Südtirol 1 0155 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige
lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol , settlement_type = Autonomous province , image_skyline = , image_alt = , image_caption = , image_flag = Flag_of_South_Tyrol.svg , flag_alt = , image_shield = Suedtirol CoA.svg , shield_size = x100px , shield_alt = Coat of arms of Tyrol , anthem = , image_map = Bolzano in Italy.svg , map_alt = , map_caption = Map highlighting the location of the province of South Tyrol in Italy (in red) , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type1 = Region , subdivision_name1 = Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol , established_title = , established_date = , seat_type = Capital(s) , seat = Bolzano , parts_type = Comuni , parts_style = para , p1 = 116 , government_footnotes = , leader_party = SVP , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Arno Kompatscher , unit_pref = Metric , area_footnotes = , area_total_km2 = 7399.97 , elevation_footnotes = , elevation_m = , population_footnotes = , population_total = 531178 , population_as_of = 1 January 2019 , population_density_km2 = auto , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €24.8 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 =
· 5th of 21 , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = 39XXX , area_code_type = Telephone prefix , area_code = 0471, 0472, 0473, 0474 , iso_code = , registration_plate = BZ , blank_name_sec2 = ISTAT , blank_info_sec2 = 021 , website = , footnotes = , official_name = , governing_body = Landtag South Tyrol (german: Südtirol; it, Alto Adige; lld, Südtirol), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano, is an autonomous province in According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language (
According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language (
South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincial Statistics Institute of the Autonomous Province of South Tyrol
Bozen/Bolzano 2007, p. 19, Table 11 The province is granted a considerable level of self-government, consisting of a large range of exclusive legislative and executive powers and a fiscal regime that allows it to retain 90% of revenue, while remaining a net contributor to the national budget. As of 2016, South Tyrol is the wealthiest province in Italy and among the wealthiest in the European Union. In the wider context of the European Union, the province is one of the three members of the Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion, which corresponds almost exactly to the historical region of Tyrol. The other members are Tyrol state in Austria, to the north and east, and the Italian Autonomous province of Trento to the south.
 ''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic County of Tyrol, a former state of the Holy Roman Empire and
''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic County of Tyrol, a former state of the Holy Roman Empire and
 South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states Tyrol and Salzburg, and by the
South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states Tyrol and Salzburg, and by the  Located between the mountains are many valleys, where the majority of the population lives.
Located between the mountains are many valleys, where the majority of the population lives.
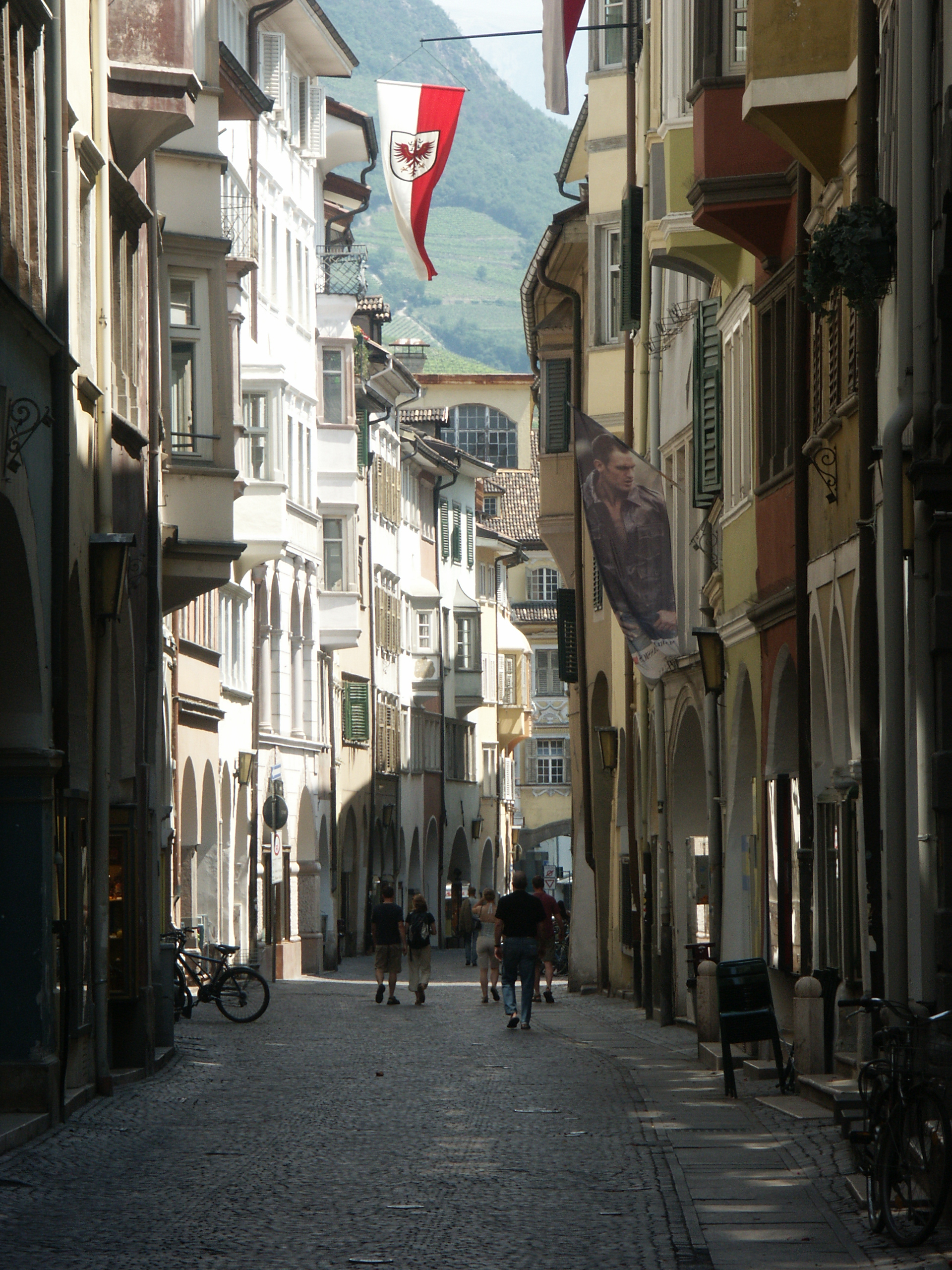



 The alpine valleys between , with a typically humid continental climate — Dfb, covering the largest part of the province. The winters are usually very cold (24-hour averages in January between ), and the summers, mild with averages between . It is a very snowy climate; snow may occur from early October to April or even May. Main municipalities in this area are Urtijëi, Badia,
The alpine valleys between , with a typically humid continental climate — Dfb, covering the largest part of the province. The winters are usually very cold (24-hour averages in January between ), and the summers, mild with averages between . It is a very snowy climate; snow may occur from early October to April or even May. Main municipalities in this area are Urtijëi, Badia,
 The periadriatic seam, which separates the Southern Alps from the Central Alps, runs through South Tyrol in a southwest-northeast direction. In South Tyrol at least three of the four main structural elements of the Alps come to light: the Southern Alpine comes to light south of the periadriatic suture, the Eastern Alpine north of it, and in the northern part of the country, east of the Brenner Pass, the Tauern window, in which the Peninsular and, according to some authors, the Helvetic are visible.
In South Tyrol, the following structure can be roughly recognized: The lowest floor forms the crystalline basement. About 280 million years ago, in the Lower Permian, multiple magmatic events occurred. At that time the Brixen granite was formed at the northern boundary of the Southern Alps, and at about the same time, further south in the Bolzano area, there was strong volcanic activity that formed the Adige Valley volcanic complex. In the Upper Permian a period began in which sedimentary rocks were formed. At first, these were partly clastic sediments, among which the Gröden sandstone is found. In the Triassic, massive carbonate platforms of dolomitic rocks then formed; this process was interrupted in the Middle Triassic by a brief but violent phase of volcanic activity.
In South Tyrol, the Eastern Alps consist mainly of metamorphic rocks, such as gneisses or mica schists, with occasional intercalations of marble and Mesozoic sedimentary rocks with metamorphic overprint (e.g., in the Ortler or southwest of the Brenner). Various metamorphic rocks are found in the Tauern Window, such as Hochstegen marble (as in Wolfendorn), Grünschiefer (as in Hochfeiler), or rocks of the Zentralgneiss (predominantly in the area of the Zillertal Main Ridge).
The province of South Tyrol has placed numerous geological natural monuments under protection. Among the best known are the Bletterbach Gorge, a 12 km (7½ mile) long canyon in the municipality of Aldein, and the Ritten Earth Pyramids, which are the largest in Europe with a height of up to .
The periadriatic seam, which separates the Southern Alps from the Central Alps, runs through South Tyrol in a southwest-northeast direction. In South Tyrol at least three of the four main structural elements of the Alps come to light: the Southern Alpine comes to light south of the periadriatic suture, the Eastern Alpine north of it, and in the northern part of the country, east of the Brenner Pass, the Tauern window, in which the Peninsular and, according to some authors, the Helvetic are visible.
In South Tyrol, the following structure can be roughly recognized: The lowest floor forms the crystalline basement. About 280 million years ago, in the Lower Permian, multiple magmatic events occurred. At that time the Brixen granite was formed at the northern boundary of the Southern Alps, and at about the same time, further south in the Bolzano area, there was strong volcanic activity that formed the Adige Valley volcanic complex. In the Upper Permian a period began in which sedimentary rocks were formed. At first, these were partly clastic sediments, among which the Gröden sandstone is found. In the Triassic, massive carbonate platforms of dolomitic rocks then formed; this process was interrupted in the Middle Triassic by a brief but violent phase of volcanic activity.
In South Tyrol, the Eastern Alps consist mainly of metamorphic rocks, such as gneisses or mica schists, with occasional intercalations of marble and Mesozoic sedimentary rocks with metamorphic overprint (e.g., in the Ortler or southwest of the Brenner). Various metamorphic rocks are found in the Tauern Window, such as Hochstegen marble (as in Wolfendorn), Grünschiefer (as in Hochfeiler), or rocks of the Zentralgneiss (predominantly in the area of the Zillertal Main Ridge).
The province of South Tyrol has placed numerous geological natural monuments under protection. Among the best known are the Bletterbach Gorge, a 12 km (7½ mile) long canyon in the municipality of Aldein, and the Ritten Earth Pyramids, which are the largest in Europe with a height of up to .
 According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by UNESCO in 2009 as a "Dolomite World Heritage Site".
Although some isolated massifs approach and show strong glaciation (especially in the Ortler Alps and on the main ridge of the Alps), South Tyrol is by far dominated by mountains with altitudes of between . Among the multitude of peaks, the Dolomites are the highest in the Alps. Among the large number of peaks, three stand out for their alpine or cultural importance: the
According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by UNESCO in 2009 as a "Dolomite World Heritage Site".
Although some isolated massifs approach and show strong glaciation (especially in the Ortler Alps and on the main ridge of the Alps), South Tyrol is by far dominated by mountains with altitudes of between . Among the multitude of peaks, the Dolomites are the highest in the Alps. Among the large number of peaks, three stand out for their alpine or cultural importance: the
 The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the Adige Valley, the
The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the Adige Valley, the
 The most important river in South Tyrol is the Adige, which rises at the Reschen Pass, flows for a distance of about to the border at the Salurner Klause, and then flows into the Po Valley and the Adriatic Sea. The Adige, whose total length of in Italy is exceeded only by the Po, drains 97% of the territory's surface area. Its river system also includes the Eisack, about long, and the Rienz, about long, the next two largest rivers in South Tyrol. They are fed by numerous rivers and streams in the tributary valleys. The most important tributaries are the Plima, the Passer, the Falschauer, the Talfer, the Ahr and the Gader. The remaining 3% of the area is drained by the and Inn river systems to the Black Sea and by the Piave river system to the Adriatic Sea, respectively.
In South Tyrol there are 176 natural lakes with an area of more than half a hectare (1¼ acre), most of which are located above altitude. Only 13 natural lakes are larger than 5 ha, and only three of them are situated below altitude: the Kalterer See (), the Großer () and the Kleiner Montiggler See (). Fourteen South Tyrolean reservoirs used for energy production include the Reschensee (), which with an area of forms the largest standing body of water in South Tyrol, the Zufrittsee () and the Arzkarsee ().
The natural monuments designated by the province of South Tyrol include numerous hydrological objects, such as streams, waterfalls, moors, glaciers and mountain lakes like the Pragser Wildsee (), the Karersee () or the Spronser Seen ().
The most important river in South Tyrol is the Adige, which rises at the Reschen Pass, flows for a distance of about to the border at the Salurner Klause, and then flows into the Po Valley and the Adriatic Sea. The Adige, whose total length of in Italy is exceeded only by the Po, drains 97% of the territory's surface area. Its river system also includes the Eisack, about long, and the Rienz, about long, the next two largest rivers in South Tyrol. They are fed by numerous rivers and streams in the tributary valleys. The most important tributaries are the Plima, the Passer, the Falschauer, the Talfer, the Ahr and the Gader. The remaining 3% of the area is drained by the and Inn river systems to the Black Sea and by the Piave river system to the Adriatic Sea, respectively.
In South Tyrol there are 176 natural lakes with an area of more than half a hectare (1¼ acre), most of which are located above altitude. Only 13 natural lakes are larger than 5 ha, and only three of them are situated below altitude: the Kalterer See (), the Großer () and the Kleiner Montiggler See (). Fourteen South Tyrolean reservoirs used for energy production include the Reschensee (), which with an area of forms the largest standing body of water in South Tyrol, the Zufrittsee () and the Arzkarsee ().
The natural monuments designated by the province of South Tyrol include numerous hydrological objects, such as streams, waterfalls, moors, glaciers and mountain lakes like the Pragser Wildsee (), the Karersee () or the Spronser Seen ().
 Approximately 50% of the area of South Tyrol is covered by forests, another 40% is above and thus largely beyond the forest demarcation line, which varies between . In each case, more than half of the total forest area is located on land with a slope steeper than 20° and at altitudes between . Approximately 24% of the forest area can be classified as protective forest preserving settlements, traffic routes and other human
Approximately 50% of the area of South Tyrol is covered by forests, another 40% is above and thus largely beyond the forest demarcation line, which varies between . In each case, more than half of the total forest area is located on land with a slope steeper than 20° and at altitudes between . Approximately 24% of the forest area can be classified as protective forest preserving settlements, traffic routes and other human

 The local government system is based upon the provisions of the Italian Constitution and the Autonomy Statute of the Region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The 1972 second Statute of Autonomy for Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol devolved most legislative and executive competences from the regional level to the provincial level, creating '' de facto'' two separate regions.
The considerable legislative power of the province is vested in an assembly, the Landtag of South Tyrol (German: ''Südtiroler Landtag''; Italian: ''Consiglio della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano''; Ladin: ''Cunsëi dla Provinzia Autonoma de Bulsan'').
The legislative powers of the assembly are defined by the second Statute of Autonomy.
The executive powers are attributed to the government (German: ''Landesregierung''; Italian: ''Giunta Provinciale'') headed by the ''
The local government system is based upon the provisions of the Italian Constitution and the Autonomy Statute of the Region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The 1972 second Statute of Autonomy for Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol devolved most legislative and executive competences from the regional level to the provincial level, creating '' de facto'' two separate regions.
The considerable legislative power of the province is vested in an assembly, the Landtag of South Tyrol (German: ''Südtiroler Landtag''; Italian: ''Consiglio della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano''; Ladin: ''Cunsëi dla Provinzia Autonoma de Bulsan'').
The legislative powers of the assembly are defined by the second Statute of Autonomy.
The executive powers are attributed to the government (German: ''Landesregierung''; Italian: ''Giunta Provinciale'') headed by the ''
 The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in Italian, Junta provinziala in Ladin) consists of a provincial governor and a variable number of provincial councilors. Currently (2021), the provincial government consists of eight provincial councilors and the provincial governor. The deputies of the provincial governor are appointed from among the provincial councilors. The current governor is Arno Kompatscher (SVP), his deputies are the provincial councilors Arnold Schuler (SVP), Giuliano Vettorato (LN) and Daniel Alfreider (SVP).
The Governor and the Provincial Councilors are elected by Parliament by secret ballot with an absolute majority of votes. The composition of the provincial government must in any case reflect the proportional distribution of the German and Italian language groups in the provincial parliament. In the past, this provision prevented the German-dominated South Tyrol People's Party (SVP) from governing alone and allowed Italian parties to participate in the provincial government. Since the Ladin language group, with just under 4% of South Tyrol's resident population, has little electoral potential, a separate provision in the autonomy statute allows Ladin representation in the provincial government regardless of their proportional representation in the provincial parliament.
The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in Italian, Junta provinziala in Ladin) consists of a provincial governor and a variable number of provincial councilors. Currently (2021), the provincial government consists of eight provincial councilors and the provincial governor. The deputies of the provincial governor are appointed from among the provincial councilors. The current governor is Arno Kompatscher (SVP), his deputies are the provincial councilors Arnold Schuler (SVP), Giuliano Vettorato (LN) and Daniel Alfreider (SVP).
The Governor and the Provincial Councilors are elected by Parliament by secret ballot with an absolute majority of votes. The composition of the provincial government must in any case reflect the proportional distribution of the German and Italian language groups in the provincial parliament. In the past, this provision prevented the German-dominated South Tyrol People's Party (SVP) from governing alone and allowed Italian parties to participate in the provincial government. Since the Ladin language group, with just under 4% of South Tyrol's resident population, has little electoral potential, a separate provision in the autonomy statute allows Ladin representation in the provincial government regardless of their proportional representation in the provincial parliament.
 In 2016 South Tyrol had a
In 2016 South Tyrol had a  The unemployment rate stood at 3.8% in 2020.
The unemployment rate stood at 3.8% in 2020.
 German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native Austro-Bavarian dialects of the German language.
German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native Austro-Bavarian dialects of the German language.
 The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is
The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige
lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol , settlement_type = Autonomous province , image_skyline = , image_alt = , image_caption = , image_flag = Flag_of_South_Tyrol.svg , flag_alt = , image_shield = Suedtirol CoA.svg , shield_size = x100px , shield_alt = Coat of arms of Tyrol , anthem = , image_map = Bolzano in Italy.svg , map_alt = , map_caption = Map highlighting the location of the province of South Tyrol in Italy (in red) , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type1 = Region , subdivision_name1 = Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol , established_title = , established_date = , seat_type = Capital(s) , seat = Bolzano , parts_type = Comuni , parts_style = para , p1 = 116 , government_footnotes = , leader_party = SVP , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Arno Kompatscher , unit_pref = Metric , area_footnotes = , area_total_km2 = 7399.97 , elevation_footnotes = , elevation_m = , population_footnotes = , population_total = 531178 , population_as_of = 1 January 2019 , population_density_km2 = auto , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €24.8 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 =
GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
, blank1_info_sec1 = €47,100 (2018)
, blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019)
, blank2_info_sec1 = 0.910· 5th of 21 , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = 39XXX , area_code_type = Telephone prefix , area_code = 0471, 0472, 0473, 0474 , iso_code = , registration_plate = BZ , blank_name_sec2 = ISTAT , blank_info_sec2 = 021 , website = , footnotes = , official_name = , governing_body = Landtag South Tyrol (german: Südtirol; it, Alto Adige; lld, Südtirol), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano, is an autonomous province in
northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
, one of the two that make up the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province is the northernmost of Italy, the second largest, with an area of and has a total population of about 534,000 inhabitants as of 2021. Its capital and largest city is Bolzano (German: ''Bozen''; Ladin: ''Balsan'' or ''Bulsan'').
 According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language (
According to the 2011 census, 62.3% of the population uses German as their first language (Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
in the written form and an Austro-Bavarian dialect in the spoken form); 23.4% of the population speaks Italian, mainly in and around the two largest cities (Bolzano, with an Italian-speaking majority, and Meran, with a slight majority German-speaking); 4.1% speaks Ladin, a Rhaeto-Romance language
Rhaeto-Romance, Rheto-Romance, or Rhaetian, is a purported subfamily of the Romance languages that is spoken in south-eastern Switzerland and north-eastern Italy. The name "Rhaeto-Romance" refers to the former Roman province of Raetia. The qu ...
; 10.2% of the population (mainly recent immigrants) speaks another language natively. Of 116 South Tyrolean municipalities, 103 have a German-speaking, eight a Ladin-speaking, and five an Italian-speaking majority.
There was large-scale immigration of Italians from the rest of Italy to Bolzano and its surroundings after 1918.Oscar Benvenuto (ed.):South Tyrol in Figures 2008", Provincial Statistics Institute of the Autonomous Province of South Tyrol
Bozen/Bolzano 2007, p. 19, Table 11 The province is granted a considerable level of self-government, consisting of a large range of exclusive legislative and executive powers and a fiscal regime that allows it to retain 90% of revenue, while remaining a net contributor to the national budget. As of 2016, South Tyrol is the wealthiest province in Italy and among the wealthiest in the European Union. In the wider context of the European Union, the province is one of the three members of the Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino Euroregion, which corresponds almost exactly to the historical region of Tyrol. The other members are Tyrol state in Austria, to the north and east, and the Italian Autonomous province of Trento to the south.
Name
 ''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic County of Tyrol, a former state of the Holy Roman Empire and
''South Tyrol'' (occasionally ''South Tirol'') is the term most commonly used in English for the province, and its usage reflects that it was created from a portion of the southern part of the historic County of Tyrol, a former state of the Holy Roman Empire and crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. ...
of the Austrian Empire of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s. German and Ladin speakers usually refer to the area as ''Südtirol''; the Italian equivalent ''Sudtirolo'' (sometimes parsed ''Sud Tirolo'') is becoming increasingly common.
''Alto Adige'' (literally translated in English: "Upper Adige"), one of the Italian names for the province, is also used in English. The term had been the name of political subdivisions along the Adige River
The Adige (; german: Etsch ; vec, Àdexe ; rm, Adisch ; lld, Adesc; la, Athesis; grc, Ἄθεσις, Áthesis, or , ''Átagis'') is the second-longest river in Italy, after the Po. It rises near the Reschen Pass in the Vinschgau in the prov ...
in the time of Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, who created the Department of Alto Adige, part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy. It was reused as the Italian name of the current province after its post-World War I creation, and was a symbol of the subsequent forced Italianization
Italianization ( it, italianizzazione; hr, talijanizacija; french: italianisation; sl, poitaljančevanje; german: Italianisierung; el, Ιταλοποίηση) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or a ...
of South Tyrol.
The official name of the province today in German is ''Autonome Provinz Bozen — Südtirol''. German speakers usually refer to it not as a ''Provinz'', but as a ''Land'' (like the Länder
Länder (singular Land) or Bundesländer (singular Bundesland) is the name for (federal) states in two German-speaking countries. It may more specifically refer to:
* States of Austria, the nine federal subdivisions of Austria
* States of Germany, ...
of Germany and Austria). Provincial institutions are referred to using the prefix ''Landes-'', such as ''Landesregierung'' (state government) and ''Landeshauptmann
Landeshauptmann (if male) or Landeshauptfrau (if female) (, "state captain", plural ''Landeshauptleute'') is the chairman of a state government and the supreme official of an Austrian state and the Italian autonomous provinces of South Tyrol an ...
'' (governor).
The official name in Italian is ''Provincia autonoma di Bolzano — Alto Adige'', in Ladin ''Provinzia autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan — Südtirol''.
History
Annexation by Italy
South Tyrol is an administrative entity originated during the First World War. The Allies promised the area to Italy in the Treaty of London of 1915 as an incentive to enter the war on their side. Until 1918, it was part of theAustro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
princely County of Tyrol, but this almost completely German-speaking territory was occupied by Italy at the end of the war in November 1918 and was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy in 1919. The province as it exists today was created in 1926 after an administrative reorganization of the Kingdom of Italy, and was incorporated together with the province of Trento into the newly created region of ''Venezia Tridentina'' ("Trentine Venetia").
With the rise of Italian Fascism, the new regime made efforts to bring forward the Italianization of South Tyrol. The German language was banished from public service, German teaching was officially forbidden, and German newspapers were censored (with the exception of the fascistic ''Alpenzeitung''). The regime also favoured immigration from other Italian regions.
The subsequent alliance between Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
declared that South Tyrol would not follow the destiny of Austria, which had been annexed by Nazi Germany. Instead the dictators agreed that the German-speaking population be transferred to German-ruled territory or dispersed around Italy, but the outbreak of the Second World War prevented them from fully carrying out their intention. Every single citizen had the free choice to give up his German cultural identity and stay in fascist Italy, or to leave his homeland and move to Nazi Germany to retain his cultural identity. The result was that in the difficult times of fascism, the individual South Tyrolean families were divided and separated.
In this tense relationship for the population, Walter Caldonazzi from Mals was part of the resistance group around the priest Heinrich Maier, which passed plans and information about production facilities for V-1 rockets, V-2 rockets, Tiger tanks, Messerschmitt Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a German World War II fighter aircraft that was, along with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the backbone of the Luftwaffe's fighter force. The Bf 109 first saw operational service in 1937 during the Spanish Civil War an ...
, and Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and other aircraft to the Allies. For after the war, the group planned an independent Austria with a monarchical form of government, which would include Austria, Bavaria and South Tyrol.
In 1943, when the Italian government signed an armistice with the Allies, the region was occupied by Germany, which reorganised it as the Operation Zone of the Alpine Foothills
The Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills (german: Operationszone Alpenvorland (OZAV); it, Zona d'operazione delle Prealpi) was a Nazi German occupation zone in the sub-Alpine area in Italy during World War II.
Origin and geography
OZAV was ...
and put it under the administration of Gauleiter Franz Hofer. The region was '' de facto'' annexed to the German Reich (with the addition of the province of Belluno
The Province of Belluno ( it, Provincia di Belluno; de-AT, Provinz Belluno; lld, Provinzia de Belum) is a province in the Veneto region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Belluno.
It has an area of and a total population of about 205,000.
...
) until the end of the war. This status ended along with the Nazi regime, and Italian rule was restored in 1945.
Gruber–De Gasperi Agreement
After the war the Allies decided that the province would remain a part of Italy, under the condition that the German-speaking population be granted a significant level of self-government. Italy and Austria negotiated an agreement in 1946, recognizing the rights of the German minority. Alcide De Gasperi, Italy's prime minister, a native of Trentino, wanted to extend the autonomy to his fellow citizens. This led to the creation of the region called ''Trentino-Alto Adige/Tiroler Etschland''. The Gruber–De Gasperi Agreement of September 1946 was signed by the Italian and Austrian Foreign Ministers, creating the autonomous region of Trentino-South Tyrol, consisting of the autonomous provinces of Trentino and South Tyrol. German and Italian were both made official languages, and German-language education was permitted once more. Still Italians were the majority in the combined region. This, together with the arrival of new Italian-speaking immigrants, led to strong dissatisfaction among South Tyroleans, which culminated in terrorist acts perpetrated by the ''Befreiungsausschuss Südtirol
The South Tyrolean Liberation Committee (german: Befreiungsausschuss Südtirol, abbreviated ''BAS'') was an underground secessionist and terrorist organisation founded by Sepp Kerschbaumer and several combatants including Georg Klotz in the mid-195 ...
'' (BAS – Liberation Committee of South Tyrol). In the first phase, only public edifices and fascist monuments were targeted. The second phase was bloodier, costing 21 lives (15 members of Italian security forces, two civilians, and four terrorists).
''Südtirolfrage''
The South Tyrolean Question (''Südtirolfrage'') became an international issue. As the implementation of the post-war agreement was deemed unsatisfactory by the Austrian government, it became a cause of significant friction with Italy and was taken up by the United Nations in 1960. A fresh round of negotiations took place in 1961 but proved unsuccessful, partly because of the campaign of terrorism. The issue was resolved in 1971, when a new Austro-Italian treaty was signed and ratified. It stipulated that disputes in South Tyrol would be submitted for settlement to the International Court of Justice in The Hague, that the province would receive greater autonomy within Italy, and that Austria would not interfere in South Tyrol's internal affairs. The new agreement proved broadly satisfactory to the parties involved, and the separatist tensions soon eased. The autonomous status granted in 1972 has resulted in a considerable level of self-government, and also allows the entity to retain almost 90% of all levied taxes.Autonomy
In 1992, Italy and Austria officially ended their dispute over the autonomy issue on the basis of the agreement of 1972. The extensive self-government provided by the current institutional framework has been advanced as a model for settling interethnic disputes and for the successful protection of linguistic minorities. This is among the reasons why the Ladin municipalities ofCortina d'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite river, in an alp ...
/Anpezo, Livinallongo del Col di Lana/Fodom and Colle Santa Lucia/Col have asked in a referendum to be detached from Veneto and reannexed to the province, from which they were separated under the fascist government.
Euroregion
In 1996, the Euroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino was formed between the Austrian state of Tyrol and the Italian provinces of South Tyrol and Trentino. The boundaries of the association correspond to the old County of Tyrol. The aim is to promote regional peace, understanding and cooperation in many areas. The region's assemblies meet together as one on various occasions, and have set up a common liaison office with the European Union in Brussels.Geography
 South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states Tyrol and Salzburg, and by the
South Tyrol is located at the northernmost point in Italy. The province is bordered by Austria to the east and north, specifically by the Austrian federal-states Tyrol and Salzburg, and by the Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
canton of Graubünden to the west. The Italian provinces of Belluno
Belluno (; lld, Belum; vec, Belùn) is a town and province in the Veneto region of northern Italy. Located about north of Venice, Belluno is the capital of the province of Belluno and the most important city in the Eastern Dolomites region ...
, Trentino, and Sondrio
Sondrio (; lmo, Sùndri; rm, Sunder; archaic german: Sünders or ; la, Sundrium) is an Italian city and ''comune'' and Provincial Capital located in the heart of the Valtellina. , Sondrio counts approximately 21,876 inhabitants (2015) and it is ...
border to the southeast, south, and southwest, respectively.
The landscape itself is mostly cultivated with different types of shrubs and forests and is highly mountainous.
Entirely located in the Alps, the province's landscape is dominated by mountains. The highest peak is the Ortler
Ortler (; it, Ortles ) is, at above sea level, the highest mountain in the Eastern Alps outside the Bernina Range. It is the main peak of the Ortler Range. It is the highest point of the Southern Limestone Alps, of South Tyrol in Italy, of Ty ...
() in the far west, which is also the highest peak in the Eastern Alps outside the Bernina Range. Even more famous are the craggy peaks of the Dolomites in the eastern part of the region.
The following mountain groups are (partially) in South Tyrol. All but the Sarntal Alps are on the border with Austria, Switzerland, or other Italian provinces. The ranges are clockwise from the west and for each the highest peak is given that is within the province or on its border.
 Located between the mountains are many valleys, where the majority of the population lives.
Located between the mountains are many valleys, where the majority of the population lives.
Administrative divisions
The province is divided into eight districts (German: ''Bezirksgemeinschaften'', Italian: ), one of them being the chief city of Bolzano. Each district is headed by a president and two bodies called the district committee and the district council. The districts are responsible for resolving intermunicipal disputes and providing roads, schools, and social services such as retirement homes. The province is further divided into 116 ''Gemeinde
Gemeinde (; plural: Gemeinden) is a German word translating to "community", "town", "parish", or "municipality".
Gemeinde may refer to:
* An administrative division encompassing a single village, town, or city:
** Gemeinde (Austria)
** Gemeinde (G ...
n'' or '' comuni''.
Districts
Largest municipalities


Climate
Climatically, South Tyrol may be divided into five distinct groups: The Adige valley area, with cold winters (24-hour averages in January of about ) and warm summers (24-hour averages in July of about ), usuallyclassified
Classified may refer to:
General
*Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive
*Classified advertising or "classifieds"
Music
*Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper
*The Classified, a 1980s American roc ...
as humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
— Cfa. It has the driest and sunniest climate of the province. The main city in this area is Bolzano.
The midlands, between , with cold winters (24-hour averages in January between ) and mild summers (24-hour averages in July between ). This is a typical oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
, classified as Cfb. It is usually wetter than the subtropical climate, and very snowy during the winters. During the spring and autumn, there is a large foggy season, but fog may occur even on summer mornings. Main towns in this area are Meran, Bruneck, Sterzing, and Brixen. Near the lakes in higher lands (between ) the humidity may make the climate in these regions milder during winter, but also cooler in summer, then, a subpolar oceanic climate, Cfc, may occur.
 The alpine valleys between , with a typically humid continental climate — Dfb, covering the largest part of the province. The winters are usually very cold (24-hour averages in January between ), and the summers, mild with averages between . It is a very snowy climate; snow may occur from early October to April or even May. Main municipalities in this area are Urtijëi, Badia,
The alpine valleys between , with a typically humid continental climate — Dfb, covering the largest part of the province. The winters are usually very cold (24-hour averages in January between ), and the summers, mild with averages between . It is a very snowy climate; snow may occur from early October to April or even May. Main municipalities in this area are Urtijëi, Badia, Sexten
Sexten (; it, Sesto ) is a ''comune'' in South Tyrol in northern Italy. The village is famous as a summer and winter sport resort in the mountains.
According to the 2011 census, 95.37% of the population speak German, 4.36% Italian and 0.27% Ladin ...
, Toblach, Stilfs
Stilfs (; it, Stelvio ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. It is located near the northern ramp of the Stelvio Pass.
The municipality of Stilfs contains the ''frazioni'' (subdivisions, mainly villages ...
, Vöran
Vöran (; it, Verano ) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about northwest of the city of Bolzano.
Geography
As of November 30, 2010, it had a population of 927 and an area of .All demographics and other ...
, and Mühlwald.
The alpine valleys between , with a subarctic climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, ge ...
— Dfc, with harsh winters (24-hour averages in January between ) and cool, short, rainy and foggy summers (24-hour averages in July of about ). These areas usually have five months below the freezing point, and snow sometimes occurs even during the summer, in September. This climate is the wettest of the province, with large rainfalls during the summer, heavy snowfalls during spring and fall. The winter is usually a little drier, marked by freezing and dry weeks, although not sufficiently dry to be classified as a Dwc climate. Main municipalities in this area are Corvara, Sëlva, Santa Cristina Gherdëina.
The highlands above , with an alpine tundra climate, ET, which becomes an ice cap climate, EF, above . The winters are cold, but sometimes not as cold as the higher valleys' winters. In January, most of the areas at have an average temperature of about , while in the valleys at about , the mean temperature may be as low as . The higher lands, above are usually extremely cold, with averages of about during the coldest month, January.
Geology
 The periadriatic seam, which separates the Southern Alps from the Central Alps, runs through South Tyrol in a southwest-northeast direction. In South Tyrol at least three of the four main structural elements of the Alps come to light: the Southern Alpine comes to light south of the periadriatic suture, the Eastern Alpine north of it, and in the northern part of the country, east of the Brenner Pass, the Tauern window, in which the Peninsular and, according to some authors, the Helvetic are visible.
In South Tyrol, the following structure can be roughly recognized: The lowest floor forms the crystalline basement. About 280 million years ago, in the Lower Permian, multiple magmatic events occurred. At that time the Brixen granite was formed at the northern boundary of the Southern Alps, and at about the same time, further south in the Bolzano area, there was strong volcanic activity that formed the Adige Valley volcanic complex. In the Upper Permian a period began in which sedimentary rocks were formed. At first, these were partly clastic sediments, among which the Gröden sandstone is found. In the Triassic, massive carbonate platforms of dolomitic rocks then formed; this process was interrupted in the Middle Triassic by a brief but violent phase of volcanic activity.
In South Tyrol, the Eastern Alps consist mainly of metamorphic rocks, such as gneisses or mica schists, with occasional intercalations of marble and Mesozoic sedimentary rocks with metamorphic overprint (e.g., in the Ortler or southwest of the Brenner). Various metamorphic rocks are found in the Tauern Window, such as Hochstegen marble (as in Wolfendorn), Grünschiefer (as in Hochfeiler), or rocks of the Zentralgneiss (predominantly in the area of the Zillertal Main Ridge).
The province of South Tyrol has placed numerous geological natural monuments under protection. Among the best known are the Bletterbach Gorge, a 12 km (7½ mile) long canyon in the municipality of Aldein, and the Ritten Earth Pyramids, which are the largest in Europe with a height of up to .
The periadriatic seam, which separates the Southern Alps from the Central Alps, runs through South Tyrol in a southwest-northeast direction. In South Tyrol at least three of the four main structural elements of the Alps come to light: the Southern Alpine comes to light south of the periadriatic suture, the Eastern Alpine north of it, and in the northern part of the country, east of the Brenner Pass, the Tauern window, in which the Peninsular and, according to some authors, the Helvetic are visible.
In South Tyrol, the following structure can be roughly recognized: The lowest floor forms the crystalline basement. About 280 million years ago, in the Lower Permian, multiple magmatic events occurred. At that time the Brixen granite was formed at the northern boundary of the Southern Alps, and at about the same time, further south in the Bolzano area, there was strong volcanic activity that formed the Adige Valley volcanic complex. In the Upper Permian a period began in which sedimentary rocks were formed. At first, these were partly clastic sediments, among which the Gröden sandstone is found. In the Triassic, massive carbonate platforms of dolomitic rocks then formed; this process was interrupted in the Middle Triassic by a brief but violent phase of volcanic activity.
In South Tyrol, the Eastern Alps consist mainly of metamorphic rocks, such as gneisses or mica schists, with occasional intercalations of marble and Mesozoic sedimentary rocks with metamorphic overprint (e.g., in the Ortler or southwest of the Brenner). Various metamorphic rocks are found in the Tauern Window, such as Hochstegen marble (as in Wolfendorn), Grünschiefer (as in Hochfeiler), or rocks of the Zentralgneiss (predominantly in the area of the Zillertal Main Ridge).
The province of South Tyrol has placed numerous geological natural monuments under protection. Among the best known are the Bletterbach Gorge, a 12 km (7½ mile) long canyon in the municipality of Aldein, and the Ritten Earth Pyramids, which are the largest in Europe with a height of up to .
Mountains
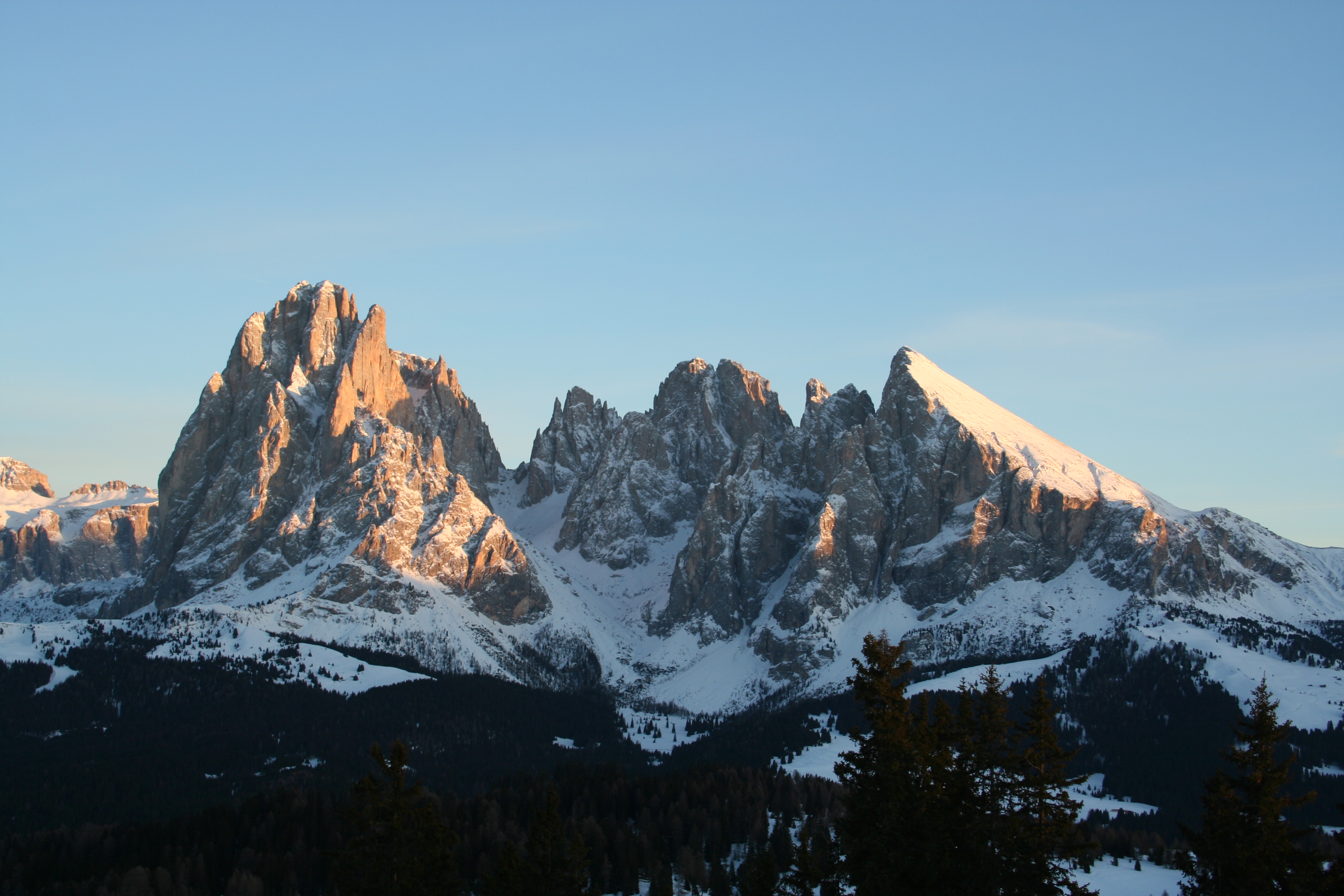
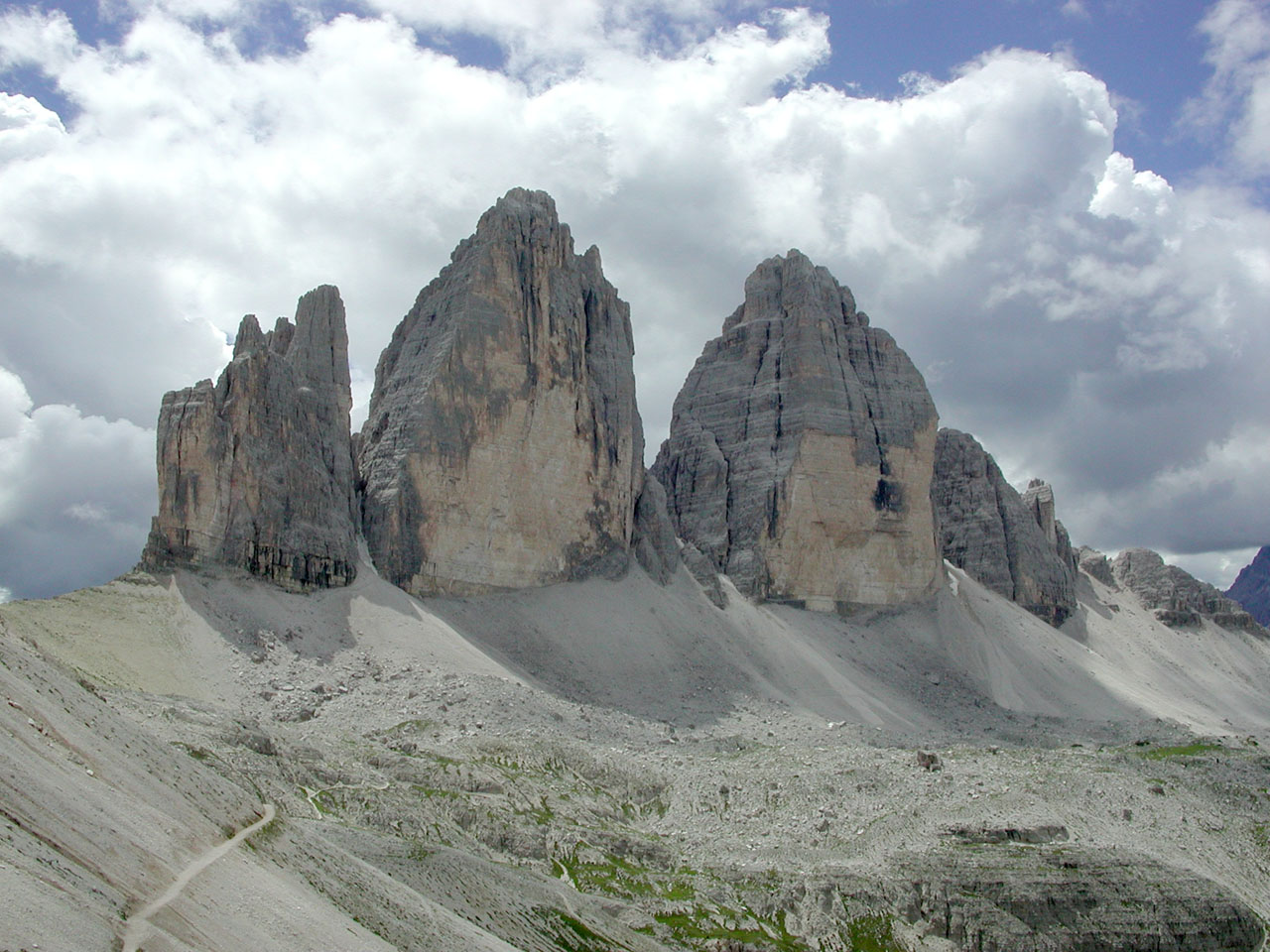
 According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by UNESCO in 2009 as a "Dolomite World Heritage Site".
Although some isolated massifs approach and show strong glaciation (especially in the Ortler Alps and on the main ridge of the Alps), South Tyrol is by far dominated by mountains with altitudes of between . Among the multitude of peaks, the Dolomites are the highest in the Alps. Among the large number of peaks, three stand out for their alpine or cultural importance: the
According to the Alpine Association, South Tyrol is home to 13 mountain groups of the Eastern Alps, of which only the Sarntal Alps are entirely within national borders. The remaining twelve are (clockwise, starting from the west): Sesvenna Group, Ötztal Alps, Stubai Alps, Zillertal Alps, Venediger Group, Rieserferner Group, Villgratner Mountains, Carnic Alps, Dolomites, Fleimstal Alps, Nonsberg Group and Ortler Alps. Of particular note are the Dolomites, parts of which were recognized by UNESCO in 2009 as a "Dolomite World Heritage Site".
Although some isolated massifs approach and show strong glaciation (especially in the Ortler Alps and on the main ridge of the Alps), South Tyrol is by far dominated by mountains with altitudes of between . Among the multitude of peaks, the Dolomites are the highest in the Alps. Among the large number of peaks, three stand out for their alpine or cultural importance: the Ortler
Ortler (; it, Ortles ) is, at above sea level, the highest mountain in the Eastern Alps outside the Bernina Range. It is the main peak of the Ortler Range. It is the highest point of the Southern Limestone Alps, of South Tyrol in Italy, of Ty ...
() as the highest mountain in South Tyrol, the Schlern () as the country's "landmark" and the Drei Zinnen () as the center of alpine climbing. Other well-known mountains are the Königspitze (), the Weißkugel (), the Similaun (), the Hochwilde (), the Sarner Weißhorn (), the Hochfeiler (), the Dreiherrnspitze (), the Hochgall (), the Peitlerkofel (), the Langkofel () and the Rosengartenspitze ().
The extensive mountain landscapes, about 34% of the total area of South Tyrol, are alpine pastures (including the of the great Alpe di Siusi). Along the main valleys, the mountain ranges descend in many places to valley bottoms over gently terraced landscapes, which are geological remains of former valley systems; situated between inhospitable high mountains and formerly boggy or deeply incised valley bottoms, these areas known as the "Mittelgebirge" (including, for example, the Schlern area) are of particular importance in terms of settlement history.
Valleys
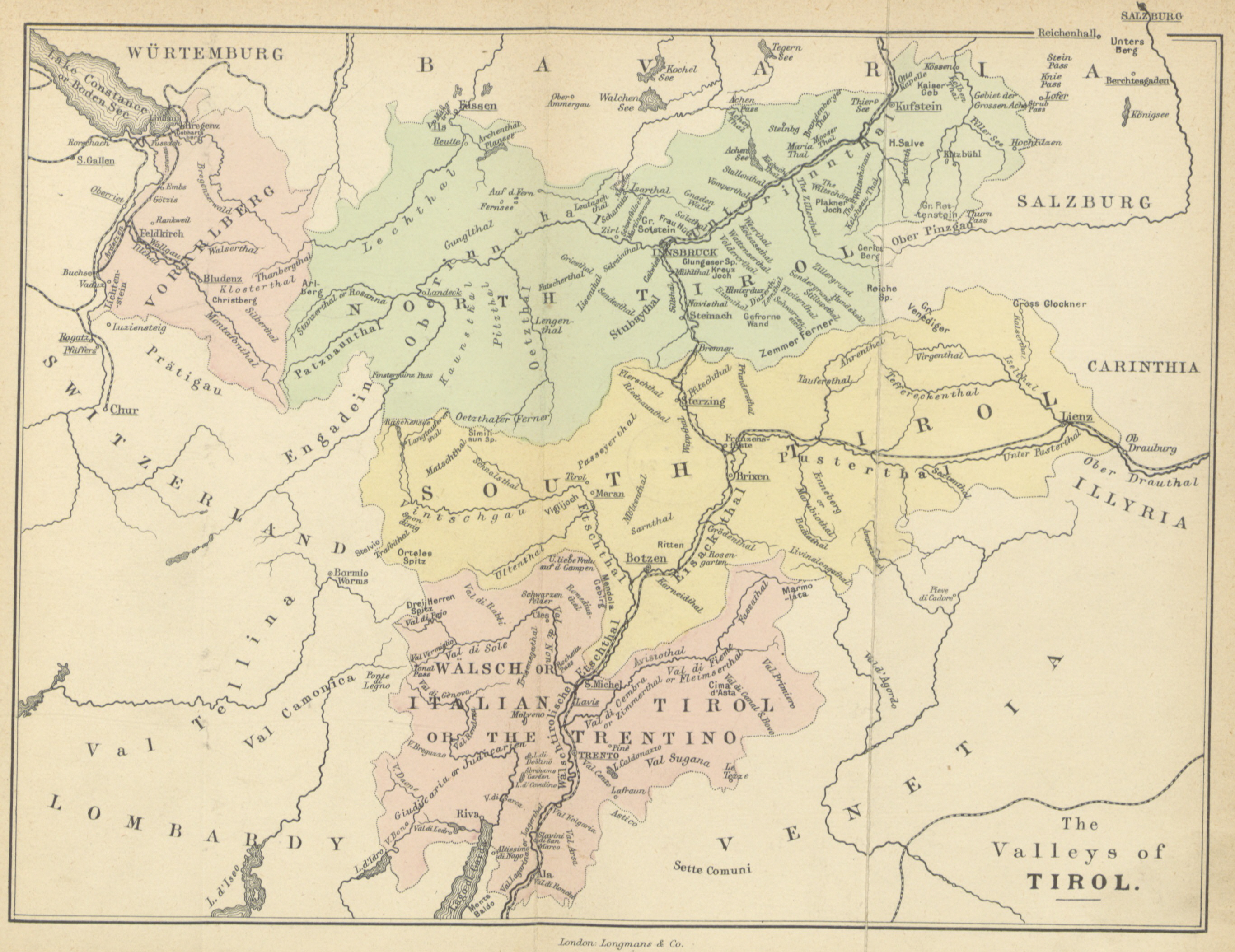
 The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the Adige Valley, the
The three main valleys of South Tyrol are the Adige Valley, the Eisack Valley
Eisack Valley ( it, Valle Isarco ; german: Eisacktal) is a district ( it, comprensorio; german: Bezirksgemeinschaft) in South Tyrol, Italy. It comprises the middle part of the valley of the Eisack, from Franzensfeste in the north to Waidbruck in ...
and the Puster Valley, formed by the Ice Age Adige glacier and its tributaries. The highest part of the Adige valley in western South Tyrol, from Reschen () to Töll (approx. ) near Merano, is called Vinschgau; the southernmost section, from Bolzano to Salurner Klause (), is divided into Überetsch and Unterland. From there, the Adige Valley continues in a southerly direction until it merges with the Po plain at Verona.
At Bolzano, the Eisack Valley merges into the Adige Valley. The Eisack Valley runs from Bolzano northeastward to Franzensfeste, where it merges with the Wipp Valley, which runs first northwestward and then northward over the Brenner Pass to Innsbruck. In the town of Brixen, the Eisack Valley meets the Puster Valley, which passes through Bruneck and reaches Lienz via the Toblacher Sattel (). In addition to the three main valleys, South Tyrol has a large number of side valleys. The most important and populated side valleys are (from west to east) Sulden, Schnals, Ulten, Passeier, Ridnaun, the Sarntal, Pfitsch, Gröden, the Gadertal, the Tauferer Ahrntal and Antholz.
In mountainous South Tyrol, about 64.5% of the total land area is above above sea level and only 14% below . Therefore, a large part of the population is concentrated in relatively small areas in the valleys at an altitude of between , mainly in the area of the extensive alluvial cones and broad basins. The most densely populated areas are in the Adige valley, where three of the four largest cities, Bolzano, Merano and Laives, are located. The flat valley bottoms are mainly used for agriculture.
Hydrography
 The most important river in South Tyrol is the Adige, which rises at the Reschen Pass, flows for a distance of about to the border at the Salurner Klause, and then flows into the Po Valley and the Adriatic Sea. The Adige, whose total length of in Italy is exceeded only by the Po, drains 97% of the territory's surface area. Its river system also includes the Eisack, about long, and the Rienz, about long, the next two largest rivers in South Tyrol. They are fed by numerous rivers and streams in the tributary valleys. The most important tributaries are the Plima, the Passer, the Falschauer, the Talfer, the Ahr and the Gader. The remaining 3% of the area is drained by the and Inn river systems to the Black Sea and by the Piave river system to the Adriatic Sea, respectively.
In South Tyrol there are 176 natural lakes with an area of more than half a hectare (1¼ acre), most of which are located above altitude. Only 13 natural lakes are larger than 5 ha, and only three of them are situated below altitude: the Kalterer See (), the Großer () and the Kleiner Montiggler See (). Fourteen South Tyrolean reservoirs used for energy production include the Reschensee (), which with an area of forms the largest standing body of water in South Tyrol, the Zufrittsee () and the Arzkarsee ().
The natural monuments designated by the province of South Tyrol include numerous hydrological objects, such as streams, waterfalls, moors, glaciers and mountain lakes like the Pragser Wildsee (), the Karersee () or the Spronser Seen ().
The most important river in South Tyrol is the Adige, which rises at the Reschen Pass, flows for a distance of about to the border at the Salurner Klause, and then flows into the Po Valley and the Adriatic Sea. The Adige, whose total length of in Italy is exceeded only by the Po, drains 97% of the territory's surface area. Its river system also includes the Eisack, about long, and the Rienz, about long, the next two largest rivers in South Tyrol. They are fed by numerous rivers and streams in the tributary valleys. The most important tributaries are the Plima, the Passer, the Falschauer, the Talfer, the Ahr and the Gader. The remaining 3% of the area is drained by the and Inn river systems to the Black Sea and by the Piave river system to the Adriatic Sea, respectively.
In South Tyrol there are 176 natural lakes with an area of more than half a hectare (1¼ acre), most of which are located above altitude. Only 13 natural lakes are larger than 5 ha, and only three of them are situated below altitude: the Kalterer See (), the Großer () and the Kleiner Montiggler See (). Fourteen South Tyrolean reservoirs used for energy production include the Reschensee (), which with an area of forms the largest standing body of water in South Tyrol, the Zufrittsee () and the Arzkarsee ().
The natural monuments designated by the province of South Tyrol include numerous hydrological objects, such as streams, waterfalls, moors, glaciers and mountain lakes like the Pragser Wildsee (), the Karersee () or the Spronser Seen ().
Vegetation
infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
. A 1997 study classified about 35% of South Tyrol's forests as near-natural or natural, about 41% as moderately modified and about 24% as heavily modified or artificial. The forests are found in the valley bottoms.
The flat valley bottoms were originally completely covered with riparian forests, of which only very small remnants remain along the rivers. The remaining areas have given way to settlements and agricultural land. On the valley slopes, sub-Mediterranean mixed deciduous forests are found up to altitude, characterized mainly by manna ash, hop hornbeam, hackberry, sweet chestnut and downy oak. From about of altitude, red beech or pine forests can appear instead, colonizing difficult and arid sites (more rarely). At altitudes between , spruce forests are found; between , montane and subalpine spruce forests predominate. The latter are often mixed with tree species such as larch, rowan, white pine and stone pine. The larch and stone pine forests at the upper edge of the forest belt occupy relatively small areas. Beyond the forest edge, subalpine dwarf shrub communities, alpine grasslands
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natural ...
and, lately, alpine tundra dominate the landscape as vegetation types.
Politics

 The local government system is based upon the provisions of the Italian Constitution and the Autonomy Statute of the Region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The 1972 second Statute of Autonomy for Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol devolved most legislative and executive competences from the regional level to the provincial level, creating '' de facto'' two separate regions.
The considerable legislative power of the province is vested in an assembly, the Landtag of South Tyrol (German: ''Südtiroler Landtag''; Italian: ''Consiglio della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano''; Ladin: ''Cunsëi dla Provinzia Autonoma de Bulsan'').
The legislative powers of the assembly are defined by the second Statute of Autonomy.
The executive powers are attributed to the government (German: ''Landesregierung''; Italian: ''Giunta Provinciale'') headed by the ''
The local government system is based upon the provisions of the Italian Constitution and the Autonomy Statute of the Region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The 1972 second Statute of Autonomy for Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol devolved most legislative and executive competences from the regional level to the provincial level, creating '' de facto'' two separate regions.
The considerable legislative power of the province is vested in an assembly, the Landtag of South Tyrol (German: ''Südtiroler Landtag''; Italian: ''Consiglio della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano''; Ladin: ''Cunsëi dla Provinzia Autonoma de Bulsan'').
The legislative powers of the assembly are defined by the second Statute of Autonomy.
The executive powers are attributed to the government (German: ''Landesregierung''; Italian: ''Giunta Provinciale'') headed by the ''Landeshauptmann
Landeshauptmann (if male) or Landeshauptfrau (if female) (, "state captain", plural ''Landeshauptleute'') is the chairman of a state government and the supreme official of an Austrian state and the Italian autonomous provinces of South Tyrol an ...
'' Arno Kompatscher. He belongs to the '' South Tyrolean People's Party'', which has been governing with a parliamentary majority since 1948. South Tyrol is characterized by long sitting presidents, having only had two presidents between 1960 and 2014 (Silvius Magnago
Silvius Magnago (5 February 1914 – 25 May 2010) was a South Tyrolean politician.
Biography
Magnago was born in Merano, which was then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, on 5 February 1914. In 1936 he graduated from the grammar school of ...
1960–1989, Luis Durnwalder 1989–2014).
A fiscal regime allows the province to retain a large part of most levied taxes, in order to execute and administer its competences. Nevertheless, South Tyrol remains a net contributor to the Italian national budget.
Last provincial elections
List of governors
Provincial Government
 The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in Italian, Junta provinziala in Ladin) consists of a provincial governor and a variable number of provincial councilors. Currently (2021), the provincial government consists of eight provincial councilors and the provincial governor. The deputies of the provincial governor are appointed from among the provincial councilors. The current governor is Arno Kompatscher (SVP), his deputies are the provincial councilors Arnold Schuler (SVP), Giuliano Vettorato (LN) and Daniel Alfreider (SVP).
The Governor and the Provincial Councilors are elected by Parliament by secret ballot with an absolute majority of votes. The composition of the provincial government must in any case reflect the proportional distribution of the German and Italian language groups in the provincial parliament. In the past, this provision prevented the German-dominated South Tyrol People's Party (SVP) from governing alone and allowed Italian parties to participate in the provincial government. Since the Ladin language group, with just under 4% of South Tyrol's resident population, has little electoral potential, a separate provision in the autonomy statute allows Ladin representation in the provincial government regardless of their proportional representation in the provincial parliament.
The provincial government (Landesregierung) of South Tyrol (formerly also called provincial committee, Giunta provinciale in Italian, Junta provinziala in Ladin) consists of a provincial governor and a variable number of provincial councilors. Currently (2021), the provincial government consists of eight provincial councilors and the provincial governor. The deputies of the provincial governor are appointed from among the provincial councilors. The current governor is Arno Kompatscher (SVP), his deputies are the provincial councilors Arnold Schuler (SVP), Giuliano Vettorato (LN) and Daniel Alfreider (SVP).
The Governor and the Provincial Councilors are elected by Parliament by secret ballot with an absolute majority of votes. The composition of the provincial government must in any case reflect the proportional distribution of the German and Italian language groups in the provincial parliament. In the past, this provision prevented the German-dominated South Tyrol People's Party (SVP) from governing alone and allowed Italian parties to participate in the provincial government. Since the Ladin language group, with just under 4% of South Tyrol's resident population, has little electoral potential, a separate provision in the autonomy statute allows Ladin representation in the provincial government regardless of their proportional representation in the provincial parliament.
Secessionist movement
Given the region's historical and cultural association with neighboring Austria, calls for the secession of South Tyrol and its reunification with Austria do surface from time to time among German- and Ladin-speakers, although falling short of an absolute majority in the province when considering also the Italian-speaking population, the majority does support a separation. Among the political parties that support South Tyrol's reunification into Austria are South Tyrolean Freedom, Die Freiheitlichen and Citizens' Union for South Tyrol.Economy
 In 2016 South Tyrol had a
In 2016 South Tyrol had a GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
of €42,600, making it the richest province in Italy and one of the richest in the European Union.
The unemployment level in 2007 was roughly 2.4% (2.0% for men and 3.0% for women). Residents are employed in a variety of sectors, from agriculture — the province is a large producer of apples, and its South Tyrol wine
South Tyrol (called in Italian ''Alto Adige'') is an autonomous province located in north-east Italy producing wine. This Austro-Italian wine region is noted for the distinct Austrian influences on the wine industry due to the region's long histor ...
are also renowned — to industry to services, especially tourism. Spas located on the Italian Alps have become a favorite for tourists seeking wellness.
South Tyrol is home to numerous mechanical engineering companies, some of which are the global market leaders in their sectors: the Leitner Group that specializes in cable cars and wind energy, TechnoAlpin AG, which is the global market leader in snow-making technology and the snow groomer company Prinoth.
Transport
The region is, together with northern and eastern Tyrol, an important transit point between southern Germany andNorthern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
. Freights by road and rail pass through here. One of the most important highways is the A22, also called the ''Autostrada del Brennero''. It connects to the Brenner Autobahn
The Brenner Autobahn ( it, Autostrada del Brennero or it, AutoBrennero, en, Brenner motorway) refers to a major European truck route that connects Innsbruck in Austria to Verona in northern Italy.
Numbered as the A13 in the Austrian section, th ...
in Austria.
The vehicle registration plate of South Tyrol is the two-letter provincial code Bz for the capital city, Bolzano. Along with the autonomous Trentino (Tn) and Aosta Valley (Ao), South Tyrol is allowed to surmount its license plates with its coat of arms.
Rail transport goes over the Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and has ...
. The Brenner Railway is a major line connecting the Austrian and Italian railways from Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
and Verona climbing the Wipptal, passing over the Brenner Pass and descending down the Eisack Valley
Eisack Valley ( it, Valle Isarco ; german: Eisacktal) is a district ( it, comprensorio; german: Bezirksgemeinschaft) in South Tyrol, Italy. It comprises the middle part of the valley of the Eisack, from Franzensfeste in the north to Waidbruck in ...
to Bolzano and then down the Adige Valley from Bolzano to Rovereto and to Verona. The line is part of the Line 1 Line 1 or 1 line may refer to:
Public transport Africa
* Line 1 (Algiers Metro), Algeria
* Cairo Metro Line 1, Egypt
Asia China
* Line 1 (Beijing Subway)
* Line 1 (Changchun Rail Transit)
* Line 1 (Changsha Metro)
* Line 1 (Changzhou Metro)
* L ...
of Trans-European Transport Networks
The Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) is a planned network of roads, railways, airports and water infrastructure in the European Union. The TEN-T network is part of a wider system of Trans-European Networks (TENs), including a telecommunic ...
(TEN-T).
Other railways are the Pustertalbahn, Ritten Railway and Vinschgaubahn. Due to the steep slopes of the mountains, a number of funiculars exist, such as the Gardena Ronda Express funicular
The Gardena Ronda Express is a funicular situated in the Val Gherdëina near Santa Cristina Gherdëina, connecting the Col Raiser lifts to the Sasslong/Ruacia and Ciampinoi lifts in northern Italy.
Trains
Two funiculars operate on the system. ...
and Mendel Funicular.
The Brenner Base Tunnel is under construction and scheduled to be completed by 2025. With a planned length of , this tunnel will increase freight train average speed to and reduce transit time by over an hour.
Larger cities used to have their own tramway system, such as the Meran Tramway and Bolzano Tramway
The Bolzano Tram is a former transport net, built to connect the various villages near Bolzano, in what is now South Tyrol, northern Italy. At the time, Zwölfmalgreien, Bolzano and Gries were three independent municipalities.
Track
The first bu ...
. These were replaced after the Second World War with buses. Many other cities and municipalities have their own bus system or are connected with each other by it.
The Bolzano Airport is the only airport serving the region.
Demographics
Languages
 German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native Austro-Bavarian dialects of the German language.
German and Italian are both official languages of South Tyrol. In some eastern municipalities Ladin is the third official language.
A majority of the inhabitants of contemporary South Tyrol speak native Austro-Bavarian dialects of the German language. Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
plays a dominant role in education and media. All citizens have the right to use their own mother tongue, even at court. Schools are separated for each language group. All traffic signs are officially bi- or trilingual. Most Italian toponyms are translations performed by Italian nationalist Ettore Tolomei, the author of the '' Prontuario dei nomi locali dell'Alto Adige''.
To reach a fair allocation of jobs in public service a system called ethnic proportion ( it, proporzionale etnica, german: ethnischer Proporz) has been established. Every ten years, when the general census of population takes place, each citizen has to declare the linguistic group to which they belong or want to be aggregated to. According to the results they decide how many people of which group are going to be employed in public service.
At the time of the annexation of the southern part of Tyrol by Italy in 1919, the overwhelming majority of the population spoke German and identified with the Austrian or German nationality: in 1910, according to the last population census before World War I, the German-speaking population numbered 224,000, the Ladin 9,000 and the Italian 7,000.
As a result of the Italianization of South Tyrol about 23% of the population are Italian-speakers (they were 33%, 138,000 of 414,000 inhabitants in the 1971 census) according to the census of 2011. 103 out of 116 comuni have a majority of German native speakers — with Martell reaching 100% — eight have a Ladin-speaking majority, and five a majority of Italian speakers. The Italian-speaking population lives mainly around the provincial capital Bolzano, where they are the majority (73.8% of the inhabitants), and partially a result of Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
's policy of Italianisation after he took power in 1922, when he encouraged immigration from the rest of Italy.
The other four comuni where the Italian-speaking population is the majority are Laives
Laives (; german: Leifers ) is a town and a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located about south of the city of Bolzano. It is one of only five mainly Italian speaking municipalities in South Tyrol, and the fourth larg ...
, Salorno, Bronzolo and Vadena. The eight comuni with Ladin majorities are: La Val, Badia, Corvara, Mareo, San Martin de Tor, Santa Cristina Gherdëina, Sëlva, Urtijëi. Most of the immigrants from South Tyrol to the United States identify themselves as being of German rather than Austrian identity. According to the United States Census Bureau, in 2015, there were 365 individuals living in the U.S. born in Italy who identified themselves as being of Austrian ancestry. By contrast, in the same year, there were 1040 individuals living in the U.S. born in Italy who identified themselves as being of German ancestry.
The linguistic breakdown according to the census of 2011:
Religion
The majority of the population is Christian, mostly in the Catholic tradition. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Bolzano-Brixen corresponds to the territory of the province of South Tyrol. Since July 27, 2011 the bishop of Bolzano-Brixen is Ivo Muser.Catholic Church
 The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is
The vast majority of the population of South Tyrol is baptized Catholic. There is archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence of early Christian sites in the area as early as Late Antiquity; Säben in the Eisack Valley became an important ecclesiastical center during this period, which was only replaced by Brixen as an episcopal see in the late Middle Ages. The territory of present-day South Tyrol was divided for centuries between the dioceses of Brixen, Chur (until 1808/1816) and Trent (until 1964).
The most famous bishop of Brixen was the polymath Nicholas of Cusa. Important figures of the regional ecclesiastical
{{Short pages monitor