|
Hazard
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would potentially allow them to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that harm being realized in a specific ''incident'', combined with the magnitude of potential harm, make up its risk. This term is often used synonymously in colloquial speech. Hazards can be classified in several ways which are not mutually exclusive. They can be classified by ''causing actor'' (for example, natural or anthropogenic), by ''physical nature'' (e.g. biological or chemical) or by ''type of damage'' (e.g., health hazard or environmental hazard). Examples of natural disasters with highly harmful impacts on a society are floods, droughts, earthquakes, tropical cyclones, lightning strikes, volcanic activity and wildfires. Technological and anthropogenic hazards include, for example, structural collapses, transport accidents, acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Hazard
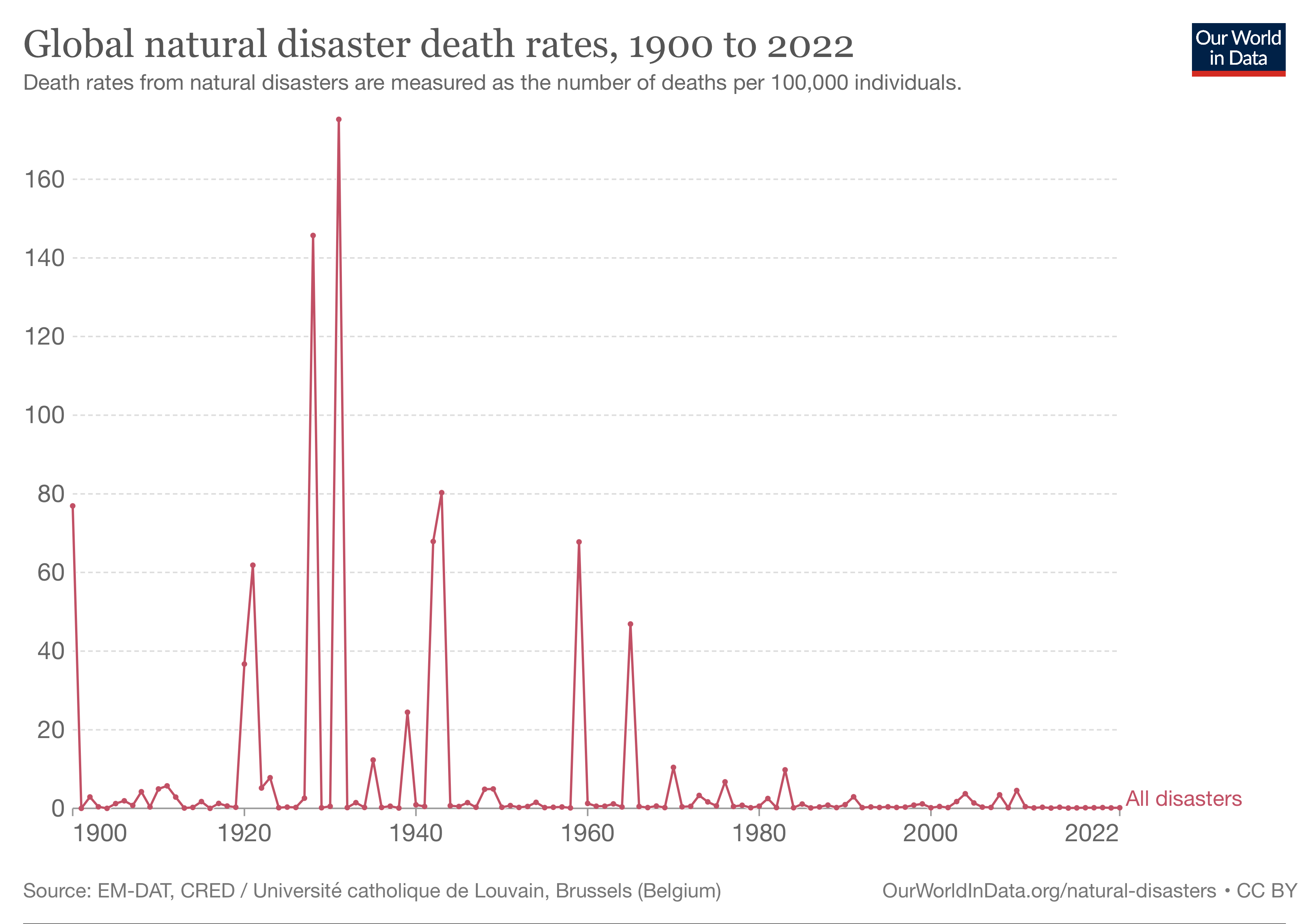
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides - including submarine landslides, tropical cyclones, volcanic activity and wildfires. Additional natural hazards include blizzards, dust storms, firestorms, hails, ice storms, sinkholes, thunderstorms, tornadoes and tsunamis. A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property. It typically causes economic damage. How bad the damage is depends on how well people are prepared for disasters and how strong the buildings, roads, and other structures are. Scholars have argued the term "natural disaster" is unsuitable and should be abandoned. Instead, the simpler term ''disaster'' could be used. At the same time, the type of hazard would be specified. A disaster happens when a natural or human-made hazard impacts a vulnerable community. It r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides - including submarine landslides, tropical cyclones, volcanism, volcanic activity and wildfires. Additional natural hazards include blizzards, dust storms, firestorms, hails, ice storms, sinkholes, thunderstorms, tornadoes and tsunamis. A natural disaster can cause list of natural disasters by death toll, loss of life or property damage, damage property. It typically causes economic damage. How bad the damage is depends on how well people are Emergency management, prepared for disasters and how strong the buildings, roads, and other Infrastructure, structures are. Scholars have argued the term "natural disaster" is unsuitable and should be abandoned. Instead, the simpler term ''disaster'' could be used. At the same time, the type of haz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Hazard
Environmental hazards are hazards that affect biomes or ecosystems. Well known examples include oil spills, water pollution, slash and burn deforestation, air pollution, ground fissures, and Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, build-up of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Types Environmental hazards can be categorized in many different ways. Broadly, environmental hazards are categorized as chemical, physical, biological, or psychological, or a combination of these. Chemical hazards are substances that can cause harm or damage to humans, animals, or the environment. They can be in the form of solids, liquids, gases, mists, dusts, fumes, and vapors. Exposure can occur through inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, or direct contact. Chemical hazards include substances such as pesticides, solvents, acids, bases, reactive metals, and poisonous gases. Exposure to these substances can result in health effects such as skin irritation, respiratory problems, organ damage, neurological effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Hazard
A biological hazard, or biohazard, is a biological substance that poses a threat (or is a hazard) to the health of living organisms, primarily humans. This could include a sample of a microorganism, virus or toxin that can adversely affect human health. A biohazard could also be a substance harmful to other living beings. The term and Hazard symbol#Biohazard sign, its associated symbol are generally used as a warning, so that those potentially exposed to the substances will know to take precautions. The biohazard symbol was developed in 1966 by Charles Baldwin, an environmental-health engineer working for the Dow Chemical Company on their containment products. It is used in the labeling of biological materials that carry a significant health risk, including viral samples and used hypodermic needles. In Unicode, the biohazard symbol is U+2623 (☣). ANSI Z535/OSHA/ISO regulation Biohazardous safety issues are identified with specified labels, signs and paragraphs established by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Hazard
Chemical hazards are Hazard, hazards present in Dangerous goods, hazardous chemicals and hazardous materials. Exposure to certain chemicals can cause Acute health hazard, acute or long-term adverse health effects. Chemical hazards are usually classified separately from biological hazards (biohazards). Chemical hazards are classified into groups that include Asphyxiant gas, asphyxiants, Corrosive substance, corrosives, Irritant (biology), irritants, sensitization (immunology), sensitizers, carcinogens, mutagens, teratogens, reactants, and Combustibility and flammability, flammables. In the workplace, exposure to chemical hazards is a type of occupational hazard. The use of personal protective equipment may substantially reduce the risk of adverse health effects from contact with hazardous materials. Long-term exposure to chemical hazards such as Silicon dioxide, silica dust, Exhaust gas, engine exhausts, tobacco smoke, and lead (among others) have been shown to increase risk of Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire (Bushfires in Australia, in Australia), desert fire, grass fire, hill fire, Peat#Peat fires, peat fire, prairie fire, vegetation fire, or veld fire. Some natural forest ecosystems Fire ecology, depend on wildfire. Modern forest management often engages in prescribed burns to mitigate fire risk and promote natural forest cycles. However, controlled burns can turn into wildfires by mistake. Wildfires can be classified by cause of ignition, physical properties, combustible material present, and the effect of weather on the fire. Wildfire severity results from a combination of factors such as available fuels, physical setting, and weather. Climatic cycles with wet periods that create substantial fuels, followed by drought and heat, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. One ISO standard, international standard definition of risk is the "effect of uncertainty on objectives". The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas (business, economics, Environmental science, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security, security, privacy, etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and general guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Environmental issues, Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding. Examples for human changes are land use changes such as deforestation and Wetland conservation, removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees. Global environmental issues also influence causes of floods, namely climate change which causes an Effects of climate change on the water cycle, intensification of the water cycle and sea level rise. For example, climate change makes Extreme weather, extreme weather events more frequent and stronger. This leads to more intense floods and increased flood risk. Natural types of floods include riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Emergency Management Agency
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS), initially created under President Jimmy Carter by Presidential Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1978 and implemented by two Executive order (United States), Executive Orders on April 1, 1979. The agency's primary purpose is to coordinate the response to a disaster that has occurred in the United States and that overwhelms the resources of local and U.S. state, state authorities. The governor of the state in which the disaster occurs must declare a state of emergency and formally request from the President of the United States, president that FEMA and the Federal government of the United States, federal government respond to the disaster. The only exception to the state's gubernatorial declaration requirement occurs when an emergency or disaster takes place on federal property or to a federal asset—for example, the 1995 Oklahoma City bombing, bombing of the Alfred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |