Tatar Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tatarstan, officially the Republic of Tatarstan, sometimes also called Tataria, is a
Tatarstan, officially the Republic of Tatarstan, sometimes also called Tataria, is a
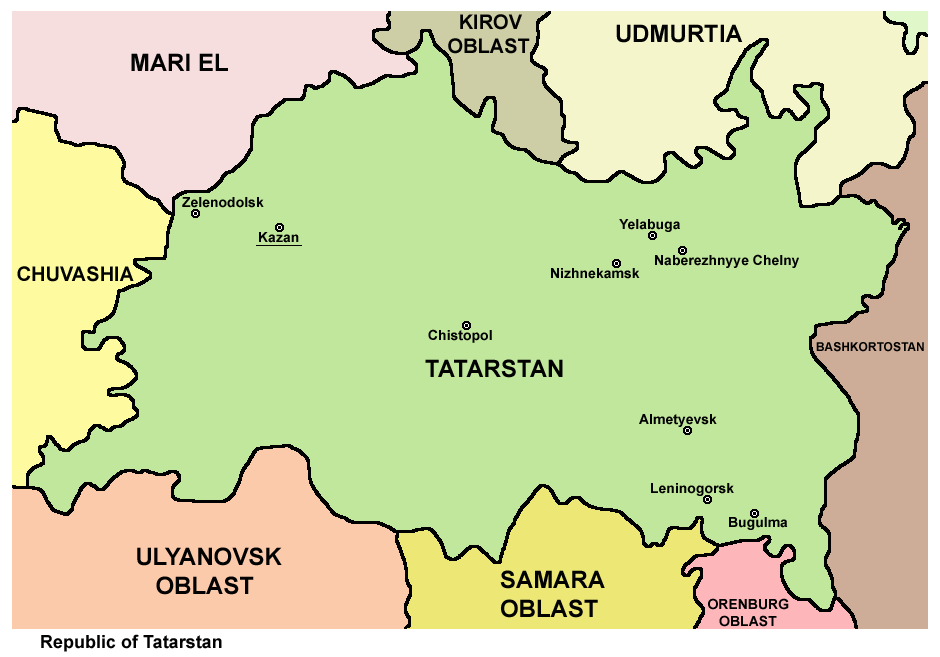 The republic is located in the center of the
The republic is located in the center of the
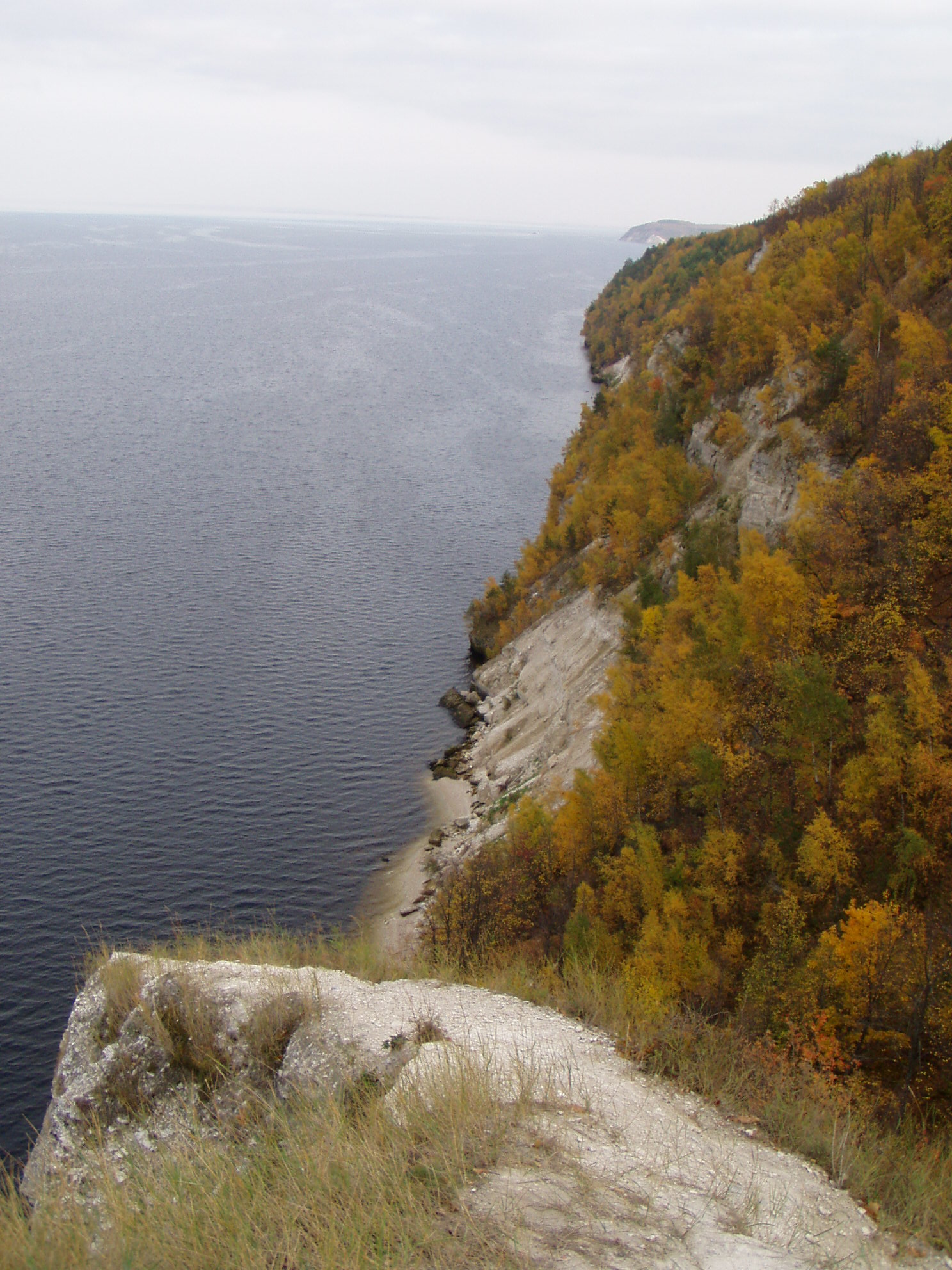


 Major rivers include:
* Azevka River
* Belaya River
*
Major rivers include:
* Azevka River
* Belaya River
*
Constitution of the Republic of Tatarstan
The districts consist of cities of district significance, urban-type settlements and rural settlements with subordinate territories that make up the primary level in the system of administrative-territorial structure of the Republic. Cities of national significance can be geographically divided into districts in the city.
 Volga Bulgaria finally fell to the armies of the
Volga Bulgaria finally fell to the armies of the
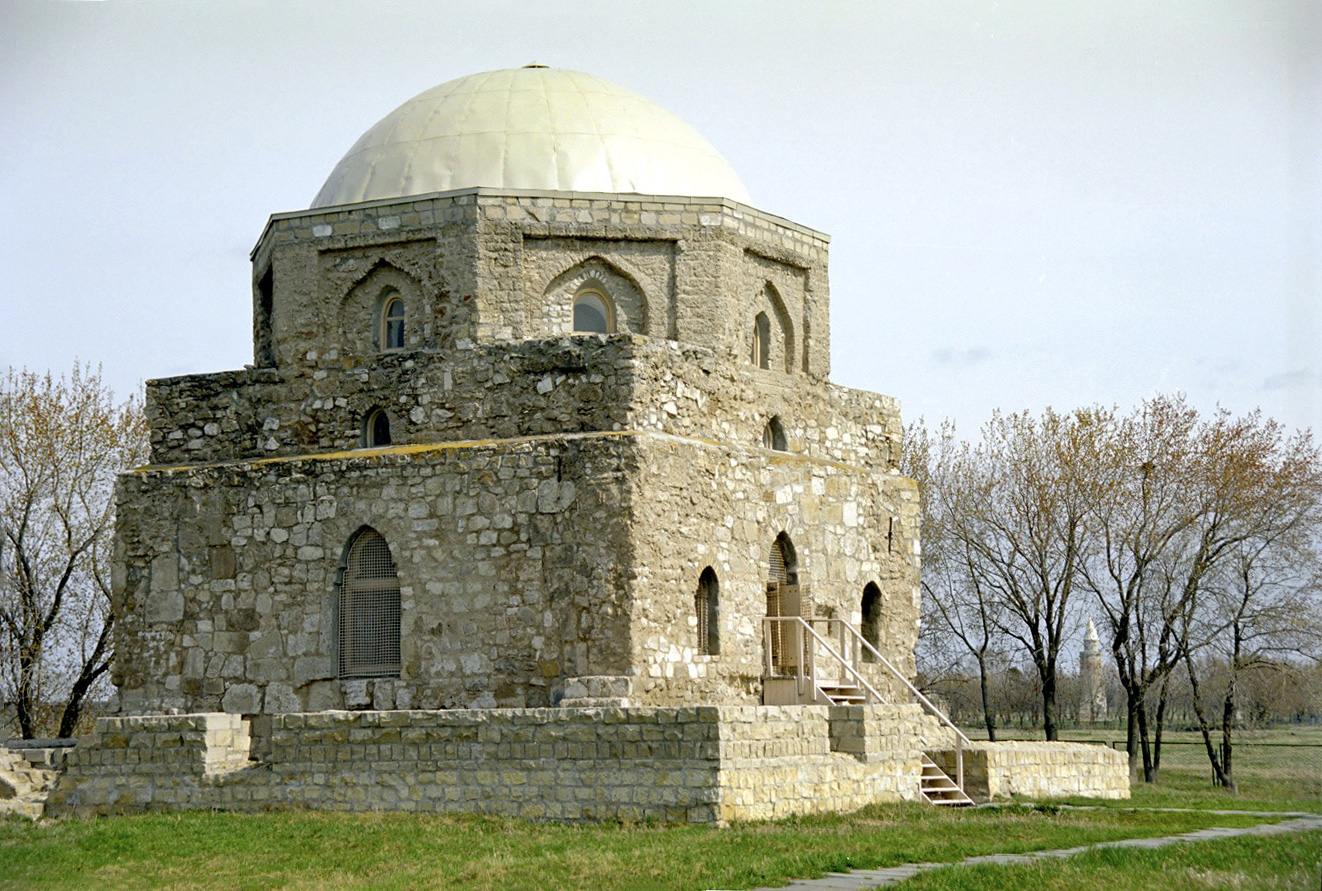 In the 19th century, Tatarstan became a centre of
In the 19th century, Tatarstan became a centre of



 Note: TFR source.
Note: TFR source.
"Ogonek", No. 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 21/04/2017
Archived
Established in 922, the first Muslim state within the boundaries of modern Russia was
 Tatarstan's
Tatarstan's
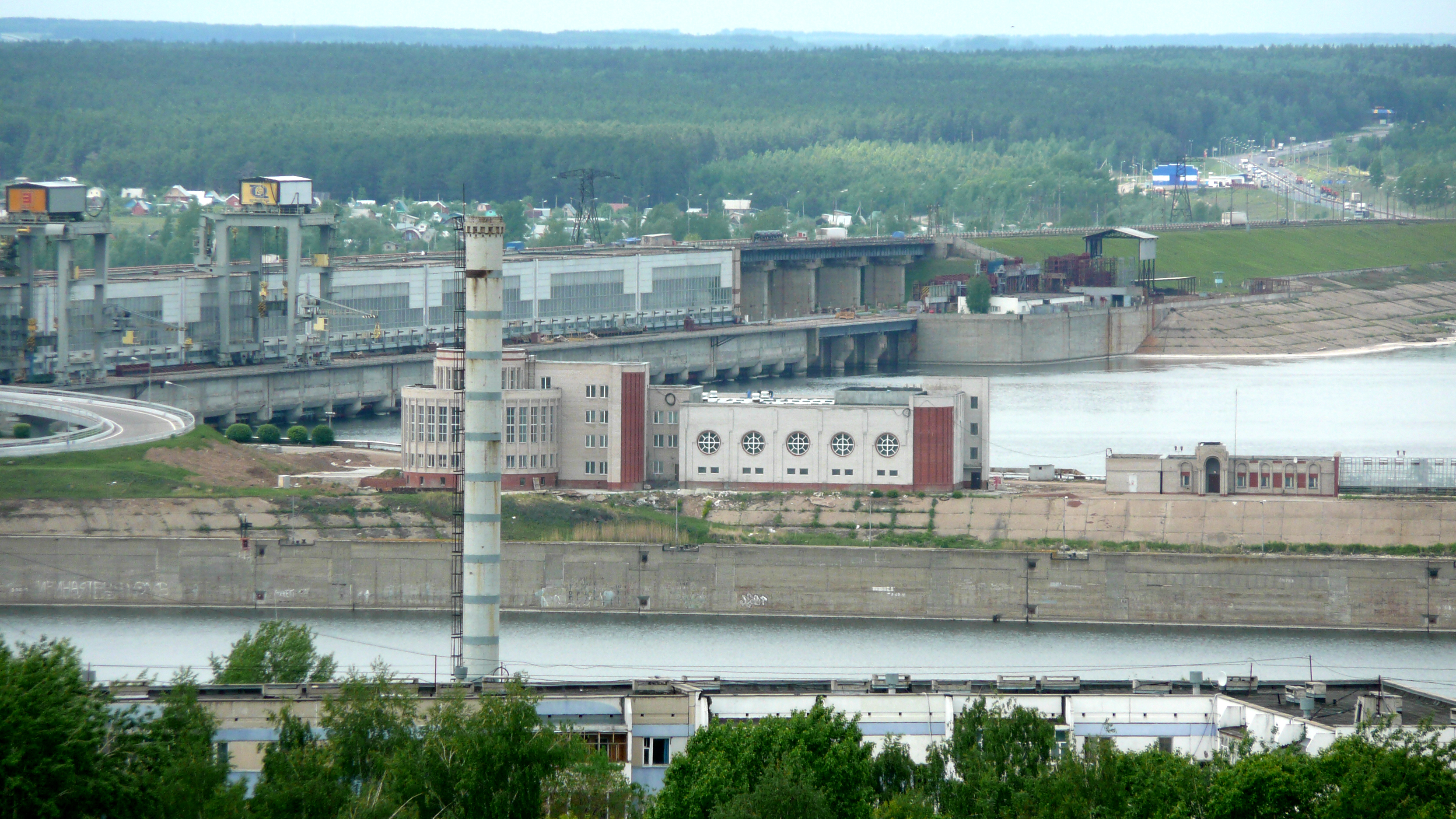 Tatarstan consists of three distinct industrial regions. The northwestern part is an old industrial region where engineering, chemical, and light industry dominate. In the newly industrial northeast region with its core in the
Tatarstan consists of three distinct industrial regions. The northwestern part is an old industrial region where engineering, chemical, and light industry dominate. In the newly industrial northeast region with its core in the
 There are three UNESCO world heritage sites in Tatarstan—
There are three UNESCO world heritage sites in Tatarstan— Currently, sanatorium and resort recreation is developing rapidly in Tatarstan. There are 46 sanatorium-resort institutions in the Republic of Tatarstan. The capacity of the objects of the sanatorium-resort complex of Tatarstan is 8847 beds; more than 4300 specialists are engaged in the service of residents. In 2016, more than 160 thousand people rested in the health resorts of the Republic of Tatarstan. 22 health resort institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan are members of the Association of health resort institutions "Health resorts of Tatarstan," including 11 sanatoriums of PJSC "Tatneft."
Since 2016, the Republic of Tatarstan has been operating the Visit Tatarstan program, the official tourism brand of the Republic, the purpose of which is to inform tourists, monitor the reputation of the Republic, develop the tourism potential of the regions of Tatarstan, conduct market research, create partner projects with local companies, and expand internationally. "Tatarstan: 1001 pleasure" is the main message that tourists receive. The Visit Tatar website, where there is information about the main sights and recreation in Tatarstan, is available in 8 languages: Tatar, Russian, English, Chinese, German, Spanish, Finnish, and Persian.
Currently, sanatorium and resort recreation is developing rapidly in Tatarstan. There are 46 sanatorium-resort institutions in the Republic of Tatarstan. The capacity of the objects of the sanatorium-resort complex of Tatarstan is 8847 beds; more than 4300 specialists are engaged in the service of residents. In 2016, more than 160 thousand people rested in the health resorts of the Republic of Tatarstan. 22 health resort institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan are members of the Association of health resort institutions "Health resorts of Tatarstan," including 11 sanatoriums of PJSC "Tatneft."
Since 2016, the Republic of Tatarstan has been operating the Visit Tatarstan program, the official tourism brand of the Republic, the purpose of which is to inform tourists, monitor the reputation of the Republic, develop the tourism potential of the regions of Tatarstan, conduct market research, create partner projects with local companies, and expand internationally. "Tatarstan: 1001 pleasure" is the main message that tourists receive. The Visit Tatar website, where there is information about the main sights and recreation in Tatarstan, is available in 8 languages: Tatar, Russian, English, Chinese, German, Spanish, Finnish, and Persian.

 *
*
 Major libraries include
Major libraries include
 With 9,175 sports venues in Tatarstan, the republic is one of the leading sports regions in Russia. Since 1973, Kazan has been making efforts to expand its sports
With 9,175 sports venues in Tatarstan, the republic is one of the leading sports regions in Russia. Since 1973, Kazan has been making efforts to expand its sports
Tatarstan: Smooth Islamization Sprinkled with Blood
''OnIslam.net.'' Accessed: Feb. 26, 2013. * Daniel Kalder. ''Lost Cosmonaut: Observations of an Anti-tourist''. * Ravil Bukharaev. ''The Model of Tatarstan: Under President Mintimer Shaimiev''. * Azadeayse Rorlich. ''The Volga Tatars: A Profile in National Resilience''. * Roderick Heather. ''Russia From Red to Black'' * Matthew Reid. ''Shattered Kremlin: Echoes of the Iron Curtain''
Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan
Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan
Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan
Tatar-Inform
information agency
Official Tourist Portal of the Republic of Tatarstan
{{Authority control States and territories established in 1920 Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Tatar topics Regions of Europe with multiple official languages 1920 establishments in Europe Observer members of the International Organization of Turkic Culture Republics of Russia
republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
located in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
. It is a part of the Volga Federal District
The Volga Federal District ( rus, Приволжский федеральный округ, p=prʲɪˈvolʂskʲɪj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is one of the eight federal districts of Russia, federal districts of Russia. It forms the south ...
; and its capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
and largest city is Kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
, an important cultural centre in Russia. The region's main source of wealth is oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
with a strong petrochemical industry
file:Jampilen Petrochemical Co. 02.jpg, 300px, Jampilen Petrochemical co., Asaluyeh, Iran
The petrochemical industry is concerned with the production and trade of petrochemicals. A major part is constituted by the plastics industry, plastics (poly ...
.
The republic borders the oblasts
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
of Kirov, Ulyanovsk
Ulyanovsk,, , known as Simbirsk until 1924, is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Volga River east of Moscow. Ulyanovsk has been the only Russian UNESCO Ci ...
, Samara
Samara, formerly known as Kuybyshev (1935–1991), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast in Russia. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara (Volga), Samara rivers, with a population of over 1.14 ...
and Orenburg
Orenburg (, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies in Eastern Europe, along the banks of the Ural River, being approximately southeast of Moscow.
Orenburg is close to the ...
, as well as the republics of Mari El
Mari El,; ; officially the Mari El Republic, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia. It is in the European Russia, European region of the country, along the northern bank of the Volga River, and administratively part of the Volga Federal ...
, Udmurtia
Udmurtia, officially the Udmurt Republic, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is administratively part of the Volga Federal District. Its capital city, capital is the types of inhabited localities in Russi ...
, Chuvashia
Chuvashia, officially known as Chuvash Republic — Chuvashia, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuvash people, a Turkic languages, Turkic ethnic group. Its capital city, capital i ...
and Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan, officially the Republic of Bashkortostan, sometimes also called Bashkiria, is a republic of Russia between the Volga river and the Ural Mountains in Eastern Europe. The republic borders Perm Krai to the north, Sverdlovsk Oblast ...
. The area of the republic is , occupying 0.4% of the total surface of the country. As of the 2021 Census, the population of Tatarstan was 4,004,809.
Tatarstan has strong cultural, linguistic and ethnic ties with its eastern neighbour, Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan, officially the Republic of Bashkortostan, sometimes also called Bashkiria, is a republic of Russia between the Volga river and the Ural Mountains in Eastern Europe. The republic borders Perm Krai to the north, Sverdlovsk Oblast ...
, which is also a republic of Russia.
The official languages of the republic are Tatar
Tatar may refer to:
Peoples
* Tatars, an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar"
* Volga Tatars, a people from the Volga-Ural region of western Russia
* Crimean Tatars, a people from the Crimea peninsula by the B ...
and Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
.
Etymology
"Tatarstan" derives from the name of the ethnic group—theTatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
—and the in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
suffix ''-stan
-stan ( Persian: ستان )(Sanskrit: ''sthān'' or ''sthānam)'' is a Persian suffix that has the meaning of "a place abounding in" or "place where anything abounds" as a suffix. It is widely used by Iranian languages (mainly Persian) and ...
'' (meaning "state" or "country" of, an ending common to many Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
n countries). Another version of the Russian name is "" (), which was official along with "Tatar ASSR
The Tatar Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as Tatar ASSR or TASSR, was an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR. The resolution for its creation was signed on 27 May 1920 and the republic was proclaimed on 25 June 1920. Kazan ...
" during Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
rule.
Correct spelling of the Persian -stan as a suffix would use i/e after a consonant. Turkish spells Tatarstan as "Tataristan", and occasionally in Tatar, it is "Tatarıstan" (Татарыстан).
Geography
 The republic is located in the center of the
The republic is located in the center of the East European Plain
The East European Plain (also called the Russian Plain, "Extending from eastern Poland through the entire European Russia to the Ural Mountains, the ''East European Plain'' encompasses all of the Baltic states and Belarus, nearly all of Ukraine, ...
, approximately east of Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
. It lies between the Volga River
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
and the Kama River
The Kama ( , ; ; ), also known as the Chulman ( ; ), is a long«Река КАМА»
Russian St ...
(a Russian St ...
tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
of the Volga), and extends east to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
.
Oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
is the dominant tree species on 87% of the total area, followed by aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species in the Populus sect. Populus, of the ''Populus'' (poplar) genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
* ''Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (China, south of ''P. tremula'')
* ''Populus da ...
, linden, birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
, and Scots pine
''Pinus sylvestris'', the Scots pine (UK), Scotch pine (US), Baltic pine, or European red pine is a species of tree in the pine family Pinaceae that is native to Eurasia. It can readily be identified by its combination of fairly short, blue-gr ...
. The total forest cover has decreased from 51.2% to 17.1% over the last 300 years.
The Volga-Kama Nature Reserve is situated in Tatarstan.
Borders
* Neighbours:Kirov Oblast
Kirov Oblast ( rus, Кировская область, p=ˈkʲirəfskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) located in Eastern Europe. Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. As of the 2010 census, the population ...
(N), Udmurt Republic
Udmurtia, officially the Udmurt Republic, is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is administratively part of the Volga Federal District. Its capital is the city of Izhevsk.
It was established as the Udmurt (until 1931 — Vots ...
(N/NE), Republic of Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan, officially the Republic of Bashkortostan, sometimes also called Bashkiria, is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia between the Volga, Volga river and the Ural Mountains in Eastern Europe. The republic borders Perm Krai to th ...
(E/SE), Orenburg Oblast
Orenburg Oblast (also Orenburzhye) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), mainly located in Eastern Europe. Its administrative center is the city of Orenburg. From 1938 to 1957, it bore the name Chkalov Oblast in honor of Valery Chkal ...
(SE), Samara Oblast
Samara Oblast (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Samara. From 1935 to 1991, it was known as Kuybyshev Oblast. As of the Rus ...
(S), Ulyanovsk Oblast
Ulyanovsk Oblast () is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It is located in the Volga Federal District. Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Ulyanovsk. It has a populat ...
(S/SW), Chuvash Republic
Chuvashia, officially known as Chuvash Republic — Chuvashia, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuvash people, a Turkic languages, Turkic ethnic group. Its capital city, capital i ...
(W), Mari El Republic
Mari El,; ; officially the Mari El Republic, is a republic of Russia. It is in the European region of the country, along the northern bank of the Volga River, and administratively part of the Volga Federal District. The republic has a populat ...
(W/NW).
* Highest point:
* Maximum N–S distance:
* Maximum E–W distance:
Rivers


 Major rivers include:
* Azevka River
* Belaya River
*
Major rivers include:
* Azevka River
* Belaya River
* Ik River
The Ik (; , ''Iq''; , ''Iq'') is a river in Russia that flows north to the Kama, joining it from the left. It flows through the Republics of Bashkortostan and Tatarstan and through Orenburg Oblast. The left tributaries of the Ik are Mellya, M ...
* Kama River
The Kama ( , ; ; ), also known as the Chulman ( ; ), is a long«Река КАМА»
Russian St ...
* Russian St ...
Volga River
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
* Vyatka River
The Vyatka is a river in Kirov Oblast and Tatarstan in Russia. It is a right tributary of the Kama.Kazanka River
The Kazanka (; ) is a river in the Russian Federation, a left tributary of the Volga. The Kazanka begins near the village of Bimeri in Arsk District and flows into the Kuybyshev Reservoir in Kazan, near the Kazan Kremlin. Other towns on the Kazan ...
* Zay River
The Zay (; ) is a river in Russia, a left-bank tributary of the Kama (river), Kama. It is long, and its drainage basin covers .Kuybyshev Reservoir
Kuybyshev Reservoir or Kuybyshevskoye Reservoir () is a reservoir of the middle Volga and lower Kama in Chuvashia, Mari El Republic, Republic of Tatarstan, Samara Oblast and Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia. It is sometimes called as Samara Reservoir an ...
* Lower Kama Reservoir
Lower Kama Reservoir or Nizhnekamsk Reservoir (; ) is the lowest reservoir from the Kama River hydroelectric cascade. It is situated in Tatarstan, Udmurtia, Bashkortostan and Perm Krai, Russian Federation. The reservoir was filled in 1978-81 up to ...
* Zainsk Reservoir
Zainsk Reservoir or Zay Reservoir (, ) is a reservoir of the Zay River near Zainsk, Tatarstan, Russian Federation. It was filled in 1963 to be a cooling pond for Zainsk TTP. It has surface area 20.5 km², a length 12 km, mean width 1.7&n ...
The biggest lake is Kaban __NOTOC__
Kaban may refer to:
People
* Kaban, a Khazar ruler; See Khalga and Kaban
* An Israeli military psychologist; See Profile 21
* Jozef Kabaň, a Slovak automobile designer
* Family name (Kabán). They live in Hungary.
Places
* Kaban ...
. The biggest swamp is Kulyagash.
Hills
* Bugulma-Belebey Upland *Volga Upland
The Volga Upland, also known as the Volga Uplands, Volga Hills, or Volga Plateau (), is a vast region of the East European Plain in the European part of Russia that lies west of the Volga River and east of the Central Russian Upland.
The uplan ...
* Vyatskiye Uvaly
Basins
* Ulema basin *Mesha basin
King Mesha ( Moabite: , vocalized as: ; Hebrew: מֵישַׁע ''Mēšaʿ'') was a king of Moab in the 9th century BC, known most famously for having the Mesha Stele inscribed and erected at Dibon, Jordan. In this inscription he calls himself "Me ...
Natural resources
The major natural resources of Tatarstan includeoil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
. It is estimated that the republic has over one billion tons of oil deposits.
Climate
* ''Average January temperature'': * ''Average July temperature:'' * ''Average annual temperature:'' + * ''Average annualprecipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
'': up to
Administrative divisions
Tatarstan's administrative and territorial divisions form 43 municipal districts and 2 urban districts (Kazan and Naberezhnye Chelny), as well as 39 urban settlements and 872 rural settlements. The republic also recognises cities of republican significance, the list of which is established by thConstitution of the Republic of Tatarstan
The districts consist of cities of district significance, urban-type settlements and rural settlements with subordinate territories that make up the primary level in the system of administrative-territorial structure of the Republic. Cities of national significance can be geographically divided into districts in the city.
History
Middle Ages
The earliest known organised state within the boundaries of Tatarstan wasVolga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
(c. 700–1238). The Volga Bulgars
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
had an advanced mercantile state with trade contacts throughout Inner Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
, the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, and the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
, which maintained its independence despite pressure by such nations as the Khazars
The Khazars ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a nomadic Turkic people who, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, a ...
, the Kievan Rus
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russ ...
, and the Cuman
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Rus' chronicles, as " ...
-Kipchaks
The Kipchaks, also spelled Qipchaqs, known as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Russian annals, were Turkic nomads and then a confederation that existed in the Middle Ages inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe.
First mentioned in the eighth cent ...
. Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
was introduced by missionaries from Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
around the time of Ibn Fadlan
Ahmad ibn Fadlan ibn al-Abbas al-Baghdadi () or simply known as Ibn Fadlan, was a 10th-century traveler from Baghdad, Abbasid Caliphate, famous for his account of his travels as a member of an embassy of the Abbasid caliph al-Muqtadir to the king ...
's journey in 922.
 Volga Bulgaria finally fell to the armies of the
Volga Bulgaria finally fell to the armies of the Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
prince Batu Khan
Batu Khan (–1255) was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire established after Genghis Khan's demise. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Khan. His '' ulus'' ruled over the Kievan ...
in the late 1230s (see Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria
The Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria lasted from 1223 to 1236. The Bulgar state, centered in lower Volga and Kama, was the center of the fur trade in Eurasia throughout most of its history. Before the Mongol conquest, Russians of Novgoro ...
). The inhabitants, a large amount of them killed and the rest mixing with the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
's Kipchaks
The Kipchaks, also spelled Qipchaqs, known as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Russian annals, were Turkic nomads and then a confederation that existed in the Middle Ages inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe.
First mentioned in the eighth cent ...
, became known as the Volga Tatars
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars (; ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of western Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are the second-largest ethnic group in Russia after ethnic Russians. ...
. In the 1430s, the region again became independent as the base of the Khanate of Kazan
The Khanate of Kazan was a Tatar state that occupied the territory of the former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El, Chuvashia, Mordovia, and parts of Udmurtia and Bashkortostan; ...
, a capital having been established in Kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
, up the Volga from the ruined capital of the Bulgars.
The Khanate of Kazan was conquered by the troops of Tsar Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all R ...
in the 1550s, with Kazan being taken in 1552. A large number of Tatars were forcibly converted
Forced conversion is the adoption of a religion or irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which were originally held, wh ...
to Christianity and were culturally Russified
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
. Cathedrals were built in Kazan; by 1593 all mosques in the area were destroyed. The Russian government forbade the construction of mosques, a prohibition that was not lifted until the 18th century by Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
. The first mosque to be rebuilt under Catherine's auspices was constructed in 1766–1770.
19th century
 In the 19th century, Tatarstan became a centre of
In the 19th century, Tatarstan became a centre of Jadidism
The Jadid movement or Jadidism was an Turco-Islamic modernist political, religious, and cultural movement in the Russian Empire in the late 19th and early 20th century. They normally referred to themselves by the Tatar terms ''Taraqqiparvarlar ...
, an Islamic movement that preached tolerance of other religions. Under the influence of local Jadidist theologians, the Bulgars were renowned for their friendly relations with other peoples of the Russian Empire. However, after the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
, religion was largely outlawed and all theologians were repressed.
20th century
During theCivil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
of 1918–1920 Tatar nationalists attempted to establish an independent republic (the Idel-Ural State
The Idel-Ural State (, , , also İdel-Ural berlege İdel-Ural ştatı), also known as the Volga-Ural State or Idel-Ural Republic, was an short-lasting autonomy of Tatars, Tatar peoples that claimed to unite Volga Tatars, Tatars, Bashkirs, and ...
, ''Idel'' being the name of the Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
in Tatar) along with the neighbouring Bashkirs
The Bashkirs ( , ) or Bashkorts (, ; , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a Republics of Russia, republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of B ...
. Initially supported by the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
, the state existed up until March 1918, when high-ranking members of its parliament were arrested by the Bolsheviks (who had turned on the state and denounced it as bourgeois) before the official declaration of its constitution. The Soviets later set up the Tatar Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Tatar Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as Tatar ASSR or TASSR, was an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. The resolution for its crea ...
, which was established on 27 May 1920. The boundaries of the republic did not include a majority of the Volga Tatars. The Tatar Union of the Godless were persecuted in Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
's 1928 purge
In history, religion and political science, a purge is a position removal or execution of people who are considered undesirable by those in power from a government, another, their team leaders, or society as a whole. A group undertaking such an ...
s.
A famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
occurred in the Tatar Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Tatar Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as Tatar ASSR or TASSR, was an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. The resolution for its crea ...
in 1921–1922 as a result of the policy of war communism
War communism or military communism (, ''Vojenný kommunizm'') was the economic and political system that existed in Soviet Russia during the Russian Civil War from 1918 to 1921. War communism began in June 1918, enforced by the Supreme Economi ...
. The famine deaths of between 500,000 and 2 million Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
in the Tatar ASSR and in the in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Volga-Ural region
Idel-Ural (, ), literally Volga-Ural, is a historical region in Eastern Europe, in what is today Russia. The name literally means ''Volga- Urals'' in the Tatar language. The frequently used Russian variant is ''Volgo-Uralye'' (). The term Idel-U ...
in 1921–1922 was catastrophic as half of the Volga Tatar
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars (; ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of western Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are the second-largest ethnic group in Russia after ethnic Russians. ...
population in the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
died.
Starting in the 1960s, schools opened in Tatarstan that taught Russian as an official second language
A second language (L2) is a language spoken in addition to one's first language (L1). A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a foreign language.
A speaker's dominant language, which ...
, as it was necessary in order to individually advance in the broader Soviet society. By the 1980s, few schools still taught the Tatar language
Tatar ( ; or ) is a Turkic languages, Turkic language spoken by the Volga Tatars mainly located in modern Tatarstan (European Russia), as well as Siberia. It should not be confused with Crimean Tatar language, Crimean Tatar or Siberian Tatar ...
.
Present day
On 30 August 1990, Tatarstan declared its sovereignty with the ''Declaration on the State Sovereignty of the Tatar Soviet Socialist Republic'' and in 1992 Tatarstan held a referendum on the new constitution, promoted by Tatarstan's President Shaymiyev and supervised by Helsinki Commission staff. Parliament opposition revolved around the Russian faction Narodovlastie (People's Power). Some 62% of those who took part voted in favour of the constitution, with ethnic Tatars supporting it much more than Russians. In the new constitution, Tatarstan is defined as a Sovereign State. However, the referendum and constitution were declared unconstitutional by the Russian Constitutional Court. Articles 1 and 3 of the Constitution as introduced in 2002 define Tatarstan as a part of the Russian Federation, removing the "sovereignty" term. On 15 February 1994, the Treaty ''On Delimitation of Jurisdictional Subjects and Mutual Delegation of Authority between the State Bodies of the Russian Federation and the State Bodies of the Republic of Tatarstan'' and Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Republic of Tatarstan (''On Delimitation of Authority in the Sphere of Foreign Economic Relations'') were signed. The power-sharing agreement was renewed on 11 July 2007, though with much of the power delegated to Tatarstan reduced. On 20 December 2008, in response to Russia recognisingAbkhazia
Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a List of states with limited recognition, partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It cover ...
and South Ossetia
South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia or the State of Alania, is a landlocked country in the South Caucasus with International recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, partial diplomatic recognition. It has an offici ...
, the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People () is the single highest executive-representative body of the Crimean Tatars in period between sessions of the Qurultay of the Crimean Tatar People. The Mejlis is a member institution of the Platform of E ...
organisation declared Tatarstan independent and asked for United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
recognition. However, this declaration was ignored both by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
and the Russian government
The Russian Government () or fully titled the Government of the Russian Federation () is the highest federal executive governmental body of the Russian Federation. It is accountable to the president of the Russian Federation and controlled by ...
. On 24 July 2017, the autonomy agreement signed in 1994 between Moscow and Kazan expired, making Tatarstan the last republic of Russia to lose its special status.
Demographics
Population:Settlements
Vital statistics


 Note: TFR source.
Note: TFR source.
Ethnic groups
There are about 2 million ethnicTatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
and 1.5 million ethnic in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
in Tatarstan, along with significant numbers of Chuvash, Mari, and Udmurts
The Udmurts (, ) are a Permian (Finno-Ugric) ethnic group in Eastern Europe, who speak the Udmurt language. They mainly live in the republic of Udmurtia in Russia.
Etymology
The name ''Udmurt'' comes from * 'meadow people,' where the first part ...
, some of whom are Tatar
Tatar may refer to:
Peoples
* Tatars, an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar"
* Volga Tatars, a people from the Volga-Ural region of western Russia
* Crimean Tatars, a people from the Crimea peninsula by the B ...
-speaking. The Ukrainian, Mordvin, and Bashkir minorities are also significant. Most Tatars are Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Musli ...
s, but a small minority known as Keräşen Tatars are Orthodox Christians, some of whom regard themselves as being distinct from other Tatars even though most Keräşen dialects differ only slightly from the Central Dialect of the Tatar language.
There is a fair degree of speculation as to the early origins of the different groups of Tatars, but most Tatars no longer view religious identity as being as important as it once was, and the religious and linguistic subgroups have intermingled considerably. Nevertheless, despite many decades of assimilation and intermingling, some Keräşen demanded and were awarded the option of being specifically enumerated in 2002. This has provoked great controversy, however, as many intellectuals have sought to portray the Tatars as homogeneous and indivisible. Although listed separately below, the Keräşen are still included in the grand total for the Tatars. Another unique ethnic group, concentrated in Tatarstan, is the Qaratay
Qaratays (Karatais, Karatays) are a Mordvins, Mordvinian ethnic group in Kamsko-Ustyinsky District, Tatarstan around the village of Mordovsky Karatay. They speak a variety of the Tatar language complemented by Moksha language, Moksha words, which ...
Mordvins
Mordvins (also Mordvinians, Mordovians; ; no equivalents in Moksha language, Moksha and Erzya language, Erzya) is an official term used in Russia and the Soviet Union to refer both to Erzyas and Mokshas since 1928.
Names
While Robert Gordon ...
.
Jews
Tatar and Udmurt Jews are special territorial groups of theAshkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language ...
, which started to be formed in the residential areas of mixed Turkic-speaking (Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
, Kryashens, in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Bashkirs
The Bashkirs ( , ) or Bashkorts (, ; , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a Republics of Russia, republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of B ...
, Chuvash people
The Chuvash people (, ; , ) also called Chuvash Tatars, are a Turkic ethnic group, a branch of the Oğurs, inhabiting an area stretching from the Idel-Ural region to Siberia.
Most of them live in the Russian republic of Chuvashia and the ...
), Finno-Ugric-speaking (Udmurts
The Udmurts (, ) are a Permian (Finno-Ugric) ethnic group in Eastern Europe, who speak the Udmurt language. They mainly live in the republic of Udmurtia in Russia.
Etymology
The name ''Udmurt'' comes from * 'meadow people,' where the first part ...
, Mari people
The Mari ( ), also formerly known as the Cheremis or Cheremisses, are a Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugric people in Eastern Europe, who have traditionally lived along the Volga and Kama River, Kama rivers in Russia. They live mostly in the Mari E ...
) and Slavic-speaking (Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
) populations. The Ashkenazi Jews first appeared in Tatarstan in the 1830s. The Jews of Udmurtia
Udmurtia, officially the Udmurt Republic, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is administratively part of the Volga Federal District. Its capital city, capital is the types of inhabited localities in Russi ...
and Tatarstan are subdivided by cultural and linguistic characteristics into two territorial groups: 1) Udmurt Jews (Udmurt Jewry), who lived on the territory of Udmurtia
Udmurtia, officially the Udmurt Republic, is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is administratively part of the Volga Federal District. Its capital city, capital is the types of inhabited localities in Russi ...
and the north of Tatarstan; 2) Tatar Jews, or Kazan Jews (Tatar Jewry or Kazan Jewry), who lived mainly in the city of Kazan and its agglomeration.
Languages
In accordance with the Constitution of the Republic of Tatarstan, the two state languages of the republic areTatar
Tatar may refer to:
Peoples
* Tatars, an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar"
* Volga Tatars, a people from the Volga-Ural region of western Russia
* Crimean Tatars, a people from the Crimea peninsula by the B ...
and Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
. According to the 2002 Russian Federal Law (''On Languages of Peoples of the Russian Federation''), the official script
An official is someone who holds an office (function or mandate, regardless of whether it carries an actual working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority (either their own or that of the ...
is Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
. Linguistic anthropologist Dr. Suzanne Wertheim notes that "some men signal ideological devotion to the Tatar cause by refusing to accommodate to Russian-dominant public space or Russian speakers", whilst women, in promoting "the Tatar state and Tatar national culture, index their pro-Tatar ideological stances more diplomatically, and with linguistic practices situated only within the Tatar-speaking community... in keeping with normative gender roles within the Tatar republic."
Religion
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
was the most common faith in Tatarstan, adhered to by 53.8% of the estimated 3.8 million population. Most of the remaining population is either Russian Orthodox Christian or non-religious.2012 Arena Atlas Religion Maps"Ogonek", No. 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 21/04/2017
Archived
Established in 922, the first Muslim state within the boundaries of modern Russia was
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
from which the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
inherited in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. Islam was introduced by missionaries from Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
around the time of Ibn Fadlan
Ahmad ibn Fadlan ibn al-Abbas al-Baghdadi () or simply known as Ibn Fadlan, was a 10th-century traveler from Baghdad, Abbasid Caliphate, famous for his account of his travels as a member of an embassy of the Abbasid caliph al-Muqtadir to the king ...
's journey in 922. Islam's long presence in Russia also extends at least as far back as the conquest of the Khanate of Kazan in 1552, which brought the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
and in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Bashkirs
The Bashkirs ( , ) or Bashkorts (, ; , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a Republics of Russia, republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of B ...
on the Middle Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
into Russia.
In the 1430s, the region became independent as the base of the Khanate of Kazan
The Khanate of Kazan was a Tatar state that occupied the territory of the former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El, Chuvashia, Mordovia, and parts of Udmurtia and Bashkortostan; ...
, a capital having been established in Kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
, 170 km up the Volga from the ruined capital of the Bulgars. The Khanate of Kazan was conquered by the troops of Tsar Ivan IV the Terrible
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was the Bu ...
in the 1550s, with Kazan being taken in 1552. Some Tatars were forcibly converted to Christianity and cathedrals were built in Kazan; by 1593, mosques in the area were destroyed. The Russian government forbade the construction of mosques, a prohibition that was not lifted until the 18th century by Catherine II
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter III ...
.
In 1990, there were only 100 mosques, but by 2004 this number had risen to well over 1,000. as many as 1,398 religious organizations were registered in Tatarstan, of which 1,055 were Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
. In September 2010, Eid al-Fitr
Eid al-Fitr () is the first of the two main Islamic holidays, festivals in Islam, the other being Eid al-Adha. It falls on the first day of Shawwal, the tenth month of the Islamic calendar. Eid al-Fitr is celebrated by Muslims worldwide becaus ...
as well as 21 May, the day the Volga Bulgars
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
embraced Islam, were made public holidays.
The Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
is the second largest active religion in Tatarstan, and has been so for more than 150 years, with an estimated 1.6 million followers made up of ethnic Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, Mordvins
Mordvins (also Mordvinians, Mordovians; ; no equivalents in Moksha language, Moksha and Erzya language, Erzya) is an official term used in Russia and the Soviet Union to refer both to Erzyas and Mokshas since 1928.
Names
While Robert Gordon ...
, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
, Mari people
The Mari ( ), also formerly known as the Cheremis or Cheremisses, are a Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugric people in Eastern Europe, who have traditionally lived along the Volga and Kama River, Kama rivers in Russia. They live mostly in the Mari E ...
, Georgians
Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and Peoples of the Caucasus, Caucasian ethnic group native to present-day Georgia (country), Georgia and surrounding areas historically associated with the Ge ...
, Chuvash and a number of Orthodox Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
which together constitute 38% of the 3.8 million population of Tatarstan. On 23 August 2010, the "Orthodox monuments of Tatarstan" exhibition was held in Kazan by the Tatarstan Ministry of Culture and the Kazan Eparchy. At all public events, an in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pag ...
Priest is called upon along with an Islamic Mufti
A mufti (; , ) is an Islamic jurist qualified to issue a nonbinding opinion ('' fatwa'') on a point of Islamic law (''sharia''). The act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Muftis and their ''fatāwa'' have played an important role thro ...
.
The Muslim Religious Board of Tatarstan frequently organizes activities, like the 'Islamic graffiti
Islamic graffiti is a genre of graffiti created by people who usually relate to the Middle East or North Africa, using Arabic or other languages for social or political messages. It is a popular art genre created by "artists, graffiti writers, desi ...
Contest' which was held on 20 November 2011.
Politics
 Tatarstan's
Tatarstan's unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature consisting of one house or assembly that legislates and votes as one. Unicameralism has become an increasingly common type of legislature, making up nearly ...
State Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative authority of China, headed by the Premier
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of S ...
consists of 100 seats: fifty for representatives of the parties and fifty for deputies from the republic's localities. The Chairman of the State Council is Farit Mukhametshin, who has served since 27 May 1998. The government is the Сabinet of Ministers. The prime minister of the Republic of Tatarstan is Alexei Pesoshin.
According to the Constitution of the Republic of Tatarstan, the Rais can be elected only by the people of Tatarstan, but due to Russian federal law, this law was suspended for an indefinite term. The Russian law on the election of governors says they should be elected by regional parliaments and that the candidate for Rais can be presented only by the president of Russia
The president of Russia, officially the president of the Russian Federation (), is the executive head of state of Russia. The president is the chair of the State Council (Russia), Federal State Council and the President of Russia#Commander-in-ch ...
.
In December 2022, regional lawmakers voted to change the title of the head of the republic from ''president'' to ''rais'' (an Arabic title for "leader"); lawmakers were expected to adopt new amendments to Tatarstan's constitution so that it would be in line with the 2020 amendments to the Constitution of Russia
The amendments of 2020, which were proposed in January 2020, are the second substantial amendments to the Constitution of Russia of 1993. To introduce these amendments, Vladimir Putin, president of Russia, held a national vote. They were approv ...
and a federal law in 2021 which abolished regional presidencies. The title of president was seen as the last remaining symbol of federalism following the centralisation reforms under Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
. Incumbent president Rustam Minnikhanov originally was to retain the title of president until his term expires in 2025 under transitional agreements, however he became Rais in February 2024.
Political status
The Republic of Tatarstan is a constituent republic of theRussian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Most of the Russian federal subjects are tied with the Russian federal government by the uniform Federal Treaty (The contract expired in 2017), but relations between the government of Tatarstan and the Russian federal government are more complex and are precisely defined in the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
of the Republic of Tatarstan. The following passage from the Constitution defines the republic's status without contradicting the Constitution of the Russian Federation:
Economy
Tatarstan is one of the most economically developed regions of Russia. The republic is highly industrialised and ranks second toSamara Oblast
Samara Oblast (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Samara. From 1935 to 1991, it was known as Kuybyshev Oblast. As of the Rus ...
in terms of industrial production per km2.
In 2021, Tatarstan's gross regional product
Gross regional domestic product (GRDP), gross domestic product of region (GDPR), or gross state product (GSP) is a statistic that measures the size of a region's economy. It is the aggregate of gross value added (GVA) of all resident producer unit ...
was €40 billion, while GRP per capita was €10,000.
The region's main source of wealth is oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
. Tatarstan produces 32 million tonnes of crude oil per year and has estimated oil reserves of more than 1 billion tons. Industrial production constitutes 45% of the Republic's gross regional domestic product
Gross regional domestic product (GRDP), gross domestic product of region (GDPR), or gross state product (GSP) is a statistic that measures the size of a region's economy. It is the aggregate of gross value added (GVA) of all resident producer unit ...
. The most developed manufacturing industries are petrochemical industry
file:Jampilen Petrochemical Co. 02.jpg, 300px, Jampilen Petrochemical co., Asaluyeh, Iran
The petrochemical industry is concerned with the production and trade of petrochemicals. A major part is constituted by the plastics industry, plastics (poly ...
and machine building. The truck-maker KamAZ is the region's largest enterprise and employs about one-fifth of Tatarstan's workforce. Kazanorgsintez, based in Kazan, is one of Russia's largest chemical companies. Tatarstan's aviation industry produces Tu-214 passenger airplanes and helicopters. The Kazan Helicopter Plant
Kazan Helicopters, Joint Stock Company is a Russian helicopter manufacturing company based at Kazan, Republic of Tatarstan. It is one of the largest helicopter manufacturers in the world.
Its products include the Mil Mi-8 and Mil Mi-17 helicopter ...
is one of the largest helicopter manufacturers in the world. Engineering, textiles, clothing, wood processing
Wood processing is an engineering discipline in the wood industry comprising the production of forest products, such as pulp and paper, construction materials, and tall oil. Paper engineering is a subfield of wood processing.
The major wo ...
, and food industries are also of key significance in Tatarstan.
Naberezhnye Chelny
Naberezhnye Chelny (, ; , ) is the second largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia. A major industrial center, Naberezhnye Chelny stands on the Kama River east of Kazan near Nizhnekamsk Reservoi ...
–Nizhnekamsk
Nizhnekamsk (, ; ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Tatarstan, Russia, located to the south of the Kama River between the cities of Naberezhnye Chelny and Chistopol. Population:
History
As its population increased, spurre ...
agglomeration
Agglomeration may refer to:
* Urban agglomeration, in standard English
* Megalopolis, in Chinese English, as defined in China's ''Standard for basic terminology of urban planning'' (GB/T 50280—98). Also known as "city cluster".
* Economies of agg ...
, major industries are automobile construction, the chemical industry, and power engineering. The southeast region has oil production with engineering under development. The north, central, south, and southwest parts of the republic are rural regions. The republic has huge water resources—the annual flow of rivers of the Republic exceeds . Soils are widely diverse, with fertile soils covering approximately one-third of the territory that contribute to successful agricultural production. The main agricultural exports from Tatarstan are wheat, barley, and peas. Due to the high development of agriculture in Tatarstan (it contributes 5.1% of the total revenue of the republic), forests occupy only 16% of its territory. The agricultural sector of the economy is represented mostly by large companies as Ak Bars Holding
OJSC Ak Bars Holding is a diversified financial holding based in Kazan, Tatarstan, Russia, and established in 1998.
Ak Bars Holding owns stakes in Zelenodolsk Shipyard, and formerly Ak Bars Aero.
The geography of the holding's presence is th ...
and "Krasnyi Vostok Agro".
The republic has a highly developed transport network. It mainly comprises highways, railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
lines, four navigable rivers — Volga (İdel), Kama (Çulman), Vyatka (Noqrat) and Belaya (Ağidel), and oil pipelines and airlines. The territory of Tatarstan is crossed by the main gas pipelines carrying natural gas from Urengoy
Urengoy (; Nenets: Пюра ңо, ''Pjura ŋo'') is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) in Purovsky District of Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Population:
History
Urengoy was founded in 1932 as a Nenets settlement. Between ...
and Yamburg
Kingisepp ( or ), formerly Yamburg (), Yam (), and Yama (; Votic: ), is a town and the administrative center of Kingiseppsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located along the Luga River southwest of St. Petersburg, east of Narva ...
to the west and the major oil pipelines supplying oil to various cities in the European part of Russia.
Tourism
 There are three UNESCO world heritage sites in Tatarstan—
There are three UNESCO world heritage sites in Tatarstan—Kazan Kremlin
The Kazan Kremlin (; ) is the chief historic citadel of Russia, situated in the city of Kazan. It was built at the behest of Ivan the Terrible on the ruins of the former castle of list of Kazan khans, Kazan khans. It was declared a World Heritage ...
, Bulgarian State Museum-Reserve, and Assumption Cathedral and Monastery of the town-island of Sviyazhsk.
The annual growth rate of tourist flow to the republic is on average 13.5%; the growth rate of the volume of services in the tourism sector is 17.0%.
At the end of 2016, on the territory of the Republic of Tatarstan there were 104 tour operators, of which 32 dealt in domestic tourism, 65 in domestic and inbound tourism, 1 in domestic and outbound tourism, and 6 in all three.
404 collective accommodation facilities (CSR) operate in the Republic of Tatarstan; are subject to classification (183 in Kazan, 196 in other municipalities of the Republic of Tatarstan). 334 collective accommodation facilities received the certificate of assignment of the category, which is 88.1% of the total number of operating.
In 2016, special attention was paid to the development of tourist centres of the Republic of Tatarstan—Kazan, Bolghar
Bolghar (; Tatar language, Tatar: Болгар, بلغار, ''Bolğar''; Chuvash language, Chuvash: Аслă Пăлхар, ''Aslă Pălhar'') was intermittently the capital of Volga Bulgaria from the 10th to the 13th centuries, along with Bilär, ...
, the town-island of Sviyazhsk, Yelabuga
Yelabuga (also spelled ''Elabuga''; ; ) is a town in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia, located on the right bank of the Kama River and east from Kazan. Population:
The evolution of name
The name of the city of Yelabuga comes from the T ...
, Chistopol
Chistopol (; ; , ''Çistay'') is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Tatarstan, Russia, located on the left bank of the Kuybyshev Reservoir, on the Kama River. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, its population was&nbs ...
, and Tetyushi Tetyushi () is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia.
;Urban localities
*Tetyushi, Republic of Tatarstan, a town in Tetyushsky District of the Republic of Tatarstan
;Rural localities
* Tetyushi, Republic of Mordovia, a '' selo'' in Bo ...
. The growth of tourist flow in the main tourist centres of the Republic compared to 2015 amounted to an average of 45.9%.
 Currently, sanatorium and resort recreation is developing rapidly in Tatarstan. There are 46 sanatorium-resort institutions in the Republic of Tatarstan. The capacity of the objects of the sanatorium-resort complex of Tatarstan is 8847 beds; more than 4300 specialists are engaged in the service of residents. In 2016, more than 160 thousand people rested in the health resorts of the Republic of Tatarstan. 22 health resort institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan are members of the Association of health resort institutions "Health resorts of Tatarstan," including 11 sanatoriums of PJSC "Tatneft."
Since 2016, the Republic of Tatarstan has been operating the Visit Tatarstan program, the official tourism brand of the Republic, the purpose of which is to inform tourists, monitor the reputation of the Republic, develop the tourism potential of the regions of Tatarstan, conduct market research, create partner projects with local companies, and expand internationally. "Tatarstan: 1001 pleasure" is the main message that tourists receive. The Visit Tatar website, where there is information about the main sights and recreation in Tatarstan, is available in 8 languages: Tatar, Russian, English, Chinese, German, Spanish, Finnish, and Persian.
Currently, sanatorium and resort recreation is developing rapidly in Tatarstan. There are 46 sanatorium-resort institutions in the Republic of Tatarstan. The capacity of the objects of the sanatorium-resort complex of Tatarstan is 8847 beds; more than 4300 specialists are engaged in the service of residents. In 2016, more than 160 thousand people rested in the health resorts of the Republic of Tatarstan. 22 health resort institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan are members of the Association of health resort institutions "Health resorts of Tatarstan," including 11 sanatoriums of PJSC "Tatneft."
Since 2016, the Republic of Tatarstan has been operating the Visit Tatarstan program, the official tourism brand of the Republic, the purpose of which is to inform tourists, monitor the reputation of the Republic, develop the tourism potential of the regions of Tatarstan, conduct market research, create partner projects with local companies, and expand internationally. "Tatarstan: 1001 pleasure" is the main message that tourists receive. The Visit Tatar website, where there is information about the main sights and recreation in Tatarstan, is available in 8 languages: Tatar, Russian, English, Chinese, German, Spanish, Finnish, and Persian.
Tourist resources of historical and cultural significance

 *
* Kazan Kremlin
The Kazan Kremlin (; ) is the chief historic citadel of Russia, situated in the city of Kazan. It was built at the behest of Ivan the Terrible on the ruins of the former castle of list of Kazan khans, Kazan khans. It was declared a World Heritage ...
* Kazan University
Kazan Federal University (; ) is a public research university located in Kazan, Russia.
The university was founded in 1804 as Imperial Kazan University, which makes it the second oldest continuously existing tertiary education institution in Rus ...
* Bolghar
Bolghar (; Tatar language, Tatar: Болгар, بلغار, ''Bolğar''; Chuvash language, Chuvash: Аслă Пăлхар, ''Aslă Pălhar'') was intermittently the capital of Volga Bulgaria from the 10th to the 13th centuries, along with Bilär, ...
* Sviyazhsk
Sviyazhsk (; ) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia, located at the confluence of the Volga and Sviyaga Rivers. It is often referred to as an island since the 1955 construction of the Kuybyshev Reservoir downstr ...
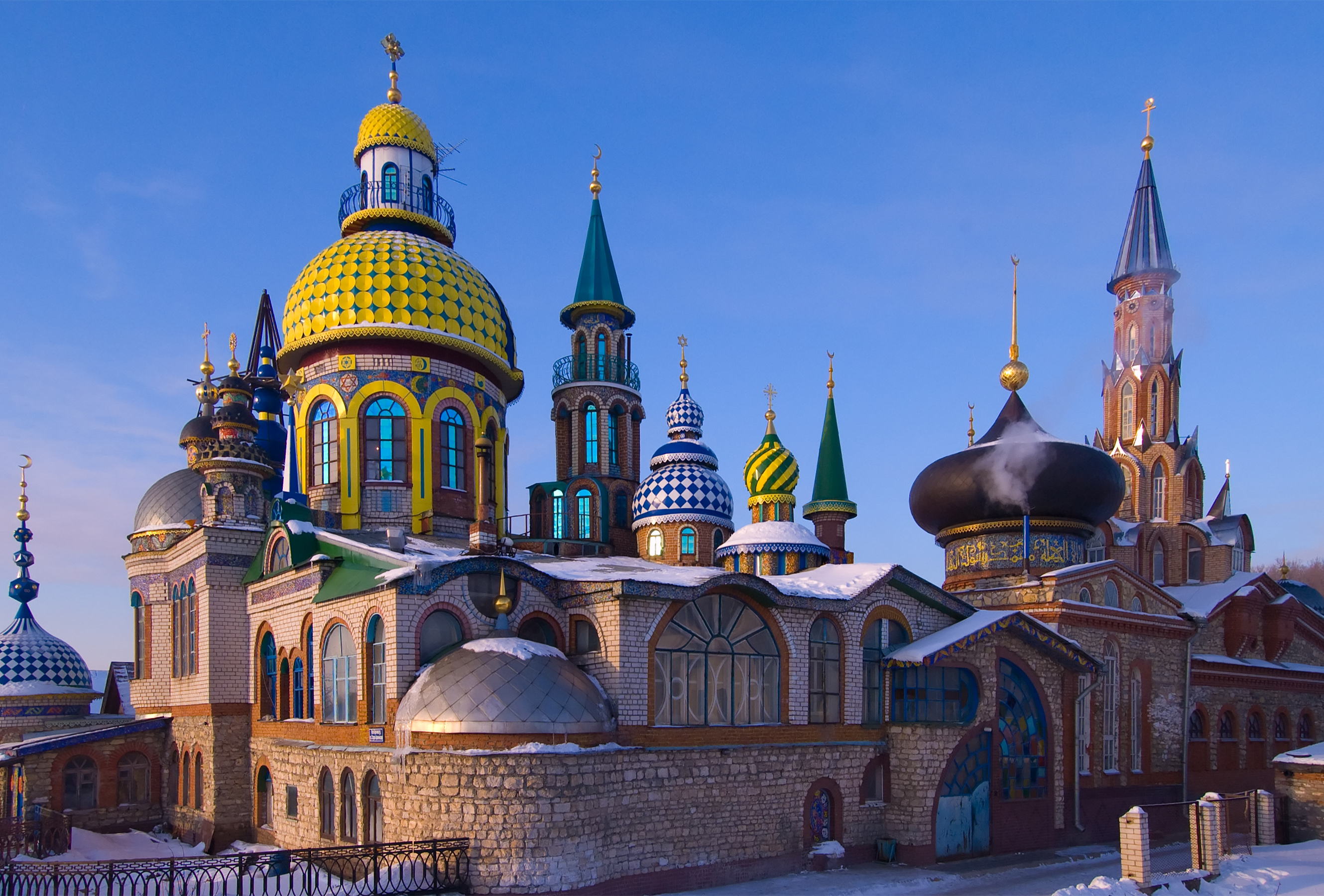
* Temple of All Religions
* Qolşärif Mosque
* Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral
* Söyembikä Tower
Söyembikä Tower (; ), also called the List of Kazan khans, Khan's Mosque, is probably the most familiar landmark and architectural symbol of Kazan.
Once the highest structure of Kazan Kremlin, that city's kremlin, it used to be one of the so- ...
* Millennium Bridge
* Old Tatar Quarter
* Galiaskar Kamal Tatar Academic Theatre
The Galiaskar Kamal Tatar Academic Theatre (, ) is the leading Tatar theater in Kazan, Russia. Named after the playwright Galiaskar Kamal, it was founded on December 22, 1906.
The first known Tatar theatrical efforts were during the 19th cen ...
* The Jalil Opera and Ballet Theatre
* The National Museum of Tatarstan
Culture
Due to Islamic rules on artistic depictions, Tatars developed a uniquely geometric artistry, of which the craft of leather mosaic is a staple. They also observe certain pre-Islamic holidays, such asSabantuy
Sabantuy is a Tatar, Idel-Uralian, Bashkir and Kazakh ('Sabantoy') summer festival, that dates back to the Volga Bulgarian epoch. At first Sabantuy was a festival of farmers in rural areas, but it later became a national holiday and now is wi ...
, which celebrates "the completion of spring sowing works."
 Major libraries include
Major libraries include Kazan State University
Kazan Federal University (; ) is a public research university located in Kazan, Russia.
The university was founded in 1804 as Imperial Kazan University, which makes it the second oldest continuously existing tertiary education institution in Rus ...
Nikolai Lobachevsky
Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky (; , ; – ) was a Russian mathematician and geometer, known primarily for his work on hyperbolic geometry, otherwise known as Lobachevskian geometry, and also for his fundamental study on Dirichlet integrals, kno ...
Scientific Library and the National Library of the Republic of Tatarstan. There are two museums of republican significance, as well as 90 museums of local importance. In the past several years, new museums appeared throughout the Republic.
There are twelve theatrical institutions in Tatarstan. The state orchestra is the National Tatarstan Orchestra.
In 1996, the Tatar singer, Guzel Ahmetova, cooperated with the German Eurodance
Eurodance (sometimes referred to as Euro-NRG) is a genre of electronic dance music that originated in the late 1980s in Europe. It combines many elements of Hip-hop, rap, techno and Eurodisco. This genre of music is heavily influenced by the use ...
group named Snap!
SNAP! is a German Eurodance group formed in 1989 by producers Michael Münzing and Luca Anzilotti. The act has undergone several lineup changes over the years, featuring American singers, songwriters, and rappers such as Thea Austin, Turbo ...
, when she sang the lyrics of the song "Rame".
Aida Garifullina
Aida Emilevna Garifullina (, ; born on 30 September 1987) is a Russian lyric soprano of Tatar descent. She was the winner of the 2013 Operalia competition and has featured in a number of productions staged at the Mariinsky Theatre, St. Petersbur ...
was born in 1987 to a Tatar family in Kazan. Following studies in Nuremberg, Germany and Vienna, Austria, she has achieved fame as a lyric soprano, in high demand both on the international operatic stage and concert platform. She is also a celebrated recording artist and a promoter of the Tatar culture.
Sports
 With 9,175 sports venues in Tatarstan, the republic is one of the leading sports regions in Russia. Since 1973, Kazan has been making efforts to expand its sports
With 9,175 sports venues in Tatarstan, the republic is one of the leading sports regions in Russia. Since 1973, Kazan has been making efforts to expand its sports infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and pri ...
, with sports being a "great source of pride" for the people of Kazan.
Tatarstan has Rubin Kazan
FC Rubin Kazan (; ) is a Russian professional football club based in the city of Kazan. They play in the Russian Premier League. Founded in 1958, Rubin played its first-ever top flight season in 2003. It has remained there through the 2021–2 ...
, a major European football team which has played in the UEFA Champions League
The UEFA Champions League (UCL) is an annual club association football competition organised by the UEFA, Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) that is contested by List of top-division football clubs in UEFA countries, top-divisio ...
and the UEFA Europa League
The UEFA Europa League (UEL), usually known simply as the Europa League, is an annual association football, football club competition organised since 1971 by the UEFA, Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) for eligible European footb ...
. Twice Russian champions, Rubin Kazan play in the Russian Premier League
The Russian Premier League (RPL; , ''Rossiyskaya premyer-liga''; РПЛ), also written as Russian Premier Liga, is a professional association football league in Russia and the highest level of the Russian football league system. It was establis ...
. Also, Tatarstan has Unics Kazan
BC UNICS () is a professional basketball club in Kazan, Russia, that plays in the VTB United League, and formerly played in the EuroLeague. On February 28, 2022, EuroLeague Basketball suspended the team because of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukr ...
which has gained a significant role in European basketball, playing in Euroleague
The EuroLeague is a European men's professional basketball club competition. The league is widely recognised as the top-tier and the most prestigious men's basketball league in Europe. The league consists of 20 teams, of which 16 are given lon ...
and EuroCup for decades.
It also has two KHL
The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL; ) is an international professional ice hockey league founded in 2008. It comprises member clubs based in Russia (20), Belarus (1), Kazakhstan (1), and China (1) for a total of 23 clubs.
It was considered in ...
teams, the successful Ak Bars Kazan
Hockey Club Ak Bars (, , ), also known as Ak Bars Kazan, is a professional ice hockey club based in Kazan, Russia. It is a member of the Kharlamov Division in the Kontinental Hockey League (KHL).
History
Founded as Mashstroy Kazan in 1956, the n ...
, which is based in the capital city of Kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
, and the Neftekhimik Nizhnekamsk, who play in the city of Nizhnekamsk
Nizhnekamsk (, ; ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Tatarstan, Russia, located to the south of the Kama River between the cities of Naberezhnye Chelny and Chistopol. Population:
History
As its population increased, spurre ...
. The state also has a Russian Major League
The All-Russian Hockey League (VHL) (, ''Vserossiyskaya hokkeinaya liga (VHL)''), also known as the Major Hockey League or Higher Hockey League (HHL), is a professional ice hockey league in Eurasia, and the second highest level of Ice Hockey Fed ...
team (the second highest hockey league in Russia), Neftyanik Almetyevsk
Neftyanik Almetyevsk is an ice hockey team in Almetyevsk, Russia. They play in the VHL, the Supreme Hockey League, which is the second level of Russian ice hockey.
History
The club was founded in 1965 as Sputnik. In 1986, they were renamed Nefty ...
, who play in the city of Almetyevsk
Almetyevsk (; ; ) is a city in Tatarstan, Russia, located on the left bank of the Zay River (Kama's tributary) southeast of Kazan. Population: 77,000 (1969); 49,000 (1959).
History
Almetyevsk is one of the youngest cities in the republic. Lo ...
. There are also two Minor Hockey League
The Junior Hockey League (JHL) (), sometimes translated as the ''Minor'' or ''Youth'' Hockey League, is a major junior ice hockey league in Eurasia, founded in 2009. It currently consists of 33 teams from 3 countries. Currently, all teams but o ...
teams which serve as affiliates for the two KHL teams. A team also exists in the Russian Hockey League
The All-Russian Hockey League B or VHL-B (, ''Pervenstvo Vserossiyskoy hokkeynoy ligi'') is an ice hockey league in Russia. It stands at the third-tier of the Russian ice hockey pyramid, below the second-level VHL and the top-tier KHL.
Histor ...
, the HC Chelny, which is based in the city of Naberezhnye Chelny
Naberezhnye Chelny (, ; , ) is the second largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia. A major industrial center, Naberezhnye Chelny stands on the Kama River east of Kazan near Nizhnekamsk Reservoi ...
. Another team plays in the MHL-B
The National Junior Hockey League (NMHL) (formerly Junior Hockey League Division B) () is the second level of the Junior Hockey League, the KHL's junior ice hockey league. The B division was established in 2011 and the inaugural season was the 201 ...
(the second level of junior ice hockey in Russia).
Nail Yakupov
Nail Railovich Yakupov (, ; born 6 October 1993) is a Russian professional ice hockey forward for Avangard Omsk of the Kontinental Hockey League (KHL). He was selected first overall by the Edmonton Oilers at the 2012 NHL Entry Draft, and als ...
is an ethnic Tatar who was drafted first overall in the 2012 NHL Entry Draft.
Former ATP No. 1 Marat Safin
Marat Mubinovich Safin ( rus, Мара́т Муби́нович Са́фин, , mɐˈrat ˈsafʲɪn, Ru-Marat-Safin.ogg; ; born 27 January 1980) is a Russian former professional tennis player and former politician. He was ranked as the List of ...
and former WTA number 1 Dinara Safina
Dinara Mubinovna Safina (, ; ; born April 27, 1986) is a Russian former professional tennis player. She was ranked as the world No. 1 in women's singles by the Women's Tennis Association (WTA) for 26 weeks, and world No. 8 in doubles. Safina ...
are of Tatar descent.
Victor Wild and Danil Sadreev are both Tatarstan Olympians, having won a bronze in parallel giant slalom and a silver in ski jumping, respectively.
Kazan hosted the XXVII Summer Universiade in 2013, the FINA World championship in aquatic sports in August 2015, and the World Junior Championship for swimming in 2022.
Education
The most important facilities of higher education includeKazan Federal University
Kazan Federal University (; ) is a public research university located in Kazan, Russia.
The university was founded in 1804 as Imperial Kazan University, which makes it the second oldest continuously existing tertiary education institution in Rus ...
, Kazan State Medical University
Kazan Medical University is a multifunctional multilevel state higher medical educational institution that meets the needs of society and the individual in higher medical education, the development of life sciences, and scientific medical knowle ...
, Kazan National Research Technological University
Kazan National Research Technological University, KNRTU is an innovational scientific educational complex. The University comprises 15 academic and research institutes; runs over 100 Specialist, Bachelor's, Master's Degree
A master's degree ( ...
, World Information Distributed University, Kazan National Research Technical University named after A.N.Tupolev and Russian Islamic University. All of these are located in the capital city, Kazan.
Public spaces
Tatarstan takes a unique participatory approach to the development of public spaces that has earned it recognition. The Tatarstan Public Spaces Development Programme aims to create spaces for meeting or recreation. The programme covers a wide spectrum of projects, including streets, squares, parks, river banks, pavilions, and sports facilities. Since 2016 (and continuing until 2022), the Architecturny Desant Architectural Bureau in Kazan has improved public spaces in each of Tatarstan's 45 municipal districts, from large cities to small villages. As of April 2019, the project had revamped 328 public spaces. By creating and rehabilitating public spaces, the programme aims to be a catalyst for positive social, economic, and environmental change. One notable example is the "Beach" at Almetyevsk, which includes public swimming pools and a terrace. Other examples include an amphitheatre in Black Lake Park, Kazan; the Central Square in Bavly; a children's playground in Bogatye Saby village, which has a unique wooden play structure; the Cube container centre in the green beach at Gorkinsko-Ometievsky forest, Kazan; and the square on Festival Boulevard, Kazan. The programme used an innovative participatory design approach, which later became mandatory for similar projects across Russia. This approach partners specialists with local residents at every stage of the project, from development, to implementation, to the ongoing use of the space. The Tatarstan Public Spaces Development Programme was announced as one of the six winners of the 2019Aga Khan Award for Architecture
The Aga Khan Award for Architecture (AKAA) is an architectural prize established by Aga Khan IV in 1977. It aims to identify and reward architectural concepts that successfully address the needs and aspirations of Muslim societies in the fie ...
. The jury was impressed by the programme's systematic approach and involvement of residents to decide the future of each space.
Each public space expresses the unique identity of that particular place, tying in its history while incorporating traditional materials. Major goals of the projects include improving the quality of life for residents and improving the environment. The Arhitekturnyi Desant team aims to provide a high quality public space, no matter the size of the settlement, including quality design, infrastructure, and materials.
Spending on the public spaces projects is helping the local economy. The number of street furniture manufacturers in the area, for example, has increased from 12 to 75 since the programme started.
See also
*KAZANSUMMIT
KAZANSUMMIT (International Economic Summit “Russia — Islamic World: KazanSummit”) is one of the leading international economic events of the Russian Federation and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC). From the first day of its exis ...
* List of Chairmen of the State Council of Tatarstan
* List of rural localities in Tatarstan
* List of Tatars
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
* Music of Tatarstan
Tatarstan is an autonomous republic within Russia, where the largest ethnic group are the Tatars. Their traditional music is a mixture of Turkic, Mongolic and Finno-Ugric elements, reportedly bridging Mongolian and Hungarian music. Nonetheless, ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * Госкомстат РФ. Государственный комитет Республики Татарстан по статистике. "Административно-территориальное деление Республики Татарстан" (''Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Republic of Tatarstan''). Казань, 1997.Further reading
* * * Ruslan KurbanovTatarstan: Smooth Islamization Sprinkled with Blood
''OnIslam.net.'' Accessed: Feb. 26, 2013. * Daniel Kalder. ''Lost Cosmonaut: Observations of an Anti-tourist''. * Ravil Bukharaev. ''The Model of Tatarstan: Under President Mintimer Shaimiev''. * Azadeayse Rorlich. ''The Volga Tatars: A Profile in National Resilience''. * Roderick Heather. ''Russia From Red to Black'' * Matthew Reid. ''Shattered Kremlin: Echoes of the Iron Curtain''
External links
Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan
Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan
Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan
Tatar-Inform
information agency
Official Tourist Portal of the Republic of Tatarstan
{{Authority control States and territories established in 1920 Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Tatar topics Regions of Europe with multiple official languages 1920 establishments in Europe Observer members of the International Organization of Turkic Culture Republics of Russia