Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of violence against
non-combatant
Non-combatant is a term of art in the law of war and international humanitarian law to refer to civilians who are not taking a direct part in hostilities. People such as combat medics and military chaplains, who are members of the belligerent arm ...
s to achieve political or ideological aims.
The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during
peacetime
Peace is a state of harmony in the absence of hostility and violence, and everything that discusses achieving human welfare through justice and peaceful conditions. In a societal sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such a ...
or in the context of
war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
against
non-combatant
Non-combatant is a term of art in the law of war and international humanitarian law to refer to civilians who are not taking a direct part in hostilities. People such as combat medics and military chaplains, who are members of the belligerent arm ...
s. There are various different
definitions of terrorism
There is no legal or scientific consensus on the definition of terrorism. Various legal systems and government agencies use different definitions of terrorism, and governments have been reluctant to formulate an agreed-upon legally-binding defin ...
, with no universal agreement about it.
Different definitions of terrorism emphasize its
randomness
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of definite pattern or predictability in information. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. ...
, its aim to instill
fear
Fear is an unpleasant emotion that arises in response to perception, perceived dangers or threats. Fear causes physiological and psychological changes. It may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the ...
, and its broader impact beyond its immediate victims.
Modern terrorism, evolving from earlier iterations, employs various tactics to pursue political goals, often leveraging fear as a strategic tool to influence decision makers. By targeting densely populated public areas such as transportation hubs, airports, shopping centers, tourist attractions, and nightlife venues, terrorists aim to instill widespread insecurity, prompting
policy changes through
psychological manipulation
In psychology, manipulation is defined as an action designed to influence or control another person, usually in an underhanded or subtle manner which facilitates one's personal aims. Methods someone may use to manipulate another person may includ ...
and undermining confidence in security measures.
The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism"
originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century,
but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during
the Troubles
The Troubles () were an ethno-nationalist conflict in Northern Ireland that lasted for about 30 years from the late 1960s to 1998. Also known internationally as the Northern Ireland conflict, it began in the late 1960s and is usually deemed t ...
in Northern Ireland, the
Basque conflict
The Basque conflict, also known as the Spain–ETA conflict, was an armed and political conflict from 1959 to 2011 between Spain and the Basque National Liberation Movement, a group of social and political Basque nationalism, Basque organization ...
and the
Israeli–Palestinian conflict
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is an ongoing military and political conflict about Territory, land and self-determination within the territory of the former Mandatory Palestine. Key aspects of the conflict include the Israeli occupation ...
. The increased use of
suicide attack
A suicide attack (also known by a wide variety of other names, see below) is a deliberate attack in which the perpetrators knowingly sacrifice their own lives as part of the attack. These attacks are a form of murder–suicide that is ofte ...
s from the 1980s onwards was typified by the
September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
in the United States in 2001. The
Global Terrorism Database
The Global Terrorism Database (GTD) is a database of terrorist incidents from 1970 onward. As of May 2021, the list extended through 2019 recording over 200,000 incidents, although data from 1993 is excluded. The database is maintained by the Na ...
, maintained by the
University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD i ...
, has recorded more than 61,000 incidents of non-state terrorism, resulting in at least 140,000 deaths between 2000 and 2014.
Various organizations and
countries
A country is a distinct part of the Earth, world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, List of states with limited r ...
have used terrorism to achieve their objectives. These include
left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social ...
and
right-wing
Right-wing politics is the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position based on natural law, economics, authority, property ...
political organizations,
nationalist groups,
religious groups,
revolutionaries
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates for, a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective to describe something producing a major and sudden impact on society.
Definition
The term—bot ...
, and
ruling governments.
In recent decades, hybrid terrorist organizations have emerged, incorporating both military and political arms.
State terrorism
State terrorism is terrorism conducted by a state against its own citizens or another state's citizens.
It contrasts with '' state-sponsored terrorism'', in which a violent non-state actor conducts an act of terror under sponsorship of a state. ...
, with its institutionalized instrumentation of terror tactics through
massacres
A massacre is an event of killing people who are not engaged in hostilities or are defenseless. It is generally used to describe a targeted killing of civilians en masse by an armed group or person.
The word is a loan of a French term for "b ...
,
genocides,
forced disappearances
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person with the support or acquiescence of a State (polity), state followed by a refusal to acknowledge the person's fate or whereabouts with the i ...
,
carpet bombings and
torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons including corporal punishment, punishment, forced confession, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimid ...
, is a deadlier form of terrorism than non-state terrorism.
Etymology and definition
Etymology

The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the
Jacobin Club
The Society of the Friends of the Constitution (), renamed the Society of the Jacobins, Friends of Freedom and Equality () after 1792 and commonly known as the Jacobin Club () or simply the Jacobins (; ), was the most influential List of polit ...
during the "
Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (French: ''La Terreur'', literally "The Terror") was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the French First Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and Capital punishment in France, nu ...
" in the
French Revolution. "Terror is nothing other than justice, prompt, severe, inflexible", said Jacobin leader
Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre ferv ...
. In 1795,
Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January ew Style, NS1729 – 9 July 1797) was an Anglo-Irish Politician, statesman, journalist, writer, literary critic, philosopher, and parliamentary orator who is regarded as the founder of the Social philosophy, soc ...
denounced the Jacobins for letting "thousands of those hell-hounds called Terrorists ... loose on the people" of France.
John Calvin
John Calvin (; ; ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French Christian theology, theologian, pastor and Protestant Reformers, reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of C ...
's rule over Geneva in the 16th century has also been described as a reign of terror.
The terms "terrorism" and "terrorist" gained renewed currency in the 1970s as a result of the
Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ) is a Palestinian nationalism, Palestinian nationalist coalition that is internationally recognized as the official representative of the Palestinians, Palestinian people in both the occupied Pale ...
(PLO), the
Irish Republican Army
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various Resistance movement, resistance organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dominantly Catholic and dedicated to anti-imperiali ...
(IRA), the
Basque separatist group, ETA, and the operations of groups such as the
Red Army Faction
The Red Army Faction (, ; RAF ),See the section "Name" also known as the Baader–Meinhof Group or Baader–Meinhof Gang ( ), was a West German far-left militant group founded in 1970 and active until 1998, considered a terrorist organisat ...
.
Leila Khaled was described as a terrorist in a 1970 issue of ''
Life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
'' magazine. A number of books on terrorism were published in the 1970s. The topic came further to the fore after the
1983 Beirut barracks bombings
On October 23, 1983, two truck bombs were detonated at buildings in Beirut, Lebanon, housing American and French service members of the Multinational Force in Lebanon (MNF), a military peacekeeping operation during the Lebanese Civil War. The ...
and again after the 2001
September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
and the
2002 Bali bombings
The 2002 Bali bombings were a series of terrorist attacks on 12 October 2002 in the tourist district of Kuta on the Indonesian island of Bali. The attacks killed 202 people (including 88 Australians, 38 Indonesians, 23 Britons, and people ...
.
Definition

No definition of terrorism has gained universal agreement. Challenges emerge due to the politically and emotionally charged nature of the term, the double standards used in applying it, and disagreement over the nature of terrorist acts and limits of the right to
self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
.
[Hoffman (1998), p. 23, Se]
the 1 Nov 1998 review by Raymond Bonner
in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' o
Inside Terrorism
/ref>Richard Baxter
Richard Baxter (12 November 1615 – 8 December 1691) was an English Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformist church leader and theologian from Rowton, Shropshire, who has been described as "the chief of English Protestant Schoolmen". He ma ...
, a leading expert on the law of war, was a skeptic: "We have cause to regret that a legal concept of 'terrorism' was ever inflicted upon us. The term is imprecise; it is ambiguous; and above all, it serves no operative legal purpose."[
Different legal systems and government agencies employ diverse definitions of terrorism, with governments showing hesitation in establishing a universally accepted, legally binding definition. ]Title 18 of the United States Code
Title 18 of the United States Code is the main criminal code of the federal government of the United States. The Title deals with federal crimes and criminal procedure. In its coverage, Title 18 is similar to most U.S. state criminal codes ...
defines terrorism as acts that are intended to intimidate or coerce civilians or government. The international community
The international community is a term used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world.
Usage
Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is typically used to imply the ...
has been slow to formulate a universally agreed, legally binding definition of this crime, and has been unable to conclude a Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism
Comprehensive may refer to:
*Comprehensive layout, the page layout of a proposed design as initially presented by the designer to a client.
*Comprehensive school, a state school that does not select its intake on the basis of academic achievement o ...
that incorporates a single, all-encompassing, legally binding, criminal law definition of terrorism. These difficulties arise from the fact that the term "terrorism" is politically and emotionally charged. The international community has instead adopted a series of sectoral conventions that define and criminalize various types of terrorist activities.
Counterterrorism analyst Bruce Hoffman has noted that it is not only individual agencies within the same governmental apparatus that cannot agree on a single definition of terrorism; experts and other long-established scholars in the field are equally incapable of reaching a consensus. In 1992, terrorism studies scholar Alex P. Schmid proposed a simple definition to the United Nations Commission on Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice (CCPCJ) as "peacetime equivalents of war crimes", but it was not accepted.[ Text may have been copied from this source, which is available under a Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) licence. (Pe]
this page
. In 2006, it was estimated that there were over 109 different definitions of terrorism.[Arie W. Kruglanski and Shira Fishman ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' Vol. 15, No. 1 (February 2006), pp. 45–48]
History
Pre-modern terrorism
Early published studies like Paul Wilkinson considered terrorism a product of 19th-century revolutionary politics. Technological developments like the pistol
A pistol is a type of handgun, characterised by a gun barrel, barrel with an integral chamber (firearms), chamber. The word "pistol" derives from the Middle French ''pistolet'' (), meaning a small gun or knife, and first appeared in the Englis ...
and dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish people, Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern German ...
made possible the relentless onslaught of successful attacks and assassinations that shook the 19th-century. For the most part, scholars considered terrorism a modern phenomenon until David C. Rapoport published his seminal article ''Fear and Trembling: Terrorism in Three Religious Traditions'' in 1984.
Rapoport proposed three case studies to demonstrate "ancient lineage" of religious terrorism, which he called "sacred terror": the "Thugs", the Assassins and the Jewish Sicarii Zealots
The Sicarii were a group of Jewish assassins who were active throughout Judaea in the years leading up to and during the First Jewish–Roman War, which took place at the end of the Second Temple period. Often associated with the Zealots (althou ...
. Rapoport argued religious terrorism has been ongoing since ancient times and that "there are signs that it is reviving in new and unusual forms". He is the first to propose that religious doctrines were more important than political rationales for some terrorist groups. Rapoport's work has since become the basis of the model of "New Terrorism" proposed by Bruce Hoffman and developed by other scholars. "New Terrorism" has had an unparalleled impact on policymaking. Critics have pointed out that the model is politically charged and over-simplified. The underlying historical assertions have received less critical attention. According to ''The Oxford Handbook on the History of Terrorism'':
Since the publication of Rapoport's article, it has become seemingly pre-requisite for standard works on terrorism to cite the three case studies and to reproduce uncritically its findings. In lieu of empirical research, authors tend to crudely paraphrase Rapoport and the assumed relevance of "Thuggee" to the study of modern terrorism is taken for granted. Yet the significance of the article is not simply a matter of citations―it has also provided the foundation for what has become known as the "New Terrorism" paradigm. While Rapoport did not suggest which late 20th century groups might exemplify the implied recurrence of "holy terror", Bruce Hoffman, recognized today as one of the world's leading terrorism experts, did not hesitate to do so. A decade after Rapoport's article. Hoffman picked up the mantle and taking the three case studies as inspiration, he formulated a model of contemporary "holy terror" or, as he defined it, "terrorism motivated by a religious imperative". Completely distinct from "secular terrorists", Hoffman argued that "religious terrorists" carry out indiscriminate acts of violence as a divine duty with no consideration for political efficacy―their aim is transcendental and "holy terror" constitutes an end in itself. Hoffman's concept has since been taken up and developed by a number of other writers, including Walter Laquer, Steven Simon and Daniel Benjamen, and rebranded as the "New Terrorism".
Birth of modern terrorism (1850-1890s)
Arguably, the first organization to use modern terrorist techniques was the Irish Republican Brotherhood
The Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB; ) was a secret oath-bound fraternal organisation dedicated to the establishment of an "independent democratic republic" in Ireland between 1858 and 1924.McGee, p. 15. Its counterpart in the United States ...
, founded in 1858 as a revolutionary Irish nationalist group that carried out attacks in England. The group initiated the Fenian dynamite campaign
The Fenian dynamite campaign (also known as the Fenian bombing campaign) was a campaign of political violence orchestrated by Irish republican paramilitary groups in Great Britain from 1881 to 1885. It involved attacks using explosives such as ...
in 1881, one of the first modern terror campaigns. Instead of earlier forms of terrorism based on political assassination, this campaign used timed explosives
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An exp ...
with the express aim of sowing fear in the very heart of metropolitan Britain, in order to achieve political gains.
Another early terrorist-type group was Narodnaya Volya
Narodnaya Volya () was a late 19th-century revolutionary socialist political organization operating in the Russian Empire, which conducted assassinations of government officials in an attempt to overthrow the autocratic Tsarist system. The org ...
, founded in Russia in 1878 as a revolutionary anarchist group inspired by Sergei Nechayev and " propaganda by the deed" theorist Carlo Pisacane.targeted killing
Targeted killing is a form of assassination carried out by governments Extrajudicial killing, outside a judicial procedure or a battlefield.
Since the late 20th century, the legal status of targeted killing has become a subject of contention wit ...
of the 'leaders of oppression', which were to become the hallmark of subsequent violence by small non-state groups, and they were convinced that the developing technologies of the age—such as the invention of dynamite, which they were the first anarchist group to make widespread use of—enabled them to strike directly and with discrimination.anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state w ...
from the state led, in the early 1890s, to France's entry into the '' Ère des attentats'' (1892-1894). This period, characterized by a surge in terrorist acts following Ravachol
François Claudius Ravachol (; born Koenigstein; 14 October 1859 – 11 July 1892) was a French illegalist anarchist mainly known for his terrorist activism, impact, the myths developed around his figure and his influence on the anarchist moveme ...
's bombings, saw several shifts that pushed terrorism toward modern terrorism. As with the Fenian campaign, terrorism shifted from being person-based to location-based, starting with the first attack of that period, the Saint-Germain bombing.
However, other major evolutions emerged during this period: the apparition of lone wolves and the birth of mass or indiscriminate terrorism. Indeed, in the second half of the Ère des attentats, three incidents laid the foundation for mass terrorism within a few months of each other. These were the Liceu bombing, the 13 November 1893 stabbing, and the Café Terminus attack. In each of these attacks, the perpetrators targeted not a specific individual but a collective enemy. Émile Henry, in particular, responsible for the Café Terminus bombing, explicitly claimed the birth of this new form of terrorism, stating that he wanted to 'strike at random'.
Modern terrorism (1900-present)
In 1920 Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky,; ; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky'' was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician, and political theorist. He was a key figure ...
wrote '' Terrorism and Communism'' to justify the Red Terror
The Red Terror () was a campaign of political repression and Mass killing, executions in Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Russia which was carried out by the Bolsheviks, chiefly through the Cheka, the Bolshevik secret police ...
and defend the moral superiority of revolutionary terrorism
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates for, a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective to describe something producing a major and sudden impact on society.
Definition
The term—bot ...
.
The assassination of the Empress of Austria Elisabeth in 1898 resulted in the International Conference of Rome for the Social Defense Against Anarchists, the first international conference against terrorism.
Types of terrorism
Depending on the country, the political system, and the time in history, the types of terrorism are varying.
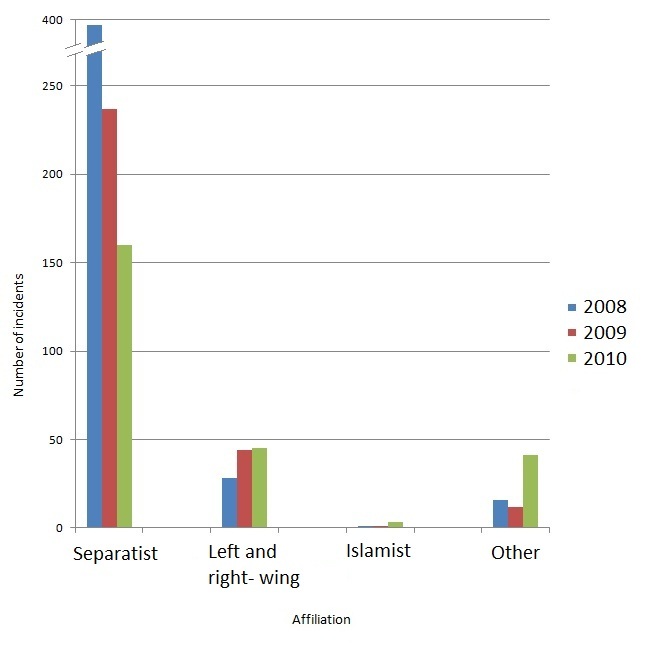 In early 1975, the Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into seven categories:
*
In early 1975, the Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into seven categories:
* Civil disorder
Civil disorder, also known as civil disturbance, civil unrest, civil strife, or turmoil, are situations when law enforcement and security forces struggle to Public order policing, maintain public order or tranquility.
Causes
Any number of thin ...
– A form of collective violence interfering with the peace
Peace is a state of harmony in the absence of hostility and violence, and everything that discusses achieving human welfare through justice and peaceful conditions. In a societal sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (suc ...
, security, and normal functioning of the community.
* Political terrorism – Violent
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence a ...
criminal behaviour designed primarily to generate fear
Fear is an unpleasant emotion that arises in response to perception, perceived dangers or threats. Fear causes physiological and psychological changes. It may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the ...
in the community, or substantial segment of it, for political purposes.
* Non-Political terrorism – Terrorism that is not aimed at political purposes, but which exhibits "conscious design to create and maintain a high degree of fear for coercive
Coercion involves compelling a party to act in an involuntary manner through the use of threats, including threats to use force against that party. It involves a set of forceful actions which violate the free will of an individual in order to in ...
purposes, but the end is individual or collective gain rather than the achievement of a political objective".
* Anonymous terrorism
Anonymous may refer to:
* Anonymity, the state of an individual's identity, or personally identifiable information, being publicly unknown
** Anonymous work, a work of art or literature that has an unnamed or unknown creator or author
* Anonym ...
– In the two decades prior to 2016–19, "fewer than half" of all terrorist attacks were either "claimed by their perpetrators or convincingly attributed by governments to specific terrorist groups". A number of theories have been advanced as to why this has happened.felon
A felony is traditionally considered a crime of high seriousness, whereas a misdemeanor is regarded as less serious. The term "felony" originated from English common law (from the French medieval word "''félonie''") to describe an offense that ...
who takes hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized—such as a relative, employer, law enforcement, or government—to act, o ...
s is a quasi-terrorist, whose methods are similar to those of the genuine terrorist but whose purposes are quite different.
* Limited political terrorism – Genuine political terrorism is characterized by a revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates for, a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective to describe something producing a major and sudden impact on society.
Definition
The term—bot ...
approach; limited political terrorism refers to "acts of terrorism which are committed for ideological
An ideology is a set of beliefs or values attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely about belief in certain knowledge, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones". Form ...
or political motives but which are not part of a concerted campaign to capture control of the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
".
* Official or state terrorism – "referring to nations whose rule is based upon fear
Fear is an unpleasant emotion that arises in response to perception, perceived dangers or threats. Fear causes physiological and psychological changes. It may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the ...
and oppression
Oppression is malicious or unjust treatment of, or exercise of power over, a group of individuals, often in the form of governmental authority. Oppression may be overt or covert, depending on how it is practiced.
No universally accepted model ...
that reach similar to terrorism or such proportions". It may be referred to as Structural Terrorism defined broadly as terrorist acts carried out by governments in pursuit of political objectives, often as part of their foreign policy.
Other sources have defined the typology of terrorism in different ways, for example, broadly classifying it into domestic terrorism and international terrorism, or using categories such as vigilante terrorism or insurgent terrorism. Some ways the typology of terrorism may be defined are:
* Political terrorism
**Sub-state terrorism
*** Social revolutionary terrorism
*** Nationalist-separatist terrorism
*** Religious extremist terrorism
**** Religious fundamentalist Terrorism
**** New religions terrorism
*** Right-wing terrorism
Right-wing terrorism, hard right terrorism, extreme right terrorism or far-right terrorism is terrorism that is motivated by a variety of different Right-wing politics, right-wing and far-right politics, far-right ideologies. It can be motivated ...
*** Left-wing terrorism
Left-wing terrorism is a form of terrorism, terrorist political violence motivated by Far-left politics, far-left ideologies, committed with the aim of overthrowing current Capitalism, capitalist systems and replacing them with Communism, comm ...
**** Communist terrorism
** State-sponsored terrorism
** State terrorism
State terrorism is terrorism conducted by a state against its own citizens or another state's citizens.
It contrasts with '' state-sponsored terrorism'', in which a violent non-state actor conducts an act of terror under sponsorship of a state. ...
* Criminal terrorism
* Pathological terrorism
Religious terrorism
According to the Global Terrorism Index by the University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD i ...
, religious extremism has overtaken Separatism, national separatism and become the main driver of terrorist attacks around the world. Since 9/11 there has been a five-fold increase in deaths from terrorist attacks. The majority of incidents over the past several years can be tied to groups with a religious agenda. Before 2000, it was nationalist separatist terrorist organizations such as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA and Chechen rebels who were behind the most attacks. The number of incidents from nationalist separatist groups has remained relatively stable in the years since while religious extremism has grown. The prevalence of Islamist groups in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria is the main driver behind these trends. Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on domestic terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists."
Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on domestic terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists."
". Anti-Defamation League 2017.
Causes and motivations
Terrorist acts frequently have a political purpose based on self-determination claims, ethnonationalist frustrations, single issue causes (like abortion or the environment), or other ideological or religious causes that terrorists claim are a moral justification for their violent acts.
Choice of terrorism as a tactic
Individuals and groups choose terrorism as a tactic because it can:
* Act as a form of asymmetric warfare in order to directly force a government to agree to demands
* Intimidate a group of people into capitulating to the demands in order to avoid future injury
* Get attention and thus political support for a cause
* Directly inspire more people to the cause (such as revolutionary acts) – propaganda of the deed
* Indirectly inspire more people to the cause by provoking a hostile response or over-reaction from enemies to the cause[The Psychology Of Terrorism](_blank)
, audio interview summarizin
Special Report: The Psychology of Terrorism
Attacks on "collaborators" are used to intimidate people from cooperating with the state in order to undermine state control. This strategy was used in Ireland, in Kenya, in Algeria and in Cyprus during their independence struggles.
Stated motives for the September 11 attacks included inspiring more fighters to join the cause of repelling the United States from Muslim countries with a successful high-profile attack. The attacks prompted some criticism from domestic and international observers regarding perceived injustices in U.S. foreign policy that provoked the attacks, but the larger practical effect was that the United States government declared a War on Terror that resulted in substantial military engagements in several Muslim-majority countries. Various commentators have inferred that al-Qaeda expected a military response and welcomed it as a provocation that would result in more Muslims fighting the United States. Some commentators believe that the resulting anger and suspicion directed toward innocent Muslims living in Western countries and the indignities inflicted upon them by security forces and the general public also contributes to radicalization of new recruits.
Causes motivating terrorism
Specific political or social causes have included:
* Independence or separatist movements
* Irredentist movements
* Adoption of a particular political philosophy, such as socialism (left-wing terrorism), anarchism, or fascism (possibly through a coup or as an ideology of an independence or separatist movement)
* Environmental protection (eco-terrorism)
* Supremacism of a particular group
** Preventing a rival group from sharing or occupying a particular territory (such as by discouraging immigration or encouraging flight)
** Subjugation of a particular population (such as Lynching in the United States, lynching of African Americans)
* Spread or dominance of a particular religion – religious terrorism
* Ending perceived government oppression
Oppression is malicious or unjust treatment of, or exercise of power over, a group of individuals, often in the form of governmental authority. Oppression may be overt or covert, depending on how it is practiced.
No universally accepted model ...
* Responding to a violent act (for example, tit-for-tat attacks in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is an ongoing military and political conflict about Territory, land and self-determination within the territory of the former Mandatory Palestine. Key aspects of the conflict include the Israeli occupation ...
, in The Troubles in Northern Ireland, or Timothy McVeigh's revenge for the Waco siege and Ruby Ridge incident)
Causes for right-wing terrorism have included white nationalism, ethnonationalism, fascism, anti-socialism, the anti-abortion movement, and tax resistance.
Sometimes terrorists on the same side fight for different reasons. For example, in the Chechen–Russian conflict secular Chechens using terrorist tactics fighting for national independence are allied with radical Islamist terrorists who have arrived from other countries.
Personal and social factors
Various personal and social factors may influence the personal choice of whether to join a terrorist group or attempt an act of terror, including:
* Identity (social science), Identity, including affiliation with a particular culture, ethnicity, or religion
* Previous exposure to violence
* Financial reward (for example, the Palestinian Authority Martyrs Fund)
* Mental illness
* Social isolation
* Perception that the cause responds to a profound injustice or indignity
A report conducted by Paul Gill, John Horgan and Paige Deckert found that for "lone wolf" terrorists:suicide attack
A suicide attack (also known by a wide variety of other names, see below) is a deliberate attack in which the perpetrators knowingly sacrifice their own lives as part of the attack. These attacks are a form of murder–suicide that is ofte ...
ers, concluded that they were unlikely to be psychologically abnormal. In comparison to economic theories of criminal behaviour, Scott Atran found that suicide terrorists exhibit none of the socially dysfunctional attributes—such as fatherless, friendless, jobless situations—or suicidal symptoms. By which he means, they do not kill themselves simply out of hopelessness or a sense of 'having nothing to lose'.
Abrahm suggests that terrorist organizations do not select terrorism for its political effectiveness.
Democracy and domestic terrorism
Terrorism is most common in nations with intermediate political freedom, and it is least common in the most democratic nations.
Some examples of terrorism in non-democratic nations include ETA (separatist group), ETA in Spain under Francisco Franco (although the group's activities increased sharply after Franco's death),
Perpetrators
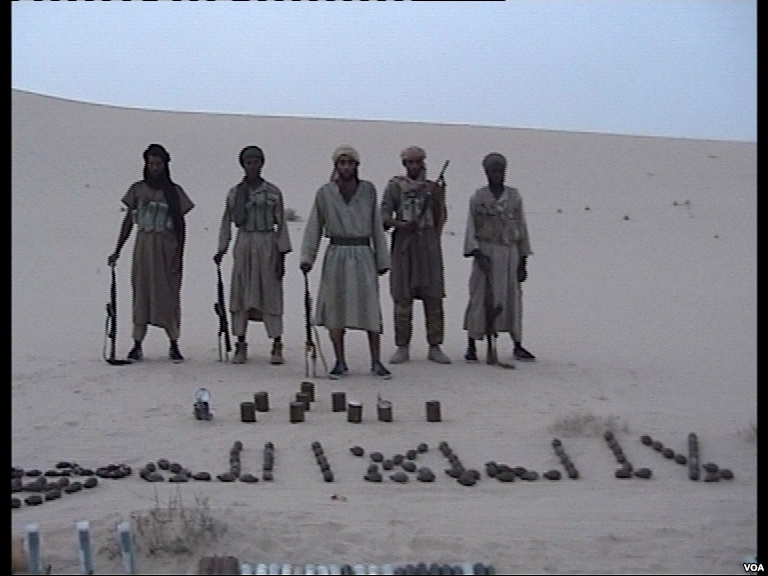 The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the
The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
, the 7 July 2005 London bombings, London underground bombing, 2008 Mumbai attacks and the 2002 Bali bombings
The 2002 Bali bombings were a series of terrorist attacks on 12 October 2002 in the tourist district of Kuta on the Indonesian island of Bali. The attacks killed 202 people (including 88 Australians, 38 Indonesians, 23 Britons, and people ...
were planned and carried out by a close clique, composed of close friends, family members and other strong social networks. These groups benefited from the free flow of information and efficient telecommunications to succeed where others had failed.
Over the years, much research has been conducted to distill a terrorist profile to explain these individuals' actions through their psychology and socio-economic circumstances. Some specialists highlight the lack of evidence supporting the idea that terrorists are typically psychologically disturbed. The careful planning and detailed execution seen in many terrorist acts are not characteristics generally associated with mentally unstable individuals. Others, like Roderick Hindery, have sought to discern profiles in the propaganda tactics used by terrorists. Some security organizations designate these groups as ''violent non-state actors''. A 2007 study by economist Alan B. Krueger found that terrorists were less likely to come from an impoverished background (28 percent versus 33 percent) and more likely to have at least a high-school education (47 percent versus 38 percent). Another analysis found only 16 percent of terrorists came from impoverished families, versus 30 percent of male Palestinians, and over 60 percent had gone beyond high school, versus 15 percent of the populace.[Library of Congress](_blank)
– Federal Research Division ''The Sociology and Psychology of Terrorism''. The majority of terrorist attacks are carried out by military age men, aged 16 to 40.
Non-state groups
 Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism, religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the secular Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians. Members of Kach (political party), Kach, a Jewish ultranationalist party, employed terrorist tactics in pursuit of what they viewed as religious imperatives. Israel and a few other countries have designated the party as a terrorist group.
Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism, religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the secular Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians. Members of Kach (political party), Kach, a Jewish ultranationalist party, employed terrorist tactics in pursuit of what they viewed as religious imperatives. Israel and a few other countries have designated the party as a terrorist group.
Funding
State-sponsored terrorism, State sponsors have constituted a major form of funding; for example, Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ) is a Palestinian nationalism, Palestinian nationalist coalition that is internationally recognized as the official representative of the Palestinians, Palestinian people in both the occupied Pale ...
, Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine and other groups sometimes considered to be terrorist organizations, were funded by the Soviet Union.[Detection of Terrorist Financing](_blank)
, U.S. National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), 2002. Revolutionary taxes "play a secondary role as one other means of intimidating the target population".
Tactics
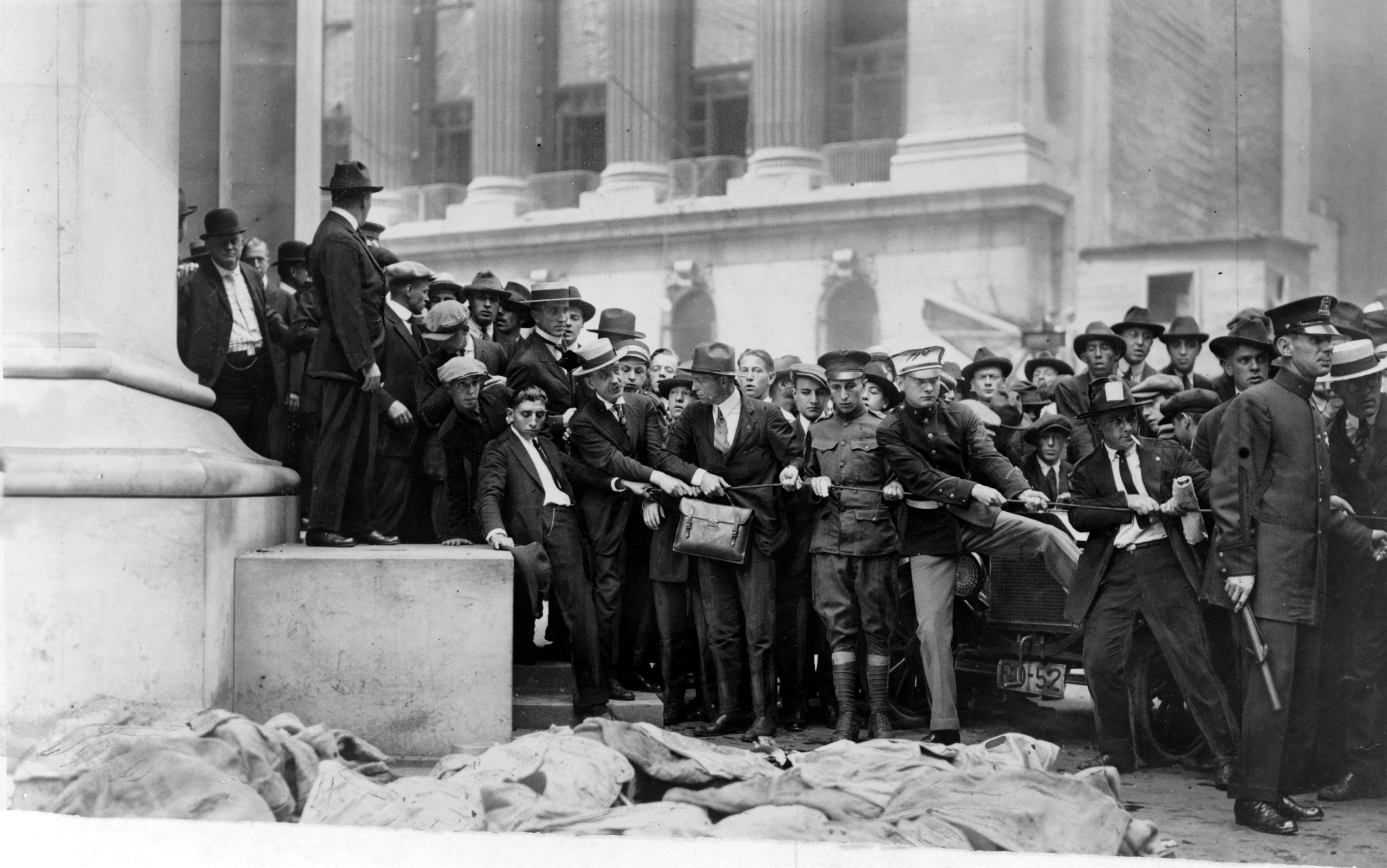 Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power.
Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power.
Attack types
Stabbing as a terrorist tactic, Stabbing attacks, a historical tactic, have reemerged as a prevalent form of terrorism in the 21st century, notably during the 2010s and 2020s.
Media spectacle
Terrorists may attempt to use the media to spread their message or manipulate their target audience. Shamil Basayev used this tactic during the Budyonnovsk hospital hostage crisis and again in the Moscow theater hostage crisis. Terrorists may also target national symbols for attention. Walter Lacquer wrote that "terrorism was always, to a large extent, about public relations and propaganda ('Propaganda by Deed' had been the slogan in the nineteenth century)".
The El Al Flight 426 hijacking is considered a turning point for modern terrorism studies. The Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) realized they could combine the tactics of targeting national symbols and civilians (in this case as hostages) to generate a mass media spectacle. Zehdi Labib Terzi made a public statement about this in 1976: "The first several hijackings aroused the consciousness of the world and awakened the media and world opinion much more ― and more effectively ― than 20 years of pleading at the United Nations".
Mass media
 Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counterterrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other:
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counterterrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other:
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
Terrorism and tourism
The connection between terrorism and tourism has been widely studied since the Luxor massacre, 1997 Luxor massacre, during which 62 people, including 58 foreign nationals, were killed by Islamist group al-Jama'a al-Islamiyya in an archaeological site in Egypt. In the 1970s, the targets of terrorists were politicians and chiefs of police while now, international tourists and visitors are selected as the main targets of attacks. The attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon on September 11, 2001, were the symbolic center, which marked a new epoch in the use of civil transport against the main power of the planet. From this event onwards, the spaces of leisure that characterized the pride of West were conceived as dangerous and frightful.
Counterterrorism strategies
 Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased Strategic intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased Strategic intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
Terrorism research
Terrorism research, also called terrorism studies, or terrorism and counter-terrorism research, is an academic field which seeks to understand the causes of terrorism, how to prevent it, as well as its impact in the broadest sense. Terrorism research can be carried out in both military and civilian contexts, for example by research centres such as the British Centre for the Study of Terrorism and Political Violence, the Norwegian Centre for Violence and Traumatic Stress Studies, and the International Centre for Counter-Terrorism (ICCT). There are several academic journals devoted to the field, including ''Perspectives on Terrorism''.
International agreements
One of the agreements that promote the international legal counterterrorist framework is the Code of Conduct Towards Achieving a World Free of Terrorism that was adopted at the 73rd session of the United Nations General Assembly in 2018. The Code of Conduct was initiated by President of Kazakhstan, Kazakhstan President Nursultan Nazarbayev. Its main goal is to implement a wide range of international commitments to counterterrorism and establish a broad global coalition towards achieving a world free of terrorism by 2045. The Code was signed by more than 70 countries.
Response in the United States
 According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in ''The Washington Post'', "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.
According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in ''The Washington Post'', "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.[Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57.] In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
Ending terrorist groups
 Jones and Libicki (2008) created a list of all the terrorist groups they could find that were active between 1968 and 2006. They found 648. Of those, 136 splintered and 244 were still active in 2006. Of the ones that ended, 43% converted to nonviolent political actions, like the
Jones and Libicki (2008) created a list of all the terrorist groups they could find that were active between 1968 and 2006. They found 648. Of those, 136 splintered and 244 were still active in 2006. Of the ones that ended, 43% converted to nonviolent political actions, like the Irish Republican Army
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various Resistance movement, resistance organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dominantly Catholic and dedicated to anti-imperiali ...
in Northern Ireland; 40% were defeated by law enforcement; 7% (20 groups) were defeated by military force; and 10% succeeded.
42 groups became large enough to be labeled an insurgency; 38 of those had ended by 2006. Of those, 47% converted to nonviolent political actors. Only 5% were ended by law enforcement, and 21% were defeated by military force. 26% won. Jones and Libicki concluded that military force may be necessary to deal with large insurgencies but are only occasionally decisive, because the military is too often seen as a bigger threat to civilians than the terrorists. To avoid that, the rules of engagement must be conscious of collateral damage and work to minimize it.
Another researcher, Audrey Cronin, lists six primary ways that terrorist groups end:
# Capture or killing of a group's leader (Decapitation)
# Entry of the group into a legitimate political process (Negotiation)
# Achievement of group aims (Success)
# Group implosion or loss of public support (Failure)
# Defeat and elimination through brute force (Repression)
# Transition from terrorism into other forms of violence (Reorientation)
State and state sponsored-terrorism
State terrorism
As with "terrorism" the concept of "state terrorism" is controversial. The Chairman of the United Nations Counter-Terrorism Committee has stated that the committee was conscious of 12 international conventions on the subject, and none of them referred to state terrorism, which was not an international legal concept. If states abused their power, they should be judged against international conventions dealing with war crimes, international human rights law, and international humanitarian law. Former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan has said that it is "time to set aside debates on so-called 'state terrorism'. The Use of force in international law, use of force by states is already thoroughly regulated under international law". He made clear that, "regardless of the differences between governments on the question of the definition of terrorism, what is clear and what we can all agree on is that any deliberate attack on innocent civilians [or non-combatants], regardless of one's cause, is unacceptable and fits into the definition of terrorism."
State terrorism has been used to refer to terrorist acts committed by governmental agents or forces. This involves the use of state resources employed by a state's foreign policies, such as using its military to directly perform acts of terrorism. Professor of Political Science Michael Stohl cites the examples that include the German The Blitz, bombing of London, the Japanese surprise attack on Pearl Harbor, the Allies of World War II, Allied Bombing of Dresden in World War II, firebombing of Dresden, and the U.S. atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. He argues that "the use of terror tactics is common in international relations and the state has been and remains a more likely employer of terrorism within the international system than insurgents." He cites the Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike option as an example of the "terror of coercive diplomacy" as a form of this, which holds the world hostage with the implied threat of using nuclear weapons in "crisis management" and he argues that the institutionalized form of terrorism has occurred as a result of changes that took place following World War II. In this analysis, state terrorism exhibited as a form of foreign policy was shaped by the presence and use of Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction, and the legitimizing of such violent behavior led to an increasingly accepted form of this behavior by the state.hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized—such as a relative, employer, law enforcement, or government—to act, o ...
s or extrajudicial killing, extrajudicial elimination campaigns are commonly considered "terror" or terrorism, for example during the Red Terror
The Red Terror () was a campaign of political repression and Mass killing, executions in Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Russia which was carried out by the Bolsheviks, chiefly through the Cheka, the Bolshevik secret police ...
or the Great Purge, Great Terror.[Nicolas Werth, Karel Bartošek, Jean-Louis Panné, Jean-Louis Margolin, Andrzej Paczkowski, Stéphane Courtois, ''The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression'', Harvard University Press, 1999, hardcover, 858 pp., ] Such actions are often described as democide or genocide, which have been argued to be equivalent to state terrorism.[Mark Aarons (2007).]
Justice Betrayed: Post-1945 Responses to Genocide
." In David A. Blumenthal and Timothy L.H. McCormack (eds).
The Legacy of Nuremberg: Civilising Influence or Institutionalised Vengeance? (International Humanitarian Law).
'' Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. pp
71
80–81
State-sponsored terrorism
A state can sponsor terrorism by funding or harboring a terrorist group. Opinions as to which acts of violence by states consist of state-sponsored terrorism vary widely. When states provide funding for groups considered by some to be terrorist, they rarely acknowledge them as such.
Impact and debate
Terrorism is a Loaded language, charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is morally wrong. Governments and non-state groups use the term to abuse or denounce opposing groups.State terrorism
State terrorism is terrorism conducted by a state against its own citizens or another state's citizens.
It contrasts with '' state-sponsored terrorism'', in which a violent non-state actor conducts an act of terror under sponsorship of a state. ...
is that perpetrated by nation states, but is not considered such by the state conducting it, making legality a grey area.
Pejorative use
The term "terrorism" is often used to abuse or denounce opposite parties, either governments or non-state groups.revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates for, a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective to describe something producing a major and sudden impact on society.
Definition
The term—bot ...
, vigilante, Insurgent, militant, paramilitary, guerrilla warfare, guerrilla, rebellion, rebel, patriot, have come into use, (including some culturally specific terms borrowed from other languages like Jihadi, mujahideen, and fedayeen), the unwillingness to self-identify as terrorists began when parties in a conflict started to describe each other as terrorists pejoratively.state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
against a mutual enemy, but later falls out with the state and starts to use those methods against its former ally.
Groups accused of terrorism understandably prefer terms reflecting legitimate military or ideological action.[Terrorism: concepts, causes, and conflict resolution](_blank)
George Mason University Institute for Conflict Analysis and Resolution, Printed by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, Fort Belvoir, Virginia, January 2003. Leading terrorism researcher Professor Martin Rudner, director of the Canadian Centre of Intelligence and Security Studies at Ottawa's Carleton University, defines "terrorist acts" as unlawful attacks for political or other ideological goals, and said:
Labelling opponents as "terrorists" has been used as a tactic to evade the usual laws of war against things such as assassinations and other extrajudicial killing, particularly by targeted killing by Israel , Israel and the war on terror , United States. Some international legal opinions suggest that terrorist activities by their very nature "deny" the civilian nature of an ostensibly civilian participant.
 Some groups, when involved in a "liberation" struggle, have been called "terrorists" by the Western governments or media. Later, these same persons, as leaders of the liberated nations, are called "statesmen" by similar organizations. Two examples of this phenomenon are the Nobel Peace Prize laureates Menachem Begin and Nelson Mandela. WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange has been called a "terrorist" by Sarah Palin and Joe Biden.
Inversely, some groups like the Afghan Mujahideen that were labelled as "freedom fighters" later became "terrorists" as alliances shifted. During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result.
Some groups, when involved in a "liberation" struggle, have been called "terrorists" by the Western governments or media. Later, these same persons, as leaders of the liberated nations, are called "statesmen" by similar organizations. Two examples of this phenomenon are the Nobel Peace Prize laureates Menachem Begin and Nelson Mandela. WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange has been called a "terrorist" by Sarah Palin and Joe Biden.
Inversely, some groups like the Afghan Mujahideen that were labelled as "freedom fighters" later became "terrorists" as alliances shifted. During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result.[Chris Clark ', June 16, 2003.]
Databases
The following terrorism databases are or were made publicly available for research purposes, and track specific acts of terrorism:
* Global Terrorism Database
The Global Terrorism Database (GTD) is a database of terrorist incidents from 1970 onward. As of May 2021, the list extended through 2019 recording over 200,000 incidents, although data from 1993 is excluded. The database is maintained by the Na ...
, an open-source database by the University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD i ...
on terrorist events around the world from 1970 through 2017 with more than 150,000 cases.
* MIPT Terrorism Knowledge Base
* Worldwide Incidents Tracking System
* Tocsearch (dynamic database)
The following public report and index provides a summary of key global trends and patterns in terrorism around the world:
* Global Terrorism Index, produced annually by the Institute for Economics and Peace
The following publicly available resources index electronic and bibliographic resources on the subject of terrorism:
* Human Security Gateway
The following terrorism databases are maintained in secrecy by the United States Government for intelligence and counterterrorism purposes:
* Terrorist Identities Datamart Environment
* Terrorist Screening Database
Jones and Libicki (2008) includes a table of 268 terrorist groups active between 1968 and 2006 with their status as of 2006: still active, splintered, converted to nonviolence, removed by law enforcement or military, or won. (These data are not in a convenient machine-readable format but are available.)
Infographics
File:Terrorist incidents map of the world 1970-2015.svg, Terrorist incidents, 1970–2015. A total of 157,520 incidents are plotted. : 1970–1999, : 2000–2015
File:The number of terrorist attacks 2000-2014 (Top 10 Countries).png, Top 10 Countries (2000–2014)
File:Terrorist incidents worldwide.svg, Worldwide non-state terrorist incidents 1970–2017
File:Share who are worried about vs. share of deaths from terrorism, OWID.svg, Share who are worried about vs. share of deaths from terrorism
See also
* Agro-terrorism
* Communist terrorism
* Crimes against humanity
* Cyberterrorism
* Definitions of terrorism
* Economic terrorism
* Economics of terrorism
* Environmental terrorism
* Fearmongering
* Government negotiation with terrorists
* Left-wing terrorism
Left-wing terrorism is a form of terrorism, terrorist political violence motivated by Far-left politics, far-left ideologies, committed with the aim of overthrowing current Capitalism, capitalist systems and replacing them with Communism, comm ...
* Right-wing terrorism
Right-wing terrorism, hard right terrorism, extreme right terrorism or far-right terrorism is terrorism that is motivated by a variety of different Right-wing politics, right-wing and far-right politics, far-right ideologies. It can be motivated ...
* List of designated terrorist groups
* List of terrorist incidents
* Narcoterrorism
* Nationalist terrorism
* Nuclear terrorism
** Global Initiative to Combat Nuclear Terrorism
* Religious terrorism
** Hindutva terrorism
** Islamic terrorism
** Christian terrorism
** Jewish religious terrorism
* Stochastic terrorism
* Terrorism and social media
* Violent extremism
Notes and references
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
Perspectives on Terrorism's Bibliography: Root Causes of Terrorism. 2017.
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* Bakker, Edwin
''Forecasting the Unpredictable: A Review of Forecasts on Terrorism 2000–2012'' (International Centre for Counter-Terrorism – The Hague, 2014)
*
* Burleigh, Michael. ''Blood and rage: a cultural history of terrorism''. Harper, 2009.
* Chaliand, Gérard and Arnaud Blin, eds. ''The history of terrorism: from antiquity to al Qaeda''. University of California Press, 2007.
* Coates, Susan W., Rosenthal, Jane, and Schechter, Daniel S. ''September 11: Trauma and Human Bonds'' (Taylor and Francis, 2003).
* Crenshaw, Martha, ed. ''Terrorism in context''. Pennsylvania State University Press, 1995.
*
* Hennigfeld, Ursula/ Packard, Stephan, ed., ''Abschied von 9/11? Distanznahme zur Katastrophe''. Berlin: Frank & Timme, 2013.
* Hennigfeld, Ursula, ed., ''Poetiken des Terrors. Narrative des 11. September 2001 im interkulturellen Vergleich''. Heidelberg: Winter, 2014.
* Hewitt, Christopher. ''Understanding terrorism in America'' (Routledge, 2003).
* Hewitt, Christopher. "Terrorism and public opinion: A five country comparison." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 2.2 (1990): 145–170.
* Jones, Sidney.
Terrorism: myths and facts
'. Jakarta: International Crisis Group, 2013.
* Land, Isaac, ed., ''Enemies of humanity: the nineteenth-century war on terrorism''. Palgrave Macmillan, 2008.
* Lee, Newton. ''Counterterrorism and Cybersecurity: Total Information Awareness (2nd Edition)''. New York: Springer, 2015.
* Lutz, James and Brenda Lutz. ''Terrorism : origins and evolution'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2005)
* Margolin, Devorah; Cook, Joana (2024). "doi:10.1080/1057610X.2024.2357178, Five Decades of Research on Women and Terrorism". ''Studies in Conflict & Terrorism''.
* Miller, Martin A. ''The foundations of modern terrorism: state, society and the dynamics of political violence''. Cambridge University Press, 2013.
*
* Neria, Yuval, Gross, Raz, Marshall, Randall D., and Susser, Ezra. ''September 11, 2001: Treatment, Research and Public Mental Health in the Wake of a Terrorist Attack'' (Cambridge University Press, 2006).
* An open-access publication, issued since November 2020 on the International Centre for Counter-Terrorism (ICCT) website, with a chapter published each week.
* Stern, Jessica. ''The Ultimate Terrorists''. (Harvard University Press 2000 reprint; 1995). 214 p.
* Tausch, Arno
Estimates on the Global Threat of Islamic State Terrorism in the Face of the 2015 Paris and Copenhagen Attacks
(December 11, 2015). ''Middle East Review of International Affairs'', Rubin Center, Research in International Affairs, Idc Herzliya, Israel, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Spring 2015).
*
Terrorism, Law & Democracy: 10 years after 9/11
', Canadian Institute for the Administration of Justice. .
United Kingdom
* Blackbourn, Jessie. "Counter-Terrorism and Civil Liberties: The United Kingdom Experience, 1968-2008." ''Journal of the Institute of Justice and International Studies'' 8 (2008): 63+
* Bonner, David. "United Kingdom: the United Kingdom response to terrorism." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 4.4 (1992): 171–205
online
* Chin, Warren. ''Britain and the war on terror: Policy, strategy and operations'' (Routledge, 2016).
* Clutterbuck, Lindsay. "Countering Irish Republican terrorism in Britain: Its origin as a police function." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 18.1 (2006) pp: 95–118.
* Greer, Steven. "Terrorism and Counter-Terrorism in the UK: From Northern Irish Troubles to Global Islamist Jihad." in ''Counter-Terrorism, Constitutionalism and Miscarriages of Justice'' (Hart Publishing, 2018) pp. 45–62.
* Hamilton, Claire. "Counter-Terrorism in the UK." in ''Contagion, Counter-Terrorism and Criminology'' (Palgrave Pivot, Cham, 2019) pp. 15–47.
* Hewitt, Steve. "Great Britain: Terrorism and counter-terrorism since 1968." in ''Routledge Handbook of Terrorism and Counterterrorism'' (Routledge, 2018) pp. 540–551.
* Martínez-Peñas, Leandro, and Manuela Fernández-Rodríguez. "Evolution of British Law on Terrorism: From Ulster to Global Terrorism (1970–2010)." in ''Post 9/11 and the State of Permanent Legal Emergency'' (Springer, 2012) pp. 201–222.
* O'Day, Alan. "Northern Ireland, Terrorism, and the British State." in ''Terrorism: Theory and Practice'' (Routledge, 2019) pp. 121–135.
* Sacopulos, Peter J. "Terrorism in Britain: Threat, reality, response." ''Studies in Conflict & Terrorism'' 12.3 (1989): 153–165.
* Staniforth, Andrew, and Fraser Sampson, eds. ''The Routledge companion to UK counter-terrorism'' (Routledge, 2012).
* Sinclair, Georgina. "Confronting terrorism: British Experiences past and present." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.2 (2014): 117–122
online
* Tinnes, Judith, ed. "Bibliography: Northern Ireland conflict (the troubles)." ''Perspectives on Terrorism'' 10.1 (2016): 83–110
online
* Wilkinson, Paul, ed. ''Terrorism: British Perspectives'' (Dartmouth, 1993).
External links
* United Nations
Conventions on Terrorism
* United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime:
UNODC – United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime – Terrorism Prevention
Terrorism and international humanitarian law
International Committee of the Red Cross
UK Counter Terrorism Policing
{{Authority control
Terrorism,
Crimes
Warfare by type
1790s neologisms
 The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the
The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the  No definition of terrorism has gained universal agreement. Challenges emerge due to the politically and emotionally charged nature of the term, the double standards used in applying it, and disagreement over the nature of terrorist acts and limits of the right to
No definition of terrorism has gained universal agreement. Challenges emerge due to the politically and emotionally charged nature of the term, the double standards used in applying it, and disagreement over the nature of terrorist acts and limits of the right to  In early 1975, the Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into seven categories:
*
In early 1975, the Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into seven categories:
*  Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on domestic terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists." The "virulent racist and Antisemitism, antisemitic" ideology of the ultra-right wing Christian Identity movement is usually accompanied by anti-government sentiments.
Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on domestic terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists." The "virulent racist and Antisemitism, antisemitic" ideology of the ultra-right wing Christian Identity movement is usually accompanied by anti-government sentiments. The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the
The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the  Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism, religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the secular Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians. Members of Kach (political party), Kach, a Jewish ultranationalist party, employed terrorist tactics in pursuit of what they viewed as religious imperatives. Israel and a few other countries have designated the party as a terrorist group.
Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism, religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the secular Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians. Members of Kach (political party), Kach, a Jewish ultranationalist party, employed terrorist tactics in pursuit of what they viewed as religious imperatives. Israel and a few other countries have designated the party as a terrorist group. Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power. Yuval Harari argues that the peacefulness of modern states makes them paradoxically more vulnerable to terrorism than pre-modern states. Harari argues that because modern states have committed themselves to reducing political violence to almost zero, terrorists can, by creating political violence, threaten the very foundations of the legitimacy of the modern state. This is in contrast to pre-modern states, where violence was a routine and recognised aspect of politics at all levels, making political violence unremarkable. Terrorism thus shocks the population of a modern state far more than a pre-modern one and consequently the state is forced to overreact in an excessive, costly and spectacular manner, which is often what the terrorists desire.
The type of people terrorists will target is dependent upon the ideology of the terrorists. A terrorist's ideology will create a class of "legitimate targets" who are deemed as its enemies and who are permitted to be targeted. This ideology will also allow the terrorists to place the blame on the victim, who is viewed as being responsible for the violence in the first place.
Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power. Yuval Harari argues that the peacefulness of modern states makes them paradoxically more vulnerable to terrorism than pre-modern states. Harari argues that because modern states have committed themselves to reducing political violence to almost zero, terrorists can, by creating political violence, threaten the very foundations of the legitimacy of the modern state. This is in contrast to pre-modern states, where violence was a routine and recognised aspect of politics at all levels, making political violence unremarkable. Terrorism thus shocks the population of a modern state far more than a pre-modern one and consequently the state is forced to overreact in an excessive, costly and spectacular manner, which is often what the terrorists desire.
The type of people terrorists will target is dependent upon the ideology of the terrorists. A terrorist's ideology will create a class of "legitimate targets" who are deemed as its enemies and who are permitted to be targeted. This ideology will also allow the terrorists to place the blame on the victim, who is viewed as being responsible for the violence in the first place.
 Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counterterrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other:
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counterterrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other:
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
 Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased Strategic intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased Strategic intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
 According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in ''The Washington Post'', "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57. In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in ''The Washington Post'', "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57. In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
 Some groups, when involved in a "liberation" struggle, have been called "terrorists" by the Western governments or media. Later, these same persons, as leaders of the liberated nations, are called "statesmen" by similar organizations. Two examples of this phenomenon are the Nobel Peace Prize laureates Menachem Begin and Nelson Mandela. WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange has been called a "terrorist" by Sarah Palin and Joe Biden.
Inversely, some groups like the Afghan Mujahideen that were labelled as "freedom fighters" later became "terrorists" as alliances shifted. During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result.Chris Clark ', June 16, 2003.
Some groups, when involved in a "liberation" struggle, have been called "terrorists" by the Western governments or media. Later, these same persons, as leaders of the liberated nations, are called "statesmen" by similar organizations. Two examples of this phenomenon are the Nobel Peace Prize laureates Menachem Begin and Nelson Mandela. WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange has been called a "terrorist" by Sarah Palin and Joe Biden.
Inversely, some groups like the Afghan Mujahideen that were labelled as "freedom fighters" later became "terrorists" as alliances shifted. During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result.Chris Clark ', June 16, 2003.