Sven Hedin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sven Anders Hedin, KNO1kl RVO,Wennerholm, Eric (1978) ''Sven Hedin – En biografi'', Bonniers, Stockholm (19 February 1865 – 26 November 1952) was a Swedish
 In 1935, Hedin made his exclusive knowledge about Central Asia available, not only to the Swedish government, but also to foreign governments such as China and Germany, in lectures and personal discussions with political representatives of Chiang Kai-shek and
In 1935, Hedin made his exclusive knowledge about Central Asia available, not only to the Swedish government, but also to foreign governments such as China and Germany, in lectures and personal discussions with political representatives of Chiang Kai-shek and  From 1931 until his death in 1952, Hedin lived in Stockholm in a modern high-rise in a preferred location, the address being Norr Mälarstrand 66. He lived with his siblings in the upper three stories and from the balcony he had a wide view over Riddarfjärden Bay and Lake
From 1931 until his death in 1952, Hedin lived in Stockholm in a modern high-rise in a preferred location, the address being Norr Mälarstrand 66. He lived with his siblings in the upper three stories and from the balcony he had a wide view over Riddarfjärden Bay and Lake
 He describes this experience in his book ''My Life as an Explorer'' as follows:
He describes this experience in his book ''My Life as an Explorer'' as follows:
geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
, topographer
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary scienc ...
, explorer, photographer, travel writer and illustrator of his own works. During four expeditions to Central Asia, he made the Transhimalaya
The Trans himalaya (also spelled Trans-Himalaya), or "Gangdise – Nyenchen Tanglha range" ( zh, s=冈底斯-念青唐古拉山脉, p=Gāngdǐsī-Niànqīngtánggǔlā Shānmài), is a mountain range in China, India and Nepal, extending in a we ...
known in the West and located sources of the Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Southwestern China, Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, and ...
, Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
and Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
Rivers. He also mapped lake Lop Nur
Lop Nur or Lop Nor (, , from an Oirat Mongolic name meaning "Lop Lake", where "Lop" is a toponym of unknown origin) is a now largely dried-up salt lake formerly located within the ''Lop Depression'' in the eastern fringe of the Tarim Basin in ...
, and the remains of cities, grave sites and the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' long wall") is a series of fortifications in China. They were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against vario ...
in the deserts of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, Ch ...
. In his book ''Från pol till pol'' (''From Pole to Pole''), Hedin describes a journey through Asia and Europe between the late 1880s and the early 1900s. While traveling, Hedin visited Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
, Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
, Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, lands of the Kyrgyz people
The Kyrgyz people (also spelled Kyrghyz, Kirgiz, and Kirghiz; or ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia. They primarily reside in Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and China. A Kyrgyz diaspora is also found in Russia, Tajik ...
and the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. The posthumous publication of his ''Central Asia Atlas'' marked the conclusion of his life's work.
Overview
At 15 years of age, Hedin witnessed the triumphal return of the Arctic explorerAdolf Erik Nordenskiöld
Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (; 18 November 183212 August 1901) was a Finland-Swedish aristocrat, geologist, mineralogist and Arctic explorer. He was a member of the noble Nordenskiöld family of scientists and held the title of a friherre (ba ...
after his first navigation of the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (, shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route about long. The Northern Sea Route (NSR) is the shortest shipping route between the western part of Eurasia and the Asia-Pacific region.
Ad ...
. From that moment on, young Sven aspired to become an explorer. His studies under the German geographer and China expert, Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen, awakened a love of Germany in Hedin and strengthened his resolve to undertake expeditions to Central Asia to explore the last uncharted areas of Asia. After obtaining a doctorate, learning several languages and dialects, and undertaking two trips through Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, he ignored the advice of Ferdinand von Richthofen to continue his geographic studies to acquaint himself with geographical research methodology; the result was that Hedin had to leave the evaluation of his expedition results later to other scientists.
Between 1894 and 1908, in three daring expeditions through the mountains and deserts of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, he mapped and researched parts of Chinese Turkestan
Turkestan,; ; ; ; also spelled Turkistan, is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and East Turkestan (Xinjiang). The region is located in the northwest of modern day China and to the northwest of its ...
(now Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
) and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
which had been unexplored by Europeans until then. Upon his return to Stockholm in 1909 he was received as triumphantly as Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. In 1902, he became the last Swede (to date) to be raised to the untitled nobility and was considered one of Sweden's most important personalities. As a member of two scientific academies, he had a voice in the selection of Nobel Prize winners for both science and literature. Hedin never married and had no children, rendering his family line now extinct.
Hedin's expedition notes laid the foundations for a precise mapping of Central Asia. He was one of the first European scientific explorers to employ indigenous scientists and research assistants on his expeditions. Although primarily an explorer, he was also the first to unearth the ruins of ancient Buddhist cities in Chinese Central Asia. However, as his main interest in archaeology was finding ancient cities, he had little interest in gathering data thorough scientific excavations. Of small stature, with a bookish, bespectacled appearance, Hedin nevertheless proved himself a determined explorer, surviving several close brushes with death from hostile forces and the elements over his long career. His scientific documentation and popular travelogues, illustrated with his own photographs, watercolor paintings and drawings, his adventure stories for young readers and his lecture tours abroad made him world-famous.
As a renowned expert on Turkestan and Tibet, he was able to obtain unrestricted access to European and Asian monarchs and politicians as well as to their geographical societies and scholarly associations. They all sought to purchase his exclusive knowledge about the power vacuum in Central Asia with gold medals, diamond-encrusted grand crosses, honorary doctorates and splendid receptions, as well as with logistic and financial support for his expeditions. Hedin, in addition to Nikolai Przhevalsky, Sir Francis Younghusband, and Sir Aurel Stein, was an active player in the British-Russian struggle for influence in Central Asia, known as the Great Game
The Great Game was a rivalry between the 19th-century British Empire, British and Russian Empire, Russian empires over influence in Central Asia, primarily in Emirate of Afghanistan, Afghanistan, Qajar Iran, Persia, and Tibet. The two colonia ...
. Their travels were supported because they filled in the "white spaces" in contemporary maps, providing valuable information.
Hedin was honored in ceremonies in:
* 1890 by King Oscar II of Sweden
Oscar II (Oscar Fredrik; 21 January 1829 – 8 December 1907) was King of Sweden from 1872 until his death in 1907 and King of Norway from 1872 to 1905.
Oscar was the son of Oscar I of Sweden, King Oscar I and Josephine of Leuchtenberg, Queen J ...
* 1890 by Shah Nāser ad-Dīn Schah
* 1896, 1909 by Czar Nicholas II of Russia
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until Abdication of Nicholas II, hi ...
* from 1898 frequently by Kaiser Franz Joseph I
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
of Austria-Hungary
* 1902 by the Viceroy of India Lord Curzon
George Nathaniel Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston (11 January 1859 – 20 March 1925), known as Lord Curzon (), was a British statesman, Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician, explorer and writer who served as Viceroy of India ...
* 1903, 1914, 1917, 1926, 1936 by Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until Abdication of Wilhelm II, his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as th ...
* 1906 by the Viceroy of India Lord Minto
* 1907, 1926, 1933 by the 9th Panchen Lama
The Panchen Lama () is a tulku of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. The Panchen Lama is one of the most important figures in the Gelug tradition, with its spiritual authority second only to the Dalai Lama. Along with the council of high la ...
Thubten Choekyi Nyima
* 1908 by Emperor Mutsuhito
* 1910 by Pope Pius X
Pope Pius X (; born Giuseppe Melchiorre Sarto; 2 June 1835 – 20 August 1914) was head of the Catholic Church from 4 August 1903 to his death in August 1914. Pius X is known for vigorously opposing Modernism in the Catholic Church, modern ...
* 1910 by U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
* 1915 and subsequently by Hindenburg
* 1929 and 1935 by Chiang Kai-shek
* 1935, 1939, 1940 (twice) by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
.
Hedin was, and remained, a figure of the 19th century who clung to its visions and methods also in the 20th century. This prevented him from discerning the fundamental social and political upheavals of the 20th century and aligning his thinking and actions accordingly.
Concerned about the security of Scandinavia, he favored the Swedish Navy
The Swedish Navy () is the maritime service branch of the Swedish Armed Forces. It is composed of surface and submarine naval units – the Fleet (), formally sometimes referred to as the Royal Navy () – as well as marine units, the Amph ...
's construction of the battleship . In World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
he specifically allied himself in his publications with the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
and its conduct of the war. Because of this political involvement, his scientific reputation was damaged among the Allied powers, along with his memberships in their geographical societies and learned associations, as well as any support for his planned expeditions.
After a less-than-successful lecture tour in 1923 through North America and Japan, he traveled on to Beijing to carry out an expedition to Chinese Turkestan (modern Xinjiang), but the region's unstable political situation thwarted this intention. He instead traveled through Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
by car and through Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
aboard the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
.
With financial support from the governments of Sweden and Germany, he led, between 1927 and 1935, an international and interdisciplinary Sino-Swedish Expedition to carry out scientific investigations in Mongolia and Chinese Turkestan, with the participation of 37 scientists from six countries. Despite Chinese counter-demonstrations and after months of negotiations in the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, was he able to make the expedition also a Chinese one by obtaining Chinese research commissions and the participation of Chinese scientists. He also concluded a contract which guaranteed freedom of travel for this expedition which, because of its arms, 300 camels, and activities in a war theater, resembled an invading army. However, the financing remained Hedin's private responsibility.
Because of failing health, the civil war in Chinese Turkestan, and a long period of captivity, Hedin, by then 70 years of age, had a difficult time after the currency depreciation of the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
raising the money required for the expedition, the logistics for assuring the supplying of the expedition in an active war zone, and obtaining access for the expedition's participants to a research area intensely contested by local warlord
Warlords are individuals who exercise military, Economy, economic, and Politics, political control over a region, often one State collapse, without a strong central or national government, typically through informal control over Militia, local ...
s. Nevertheless, the expedition was a scientific success. The archaeological artifacts which had been sent to Sweden were scientifically assessed for three years (or four years according to Chung-Chang Shen (C.C. Shen), who was the administrative officer for the Sino-Swedish Expedition Council, and drafted the contract), after which they were returned to China under the terms of the contract.
Starting in 1937, the scientific material assembled during the expedition was published in over 50 volumes by Hedin and other expedition participants, thereby making it available for worldwide research on eastern Asia. When he ran out of money to pay printing costs, he pawned his extensive and valuable library, which filled several rooms, making possible the publication of additional volumes.
 In 1935, Hedin made his exclusive knowledge about Central Asia available, not only to the Swedish government, but also to foreign governments such as China and Germany, in lectures and personal discussions with political representatives of Chiang Kai-shek and
In 1935, Hedin made his exclusive knowledge about Central Asia available, not only to the Swedish government, but also to foreign governments such as China and Germany, in lectures and personal discussions with political representatives of Chiang Kai-shek and Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
.
Although he was not a National Socialist, Hedin's hope that Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
would protect Scandinavia from invasion by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, brought him in dangerous proximity to representatives of National Socialism, who exploited him as an author. This destroyed his reputation and put him into social and scientific isolation. However, in correspondence and personal conversations with leading Nazis, his successful intercessions achieved the pardoning of ten people condemned to death and the release or survival of Jews who had been deported to Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps (), including subcamp (SS), subcamps on its own territory and in parts of German-occupied Europe.
The first camps were established in March 1933 immediately af ...
.
At the end of the war, United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
troops deliberately confiscated documents relating to Hedin's planned ''Central Asia Atlas''. The ''U.S. Army Map Service'' later solicited Hedin's assistance and financed the printing and publication of his life's work, the ''Central Asia Atlas''. Whoever compares this atlas with '' Adolf Stielers Hand Atlas'' of 1891 can appreciate what Hedin accomplished between 1893 and 1935.
Although Hedin's research was taboo in Germany and Sweden because of his conduct relating to Nazi Germany, and stagnated for decades in Germany, the scientific documentation of his expeditions was translated into Chinese by the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS) is a Chinese state research institute and think tank. It is a ministry-level institution under the State Council of the People's Republic of China. The CASS is the highest academic institution and c ...
and incorporated into Chinese research. Following recommendations made by Hedin to the Chinese Nationalist government in 1935, the routes he selected were used to construct streets and train tracks, as well as dams and canals to irrigate new farms being established in the Tarim and Yanji basins in Xinjiang and the deposits of iron, manganese, oil, coal and gold discovered during the Sino-Swedish Expedition were opened up for mining. Among the discoveries of this expedition should also be counted the many Asian plants and animals unheard of until that date, as well as fossil remains of dinosaurs and other extinct animals. Many were named after Hedin, the species-level scientific classification
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
being ''hedini''. But one discovery remained unknown to Chinese researchers until the turn of the millennium: in the Lop Nur desert, Hedin discovered in 1933 and 1934 ruins of signal towers which prove that the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' long wall") is a series of fortifications in China. They were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against vario ...
once extended as far west as Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
.
 From 1931 until his death in 1952, Hedin lived in Stockholm in a modern high-rise in a preferred location, the address being Norr Mälarstrand 66. He lived with his siblings in the upper three stories and from the balcony he had a wide view over Riddarfjärden Bay and Lake
From 1931 until his death in 1952, Hedin lived in Stockholm in a modern high-rise in a preferred location, the address being Norr Mälarstrand 66. He lived with his siblings in the upper three stories and from the balcony he had a wide view over Riddarfjärden Bay and Lake Mälaren
Mälaren ( , , or ), historically referred to as Lake Malar in English, is the third-largest freshwater lake in Sweden (after Vänern and Vättern). Its area is and its greatest depth is 64 m (210 ft). Mälaren spans from east to west. The l ...
to the island of Långholmen. In the entryway to the stairwell is to be found a decorative stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and ...
relief map of Hedin's research area in Central Asia and a relief of the Lama temple, a copy of which he had brought to Chicago for the 1933 World's Fair.
On 29 October 1952, Hedin's will granted the rights to his books and his extensive personal effects to the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences () is one of the Swedish Royal Academies, royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special responsibility for promoting nat ...
; the Sven Hedin Foundation established soon thereafter holds all the rights of ownership.
Hedin died at Stockholm in 1952. The memorial service was attended by representatives of the Swedish royal household, the Swedish government, the Swedish Academy, and the diplomatic service. He is buried in the cemetery of Adolf Fredrik church in Stockholm.
Biography
Childhood influences
Sven Hedin was born in Stockholm, the son of Ludwig Hedin, Chief Architect of Stockholm. When he was 15 years old Hedin witnessed the triumphal return of the Swedish Arctic explorerAdolf Erik Nordenskiöld
Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (; 18 November 183212 August 1901) was a Finland-Swedish aristocrat, geologist, mineralogist and Arctic explorer. He was a member of the noble Nordenskiöld family of scientists and held the title of a friherre (ba ...
after his first navigation of the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (, shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route about long. The Northern Sea Route (NSR) is the shortest shipping route between the western part of Eurasia and the Asia-Pacific region.
Ad ...
.
 He describes this experience in his book ''My Life as an Explorer'' as follows:
He describes this experience in his book ''My Life as an Explorer'' as follows:
On 24 April 1880, the steamer Vega sailed into Stockholms ström. The entire city was illuminated. The buildings around the harbor glowed in the light of innumerable lamps and torches. Gas flames depicted the constellation of Vega on the castle. Amidst this sea of light the famous ship glided into the harbor. I was standing on the Södermalm heights with my parents and siblings, from which we had a superb view. I was gripped by great nervous tension. I will remember this day until I die, as it was decisive for my future. Thunderous jubilation resounded from quays, streets, windows and rooftops. "That is how I want to return home some day," I thought to myself.
First trip to Iran (Persia)
In May 1885, Hedin graduated from Beskowska secondary school in Stockholm. He then accepted an offer to accompany the student Erhard Sandgren as his private tutor toBaku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
, where Sandgren's father was working as an engineer in the oil fields of Robert Nobel
Robert Hjalmar Nobel ( , ; 4 August 1829 – 7 August 1896) was a Swedish businessman, industrialist and investor. He was the founder of Branobel, and a pioneer in the Russian oil industry.
Biography
Robert Nobel was born in Maria Magdalena pa ...
. Afterward he attended a course in topography for general staff officers for one month in summer 1885 and took a few weeks of instruction in portrait drawing; this comprised his entire training in those areas.
On 15 August 1885, he traveled to Baku with Erhard Sandgren and instructed him there for seven months, and he himself began to learn the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, French, German, Persian, Russian, English and Tatar languages. He later learned several Persian dialects as well as Turkish, Kyrgyz, Mongolian, Tibetan and some Chinese.
On 6 April 1886, Hedin left Baku for Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
(then called Persia), traveling by paddle steamer
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine driving paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, whereby the first uses were wh ...
over the Caspian Sea, riding through the Alborz
The Alborz ( ) range, also spelled as Alburz, Elburz or Elborz, is a mountain range in northern Iran that stretches from the border of Azerbaijan along the western and entire southern coast of the Caspian Sea and finally runs northeast and merge ...
Range to Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
, Esfahan, Shiraz
Shiraz (; ) is the List of largest cities of Iran, fifth-most-populous city of Iran and the capital of Fars province, which has been historically known as Pars (Sasanian province), Pars () and Persis. As of the 2016 national census, the popu ...
and the harbor city of Bushehr
Bushehr (; ) is a port city in the Central District (Bushehr County), Central District of Bushehr County, Bushehr province, Bushehr province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district.
Etymology
The roots of the n ...
. From there he took a ship up the Tigris River to Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
(then in Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
), returning to Tehran via Kermanshah
Kermanshah is a city in the Central District (Kermanshah County), Central District of Kermanshah province, Kermanshah province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. The city is from Tehran in the western pa ...
, and then travelling through the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
and over the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. Hedin then returned to Sweden, arriving on 18 September 1886.
In 1887, Hedin published a book about these travels entitled ''Through Persia, Mesopotamia and the Caucasus''.
Studies
From 1886 to 1888, Hedin studied under the geologist Waldemar Brøgger in Stockholm and Uppsala the subjects of geology,mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
, zoology
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the anatomy, structure, embryology, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and ...
and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. In December 1888, he became a ''Candidate in Philosophy''. From October 1889 to March 1890 he studied in Berlin under Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen.
Second trip to Iran
On 12 May 1890, he accompanied as interpreter and vice-consul a Swedish legation to Iran which was to present theShah
Shāh (; ) is a royal title meaning "king" in the Persian language.Yarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII, no. 1 (1989) Though chiefly associated with the monarchs of Iran, it was also used to refer to the leaders of numerous Per ...
of Iran with the insignia of the Order of the Seraphim
The Royal Order of the Seraphim (; ''Seraphim'' being a category of angels) is the highest order of chivalry of the Kingdom of Sweden. It was created by Frederick I of Sweden, King Frederick I on 23 February 1748, together with the Order of the ...
. As part of the Swedish legation, he was at an audience of the shah Naser al-Din Shah Qajar
Naser al-Din Shah Qajar (; ; 17 July 1831 – 1 May 1896) was the fourth Shah of Qajar Iran from 5 September 1848 to 1 May 1896 when he was assassinated. During his rule there was internal pressure from the people of Iran, as well as external ...
in Tehran. He spoke with him and later accompanied him to the Elburz Mountain Range. On 11 July 1890, he and three others climbed Mount Damavand where he collected primary material for his dissertation. Starting in September he traveled on the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
via cities Mashhad
Mashhad ( ; ), historically also known as Mashad, Meshhed, or Meshed in English, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. ...
, Ashgabat
Ashgabat (Turkmen language, Turkmen: ''Aşgabat'') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Turkmenistan. It lies between the Karakum Desert and the Kopet Dag, Kopetdag mountain range in Central Asia, approximately 50 km (30 ...
, Bukhara
Bukhara ( ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan by population, with 280,187 residents . It is the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and t ...
, Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
, Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
and Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar ...
to the western outskirts of the Taklamakan Desert. On the trip home, he visited the grave of the Russian Asian scholar, Nikolai Przhevalsky in Karakol on the shore of Lake Issyk Kul
Issyk-Kul () or Ysyk-Köl (, ; ) is an endorheic saline lake in the western Tianshan Mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan, just south of a dividing range separating Kyrgyzstan from Kazakhstan. It is the eighth-deepest lake in the world, the eleve ...
. On 29 March 1891, he was back in Stockholm. He published the books ''King Oscar's Legation to the Shah of Persia in 1890'' and ''Through Chorasan and Turkestan'' about this journey.
Doctorate and career path
On 27 April 1892, Hedin traveled to Berlin to continue his studies under Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen. Beginning of July he went toUniversity of Halle-Wittenberg
Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (), also referred to as MLU, is a public research university in the cities of Halle and Wittenberg. It is the largest and oldest university in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. MLU offers German and i ...
, Halle, attending lectures by Alfred Kirchhoff
Alfred Kirchhoff (23 May 1838 in Erfurt – 8 February 1907 in Leipzig, Mockau) was a German geographer and naturalist.
Biography
He was educated at University of Jena, Jena and University of Bonn, Bonn, and for several years was an instructo ...
. Yet in the same month, he received the degree of ''Doctor of Philosophy'' with a 28-page dissertation entitled ''Personal Observations of Damavand''. This dissertation is a summary of one part of his book, ''King Oscar's Legation to the Shah of Persia in 1890''. Eric Wennerholm remarked on the subject: I can only come to the conclusion that Sven edinreceived his doctorate when he was 27 years old after studying for a grand total of only eight months and collecting primary material for one-and-a-half days on the snow-clad peak of Mount Damavand.Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen not only encouraged Hedin to absolve cursory studies, but also to become thoroughly acquainted with all branches of geographic science and the methodologies of the salient research work, so that he could later work as an explorer. Hedin abstained from doing this with an explanation he supplied in old age:
I was not up to this challenge. I had gotten out onto the wild routes of Asia too early, I had perceived too much of the splendor and magnificence of the Orient, the silence of the deserts and the loneliness of long journeys. I could not get used to the idea of spending a long period of time back in school.Hedin had therewith decided to become an explorer. He was attracted to the idea of traveling to the last mysterious portions of Asia and filling in the gaps by mapping an area completely unknown in Europe. As an explorer, Hedin became important for the Asian and European powers, who courted him, invited him to give numerous lectures, and hoped to obtain from him in return topographic, economic and strategic information about inner Asia, which they considered part of their sphere of influence. As the era of discovery came to a close around 1920, Hedin contented himself with organizing the Sino-Swedish Expedition for qualified scientific explorers.
First expedition
Between 1893 and 1897, Hedin investigated thePamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a Mountain range, range of mountains between Central Asia and South Asia. They are located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya ...
, travelling through the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, Ch ...
in Xinjiang region, across the Taklamakan Desert
The Taklamakan Desert ( ) is a desert in northwest China's Xinjiang region. Located inside the Tarim Basin in Southern Xinjiang, it is bounded by the Kunlun Mountains to the south, the Pamir Mountains to the west, the Tian Shan range to the ...
, Lake Kara-Koshun
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
and Lake Bosten, proceeding to study northern Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
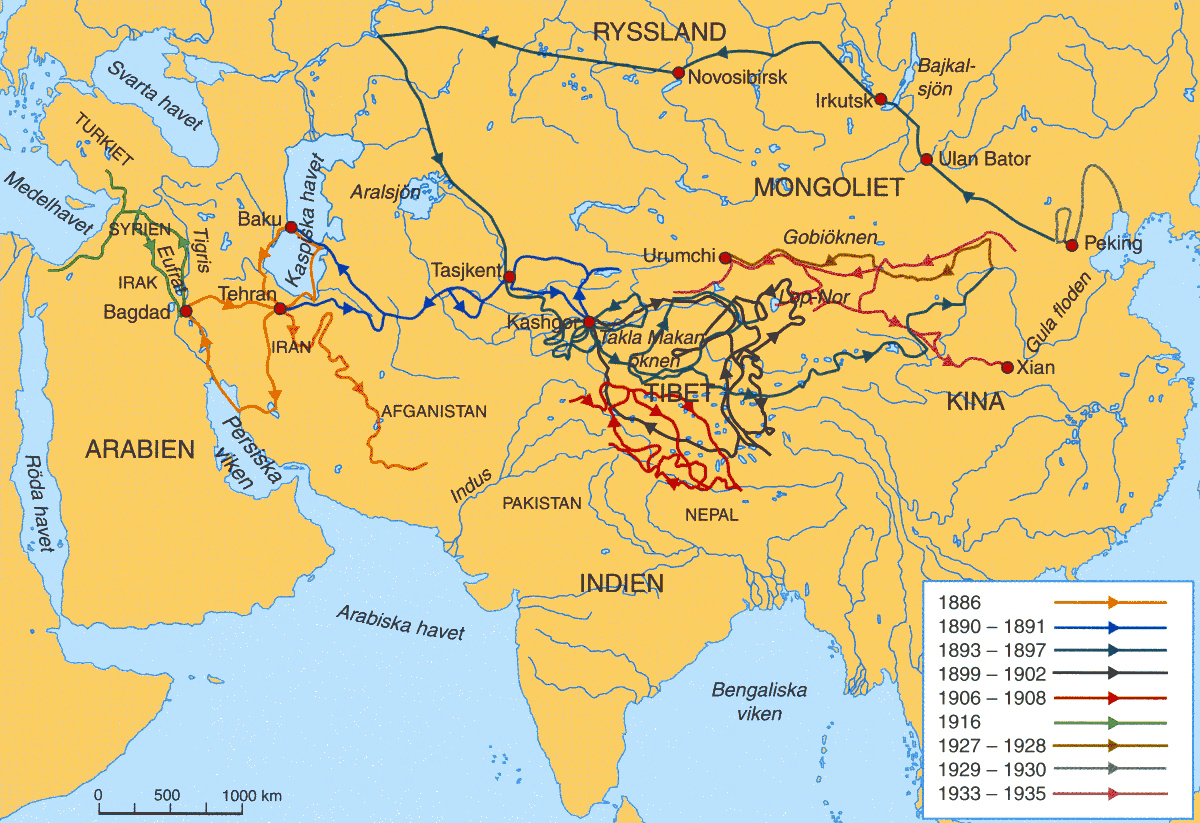
. He covered on this journey and mapped of them on 552 sheets. Approximately led through previously uncharted areas.
He started out on this expedition on 16 October 1893, from Stockholm, traveling via Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
and Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
to the Pamir Mountains. Several attempts to climb the high Muztagata—called the Father of the Glaciers—in the Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a Mountain range, range of mountains between Central Asia and South Asia. They are located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya ...
were unsuccessful. He remained in Kashgar until April 1895 and then left on 10 April with three local escorts from the village of Merket to cross the Taklamakan Desert
The Taklamakan Desert ( ) is a desert in northwest China's Xinjiang region. Located inside the Tarim Basin in Southern Xinjiang, it is bounded by the Kunlun Mountains to the south, the Pamir Mountains to the west, the Tian Shan range to the ...
via Tusluk to the Khotan River
The Hotan River (also known as the Khotan River or the Ho-t'ien River) is formed by the union of the White Jade River, White Jade (Yurungkash) and Karakash River, Karakash (Black Jade) Rivers, which flow north from the Kunlun Mountains into the ...
. Since their water supply was insufficient, seven camels died of thirst, as did two of his escorts (according to Hedin's dramatized and probably inaccurate account). Bruno Baumann traveled on this route in April 2000 with a camel caravan and ascertained that at least one of the escorts who, according to Hedin, had died of thirst had survived, and that it is impossible for a camel caravan traveling in springtime on this route to carry enough drinking water for both camels and travelers.
According to other sources, Hedin had neglected to completely fill the drinking water containers for his caravan at the beginning of the expedition and set out for the desert with only half as much water as could actually be carried. When he noticed the mistake, it was too late to return. Obsessed by his urge to carry out his research, Hedin deserted the caravan and proceeded alone on horseback with his servant. When that escort also collapsed from thirst, Hedin left him behind as well, but managed to reach a water source at the last desperate moment. He did, however, return to his servant with water and rescued him. Nevertheless, his ruthless behavior earned him massive criticism.
In January 1896, after a stopover in Kashgar, Hedin visited the 1,500-year-old abandoned cities of Dandan Oilik and Kara Dung
Kara or KARA may refer to:
Geography Localities
* Kara, Chad, a sub-prefecture
* Kára, Hungary, a village
* Kara, Uttar Pradesh, India, a township
* Kara, Iran, a village in Lorestan Province
* Kara, Republic of Dagestan, a rural locality in Dag ...
, which are located northeast of Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an ...
in the Taklamakan Desert. At the beginning of March, he discovered Lake Bosten, one of the largest inland bodies of water in Central Asia. He reported that this lake is supplied by a single mighty feeder stream, the Kaidu River. He mapped Lake Kara-Koshun and returned on 27 May to Khotan. On 29 June, he started out from there with his caravan across northern Tibet and China to Beijing, where he arrived on 2 March 1897. He returned to Stockholm via Mongolia and Russia.
Second expedition
Another expedition in Central Asia followed in 1899–1902 through the Tarim Basin, Tibet and Kashmir to Calcutta. Hedin navigated theYarkand
Yarkant County,, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also SASM/GNC ro ...
, Tarim and Kaidu rivers and found the dry riverbed of the Kum-darja as well as the dried out lake bed of Lop Nur
Lop Nur or Lop Nor (, , from an Oirat Mongolic name meaning "Lop Lake", where "Lop" is a toponym of unknown origin) is a now largely dried-up salt lake formerly located within the ''Lop Depression'' in the eastern fringe of the Tarim Basin in ...
. Near Lop Nur, he discovered the ruins of the former walled royal city and later Chinese garrison town of Loulan, containing the brick building of the Imperial Chinese Army commander, a stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
, and 19 dwellings built of poplar wood. He also found a wooden wheel from a horse-drawn cart (called an arabas) as well as several hundred documents written on wood, paper and silk in the Kharosthi
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside vari ...
script. These provided information about the history of the city of Loulan
Loulan ( zh, t=, p=Lóulán < ''lo-lɑn'' <
 The first part of the expedition, from 1927 to 1932, led from Beijing via
The first part of the expedition, from 1927 to 1932, led from Beijing via  One aspect of the geography of central Asia which intensively occupied Hedin for decades was what he called the "wandering lake"
One aspect of the geography of central Asia which intensively occupied Hedin for decades was what he called the "wandering lake"
Hedin was trying to discover the mythological place of Agartha and reproached the Polish explorer and visiting professor Antoni Ossendowski for having been gone where the Swedish explorer wasn't able to come, and thus was personally invited by
 Because of his outstanding services, Hedin was raised to the untitled nobility by King Oskar II in 1902, the last time any Swede was to receive a charter of nobility. Oskar II suggested that he prefix the name Hedin with one of the two common predicates of nobility in Sweden, "af" or "von", but Hedin abstained from doing so in his written response to the king. In many noble families in Sweden, it was customary to do without the title of nobility. The coat of arms of Hedin, together with those of some two thousand noble families, is to be found on a wall of the Great Hall in Riddarhuset, the assembly house of Swedish nobility in Stockholm's inner city,
Because of his outstanding services, Hedin was raised to the untitled nobility by King Oskar II in 1902, the last time any Swede was to receive a charter of nobility. Oskar II suggested that he prefix the name Hedin with one of the two common predicates of nobility in Sweden, "af" or "von", but Hedin abstained from doing so in his written response to the king. In many noble families in Sweden, it was customary to do without the title of nobility. The coat of arms of Hedin, together with those of some two thousand noble families, is to be found on a wall of the Great Hall in Riddarhuset, the assembly house of Swedish nobility in Stockholm's inner city,
Volume 4
* Sven Hedin: ''Trans-Himalaya: Discoveries and Adventures in Tibet, Volume 1'' 190
* Sven Hedin: ''Southern Tibet''. 11 text and 3 map volumes. Stockholm 1917–1922
VOL. VIII
* ''Reports from the scientific expedition to the north-western provinces of China under leadership of Dr. Sven Hedin. The sino-Swedish expedition''. Over 50 volumes to date, contains primary and secondary literature. Stockholm 1937 ff. * Sven Hedin: ''Central Asia atlas''. Maps, Statens etnografiska museum. Stockholm 1966. (appeared in the series ''Reports from the scientific expedition to the north-western provinces of China under the leadership of Dr. Sven Hedin. The sino-Swedish expedition''; Ausgabe 47. 1. Geography; 1) *
Central Asia and Tibet: Towards the Holy City of Lassa, Volume 1
THROUGH ASIA
* Through Asia, Volume 1
Scanned works
* ttp://idp.bl.uk/archives/news21/idpnews_21.a4d#2 article on Sven Hedin, available also a
PDF
*
British Indian intelligence on Sven Hedin. National Archives of India (1928)
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Hedin, Sven 1865 births 1952 deaths Scientists from Stockholm Explorers of Asia Explorers of Central Asia Explorers of Tibet Geopoliticians Members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences Members of the Swedish Academy Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of War Sciences Swedish explorers Swedish geographers Swedish topographers Swedish people of Jewish descent Swedish Christians Swedish sinologists Stockholm University alumni Uppsala University alumni Humboldt University of Berlin alumni Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg alumni Recipients of the Cullum Geographical Medal Honorary Knights Commander of the Order of the Indian Empire Commanders First Class of the Order of the Polar Star Knights of the Order of Vasa Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Swedish monarchists Explorers of Iran Members of the German Academy of Sciences at Berlin Victoria Medal recipients Explorers of South Asia Members of the Royal Society of Sciences in Uppsala Himalayan studies 20th-century Swedish nobility Recipients of the Cothenius Medal
Lhasa
Lhasa, officially the Chengguan District of Lhasa City, is the inner urban district of Lhasa (city), Lhasa City, Tibet Autonomous Region, Southwestern China.
Lhasa is the second most populous urban area on the Tibetan Plateau after Xining ...
, which was forbidden to Europeans. He continued to Leh
Leh () is a city in Indian-administered Ladakh in the Kashmir#Kashmir_dispute, disputed Kashmir region. The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the WP:TE ...
, in Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
district, India. From Leh, Hedin's route took him to Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, Delhi, Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
, Lucknow
Lucknow () is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the largest city of the List of state and union territory capitals in India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is the administrative headquarters of the epon ...
, Benares
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges, Ganges river in North India, northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hinduism, Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city ...
to Calcutta
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta (List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern ba ...
, meeting there with George Nathaniel Curzon, England's then Viceroy to India.
This expedition resulted in 1,149 pages of maps, on which Hedin depicted newly discovered lands. He was the first to describe yardang formations in the Lop Desert.
Third expedition
Between 1905 and 1908, Hedin investigated the Central Iranian desert basins, the western highlands ofTibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
and the Transhimalaya
The Trans himalaya (also spelled Trans-Himalaya), or "Gangdise – Nyenchen Tanglha range" ( zh, s=冈底斯-念青唐古拉山脉, p=Gāngdǐsī-Niànqīngtánggǔlā Shānmài), is a mountain range in China, India and Nepal, extending in a we ...
, which for a time was afterward called the Hedin Range. He visited the 9th Panchen Lama in the cloistered city of Tashilhunpo in Shigatse
Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê () or Rikaze ( zh, s=日喀则, p=Rìkāzé), is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its area of jurisdiction, with an area of , corresponds to the histo ...
. Hedin was the first European to reach the Kailash region, including the sacred Lake Manasarovar
Lake Manasarovar also called Mapam Yumtso (; ) locally, is a high altitude freshwater lake near Mount Kailash in Burang County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It is located at an elevation of , near the western trijunction ...
and Mount Kailash
Mount Kailash (also Kailasa; ''Kangrinboqê'' or ''Gang Rinpoche''; ; ; , ) is a mountain in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It lies in the Kailash Range (Gangdisê Mountains) of the Transhimalaya, in the western part ...
, the midpoint of the earth according to Buddhist and Hindu mythology. The most important goal of the expedition was the search for the sources of the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
and Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Southwestern China, Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, and ...
Rivers, both of which Hedin found. From India, he returned via Japan and Russia to Stockholm.
He returned from this expedition with a collection of geological samples which are kept and studied in the Bavarian State Collection of Paleontology and Geology of Munich University. These sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s—such as breccia
Breccia ( , ; ) is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or Rock (geology), rocks cementation (geology), cemented together by a fine-grained matrix (geology), matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language ...
, conglomerate, limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, and slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic ro ...
, as well as volcanic rock
Volcanic rocks (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) are rocks formed from lava erupted from a volcano. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and me ...
and granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
—highlight the geological diversity of the regions visited by Hedin during this expedition.

Mongolia
In 1923, Hedin traveled toBeijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
via the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
—where he visited the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile ().
The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon Nati ...
—and the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
. Because of political and social unrest in China, he had to abandon an expedition to Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
. Instead, he traveled with Frans August Larson (called the "Duke of Mongolia") in November and December in a Dodge
Dodge is an American brand of automobiles and a division of Stellantis, based in Auburn Hills, Michigan. Dodge vehicles have historically included performance cars, and for much of its existence, Dodge was Chrysler's mid-priced brand above P ...
automobile from Peking
Beijing, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's most populous national capital city as well as China's second largest city by urban area after Shanghai. It is l ...
through Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
via Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities in Mongolia, most populous city of Mongolia. It has a population of 1.6 million, and it is the coldest capital city in the world by average yearly temperature. The municipa ...
to Ulan-Ude
Ulan-Ude (; , ; , ) is the capital city of Buryatia, Russia, located about southeast of Lake Baikal on the Uda River, Buryatia, Uda River at its confluence with the Selenga River, Selenga. According to the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, 43 ...
, Russia and from there on the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
to Moscow.
Fourth expedition
Between 1927 and 1935, Hedin led an international Sino-Swedish Expedition which investigated themeteorological
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture ...
, topographic and prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
situation in Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (, , ; ) is a large, cold desert and grassland region in North China and southern Mongolia. It is the sixth-largest desert in the world. The name of the desert comes from the Mongolian word ''gobi'', used to refer to all of th ...
and Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
.
Hedin described it as a peripatetic university in which the participating scientists worked almost independently, while he—like a local manager—negotiated with local authorities, made decisions, organized whatever was necessary, raised funds and recorded the route followed. He gave archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
s, astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galax ...
s, botanist
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
s, geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
s, geologists, meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists ...
s and zoologist
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the structure, embryology, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. Zoology is one ...
s from Sweden, Germany and China an opportunity to participate in the expedition and carry out research in their areas of specialty.
Hedin met Chiang Kai-shek in Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
, who thereupon became a patron of the expedition. The Sino-Swedish Expedition was honored with a Chinese postage stamp series which had a print run of 25,000. The four stamps show camels at a camp with the expedition flag and bear the Chinese text, "Postal Service of the Prosperous Middle Kingdom" and in Latin underneath, "Scientific Expedition to the Northwestern Province of China 1927–1933". A painting in the Beijing Palace Museum entitled ''Nomads in the Desert'' served as model for the series. Of the 25,000 sets, 4,000 were sold across the counter and 21,500 came into the possession of the expedition. Hedin used them to finance the expedition, selling them for a price of five dollars per set. The stamps were unwelcome at the time due to the high price Hedin was selling them at, but years later became valuable treasures among collectors.
 The first part of the expedition, from 1927 to 1932, led from Beijing via
The first part of the expedition, from 1927 to 1932, led from Beijing via Baotou
Baotou; is the largest city by urban population in Inner Mongolia, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, as of the 2020 census, its built-up (''or metro'') area made up of its 5 urban districts is home to 2,261,089 people with a total po ...
to Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, over the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (, , ; ) is a large, cold desert and grassland region in North China and southern Mongolia. It is the sixth-largest desert in the world. The name of the desert comes from the Mongolian word ''gobi'', used to refer to all of th ...
, through Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
to Ürümqi
Ürümqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the ...
, and into the northern and eastern parts of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, Ch ...
. The expedition had a wealth of scientific results which are being published up to the present time. For example, the discovery of specific deposits of iron, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, oil, coal and gold reserves was of great economic relevance for China. In recognition of his achievements, the Berlin Geographical Society presented him with the ''Ferdinand von Richthofen Medal'' in 1933; the same honor was also awarded to Erich von Drygalski
Erich Dagobert von Drygalski (; February 9, 1865 – January 10, 1949) was a German geographer, geophysicist and polar scientist, born in Königsberg, East Prussia.
Between 1882 and 1887, Drygalski studied mathematics and natural science at ...
for his Gauss Expedition
The ''Gauss'' expedition of 1901–1903 (also known as the ''Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901–1903)'' was the first German expedition to Antarctica. It was led by geologist Erich von Drygalski in the ship , named after the mathematician and p ...
to the Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
; and to Alfred Philippson for his research on the Aegean Region
The Aegean region () is one of the 7 Geographical regions of Turkey, geographical regions of Turkey. The largest city in the region is İzmir. Other big cities are Manisa, Aydın, Denizli, Muğla, Afyonkarahisar and Kütahya.
Located in w ...
.
From the end of 1933 to 1934, Hedin led—on behalf of the Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT) is a major political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). It was the one party state, sole ruling party of the country Republic of China (1912-1949), during its rule from 1927 to 1949 in Mainland China until Retreat ...
government under Chiang Kai-shek in Nanjing—a Chinese expedition to investigate irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
measures and draw up plans and maps for the construction of two roads suitable for automobiles along the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
from Beijing to Xinjiang. Following his plans, major irrigation facilities were constructed, settlements erected, and roads built on the Silk Road from Beijing to Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar ...
, which made it possible to completely bypass the rough terrain of Tarim Basin.
 One aspect of the geography of central Asia which intensively occupied Hedin for decades was what he called the "wandering lake"
One aspect of the geography of central Asia which intensively occupied Hedin for decades was what he called the "wandering lake" Lop Nur
Lop Nur or Lop Nor (, , from an Oirat Mongolic name meaning "Lop Lake", where "Lop" is a toponym of unknown origin) is a now largely dried-up salt lake formerly located within the ''Lop Depression'' in the eastern fringe of the Tarim Basin in ...
. In May 1934, he began a river expedition to this lake. For two months he navigated the Kaidu River and the Kum-Darja to Lop Nur, which had been filled with water since 1921. After the lake dried out in 1971 as a consequence of irrigation activities, the above-mentioned transportation link enabled the People's Republic of China to construct a nuclear weapon test site at Lop Nur.
His caravan of truck lorries was hijacked by the Chinese Muslim General Ma Zhongying who was retreating from northern Xinjiang along with his Kuomintang 36th Division (National Revolutionary Army)
The New 36th Division was a cavalry division in the National Revolutionary Army. It was created in 1932 by the Kuomintang for General Ma Zhongying, who was also its first commander. It was made almost entirely out of Hui Muslim troops, all of ...
from the Soviet Invasion of Xinjiang. While Hedin was detained by Ma Zhongying, he met General Ma Hushan, and Kemal Kaya Effendi.
Ma Zhongying's adjutant claimed to Hedin that Ma Zhongying had the entire region of Tian-shan-nan-lu (southern Xinjiang) under his control and Sven could pass through safely without any trouble. Hedin did not believe his assertions. Some of Ma Zhongying's Tungan (Chinese speaking Muslim) troops attacked Hedin's expedition by shooting at their vehicles.
For the return trip, Hedin selected the southern Silk Road route via Hotan
Hotan (also known by other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an administrative area in its own right i ...
to Xi'an
Xi'an is the list of capitals in China, capital of the Chinese province of Shaanxi. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong plain, the city is the third-most populous city in Western China after Chongqing and Chengdu, as well as the most populou ...
, where the expedition arrived on 7 February 1935. He continued on to Beijing to meet with President Lin Sen
Lin Sen (; 16 March 1868 – 1 August 1943)), sobriquet Zhang Ren ( zh, c=長仁, w=Chang-jen, labels=no) was a Chinese politician who served as Chairman of the National Government of China, Chairman of the Nationalist government, National Gove ...
and to Nanjing to Chiang Kai-shek. He celebrated his 70th birthday on 19 February 1935 in the presence of 250 members of the Kuomintang government, to whom he reported interesting facts about the Sino-Swedish Expedition. On this day, he was awarded the Brilliant Jade Order, Second Class.
At the end of the expedition, Hedin was in a difficult financial situation. He had considerable debts at the German-Asian Bank in Beijing, which he repaid with the royalties and fees received for his books and lectures. In the months after his return, he held 111 lectures in 91 German cities as well as 19 lectures in neighboring countries. To accomplish this lecture tour, he covered a stretch as long as the equator, by train and by car—in a time period of five months. He met Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
in Berlin before his lecture on 14 April 1935.
Political views
Hedin was a monarchist. From 1905 onwards he took a stand against the move toward democracy in his Swedish homeland. He warned of the dangers he assumed to be coming from Czarist Russia, and called for an alliance with the German Empire. Therefore, he advocated a strengthened national defence, with a vigilant military preparedness.August Strindberg
Johan August Strindberg (; ; 22 January 184914 May 1912) was a Swedish playwright, novelist, poet, essayist, and painter.Lane (1998), 1040. A prolific writer who often drew directly on his personal experience, Strindberg wrote more than 60 pla ...
was one of his opponents on this issue, which divided Swedish politics at the time. In 1912 Hedin publicly supported the ''Swedish coastal defense ship Society''. He helped collect public donations for the building of the coastal defense ship , which the Liberal and anti-militarist government of Karl Staaff had been unwilling to finance. In early 1914, when the Liberal government enacted cutbacks to the country's defenses, Hedin wrote the Courtyard Speech, in which King Gustaf V promised to strengthen the country's defenses. The speech led to a political crisis that ended with Staaff and his government resigning and being replaced by a non-party, more conservative government.
He developed a lasting affinity for the German empire, with which he became acquainted during his formal studies. This is also shown in his admiration for Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as the Hohenzollern dynasty ...
, whom he even visited in exile in the Netherlands. Influenced by imperial Russian and later the Soviet union's attempts to dominate and control territories outside its borders, especially in Central Asia and Turkestan, Hedin felt that Soviet Russia posed a great threat to the West, which may be part of the reason why he supported Germany during both World Wars.
He viewed World War I as a struggle of the German race (particularly against Russia) and took sides in books like ''Ein Volk in Waffen. Den deutschen Soldaten gewidmet'' (A People in Arms. Dedicated to the German Soldier). As a consequence, he lost friends in France and England and was expelled from the British Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
, and from the Imperial Russian Geographical Society
The Russian Geographical Society (), or RGO, is a learned society based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It promotes geography, exploration and nature protection with research programs in fields including oceanography, ethnography, ecology and stati ...
. Germany's defeat in World War I and the associated loss of its international reputation affected him deeply. That Sweden gave asylum to Wolfgang Kapp as a political refugee after the failure of the Kapp Putsch is said to be primarily attributable to his efforts.
Hedin and Nazi Germany
Hedin's conservative and pro-German views eventually translated into sympathy for theThird Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
, and this would draw him into increasing controversy towards the end of his life. Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
had been an early admirer of Hedin, who was in turn impressed with Hitler's nationalism. He saw the German leader's rise to power as a revival of German fortunes, and welcomed its challenge against Soviet Communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
. He was not an entirely uncritical supporter of the Nazis, however. His own views were shaped by traditionalist, Christian and conservative values, while National Socialism was in part a modern revolutionary-populist movement. Hedin objected to some aspects of National Socialist rule, and occasionally attempted to convince the German government to relent in its anti-religious and anti-Semitic campaigns.
Hedin met Adolf Hitler and other leading Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor ...
leaders repeatedly and was in regular correspondence with them. The politely-worded correspondence usually concerned scheduling matters, birthday congratulations, Hedin's planned or completed publications, and requests by Hedin for pardons for people condemned to death, and for mercy, release and permission to leave the country for people interned in prisons or concentration camps. In correspondence with Joseph Goebbels
Paul Joseph Goebbels (; 29 October 1897 – 1 May 1945) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician and philologist who was the ''Gauleiter'' (district leader) of Berlin, chief Propaganda in Nazi Germany, propagandist for the Nazi Party, and ...
and Hans Dräger, Hedin was able to achieve the printing of the ''Daily Watchwords
The ''Daily Watchwords'' () is an annual, globally distributed publication of the Moravian Church.
It was started on 3 May 1728, and is now published in 50 languages, making it the oldest and most widely read daily devotional work in the world. ...
'' year after year. Hedin directly interviewed Hitler in October 1939, one month after the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
, where Hitler claimed that there could be peace if the United Kingdom and France recognized the German occupation of Czechoslovakia
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
.
On 29 October 1942, Hitler read Hedin's book entitled, ''America in the Battle of the Continents''. In the book Hedin promoted the view that President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
was responsible for the outbreak of war in 1939 and that Hitler had done everything in his power to prevent war. Moreover, Hedin argued that the origins of the Second World War lay not in German belligerence but in the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
. This book deeply influenced Hitler and reaffirmed his views on the origins of the war and who was responsible for it. In a letter to Hedin the following day Hitler wrote, "I thank you warmly for the attention you have shown me. I have already read the book and welcome in particular that you so explicitly detailed the offers I made to Poland at the beginning of the War". Hitler continued, "without question, the individual guilty of this war, as you correctly state at the end of your book, is exclusively the American President Roosevelt."
The Nazis attempted to achieve a close connection to Hedin by bestowing awards upon him—later scholars have noted that "honors were heaped upon this prominent sympathizer." They asked him to present an address on ''Sport as a Teacher'' at the 1936 Summer Olympics
The 1936 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XI Olympiad () and officially branded as Berlin 1936, were an international multi-sport event held from 1 to 16 August 1936 in Berlin, then capital of Nazi Germany. Berlin won the bid to ...
in Berlin's Olympic Stadium
''Olympic Stadium'' is the name usually given to the main stadium of an Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports ...
. They made him an honorary member of the ''German-Swedish Union Berlin'' () In 1938, they presented him with the City of Berlin's ''Badge of Honor'' (). For his 75th birthday on 19 February 1940 they awarded him the Order of the German Eagle; shortly before that date it had been presented to Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist and business magnate. As the founder of the Ford Motor Company, he is credited as a pioneer in making automob ...
and Charles Lindbergh
Charles Augustus Lindbergh (February 4, 1902 – August 26, 1974) was an American aviator, military officer, and author. On May 20–21, 1927, he made the first nonstop flight from New York (state), New York to Paris, a distance of . His aircra ...
. On New Year's Day 1943 they released the Oslo professor of philology and university rector Didrik Arup Seip from the Sachsenhausen concentration camp
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners t ...
at Hedin's request to obtain Hedin's agreement to accept additional honors during the 470th anniversary of Munich University. On 15 January 1943, he received the ''Gold Medal of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences'' (Goldmedaille der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften). On 16 January 1943 he received an honorary doctorate from the faculty of natural sciences of Munich University. On the same day, the Nazis founded in his absence the ''Sven Hedin Institute for Inner Asian Research'' located at Mittersill Castle, which was supposed to serve the long-term advancement of the scientific legacy of Hedin and Wilhelm Filchner as Asian experts. However, it was instead misused by Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician and military leader who was the 4th of the (Protection Squadron; SS), a leading member of the Nazi Party, and one of the most powerful p ...
as an institute of the ''Research Association for German Genealogical Inheritance'' (Forschungsgemeinschaft Deutsches Ahnenerbe e.V.). On 21 January 1943, he was requested to sign the ''Golden Book of the city of Munich''.
Hedin supported the Nazis in his journalistic activities. After the collapse of Nazi Germany, he did not regret his collaboration with the Nazis because this cooperation had made it possible to rescue numerous Nazi victims from execution, or death in extermination camps.
Senior Jewish German archeologist Werner Scheimberg, sent in the expedition by the Thule Society,. The present source is an ''historical-based'' fictional-novelist book, but he is the publisher of the '"Daurio 2018"'s reference, with a coherent content. "had been one of the companions of the Swedish explorer Sven Hedin on his excursions in the East, with archaeological and to some extent esoteric purposes". Hedin was trying to discover the mythological place of Agartha and reproached the Polish explorer and visiting professor Antoni Ossendowski for having been gone where the Swedish explorer wasn't able to come, and thus was personally invited by
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
in Berlin and honoured by the Führer during his 75th birthday feast.
Criticism of National Socialism
Johannes Paul wrote in 1954 about Hedin:Much of what happened in the early days of Nazi rule had his approval. However, he did not hesitate to criticize whenever he considered this to be necessary, particularly in cases of Jewish persecution, conflict with the churches and bars to freedom of science.In 1937 Hedin refused to publish his book ''Deutschland und der Weltfrieden'' (Germany and World Peace) in Germany because the Reich Ministry for Public Enlightenment and Propaganda insisted on the deletion of Nazi-critical passages. In a letter Hedin wrote to State Secretary Walther Funk dated 16 April 1937, it becomes clear what his criticism of National Socialism was in this time before the establishment of extermination camps:
When we first discussed my plan to write a book, I stated that I only wanted to write objectively, scientifically, possibly critically, according to my conscience, and you considered that to be completely acceptable and natural. Now I emphasized in a very friendly and mild form that the removal of distinguished Jewish professors who have performed great services for mankind is detrimental to Germany and that this has given rise to many agitators against Germany abroad. So I took this position only in the interest of Germany. My worry that the education of German youth, which I otherwise praise and admire everywhere, is deficient in questions of religion and the hereafter comes from my love and sympathy for the German nation, and as aHedin later published this book in Sweden.Christian A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...I consider it my duty to state this openly, and, to be sure, in the firm conviction that Luther’s nation, which is religious through and through, will understand me. So far I have never gone against my conscience and will not do it now either. Therefore, no deletions will be made.
Efforts on behalf of deported Jews
After he refused to remove his criticism of National Socialism from his book ''Deutschland und der Weltfrieden'', the Nazis confiscated the passports of Hedin's Jewish friend Alfred Philippson and his family in 1938 to prevent their intended departure to American exile and retain them in Germany as a bargaining chip when dealing with Hedin. The consequence was that Hedin expressed himself more favorably about Nazi Germany in his book ''Fünfzig Jahre Deutschland'', subjugated himself against his conscience to the censorship of the Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda, and published the book in Germany. On 8 June 1942, the Nazis increased the pressure on Hedin by deporting Alfred Philippson and his family to the Theresienstadt concentration camp. By doing so, they accomplished their goal of forcing Hedin against his conscience to write his book ''Amerika im Kampf der Kontinente'' in collaboration with the Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda and other government agencies and to publish it in Germany in 1942. In return, the Nazis classified Alfred Philippson as "A-prominent" and granted his family privileges which enabled them to survive. For a long time Hedin was in correspondence with Alfred Philippson and regularly sent food parcels to him in Theresienstadt concentration camp. On 29 May 1946, Alfred Philippson wrote to him (translation, abbreviated quotation):My dear Hedin! Now that letters can be sent abroad I have the opportunity to write to you…. We frequently think with deep gratitude of our rescuer, who alone is responsible for our being able to survive the horrible period of three years of incarceration and hunger in Theresienstadt concentration camp, at my age a veritable wonder. You will have learned that we few survivors were finally liberated just a few days before our intended gassing. We, my wife, daughter and I, were then brought on 9–10 July 1945 in a bus of the city of Bonn here to our home town, almost half of which is now destroyed….Hedin responded on 19 July 1946 (translation, abbreviated quotation):
…It was wonderful to find out that our efforts were not in vain. In these difficult years we attempted to rescue over one hundred other unfortunate people who had been deported to Poland, but in most cases without success. We were however able to help a few Norwegians. My home in Stockholm was turned into something like an information and assistance office, and I was excellently supported by Dr. Paul Grassmann, press attaché in the German embassy in Stockholm. He too undertook everything possible to further this humanitarian work. But almost no case was as fortunate as yours, dear friend! And how wonderful, that you are back in Bonn….The names and fates of the over one hundred deported Jews whom Hedin tried to save have not yet been researched.
Efforts on behalf of deported Norwegians
Hedin supported the cause of the Norwegian author Arnulf Øverland and for the Oslo professor of philology and university director Didrik Arup Seip, who were interned in theSachsenhausen concentration camp
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners t ...
. He achieved the release of Didrik Arup Seip, but his efforts to free Arnulf Øverland were unsuccessful. Nevertheless, Arnulf Øverland survived the concentration camp.
Efforts on behalf of Norwegian activists
After the third senate of the highest German military court (Reichskriegsgericht) in Berlin condemned to death for alleged espionage the ten Norwegians Sigurd Jakobsen, Gunnar Hellesen, Helge Børseth, Siegmund Brommeland, Peter Andree Hjelmervik, Siegmund Rasmussen, Gunnar Carlsen, Knud Gjerstad, Christian Oftedahl and Frithiof Lund on 24 February 1941, Hedin successfully appealed via Colonel General Nikolaus von Falkenhorst to Adolf Hitler for their reprieve. Their death sentences were converted on 17 June 1941 by Adolf Hitler to ten years of forced labor. The Norwegians Carl W. Mueller, Knud Naerum, Peder Fagerland, Ottar Ryan, Tor Gerrard Rydland, Hans Bernhard Risanger and Arne Sørvag who had been condemned to forced labor under the same charge received reduced sentences at Hedin's request. Unfortunately, Hans Bernhard Risanger died in prison just a few days before his release. Falkenhorst was sentenced by a joint British-Norwegian military tribunal to be executed by firing squad on 2 August 1946 due to his role in the summary execution of British prisoners of war during Operation Freshman. Hedin intervened on his behalf on 4 December 1946, arguing that Falkenhorst had likewise striven to pardon the ten Norwegians condemned to death. Falkenhorst's death sentence was commuted to 20 years in prison. He was released early from Werl Prison on 13 July 1953.Awards
 Because of his outstanding services, Hedin was raised to the untitled nobility by King Oskar II in 1902, the last time any Swede was to receive a charter of nobility. Oskar II suggested that he prefix the name Hedin with one of the two common predicates of nobility in Sweden, "af" or "von", but Hedin abstained from doing so in his written response to the king. In many noble families in Sweden, it was customary to do without the title of nobility. The coat of arms of Hedin, together with those of some two thousand noble families, is to be found on a wall of the Great Hall in Riddarhuset, the assembly house of Swedish nobility in Stockholm's inner city,
Because of his outstanding services, Hedin was raised to the untitled nobility by King Oskar II in 1902, the last time any Swede was to receive a charter of nobility. Oskar II suggested that he prefix the name Hedin with one of the two common predicates of nobility in Sweden, "af" or "von", but Hedin abstained from doing so in his written response to the king. In many noble families in Sweden, it was customary to do without the title of nobility. The coat of arms of Hedin, together with those of some two thousand noble families, is to be found on a wall of the Great Hall in Riddarhuset, the assembly house of Swedish nobility in Stockholm's inner city, Gamla Stan
Gamla Stan (, "The Old Town"), until 1980 officially Staden mellan broarna ("The Town between the Bridges"), is the old town of Stockholm, Sweden. Gamla Stan consists primarily of the island Stadsholmen. Gamla Stan includes the surrounding islets ...
.
In 1905, Hedin was admitted to membership in the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences () is one of the Swedish Royal Academies, royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special responsibility for promoting nat ...
and in 1909 to the Royal Swedish Academy of War Sciences. From 1913 to 1952 he held the sixth of 18 chairs as an elected member of the Swedish Academy
The Swedish Academy (), founded in 1786 by King Gustav III, is one of the Royal Academies of Sweden. Its 18 members, who are elected for life, comprise the highest Swedish language authority. Outside Scandinavia, it is best known as the body t ...
. In this position, he had a vote in the selection of Nobel Prize winners.
He was an honorary member of numerous Swedish and foreign scientific societies and institutions which honored him with some 40 gold medals; 27 of these medals can be viewed in Stockholm in a display case in the Royal Coin Cabinet.
He received honorary doctorates from Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
(1909), Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
(1909), Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; ; ) is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fifth-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, and with a population of about 163,000, of which roughly a quarter consists of studen ...
(1928), Uppsala
Uppsala ( ; ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the capital of Uppsala County and the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Loc ...
(1935), and Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
(1943) universities and from the Handelshochschule Berlin (1931) (all Dr. phil. h.c.), from Breslau University (1915, Dr. jur. h.c.), and from Rostock University (1919, Dr. med. h.c.).
Numerous countries presented him with medals. In Sweden he became a Commander 1st Class of the Royal Order of the North Star (KNO1kl) with a brilliant badge and Knight of the Royal Order of Vasa (RVO). In the United Kingdom he was named Knight Commander of the Order of the Indian Empire by King Edward VII. As a foreigner, he was not authorized to use the associated title of Sir, but he could place the designation KCIE after his family name Hedin. Hedin was also a Grand Cross
Grand Cross is the highest class in many orders, and manifested in its insignia. Exceptionally, the highest class may be referred to as Grand Cordon or equivalent. In other cases, there may exist a rank even higher than Grand Cross, e.g. Gran ...
of the Order of the German Eagle.
In his honor have been named a glacier, the Sven Hedin Glacier
Sven Hedin Glacier is a glacier north of Princess Marie Bay on central Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada. The glacier has the name of Sven Hedin. The Oxford University Ellesmere Land expedition visited the glacier in the year 1935. The Glacier appe ...
; a lunar crater Hedin; a genus of flowering plants, '' Hedinia''; a species of the flowering plant, ''Gentiana hedini'' (now a synonym of ''Comastoma falcatum'' ); the beetles ''Longitarsus hedini'' and ''Coleoptera hedini''; a butterfly, ''Fumea hedini Caradja''; a spider, ''Dictyna hedini''; a fossil hoofed mammal, ''Tsaidamotherium hedini''; a fossil Therapsid (a "mammal-like reptile") '' Lystrosaurus hedini''; and streets and squares in the cities of various countries (for example, "Hedinsgatan" at Tessinparken in Stockholm).
A permanent exhibition of articles found by Hedin on his expeditions is located in the Stockholm Ethnographic Museum.
In the Adolf Frederick church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
can be found the Sven Hedin memorial plaque by Liss Eriksson. The plaque was installed in 1959. On it, a globe with Asia to the fore can be seen, crowned with a camel. It bears the Swedish epitaph:
The Sven Hedin Firn in North Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
was named after him.
Research on Hedin
Source material
A survey of the extensive sources for Hedin research shows that it would be difficult at present to come to a fair assessment of the personality and achievements of Hedin. Most of the source material has not yet been subjected to scientific scrutiny. Even the DFG project ''Sven Hedin und die deutsche Geographie'' had to restrict itself to a small selection and a random examination of the source material. The sources for Hedin research are located in numerous archives (and include primary literature, correspondence, newspaper articles, obituaries and secondary literature). * Hedin's own publications amount to some 30,000 pages. * There are about 2,500 drawings and watercolors, films and many photographs. * To this should be added 25 volumes with travel and expedition notes and 145 volumes of the diaries he regularly maintained between 1930 and 1952, totaling 8,257 pages. * The extensive holdings of the Hedin Foundation (Sven Hedins Stiftelse), which holds Hedin effects in trust, are to be found in the Ethnographic Museum and in theNational Archives
National archives are the archives of a country. The concept evolved in various nations at the dawn of modernity based on the impact of nationalism upon bureaucratic processes of paperwork retention.
Conceptual development
From the Middle Ages i ...
in Stockholm.
* Hedin's correspondence is in the archive of the German Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* United ...
in Bonn, in the German Federal Archives
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952.
They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture ...
in Koblenz, at the Leibniz Institute for Regional Geography in Leipzig, and above all in the Ethnographic Museum and in the National Archives in Stockholm. Most of the correspondence in Hedin's estate is in the National Archives and accessible to researchers and the general public. It includes about 50,000 letters organized alphabetically according to country and sender as well as some 30,000 additional unsorted letters.
* The scientific effects as well as a collection of newspaper articles about Hedin organized by year (1895–1952) in 60 bound folios can be found in the Ethnographic Museum.
* The finds from Tibet, Mongolia and Xinjiang are, among other places, in Stockholm in the Ethnographic Museum (some 8,000 individual items), in the Institutes of Geology, Minearology and Paleontology of the Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation.
Initially fou ...
, in the depots of the Bavarian State Collection of Paleontology and Geology in Munich, and in the National Museum of China
The National Museum of China is an art museum, art and history museum located on the eastern side of Tiananmen Square in Beijing. The National Museum of China has a total construction area of about 200,000 square meters, a collection of more than ...
, Beijing.
Hedin's documentation
During his expeditions Hedin saw the focus of his work as being in field research. He recorded routes by plotting many thousands of kilometers of his caravan itinerary with the detail of a high resolution topographical map and supplemented them with innumerable altitude measurements and latitude and longitude data. At the same time he combined his field maps with panoramic drawings. He drafted the first precise maps of areas unresearched until that date: the Pamir mountains, the Taklamakan desert, Tibet, the Silk Road and the Himalayas. He was, as far as can be scientifically confirmed, the first European to recognize that the Himalayas were a continuous mountain range. He systematically studied the lakes of inner Asia, made careful climatological observations over many years, and started extensive collections of rocks, plants, animals and antiquities. Underway he prepared watercolor paintings, sketches, drawings and photographs, which he later published in his works. The photographs and maps with the highest quality printing are to be found in the original Swedish publications. Hedin prepared a scientific publication for each of his expeditions. The extent of documentation increased dramatically from expedition to expedition. His research report about the first expedition was published in 1900 as ''Die geographisch-wissenschaftlichen Ergebnisse meiner Reisen in Zentralasien 1894–97'' (Supplement 28 to ''Petermanns Mitteilungen''), Gotha 1900. The publication about the second expedition, ''Scientific Results of a Journey in Central Asia'', increased to six text and two atlas volumes. ''Southern Tibet'', the scientific publication on the third expedition, totalled twelve volumes, three of which were atlases. The results of the Sino-Swedish Expedition were published under the title of ''Reports from the scientific expedition to the north-western provinces of China under leadership of Dr. Sven Hedin. The sino-Swedish expedition''. This publication went through 49 editions. This documentation was splendidly produced, which made the price so high that only a few libraries and institutes were able to purchase it. The immense printing costs had to be borne for the most part by Hedin himself, as was also true for the cost of the expeditions. He used the fees and royalties which he received from his popular science books and for his lectures for the purpose. Hedin did not himself subject his documentation to scientific evaluation, but rather handed it over to other scientists for the purpose. Since he shared his experiences during his expeditions as popular science and incorporated them in a large number of lectures, travelogues, books for young people and adventure books, he became known to the general public. He soon became famous as one of the most well-recognized personalities of his time. D. Henze wrote the following about an exhibition at the Deutsches Museum entitled ''Sven Hedin, the last explorer'':He was a pioneer and pathfinder in the transitional period to a century of specialized research. No other single person illuminated and represented unknown territories more extensively than he. His maps alone are a unique creation. And the artist did not take second place to the savant, who deep in the night rapidly and apparently without effort rapidly created awe inspiring works. The discipline of geography, at least in Germany, has so far only concerned itself with his popularized reports. The consistent inclusion of the enormous, still unmined treasures in his scientific work are yet to be incorporated in the regional geography of Asia.
Current Hedin research
A scientific assessment of Hedin's character and his relationship to National Socialism was undertaken in the late 1990s and early 2000s at Bonn University by Professor Hans Böhm, Dipl.-Geogr. Astrid Mehmel and Christoph Sieker M.A. as part of the DFG Project ''Sven Hedin und die deutsche Geographie'' (''Sven Hedin and German Geography'').Literature
Primary
Scientific documentation
* Sven Hedin: ''Die geographisch-wissenschaftlichen Ergebnisse meiner Reisen in Zentralasien 1894–97''. Supplementary volume 28 to ''Petermanns Mitteilungen''. Gotha 1900. * Sven Hedin: ''Scientific results of a journey in Central-Asia''. 10 text and 2 map volumes. Stockholm 1904–1907Volume 4
* Sven Hedin: ''Trans-Himalaya: Discoveries and Adventures in Tibet, Volume 1'' 190
* Sven Hedin: ''Southern Tibet''. 11 text and 3 map volumes. Stockholm 1917–1922
VOL. VIII
* ''Reports from the scientific expedition to the north-western provinces of China under leadership of Dr. Sven Hedin. The sino-Swedish expedition''. Over 50 volumes to date, contains primary and secondary literature. Stockholm 1937 ff. * Sven Hedin: ''Central Asia atlas''. Maps, Statens etnografiska museum. Stockholm 1966. (appeared in the series ''Reports from the scientific expedition to the north-western provinces of China under the leadership of Dr. Sven Hedin. The sino-Swedish expedition''; Ausgabe 47. 1. Geography; 1) *
Central Asia and Tibet: Towards the Holy City of Lassa, Volume 1
THROUGH ASIA
* Through Asia, Volume 1
German editions
a) Biography *Verwehte Spuren. Orientfahrten des Reise-Bengt und anderer Reisenden im 17. Jahrhundert, Leipzig 1923. b) Popular works * ''Durch Asiens Wüsten. Drei Jahre auf neuen Wegen in Pamir, Lop-nor, Tibet und China'', 2 vol., Leipzig 1899; neue Ausgabe Wiesbaden 1981. * ''Im Herzen von Asien. Zehntausend Kilometer auf unbekannten Pfaden'', 2 vol., Leipzig 1903. * ''Abenteuer in Tibet'', Leipzig 1904; new edition Wiesbaden 1980. * ''Transhimalaja. Entdeckungen und Abenteuer in Tibet'', Leipzig 1909–1912; new edition Wiesbaden 1985. * ''Zu Land nach Indien durch Persien. Seistan und Bclutschistan'', 2 vol., Leipzig 1910. * ''Von Pol zu Pol'', 3 vol., Leipzig 1911–1912; new edition Wiesbaden 1980. * ''Bagdad – Babylon – Ninive'', Leipzig 1918 * ''Jerusalem'', Leipzig 1918. * ''General Prschewalskij in Innerasien'', Leipzig 1922. * ''Meine erste Reise'', Leipzig 1922. * ''An der Schwelle Innerasiens'', Leipzig 1923. * ''Mount Everest'', Leipzig 1923. * ''Persien und Mesopotamien, zwei asiatische Probleme'', Leipzig 1923. * ''Von Peking nach Moskau'', Leipzig 1924. * ''Gran Canon. Mein Besuch im amerikanischen Wunderland'', Leipzig 1926. * ''Auf großer Fahrt. Meine Expedition mit Schweden, Deutschen und Chinesen durch die Wüste Gobi 1927– 1928'', Leipzig 1929. * ''Rätsel der Gobi. Die Fortsetzung der Großen Fahrt durch Innerasien in den Jahren 1928–1930'', Leipzig 1931. * ''Jehol, die Kaiserstadt'', Leipzig 1932. * ''Die Flucht des Großen Pferdes'', Leipzig 1935. * ''Die Seidenstraße'', Leipzig 1936. * ''Der wandernde See'', Leipzig 1937. * ''Im Verbotenen Land'', Leipzig 1937 ;c) Political works * ''Ein Warnungsruf'', Leipzig 1912. * ''Ein Volk in Waffen'', Leipzig 1915. * ''Nach Osten!'', Leipzig 1916. * ''Deutschland und der Weltfriede'', Leipzig 1937 (unlike its translations, the original German edition of this title was printed but never delivered; only five copies were bound, one of which is in the possession of the F. A. Brockhaus Verlag, Wiesbaden). * ''Amerika im Kampf der Kontinente'', Leipzig 1942 ;d) Autobiographical works * ''Mein Leben als Entdecker'', Leipzig 1926. * ''Eroberungszüge in Tibet'', Leipzig 1940. * ''Ohne Auftrag in Berlin'', Buenos Aires 1949; Tübingen-Stuttgart 1950. * ''Große Männer, denen ich begegnete'', 2 volumes, Wiesbaden 1951. * ''Meine Hunde in Asien'', Wiesbaden 1953. * ''Mein Leben als Zeichner'', published by Gösta Montell in commemoration of Hedin's 100th birthday, Wiesbaden 1965. ;e) Fiction * ''Tsangpo Lamas Wallfahrt'', 2 vol., Leipzig 1921–1923. Most German publications on Hedin were translated by F.A. Brockhaus Verlag from Swedish into German. To this extent Swedish editions are the original text. Often after the first edition appeared, F.A. Brockhaus Verlag published abridged versions with the same title. Hedin had not only an important business relationship with the publisher Albert Brockhaus, but also a close friendship. Their correspondence can be found in the Riksarkivet in Stockholm. There is a publication on this subject: * Sven Hedin, Albert Brockhaus: ''Sven Hedin und Albert Brockhaus. Eine Freundschaft in Briefen zwischen Autor und Verleger''. F. A. Brockhaus, Leipzig 1942.Bibliography
* Willy Hess: ''Die Werke Sven Hedins. Versuch eines vollständigen Verzeichnisses''. ''Sven Hedin – Leben und Briefe'', Vol. I. Stockholm 1962. likewise.: First Supplement. Stockholm 1965 * Manfred Kleiner: ''Sven Anders Hedin 1865–1952 – eine Bibliografie der Sekundärliteratur''. Self-published Manfred Kleinert, Princeton 2001.Biographies
* Detlef Brennecke: ''Sven Hedin mit Selbstzeugnissen und Bilddokumenten''. Rowohlt, Reinbek bei Hamburg 1986, 1991. * Johannes Paul: ''Abenteuerliche Lebensreise – Sieben biografische Essays''. including: ''Sven Hedin. Der letzte Entdeckungsreisende''. Wilhelm Köhler Verlag, Minden 1954, pp. 317–378. * Alma Hedin: ''Mein Bruder Sven. Nach Briefen und Erinnerungen''. Brockhaus Verlag, Leipzig 1925. * Eric Wennerholm: ''Sven Hedin 1865–1952''. F. A. Brockhaus Verlag, Wiesbaden 1978. * Axel Odelberg: ''Äventyr på Riktigt Berättelsen om Upptäckaren Sven Hedin''. Norstedts, Stockholm 2008 (new biography in Swedish, 600 pages).Hedin and National Socialism
* Mehmel, Astrid: ''Sven Hedin und nationalsozialistische Expansionspolitik''. In: ''Geopolitik. Grenzgänge im Zeitgeist'' Bd. 1 .1 1890 bis 1945 ed. by Irene Diekmann, Peter Krüger und Julius H. Schoeps, Potsdam 2000, pp. 189–238. * Danielsson, S.K.: ''The Intellectual Unmasked: Sven Hedin's Political Life from Pan-Germanism to National Socialism''. Dissertation, Minnesota, 2005.See also
* List of explorations * Swedish intervention in Persia * Sino-Swedish Expedition *Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld
Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (; 18 November 183212 August 1901) was a Finland-Swedish aristocrat, geologist, mineralogist and Arctic explorer. He was a member of the noble Nordenskiöld family of scientists and held the title of a friherre (ba ...
* Vega expeditionReferences
Further reading
* * * * Tommy Lundmark (2014) ''Sven Hedin institutet. En rasbiologisk upptäcksresa i Tredje riket.'' ) (Swedish)External links
* * *Scanned works
* ttp://idp.bl.uk/archives/news21/idpnews_21.a4d#2 article on Sven Hedin, available also a
*
British Indian intelligence on Sven Hedin. National Archives of India (1928)
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Hedin, Sven 1865 births 1952 deaths Scientists from Stockholm Explorers of Asia Explorers of Central Asia Explorers of Tibet Geopoliticians Members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences Members of the Swedish Academy Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of War Sciences Swedish explorers Swedish geographers Swedish topographers Swedish people of Jewish descent Swedish Christians Swedish sinologists Stockholm University alumni Uppsala University alumni Humboldt University of Berlin alumni Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg alumni Recipients of the Cullum Geographical Medal Honorary Knights Commander of the Order of the Indian Empire Commanders First Class of the Order of the Polar Star Knights of the Order of Vasa Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Swedish monarchists Explorers of Iran Members of the German Academy of Sciences at Berlin Victoria Medal recipients Explorers of South Asia Members of the Royal Society of Sciences in Uppsala Himalayan studies 20th-century Swedish nobility Recipients of the Cothenius Medal