in the Midwest)
* Munising Falls
* National Ski Hall of Fame
* Northern Michigan University
Northern Michigan University (Northern Michigan, Northern or NMU) is a public university in Marquette, Michigan, United States. It was established in 1899 by the Michigan Legislature as Northern State Normal School. In 1963, the state designa ...
* Marquette Ore Dock
* Paulding Light
* Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore
* Pine Mountain ski jump in Iron Mountain is one of the largest artificial ski jumps in the world.
* Point Iroquois Lighthouse
* Porcupine Mountains State Park
* Presque Isle Park, Marquette, Michigan
Marquette ( ) is the county seat of Marquette County, Michigan, Marquette County and the largest city in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, United States. Located on the shores of Lake Superior, Marquette is a major port known primarily for shippin ...
* Quincy Copper Mine offering guided tours
* Seney National Wildlife Refuge
* Ski Brule in Iron River
* The Soo Locks
* Suicide Hill Ski Jump, Ishpeming, Michigan
Ishpeming ( ) is a city in Marquette County, Michigan, United States. Located in the Upper Peninsula, the population was 6,140 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, less than it was in the 1950s and 1960s when the Iron ore mines employ ...
* Sylvania Wilderness
* Tahquamenon Falls State Park
* Upper Peninsula Children's Museum – Marquette
Casinos
American Indian casinos contribute to the tourist attractions and are popular in the UP. Originally the casinos were simple, one-room affairs. Some of the casinos are now quite elaborate and are being developed as part of resort and conference facilities, including features such as golf courses, pool and spa, dining, and rooms to accommodate guests. * Bay Mills Resort & Casino – Brimley * Island Resort & Casino – Harris * Kewadin Casinos –Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by coun ...
; Hessel; Manistique; St. Ignace; Sault Ste. Marie
* Kings Club Casino – Brimley (Closed permanently)
* Lac Vieux Desert Casino – Watersmeet
* Ojibwa Casinos – Baraga; Marquette
Transportation
 The Upper Peninsula is separated from the Lower by the
The Upper Peninsula is separated from the Lower by the Straits of Mackinac
The Straits of Mackinac ( ; ) are the short waterways between the U.S. state of Michigan's Upper and Lower Peninsulas, traversed by the Mackinac Bridge. The main strait is wide with a maximum depth of , and connects the Great Lakes of Lake M ...
, five miles (8 km) across at the narrowest, and is connected to it by the Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ; also referred to as the Mighty Mac or Big Mac) is a suspension bridge that connects the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper and Lower Peninsula of Michigan, Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. It spans the Str ...
at St. Ignace, one of the longest suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridg ...
s in the world. Until the bridge was completed in 1957, travel between the two peninsulas was difficult and slow (and sometimes even impossible during winter). In 1881, the Mackinac Transportation Company was established by three railroads, the Michigan Central Railroad
The Michigan Central Railroad (reporting mark MC) was originally chartered in 1832 to establish rail service between Detroit, Michigan, and St. Joseph, Michigan. The railroad later operated in the states of Michigan, Indiana, and Illinois in th ...
, the Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad, and the Detroit, Mackinac and Marquette Railroad, to operate a railroad car ferry across the Straits. Beginning in 1923, the State of Michigan operated automobile ferries between the two peninsulas. At the busiest times of year the wait was several hours long, much longer at holidays. In winter, travel was possible over the ice only after the straits had solidly frozen.
Highways
There are oneInterstate Highway
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, or the Eisenhower Interstate System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Hi ...
, five US Highways and 24 other state highways
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
in the Upper Peninsula. Interstate 75 is the only freeway in the region and runs from the Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ; also referred to as the Mighty Mac or Big Mac) is a suspension bridge that connects the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper and Lower Peninsula of Michigan, Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. It spans the Str ...
at St. Ignace to the International Bridge at Sault Ste. Marie. Two highways run the east–west length of the peninsula, US Highway 2 along the south and M-28 to the north. US 41 runs north–south through the central and western UP, connecting Menominee, Escanaba, Marquette and Houghton before terminating near the tip of the Keweenaw at Copper Harbor. M-185 encircles Mackinac Island as the only state highway in the country without motor vehicles.
The United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency within the United States Department of Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture. It administers the nation's 154 United States National Forest, national forests and 20 United States Natio ...
and Federal Highway Administration
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program a ...
have designated certain roads within the several National Forests in the UP as Federal Forest Highways. State-maintained highways closest to the Upper Peninsula's Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
shorelines are marked by the Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT) with signs indicating that they are part of the Great Lakes Circle Tour, a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River. MDOT has also designated five UP highways as Pure Michigan Byway
A Pure Michigan Byway is the designation for a segment of the Michigan State Trunkline Highway System, State Trunkline Highway System in the US state of Michigan that is a "scenic, recreational, or historic route that is representative of Michiga ...
s for their historic, recreational or scenic qualities. They are: US 2 in Iron County (Iron County Heritage Trail) and in Schoolcraft and Mackinac counties (Top of the Lake Scenic Byway), US 41 from Houghton to Copper Harbor (Copper County Trail, also a National Scenic Byway
A National Scenic Byway is a road recognized by the United States Department of Transportation for one or more of six "intrinsic qualities": archeological, cultural, historic, natural, recreational, and scenic. The program was established by Co ...
), M-35 (UP Hidden Coast Recreational Heritage Trail), M-123 (Tahquamenon Scenic Heritage Route) and M-134 (M-134 North Huron Byway)
Airports
There are 43 airports in the Upper Peninsula. Of these, six airports have commercial passenger service: Gogebic-Iron County Airport north of Ironwood, Houghton County Memorial Airport southwest of Calumet, Ford Airport west of Iron Mountain, Sawyer International Airport south of Marquette, Delta County Airport inEscanaba
Escanaba ( ), commonly shortened to Esky, is a port city and the county seat of Delta County, Michigan, Delta County in the U.S. state of Michigan, located on Little Bay de Noc in the state's Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula. The popu ...
, and Chippewa County International Airport south of Sault Ste. Marie. There are 19 other public use airports with a hard surface runway. These are used for general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations except for commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services for other ...
and charter. Notably, Mackinac Island
Mackinac Island ( , ; ; ; ) is an island and resort area, covering in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac and "Mitchimakinak" in Ojibwemowin, meaning "Great Turtle". It is located in ...
, Beaver Island, and Drummond Island are all accessible by airports. There are five public access airports with turf runways and thirteen airports for the private use of their owners. There is only one control tower
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled a ...
in the Upper Peninsula, at Sawyer.
Ferries and bridges
Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ; also referred to as the Mighty Mac or Big Mac) is a suspension bridge that connects the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper and Lower Peninsula of Michigan, Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. It spans the Str ...
, connecting the Lower Peninsula of Michigan with the Upper;
* Sault Ste. Marie International Bridge, which connects the city of Sault Ste. Marie to its twin city of Sault Ste. Marie in Canada; and
* Portage Lift Bridge, which crosses Portage Lake. The Portage Lift Bridge is the world's heaviest and widest double-decked vertical lift bridge. Its center span lifts to provide about of clearance for ships. Since rail traffic was discontinued in the Keweenaw, the lower deck is used to accommodate snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a snowmachine (chiefly Alaskan), motor sled (chiefly Canadian), motor sledge, skimobile, snow scooter, or simply a sled is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow.
Their engines normally ...
traffic in the winter. As the only land-based link between the north and south sections of the Keweenaw Peninsula, the bridge is crucial to transportation.
Railways
* Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad: Transports iron ore over a line from the Empire-Tilden Mine (operated by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.), south of Ishpeming and Negaunee, to Marquette's port on Lake Superior. * Two railroads originally crossed the Upper Peninsula east to west: the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railway, informally known as the Soo Line, running west from Sault Ste. Marie roughly along the Lake Michigan shore, and the Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railroad running west from St. Ignace roughly along the Lake Superior shore. In 1960, both railroads were merged into the Soo Line Railroad, the U.S. arm of theCanadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway () , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Kansas City, Canadian Pacific Ka ...
. The Soo Line trackage in the Upper Peninsula was purchased by the Wisconsin Central Railroad in 1987. In 1997, the Wisconsin Central also purchased from the Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad is a Railroad classes, Class I freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United Stat ...
the former Chicago and North Western Railway
The Chicago and North Western was a Railroad classes#Class I, Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over of t ...
line running into the Upper Peninsula from Wisconsin. The Wisconsin Central was in turn purchased by the Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company () is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue a ...
in 2001. The Canadian National now operates much of the remaining railroad trackage in the Upper Peninsula.
* Escanaba and Lake Superior Railroad: Chartered in 1898, the E&LS is an industrial beltline railroad with of trackage connecting Escanaba, Ontonagon, Republic, and Green Bay, Wisconsin
Green Bay is a city in Brown County, Wisconsin, United States, and its county seat. It is located at the head of Green Bay (Lake Michigan), Green Bay (known locally as "the bay of Green Bay"), a sub-basin of Lake Michigan at the mouth of the F ...
, with a common junction at Channing, and a spur to Nestoria from Sidnaw.
* Mineral Range Railroad: Since 2002, this railroad has been operating a industrial track from Ishpeming to National Mine to serve an explosives plant. The railroad expanded in 2014 to include of former Canadian National and Lake Superior and Ishpeming rail lines between Ishpeming and Humboldt to serve the Humboldt Mill. The railroad takes its name from the former Mineral Range Railroad in the Keweenaw Peninsula
The Keweenaw Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. Part of the greater landmass of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula, the Keweenaw Peninsula projects about northeasterly into Lake Superior, forming Keweena ...
.
* Grand Elk Railroad: Originally formed in 2009 in the Lower Peninsula, the railroad owned by Watco expanded to the UP in 2021 to operate former Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic lines that were divested by Canadian National. This includes a line from Trout Lake to Munising and an out of service line to a former mine in White Pine.
Bus systems
Despite its rural character, there are public buses in several counties of the Upper Peninsula. These include MarqTran serving Marquette, as well as intercity services provided by Indian Trails.Notable people
* Nick Baumgartner, Olympic gold medalist in mixed snowboard cross at the2022 Winter Olympics
The 2022 Winter Olympics, officially called the XXIV Olympic Winter Games () and commonly known as Beijing 2022 (2022), were an international winter multi-sport event held from 4 to 20 February 2022 in Beijing, China, and surrounding areas wit ...
, is from Iron River.
* Da Yoopers, comedy music/sketch group
* Robert J. Flaherty, the filmmaker who directed and produced the documentary '' Nanook of the North'', in 1922, from Iron Mountain.
* George Gipp, the "Gipper"—immortalized in the film ''Knute Rockne, All American
''Knute Rockne, All American'' is a 1940 American biographical film that tells the story of Knute Rockne, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame's legendary football coach. It stars Pat O'Brien (actor), Pat O'Brien as Rockne and Ronald Reagan as p ...
''—was born in Laurium. He was the first All-American player of the Notre Dame football program.
* Crystal Hayes, 2005 Miss Michigan, from Rock.
* Tom Izzo, Michigan State basketball coach a native of Iron Mountain, attended Northern Michigan University
Northern Michigan University (Northern Michigan, Northern or NMU) is a public university in Marquette, Michigan, United States. It was established in 1899 by the Michigan Legislature as Northern State Normal School. In 1963, the state designa ...
.
* Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson, aircraft engineer and aeronautical innovator, was born in Ishpeming.
* John Lautner, one of Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright Sr. (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed List of Frank Lloyd Wright works, more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key ...
's most successful Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Britons (Celtic people), Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the ''Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to ...
fellows, a native of Marquette and alumnus of NMU.
* Mitchell Leisen
James Mitchell Leisen (October 6, 1898 – October 28, 1972) was an American film director, director, art director, and costume designer.
Film career
He entered the film industry in the 1920s, beginning in the art and costume departments. He d ...
, film director, was born Menominee
The Menominee ( ; meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recognized tribe of Na ...
in 1898.
* Steve Mariucci, former San Francisco 49ers
The San Francisco 49ers (also written as the San Francisco Forty-Niners and nicknamed the Niners) are a professional American football team based in the San Francisco Bay Area. The 49ers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member ...
and Detroit Lions
The Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit. The Lions compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC North, North division. The team plays their home game ...
head coach; a native of Iron Mountain, attended Northern Michigan University.
* Terry O'Quinn, actor on ''Lost'', was born in Sault Ste. Marie in 1952 and grew up in Newberry.
* Chase Osborn was the only Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
of Michigan from the Upper Peninsula (1911–1913).
* Pam Reed, ultrarunner, grew up in Palmer, and graduated from Michigan Technological University.
* Gene Ronzani was a professional football running back for the Chicago Bears
The Chicago Bears are a professional American football team based in Chicago. The Bears compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC North, North division. They are one of two remaining ...
and head coach of the Green Bay Packers
The Green Bay Packers are a professional American football team based in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The Packers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC North, North division. They ar ...
from 1950 to 1953; born in Iron Mountain.
* Abby Roque, the first indigenous person to play for the United States women's national ice hockey team and an Olympic medalist, played high school hockey in Sault Ste. Marie.
* Rob Rubick, Detroit Lions tight end and current Fox Sports Detroit analyst, from Newberry.
* Glenn T. Seaborg, a Nobel Prize-winning chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...
and major contributor in the discovery of several of the transuranium elements, was born in Ishpeming.
* Mike Shaw
Michael Paul Shaw (May 9, 1957 – September 11, 2010) was an American professional wrestler who was best known for his stint in World Championship Wrestling (WCW) as Norman the Lunatic, and as Bastion Booger in the World Wrestling Federation ...
, professional wrestler, was born in Skandia
Skandia is a Swedish financial services corporation that provides insurance, banking and asset management services.
Between 2006 and 2015, the financial group underwent major changes. From an insurance company with the main emphasis on non-l ...
.
* Matthew Songer, founder of Pioneer Surgical Technology, lives in Marquette.
* Mary Chase Perry Stratton, founder of Pewabic Pottery, was born in Hancock.
* Lou Thesz, professional wrestler who held the NWA World Heavyweight Championship
The NWA World's Heavyweight Championship is a men's professional wrestling Professional wrestling championship#World championships, world heavyweight championship owned and promoted by the National Wrestling Alliance (NWA), an American professiona ...
longer than anyone in history, was born in Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, on April 24, 1916.
* James Tolkan, an actor who appeared in ''Back to the Future
''Back to the Future'' is a 1985 American science fiction film directed by Robert Zemeckis and written by Zemeckis and Bob Gale. It stars Michael J. Fox, Christopher Lloyd, Lea Thompson, Crispin Glover, and Thomas F. Wilson. Set in 1985 ...
'' and ''Top Gun
''Top Gun'' is a 1986 American action drama film directed by Tony Scott and produced by Don Simpson and Jerry Bruckheimer, with distribution by Paramount Pictures. The screenplay was written by Jim Cash and Jack Epps Jr., and was inspired ...
'', born in Calumet.
* John D. Voelker, Justice of the Michigan Supreme Court
The Michigan Supreme Court is the highest court in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is Michigan's court of last resort and consists of seven justices. The Court is located in the Michigan Hall of Justice at 925 Ottawa Street in Lansing, the s ...
, wrote the best-selling book '' Anatomy of a Murder'' under the pen name Robert Traver. Directed by Otto Preminger
Otto Ludwig Preminger ( ; ; 5 December 1905 – 23 April 1986) was an Austrian Americans, Austrian-American film and theatre director, film producer, and actor. He directed more than 35 feature films in a five-decade career after leaving the the ...
, the film was shot in Big Bay and Ishpeming with some courtroom scenes in Marquette.
* Bill Ivey, the former head of the National Endowment for the Arts under the Clinton Administration was born in Calumet.
* Jake Witt is an American football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular American football field, field with goalposts at e ...
Offensive tackle
Offensive may refer to:
* Offensive (military), type of military operation
* Offensive, the former name of the Dutch political party Socialist Alternative
* Fighting words, spoken words which would have a tendency to cause acts of violence by the ...
for the Indianapolis Colts
The Indianapolis Colts are a professional American football team based in Indianapolis. The Colts compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC South, South division. Since the 2008 India ...
of the National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
(NFL). He was drafted in the 7th Round of the 2023 NFL draft with the 236th overall pick.
See also
*List of counties in Michigan
There are 83 counties in the U.S. state of Michigan. The boundaries of these counties have not changed substantially since 1897. However, throughout the 19th century, the state legislature frequently adjusted county boundaries. County creation ...
* Heikki Lunta, mythological character
* Stormy Kromer cap
Notes
References
Further reading
* * 113 pages. * * 376 pages. * 270 pages. * * *External links
Upper Peninsula of Michigan Travel
Western Upper Peninsula of Michigan
{{DEFAULTSORT:Upper Peninsula Of Michigan Regions of Michigan Cultural regions of the United States