Tennis Elbow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an
 The exact cause of lateral epicondylitis remains unclear. However, it is often linked to repetitive microtrauma resulting from excessive gripping, wrist extension, radial deviation, and/or forearm
The exact cause of lateral epicondylitis remains unclear. However, it is often linked to repetitive microtrauma resulting from excessive gripping, wrist extension, radial deviation, and/or forearm 

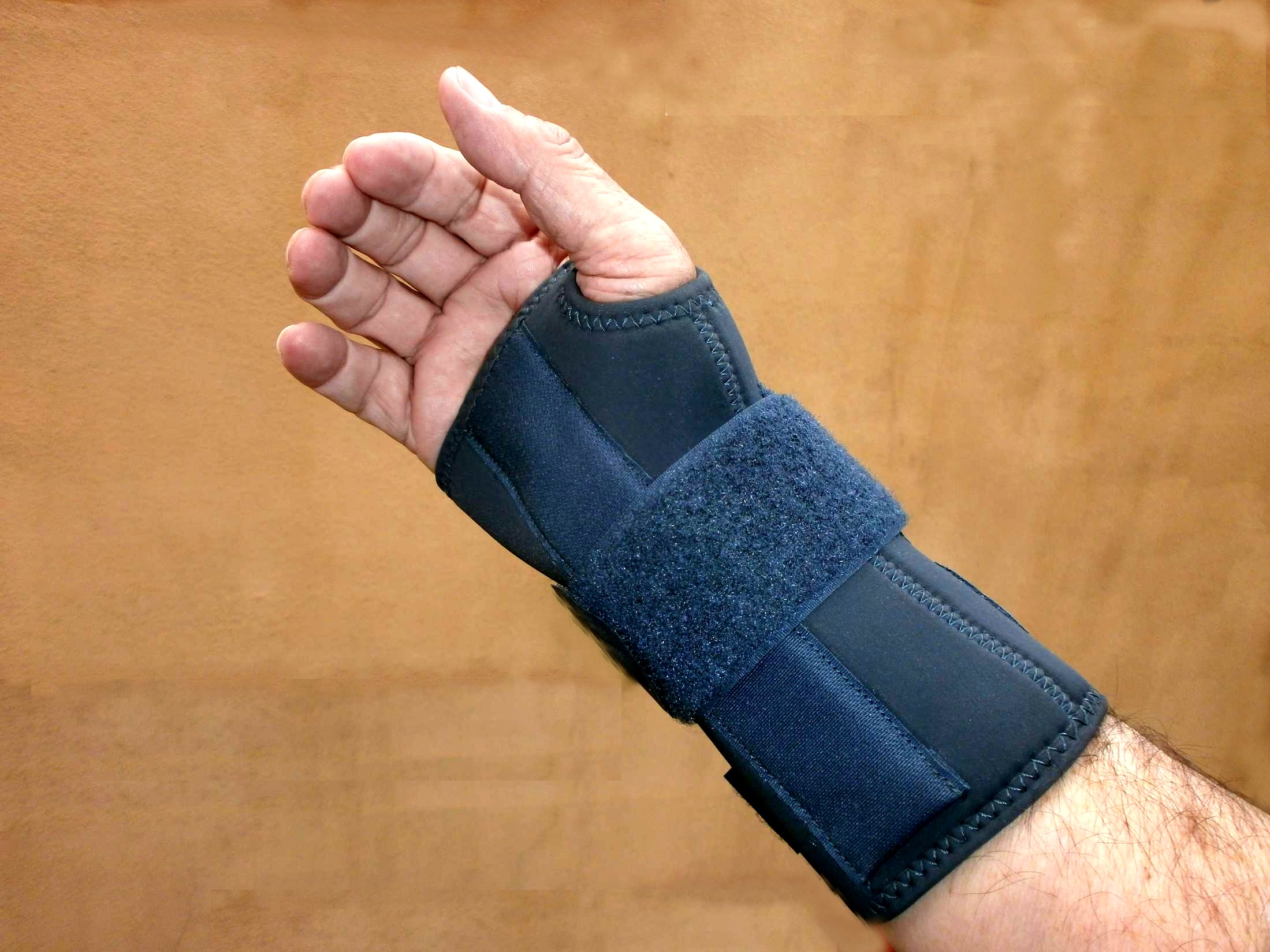 Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow; however, long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow; however, long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
enthesopathy
An enthesopathy refers to a disorder involving the attachment of a tendon or ligament to a bone. This site of attachment is known as the entheses, enthesis (pl. entheses).
If the condition is known to be Inflammation, inflammatory, it can more pr ...
(attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the ext ...
on the lateral epicondyle
An epicondyle () is a rounded eminence on a bone that lies upon a condyle ('' epi-'', "upon" + ''condyle'', from a root meaning "knuckle" or "rounded articular area"). There are various epicondyles in the human skeleton
The human skeleton is ...
. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the lateral epicondyle. Symptoms range from mild tenderness to severe, persistent pain. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
. It usually has a gradual onset, but it can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury.
Tennis elbow is often idiopathic. Its cause and pathogenesis are unknown. It likely involves tendinosis, a degeneration of the local tendon.
It is thought this condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the back of the forearm, but this is not supported by evidence. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports (including paddle sports), but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activities. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and examination. Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
is not very useful.
Untreated enthesopathy usually resolves in 1–2 years. Treating the symptoms and pain involves medications such as NSAIDS or acetaminophen, a wrist brace, or a strap over the upper forearm. The role of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
injections as a form of treatment is still debated. Recent studies suggests that corticosteroid injections may delay symptom resolution.
Signs and symptoms
Patients typically feel pain or burning around the outer part of the elbow ( lateral epicondyle of the humerus), which can move down the forearm and sometimes up to the upper arm. The pain is worsened by activities that involve wrist extension, such as gripping objects. Pain intensity varies from mild to severe and can be intermittent or constant, significantly impacting daily life. Patients also commonly report grip weakness and difficulty lifting.Terminology
The term "tennis elbow" is widely used (although informal), but the condition affects non-tennis
Tennis is a List of racket sports, racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles (tennis), singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles (tennis), doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket st ...
players. More recently, with the explosive growth of pickleball
Pickleball is a racket or paddle sport in which two or four players use a smooth-faced paddle to hit a perforated, hollow plastic ball over a net until one side is unable to return the ball or commits a rule infraction. Pickleball is played i ...
, the term "pickleball elbow" is frequently used. Historically, the medical term "lateral epicondylitis" was most commonly used for the condition, but "itis" implies inflammation and the condition is not inflammatory. It is also referred to as enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis origin.
Since histological findings reveal noninflammatory tissue, the terms "lateral elbow tendinopathy
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tenn ...
" and " tendinosis" are suggested. In 2019, a group of international experts suggested that "lateral elbow tendinopathy" was the most appropriate terminology. But a disease of an attachment point (or enthesia) is most accurately referred to as an "enthesopathy
An enthesopathy refers to a disorder involving the attachment of a tendon or ligament to a bone. This site of attachment is known as the entheses, enthesis (pl. entheses).
If the condition is known to be Inflammation, inflammatory, it can more pr ...
."
Causes
 The exact cause of lateral epicondylitis remains unclear. However, it is often linked to repetitive microtrauma resulting from excessive gripping, wrist extension, radial deviation, and/or forearm
The exact cause of lateral epicondylitis remains unclear. However, it is often linked to repetitive microtrauma resulting from excessive gripping, wrist extension, radial deviation, and/or forearm supination
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
.
Traditionally, people have speculated that tennis elbow is a type of repetitive strain injury
A repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury to part of the musculoskeletal or nervous system caused by repetitive use, vibrations, compression or long periods in a fixed position. Other common names include repetitive stress injury, repetitiv ...
resulting from tendon overuse and failed healing of the tendon, but there is no evidence of injury or repair, and misinterpretation of painful activities as a source of damage is common.
Pathophysiology
Theextensor carpi radialis brevis
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the ext ...
is the most commonly affected muscle in lateral epicondylitis (LE), along with other extensor carpal muscles. Due to its unique origin, the ECRB tendon is prone to abrasion during elbow movements, leading to repetitive microtrauma.
Lateral epicondylitis was initially considered an inflammatory process, however there is no evidence of inflammation or repair. Therefore, the disorder is more appropriately referred to as '' tendinosis'' or ''tendinopopathy.'' Tendinosis, a degenerative condition with fibroblasts, abnormal collagen, and increased blood vessels. Repetitive stress causes microtears, scar tissue formation, and biomechanical changes, worsening symptoms over time.
Recently, successful results of a prospective therapeutic study of tennis elbow were published. It was observed that tennis elbow symptoms were most painful after awakening. It was hypothesized that a very common sleep position was interfering with healing and causing pain. The study evaluated if changing this position would avoid pressure on the lateral elbow while asleep. Patients who changed this sleep position reported successful resolution of symptoms, whereas those who were unable to change continued to have pain. The conclusion reached is that the pathophysiology of tennis elbow is due to an initial microscopic tear from a sprain/strain. This initial injury is aggravated at night by pressure on the sprain which delays healing. In other words, tennis elbow is neither a tendonitis
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tenn ...
nor a tendinosis, but more like a pressure sore. If the pressure is removed the initial injury goes on to heal. The importance of this finding is that other conditions characterized by nocturnal or early morning symptoms may also be worsened by a “pathological sleep position.” We know this applies to carpal and cubital tunnel syndrome, plantar fasciitis, shoulder/neck pain and Gerd.
Clinical evaluation
Physical examination
Diagnosis is based on symptoms and clinical signs that are discrete and characteristic. For example, the extension of the elbow and flexion of the wrist causes outer elbow pain. The physical examination usually reveals marked tenderness at the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle from the lateral epicondyle (extensor carpi radialis brevis origin). Pain may worsen with resisted wrist extension, middle finger extension, and forearm supination with an extended elbow, although normal elbow movement is often maintained, even in severe cases.Cozen's test
Cozen's test is aphysical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
performed to evaluate for tennis elbow involving pain with resisted wrist extension. The test is said to be positive if a resisted wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
extension triggers pain to the lateral aspect of the elbow owing to stress placed upon the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the ext ...
muscle. The test is performed with extended elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and t ...
. NOTE: With elbow flexed the extensor carpi radialis longus is in a shortened position as its origin is the lateral supracondylar ridge
The lateral supracondylar ridge is a prominent, rough margin on the lower part of the lateral border of the humerus. It presents an anterior lip for the origin of forearm extensors, including the brachioradialis muscle above, and the extensor ca ...
of the humerus. To rule out the ECRB (extensor carpi radialis brevis
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the ext ...
), repeat the test with the elbow in full extension.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is not necessary or helpful. Radiographs (X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s) may demonstrate calcification where the extensor muscles attach to the lateral epicondyle. Medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes Medical diagnosis, diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of ...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) can demonstrate the pathology, but are not helpful for diagnosis and do not influence treatment.
Longitudinal sonogram of the lateral elbow displays thickening and heterogeneity of the common extensor tendon that is consistent with tendinosis, as the ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
reveals calcifications, intrasubstance tears, and marked irregularity of the lateral epicondyle. Although the term “epicondylitis” is frequently used to describe this disorder, most histopathologic findings of studies have displayed no evidence of an acute, or a chronic inflammatory process. Histologic studies have demonstrated that this condition is the result of tendon degeneration, which replaces normal tissue with a disorganized arrangement of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
. Colour Doppler ultrasound reveals structural tendon changes, with vascularity and hypo-echoic areas that correspond to the areas of pain in the extensor origin.
Table of Clinical classification of lateral epicondylitis phases.
Prevention
Activity modification is the best way to prevent the occurrence of lateral epicondylitis. Prevention can include avoiding extreme end range motions in extension and flexion, limit repetitive hand and wrist motions, and modification of heavy lifting with extended arms. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol drinking, and dietary habits are known to influence the prognosis of various medical conditions. Smokers showed a higher chance of developing lateral epicondylitis compared to non-smokers. Current research indicates that alcohol intake is not significantly associated with lateral epicondylitis.Treatment
Non-Operative Treatment
Non operative treatment resolves 90% of symptomatic lateral epicondylitis. Nonoperative care usually includes activity modification,physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, bracing, extracorporeal shock-wave therapy, and acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
. Modifying activity and avoiding overuse are key to treatment. Lifting with the palm up and avoiding palm-down movements can shift strain from the lateral to the medial epicondyle, easing pain. Patients should also improve lifestyle habits and avoid triggering activities. Following the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation) can help relieve pain initially.
Exercises
Stretching and isometric strengthening are the most common recommended exercises. The muscle is stretched with the elbow straight and the wrist passively flexed. Isometric strengthening can be done by pushing the top of the hand up against the undersurface of a table and holding the wrist straight.Orthotic devices

 Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow; however, long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
Orthosis is a device externally used on the limb to improve the function or reduce the pain. Orthotics may be useful in tennis elbow; however, long-term effects are unknown. There are two main types of orthoses prescribed for this problem: counterforce elbow orthoses and wrist extension orthoses. Counterforce orthosis has a circumferential structure surrounding the arm. This orthosis usually has a strap which applies a binding force over the origin of the wrist extensors. The applied force by orthosis reduces the elongation within the musculotendinous fibers. Wrist extensor orthosis maintains the wrist in the slight extension.
Speculative treatments
Other approaches that are not experimentally tested include eccentric exercise using a rubber bar, joint manipulation directed at the elbow and wrist, spinal manipulation directed at the cervical and thoracic spinal regions, low level laser therapy, and extracorporeal shockwave therapy.Medication
Recent studies demonstrate that topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications are effective within four weeks for lateral epicondylitis. Evidence for oral NSAIDs is mixed. Research indicates thatcorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
injections improved outcomes more effectively than NSAIDs within four weeks but offered no long-term benefits at 12 months.
Other studies suggest that, while helpful for short-term pain relief, corticosteroid injections are less effective than watchful waiting or physical therapy after one year. Repeated injections can also lead to tendon rupture and muscle atrophy. Thus, clinicians should be cautious with corticosteroid use for lateral epicondylitis due to limited long-term effectiveness and possible adverse effects.
Alternative Treatments
While many alternative treatments, such asshockwave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
, laser, low-frequency electrical nerve stimulation, ultrasound, and pulsed magnetic wave therapies, have been used, none have been proven effective. Current evidence is inconclusive on the effectiveness of acupuncture for lateral epicondylitits.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
Platelet-Rich Plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), also known as autologous conditioned plasma, is a concentrate of plasma protein derived from whole blood, centrifuged to remove red blood cells but retaining platelets. Though promoted for treating various medical con ...
(PRP) has emerged as a potential treatment for lateral epicondylitis. PRP is derived from the patient's own blood and contains concentrated platelets, which are rich in growth factors. These growth factors are believed to initiate and accelerate tissue repair and regeneration support healing of the tendons and connective tissue and promote the growth of new blood vessels, aiding the recovery process.
The PRP procedure for lateral epicondylitis involves extracting a small amount of the patient's blood, separating the plasma through centrifugation, and re-injecting it directly into the lateral epicondyle. While good outcomes have been reported with PRP for lateral epicondylitis, the overall literature is still unclear on its effectiveness. Additionally, variations in PRP preparation methods and injection techniques across different commercial systems add further complexity to assessing its effectiveness.
Overall, current research on PRP as a treatment for lateral epicondylitis is promising. However, more studies are needed to provide clear evidence of its effectiveness.
Surgery
Most patients with lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) improve with conservative treatments and do not need surgery. However, if symptoms persist despite prolonged conservative therapy, surgical options should be reconsidered. Several surgical procedures are available for lateral epicondylitis, most involving the removal of damaged tissue from the ECRB and scraping of the lateral epicondyle. This procedure can be done through open,percutaneous
{{More citations needed, date=January 2021
In surgery, a percutaneous procedurei.e. Granger et al., 2012 is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using ...
, or arthroscopic
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic or keyhole surgery) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the j ...
methods.
Percutaneous Surgery
Percutaneous surgical approach is mainly used for releasing the common extensor tendon origin at the lateral epicondyle. This technique has been demonstrated to be safe, reliable, and cost-effective Good midterm outcomes in pain relief have been widely reported with a percutaneous surgical approach. However there is some limited evidence reported that arthroscopic and open techniques achieved a better prognosis than the percutaneous surgical approach for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis. In recent years, a new technique termed as ultrasound-guided percutaneous tenotomy has been reported as a safe and effective for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis, with improvements in symptoms, function, and ultrasound imaging at 1-year follow-up.Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive option for treating lateral epicondylitis. This technique fully visualizes theelbow joint
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the ...
, and leads to a quicker return to work. In the past, studies have shown good long term effects and fewer complications with arthroscopic surgery compared to open or percutaneous approaches. However, the literature is currently mixed with some recent reviews suggest no significant differences among open, arthroscopic, and percutaneous
{{More citations needed, date=January 2021
In surgery, a percutaneous procedurei.e. Granger et al., 2012 is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using ...
methods regarding recovery time, complication rates, or patient satisfaction. While others state that arthroscopic surgery may allow for a quicker return to work, suggesting a potential advantage in the early postoperative period. While results are generally positive, arthroscopic surgery carries risks of injury to the radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the Posterior compartment of the ...
and lateral ulnar collateral ligament.
Epidemiology
Tennis Elbow is a commonly seen condition and has been reported to affect 1% to 3% of adults each year. The incidence of lateral elbow tendinosis has declined, which could be due to shifts in diagnostic practices or an actual drop in cases. Understanding the typical disease progression can help patients and providers choose the best treatment approach.Symptoms of lateral epicondylitis
Symptoms suggestive of lateral epicondylitis are present in about 1% of the adult population and are most common between ages 40 and 60. The prevalence varies somewhat between studies, likely as a result of varied diagnostic criteria and limited reliability between different observers. The data regarding symptoms of lateral epicondylitis in relation to occupations and sports are inconsistent and inconclusive. The shortcomings of the evidence that addresses the relationship between symptoms and occupation/sport include: variation in diagnostic criteria, limited reliability of diagnosis, confounding association of psychosocial factors, selection bias due to a high non-response rate, and the fact that exposures are usually by subjective patient reports and symptomatic patients might receive greater exposure.History
German physician F. Runge is usually credited for the first description of the condition, calling it "writer's cramp" (''Schreibekrampf'') in 1873. Later, it was called as "washer women's elbow". British surgeon Henry Morris published an article in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'' describing "lawn tennis arm" in 1883. The popular term "tennis elbow" first appeared the same year in a paper by H. P. Major, described as "lawn-tennis elbow".
See also
* Golfer's elbow *Olecranon bursitis
Olecranon bursitis is a condition characterized by swelling, redness, and pain at the tip of the elbow. If the underlying cause is due to an infection, fever may be present. The condition is relatively common and is one of the most frequent ty ...
* Radial tunnel syndrome
* Repetitive strain injury
A repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury to part of the musculoskeletal or nervous system caused by repetitive use, vibrations, compression or long periods in a fixed position. Other common names include repetitive stress injury, repetitiv ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Tennis Elbow Inflammations Overuse injuries Skeletal disorders Soft tissue disorders Sports injuries Tennis culture Tennis terminology Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate