|
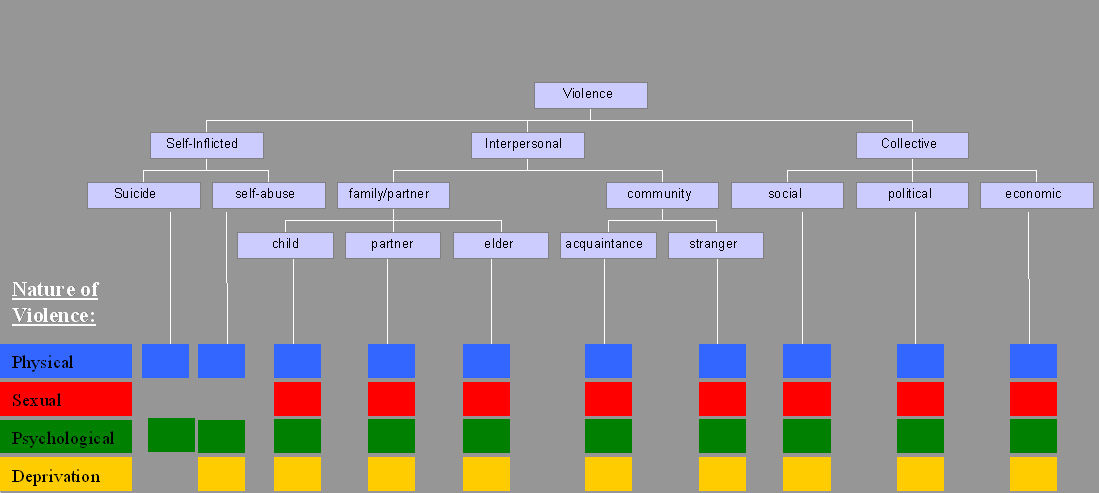
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communal Violence
Communal violence is a form of violence that is perpetrated across ethnic or communal lines, where the violent parties feel solidarity for their respective groups and victims are chosen based upon group membership. The term includes conflicts, riots and other forms of violence between communities of different religious faith or ethnic origins. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime includes any conflict and form of violence between communities of different religious groups, different sects or tribes of same religious group, clans, ethnic origins or national origin as communal violence.Homicide, Violence and Conflict UNODC, United Nations However, this excludes conflict between two individuals or two families. Communal violence is found in Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and Oceania. The term "communal vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Violence
Structural violence is a form of violence wherein some social structure or social institution may harm people by preventing them from meeting their basic needs or rights. The term was coined by Norwegian sociologist Johan Galtung, who introduced it in his 1969 article "Violence, Peace, and Peace Research". Some examples of structural violence as proposed by Galtung include institutionalized racism, sexism, and classism, among others. Structural violence and direct violence are said to be highly interdependent, including family violence, gender violence, hate crimes, racial violence, police violence, state violence, terrorism, and war. It is very closely linked to social injustice insofar as it affects people differently in various social structures. Definitions Galtung According to Johan Galtung, rather than conveying a physical image, ''structural violence'' is an "avoidable impairment of fundamental human needs." Galtung contrasts structural violence wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Violence
Political violence is violence which is perpetrated in order to achieve political goals. It can include violence which is used by a State (polity), state against other states (war), violence which is used by a state against civilians and non-state actors (forced disappearance, psychological warfare, police brutality, targeted killings, torture, ethnic cleansing, or genocide), and violence which is used by violent non-state actors against states and civilians (kidnappings, assassinations, Terrorism, terrorist attacks, torture, Psychological warfare, psychological and/or guerrilla warfare). It can also describe politically motivated violence which is used by violent non-state actors against a state (rebellion, rioting, treason, or coup d'état) or it can describe violence which is used against other non-state actors and/or civilians. Non-action on the part of a government can also be characterized as a form of political violence, such as refusing to alleviate famine or otherwise de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Violence
Slow violence is violence which occurs gradually and is not necessarily visible. Slow violence is incremental and is dynamic across time,Ahman, Chloe. “‘IT’S EXHAUSTING TO CREATE AN EVENT OUT OF NOTHING’: Slow Violence and the Manipulation of Time.” Cultural Anthropology 33, no. 1 (2018): 142–71. doi:10.14506/ca33.1.06. in contrast with a conception of general violence as an event or action that is immediate, explosive and spectacular. Outcomes of slow violence include environmental degradation, long-term pollution and climate change. Slow violence is also closely linked to many instances of environmental racism. The origins of the concept of slow violence can be traced back to the 1960s with the introduction of the idea of structural violence. In 1969, Johan Galtung conceived of structural violence. Some views include that structural violence and slow violence are closely linked, as structural inequality can morph into forms of slow violence. However, slow violence is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Determinants Of Violence Against Civilians
Civilian victimization is the intentional use of violence against noncombatants in a conflict. It includes both lethal forms of violence (such as killings), as well as non-lethal forms of violence such as torture, forced expulsion, and rape. According to this definition, civilian victimization is only a subset of harm that occurs to civilians during conflict, excluding that considered collateral damage of military activity. However, "the distinction between intentional and unintentional violence is highly ambivalent" and difficult to determine in many cases. Scholars have identified various factors that may either provide incentives for the use of violence against civilians, or create incentives for restraint. Violence against civilians occurs in many types of civil conflict, and can include any acts in which force is used to harm or damage civilians or civilian targets. It can be lethal or nonlethal. During periods of armed conflict, there are structures, actors, and processe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Violence
Economic Violence is a form of structural violence in which specific groups of people are deprived of critical economic resources. Bandy X. Lee, a psychiatrist and scholar on the subject of violence, asserts that such economic impediments are among the "avoidable limitations that society places on groups of people hichconstrain them from meeting their basic needs and achieving the quality of life that would otherwise be possible." As with other forms of Structural Violence, Lee notes that it is typically inflicted by institutions to the effect of exercising power over vulnerable groups. "Economic Violence" may also refer to Economic Abuse, a form of interpersonal domestic violence. History of Economic Violence The emergence of economic violence as a structural force can be traced to the development of primitive accumulation in medieval Europe. Economists Adam Smith and Karl Marx identified primitive accumulation as the means through which feudal lords and owners of the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse committed with the necessary Intention (criminal law), intention as defined by the law in a specific jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the crime of killing a person with malice aforethought or with recklessness manifesting extreme indifference to the value of human life.") This state of mind may, depending upon the jurisdiction, distinguish murder from other forms of unlawful homicide, such as manslaughter. Manslaughter is killing committed in the absence of Malice (law), ''malice'',This is "malice" in a technical legal sense, not the more usual English sense denoting an emotional state. See malice (law). such as in the case of voluntary manslaughter brought about by reasonable Provocation (legal), provocation, or diminished capacity. Involuntary manslaughter, ''Invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Terrorism
Stochastic terrorism is a form of political violence instigated by hostile public rhetoric directed at a group or an individual. Unlike incitement to terrorism, stochastic terrorism is accomplished with indirect, vague or coded language, which grants the instigator plausible deniability for any associated violence. A key element of stochastic terrorism is the use of media for propagation, where the person carrying out the violence may not have direct connection to any other users of violent rhetoric. Defining features Although stochastic terrorism is considered an academic term without a formal legal definition, it is differentiated from other forms of terrorism due to its public, indirect, and seemingly random nature. # Speech: A public figure or group disseminates violent, inflammatory rhetoric via mass-media, directed at people or groups of people, sometimes suggesting or legitimizing the use of violence. This speech tends to be protected due to the use of ambiguous coded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Violence
State violence is the use of force, intimidation, or oppression by a government against its citizens. State violence can happen through law enforcement or military force, as well as through other branches of government and bureaucracy. State violence is often justified by regimes under the pretext of maintaining law and order. Forms State sponsored genocide Genocide generally involves the direct mass killing of members of a national, ethnical, racial or religious group. Perpetrators of genocide are most often state actors. State surveillance Government surveillance is a tool used by government agencies to protect citizens from potential attacks from terrorists, extremists, or dissidents. Surveillance methods can include monitoring phone calls, video surveillance, or tracking internet usage. Although surveillance was designed to protect national security, it has the potential to perpetuate state violence. The use of surveilling technology can be used to encroach upon citize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; improving economic conditions; and dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT). Although crisis hotlines, like 988 in North America and 13 11 14 in Australia, are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately 1.5% of total deaths. In a given year, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, developmental, Intellectual disability, intellectual, mental disorder#Disability, mental, physical disability, physical, Sense, sensory, or a combination of multiple factors. Disabilities can be Birth defect, present from birth or can be acquired during a person's lifetime. Historically, disabilities have only been recognized based on a narrow set of criteria—however, disabilities are not binary and can be present in unique characteristics depending on the individual. A disability may be readily visible, or Invisible disability, invisible in nature. The United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities defines disability as including: Disabilities have been perceived differently throughout history, through a variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |