|
Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tennis elbow, golfer's elbow), wrist, hip, knee ( jumper's knee, popliteus tendinopathy), or ankle ( Achilles tendinitis). Causes may include an injury or repetitive activities. Less common causes include infection, arthritis, gout, thyroid disease, diabetes and the use of quinolone antibiotic medicines. Groups at risk include people who do manual labor, musicians, and athletes. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms, examination, and occasionally medical imaging. A few weeks following an injury little inflammation remains, with the underlying problem related to weak or disrupted tendon fibrils. Treatment may include rest, NSAIDs, splinting, and physiotherapy. Less commonly steroid injections or surgery may be done. About 80% of over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis, also known as Achilles tendinopathy, is soreness of the Achilles tendon. It is accompanied by alterations in the tendon's structure and mechanical properties. The most common symptoms are pain and swelling around the back of the ankle. The pain is typically worse at the start of exercise and decreases thereafter. Stiffness of the ankle may also be present. Onset is generally gradual. Achilles tendinopathy is idiopathic, meaning the cause is not well understood. Theories of causation include overuse such as running, a lifestyle that includes little exercise, high-heel shoes, rheumatoid arthritis, and medications of the fluoroquinolone or steroid class. Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms and examination. Proposed interventions to treat tendinopathy have limited or no scientific evidence to support them, such as pre-exercise stretching, strengthening calf muscles, avoiding over-training, adjustment of running mechanics, and selection of footwear. Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Patellar Tendinitis
Patellar tendinitis, also known as jumper's knee, is an overuse injury of the tendon that straightens the knee. Symptoms include pain in the front of the knee. Typically the pain and tenderness is at the lower part of the kneecap, though the upper part may also be affected. Generally there is no pain when the person is at rest. Complications may include patellar tendon rupture. Risk factors include being involved in athletics and being overweight. It is particularly common in athletes who are involved in jumping sports such as basketball and volleyball. Other risk factors include sex, age, occupation, and physical activity level. It is increasingly more likely to be developed with increasing age. The underlying mechanism involves small tears in the tendon connecting the kneecap with the shinbone. Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms and examination. Other conditions that can appear similar include infrapatellar bursitis, chondromalacia patella and patellofemoral syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus (heel) bone. These muscles, acting via the tendon, cause plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint, and (except the soleus) flexion at the knee. Abnormalities of the Achilles tendon include inflammation ( Achilles tendinitis), degeneration, rupture, and becoming embedded with cholesterol deposits ( xanthomas). The Achilles tendon was named in 1693 after the Greek hero Achilles. History The oldest-known written record of the tendon being named after Achilles is in 1693 by the Flemish/Dutch anatomist Philip Verheyen. In his widely used text he described the tendon's location and said that it was commonly called "the cord of Achilles." The tendon has been described as early as the time of Hippocrates, who described it as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calcific Tendinitis
Calcific tendinitis is a common condition where deposits of calcium phosphate form in a tendon, sometimes causing pain at the affected site. Deposits can occur in several places in the body, but are by far most common in the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Around 80% of those with deposits experience symptoms, typically chronic pain during certain shoulder movements, or sharp acute pain that worsens at night. Calcific tendinitis is typically diagnosed by physical exam and X-ray imaging. The disease often resolves completely on its own, but is typically treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain, rest and physical therapy to promote healing, and in some cases various procedures to breakdown and/or remove the calcium deposits. Adults aged 30–50 are most commonly affected by calcific tendinitis. It is twice as common in women as men, and is not associated with exercise. Calcifications in the rotator cuff were first described by Ernest Codman in 1934. The name, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
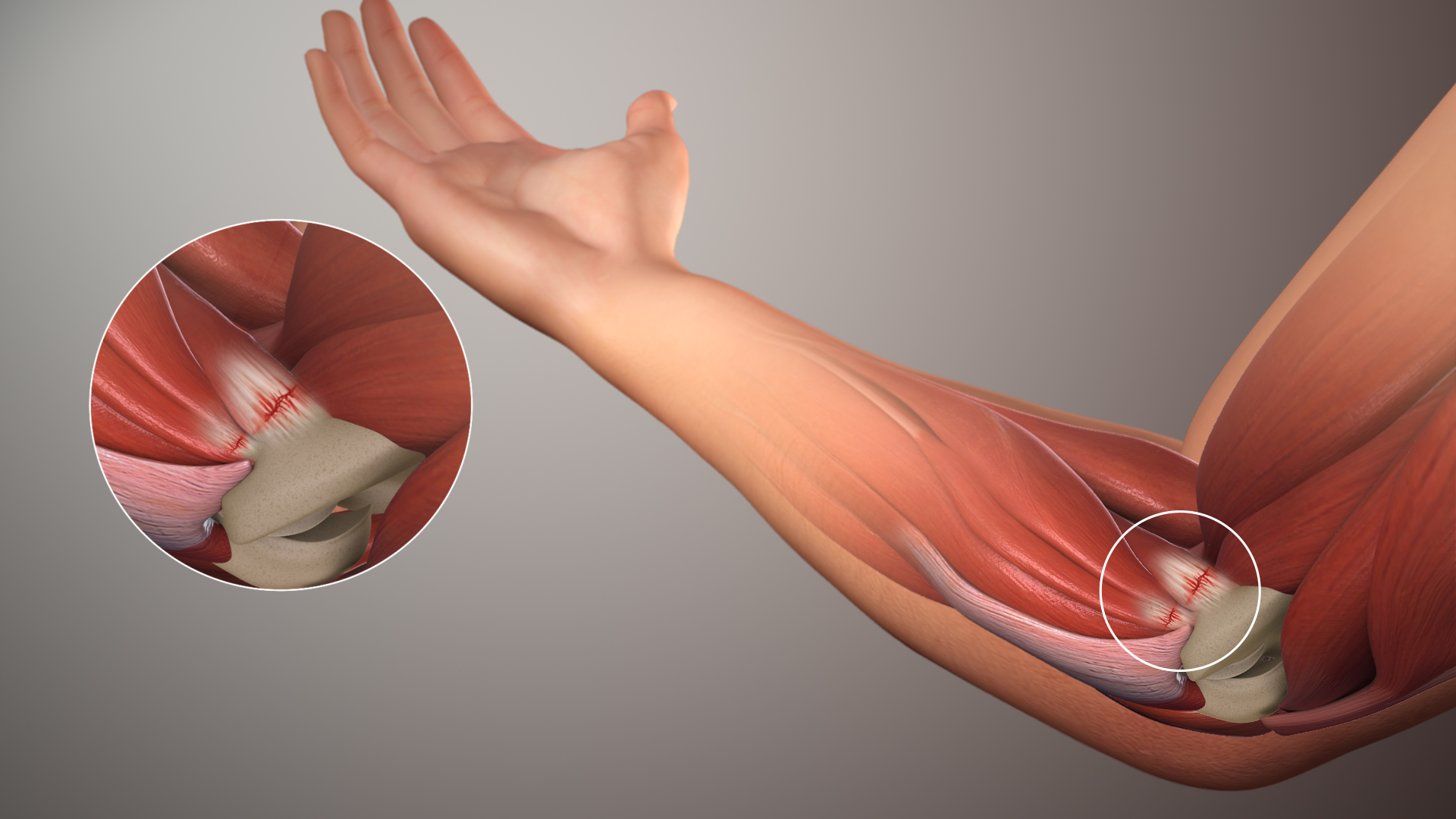
Lateral Epicondylitis
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an enthesopathy (attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the lateral epicondyle. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, lateral epicondyle. Symptoms range from mild tenderness to severe, persistent pain. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm. It usually has a gradual onset, but it can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury. Tennis elbow is often idiopathic. Its cause and pathogenesis are unknown. It likely involves Tendinopathy, tendinosis, a degeneration of the local tendon. It is thought this condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, back of the forearm, but this is not supported by evidence. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports (including paddle sports), but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension (physics), tension. Tendons, like ligaments, are made of collagen. The difference is that ligaments connect bone to bone, while tendons connect muscle to bone. There are about 4,000 tendons in the adult human body. Structure A tendon is made of dense regular connective tissue, whose main cellular components are special fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tendon cells synthesize the tendon's extracellular matrix, which abounds with densely-packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers run parallel to each other and are grouped into fascicles. Each fascicle is bound by an endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibers. A set of fascicles is bound by an epitenon, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an enthesopathy (attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the lateral epicondyle. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the lateral epicondyle. Symptoms range from mild tenderness to severe, persistent pain. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm. It usually has a gradual onset, but it can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury. Tennis elbow is often idiopathic. Its cause and pathogenesis are unknown. It likely involves tendinosis, a degeneration of the local tendon. It is thought this condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the back of the forearm, but this is not supported by evidence. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports (including paddle sports), but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activities. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and examination. Medical imaging is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well. Shoulder pain may be localized or may be referred to areas around the shoulder or down the arm. Other regions within the body (such as gallbladder, liver, or heart disease, or disease of the cervical spine of the neck) also may generate pain that the brain may interpret as arising from the shoulder. Shoulder structures and functions The shoulder joint is composed of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) (see diagram). Two joints facilitate shoulder movement. The acromioclavicular (AC) joint is located between the acromio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quinolone Antibiotic
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production. Quinolone antibiotics are classified into four generations based on their spectrum of activity and chemical modifications. The first-generation quinolones, such as nalidixic acid, primarily target Gram-negative bacteria and are mainly used for urinary tract infections. Second-generation quinolones introduced fluorine atoms into their structure, creating fluoroquinolones, which significantly expanded their antibacterial activity to include some Gram-positive bacteria. Third-generation fluoroquinolones further improved Gram-positive coverage, while fourth-generation fluoroquinolones offer broad-spectrum activity, including anaerobic bacteria. Only quinolone antibiotics in generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Golfer's Elbow
Golfer's elbow, or medial epicondylitis, is tendinosis (or more precisely enthesopathy) of the medial common flexor tendon on the inside of the elbow. It is similar to tennis elbow, which affects the outside of the elbow at the lateral epicondyle. The tendinopathy results from overload or repetitive use of the arm, causing an injury similar to ulnar collateral ligament injury of the elbow in "pitcher's elbow". Description The anterior-medial forearm contains several muscles that flex the wrist and pronate the forearm. These muscles have a common tendinous attachment at the medial epicondyle of the humerus at the elbow joint. The flexor and pronator muscles of the forearm include the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor digitorum superficialis, all of which originate on the medial epicondyle and are innervated by the median nerve. The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle also inserts on the medial epicondyle and is innervated by the ulnar nerve. Together, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |