|
Altitudes
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. In aviation, altitude is typically measured relative to mean sea level or above ground level to ensure safe navigation and flight operations. In geometry and geographical surveys, altitude helps create accurate topographic maps and understand the terrain's elevation. For high-altitude trekking and sports, knowing and adapting to altitude is vital for performance and safety. Higher altitudes mean reduced oxygen levels, which can lead to altitude sickness if proper acclimatization measures are not taken. Vertical distance measurements in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. In aviation, altitude is typically measured relative to mean sea level or above ground level to ensure safe navigation and flight operations. In geometry and geographical surveys, altitude helps create accurate topographic maps and understand the terrain's elevation. For high-altitude trekking and sports, knowing and adapting to altitude is vital for performance and safety. Higher altitudes mean reduced oxygen levels, which can lead to altitude sickness if proper acclimatization measures are not taken. Vertical distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
International Standard Atmosphere
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. It has been established to provide a common reference for temperature and pressure and consists of tables of values at various altitudes, plus some formulas by which those values were derived. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) publishes the ISA as an international standard, ISO 2533:1975.International Organization for Standardization, Standard Atmosphere', ISO 2533:1975, 1975. Other standards organizations, such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the United States Government, publish extensions or subsets of the same atmospheric model under their own standards-making authority. Description The ISA mathematical model divides the atmosphere into layers with an assumed linear distribution of absolute temperature ''T'' against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transition Altitude
In aviation, a flight level (FL) is an aircraft's altitude as determined by a pressure altimeter using the International Standard Atmosphere. It is expressed in hundreds of feet or metres. The altimeter setting used is the ISA sea level pressure of 1013 hPa or 29.92 inHg. The actual surface pressure will vary from this at different locations and times. Therefore, by using a standard pressure setting, every aircraft has the same altimeter setting, and vertical clearance can be maintained during cruise flight. Background Flight levels are used to ensure safe vertical separation between aircraft. Historically, altitude has been measured using an altimeter, essentially a calibrated barometer. An altimeter measures ambient air pressure, which decreases with increasing altitude following the barometric formula. It displays the corresponding altitude. If aircraft altimeters were not calibrated consistently, then two aircraft could be flying at the same altitude even thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
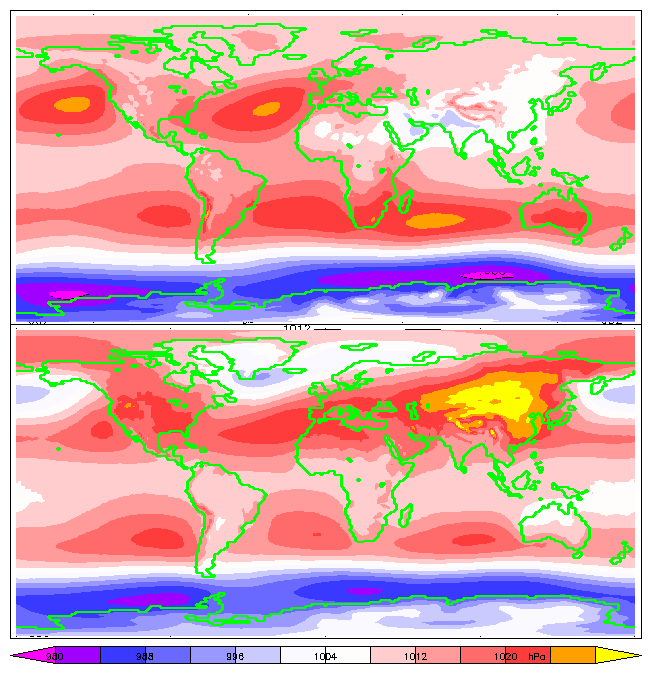
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mean Sea Level Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Air Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The Standard atmosphere (unit), standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 Bar (unit), millibars, 760millimetre of mercury, mm Hg, 29.9212inch of mercury, inchesHg, or 14.696pounds per square inch, psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the International Standard Atmosphere, ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the fluid pressure, hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of Earth's atmosphere, air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and ''sphere, sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mesosphere
The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere (sometimes called the stratopause), and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures below . The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season (higher in winter and at the tropics, lower in summer and at the poles), but the lower boundary is usually located at altitudes from above sea level, and the upper boundary (the mesopause) is usually from . The stratosphere and mesosphere are sometimes collectively referred to as the "middle atmosphere", which spans altitudes approximately between above Earth's surface. The mesopause, at an altitude of , separates the mesosphere from the thermosphere—the second-outermost la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher (closer to outer space) and the cooler layers lower (closer to the planetary surface of the Earth). The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer, where ozone is exothermically photolyzed into oxygen in a cyclical fashion. This temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, where temperature decreases with altitude, and between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at mid-latitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Height Above Sea Level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of a location's vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) in reference to a vertical datum based on a historic mean sea level. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric height. The zero level varies in different countries due to different reference points and historic measurement periods. Climate change and other forces can cause sea levels and elevations to vary over time. Uses Elevation or altitude above sea level is a standard measurement for: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Mining infrastructure, particularly underground. * Flying objects such as airplanes or helicopters below a Transition Altitude defined by local regulations. Units and abbreviations Elevation or altitude is generally expressed as "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, or " feet above mean sea level" in United States customary and imperial units. Common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |