|
Denyen
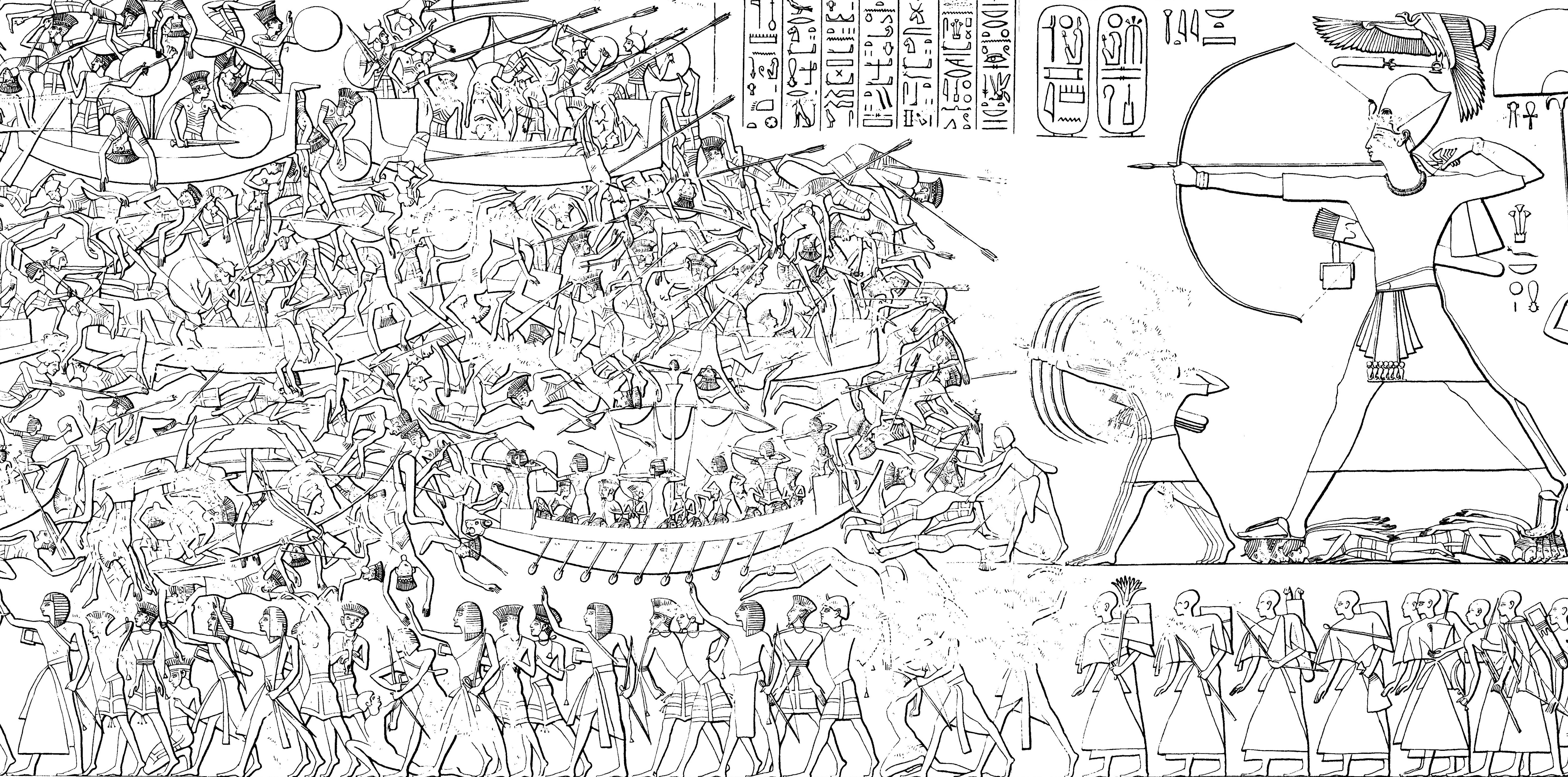
The Denyen (Egyptian: ''dꜣjnjnjw'') is purported to be one of the groups constituting the Sea Peoples. They were raiders associated with the Eastern Mediterranean Dark Ages who attacked Egypt in 1207 BC in alliance with the Libyans and other Sea Peoples, as well as during the reign of Ramesses III."A dictionary of archaeology" Ian Shaw, Robert Jameson. Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. , . p. 515 The allowed them to settle in , which was largely controlled by the Sea Peoples into the 11th century BC. Origin ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Ancient Egypt, Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was proposed by the 19th-century Egyptology, Egyptologists Emmanuel de Rougé and Gaston Maspero, on the basis of primary sources such as the reliefs on the Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III at Medinet Habu (temple), Medinet Habu. Subsequent research developed the hypothesis further, attempting to link these sources to other Late Bronze Age evidence of migration, piracy, and destruction. While initial versions of the hypothesis regarded the Sea Peoples as a primary cause of the Late Bronze Age collapse, more recent versions generally regard them as a symptom of events which were already in motion before their purported attacks. The Sea Peoples included well-attested groups such as the Lukka, as well as others such as the Weshesh whose origins are unknown. Hypotheses regarding the origin of the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denyen Medinet Habu
The Denyen (Egyptian: ''dꜣjnjnjw'') is purported to be one of the groups constituting the Sea Peoples. They were raiders associated with the Eastern Mediterranean Dark Ages who attacked Egypt in 1207 BC in alliance with the Libyans and other Sea Peoples, as well as during the reign of Ramesses III."A dictionary of archaeology" Ian Shaw, Robert Jameson. Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. , . p. 515 The allowed them to settle in , which was largely controlled by the Sea Peoples into the 11th century BC. Origin ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adana
Adana is a large city in southern Turkey. The city is situated on the Seyhan River, inland from the northeastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea. It is the administrative seat of the Adana Province, Adana province, and has a population of 1 816 750 (Seyhan, Yuregir, Cukurova, Saricam), making it the largest city in the Mediterranean Region, Turkey, Mediterranean Region of Turkey. Adana lies in the heart of Cilicia, which some say, was once one of the most important regions of the Classical antiquity, classical world. Home to six million people, Cilicia is an important agricultural area, owing to the large fertile plain of Çukurova. Adana is a centre for regional trade, healthcare, and public and private services. Agriculture and logistics are important parts of the economy. The city is connected to Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus and Mersin by TCDD Taşımacılık, TCDD train. The closest public airport is Çukurova International Airport. Etymology The name Adana (; ; ) has been used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mopsus
Mopsus (; Ancient Greek: Μόψος, ''Mopsos'') was the name of one of two famous seers in Greek mythology; his rival being Calchas. A historical or legendary ''Mopsos'' or ''Mukšuš'' may have been the founder of a house in power at widespread sites in the coastal plains of Pamphylia and Cilicia (in today's Turkey) during the early Iron Age. Mythological figures * Mopsus, son of Manto either by Rhacius or Apollo. * Mopsus, an Argonaut and son of Ampyx by a nymph. * Mopsus, a Thracian commander who had lived long before the Trojan War. Along with Sipylus the Scythian, this Mopsus had been driven into exile from Thrace by its king Lycurgus. Sometime later, he and Sipylus defeated the Libyan Amazons in a pitched battle, in which their queen Myrine was slain, and the Thracians pursued the surviving Amazons all the way to Libya. * Mopsus is also the name chosen by Virgil for the young singer who makes a song about the death of Daphnis in Eclogue 5. The name recurs in Ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. Some scholars date his reign from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC, and he is considered the last pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom to have wielded substantial power. His long reign saw the decline of Egyptian political and economic power, linked to a series of invasions and internal economic problems that also plagued pharaohs before him. This coincided with a decline in the cultural sphere of Ancient Egypt. However, his successful defense was able to slow down the decline, although it still meant that his successors would have a weaker military. He has also been described as a "warrior Pharaoh" due to his strong military strategies. He led the way by defeating the invaders known as "the Sea Peoples", who had caused destruction in other civilizations and empires. He was able to save Egypt from collapsing at the time when Late Bronze Age c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period owing to the predominance of rulers with the given name "Ramesses". This dynasty is generally considered to mark the beginning of the decline of Ancient Egypt at the transition from the Late Bronze to Iron Age. During the period of the Twentieth Dynasty, Ancient Egypt faced the crisis of invasions by Sea Peoples. The dynasty successfully defended Egypt, while sustaining heavy damage. History After the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt entered into a period of civil war. Because of lost historical records, the cause of the civil war is unknown. The war was ended with the accession to the throne by Setnakhte, who founded the 20th Dynasty of Egypt. From the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mopsuestia
Mopsuestia ( and Μόψου ''Mopsou'' and Μόψου πόλις and Μόψος; Byzantine Greek: ''Mamista'', ''Manistra'', ''Mampsista''; Arabic: ''al-Maṣṣīṣah''; Armenian: ''Msis'', ''Mises'', ''Mam(u)estia''; modern Yakapınar) is an ancient city in Cilicia Campestris on the Pyramus River (now the Ceyhan River) located approximately east of ancient Antiochia in Cilicia (present-day Adana, southern Turkey). From the city's harbor, the river is navigable to the Mediterranean Sea, a distance of over 40 km (24 mi). The 1879 book ''A Latin Dictionary'', the 1898 book '' Dictionary of Classical Antiquities'', the 1913 ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the 1920 ''La Cilicie'' mention that the city at that time was called Missis or Messis, but in 1960 the name changed to Yakapınar. History The founding of this city is attributed to the seer Mopsus, from whom the city also took its name, who lived before the Trojan War, although it is scarcely mentioned before the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of The Greeks
The Greeks () have been identified by many ethnonyms. The most common native ethnonym is ''Hellene'' (), pl. ''Greeks, Hellenes'' (); the name ''Greeks'' () was used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans and gradually entered the European languages through its use in Latin. The mythological patriarch Hellen is the named progenitor of the Greeks, Greek peoples; his descendants the Aeolians, Dorians, Achaeans (tribe), Achaeans and Ionians correspond to the main Greek tribes and to the main dialects spoken in Greece and Asia Minor, Asia Minor (Anatolia). The first Greek language, Greek-speaking people, called Mycenean Greece, Myceneans or Mycenean-Achaeans by historians, entered present-day Greece sometime in the Neolithic era or the Bronze Age. Homer refers to "Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans" as the dominant tribe during the Trojan War period usually dated to the 12th–11th centuries BC, using ''Hellenes'' to describe a relatively small tribe in Thessaly. The Dorians, an important Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in modern-day Turkey in the early 2nd millennium BC. The Hittites formed a series of Polity, polities in north-central Anatolia, including the kingdom of Kussara (before 1750 BC), the Kültepe, Kanesh or Nesha Kingdom (–1650 BC), and an empire centered on their capital, Hattusa (around 1650 BC). Known in modern times as the Hittite Empire, it reached its peak during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed most of Anatolia and parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia, bordering the rival empires of the Hurri-Mitanni and Assyrians. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Hittites were one of the dominant powers of the Near East, coming into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of islands in the Mediterranean, third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia. It is located southeast of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel and Palestine, and north of Egypt. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. Cyprus hosts the British Overseas Territories, British military bases Akrotiri and Dhekelia, whilst the northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Northern Cyprus, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which is separated from the Republic of Cyprus by the United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus, United Nations Buffer Zone. Cyprus was first settled by hunter-gatherers around 13,000 years ago, with farming communities em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Burkert
Walter Burkert (; 2 February 1931 – 11 March 2015) was a German scholar of Greek mythology and cult. A professor of classics at the University of Zurich, Switzerland, he taught in the UK and the US. He has influenced generations of students of religion since the 1960s, combining in the modern way the findings of archaeology and epigraphy with the work of poets, historians, and philosophers. He was a member of both the American Philosophical Society and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He published books on the balance between lore and science among the followers of Pythagoras, and more extensively on ritual and archaic cult survival, on the ritual killing at the heart of religion, on mystery religions, and on the reception in the Hellenic world of Near Eastern and Persian culture, which sets Greek religion in its wider Aegean and Near Eastern context. Personal life Burkert was born in Neuendettelsau. He married Maria Bosch in 1957 and they had three childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mopsucrene
Mopsucrene or Mopsoukrene () was a town in the eastern part of ancient Cilicia, on the river Cydnus, and not far from the frontier of Cataonia to which Ptolemy, in fact, assigns it. Its site was on the southern slope of Mount Taurus, and in the neighbourhood of the mountain pass leading from Cilicia into Cappadocia, north of Tarsus. The town is named after the seer Mopsus, its name means "Springs of Mopsus". It is celebrated in history as the place where the emperor Constantius II died (3 November 361). In the Antonine Itinerary, it is called Namsucrone; in the Jerusalem Itinerary, it is called Mansverine. Its site was likely the same as the settlement and ''mutatio'' called Mapsoukrenai. See also *Mopsuestia Mopsuestia ( and Μόψου ''Mopsou'' and Μόψου πόλις and Μόψος; Byzantine Greek: ''Mamista'', ''Manistra'', ''Mampsista''; Arabic: ''al-Maṣṣīṣah''; Armenian: ''Msis'', ''Mises'', ''Mam(u)estia''; modern Yakapınar) is an a ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |