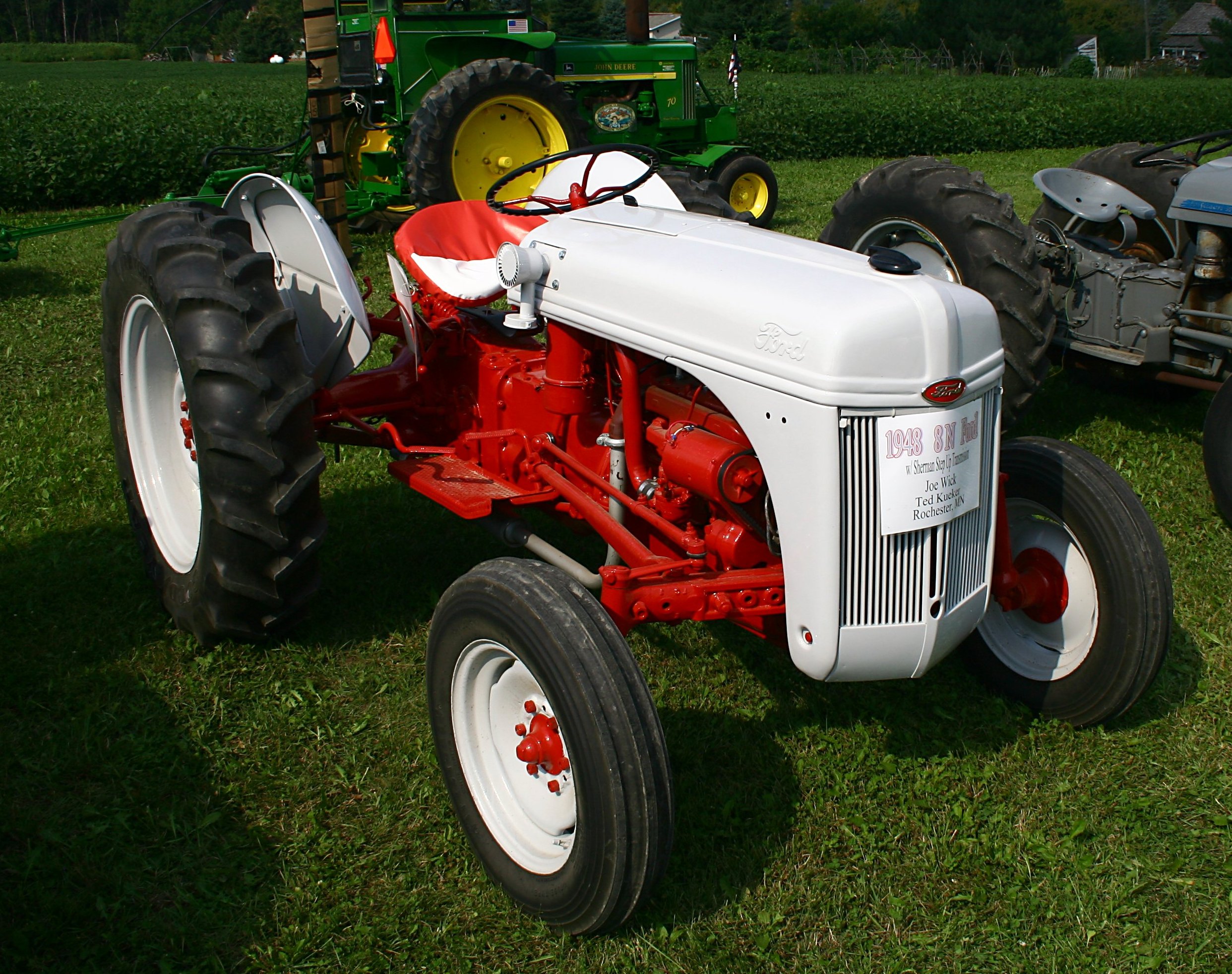

A tractor is an
engineering vehicle
Heavy equipment, heavy machinery, earthmovers, construction vehicles, or construction equipment, refers to heavy-duty vehicles specially designed to execute construction tasks, most frequently involving earthwork operations or other large con ...
specifically designed to deliver a high
tractive effort
In railway engineering, the term tractive effort describes the pulling or pushing capability of a locomotive. The published tractive force value for any vehicle may be theoretical—that is, calculated from known or implied mechanical proper ...
(or
torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a
trailer or machinery such as that used in
agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
,
mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
or
construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
. Most commonly, the term is used to describe a
farm
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used fo ...
vehicle that provides the power and traction to
mechanize agricultural tasks, especially (and originally)
tillage
Tillage is the agriculture, agricultural preparation of soil by mechanical wikt:agitation#Noun, agitation of various types, such as digging, stirring, and overturning. Examples of manual labour, human-powered tilling methods using hand tools inc ...
, and now many more.
Agricultural implements may be towed behind or mounted on the tractor, and the tractor may also provide a source of power if the implement is mechanised.


Etymology
The word ''tractor'' was taken from
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, being the
agent noun
In linguistics, an agent noun (in Latin, ) is a word that is derived from another word denoting an action, and that identifies an entity that does that action. For example, ''driver'' is an agent noun formed from the verb ''drive''.
Usually, '' ...
of ''trahere'' "to pull". The first recorded use of the word meaning "an engine or vehicle for pulling wagons or plows" occurred in 1896, from the earlier term "
traction motor" (1859).
National variations
In the
UK,
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
,
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
,
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
,
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
,
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
,
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
,
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
,
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, and
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, the word "tractor" usually means "farm tractor", and the use of the word "tractor" to mean other types of vehicles is familiar to the vehicle trade, but unfamiliar to much of the general public. In
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and the
US, the word may also refer to the
road tractor portion of a
tractor trailer truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construct ...
, but also usually refers to the piece of farm equipment.
History
Traction engines

The first powered farm implements in the early 19th century were
portable engine
A portable engine is an engine, either a steam engine or an internal combustion engine, that sits in one place while operating (providing power to machinery), but (unlike a stationary engine) is wikt:portable#Adjective, portable and thus can be ...
s – steam engines on wheels that could be used to drive mechanical farm machinery by way of a flexible belt.
Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He ...
designed the first 'semi-portable'
stationary steam engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam car ...
for agricultural use, known as a "barn engine" in 1812, and it was used to drive a corn threshing machine.
The truly portable engine was invented in 1839 by William Tuxford of
Boston, Lincolnshire
Boston is a market town and inland port in the borough of the same name in the county of Lincolnshire, England. It lies to the south-east of Lincoln, east of Nottingham and north-east of Peterborough. The town had a population of 45,339 at ...
who started manufacture of an engine built around a locomotive-style boiler with horizontal smoke tubes. A large
flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device that uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy, a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, a ...
was mounted on the crankshaft, and a stout leather belt was used to transfer the drive to the equipment being driven. In the 1850s,
John Fowler used a Clayton & Shuttleworth portable engine to drive apparatus in the first public demonstrations of the application of cable haulage to cultivation.
In parallel with the early portable engine development, many engineers attempted to make them self-propelled – the fore-runners of the
traction engine
A traction engine is a steam engine, steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin ''tractus'', meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any ...
. In most cases this was achieved by fitting a sprocket on the end of the crankshaft, and running a chain from this to a larger sprocket on the rear axle. These experiments met with mixed success.
The first proper
traction engine
A traction engine is a steam engine, steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin ''tractus'', meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any ...
, in the form recognisable today, was developed in 1859 when British engineer
Thomas Aveling modified a
Clayton & Shuttleworth portable engine
A portable engine is an engine, either a steam engine or an internal combustion engine, that sits in one place while operating (providing power to machinery), but (unlike a stationary engine) is wikt:portable#Adjective, portable and thus can be ...
, which had to be hauled from job to job by horses, into a self-propelled one. The alteration was made by fitting a long driving chain between the crankshaft and the rear axle.
The first half of the 1860s was a period of great experimentation but by the end of the decade the standard form of the traction engine had evolved and changed little over the next sixty years. It was widely adopted for agricultural use. The first tractors were steam-powered
plowing engines. They were used in pairs, placed on either side of a field to haul a plow back and forth between them using a wire cable. In Britain
Mann's and
Garrett developed
steam tractor
A steam tractor is a tractor powered by a steam engine which is used for pulling.
In North America, the term ''steam tractor'' usually refers to a type of agriculture, agricultural tractor powered by a steam engine, used extensively in the l ...
s for direct ploughing, but the heavy, wet soil of England meant that these designs were less economical than a team of horses. In the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, where soil conditions permitted, steam tractors were used to direct-haul plows. Steam-powered
agricultural engines remained in use well into the 20th century until reliable internal combustion engines had been developed.
Fuel

The first gasoline powered tractors were built in Illinois, by John Charter combining single cylinder Otto engines with a Rumley Steam engine chassis, in 1889. In 1892,
John Froelich
John Froelich (November 24, 1849 – May 24, 1933) was an American inventor and entrepreneur, who invented the first stable gasoline-powered tractor with forward and reverse gears. He received several patents relating to tractors and internal comb ...
built a gasoline-powered tractor in
Clayton County, Iowa
Clayton County is a County (United States), county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 17,043. Its county seat is Elkader, Iowa, Elkader. The county was established in 1837 and ...
, US. A Van Duzen single-cylinder gasoline engine was mounted on a Robinson engine chassis, which could be controlled and propelled by Froelich's gear box. After receiving a patent, Froelich started up the
Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company
The Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company was the first company to manufacture and sell gasoline powered farm tractors. Based in Waterloo, Iowa, the company was created by John Froelich and a group of Iowa businessmen in 1893, and was originally named ...
and invested all of his assets. The venture was very unsuccessful, and by 1895 all was lost and he went out of business.
Richard Hornsby & Sons
Richard Hornsby & Sons was an engine and machinery manufacturer in Grantham, Lincolnshire, Grantham, Lincolnshire, England from 1828 until 1918. The company was a pioneer in the manufacture of the Hornsby-Akroyd oil engine, oil engine develop ...
are credited with producing and selling the first oil-engined tractor in Britain, invented by
Herbert Akroyd Stuart. The Hornsby-Akroyd Patent Safety Oil Traction Engine was made in 1896 with a engine. In 1897, it was bought by Mr. Locke-King, the first recorded British tractor sale. That year, it won a Silver Medal from the
Royal Agricultural Society of England
The Royal Agricultural Society of England (RASE) promotes the scientific development of English agriculture. It was established in 1838 with the motto "Practice with Science" and was known as the English Agricultural Society until it received i ...
. It later returned to the factory for a caterpillar track fitting.
The first commercially successful light-weight petrol-powered general purpose tractor was built by
Dan Albone, a British inventor in 1901. He filed for a patent on 15 February 1902 for his tractor design and then formed Ivel Agricultural Motors Limited. The other directors were
Selwyn Edge,
Charles Jarrott
Charles Jarrott (16 June 19274 March 2011) was a British film and television director. He was best known for costume dramas he directed for producer Hal B. Wallis, among them '' Anne of the Thousand Days'', which earned him a Golden Globe for B ...
, John Hewitt and
Lord Willoughby. He called his machine the Ivel Agricultural Motor; the word "tractor" came into common use after Hart-Parr created it. The Ivel Agricultural Motor was light, powerful and compact. It had one front wheel, with a solid rubber tyre, and two large rear wheels like a modern tractor. The engine used water cooling, utilizing the thermo-syphon effect. It had one forward and one reverse gear. A pulley wheel on the left hand side allowed it to be used as a
stationary engine, driving a wide range of agricultural machinery. The 1903 sale price was £300. His tractor won a medal at the
Royal Agricultural Show, in 1903 and 1904. About 500 were built, and many were exported all over the world. The original engine was made by Payne & Co. of
Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
. After 1906, French
Aster engines were used.
The first successful American tractor was built by
Charles W. Hart and
Charles H. Parr. They developed a two-cylinder gasoline engine and set up their business in
Charles City, Iowa
Charles City is a city in and the county seat of Floyd County, Iowa, United States. Charles City is a significant commercial and transportation center for the area. U.S. Route 18 in Iowa, U.S. Routes 18 and U.S. Route 218, 218, Iowa Highway 14, ...
. In 1903, the firm built 15 tractors. Their #3 is the oldest surviving internal combustion engine tractor in the United States, and is on display at the Smithsonian National Museum of American History in Washington, D.C. The two-cylinder engine has a unique hit-and-miss firing cycle that produced at the belt and at the drawbar.

In 1908, the
Saunderson Tractor and Implement Co. of
Bedford
Bedford is a market town in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 Census, the population was 106,940. Bedford is the county town of Bedfordshire and seat of the Borough of Bedford local government district.
Bedford was founded at a ford (crossin ...
introduced a four-wheel design, and became the largest tractor manufacturer in Britain at the time. While the earlier, heavier tractors were initially very successful, it became increasingly apparent at this time that the weight of a large supporting frame was less efficient than lighter designs. Henry Ford introduced a light-weight, mass-produced design which largely displaced the heavier designs. Some companies halfheartedly followed suit with mediocre designs, as if to disprove the concept, but they were largely unsuccessful in that endeavor.
While unpopular at first, these gasoline-powered machines began to catch on in the 1910s, when they became smaller and more affordable.
Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist and business magnate. As the founder of the Ford Motor Company, he is credited as a pioneer in making automob ...
introduced the
Fordson, a wildly popular mass-produced tractor, in 1917. They were built in the U.S., Ireland, England and Russia, and by 1923, Fordson had 77% of the U.S. market. The Fordson dispensed with a frame, using the strength of the engine block to hold the machine together. By the 1920s, tractors with gasoline-powered
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s had become the norm.

The first three-point hitches were experimented with in 1917. After
Harry Ferguson
Henry George Ferguson (4 November 188425 October 1960) was an Irish mechanic and inventor who is noted for his role in the development of the modern agricultural tractor and its Three-point hitch, three-point linkage system, for being the firs ...
applied for a British patent for his
three-point hitch
The three-point hitch (British English: three-point linkage) is a widely used type of hitch for attaching ploughs and other farm equipment, implements to an agricultural or industrial tractor. The three points resemble either a triangle, or the le ...
in 1926, they became popular. A three-point attachment of the implement to the tractor is the simplest and the only statically determinate way of joining two bodies in engineering. The
Ferguson-Brown Company produced the Model A Ferguson-Brown tractor with a Ferguson-designed
hydraulic
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
hitch. In 1938 Ferguson entered into a collaboration with Henry Ford to produce the
Ford-Ferguson 9N tractor. The three-point hitch soon became the favorite hitch attachment system among farmers around the world. This tractor model also included a rear
Power Take Off (PTO) shaft that could be used to power three point hitch mounted implements such as sickle-bar mowers.
Electric
In 1969,
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston.
Over the year ...
introduced the
Elec-Trak, the first commercial,
electric tractor (electric-powered garden tractor). The Elec-Trak was manufactured by General Electric until 1975.
Electric tractors are manufactured by a German company,
Fendt
Fendt is a German agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in 1930 by Xaver Fendt in Marktoberdorf, Allgäu region, Germany. Fendt manufactures tractors, combine harvesters, balers, telescopic handlers and row crop Planter (farm implement), ...
, and by US companies,
Solectrac and Monarch Tractor.
John Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
's protoype electric tractor is a plug-in, powered by an electrical cable.
Kubota
is a Japanese multinational corporation based in Osaka. It was established in 1890. The corporation produces many products including tractors and other agricultural machinery, Heavy equipment, construction equipment, engines, vending machines, P ...
is prototyping an autonomous electric tractor.
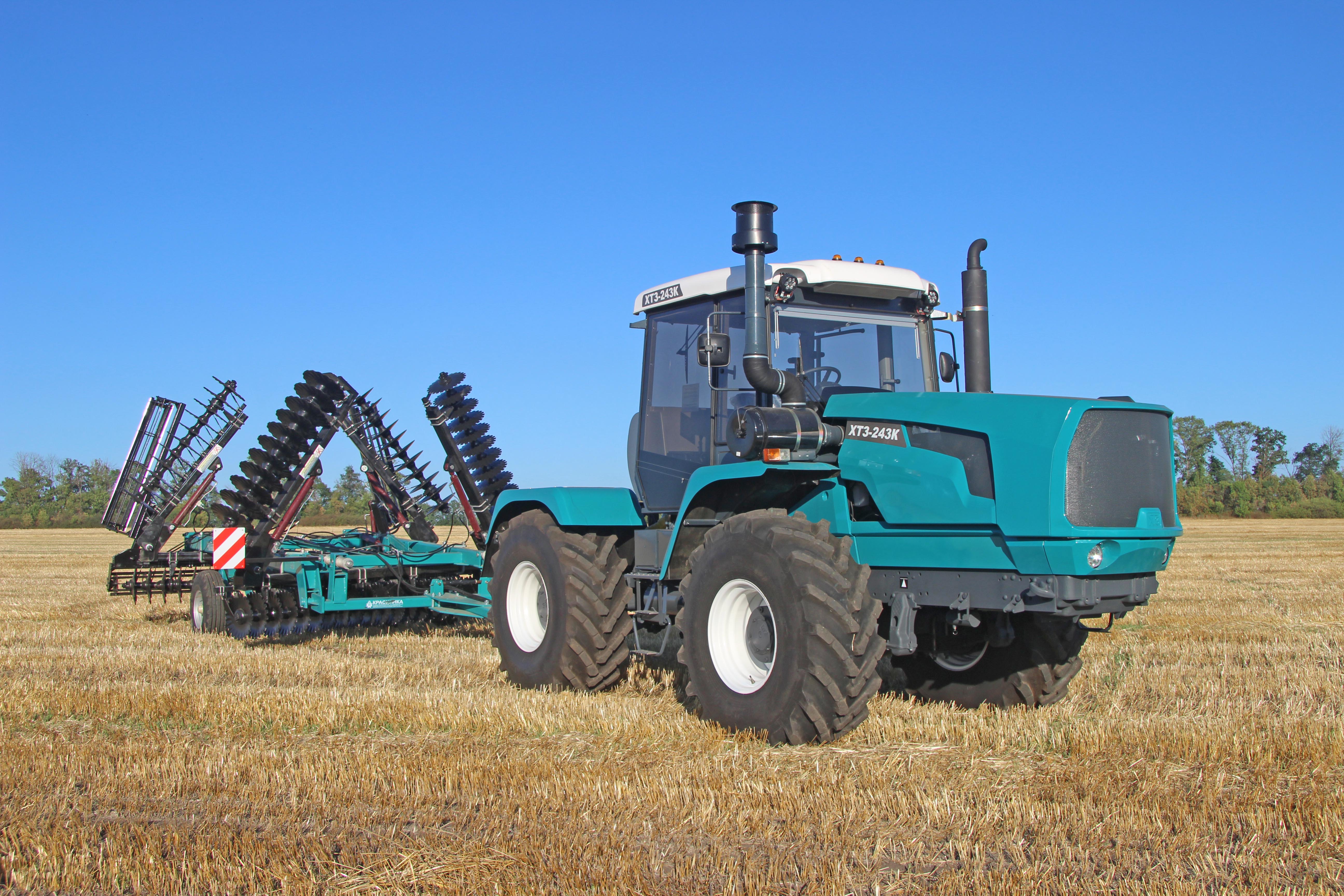
Design, power and transmission
Configuration
Tractors can be generally classified by number of axles or wheels, with main categories of
two-wheel tractor
Two-wheel tractor or walking tractor (, , ) are generic terms understood in the US and in parts of Europe to represent a single-axle tractor, which is a tractor with one axle, self-powered and self-propelled, which can pull and power various f ...
s (single-axle tractors) and four-wheel tractors (two-axle tractors); more axles are possible but uncommon. Among four-wheel tractors (two-axle tractors), most are
two-wheel drive
Two-wheel-drive (2WD) denotes vehicles with a drivetrain that allows two wheels to be driven, and receive power and torque from the engine, simultaneously.
Four-wheeled vehicles
For four-wheeled vehicles (and by extension, vehicles with six, ...
(usually
at the rear); but many are two-wheel drive with front wheel assist,
four-wheel drive
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case pr ...
(often with articulated steering), or
track crawler (with steel or rubber tracks).

The classic farm tractor is a simple open
vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
, with two very large driving wheels on an axle below a single seat (the seat and
steering
Steering is the control of the direction of motion or the components that enable its control. Steering is achieved through various arrangements, among them ailerons for airplanes, rudders for boats, cylic tilting of rotors for helicopters, ...
wheel consequently are in the center), and the engine in front of the driver, with two steerable wheels below the engine compartment. This basic design has remained unchanged for a number of years after being pioneered by Wallis, but enclosed cabs are fitted on almost all modern models, for operator safety and comfort.
In some localities with heavy or wet soils, notably in the Central Valley of California, the
"Caterpillar" or
"crawler" type of tracked tractor became popular due to superior traction and flotation. These were usually maneuvered through the use of turning brake pedals and separate track clutches operated by levers rather than a steering wheel.


Four-wheel drive tractors began to appear in the 1960s. Some four-wheel drive tractors have the standard "two large, two small" configuration typical of smaller tractors, while some have four large, powered wheels. The larger tractors are typically an articulated, center-hinged design steered by hydraulic cylinders that move the forward power unit while the trailing unit is not steered separately.

In the early 21st century, articulated or non-articulated, steerable multitrack tractors have largely supplanted the Caterpillar type for farm use. Larger types of modern farm tractors include articulated four-wheel or eight-wheel drive units with one or two power units which are hinged in the middle and steered by hydraulic clutches or pumps. A relatively recent development is the replacement of wheels or steel crawler-type tracks with flexible, steel-reinforced rubber tracks, usually powered by hydrostatic or completely hydraulic driving mechanisms. The configuration of these tractors bears little resemblance to the classic farm tractor design.
Engine and fuels
The predecessors of modern tractors, traction engines, used
steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
s for power.
Gasoline and kerosene
Since the turn of the 20th century,
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s have been the power source of choice. Between 1900 and 1960,
gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When for ...
was the predominant fuel, with
kerosene
Kerosene, or paraffin, is a combustibility, combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in Aviation fuel, aviation as well as households. Its name derives from the Greek (''kērós'') meaning " ...
(the
Rumely Oil Pull was the most notable of this kind)being a common alternative. Generally, one engine could burn any of those, although cold starting was easiest on gasoline. Often, a small auxiliary fuel tank was available to hold gasoline for cold starting and warm-up, while the main fuel tank held whatever fuel was most convenient or least expensive for the particular farmer. In the United Kingdom, a gasoline-kerosene engine is known as a
petrol-paraffin engine.
Diesel
Dieselisation
Dieselisation (US: dieselization) is the process of equipping vehicles with a diesel engine or diesel engines.
It can involve replacing an internal combustion engine powered by petrol (US: gasoline) fuel with an engine powered by diesel fuel, ...
gained momentum starting in the 1960s, and modern farm tractors usually employ
diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compr ...
s, which range in power output from 18 to 575
horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are t ...
(15 to 480 kW). Size and output are dependent on application, with smaller tractors used for
lawn mowing, landscaping, orchard work, and
truck farming, and larger tractors for vast fields of wheat, corn, soy, and other bulk crops.
Liquefied petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas, also referred to as liquid petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas), is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, Butane, ''n''-butane and isobutane. It can also contain some ...
(LPG) or
propane
Propane () is a three-carbon chain alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but becomes liquid when compressed for transportation and storage. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum ref ...
also have been used as tractor fuels, but require special pressurized fuel tanks and filling equipment and produced less power, so are less prevalent in most markets. Most are confined for inside work due to their clean burning.
Wood
During the Second World War, petroleum-based fuel was scarce in Europe, so European vehicles including tractors were commonly converted to use a
wood gas generator or "gasifier."
Biodiesel
In some countries such as Germany,
biodiesel
Biodiesel is a renewable biofuel, a form of diesel fuel, derived from biological sources like vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled greases, and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made from fats.
The roots of bi ...
is often used. Some other biofuels such as straight vegetable oil are also being used by some farmers.
Electric powered
Prototype battery powered
electric tractors are being developed by a German company,
Fendt
Fendt is a German agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in 1930 by Xaver Fendt in Marktoberdorf, Allgäu region, Germany. Fendt manufactures tractors, combine harvesters, balers, telescopic handlers and row crop Planter (farm implement), ...
, and by two US companies,
Solectrac and Monarch Tractor.
John Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
's protoype electric tractor is a plug-in, powered by an electrical cable.
Kubota
is a Japanese multinational corporation based in Osaka. It was established in 1890. The corporation produces many products including tractors and other agricultural machinery, Heavy equipment, construction equipment, engines, vending machines, P ...
is prototyping an autonomous electric tractor.
Transmission
Most older farm tractors use a
manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canadian English, Canada, British English, the United Kingdom and American English, the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed ...
with several
gear
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion and/or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or ...
ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
s, typically three to six, sometimes multiplied into two or three ranges. This arrangement provides a set of discrete ratios that, combined with the varying of the throttle, allow final-drive speeds from less than one up to about 25 miles per hour (40 km/h), with the lower speeds used for working the land and the highest speed used on the road.
Slow, controllable speeds are necessary for most of the operations performed with a tractor. They help give the farmer a larger degree of control in certain situations, such as field work. When travelling on public roads, the
slow operating speeds can cause problems, such as long queues or tailbacks, which can delay or annoy motorists in cars and trucks. These motorists are responsible for being duly careful around farm tractors and sharing the road with them, but many shirk this responsibility, so various ways to minimize the interaction or minimize the speed differential are employed where feasible. Some countries (for example the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
) employ a
road sign
Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduc ...
on some roads that means "no farm tractors". Some modern tractors, such as the
JCB Fastrac, are now capable of much higher road speeds of around 50 mph (80 km/h).

Older tractors usually have
unsynchronized transmission designs, which often require the operator to engage the clutch to shift between gears. This mode of use is inherently unsuited to some of the work tractors do, and has been circumvented in various ways over the years. For existing unsynchronized tractors, the methods of circumvention are
double clutching or power-shifting, both of which require the operator to rely on skill to speed-match the gears while shifting, and are undesirable from a risk-mitigation standpoint because of what can go wrong if the operator makes a mistake – transmission damage is possible, and loss of vehicle control can occur if the tractor is towing a heavy load either uphill or downhill – something that tractors often do. Therefore, operator's manuals for most of these tractors state one must always stop the tractor before shifting.
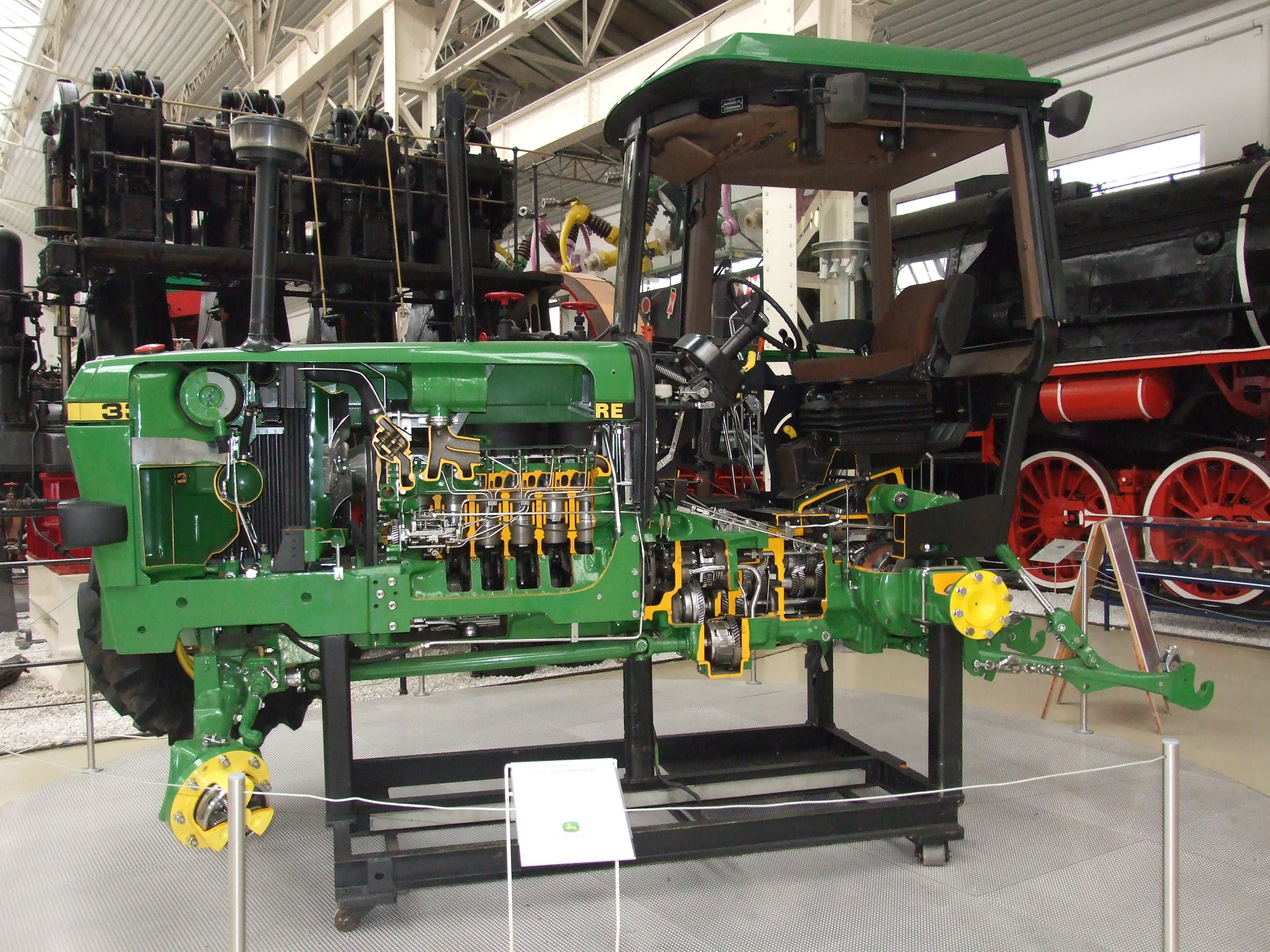

In newer designs, unsynchronized transmission designs were replaced with
synchronization
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the Conductor (music), conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are sa ...
or with
continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automated Transmission (mechanical device), transmission that can change through a continuous range of gear ratios, typically resulting in better fuel economy in gasoline applications. This contr ...
s (CVTs). Either a synchronized manual transmission with enough available gear ratios (often achieved with dual ranges, high and low) or a CVT allow the engine speed to be matched to the desired final-drive speed, while keeping engine speed within the appropriate speed (as measured in rotations per minute or rpm) range for power generation (the working range) (whereas throttling back to achieve the desired final-drive speed is a trade-off that leaves the working range). The problems, solutions, and developments described here also describe the history of transmission evolution in
semi-trailer truck
A semi-trailer truck (also known by a wide variety of other terms – see below) is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-trailer attaches to the tractor with a type of hitch called ...
s. The biggest difference is fleet turnover; whereas most of the old
road tractors have long since been scrapped, many of the old farm tractors are still in use. Therefore, old transmission design and operation is primarily just of historical interest in trucking, whereas in farming it still often affects daily life.
Hitches and power applications
The power produced by the engine must be transmitted to the implement or equipment to do the actual work intended for the equipment. This may be accomplished via a drawbar or hitch system if the implement is to be towed or otherwise pulled through the tractive power of the engine, or via a pulley or power takeoff system if the implement is stationary, or a combination of the two.
Drawbars
Plows
A plough or ( US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden ...
and other tillage equipment are most commonly connected to the tractor via a
drawbar. The classic drawbar is simply a steel bar attached to the tractor (or in some cases, as in the early Fordsons, cast as part of the rear transmission housing) to which the hitch of the implement was attached with a pin or by a loop and
clevis
A clevis fastener is a two-piece fastener system consisting of a ''clevis'' and a ''clevis pin head''.
Terms
The ''clevis'' is a U-shaped piece that has holes at the end of the prongs to accept the clevis pin. The ''clevis pin'' is similar to a ...
. The implement could be readily attached and removed, allowing the tractor to be used for other purposes on a daily basis. If the tractor was equipped with a swinging drawbar, then it could be set at the center or offset from center to allow the tractor to run outside the path of the implement.
The drawbar system necessitated the implement having its own running gear (usually wheels) and in the case of a plow, chisel cultivator or harrow, some sort of lift mechanism to raise it out of the ground at turns or for transport. Drawbars necessarily posed a rollover risk depending on how the tractive torque was applied. The Fordson tractor was prone to roll backward due to an excessively short wheelbase. The linkage between the implement and the tractor usually had some slack which could lead to jerky starts and greater wear and tear on the tractor and the equipment.

Drawbars were appropriate to the dawn of mechanization, because they were very simple in concept and because as the tractor replaced the horse, existing horse-drawn implements usually already had running gear. As the history of mechanization progressed, the advantages of other hitching systems became apparent, leading to new developments (see below). Depending on the function for which a tractor is used, though, the drawbar is still one of the usual means of attaching an implement to a tractor (see photo at left).
Fixed mounts
Some tractor manufacturers produced matching equipment that could be directly mounted on the tractor. Examples included front-end loaders, belly mowers, row crop cultivators, corn pickers and corn planters. In most cases, these fixed mounts were proprietary and unique to each make of tractor, so an implement produced by John Deere, for example, could not be attached to a Minneapolis Moline tractor. Another disadvantage was mounting usually required some time and labor, resulting in the implement being semi-permanently attached with bolts or other mounting hardware. Usually, it was impractical to remove the implement and reinstall it on a day-to-day basis. As a result, the tractor was unavailable for other uses and dedicated to a single use for an appreciable period of time. An implement was generally mounted at the beginning of its season of use (such as tillage, planting or harvesting) and removed when the season ended.
Three-point and quick
The drawbar system was virtually the exclusive method of attaching implements (other than direct attachment to the tractor) before
Harry Ferguson
Henry George Ferguson (4 November 188425 October 1960) was an Irish mechanic and inventor who is noted for his role in the development of the modern agricultural tractor and its Three-point hitch, three-point linkage system, for being the firs ...
developed the
three-point hitch
The three-point hitch (British English: three-point linkage) is a widely used type of hitch for attaching ploughs and other farm equipment, implements to an agricultural or industrial tractor. The three points resemble either a triangle, or the le ...
. Equipment attached to the three-point hitch can be raised or lowered
hydraulic
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
ally with a control lever. The equipment attached to the three-point hitch is usually completely supported by the tractor. Another way to attach an implement is via a quick hitch, which is attached to the three-point hitch. This enables a single person to attach an implement quicker and put the person in less danger when attaching the implement.

The three-point hitch revolutionized farm tractors and their implements. While the
Ferguson System was still under patent, other manufacturers developed new hitching systems to try to fend off some of Ferguson's competitive advantage. For example, International Harvester's
Farmall tractors gained a two-point "Fast Hitch", and John Deere had a power lift that was somewhat similar to the more flexible Ferguson invention. Once the patent protection expired on the three-point hitch, it became an industry standard.
Almost every tractor today features Ferguson's three-point linkage or a derivative of it. This hitch allows for easy attachment and detachment of implements while allowing the implement to function as a part of the tractor, almost as if it were attached by a fixed mount. Previously, when the implement hit an obstacle, the towing link broke or the tractor flipped over. Ferguson's idea was to combine a connection via two lower and one upper lift arms that were connected to a hydraulic lifting ram. The ram was, in turn, connected to the upper of the three links so the increased drag (as when a plough hits a rock) caused the hydraulics to lift the implement until the obstacle was passed.
Recently,
Bobcat's patent on its front loader connection (inspired by these earlier systems) has expired, and compact tractors are now being outfitted with quick-connect attachments for their
front-end loaders.
Power take-off systems and hydraulics
In addition to towing an implement or supplying tractive power through the wheels, most tractors have a means to transfer power to another machine such as a
baler
A baler or hay baler is a piece of farm machinery used to compress a cut and raked crop (such as hay, cotton, flax straw, salt marsh hay, or silage) into compact bales that are easy to handle, transport, and store. Often, bales are config ...
,
swather, or
mower
A mower is a person or machine that cuts (mows) grass or other plants that grow on the ground. Usually mowing is distinguished from reaping, which uses similar implements, but is the traditional term for harvesting grain crops, e.g. with reape ...
. Unless it functions solely by pulling it through or over the ground, a towed implement needs its own power source (such as a baler or combine with a separate engine) or else a means of transmitting power from the tractor to the mechanical operations of the equipment.
Early tractors used
belts or cables wrapped around the
flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device that uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy, a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, a ...
or a separate belt pulley to power stationary equipment, such as a threshing machine, buzz saw, silage blower, or stationary baler. In most cases, it was impractical for the tractor and equipment to move with a flexible belt or cable between them, so this system required the tractor to remain in one location, with the work brought to the equipment, or the tractor to be relocated at each turn and the power set-up reapplied (as in cable-drawn plowing systems used in early steam tractor operations).

Modern tractors use a
power take-off
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is one of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and power transmission#Mechanical power, transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate ...
(PTO) shaft to provide rotary power to machinery that may be stationary or pulled. The PTO shaft generally is at the rear of the tractor, and can be connected to an implement that is either towed by a drawbar or a three-point hitch. This eliminates the need for a separate, implement-mounted power source, which is almost never seen in modern farm equipment. It is also optional to get a front PTO as well when buying a new tractor.
Virtually all modern tractors can also provide external
hydraulic fluid
A hydraulic fluid or hydraulic liquid is the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water. Examples of equipment that might use hydraulic fluids are excavators and backho ...
and
electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
al power to the equipment they are towing, either by hoses or wires.
Operation
Modern tractors have many electrical switches and levers in the cab for controlling the multitude of different functions available on the tractor.
Pedals
Some modern farm tractors retain a traditional
manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canadian English, Canada, British English, the United Kingdom and American English, the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed ...
; increasingly they have hydraulically driven powershift
transmissions and CVT, which vastly simplify operation.
Those with powershift transmissions have identical pedal arrangements on the floor for the operator to actuate, replacing a
clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that allows an output shaft to be disconnected from a rotating input shaft. The clutch's input shaft is typically attached to a motor, while the clutch's output shaft is connected to the mechanism that does th ...
pedal on the far left with an inching pedal that cuts off hydraulic flow to the clutches. Twinned
brake
A brake is a machine, mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for Acceleration, slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of ...
pedals – one each for left and right side wheels – are placed together on the right side. Some have a pedal for a foot
throttle
A throttle is a mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by construction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ha ...
on the far right. Unlike automobiles, throttle speed can also be controlled by a hand-operated lever ("hand throttle"), which may be set to a fixed position. This helps provide a constant speed in field work. It also helps provide continuous power for stationary tractors that are operating an implement by
PTO shaft or axle driven belt. The foot throttle gives the operator more automobile-like control over the speed of a mobile tractor in any operation.
Some modern tractors also have (or offer as optional equipment) a button on the gear stick for controlling the clutch, in addition to the standard pedal, allowing for gear changes and the tractor to be brought to a stop without using the foot pedal to engage the clutch. Others have a button for temporarily increasing throttle speed to improve hydraulic flow to implements, such as a front end loader bucket.
Independent left and right brake pedals are provided to allow improved steering (by engaging the side one wishes to turn to, slowing or stopping its wheel) and improved traction in soft and slippery conditions (by transferring rotation to the wheel with better grip). Some users prefer to lock both pedals together, or utilize a partial lock that allows the left pedal to be depressed independently but engages both when the right is applied. This may be in the form of a swinging or sliding bolt that may be readily engaged or disengaged in the field without tools.
Foot pedal throttle control is mostly a returning feature of newer tractors. In the
UK, foot pedal use to control engine speed while travelling on the road is mandatory. Some tractors, especially those designed for row-crop work, have a 'de-accelerator' pedal, which operates in the reverse fashion of an automobile throttle, slowing the engine when applied. This allows control over the speed of a tractor with its throttle set high for work, as when repeatedly slowing to make U-turns at the end of crop rows in fields.
A front-facing foot button is traditionally included just ahead of the driver's seat (designed to be pressed by the operator's heel) to engage the rear
differential lock (diff-lock), which prevents wheel slip. The differential normally allows driving wheels to operate at their own speeds, as required, for example, by the different radius each takes in a turn. This allows the outside wheel to travel faster than the inside wheel, thereby traveling further during a turn. In low-traction conditions on a soft surface, the same mechanism can allow one wheel to slip, wasting its torque and further reducing traction. The differential lock overrides this, forcing both wheels to turn at the same speed, reducing wheel slip and improving traction. Care must be taken to unlock the differential before turning, usually by hitting the pedal a second time, since the tractor with good traction cannot perform a turn with the diff-lock engaged. In many modern tractors, this pedal is replaced with an electrical switch.
Levers and switches
Many functions once controlled with levers have been replaced with some model of electrical switch with the rise of indirect computer controlling of functions in modern tractors.
Until the late of the 1950s, tractors had a single register of gears, hence one gear stick, often with three to five forward gears and one reverse. Then, group gears were introduced, and another gear stick was added. Later, control of the forward-reverse direction was moved to a special stick attached at the side of the steering wheel, which allowed forward or reverse travel in any gear. Now, with
CVTs or other gear types, fewer sticks control the transmission, and some are replaced with electrical switches or are totally computer-controlled.
The three-point hitch was controlled with a lever for adjusting the position, or as with the earliest ones, just the function for raising or lowering the hitch. With modern electrical systems, it is often replaced with a potentiometer for the lower bound position and another one for the upper bound, and a switch allowing automatic adjustment of the hitch between these settings.
The external hydraulics also originally had levers, but now are often replaced with some form of electrical switch; the same is true for the
power take-off
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is one of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and power transmission#Mechanical power, transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate ...
shaft.
Safety
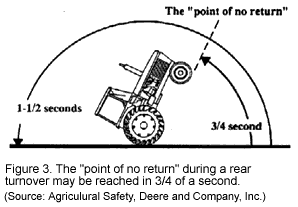

Agriculture in the United States is one of the most hazardous industries, only surpassed
by mining and construction. No other farm machine is so identified with the
hazard
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would potentially allow them to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that ...
s of production agriculture as the tractor.
Tractor-related injuries account for approximately 32% of the fatalities and 6% of the nonfatal injuries in agriculture. Over 50% is attributed to tractor overturns.
[Donham, K., D. Osterberg, M.L. Meyers, and C. Lehtola. 1999. Final report tractor risk abatement and control: the policy conference, September 10–12, 1997. The University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa.]
The
roll-over protection structure
A rollover protection structure or rollover protection system (ROPS) ( or ) is a system or structure intended to protect equipment operators and motorists from injuries caused by vehicle overturns or rollovers. Like rollcages and rollbars in c ...
(ROPS) and seat belt, when worn, are the most important safety devices to protect operators from death during tractor
overturn
''Overturn'' is a video game developed by Japanese company Studio Zan for WiiWare. It was released in Japan on December 2, 2008, in North America on August 3, 2009, and in Europe on February 12, 2010, by Gamebridge as ''Overturn: Mecha Wars''.
...
s.
Modern tractors have a ROPS to prevent an operator from being crushed when overturning. This is especially important in open-air tractors, where the ROPS is a steel beam that extends above the operator's seat. For tractors with operator cabs, the ROPS is part
of the
frame
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
of the cab. A ROPS with enclosed cab further reduces the likelihood of serious injury because the operator is protected by the sides and windows of the cab.
These structures were first required by legislation in Sweden in 1959. Before they were required, some farmers died when their tractors rolled on top of them. Row-crop tractors, before ROPS, were particularly dangerous because of their 'tricycle' design with the two front wheels spaced close together and angled inward toward the ground. Some
farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer ...
s were killed by rollovers while operating tractors along
steep slopes
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a Line (mathematics), line is a number that describes the direction (geometry), direction of the line on a plane (geometry), plane. Often denoted by the letter ''m'', slope is calculated as the ratio of t ...
. Others have been killed while attempting to tow or pull an excessive load from above axle height, or when cold weather caused the tires to freeze to the ground, in both cases causing the tractor to pivot around the rear axle.
ROPS were first required in the United States in 1986, non-retroactively. ROPS adoption by farmers is thus incomplete. To treat this problem, CROPS (cost-effective roll-over protection structures) have been developed to encourage farmers to retrofit older tractors.
[
For the ROPS to work as designed, the operator must stay within its protective frame and wear the seat belt.
In addition to ROPS, U.S. manufacturers add instructional seats on tractors with enclosed cabs. The tractors have a ROPS with seatbelts for both the operator and passenger. This instructional seat is intended to be used for training new tractor operators, but can also be used to diagnose machine problems.]International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
M ...
's ISO standard 23205:2014 specifies the minimum design and performance requirements for an instructional seat and states that the instructional seat is neither intended for, nor is it designed for use by children.
Applications and variations
Farm
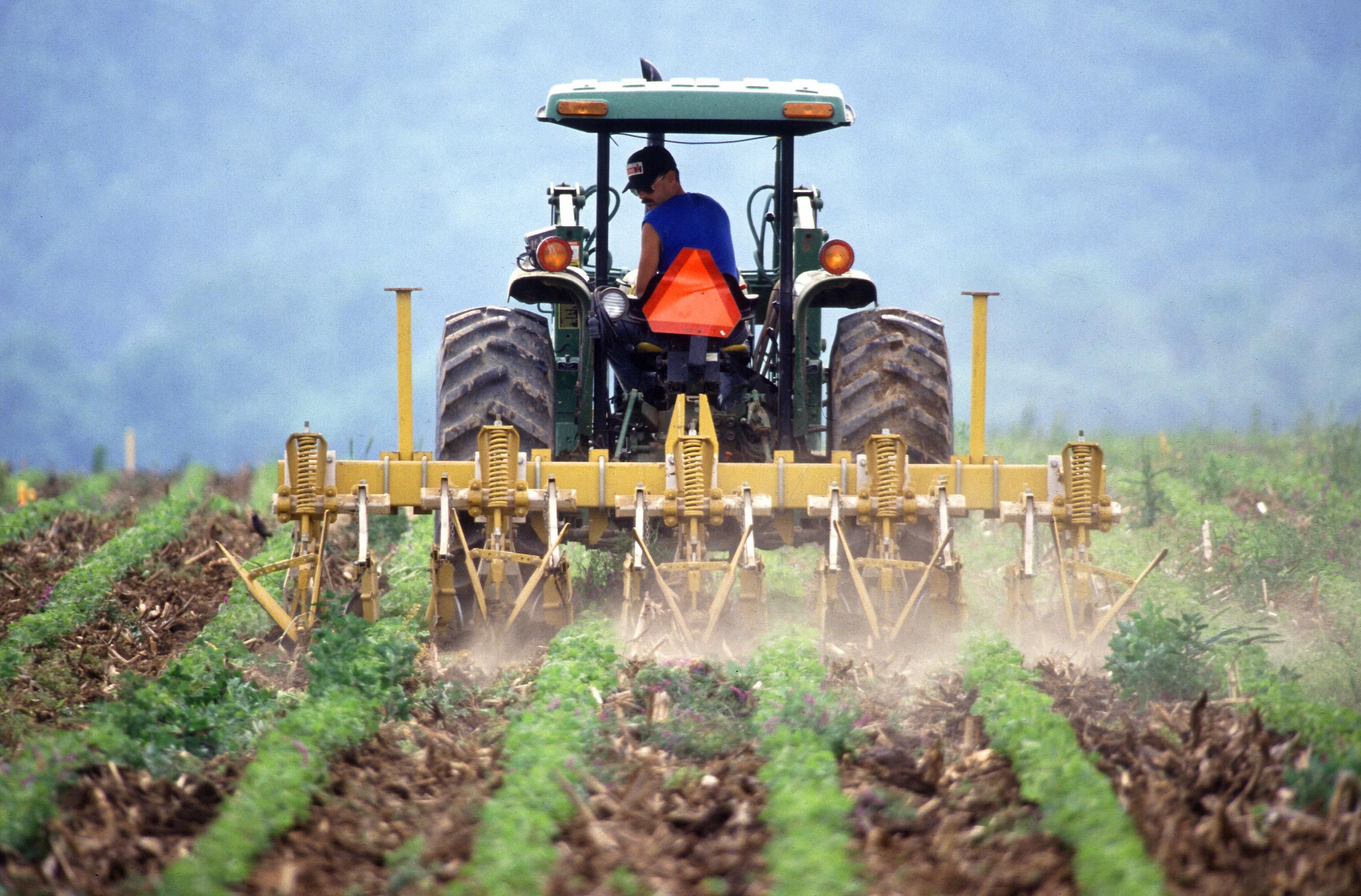
 The most common use of the term "tractor" is for the
The most common use of the term "tractor" is for the vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
s used on farm
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used fo ...
s. The farm tractor is used for pulling or pushing agricultural
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created f ...
machinery or trailers, for plow
A plough or (Differences between American and British spellings, US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs ...
ing, tilling, disking, harrowing, planting, and similar tasks.
 A variety of specialty farm tractors have been developed for particular uses. These include "row crop" tractors with adjustable tread width to allow the tractor to pass down rows of
A variety of specialty farm tractors have been developed for particular uses. These include "row crop" tractors with adjustable tread width to allow the tractor to pass down rows of cereals
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize (Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, suc ...
, maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, tomatoes
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originated from and was d ...
or other crops without crushing the plants, "wheatland" or "standard" tractors with fixed wheels and a lower center of gravity for plowing and other heavy field work for broadcast crops, and "high crop" tractors with adjustable tread and increased ground clearance, often used in the cultivation of cotton and other high-growing row crop plant operations, and "utility tractors", typically smaller tractors with a low center of gravity and short turning radius, used for general purposes around the farmstead. Many utility tractors are used for nonfarm grading, landscape maintenance and excavation purposes, particularly with loaders, backhoes, pallet forks and similar devices. Small garden or lawn tractors designed for suburban and semirural gardening and landscape maintenance are produced in a variety of configurations, and also find numerous uses on a farmstead.
Some farm-type tractors are found elsewhere than on farms: with large universities' gardening departments, in public parks, or for highway workman use with blowtorch
A blowtorch, also referred to as a blowlamp, is an ambient air fuel-burning tool used for applying flame and heat to various applications, usually in metalworking, but occasionally for foods like crème brûlée.
Description
Early blowtorches ...
cylinders strapped to the sides and a pneumatic drill air compressor
An air compressor is a machine that takes ambient air from the surroundings and discharges it at a higher pressure. It is an application of a gas compressor and a Pneumatics, pneumatic device that energy conversion, converts mechanical power (from ...
permanently fastened over the power take-off
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is one of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and power transmission#Mechanical power, transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate ...
. These are often fitted with grass (turf) tyres which are less damaging to soft surfaces than agricultural tires.
Precision
Space technology
Space technology is technology for use in outer space. Space technology includes space vehicles such as spacecraft, satellites, space stations and orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicles; :Spacecraft communication, deep-space communication; :S ...
has been incorporated into agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
in the form of GPS devices, and robust on-board computers
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ('' computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', ...
installed as optional features on farm tractors. These technologies are used in modern, precision farming
Precision agriculture (PA) is a management strategy that gathers, processes and analyzes temporal, spatial and individual plant and animal data and combines it with other information to support management decisions according to estimated varia ...
techniques. The spin-off
Spin-off, Spin Off, Spin-Off, or Spinoff may refer to: Entertainment and media
*Spinoff (media), a media work derived from an existing work
*''The Spinoff'', a New Zealand current affairs magazine
* ''Spin Off'' (Canadian game show), a 2013 Canad ...
s from the space race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
have actually facilitated automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
in plowing and the use of autosteer systems ( drone on tractors that are manned but only steered at the end of a row), the idea being to neither overlap and use more fuel nor leave streaks when performing jobs such as cultivating. Several tractor companies have also been working on producing a driverless tractor
A driverless tractor is an autonomous farm vehicle that delivers a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds for the purposes of tillage and other agricultural tasks. It is considered driverless because it operates without the presence of a ...
.
Engineering
 The durability and engine power of tractors made them very suitable for engineering tasks. Tractors can be fitted with engineering tools such as dozer blades,
The durability and engine power of tractors made them very suitable for engineering tasks. Tractors can be fitted with engineering tools such as dozer blades, bucket
A bucket is typically a watertight, vertical Cylinder (geometry), cylinder or Truncation (geometry), truncated Cone (geometry), cone or square, with an open top and a flat bottom that is attached to a semicircular carrying handle (grip), handle ...
s, hoes, rippers, etc. The most common attachments for the front of a tractor are dozer blades or buckets. When attached to engineering tools, the tractor is called an engineering vehicle
Heavy equipment, heavy machinery, earthmovers, construction vehicles, or construction equipment, refers to heavy-duty vehicles specially designed to execute construction tasks, most frequently involving earthwork operations or other large con ...
.
A bulldozer
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large tractor equipped with a metal #Blade, blade at the front for pushing material (soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock) during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous tracks, ...
is a track-type tractor with a blade attached in the front and a rope-winch behind. Bulldozers are very powerful tractors and have excellent ground-hold, as their main tasks are to push or drag.
Bulldozers have been further modified over time to evolve into new machines which are capable of working in ways that the original bulldozer can not. One example is that loader tractors were created by removing the blade and substituting a large volume bucket and hydraulic arms which can raise and lower the bucket, thus making it useful for scooping up earth, rock and similar loose material to load it into trucks.
A front-loader or loader is a tractor with an engineering tool which consists of two hydraulic powered arms on either side of the front engine compartment and a tilting implement. This is usually a wide-open box called a bucket, but other common attachments are a pallet fork and a bale grappler.
Other modifications to the original bulldozer include making the machine smaller to let it operate in small work areas where movement is limited. Also, tiny wheeled loaders, officially called skid-steer loader
A skid loader, skid-steer loader (SSL), or skidsteer is any of a class of compact heavy equipment with lift arms that can attach to a wide variety of buckets and other labor-saving tools or attachments.
The wheels typically have no separate ste ...
s, but nicknamed "Bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the wildcat, bay lynx, or red lynx, is one of the four extant species within the medium-sized wild cat genus '' Lynx''. Native to North America, it ranges from southern Canada through most of the c ...
" after the original manufacturer, are particularly suited for small excavation projects in confined areas.
Backhoe
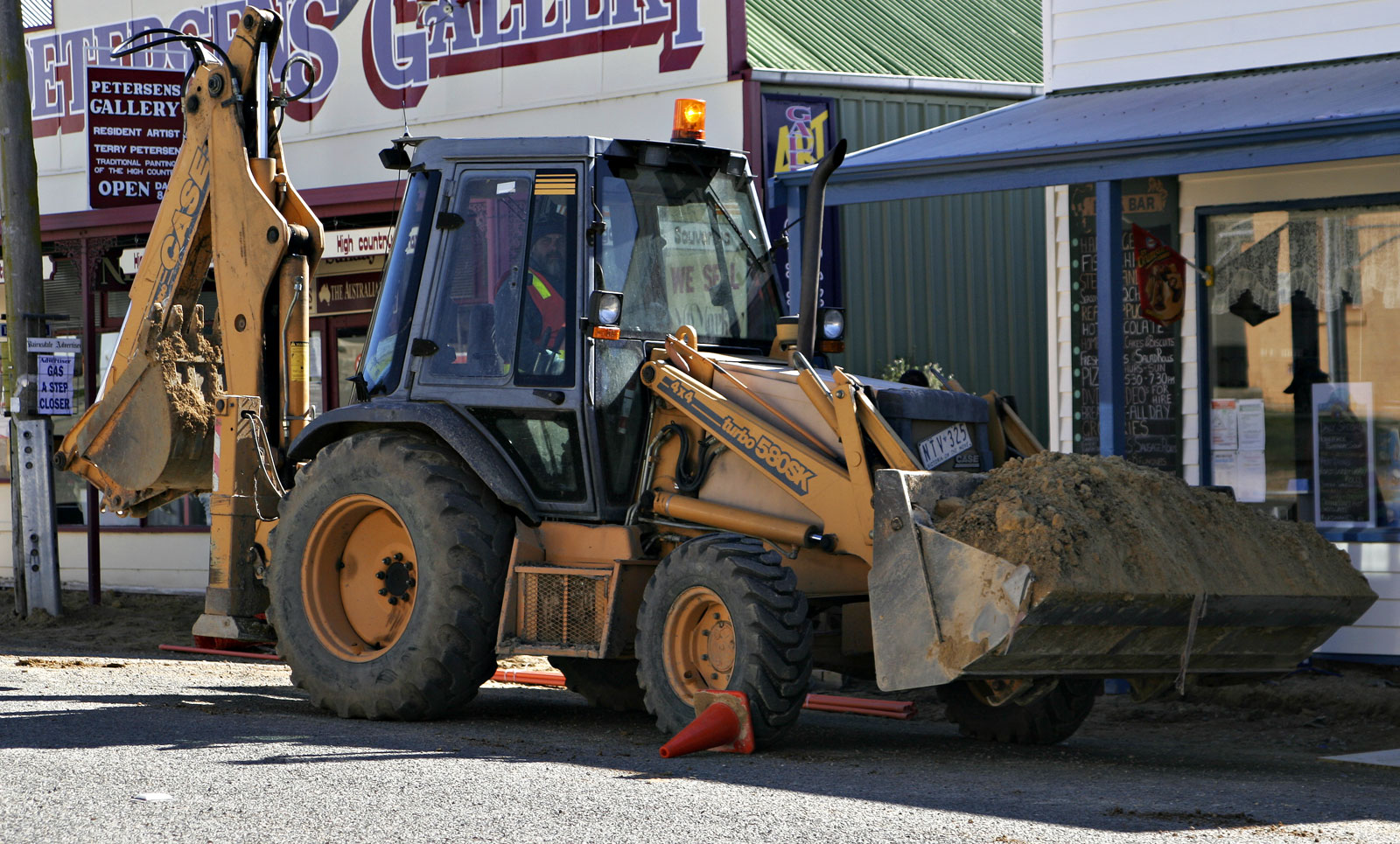 The most common variation of the classic farm tractor is the backhoe, also called a backhoe-loader. As the name implies, it has a loader assembly on the front and a
The most common variation of the classic farm tractor is the backhoe, also called a backhoe-loader. As the name implies, it has a loader assembly on the front and a backhoe
A backhoe is a type of excavating equipment, or excavator, consisting of a digging bucket on the end of a two-part articulated arm. It is typically mounted on the back of a tractor or loader (equipment), front loader, the latter forming a "backh ...
on the back. Backhoes attach to a three-point hitch on farm or industrial tractors. Industrial tractors are often heavier in construction, particularly with regards to the use of a steel grill for protection from rocks and the use of construction tires. When the backhoe is permanently attached, the machine usually has a seat that can swivel to the rear to face the hoe controls. Removable backhoe attachments almost always have a separate seat on the attachment.
Backhoe-loaders are very common and can be used for a wide variety of tasks: construction, small demolitions, light transportation of building materials, powering building equipment, digging holes, loading trucks, breaking asphalt
Asphalt most often refers to:
* Bitumen, also known as "liquid asphalt cement" or simply "asphalt", a viscous form of petroleum mainly used as a binder in asphalt concrete
* Asphalt concrete, a mixture of bitumen with coarse and fine aggregates, u ...
and paving roads. Some buckets have retractable bottoms, enabling them to empty their loads more quickly and efficiently. Buckets with retractable bottoms are also often used for grading and scratching off sand. The front assembly may be a removable attachment or permanently mounted. Often the bucket can be replaced with other devices or tools.
Their relatively small frames and precise controls make backhoe-loaders very useful and common in urban engineering projects, such as construction and repair
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installat ...
s in areas too small for larger equipment. Their versatility and compact size make them one of the most popular urban construction vehicles.
In the UK and Ireland, the word " JCB" is used colloquial
Colloquialism (also called ''colloquial language'', ''colloquial speech'', ''everyday language'', or ''general parlance'') is the linguistic style used for casual and informal communication. It is the most common form of speech in conversation amo ...
ly as a genericized trademark
A generic trademark, also known as a genericized trademark or proprietary eponym, is a trademark or brand name that, because of its popularity or significance, has become the generic term for, or synonymous with, a general class of products or ...
for any such type of engineering vehicle. The term JCB now appears in the Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
, although it is still legally a trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a form of intellectual property that consists of a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination that identifies a Good (economics and accounting), product or Service (economics), service f ...
of J. C. Bamford Ltd. The term "digger" is also commonly used.
Compact utility
 A compact utility tractor (CUT) is a smaller version of an agricultural tractor, but designed primarily for landscaping and estate management tasks, rather than for planting and harvesting on a commercial scale. Typical CUTs range from with available
A compact utility tractor (CUT) is a smaller version of an agricultural tractor, but designed primarily for landscaping and estate management tasks, rather than for planting and harvesting on a commercial scale. Typical CUTs range from with available power take-off
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is one of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and power transmission#Mechanical power, transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate ...
(PTO) power ranging from . CUTs are often equipped with both a mid-mounted and a standard rear PTO, especially those below . The mid-mount PTO shaft typically rotates at/near 2000 rpm and is typically used to power mid-mount finish mowers, front-mounted snow blower
A snow blower or snowblower or snow thrower is a machine for removing snow from an area where it is problematic, such as a driveway, sidewalk, roadway, railroad track, ice rink, or runway. The commonly used term "snow blower" is a misnomer, a ...
s or front-mounted rotary brooms. The rear PTO is standardized at 540 rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines.
One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 def ...
for the North American markets, but in some parts of the world, a dual 540/1000 rpm PTO is standard, and implements are available for either standard in those markets.

 One of the most common attachments for a CUT is the front-end loader or FEL. Like the larger agricultural tractors, a CUT will have an adjustable, hydraulically controlled
One of the most common attachments for a CUT is the front-end loader or FEL. Like the larger agricultural tractors, a CUT will have an adjustable, hydraulically controlled three-point hitch
The three-point hitch (British English: three-point linkage) is a widely used type of hitch for attaching ploughs and other farm equipment, implements to an agricultural or industrial tractor. The three points resemble either a triangle, or the le ...
. Typically, a CUT will have four-wheel drive, or more correctly four-wheel assist. Modern CUTs often feature hydrostatic transmissions, but many variants of gear-drive transmissions are also offered from low priced, simple gear transmissions to synchronized transmissions to advanced glide-shift transmissions. All modern CUTs feature government-mandated roll over protection structures just like agricultural tractors. The most well-known brands in North America include Kubota
is a Japanese multinational corporation based in Osaka. It was established in 1890. The corporation produces many products including tractors and other agricultural machinery, Heavy equipment, construction equipment, engines, vending machines, P ...
, John Deere Tractor, New Holland Ag
New Holland is a global full-line agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in New Holland, Pennsylvania, New Holland, Pennsylvania, and now based in Turin, Italy. New Holland's products include tractors, combine harvesters, balers, forage har ...
, Case-Farmall and Massey Ferguson. Although less common, compact backhoes are often attached to compact utility tractors.
Compact utility tractors require special, smaller implements than full-sized agricultural tractors. Very common implements include the box blade, the grader
A grader, also commonly referred to as a road grader, motor grader, or simply blade, is a form of heavy equipment with a long blade used to create a flat surface during Grading (engineering), grading. Although the earliest models were towed b ...
blade, the landscape rake, the post hole digger (or post hole auger), the rotary cutter (slasher or a brush hog), a mid- or rear-mount finish mower, a broadcast seeder, a subsoiler
A subsoiler or flat lifter is a tractor-mounted farm implement used for deep tillage, loosening and breaking up soil at depths below the levels worked by moldboard ploughs, disc harrows, or rototillers. Most such tools will break up and turn ove ...
and the rototiller
A cultivator (also known as a rotavator) is a piece of agricultural equipment used for secondary tillage. One sense of the name refers to frames with ''teeth'' (also called ''shanks'') that pierce the soil as they are dragged through it li ...
(rotary tiller). In northern climates, a rear-mounted snow blower is very common; some smaller CUT models are available with front-mounted snow blowers powered by mid-PTO shafts. Implement brands outnumber tractor brands, so CUT owners have a wide selection of implements.
For small-scale farming or large-scale gardening, some planting and harvesting implements are sized for CUTs. One- and two-row planting units are commonly available, as are cultivators, sprayers and different types of seeders (slit, rotary and drop). One of the first CUTs offered for small farms of three to 30 acres and for small jobs on larger farms was a three-wheeled unit, with the rear wheel being the drive wheel, offered by Sears & Roebuck in 1954 and priced at $598 for the basic model.
An even smaller variant of the compact utility tractor is the ''subcompact utility tractor''. Although these tractors are often barely larger than a riding lawn mower, these tractors have all the same features of a compact tractor, such as a three-point hitch, power steering, four-wheel-drive, and front-end loader. These tractors are generally marketed towards homeowners who intend to mostly use them for lawn mowing, with the occasional light landscaping task.
Standard
The earliest tractors were called "standard" tractors, and were intended almost solely for plowing and harrowing
In agriculture, a harrow is a farm implement used for surface tillage. It is used after ploughing for breaking up and smoothing out the surface of the soil. The purpose of harrowing is to break up clods and to provide a soil structure, calle ...
before planting, which were difficult tasks for humans and draft animals. They were characterized by a low, rearward seating position, fixed-width tread, and low ground clearance. These early tractors were cumbersome, and ill-suited to enter a field of planted row crops for weed control. The "standard" tractor definition is no longer in current use. However, tractors with fixed wheel spacing and a low center of gravity are well-suited as loaders, forklifts and backhoes, so that the configuration continues in use without the "standard" nomenclature.
Row-crop
A general-purpose or row-crop tractor is tailored specifically to the growing of crops grown in rows, and most especially to cultivating these crops. These tractors are universal machines, capable of both primary tillage and cultivation of a crop.
 The row-crop tractor category evolved rather than appearing overnight, but the
The row-crop tractor category evolved rather than appearing overnight, but the International Harvester
The International Harvester Company (often abbreviated IH or International) was an American manufacturer of agricultural and construction equipment, automobiles, commercial trucks, lawn and garden products, household equipment, and more. It wa ...
(IH) Farmall is often considered the "first" tractor of the category. Some earlier tractors of the 1910s and 1920s approached the form factor from the heavier side, as did motorized cultivators from the lighter side, but the Farmall brought all of the salient features together into one package, with a capable distribution network to ensure its commercial success. In the new form factor that the Farmall popularized, the cultivator
A cultivator (also known as a rotavator) is a piece of agricultural machinery, agricultural equipment used for secondary tillage. One sense of the name refers to frames with ''teeth'' (also called ''shanks'') that pierce the soil as they ar ...
was mounted in the front so it was easily visible. Additionally, the tractor had a narrow front end; the front tires were spaced very closely and angled in toward the bottom. The back wheels straddled two rows with their spacing adjustable depending on row spacing, and the unit could cultivate four rows at once. Where wide front wheels were used, they often could be adjusted as well. Tractors with non-adjustable spacing were called "standard" or "wheatland", and were chiefly meant for pulling plows or other towed implements, typically with a lower overall tractor height than row-crop models.
From 1924 until 1963, Farmalls were the largest selling row-crop tractors.
To compete, John Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
designed the Model C, which had a wide front and could cultivate three rows at once. Only 112 prototypes were made, as Deere realized it would lose sales to Farmall if its model did less. In 1928, Deere released the Model C anyway, only as the Model GP (General Purpose) to avoid confusion with the Model D when ordered over the then unclear telephone.Case IH
Case IH is an American agricultural machinery manufacturer. It was created in 1985 when Tenneco bought selected assets of the agricultural division from International Harvester and merged it into its J.I. Case Company (IH then became Navistar) ...
and New Holland of CNH Industrial
CNH Industrial N.V. is an Italian-American multinational corporation with global headquarters in Basildon, United Kingdom, but controlled and mostly owned by the multinational investment company Exor (company), Exor, which in turn is controlled ...
both produce high horsepower front-wheel-assist row crop tractors with available rear tracks. Case IH also has a four-wheel drive track system called Rowtrac.
John Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
has an extensive line of available row crop tractors ranging from .
Modern row crop tractors have rollover protection systems in the form of a reinforced cab or a roll bar.
Garden
 Garden tractors, sometimes called lawn tractors, are small, light tractors designed for use in domestic
Garden tractors, sometimes called lawn tractors, are small, light tractors designed for use in domestic garden
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate bot ...
s, lawns, and small estates. Lawn tractors are designed for cutting grass
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family (biology), family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and spe ...
and snow removal, while garden tractors are for small property cultivation. In the U.S., the term riding lawn mower today often is used to refer to mid- or rear-engined machines. Front-engined tractor layout machines designed primarily for cutting grass and light towing are called lawn tractors
A lawn mower (also known as a grass cutter or simply mower, also often spelled lawnmower) is a device utilizing one or more revolving blades (or a reel) to cut a grass surface to an even height. The height of the cut grass may be fixed by the ...
; heavier-duty tractors of similar size are garden tractors. Garden tractors are capable of mounting a wider array of attachments than lawn tractors. Unlike lawn tractors and rear-engined riding mowers, garden tractors are powered by horizontal-crankshaft engines with a belt-drive to transaxle
A transaxle is single mechanical device which combines the functions of an automobile's transmission (mechanics), transmission, axle, and differential (mechanics), differential into one integrated assembly. It can be produced in both manual tra ...
-type transmissions (usually of four or five speeds, although some may also have two-speed reduction gearboxes, drive-shafts, or hydrostatic or hydraulic drives). Garden tractors from Wheel Horse, Cub Cadet, Economy (Power King)
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
, John Deere, Massey Ferguson
Massey Ferguson is an agricultural machinery manufacturer, established in 1953 through the merger of farm equipment makers Massey-Harris of Canada and the Ferguson Company of Ireland. It was based in Coventry then moved to Beauvais in 2003 when ...
and Case Ingersoll are built in this manner. The engines are generally one- or two-cylinder petrol (gasoline) engines, although diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compr ...
models are also available, especially in Europe. Typically, diesel-powered garden tractors are larger and heavier-duty than gasoline-powered units and compare more similarly to compact utility tractors.
Visually, the distinction between a garden tractor and a lawn tractor is often hard to make – generally, garden tractors are more sturdily built, with stronger frames, 12-inch or larger wheels mounted with multiple lugs (most lawn tractors have a single bolt or clip on the hub), heavier transaxles, and ability to accommodate a wide range of front, belly, and rear mounted attachments.
Two-wheel
Although most people think primarily of four-wheel vehicles when they think of tractors, a tractor may have one or more axles. The key benefit is the power itself, which only takes one axle to provide. Single-axle tractors, more often called two-wheel tractor
Two-wheel tractor or walking tractor (, , ) are generic terms understood in the US and in parts of Europe to represent a single-axle tractor, which is a tractor with one axle, self-powered and self-propelled, which can pull and power various f ...
s or walk-behind tractors, have had many users since the introduction of the internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
tractors. They tend to be small and affordable, this was especially true before the 1960s when a walk-behind tractor could often be more affordable than a two-axle tractor of comparable power. Today's compact utility tractors and advanced garden tractors may negate most of that market advantage, but two-wheel tractors still have a following, especially among those who already own one. Countries where two-wheel tractors are especially prevalent today include Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, and other Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
countries. Most two-wheel tractors today are specialty tractors made for one purpose, such as snow blower
A snow blower or snowblower or snow thrower is a machine for removing snow from an area where it is problematic, such as a driveway, sidewalk, roadway, railroad track, ice rink, or runway. The commonly used term "snow blower" is a misnomer, a ...
s, push tillers, and self propelled push mowers.
Orchard
Tractors tailored to use in fruit orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit tree, fruit- or nut (fruit), nut-producing trees that are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also so ...
s typically have features suited to passing under tree branches with impunity. These include a lower overall profile; reduced tree-branch-snagging risk (via underslung exhaust pipes rather than smoke-stack-style exhaust, and large sheetmetal cowling
A cowling (or cowl) is the removable covering of a vehicle's engine, most often found on automobiles, motorcycles, airplanes, and on outboard boat motors. On airplanes, cowlings are used to reduce drag and to cool the engine. On boats, cowlings ...
s and fairings that allow branches to deflect and slide off rather than catch); spark arrestor
A spark arrester (sometimes spark arrestor) is any device which prevents the emission of flammable debris from combustion sources, such as internal combustion engines, fireplaces, and wood-burning stoves.
Spark arresters play a critical role i ...
s on the exhaust tips; and often wire cages to protect the operator from snags.
Automobile conversions and other homemade versions



 The ingenuity of farm mechanics, coupled in some cases with OEM or aftermarket assistance, has often resulted in the conversion of automobiles for use as farm tractors. In the United States, this trend was especially strong from the 1910s through 1950s. It began early in the development of vehicles powered by internal combustion engines, with blacksmiths and amateur mechanics tinkering in their shops. Especially during the
The ingenuity of farm mechanics, coupled in some cases with OEM or aftermarket assistance, has often resulted in the conversion of automobiles for use as farm tractors. In the United States, this trend was especially strong from the 1910s through 1950s. It began early in the development of vehicles powered by internal combustion engines, with blacksmiths and amateur mechanics tinkering in their shops. Especially during the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, dozens of manufacturers (Montgomery Ward
Montgomery Ward is the name of two successive U.S. retail corporations. The original Montgomery Ward & Co. was a mail-order business and later a department store chain that operated between 1872 and 2001; its common nickname was "Monkey Wards". ...
among them) marketed aftermarket kits for converting Ford Model T
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by the Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first mass-affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. Th ...
s for use as tractors.Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, although this term was usually reserved for automobiles converted to horse-drawn buggy use when gasoline was unavailable or unaffordable. During the same period, another common name was " Doodlebug", after the popular kit by the same name.) Ford even considered producing an "official" optional kit.World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, a shortage of tractors in Sweden led to the development of the so-called EPA tractor ( EPA was a chain of discount stores and it was often used to signify something lacking in quality). An EPA tractor was simply an automobile, truck, or lorry, with the passenger space cut off behind the front seats, equipped with two gearboxes in a row. When done to an older car with a ladder frame, the result was similar to a tractor and could be used as one. After the war it remained popular as a way for young people without a driver's license
A driver's license, driving licence, or driving permit is a legal authorization, or the official document confirming such an authorization, for a specific individual to operate one or more types of motorized vehicles—such as motorcycles, ca ...
to own something similar to a car. Since it was legally seen as a tractor, it could be driven from 16 years of age and only required a tractor license. Eventually, the legal loophole was closed and no new EPA tractors were allowed to be made, but the remaining ones were still legal, which led to inflated prices and many protests from people who preferred EPA tractors to ordinary cars.
The Swedish government eventually replaced them with the so called "A-tractor" which now had its speed limited to 30 km/h and allowed people aged 16 and older to drive the cars with a moped license.
The German occupation of Italy during World resulted in a severe shortage of mechanized farm equipment. The destruction of tractors was a sort of scorched-earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy of destroying everything that allows an enemy military force to be able to fight a war, including the deprivation and destruction of water, food, humans, animals, plants and any kind of tools and i ...
strategy used to reduce the independence of the conquered. The shortage of tractors in that area of Europe was the origin of Lamborghini
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. ( , ), usually referred to as Lamborghini or colloquially Lambo, is an Italian manufacturer of luxury sports cars and SUVs based in Sant'Agata Bolognese. The company is owned by the Volkswagen Group through its su ...
. The war was also the inspiration for dual-purpose vehicles such as the Land Rover
Land Rover is a brand of predominantly four-wheel drive, off-road capable vehicles, owned by British multinational car manufacturer Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), since 2008 a subsidiary of India's Tata Motors. JLR builds Land Rovers in Brazil ...
. Based on the Jeep, the company made a vehicle that combined PTO, tillage, 4wd, and transportation.
In March 1975, a similar type of vehicle was introduced in Sweden, the ''A tractor'' rom ''arbetstraktor'' (work tractor) the main difference is an A tractor has a top speed of 30 km/h. This is usually done by fitting two gearboxes in a row and only using one. The Volvo Duett
The Volvo Duett is an automobile from Volvo that was in production from 1953 until 1969.
The name ''Duett'' was intended to signify a car that could be used as a delivery vehicle during the week and as a comfortable sedan away from work.
The Duet ...
was, for a long time, the primary choice for conversion to an EPA or A tractor, but since supplies have dried up, other cars have been used, in most cases another Volvo
The Volvo Group (; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distribution and sale of truck ...
. The SFRO is a Swedish organization advocating homebuilt and modified vehicles.
Another type of homemade tractors are ones that are fabricated from scratch. The " from scratch" description is relative, as often individual components will be repurposed from earlier vehicles or machinery (e.g., engines, gearboxes, axle housings), but the tractor's overall chassis
A chassis (, ; plural ''chassis'' from French châssis ) is the load-bearing framework of a manufactured object, which structurally supports the object in its construction and function. An example of a chassis is a vehicle frame, the underpart ...
is essentially designed and built by the owner (e.g., a frame is welded from bar stock
Bar stock, also (colloquially) known as blank, slug or billet, is a common form of raw purified metal, used by industry to manufacture metal parts and products. Bar stock is available in a variety of extrusion shapes and lengths. The most commo ...
channel stock, angle stock, flat stock, etc.). As with automobile conversions, the heyday of this type of tractor, at least in developed economies, lies in the past, when there were large populations of blue-collar workers for whom metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
and farming
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
were prevalent parts of their lives. (For example, many 19th- and 20th-century New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
and Midwestern
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
machinists and factory workers had grown up on farms.) Backyard fabrication was a natural activity to them (whereas it might seem daunting to most people today).
Nomenclature
The term "tractor" (US and Canada) or "tractor unit" (UK) is also applied to:
* Road tractors, tractor unit
A tractor unit, also known as a truck unit, lorry unit, power unit, prime mover, ten-wheeler, semi-tractor, semi-truck, semi-lorry, tractor cab, truck cab, lorry cab, big rig tractor, big rig truck or big rig lorry or simply a tractor, truck, ...
s or traction heads, familiar as the front end of an articulated lorry
A semi-trailer truck (also known by a wide variety of other terms – see below) is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-trailer attaches to the tractor with a type of hitch called a ...
/ semi-trailer truck
A semi-trailer truck (also known by a wide variety of other terms – see below) is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-trailer attaches to the tractor with a type of hitch called ...
. They are heavy-duty vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
s with large engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ge ...
s and several axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotation, rotating wheel and axle, wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In ...
s.
** The majority of these tractors are designed to pull long semi-trailer
A semi-trailer is a trailer (vehicle), trailer without a front axle. The combination of a semi-trailer and a tractor truck is called a ''semi-trailer truck'' (also known simply as a "semi-trailer", "tractor trailer", or "semi" in the United Sta ...
s, most often to transport freight over a significant distance, and is connected to the trailer with a fifth wheel coupling. In England, this type of "tractor" is often called an " artic cab" (short for "articulated" cab).
** A minority is the ballast tractor
A ballast tractor is a specially weighted tractor unit of a heavy hauler combination. It is designed to utilize a drawbar to pull or push heavy or exceptionally large trailer loads which are loaded in a hydraulic modular trailer. When feasi ...
, whose load is hauled from a drawbar.
* Pushback tractors are used on airports to move aircraft on the ground, most commonly pushing aircraft away from their parking stands.
* Locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for ...
tractors (engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ge ...
s) or rail car movers – the amalgamation of machine
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromol ...
s, electrical generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an extern ...
s, controls and devices that comprise the traction component of railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
s
* Artillery tractor
An artillery tractor, also referred to as a gun tractor, is a specialized heavy-duty form of tractor unit used to tow artillery pieces of varying weights and calibres. It may be wheeled, tracked, or half-tracked.
Traction
There are two m ...
s – vehicles used to tow artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
pieces of varying weights.
* NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
and other space agencies use very large tractors to move large launch vehicle
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage ...
s and Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
s between their hangars and launch pad
A launch pad is an above-ground facility from which a rocket-powered missile or space vehicle is vertically launched. The term ''launch pad'' can be used to describe just the central launch platform (mobile launcher platform), or the entire c ...
s.
* A pipe-tractor is a device used for conveying advanced instruments into pipes for measurement and data logging, and the purging of well holes, sewer pipes and other inaccessible tubes.
File:UP Diesel.png, Diesel-electric locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for ...
at work
File:Trackmobile.jpg, A Trackmobile 4150
File:Tractor-powered Roadroller.jpg, A tractor-driven road roller
A road roller (sometimes called a roller-compactor, or just roller) is a compactor-type engineering vehicle used to compact soil, gravel, concrete, or asphalt in the construction of roads and foundations. Similar rollers are used also at lan ...
File:Airplane pushing vehicle.jpg, Aircraft pushback tractor
File:Backing it in 2.jpg, Road tractor pulling a flatbed trailer
File:Mercedes-Benz-Museum 2015-01 by-RaBoe 187.jpg, Unimog 70200
The Unimog 70200 is the first series production model of the Unimog series, made by . It was manufactured in Boehringer's Göppingen plant from June 1948 to April 1951. In total, 600 units of the 70200 were made. Manufacture of the Unimog was sol ...
File:Tractor for hauling logs, Maine IMG 2036.JPG, A Lombard steam log hauler
Nebraska tests
Nebraska tractor tests are tests mandated by the Nebraska
Nebraska ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Ka ...
Tractor Test Law and administered by the University of Nebraska
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, that objectively test the performance of all brands of tractors, 40 horsepower or more, sold in Nebraska. In the 1910s and 1920s, an era of snake oil
Snake oil is a term used to describe False advertising, deceptive marketing, health care fraud, or a scam. Similarly, snake oil salesman is a common label used to describe someone who sells, promotes, or is a general proponent of some valueless ...
sales and advertising tactics, the Nebraska tests helped farmers throughout North America to see through marketing claims and make informed buying decisions. The tests continue today, making sure tractors fulfill the manufacturer's advertised claims.
Manufacturers
Some of the many tractor manufacturers and brands worldwide include:
* Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
* Case IH
Case IH is an American agricultural machinery manufacturer. It was created in 1985 when Tenneco bought selected assets of the agricultural division from International Harvester and merged it into its J.I. Case Company (IH then became Navistar) ...
* Caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder ...
* Claas
* Challenger
* Deutz-Fahr
* Fendt
Fendt is a German agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in 1930 by Xaver Fendt in Marktoberdorf, Allgäu region, Germany. Fendt manufactures tractors, combine harvesters, balers, telescopic handlers and row crop Planter (farm implement), ...
* ITMCO
* Iseki
* JCB
* John Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
* Lamborghini
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. ( , ), usually referred to as Lamborghini or colloquially Lambo, is an Italian manufacturer of luxury sports cars and SUVs based in Sant'Agata Bolognese. The company is owned by the Volkswagen Group through its su ...
* Landini
* Kubota
is a Japanese multinational corporation based in Osaka. It was established in 1890. The corporation produces many products including tractors and other agricultural machinery, Heavy equipment, construction equipment, engines, vending machines, P ...
* Mahindra Tractors
Mahindra Tractors is an Indian agricultural machinery manufacturer. It is part of the Mahindra & Mahindra corporation. In 2010, Mahindra became the world's highest-selling tractor brand by volume. Mahindra's largest consumer base is in India. I ...
* Massey Ferguson
Massey Ferguson is an agricultural machinery manufacturer, established in 1953 through the merger of farm equipment makers Massey-Harris of Canada and the Ferguson Company of Ireland. It was based in Coventry then moved to Beauvais in 2003 when ...
* McCormick
* Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz (), commonly referred to simply as Mercedes and occasionally as Benz, is a German automotive brand that was founded in 1926. Mercedes-Benz AG (a subsidiary of the Mercedes-Benz Group, established in 2019) is based in Stuttgart, ...
* New Holland
* SAME
* Steyr
Steyr (; ) is a statutory city (Austria), statutory city, located in the Austrian federal state of Upper Austria. It is the administrative capital, though not part of Steyr-Land District. Steyr is Austria's 12th most populated town and the 3rd lar ...
* TAFE
Technical and further education or simply TAFE () is the common name in Australia for vocational education, as a subset of tertiary education. TAFE institutions provide a wide range of predominantly vocational courses. Colloquially also known ...
* Ursus
* Valtra
* Zetor
Zetor (since January 1, 2007, officially Zetor Tractors a.s.) is a Czech agricultural machinery manufacturer. It was founded in 1946. The company is based in Brno, Czech Republic. Since June 29, 2002, the only shareholder has been a Slovak com ...
In addition to commercial manufacturers, the Open Source Ecology group has developed several working prototypes of an open source hardware
Open-source hardware (OSH, OSHW) consists of physical artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by this open-source culture movemen ...
tractor called the LifeTrac as part of its Global Village Construction Set.
Gallery
File:Trator.JPG, A Ford tractor in Brazil
File:Tractors.jpg, Modern tractors, an Ursus 11054 and Fendt
Fendt is a German agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in 1930 by Xaver Fendt in Marktoberdorf, Allgäu region, Germany. Fendt manufactures tractors, combine harvesters, balers, telescopic handlers and row crop Planter (farm implement), ...
820
File:A John Deere 9320 at a construction site in the US.jpg, A John Deere
Deere & Company, Trade name, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, Transmission (mechanical device), transmi ...
9320 at a construction site in the US
File:Mahindra tractor model1.jpg, A scale model of a modern Ursus and Fendt tractor in Germany
File:Balnain 1997a (1).jpg, Farm tractor in Balnain, Scotland
File:Traktor na oranju.JPG, A tractor pulling a chisel plow in Slovenia
See also
* Agricultural machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the machine (mechanical), mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are list of agricultural machinery, many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractor ...
* Artillery tractor
An artillery tractor, also referred to as a gun tractor, is a specialized heavy-duty form of tractor unit used to tow artillery pieces of varying weights and calibres. It may be wheeled, tracked, or half-tracked.
Traction
There are two m ...
* Ballast tractor
A ballast tractor is a specially weighted tractor unit of a heavy hauler combination. It is designed to utilize a drawbar to pull or push heavy or exceptionally large trailer loads which are loaded in a hydraulic modular trailer. When feasi ...
* Big Bud 747
The Big Bud 747 or 16V-747 Big Bud is a large, custom-made farm tractor built in Havre, Montana, Havre, Montana, in 1977. It has 1100 horsepower. It is billed by the owners and exhibitors as the "World's Largest Farm Tractor". It is about twice t ...
, the world's largest farm tractor
* Driverless tractor
A driverless tractor is an autonomous farm vehicle that delivers a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds for the purposes of tillage and other agricultural tasks. It is considered driverless because it operates without the presence of a ...
* Heavy equipment
Heavy equipment, heavy machinery, earthmovers, construction vehicles, or construction equipment, refers to heavy-duty vehicles specially designed to execute construction tasks, most frequently involving earthwork operations or other large con ...
* Lester F. Larsen Tractor Museum
* Non-road engine
Non-road engines (or non-road mobile machinery in the European Union) are internal combustion engines that are used for other purposes than a motor vehicle that is used on a public roadway. The term is commonly used by regulators to classify t ...
* Power take-off
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is one of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and power transmission#Mechanical power, transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate ...
* Railcar mover
* Terminal tractor
A terminal tractor, known in the United States as a shag truck, shunt truck, spotter truck, spotting tractor, yard truck, yard shifter, yard dog, yard goat, yard horse, yard mule, yard jockey, yard spotter, hostler, or mule, is a kind of semi-t ...
* Tractor pulling
* Tractor unit
A tractor unit, also known as a truck unit, lorry unit, power unit, prime mover, ten-wheeler, semi-tractor, semi-truck, semi-lorry, tractor cab, truck cab, lorry cab, big rig tractor, big rig truck or big rig lorry or simply a tractor, truck, ...
* Two-wheel tractor
Two-wheel tractor or walking tractor (, , ) are generic terms understood in the US and in parts of Europe to represent a single-axle tractor, which is a tractor with one axle, self-powered and self-propelled, which can pull and power various f ...
* Unimog 70200
The Unimog 70200 is the first series production model of the Unimog series, made by . It was manufactured in Boehringer's Göppingen plant from June 1948 to April 1951. In total, 600 units of the 70200 were made. Manufacture of the Unimog was sol ...
* DT-20
References
}
External links
Tractor information
Purdue University Tractor Safety Article re: ROPS, PTO, etcNebraska Tractor Test LaboratoryHistorical Tractor Test Reports and Manufacturers' Literature
Reports on 400+ models 1903–2006
A History of Tractors
at the Canada Agriculture Museum
Tractor safety
EU Working Group on Agricultural Tractors – Work Safety
* EU Directives on tractor design
o
(National Agricultural Safety Database The Centers for Agricultural Safety and Health (CASH) are a set of 12 NIOSH-funded agencies focused on occupational health in industry involving food or plant products, such as fishing, forestry, and agriculture. The agencies were established in 199 ...
)
Tractor Safety
(National Safety Council
The National Safety Council (NSC) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit, public service organization promoting health and safety in the United States. Headquartered in Itasca, Illinois, NSC is a member organization, founded in 1913 and granted a congress ...
)
Adaptive Tractor Overturn Prediction System
CDC – Agricultural Safety: Cost-effective Rollover Protective Structures – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic
{{Authority control
Agricultural machinery
Engineering vehicles
Heavy equipment
Vehicles introduced in 1901
 A tractor is an
A tractor is an 
 In 1908, the Saunderson Tractor and Implement Co. of
In 1908, the Saunderson Tractor and Implement Co. of  The first three-point hitches were experimented with in 1917. After
The first three-point hitches were experimented with in 1917. After  The classic farm tractor is a simple open
The classic farm tractor is a simple open 
 Four-wheel drive tractors began to appear in the 1960s. Some four-wheel drive tractors have the standard "two large, two small" configuration typical of smaller tractors, while some have four large, powered wheels. The larger tractors are typically an articulated, center-hinged design steered by hydraulic cylinders that move the forward power unit while the trailing unit is not steered separately.
Four-wheel drive tractors began to appear in the 1960s. Some four-wheel drive tractors have the standard "two large, two small" configuration typical of smaller tractors, while some have four large, powered wheels. The larger tractors are typically an articulated, center-hinged design steered by hydraulic cylinders that move the forward power unit while the trailing unit is not steered separately.
 In the early 21st century, articulated or non-articulated, steerable multitrack tractors have largely supplanted the Caterpillar type for farm use. Larger types of modern farm tractors include articulated four-wheel or eight-wheel drive units with one or two power units which are hinged in the middle and steered by hydraulic clutches or pumps. A relatively recent development is the replacement of wheels or steel crawler-type tracks with flexible, steel-reinforced rubber tracks, usually powered by hydrostatic or completely hydraulic driving mechanisms. The configuration of these tractors bears little resemblance to the classic farm tractor design.
In the early 21st century, articulated or non-articulated, steerable multitrack tractors have largely supplanted the Caterpillar type for farm use. Larger types of modern farm tractors include articulated four-wheel or eight-wheel drive units with one or two power units which are hinged in the middle and steered by hydraulic clutches or pumps. A relatively recent development is the replacement of wheels or steel crawler-type tracks with flexible, steel-reinforced rubber tracks, usually powered by hydrostatic or completely hydraulic driving mechanisms. The configuration of these tractors bears little resemblance to the classic farm tractor design.
 The three-point hitch revolutionized farm tractors and their implements. While the Ferguson System was still under patent, other manufacturers developed new hitching systems to try to fend off some of Ferguson's competitive advantage. For example, International Harvester's Farmall tractors gained a two-point "Fast Hitch", and John Deere had a power lift that was somewhat similar to the more flexible Ferguson invention. Once the patent protection expired on the three-point hitch, it became an industry standard.
Almost every tractor today features Ferguson's three-point linkage or a derivative of it. This hitch allows for easy attachment and detachment of implements while allowing the implement to function as a part of the tractor, almost as if it were attached by a fixed mount. Previously, when the implement hit an obstacle, the towing link broke or the tractor flipped over. Ferguson's idea was to combine a connection via two lower and one upper lift arms that were connected to a hydraulic lifting ram. The ram was, in turn, connected to the upper of the three links so the increased drag (as when a plough hits a rock) caused the hydraulics to lift the implement until the obstacle was passed.
Recently, Bobcat's patent on its front loader connection (inspired by these earlier systems) has expired, and compact tractors are now being outfitted with quick-connect attachments for their front-end loaders.
The three-point hitch revolutionized farm tractors and their implements. While the Ferguson System was still under patent, other manufacturers developed new hitching systems to try to fend off some of Ferguson's competitive advantage. For example, International Harvester's Farmall tractors gained a two-point "Fast Hitch", and John Deere had a power lift that was somewhat similar to the more flexible Ferguson invention. Once the patent protection expired on the three-point hitch, it became an industry standard.
Almost every tractor today features Ferguson's three-point linkage or a derivative of it. This hitch allows for easy attachment and detachment of implements while allowing the implement to function as a part of the tractor, almost as if it were attached by a fixed mount. Previously, when the implement hit an obstacle, the towing link broke or the tractor flipped over. Ferguson's idea was to combine a connection via two lower and one upper lift arms that were connected to a hydraulic lifting ram. The ram was, in turn, connected to the upper of the three links so the increased drag (as when a plough hits a rock) caused the hydraulics to lift the implement until the obstacle was passed.
Recently, Bobcat's patent on its front loader connection (inspired by these earlier systems) has expired, and compact tractors are now being outfitted with quick-connect attachments for their front-end loaders.
 Modern tractors use a
Modern tractors use a 
 Agriculture in the United States is one of the most hazardous industries, only surpassed
by mining and construction. No other farm machine is so identified with the
Agriculture in the United States is one of the most hazardous industries, only surpassed
by mining and construction. No other farm machine is so identified with the 
 The most common use of the term "tractor" is for the
The most common use of the term "tractor" is for the  A variety of specialty farm tractors have been developed for particular uses. These include "row crop" tractors with adjustable tread width to allow the tractor to pass down rows of
A variety of specialty farm tractors have been developed for particular uses. These include "row crop" tractors with adjustable tread width to allow the tractor to pass down rows of  The durability and engine power of tractors made them very suitable for engineering tasks. Tractors can be fitted with engineering tools such as dozer blades,
The durability and engine power of tractors made them very suitable for engineering tasks. Tractors can be fitted with engineering tools such as dozer blades,  The most common variation of the classic farm tractor is the backhoe, also called a backhoe-loader. As the name implies, it has a loader assembly on the front and a
The most common variation of the classic farm tractor is the backhoe, also called a backhoe-loader. As the name implies, it has a loader assembly on the front and a  A compact utility tractor (CUT) is a smaller version of an agricultural tractor, but designed primarily for landscaping and estate management tasks, rather than for planting and harvesting on a commercial scale. Typical CUTs range from with available
A compact utility tractor (CUT) is a smaller version of an agricultural tractor, but designed primarily for landscaping and estate management tasks, rather than for planting and harvesting on a commercial scale. Typical CUTs range from with available 
 One of the most common attachments for a CUT is the front-end loader or FEL. Like the larger agricultural tractors, a CUT will have an adjustable, hydraulically controlled
One of the most common attachments for a CUT is the front-end loader or FEL. Like the larger agricultural tractors, a CUT will have an adjustable, hydraulically controlled  Garden tractors, sometimes called lawn tractors, are small, light tractors designed for use in domestic
Garden tractors, sometimes called lawn tractors, are small, light tractors designed for use in domestic 



 The ingenuity of farm mechanics, coupled in some cases with OEM or aftermarket assistance, has often resulted in the conversion of automobiles for use as farm tractors. In the United States, this trend was especially strong from the 1910s through 1950s. It began early in the development of vehicles powered by internal combustion engines, with blacksmiths and amateur mechanics tinkering in their shops. Especially during the
The ingenuity of farm mechanics, coupled in some cases with OEM or aftermarket assistance, has often resulted in the conversion of automobiles for use as farm tractors. In the United States, this trend was especially strong from the 1910s through 1950s. It began early in the development of vehicles powered by internal combustion engines, with blacksmiths and amateur mechanics tinkering in their shops. Especially during the