|
Lateral Epicondylitis
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an enthesopathy (attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the lateral epicondyle. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, lateral epicondyle. Symptoms range from mild tenderness to severe, persistent pain. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm. It usually has a gradual onset, but it can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury. Tennis elbow is often idiopathic. Its cause and pathogenesis are unknown. It likely involves Tendinopathy, tendinosis, a degeneration of the local tendon. It is thought this condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, back of the forearm, but this is not supported by evidence. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports (including paddle sports), but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow-joint
The elbow is the region between the arm, upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, lateral and the Medial epicondyle of the humerus, medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius (bone), radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for primate, humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pickleball
Pickleball is a racket or paddle sport in which two or four players use a smooth-faced paddle to hit a perforated, hollow plastic ball over a net until one side is unable to return the ball or commits a rule infraction. Pickleball is played indoors and outdoors. It was invented in 1965 as a children's backyard game in the United States, on Bainbridge Island in Washington State. In 2021, pickleball was named the official state sport of Washington. Aspects of the sport resemble tennis and table tennis played on a doubles badminton court, but pickleball has specific scoring rules, paddles, balls and court lines. On each side of the net is a known as the '' non-volley zone'' (or ''kitchen''); a player standing there may not strike the ball before it has bounced. The hard plastic pickleball produces less bounce than a tennis ball. The limited bounce, non-volley zones, and underhanded stroke, with which all serves must be made, give the game a dynamic pace. Slow soft shots in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extension (kinesiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
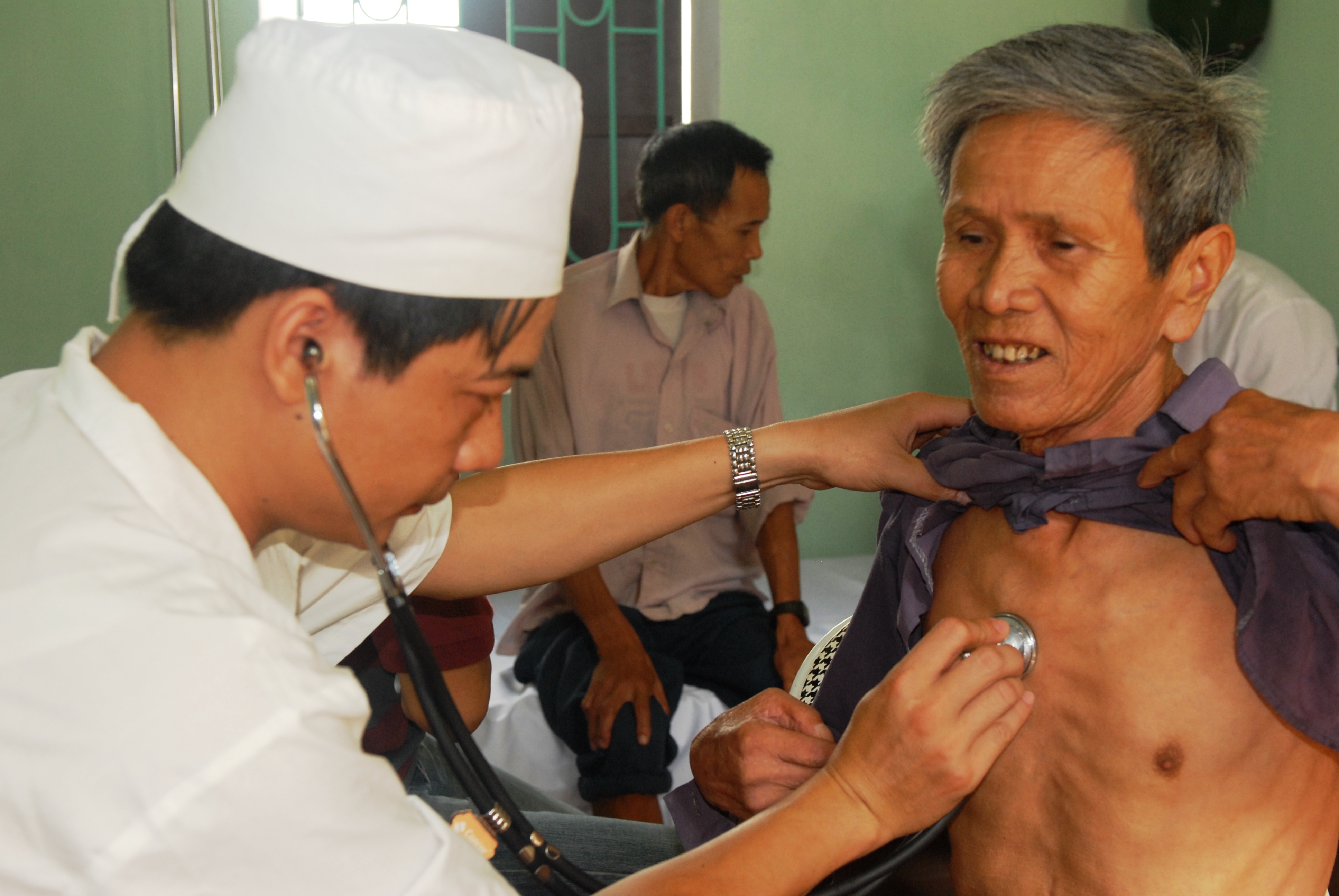
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the extensor carpi radialis brevis. Origin and insertion It arises from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, by the common extensor tendon; from the radial collateral ligament of the elbow-joint; from a strong aponeurosis which covers its surface; and from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox The fibres end approximately at the middle of the forearm in the form of a flat tendon, which is closely connected with that of the extensor carpi radialis longus, and accompanies it to the wrist; it passes beneath the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, beneath the extensor retinaculum, and inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendonitis
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tennis elbow, golfer's elbow), wrist, hip, knee ( jumper's knee, popliteus tendinopathy), or ankle ( Achilles tendinitis). Causes may include an injury or repetitive activities. Less common causes include infection, arthritis, gout, thyroid disease, diabetes and the use of quinolone antibiotic medicines. Groups at risk include people who do manual labor, musicians, and athletes. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms, examination, and occasionally medical imaging. A few weeks following an injury little inflammation remains, with the underlying problem related to weak or disrupted tendon fibrils. Treatment may include rest, NSAIDs, splinting, and physiotherapy. Less commonly steroid injections or surgery may be done. About 80% of over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the extensor carpi radialis brevis. Origin and insertion It arises from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, by the common extensor tendon; from the radial collateral ligament of the elbow-joint; from a strong aponeurosis which covers its surface; and from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox The fibres end approximately at the middle of the forearm in the form of a flat tendon, which is closely connected with that of the extensor carpi radialis longus, and accompanies it to the wrist; it passes beneath the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, beneath the extensor retinaculum, and inserts into the lateral dorsal surface of the base of the third metacarpal bone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repetitive Strain Injury
A repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury to part of the musculoskeletal or nervous system caused by repetitive use, vibrations, compression or long periods in a fixed position. Other common names include repetitive stress injury, repetitive stress disorders, cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs), and overuse syndrome. Signs and symptoms Some examples of symptoms experienced by patients with RSI are aching, pulsing pain, tingling and extremity weakness, initially presenting with intermittent discomfort and then with a higher degree of frequency. Definition Repetitive strain injury (RSI) and associative trauma orders are umbrella terms used to refer to several discrete conditions that can be associated with repetitive tasks, forceful exertions, vibrations, mechanical compression, sustained or awkward positions, or repetitive eccentric contractions. The exact terminology is controversial, but the terms now used by the United States Department of Labor and the National Institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an enthesopathy (attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the lateral epicondyle. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the lateral epicondyle. Symptoms range from mild tenderness to severe, persistent pain. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm. It usually has a gradual onset, but it can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury. Tennis elbow is often idiopathic. Its cause and pathogenesis are unknown. It likely involves tendinosis, a degeneration of the local tendon. It is thought this condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the back of the forearm, but this is not supported by evidence. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports (including paddle sports), but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activities. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and examination. Medical imaging is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Journal Of Sports Medicine
The ''British Journal of Sports Medicine'' is a twice-monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering sports science and sports medicine including sport physiotherapy. It is published by the BMJ Group. It was established in 1964 and the editor-in-chief from 2008 to 2020 was Karim M. Khan (University of British Columbia). Jonathan Drezner (University of Washington) has been editor-in-chief since January 1, 2021. Abstracting and indexing According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 11.8. International Olympic Committee consensus statements Since 2009, the journal has partnered with the International Olympic Committee to produce regular consensus statements regarding important issues in sports injury prevention and elite sport. Some of the recent examples include Consensus Statements on concussions in sport (the "Berlin guidelines"), relative energy deficiency in sport, the relationship between training load and injury, mental health issues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |