Syrian Greek on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Greeks in Syria arrived in the 7th century BC and became more prominent during the
Relations with Syria There are also about 8,000 Greek-speaking Muslims of
 The history of Greeks in Syria traditionally begins with
The history of Greeks in Syria traditionally begins with
 Throughout the Middle Ages,
Throughout the Middle Ages,
 The Arab conquest of Syria (Arabic: الفتح الإسلامي لبلاد الشام) occurred in the first half of the 7th century, and refers to the conquest of the Levant, which later became known as the Islamic Province of
The Arab conquest of Syria (Arabic: الفتح الإسلامي لبلاد الشام) occurred in the first half of the 7th century, and refers to the conquest of the Levant, which later became known as the Islamic Province of
by Roula Tsokalidou. Proceedings ''II Simposio Internacional Bilingüismo''. Retrieved 18-12-08 Greek Muslims constitute a majority of Al-Hamidiyah's population. By 1988, many Greek Muslims from both
Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
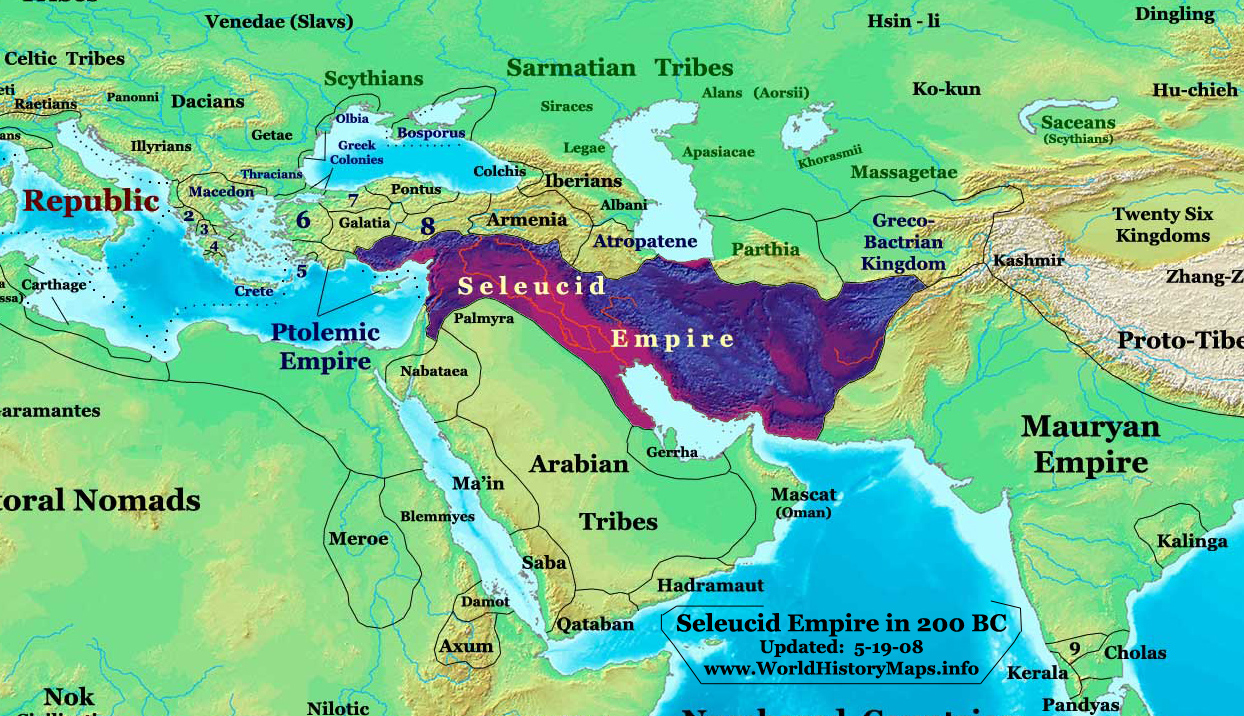
and when the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
was centered there. Today, there is a Greek community of about 4,500 in Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, most of whom have Syrian nationality and who live mainly in Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
(the country's main trading and financial centre), Baniyas
Baniyas ( ') is a Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal city in Tartous Governorate, western Syria, located south of Latakia and north of Tartous.
It is known for its citrus fruit orchards and its export of wood. North of the city is an B ...
, Tartous
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''Ṭarṭūs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (after Latakia), an ...
, and Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
, the capital.Greek Ministry of Foreign AffairsRelations with Syria There are also about 8,000 Greek-speaking Muslims of
Cretan
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
origin in Al-Hamidiyah.
History
Greek presence is attested from early on, and in fact, thename of Syria
The name ''Syria'' is latinized from the Greek (). In toponymic typology, the term ''Syria'' is classified among choronyms (proper names of regions and countries). The origin and usage of the term has been the subject of interest, both among ...
itself is from a Greek word for Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
.
Iron Age
The AncientLevant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
had been initially dominated by a number of indigenous Semitic speaking peoples; the Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
ites, the Amorites
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Eg ...
and Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
ns, in addition to Indo-European powers; the Luwians
The Luwians (also known as Luvians) were an ancient people in Anatolia who spoke the Luwian language. During the Bronze Age, Luwians formed part of the population of the Hittite Empire and adjoining states such as Kizzuwatna. During the Hittite ...
, Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
and the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
. However, during the collapse of the Late Bronze Age, the coastal regions came under attack from a collection of nine seafaring tribes known as the Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Ancient Egypt, Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was proposed by the 19th-century Egyptology, Egyptologis ...
. The transitional period is believed by historians to have been a violent, sudden and culturally disruptive time. During this period, the Eastern Mediterranean saw the fall of the Mycenaean Kingdoms, the Hittite Empire in Anatolia and Syria, and the New Kingdom of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, ...
in Syria and Canaan.
Among the Sea Peoples were the first ethnic Greeks to migrate to the Levant. At least three of the nine tribes of the Sea Peoples are believed to have been ethnic Greeks; the Denyen
The Denyen (Egyptian: ''dꜣjnjnjw'') is purported to be one of the groups constituting the Sea Peoples.
They were raiders associated with the Eastern Mediterranean Dark Ages who attacked Egypt in 1207 BC in alliance with the Libyans and other S ...
, Ekwesh
The Achaeans or Akhaians (; , "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively.
The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwe ...
, and the Peleset, although some also include the Tjeker
The Tjeker or Tjekker (Egyptian: ''ṯꜣkꜣr'' or ''ṯꜣkkꜣr'') were one of the Sea Peoples.
Known mainly from the "Story of Wenamun", the Tjeker are also documented earlier, at Medinet Habu, as raiders defeated by Pharaoh Ramesses III of ...
. According to scholars, the Peleset were allowed to settle the coastal strip from Gaza to Joppa becoming the Philistines
Philistines (; LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines origi ...
. While the Denyen settled from Joppa to Acre, and the Tjeker in Acre. The political vacuum, which resulted from the collapse of the Hittite and Egyptian Empire's saw the rise of the Syro-Hittite states
The states called Neo-Hittite, Syro-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works) were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of ...
, the Philistine, and Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n Civilizations, and eventually the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
.
Al-Mina
Al-Mina (Arabic: "the port") is the modern name given by Leonard Woolley to an ancient trading post on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of northern Syria (region), Syria, at the mouth of the Orontes River. It is now located in Hatay pr ...
was a Greek trading colony.
Hellenistic Age
 The history of Greeks in Syria traditionally begins with
The history of Greeks in Syria traditionally begins with Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
's conquest of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
. In the aftermath of Alexander's death, his empire was divided into several successor states, and thus ushering in the beginning of the Hellenistic Age. For the Levant and Mesopotamia, it meant coming under the control of Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to fo ...
and the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
. The Hellenistic period was characterized by a new wave of Greek colonization. Ethnic Greek colonists came from all parts of the Greek world, not, as before, from a specific "mother city".Ulrich Wilcken, ''Griechische Geschichte im Rahmen der Altertumsgeschichte''. The main centers of this new cultural expansion of Hellenism in the Levant were cities like Antioch, and the other cities of the Tetrapolis Seleukis. The mixture of Greek-speakers gave birth to a common Attic-based dialect, known as Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
, which became the lingua franca throughout the Hellenistic world.
The Seleucid Empire was a major empire of Hellenistic culture that maintained the pre-eminence of Greek customs in which a Greek political elite dominated, in newly founded urban areas.Glubb, Sir John Bagot 1967 34''Britannica'', "Seleucid kingdom", 2008, O.Ed. The Greek population of the cities who formed the dominant elite were reinforced by emigration from Greece. The creation of new Greek cities were aided by the fact that the Greek mainland was overpopulated and therefore made the vast Seleucid Empire ripe for colonization. Apart from these cities, there were also a large number of Seleucid garrisons (choria), military colonies (katoikias) and Greek villages (komai) which the Seleucids planted throughout the empire to cement their rule.
Roman Era
Levantine Hellenism flourished under Roman rule in several regions, such as theDecapolis
The Decapolis (Greek: ) was a group of ten Greek Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Greek and late Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BC and AD. Most of the cities were located to the east of the Jordan ...
. Antiochians in the Northern Levant found themselves under Roman rule when Seleukeia was eventually annexed by the Roman Republic in 64 BC, by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War. While those in the Southern Levant were absorbed gradually into the Roman State. Eventually, in 135 AD, after the Bar Kokhba revolt the North and South were merged into the Roman province of Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina ( ) was the renamed Roman province formerly known as Judaea, following the Roman suppression of the Bar Kokhba revolt, in what then became known as the Palestine region between the early 2nd and late 4th centuries AD. The pr ...
, which existed until about 390. During its existence, the population of Syria Palaestina in the north consisted of a mixed Polytheistic population of Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civi ...
, Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
and Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
which formed the majority, as well as what remained of Greek colonists, Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
societies of Itureans
Iturea or Ituraea (, ''Itouraía'') is the Greek name of a Levantine region north of Galilee during the Late Hellenistic and early Roman periods. It extended from Mount Lebanon across the plain of Marsyas to the Anti-Lebanon Mountains in Syri ...
, and later also the Ghassanids
The Ghassanids, also known as the Jafnids, were an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe. Originally from South Arabia, they migrated to the Levant in the 3rd century and established what would eventually become a Christian state, Christian kingdom unde ...
. In the East, Arameans and Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
made up the majority. In the South, Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
, Nabateans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Pet ...
and Greco-Romans made up the majority near the end of the 2nd century.
Byzantine Era
Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia ...
self-identified as Romaioi or Romioi (Greek: Ῥωμαῖοι, Ρωμιοί, meaning "Romans") and Graikoi (Γραικοῖ, meaning "Greeks"). Linguistically, they spoke Byzantine or Medieval Greek, known as "Romaic" which is situated between the Hellenistic (Koine), and modern phases of the language. Byzantines, perceived themselves as the descendants of classical Greece,; ; . the political heirs of imperial Rome, and followers of the Apostles. Thus, their sense of "Romanity" was different from that of their contemporaries in the West. "Romaic" was the name of the vulgar Greek language, as opposed to "Hellenic" which was its literary or doctrinal form.
The Byzantine dominion in the Levant known as the Diocese of the East
The Diocese of the East, also called the Diocese of Oriens, (; ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the western Middle East, between the Mediterranean Sea and Mesopotamia. During late Antiquity, it was one of t ...
, was one of the major commercial, agricultural, religious, and intellectual areas of the Empire, and its strategic location facing the Sassanid Empire and the unruly desert tribes gave it exceptional military importance. The entire area of the former diocese came under Sassanid occupation between 609 and 628, but it was retaken by the Emperor Heraclius until its irreversible lost to the Arabs after the Battle of Yarmouk
The Battle of the Yarmuk (also spelled Yarmouk; ) was a major battle between the army of the Byzantine Empire and the Arab Muslim forces of the Rashidun Caliphate. The battle consisted of a series of engagements that lasted for six days in Aug ...
and the fall of Antioch.
Arab Conquest
Bilad al-Sham
Bilad al-Sham (), often referred to as Islamic Syria or simply Syria in English-language sources, was a province of the Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and Fatimid caliphates. It roughly corresponded with the Byzantine Diocese of the East, con ...
. On the eve of the Arab Muslim conquests the Byzantines were still in the process of rebuilding their authority in the Levant, which had been lost to them for almost twenty years. At the time of the Arab conquest, Bilad al-Sham was inhabited mainly by local Aramaic-speaking Christians, Ghassanid and Nabatean Arabs, as well as Greeks, and by non-Christian minorities of Jews, Samaritans, and Itureans. The population of the region did not become predominantly Muslim and Arab in identity until nearly a millennium after the conquest.
In Southern Levant
The Muslim Arab army attacked Jerusalem, held by the Byzantines in November 636. For four months the siege continued. Ultimately, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem, Sophronius, agreed to surrender Jerusalem to Caliph Umar in person. Umar, then at Medina, agreed to these terms and traveled to Jerusalem to sign the capitulation in the spring of 637.Sophronius of Jerusalem
Sophronius (; ; c. 560 – March 11, 638), called Sophronius the Sophist, was the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of the city known as Aelia Capitolina and then Jerusalem from 634 until his death. He is venerated as a saint in the Eastern Orthodox and ...
also negotiated a pact with Caliph Umar, known as the Umariyya Covenant or Covenant of Omar, allowing for religious freedom for Christians in exchange for jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
, a tax to be paid to conquered non-Muslims, called "dhimmis". While the majority population of Jerusalem during the time of Arab conquest was Greek - Christian, the majority of Palestine population about 300,000-400,000 inhabitants, was still Jewish. In the aftermath the process of cultural Arabization
Arabization or Arabicization () is a sociology, sociological process of cultural change in which a non-Arab society becomes Arabs, Arab, meaning it either directly adopts or becomes strongly influenced by the Arabic, Arabic language, Arab cultu ...
and Islamization took place, combining immigration to Palestine with the adoption of Arabic language and conversion of the part of local population to Islam.
Present situation
Damascus has been home to an organized Greek community since 1913, but there are also significant numbers ofGreek Muslims
Greek Muslims, also known as Grecophone Muslims, are Muslims of Greeks, Greek ethnic origin whose adoption of Islam (and often the Turkish language and identity in more recent times) dates either from the contact of early Arabic dynasties of th ...
originally from Ottoman Crete who have been living in several coastal towns and villages of Syria and Lebanon since the late Ottoman era. They were resettled there by Sultan Abdul Hamid II
Abdulhamid II or Abdul Hamid II (; ; 21 September 184210 February 1918) was the 34th sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1876 to 1909, and the last sultan to exert effective control over the fracturing state. He oversaw a Decline and modernizati ...
following the Greco-Turkish War in 1897–98, in which the Ottoman Empire lost Crete to the Kingdom of Greece. The most notable but still understudied Cretan Muslim village in Syria is al-Hamidiyah, many of whose inhabitants continue to speak Greek as their first language. There, of course, is also a significant Greco-Syrian population in Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
as well as smaller communities in Latakia
Latakia (; ; Syrian Arabic, Syrian pronunciation: ) is the principal port city of Syria and capital city of the Latakia Governorate located on the Mediterranean coast. Historically, it has also been known as Laodicea in Syria or Laodicea ad Mar ...
, Tartus
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''Ṭarṭūs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French language, French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (af ...
and Homs
Homs ( ; ), known in pre-Islamic times as Emesa ( ; ), is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is Metres above sea level, above sea level and is located north of Damascus. Located on the Orontes River, Homs is ...
.
There are about 8,000 Greek-speaking Muslims of Cretan origin in Al-Hamidiyah, Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
.Greek-Speaking Enclaves of Lebanon and Syriaby Roula Tsokalidou. Proceedings ''II Simposio Internacional Bilingüismo''. Retrieved 18-12-08 Greek Muslims constitute a majority of Al-Hamidiyah's population. By 1988, many Greek Muslims from both
Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
had reported being subject to discrimination by the Greek embassy because of their religious affiliation. The community members would be regarded with indifference and even hostility and would be denied visas and opportunities to improve their Greek through trips to Greece.
Because of the Syrian Civil War, many Muslim Greeks sought refuge in nearby Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
and even some went to their original homeland of Crete, yet they are still considered as foreigners.
See also
* Greece–Syria relations *Antiochian Greek Christians
Antiochian Greek Christians (also known as Rūm) are an ethnoreligious Eastern Christian group native to the Levant. The majority of its members identify as Arab, and some of the members reject the Arab label, and identify as Greek. They are eit ...
* Greeks in Armenia
*Greeks in Israel
For millennia, the Greeks in Israel have been prominently present in Land of Israel, the land. Greek expatriates comprise most of the leadership of the Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, Eastern Greek Orthodox Church in Israel and the Palestini ...
* Greeks in Lebanon
*Greeks in Turkey
The Greeks in Turkey () constitute a small population of Greek and Greek-speaking Eastern Orthodox Christians who mostly live in Istanbul, as well as on the two islands of the western entrance to the Dardanelles: Imbros and Tenedos ( and ''Bo ...
References
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Greeks In Syria Antiochian Greeks Ethnic groups in SyriaSyria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
Persecution of Christians in the Ottoman Empire
Greece–Syria relations