|
Al-Mina
Al-Mina (Arabic: "the port") is the modern name given by Leonard Woolley to an ancient trading post on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of northern Syria (region), Syria, at the mouth of the Orontes River. It is now located in Hatay province in Turkey, in the urban area of Samandağ. Because of the changes in the coastline, it is now about 2 km away from the coast. Archaeology The site, located in the large archaeological area of the Amuq plain, was excavated in 1936 by Leonard Woolley, who considered it to be an early Colonies in antiquity, Greek trading colony, founded a little before 800 BC, in direct competition with the Phoenicians to the south. He argued that substantial amounts of Greek pottery at the site established its early Euboean connections, while the Syrian and Phoenician cooking pottery reflected a cultural mix typical of an Marketplace, emporium. Disappointed in not finding a Bronze-Age port, Woolley soon moved his interests to the earlier, more :wikt:u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orontes River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Nahr al-ʿĀṣī, or simply Asi (, ; ) is a long river in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Hatay Province, Turkey. As the chief river of the northern Levant, the Orontes has been the site of many major battles including the Battle of Kadesh (13th century BCE), and water distribution remains a controversial issue between the countries in the region. Among the most important cities on the river are Homs, Hama, Jisr al-Shughur, and Antakya (the ancient Antioch, which was also known as "Antioch on the Orontes"). Names In the 9th century BCE, the ancient Assyrian people, Assyrians referred to the river as Arantu, and the nearby Egyptians called it Araunti. The etymology of the name is unknown, yet some sources indicate that it might be derived from ''Arnt'' which means "lioness" in Syriac languages; others called it ''Alimas'', a "water goddess" in Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amuq Plain
The Amik Valley (; ) is a plain in Hatay Province, southern Turkey. It is close to the city of Antakya (Antioch on the Orontes River). Along with Dabiq in northwestern Syria, it is believed to be one of two possible sites of the battle of Armageddon according to Islamic eschatology. Archaeological significance It is notable for a series of archaeological sites in the "plain of Antioch". The primary sites of the series are Tell al-Judaidah, Chatal Höyük (Amuq) (not to be confused with Çatalhöyük in Anatolia), Tell Tayinat, Tell Kurdu, Alalakh, and Tell Dhahab. Al-Mina, at the mouth of the Orontes river, was the main ancient port of the area. Lake Amik was an ancient lake in the area, that was located in the centre of Amik Plain. Tell Judaidah was surveyed by Robert Braidwood and excavated by C. MacEwan of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago in the 1930s. There is also archaeological evidence for Caspian tigers in this valley (Ellerman and Morriso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories'', a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars, among other subjects such as the rise of the Achaemenid dynasty of Cyrus. He has been described as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero, and the " Father of Lies" by others. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus was criticized in his times for his inclusion of "legends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus (city)
Tarsus (; Hittite: 𒋫𒅈𒊭 ; ; ; ) is a municipality and district of Mersin Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,029 km2, and its population is 350,732 (2022). It is a historic city, inland from the Mediterranean Sea. It is part of the Adana-Mersin metropolitan area, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Turkey. Tarsus forms an administrative district in the eastern part of Mersin Province and lies at the heart of the region. With a history going back over 6,000 years, Tarsus has long been an important stop for traders and a focal point of many civilisations. During the Roman Empire, it was the capital of the province of Cilicia. It was the scene of the first meeting between Mark Antony and Cleopatra, and the birthplace of Paul the Apostle. Tarsus was served by Adana Şakirpaşa Airport, replaced in August 2024 by Çukurova International Airport; and is connected by Turkish State Railways to both Adana and Mersin. Etymology The ancient name Tarsos is derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of islands in the Mediterranean, third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia. It is located southeast of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel and Palestine, and north of Egypt. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. Cyprus hosts the British Overseas Territories, British military bases Akrotiri and Dhekelia, whilst the northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Northern Cyprus, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which is separated from the Republic of Cyprus by the United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus, United Nations Buffer Zone. Cyprus was first settled by hunter-gatherers around 13,000 years ago, with farming communities em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of the modern Middle East. Just beyond it lies southwestern Iran, where the region transitions into the Iranian plateau, Persian plateau, marking the shift from the Arab world to Iran. In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia also includes parts of present-day Iran (southwest), Turkey (southeast), Syria (northeast), and Kuwait. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture". It is recognised as the cradle of some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian period, Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian period, Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian Empire, Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC), and Post-imperial Assyria, post-imperial (609 BC– AD 240) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC, but there is no evidence that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur, in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kings starting with Puzur-Ashur I began rulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wolfram (2008). "URARTU IN IRAN". ''Encyclopædia Iranica''. Its kings left behind cuneiform inscriptions in the Urartian language, a member of the Hurro-Urartian languages, Hurro-Urartian language family. Urartu extended from the Euphrates in the west to the region west of Ardabil in Iran, and from Lake Çıldır near Ardahan in Turkey to the region of Rawandiz in Iraqi Kurdistan. The kingdom emerged in the mid-9th century BC and dominated the Armenian Highlands in the 8th and 7th centuries BC. Urartu frequently warred with Neo-Assyrian Empire, Assyria and became, for a time, the most powerful state in the Near East. Weakened by constant conflict, it was eventually conquered, either by the Iranian peoples, Iranian Medes in the early 6th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
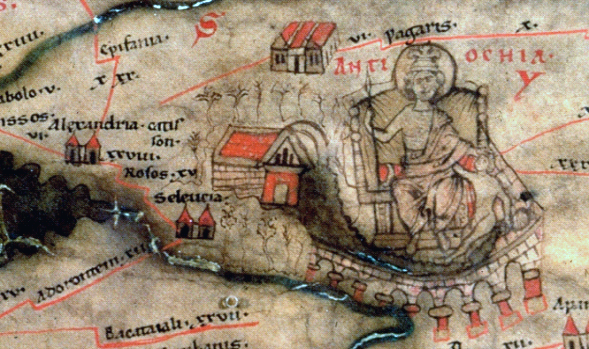
Seleucia Pieria
Seleucia in Pieria (Greek Σελεύκεια ἐν Πιερίᾳ), also known in English as Seleucia by the Sea, and later named Suedia, was a Hellenistic town, the seaport of Antioch ad Orontes ( Syria Prima), the Seleucid capital, modern Antakya (Turkey). The city was built slightly to the north of the estuary of the river Orontes, between small rivers on the western slopes of the Coryphaeus, one of the southern summits of the Amanus Mountains. According to Pausanias and Malalas, there was a previous city here named Palaeopolis ("Old City"). At present, it is located at the seaside village of Çevlik near the town of Samandağ in the Hatay Province of Turkey. Seleucia, Apamea, Laodicea, and Antioch formed the Syrian tetrapolis. History Seleucid period Seleucia Pieria was founded in ca. 300 BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of the successors of the Macedonian conqueror Alexander the Great and the founder of the Seleucid Empire. The Macedonians called the landscape Pieri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Ptolemy was ''basileus'' and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death in 282 BC, and his descendants continued to rule Egypt until 30 BC. During their rule, Egypt became a thriving bastion of Hellenistic civilization and Alexandria a great seat of Greek culture. Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |