Stonehenge is a
prehistoric megalithic structure on
Salisbury Plain in
Wiltshire, England, west of
Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical
sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting horizontal
lintel stones, held in place with
mortise and tenon joints, a feature unique among contemporary monuments. Inside is a ring of smaller
bluestones. Inside these are free-standing
trilithons, two bulkier vertical sarsens joined by one lintel. The whole monument, now ruinous, is aligned towards the sunrise on the
summer solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest peri ...
and sunset on the
winter solstice
The winter solstice, or hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's geographical pole, poles reaches its maximum axial tilt, tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern Hemisphere, Northern and So ...
. The stones are set within
earthworks in the middle of the densest complex of
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
and
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
monuments in England, including several hundred ''
tumuli
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found through ...
'' (burial mounds).
Stonehenge was constructed in several phases beginning about 3100 BC and continuing until about 1600 BC. The famous circle of large sarsen stones were placed between 2600 BC and 2400 BC. The surrounding circular earth bank and ditch, which constitute the earliest phase of the monument, have been dated to about 3100 BC.
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
suggests that the
bluestones were given their current positions between 2400 and 2200 BC,
although they may have been at the site as early as 3000 BC.
One of the most famous landmarks in the United Kingdom, Stonehenge is regarded as a British cultural icon. It has been a legally protected
scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage, visu ...
since the
Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882
The Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882 ( 45 & 46 Vict. c. 73) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was introduced by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, recognising the need for a governmental administration on the protection ...
was passed.
The
site and its surroundings were added to
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
's list of
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
s in 1986. Stonehenge is owned by
the Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
and managed by
English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
; the
surrounding land is owned by the
National Trust.
Stonehenge could have been a burial ground from its earliest beginnings. Deposits containing human bone date from as early as 3000 BC, when the ditch and bank were first dug, and continued for at least another 500 years.
Etymology

The ''
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
'' cites
Ælfric's 10th-century glossary, in which ''henge-cliff'' is given the meaning , or stone; thus, the ''stanenges'' or ''Stanheng'' "not far from
Salisbury
Salisbury ( , ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wi ...
" recorded by 11th-century writers are "stones supported in the air". In 1740,
William Stukeley notes: "Pendulous rocks are now called henges in Yorkshire ... I doubt not, Stonehenge in Saxon signifies the hanging stones."
's ''Stonehenge Complete'' gives the derivation of the name ''Stonehenge'' as coming from the
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
words , and either (because the stone
lintels hinge on the upright stones) or or or (though elsewhere in his book, Chippindale cites the etymology).
The "henge" portion has given its name to a class of monuments known as
henge
A henge can be one of three related types of Neolithic Earthworks (archaeology), earthwork. The essential characteristic of all three is that they feature a ring-shaped bank and ditch, with the ditch inside the bank. Because the internal ditches ...
s.
Archaeologists define henges as earthworks consisting of a circular banked enclosure with an internal ditch. As often happens in archaeological terminology, this is a holdover from
antiquarian use.
Early history
 Mike Parker Pearson
Mike Parker Pearson, leader of the
Stonehenge Riverside Project based around
Durrington Walls, noted that Stonehenge appears to have been associated with burial from the earliest period of its existence:
Stonehenge evolved in several construction phases spanning at least 1500 years. There is evidence of large-scale construction on and around the monument that perhaps extends the landscape's time frame to 6500 years. Dating and understanding the various phases of activity are complicated by
disturbance of the natural
chalk by
periglacial effects and animal burrowing, poor quality early
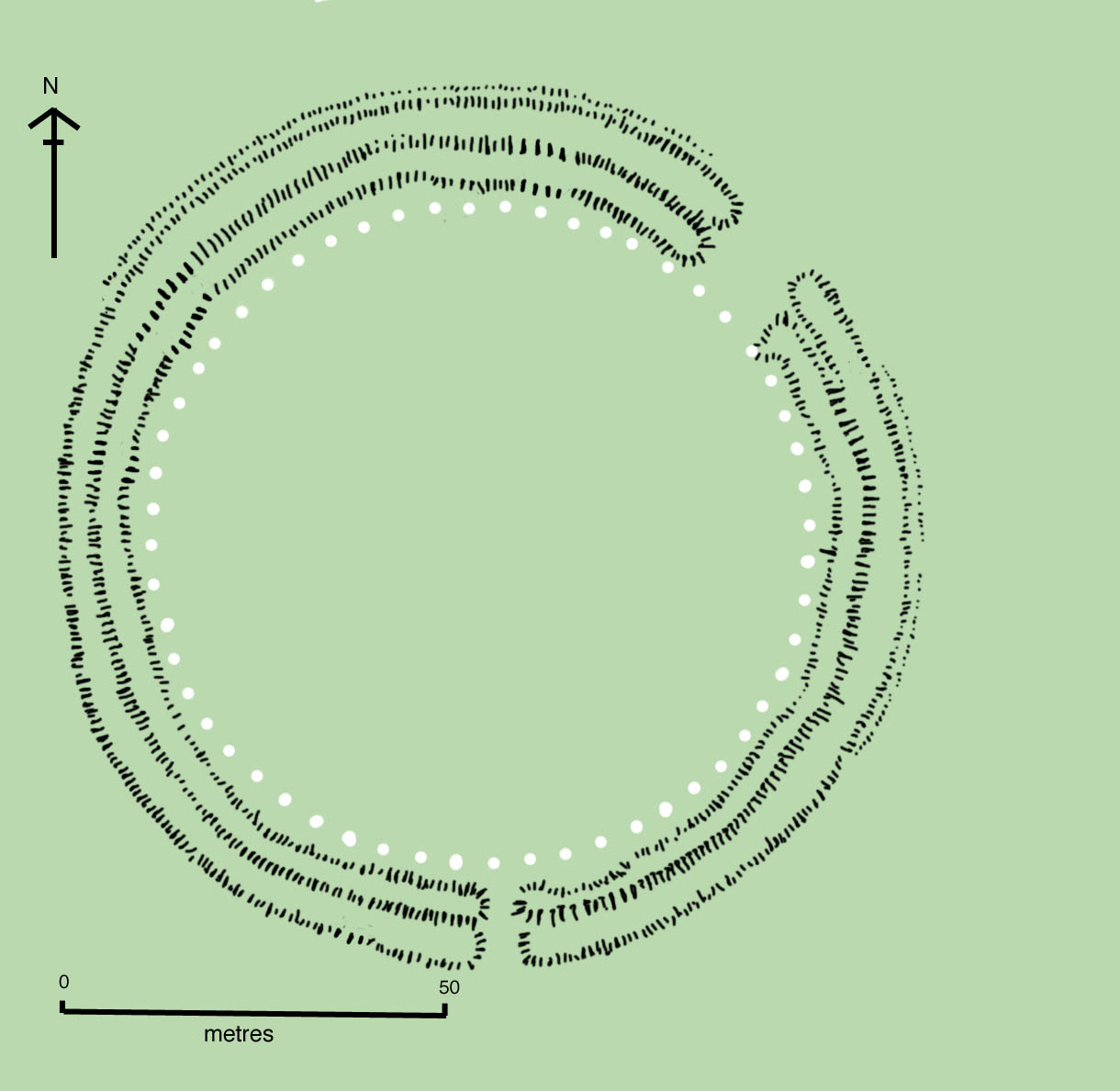
excavation records, and a lack of accurate, scientifically verified dates. The modern phasing most generally agreed to by archaeologists is detailed below. Features mentioned in the text are numbered and shown on the plan, right.
Before the monument (from 8000 BC)
Archaeologists have found four, or possibly five, large
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μÎσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
postholes (one may have been a natural
tree throw), which date to around 8000 BC, beneath the nearby old tourist car park in use until 2013. These held pine posts around in diameter, which were erected and eventually rotted in place. Three of the posts (and possibly four) were in an east–west alignment which may have had
ritual
A ritual is a repeated, structured sequence of actions or behaviors that alters the internal or external state of an individual, group, or environment, regardless of conscious understanding, emotional context, or symbolic meaning. Traditionally ...
significance. Another Mesolithic astronomical site in Britain is
Warren Field in
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire (; ) is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland#council areas of Scotland, council areas of Scotland.
It takes its name from the Shires of Scotland, historic county of Aberdeenshire (historic), Aberdeenshire, which had substantial ...
, which is considered the world's oldest
lunisolar calendar, corrected yearly by observing the
midwinter solstice. Similar but later sites have been found in
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
. A settlement that may have been contemporaneous with the posts has been found at
Blick Mead, a reliable year-round spring from Stonehenge.
was then still wooded, but, 4,000 years later, during the earlier Neolithic, people built a
causewayed enclosure at
Robin Hood's Ball, and
long barrow tombs in the surrounding landscape. In approximately 3500 BC, a
Stonehenge Cursus was built north of the site as the first farmers began to clear the trees and develop the area. Other previously overlooked stone or wooden structures and burial mounds may date as far back as 4000 BC.
Charcoal from the 'Blick Mead' camp from Stonehenge (near the
Vespasian's Camp site) has been dated to 4000 BC.
The
University of Buckingham's Humanities Research Institute believes that the community who built Stonehenge lived here for several millennia, making it potentially "one of the pivotal places in the history of the Stonehenge landscape."
Stonehenge 1 (c. 3100 BC)
The first monument consisted of a circular bank and ditch
enclosure
Enclosure or inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or "common land", enclosing it, and by doing so depriving commoners of their traditional rights of access and usage. Agreements to enc ...
made of
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
(
Santonian
The Santonian is an age in the geologic timescale or a chronostratigraphic stage. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 86.3 ± 0.7 mya ( million years ago) and 83.6 ± 0.7 m ...
Age) Seaford
chalk, measuring about in diameter, with a large entrance to the north east and a smaller one to the south. It stood in open
grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
on a slightly sloping spot.
The builders placed the bones of
deer and
oxen in the bottom of the ditch, as well as some worked
flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
tools. The bones were considerably older than the antler picks used to dig the ditch, and the people who buried them had looked after them for some time prior to burial. The ditch was continuous but had been dug in sections, like the ditches of the earlier causewayed enclosures in the area. The chalk dug from the ditch was piled up to form the bank. This first stage is dated to around 3100 BC, after which the ditch began to silt up naturally. Within the outer edge of the enclosed area is a circle of 56 pits, each about in diameter, known as the
Aubrey holes after
John Aubrey, the 17th-century
antiquarian who was thought to have first identified them. These pits and the bank and ditch together are known as the Palisade or Gate Ditch. The pits may have contained standing timbers creating a
timber circle, although there is no excavated evidence of them. A recent excavation has suggested that the Aubrey Holes may have originally been used to erect a
bluestone circle. If this were the case, it would advance the earliest known stone structure at the monument by some 500 years.
In 2013, a team of archaeologists, led by
Mike Parker Pearson, excavated more than 50,000 cremated bone fragments, from 63 individuals, buried at Stonehenge.
These remains were originally buried individually in the Aubrey holes, but were exhumed in 1920 during an excavation by
William Hawley, who considered them unimportant and in 1935 re-buried them together in one hole, Aubrey Hole 7.
Physical and chemical analysis of the remains has shown that the cremated were almost equally men and women, and included some children.
There is evidence that the underlying chalk beneath the graves was crushed by substantial weight, so the team concluded that the first bluestones brought from Wales were probably used as grave markers.
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
of the remains has put the date of the site 500 years earlier than previously estimated, to around 3000 BC.
A 2018 study of the
strontium content of the bones found that many of the individuals buried there around the time of construction had probably come from near the source of the bluestone in Wales and had not extensively lived in the area of Stonehenge before death.
Between 2017 and 2021, studies by Professor Parker Pearson (UCL) and his team
suggested that the
bluestones used in Stonehenge had been moved there following dismantling of a stone circle of identical size to the first known Stonehenge circle (110m) at the Welsh site of
Waun Mawn in the
Preseli Hills.
[ It had contained bluestones, one of which showed evidence of having been reused in Stonehenge. The stone was identified by its unusual pentagonal shape and by luminescence soil dating from the filled-in sockets which showed the circle had been erected around 3400–3200 BC, and dismantled around 300–400 years later, consistent with the dates attributed to the creation of Stonehenge.][ The cessation of human activity in that area at the same time suggested migration as a reason, but it is believed that other stones may have come from other sources.][
]
Stonehenge 2 (c. 2900 BC)
The second phase of construction occurred approximately between 2900 and 2600 BC.cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse through Combustion, burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India, Nepal, and ...
burials dating to the two centuries after the monument's inception. It seems that whatever the holes' initial function, it changed to become a funerary one during Phase two. Thirty further cremations were placed in the enclosure's ditch and at other points within the monument, mostly in the eastern half. Stonehenge is therefore interpreted as functioning as an enclosed cremation cemetery at this time,
Stonehenge 3 I (c. 2600 BC)
 Archaeological excavation has indicated that around 2600 BC, the builders abandoned timber in favour of stone and dug two concentric arrays of holes (the Q and R Holes) in the centre of the site. These stone sockets are only partly known (hence on present evidence are sometimes described as forming 'crescents'); however, they could be the remains of a double ring. Again, there is little firm dating evidence for this phase. The holes held up to 80 standing stones (shown blue on the plan), only 43 of which can be traced today. It is generally accepted that the bluestones (some of which are made of dolerite, an igneous rock), were transported by the builders from the Preseli Hills, away in modern-day
Archaeological excavation has indicated that around 2600 BC, the builders abandoned timber in favour of stone and dug two concentric arrays of holes (the Q and R Holes) in the centre of the site. These stone sockets are only partly known (hence on present evidence are sometimes described as forming 'crescents'); however, they could be the remains of a double ring. Again, there is little firm dating evidence for this phase. The holes held up to 80 standing stones (shown blue on the plan), only 43 of which can be traced today. It is generally accepted that the bluestones (some of which are made of dolerite, an igneous rock), were transported by the builders from the Preseli Hills, away in modern-day Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire ( ; ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county in the South West Wales, south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and otherwise by the sea. Haverfordwest is the largest town and ...
in Wales. Another theory is that they were brought much nearer to the site as glacial erratics by the Irish Sea Glacier although there is no evidence of glacial deposition within southern central England.
Stonehenge 3 II (2600 BC to 2400 BC)

 During the next major phase of activity, 30 enormous
During the next major phase of activity, 30 enormous Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
–Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
sarsen stones (shown grey on the plan) were brought to the site. They came from a quarry around north of Stonehenge, in West Woods, Wiltshire.[Pearson ''et al.'' 2013] Each standing stone was around high, wide, and deep, weighing around 26 tons. Each had clearly been worked with the final visual effect in mind: The orthostats widen slightly towards the top in order that their perspective remains constant when viewed from the ground, while the lintel stones curve slightly to continue the circular appearance of the earlier monument.[Fernie 1994]
The inward-facing surfaces of the stones are smoother and more finely worked than the outer surfaces. The average thickness of the stones is and the average distance between them is . A total of 75 stones would have been needed to complete the circle (60 stones) and the trilithon horseshoe (15 stones). It was thought the ring might have been left incomplete, but an exceptionally dry summer in 2013 revealed patches of parched grass which may correspond to the location of missing sarsens. The lintel stones are each around long, wide and thick. The tops of the lintels are above the ground.
Within this circle stood five trilithons of dressed sarsen stone arranged in a horseshoe shape across, with its open end facing northeast. These huge stones, ten uprights and five lintels, weigh up to 50 tons each. They were linked using complex jointing. They are arranged symmetrically. The smallest pair of trilithons were around tall, the next pair a little higher, and the largest, single trilithon in the south-west corner would have been tall. Only one upright from the Great Trilithon still stands, of which is visible and a further is below ground. The images of a 'dagger' and 14 'axeheads' have been carved on one of the sarsens, known as stone 53; further carvings of axeheads have been seen on the outer faces of stones 3, 4, and 5. The carvings are difficult to date but are morphologically similar to late Bronze Age weapons. Early 21st century laser scanning of the carvings supports this interpretation. The pair of trilithons in the north east are smallest, measuring around in height; the largest, which is in the south-west of the horseshoe, is almost tall.
This ambitious phase has been radiocarbon dated to between 2600 and 2400 BC, slightly earlier than the Stonehenge Archer, discovered in the outer ditch of the monument in 1978, and the two sets of burials, known as the Amesbury Archer and the Boscombe Bowmen, discovered to the west. Analysis of animal teeth found away at Durrington Walls, thought by Parker Pearson to be the 'builders camp', suggests that, during some period between 2600 and 2400 BC, as many as 4,000 people gathered at the site for the mid-winter and mid-summer festivals; the evidence showed that the animals had been slaughtered around nine months or 15 months after their spring birth. Strontium isotope analysis of the animal teeth showed that some had been brought from as far afield as the Scottish Highlands for the celebrations.summer solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest peri ...
and led from the river to the timber circle. Evidence of huge fires on the banks of the Avon between the two avenues also suggests that both circles were linked. They were perhaps used as a procession route on the longest and shortest days of the year. Parker Pearson speculates that the wooden circle at Durrington Walls was the centre of a 'land of the living', whilst the stone circle represented a 'land of the dead', with the Avon serving as a journey between the two.
Stonehenge 3 III (2400 BC to 2280 BC)
Later in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, although the exact details of activities during this period are still unclear, the bluestones appear to have been re-erected. They were placed within the outer sarsen circle and may have been trimmed in some way. Like the sarsens, a few have timber-working style cuts in them suggesting that, during this phase, they may have been linked with lintels and were part of a larger structure.
Stonehenge 3 IV (2280 BC to 1930 BC)
This phase saw further rearrangement of the bluestones. They were arranged in a circle between the two rings of sarsens and in an oval at the centre of the inner ring. Some archaeologists argue that some of these bluestones were from a second group brought from Wales. All the stones formed well-spaced uprights without any of the linking lintels inferred in Stonehenge 3 III. The Altar Stone may have been moved within the oval at this time and re-erected vertically. Although this would seem the most impressive phase of work, Stonehenge 3 IV was rather shabbily built compared to its immediate predecessors, as the newly re-installed bluestones were not well-founded and began to fall over. However, only minor changes were made after this phase.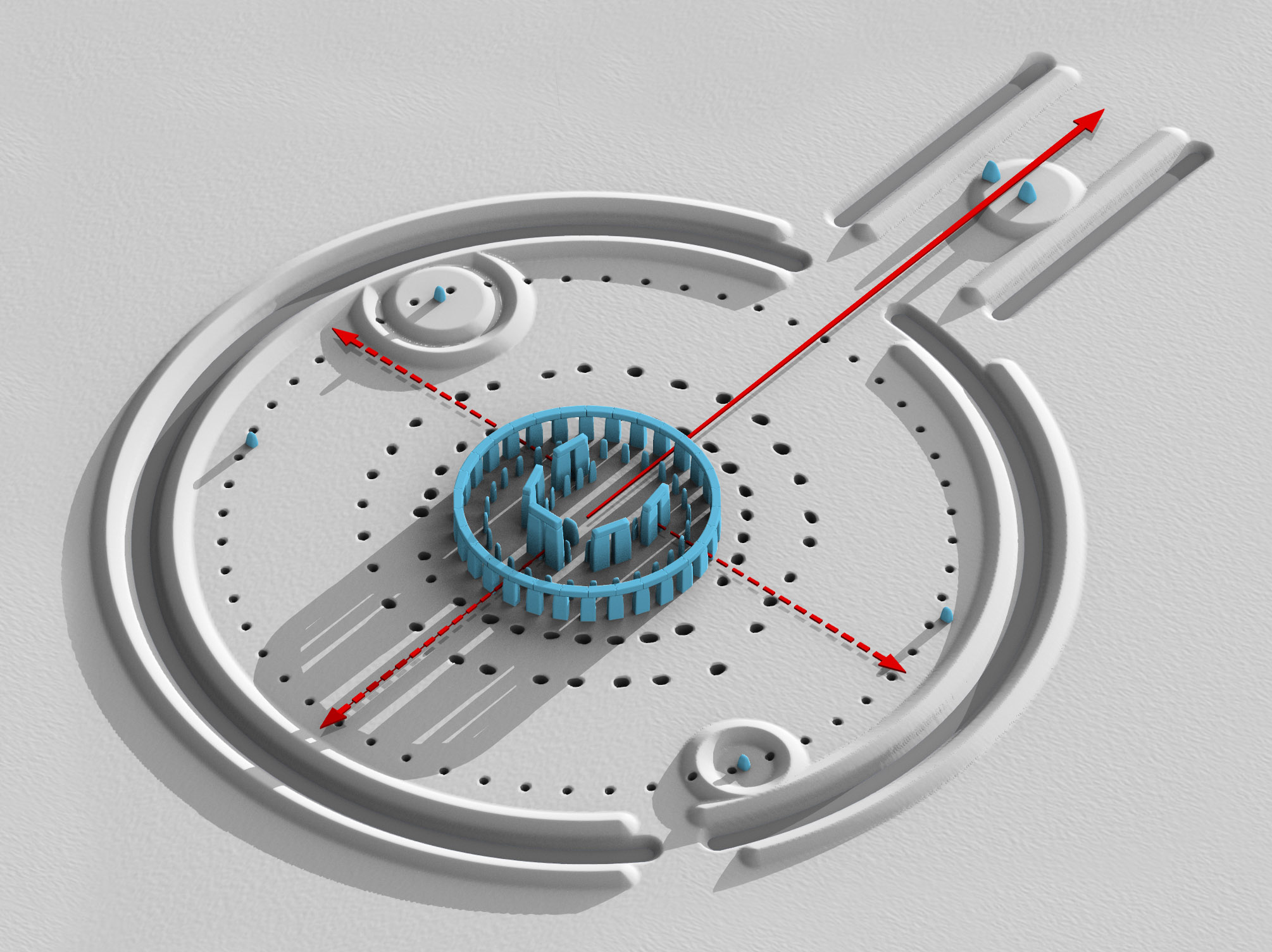
Stonehenge 3 V (1930 BC to 1600 BC)
Soon afterwards, the northeastern section of the Phase 3 IV bluestone circle was removed, creating a horseshoe-shaped setting (the Bluestone Horseshoe) which mirrored the shape of the central sarsen Trilithons. This phase is contemporary with the Seahenge site in Norfolk.
After the monument (1600 BC on)
The Y and Z Holes are the last known construction at Stonehenge, built about 1600 BC, and the last usage of it was probably during the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
. Roman coins and medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
artefacts have all been found in or around the monument but it is unknown whether the monument was in continuous use throughout British prehistory and beyond, or exactly how it would have been used. Notable is the massive Iron Age hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. So ...
known as Vespasian's Camp (despite its name, not a Roman site) built alongside the Avenue near the Avon. A decapitated seventh-century Saxon man was excavated from Stonehenge in 1923. The site was known to scholars during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and since then it has been studied and adopted by numerous groups.
Function and construction
Stonehenge was produced by a culture that left no written records. Many aspects of Stonehenge, such as how it was built and for what purposes it was used, remain subject to debate. A number of myths surround the stones.[ More recently, two major new theories have been proposed. Geoffrey Wainwright, president of the ]Society of Antiquaries of London
The Society of Antiquaries of London (SAL) is a learned society of historians and archaeologists in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1707, received its royal charter in 1751 and is a Charitable organization, registered charity. It is based ...
, and Timothy Darvill, of Bournemouth University, have suggested that Stonehenge was a place of healing—the primeval equivalent of Lourdes. They argue that this accounts for the high number of burials in the area and for the evidence of trauma deformity in some of the graves. However, they do concede that the site was probably multifunctional and used for ancestor worship as well. Isotope analysis indicates that some of the buried individuals were from other regions. A teenage boy buried approximately 1550 BC was raised near the Mediterranean Sea; a metal worker from 2300 BC dubbed the " Amesbury Archer" grew up near the Alpine foothills of Germany; and the " Boscombe Bowmen" probably arrived from Wales or Brittany, France.[ Both explanations were first mooted in the twelfth century by Geoffrey of Monmouth, who extolled the curative properties of the stones and was also the first to advance the idea that Stonehenge was constructed as a funerary monument.
There are other hypotheses and theories. According to a team of British researchers led by Mike Parker Pearson of the University of Sheffield, Stonehenge may have been built as a symbol of "peace and unity", indicated in part by the fact that at the time of its construction, Britain's Neolithic people were experiencing a period of cultural unification.]
Stonehenge-builders and DNA studies
There is evidence to suggest that despite the introduction of farming in the British Isles, the practice of cereal cultivation fell out of favor between 3300 and 1500 BC, with much of the population reverting to a pastoralist subsistence pattern
A subsistence pattern – alternatively known as a subsistence strategy – is the means by which a society satisfies its basic needs for survival. This encompasses the attainment of nutrition, water, and shelter. The five broad categories of sub ...
focused on hazelnut gathering and pig and cattle rearing. A majority of the major phases of Stonehenge's construction took place during such a period where evidence of large-scale agriculture is equivocal. Similar associations between non-cereal farming subsistence patterns and monumental construction are also seen at Poverty Point and Sannai Maruyama.
Stonehenge I and II
Researchers studying DNA extracted from Neolithic human remains across Britain determined that the people who built Stonehenge I and II were closely related to Iberian and Central European Early and Middle Neolithic populations, modelled as having about 75% ancestry from Early European Farmers who came from the Eastern Mediterranean, travelling west from there, and 25% ancestry coming from Western Hunter-Gatherers from western Europe. These farmers moved to Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
before heading north, reaching Britain in about 4,000 BC. Most of the ancestry of British Neolithic farmers came from the people who followed this route, with a minor contribution from groups who followed the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
into Central and Western Europe.[Paul Rincon]
Stonehenge: DNA reveals origin of builders.
BBC News website, 16 April 2019 Their agricultural techniques seem to have come originally from Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
,
Stonehenge III (megalithic structure)
At the time the megalithic Stonehenge 3 II was constructed (2600–2400 BC) by Neolithic people, the Bell Beaker people arrived, around 2,500 BC, migrating from mainland Europe.[National History Museum (2021)]
''Burials near Stonehenge reveal how cultures merged in the Bronze Age''
/ref> They lived side by side for ca. 500 years, with the Bell Beaker people probably incorporating the henge-structures into their belief-system.Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
whose ancestors migrated from the Pontic–Caspian steppe,
Modern history
Archaeological research and restoration
1600–1900
Throughout recorded history, Stonehenge and its surrounding monuments have attracted attention from antiquarians and archaeologists. John Aubrey was one of the first to examine the site with a scientific eye in 1666, and, in his plan of the monument, he recorded the pits that now bear his name, the Aubrey holes. William Stukeley continued Aubrey's work in the early eighteenth century, but took an interest in the surrounding monuments as well, identifying (somewhat incorrectly) the Cursus and the Avenue. He also began the excavation of many of the barrows in the area, and it was his interpretation of the landscape that associated it with the Druids. Stukeley was so fascinated with Druids that he originally named Disc Barrows as Druids' Barrows.
The most accurate early plan of Stonehenge was that made by Bath architect John Wood in 1740. His original annotated survey has now been computer-redrawn and published.Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
dabbled in archaeology at the stones, experimenting with the rate at which remains sink into the earth, for his book '' The Formation of Vegetable Mould Through the Action of Worms''.
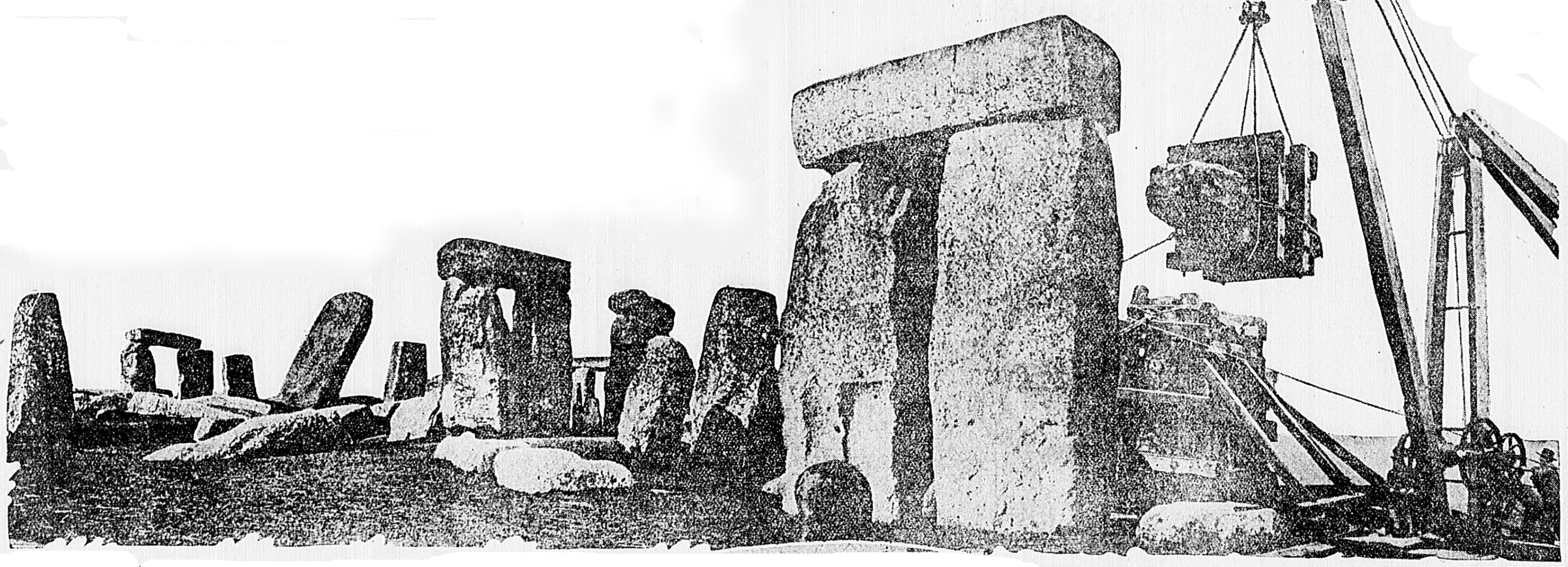
Stone 22 fell during a fierce storm on 31 December 1900.

1901–2000
William Gowland oversaw the first major restoration of the monument in 1901, which involved the straightening and concrete setting of sarsen stone number 56 which was in danger of falling. In straightening the stone he moved it about half a metre from its original position.port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
in the Slaughter Stone socket left by Cunnington, helped to rediscover Aubrey's pits inside the bank and located the concentric circular holes outside the Sarsen Circle called the Y and Z Holes.University of the West of England
The University of the West of England (also known as UWE Bristol) is a Public university, public research university, located in and around Bristol, England, UK. With more than 39,912 students and 4,300 staff, it is the largest provider of hi ...
, campaigned to give the public more knowledge of the various restorations and, in 2004, English Heritage included pictures of the work in progress in its book ''Stonehenge: A History in Photographs''.
21st century
More recent excavations include a series of digs held between 2003 and 2008 known as the Stonehenge Riverside Project, led by Mike Parker Pearson. This project mainly investigated other monuments in the landscape and their relationship to the stones—notably, Durrington Walls, where another "Avenue" leading to the River Avon was discovered. The point where the Stonehenge Avenue meets the river was also excavated and revealed a previously unknown circular area which probably housed four further stones, most likely as a marker for the starting point of the avenue.
In April 2008, Tim Darvill of the University of Bournemouth and Geoff Wainwright of the Society of Antiquaries began another dig inside the stone circle to retrieve datable fragments of the original bluestone pillars. They were able to date the erection of some bluestones to 2300 BC,[''Discoveries Provide Evidence of a Celestial Procession at Stonehenge'']
, ''University of Birmingham Press Release'', 26 November 2011 The new discovery was made as part of the Stonehenge Hidden Landscape Project which began in the summer of 2010. The project uses non-invasive geophysical imaging technique to reveal and visually recreate the landscape. According to team leader Vince Gaffney, this discovery may provide a direct link between the rituals and astronomical events to activities within the Cursus at Stonehenge.[
In December 2011, geologists from University of Leicester and the National Museum of Wales announced the discovery of the source of some of the ]rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
fragments found in the Stonehenge debitage
In archaeology, debitage is all the material produced during the process of lithic reduction – the production of stone tools and weapons by knapping stone. This Assemblage (archaeology), assemblage may include the different kinds of lithic fla ...
. These fragments do not seem to match any of the standing stones or bluestone stumps. The researchers have identified the source as a long rock outcrop called Craig Rhos-y-felin (), near Pont Saeson in north Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire ( ; ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county in the South West Wales, south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and otherwise by the sea. Haverfordwest is the largest town and ...
, located from Stonehenge.
In 2014, the University of Birmingham
The University of Birmingham (informally Birmingham University) is a Public university, public research university in Birmingham, England. It received its royal charter in 1900 as a successor to Queen's College, Birmingham (founded in 1825 as ...
announced findings including evidence of adjacent stone and wooden structures and burial mounds near Durrington, overlooked previously, that may date as far back as 4000 BC.
Origin of sarsens, bluestones and other modern developments
 In July 2020, a study led by David Nash of the University of Brighton concluded that the large sarsen stones were "a direct chemical match" to those found at West Woods near Marlborough, Wiltshire, some 15 miles (25 km) north of Stonehenge.
In July 2020, a study led by David Nash of the University of Brighton concluded that the large sarsen stones were "a direct chemical match" to those found at West Woods near Marlborough, Wiltshire, some 15 miles (25 km) north of Stonehenge.[
][
]
The circle at Waun Mawn also contained a hole from one stone which had a distinctive pentagonal shape, very closely matching the one pentagonal stone at Stonehenge (stonehole 91 at Waun Mawn / stone 62 at Stonehenge).[
]
In February 2021, archaeologists announced the discovery of "vast troves of Neolithic and Bronze Age artifacts"field survey
Field research, field studies, or fieldwork is the collection of raw data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting. The approaches and methods used in field research vary across disciplines. For example, biologists who conduct f ...
around Stonehenge. Based on the shape of the pits and the artifacts found inside, the study's lead author, Philippe De Smedt, assumed that six of the 9 large pits excavated were made by prehistoric humans. One of the oldest was about 10000 years old and contained hunting tools.
In August 2024, the journal Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
published research from a team at Curtin University in Australia identifying the origin of the Altar Stone, which is partially buried by a collapsed sarsen stone, as having come from the Orcadian Basin in northeast Scotland, some 700 km away.[
]
Folklore
"Heel Stone", "Friar's Heel", or "Sun-Stone"
The Heel Stone lies northeast of the sarsen circle, beside the end portion of Stonehenge Avenue.Summer solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest peri ...
an observer standing within the stone circle, looking northeast through the entrance, would see the Sun rise in the approximate direction of the Heel Stone, and the Sun has often been photographed over it.
A folk tale relates the origin of the Friar's Heel reference.
'' Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable'' attributes this tale to Geoffrey of Monmouth. Though book eight of Geoffrey's ''Historia Regum Britanniae
(''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a fictitious account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. It chronicles the lives of the List of legendary kings o ...
'' describes how Stonehenge was built, the two stories are entirely different.
The name is not unique; there was a monolith with the same name recorded in the nineteenth century by antiquarian Charles Warne at Long Bredy in Dorset.
Arthurian legend
 The twelfth-century ''
The twelfth-century ''Historia Regum Britanniae
(''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a fictitious account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. It chronicles the lives of the List of legendary kings o ...
'' ("History of the Kings of Britain"), by Geoffrey of Monmouth, includes a legend of Stonehenge's origin, describing how Stonehenge was brought from Ireland with the help of the wizard Merlin. Geoffrey's story spread widely, with variations of it appearing in adaptations of his work, such as Wace's Norman French '' Roman de Brut'', Layamon's Middle English '' Brut'', and the Welsh '' Brut y Brenhinedd''.
According to the tale, the stones of Stonehenge were healing stones, which giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''wiktionary:gigas, gigas'', cognate wiktionary:giga-, giga-) are beings of humanoid appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''gia ...
s had brought from Africa to Ireland. They had been raised on Mount Killaraus to form a stone circle, known as the Giant's Ring or Giant's Round. The fifth-century king Aurelius Ambrosius wished to build a great memorial to the British Celtic nobles slain by the Saxons at Salisbury. Merlin advised him to use the Giant's Ring. The king sent Merlin and Uther Pendragon (King Arthur
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Great Britain, Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In Wales, Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a le ...
's father) with 15,000 men to bring it from Ireland. They defeated an Irish army led by Gillomanius, but were unable to move the huge stones. With Merlin's help, they transported the stones to Britain and re-erected them as they had stood. Mount Killaraus may refer to the Hill of Uisneach. Although the tale is fiction, archaeologist Mike Parker Pearson suggests it may hold a "grain of truth" as the Stonehenge bluestones were likely brought from the Waun Mawn stone circle on the Irish Sea coast of Wales.
Another legend tells how the invading Saxon king Hengist invited British Celtic warriors to a feast but treacherously ordered his men to massacre the guests, killing 420 of them. Hengist erected Stonehenge on the site to show his remorse.
Sixteenth century to present
Stonehenge has changed ownership several times since King Henry VIII acquired Amesbury Abbey and its surrounding lands. In 1540 Henry gave the estate to the Earl of Hertford. It subsequently passed to Lord Carleton and then the Marquess of Queensberry. The Antrobus family of Cheshire bought the estate in 1824.
Acquisition for the nation
Stonehenge was one of several lots put up for auction in 1915 by Sir Cosmo Gordon Antrobus, after he inherited the estate from his brother. The auction by Knight Frank & Rutley estate agents in Salisbury was held on 21 September 1915 and included "Lot 15. Stonehenge with about 30 acres, 2 rods, 37 perches 2.44 haof adjoining downland."[
]
Saving the skyline
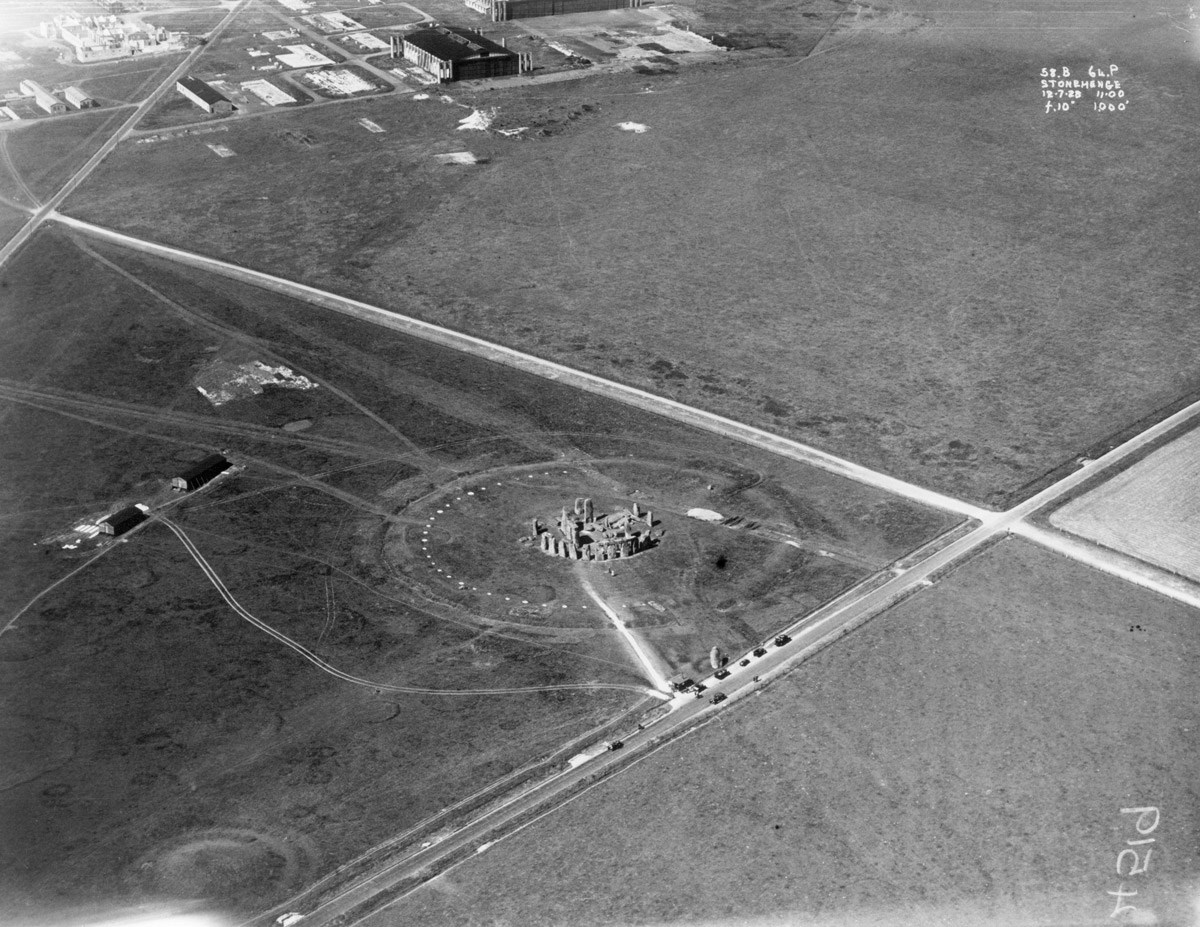 The plot bought by Chubb and gifted to the nation was only in size, and various buildings stood within clear sight of the monument, the most prominent being Stonehenge Aerodrome. Some from the stones, the aerodrome was built during the First World War for the
The plot bought by Chubb and gifted to the nation was only in size, and various buildings stood within clear sight of the monument, the most prominent being Stonehenge Aerodrome. Some from the stones, the aerodrome was built during the First World War for the Royal Flying Corps
The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC sup ...
and its large stone and brick hangars dominated the skyline.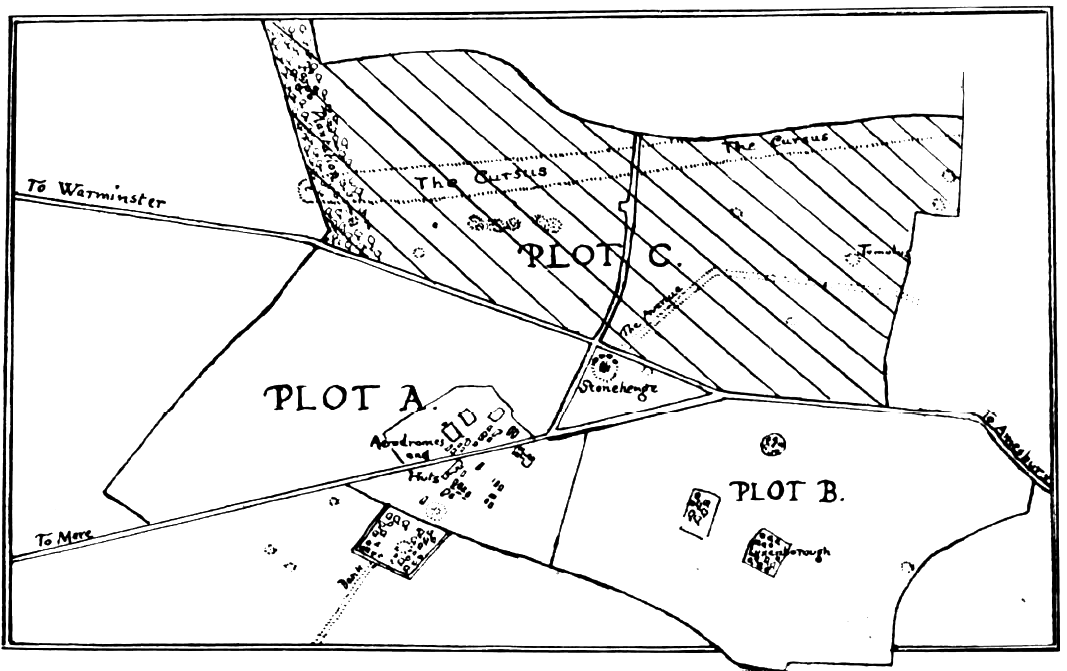 In 1927 the land around Stonehenge was put up for auction in three plots. Plot A lay immediately west of the monument and included the (by now disused) Stonehenge Aerodrome, Plot B was to the south on the other side of the main road, and Plot C on the north side included part of the Stonehenge Cursus.
In 1927 the land around Stonehenge was put up for auction in three plots. Plot A lay immediately west of the monument and included the (by now disused) Stonehenge Aerodrome, Plot B was to the south on the other side of the main road, and Plot C on the north side included part of the Stonehenge Cursus.George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
George w ...
as the lead subscriber, and by October 1927 £8,000 had been raised, which was enough to purchase Plot A and start the demolition of the aerodrome. The fund continued for a number of years to secure the remaining land around the henge for the nation, with fundraising for Plot C continuing through 1929.[
The land was taken into the management of the National Trust to preserve. The last large aircraft hangar was removed in 1930, and by the middle of the 1930s the aerodrome site was cleared.]
Neopaganism
 During the twentieth century, Stonehenge began to revive as a place of religious significance, this time by adherents of Neopaganism and
During the twentieth century, Stonehenge began to revive as a place of religious significance, this time by adherents of Neopaganism and New Age
New Age is a range of Spirituality, spiritual or Religion, religious practices and beliefs that rapidly grew in Western world, Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclecticism, eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise d ...
beliefs, particularly the Neo-druids. The historian Ronald Hutton would later remark that "it was a great, and potentially uncomfortable, irony that modern Druids had arrived at Stonehenge just as archaeologists were evicting the ancient Druids from it." The first such Neo-druidic group to make use of the megalithic monument was the Ancient Order of Druids, who performed a mass initiation ceremony there in August 1905, in which they admitted 259 new members into their organisation. This assembly was largely ridiculed in the press, who mocked the fact that the Neo-druids were dressed up in costumes consisting of white robes and fake beards.
 The earlier rituals were complemented by the Stonehenge Free Festival, loosely organised by the Polytantric Circle, held between 1972 and 1984, during which time the number of midsummer visitors had risen to around 30,000. However, in 1985, the site was closed to festivalgoers by a High Court injunction.
The earlier rituals were complemented by the Stonehenge Free Festival, loosely organised by the Polytantric Circle, held between 1972 and 1984, during which time the number of midsummer visitors had risen to around 30,000. However, in 1985, the site was closed to festivalgoers by a High Court injunction.winter
Winter is the coldest and darkest season of the year in temperate and polar climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Dif ...
and summer solstices, and the vernal and autumnal equinoxes.European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). The court hears applications alleging that a co ...
ruling obtained by campaigners such as Arthur Uther Pendragon, the restrictions were lifted.
Setting and access
 When Stonehenge was first opened to the public it was possible to walk among and even climb on the stones, but the stones were roped off in 1977 as a result of serious erosion. Visitors are no longer permitted to touch the stones but are able to walk around the monument from a short distance away.
When Stonehenge was first opened to the public it was possible to walk among and even climb on the stones, but the stones were roped off in 1977 as a result of serious erosion. Visitors are no longer permitted to touch the stones but are able to walk around the monument from a short distance away. English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
does, however, permit access during the summer and winter solstice, and the spring and autumn equinox. Additionally, visitors can make special bookings to access the stones throughout the year. Approximately 30,000 local residents are entitled to free admission to Stonehenge under an agreement made in 1921.
As motorised traffic increased, the setting of the monument began to be affected by the proximity of the two roads – on the north side the A344 to Shrewton and Devizes which passed within three metres of the Heel Stone, In 2009, the government gave approval for a £25 million scheme to create a smaller visitors' centre and close the A344, although this was dependent on funding and local authority planning consent. In 2010, Wiltshire Council granted planning permission for a centre to the west, and English Heritage confirmed that funds to build it would be available, supported by a £10m grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund. In June 2013, the A344 was closed to begin the work of removing the section of road and replacing it with grass. The centre, designed by Denton Corker Marshall, opened to the public in December 2013.
An announcement in November 2020 stated that a plan to construct a four-lane tunnel to take traffic below the site had been approved. This was intended to eliminate the section of the A303 that runs close to the circle. The plan had received opposition from a group of "archaeologists, environmentalists and modern-day druids" according to '' National Geographic'' but was supported by others who wanted to "restore the landscape to its original setting and improve the experience for visitors". Opponents of the plan were concerned that artifacts that are underground in the area would be lost, or that excavation in the area could de-stabilize the stones, leading to their sinking, shifting or perhaps falling.
In 2009, the government gave approval for a £25 million scheme to create a smaller visitors' centre and close the A344, although this was dependent on funding and local authority planning consent. In 2010, Wiltshire Council granted planning permission for a centre to the west, and English Heritage confirmed that funds to build it would be available, supported by a £10m grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund. In June 2013, the A344 was closed to begin the work of removing the section of road and replacing it with grass. The centre, designed by Denton Corker Marshall, opened to the public in December 2013.
An announcement in November 2020 stated that a plan to construct a four-lane tunnel to take traffic below the site had been approved. This was intended to eliminate the section of the A303 that runs close to the circle. The plan had received opposition from a group of "archaeologists, environmentalists and modern-day druids" according to '' National Geographic'' but was supported by others who wanted to "restore the landscape to its original setting and improve the experience for visitors". Opponents of the plan were concerned that artifacts that are underground in the area would be lost, or that excavation in the area could de-stabilize the stones, leading to their sinking, shifting or perhaps falling.
Vandalism
The site has suffered vandalism intermittently for centuries. Until the 17th century, stones disappeared from the site, to be employed at building sites. In the 19th century, tourists employed chisels to cut rock chips off the megaliths as souvenirs. On 19 June 2024, climate protesters from Just Stop Oil vandalised three of the standing stones by spraying orange cornflour powder paint onto them.
On 19 June 2024, climate protesters from Just Stop Oil vandalised three of the standing stones by spraying orange cornflour powder paint onto them. English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
called the defacement "extremely upsetting" and began an investigation to assess the damage caused by the paint, before removing it with blown air and reporting that there was "no visible damage" to the stones.World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
, a Scheduled Ancient Monument, and a place sacred to many. Conversely, Sarah Kerr, a lecturer in archaeology at University College Cork, noted that the effects of climate change
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an Instrumental temperature record, overall warming trend, Effects of climate change on the ...
pose a much greater threat to Stonehenge and other British heritage sites than Just Stop Oil's protest, which was washed away without causing damage.
In popular culture
See also
Historical context
*
*
*
*
Other monuments in the Stonehenge ritual landscape
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
About Stonehenge and replicas of Stonehenge
*
*
*
*
*
*
Fiction
* ''Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, to ...
'', novel
Similar sites
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Carhenge – replica of Stonehenge near the city of Alliance, Nebraska
*
* Goloring – ancient earthworks near Koblenz, Germany
* – Calendar circle built circa 4900 BC in Germany
*
*
*
* Nabta Playa – Calendar circle built circa 5000 BC in Egypt
*
*
*
Sites with similar sunrise or sunset alignments
*
*
Museums with collections from the World Heritage Site
*
*
Footnotes
References
Sources
* Atkinson, R.J.C., ''Stonehenge'' (Penguin Books, 1956)
* Bender, B, ''Stonehenge: Making Space'' (Berg Publishers, 1998)
* Burl, A., ''Great Stone Circles'' (Yale University Press, 1999)
*
* Aubrey Burl, ''Prehistoric Stone Circles'' (Shire, 2001) (In Burl's ''Stonehenge'' (Constable, 2006), he notes, cf. the meaning of the name in paragraph two above, that "the Saxons called the ring 'the hanging stones', as though they were gibbets.")
*
* Chippindale, C, ''Stonehenge Complete'' (Thames and Hudson, London, 2004)
* Chippindale, C, et al., ''Who owns Stonehenge?'' (B T Batsford Ltd, 1990)
* Cleal, R. M. J., Walker, K. E. & Montague, R., '' Stonehenge in its landscape'' (English Heritage, London, 1995)
* Cunliffe, B., & Renfrew, C, ''Science and Stonehenge'' (The British Academy 92, Oxford University Press, 1997)
* Exon et al., Sally Exon, Vincent Gaffney, Ann Woodward, Ron Yortson, ''Stonehenge Landscapes: Journeys Through Real-and-imagined Worlds'', 2000, Archaeopress,
google books
* Fernie, E.C. (1994). "Stonehenge as Architecture". ''Art History''. 17'' (2): 147–159.
* Godsell, Andrew "Stonehenge: Older Than the Centuries" in "Legends of British History" (2008)
* Hall, R, Leather, K., & Dobson, G., ''Stonehenge Aotearoa'' (Awa Press, 2005)
* Hawley, Lt-Col W, ''The Excavations at Stonehenge.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 1, Oxford University Press, 19–41). 1921.
* Hawley, Lt-Col W., ''Second Report on the Excavations at Stonehenge.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 2, Oxford University Press, 1922)
* Hawley, Lt-Col W., ''Third Report on the Excavations at Stonehenge.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 3, Oxford University Press, 1923)
* Hawley, Lt-Col W, ''Fourth Report on the Excavations at Stonehenge.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 4, Oxford University Press, 1923)
* Hawley, Lt-Col W., ''Report on the Excavations at Stonehenge during the season of 1923.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 5, Oxford University Press, 1925)
* Hawley, Lt-Col W., ''Report on the Excavations at Stonehenge during the season of 1924.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 6, Oxford University Press, 1926)
* Hawley, Lt-Col W., ''Report on the Excavations at Stonehenge during 1925 and 1926.'' (The Antiquaries Journal 8, Oxford University Press, 1928)
* Hutton, R., ''From Universal Bond to Public Free For All'' (British Archaeology 83, 2005)
* Hutton, Ronald, ''Blood and Mistletoe: The History of the Druids in Britain'' (Yale University Press, London, 2009
* John, Brian, "The Bluestone Enigma: Stonehenge, Preseli and the Ice Age" (Greencroft Books, 2008)
* Johnson, Anthony, ''Solving Stonehenge: The New Key to an Ancient Enigma'' (Thames & Hudson, 2008)
* Legg, Rodney, "Stonehenge Antiquaries" (Dorset Publishing Company, 1986)
*
* Mooney, J., ''Encyclopedia of the Bizarre'' (Black Dog & Leventhal Publishers, 2002)
* Newall, R. S., ''Stonehenge, Wiltshire – Ancient monuments and historic buildings'' (Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, 1959)
* North, J., ''Stonehenge: Ritual Origins and Astronomy'' (HarperCollins, 1997)
*
*
* Pearson, M. P.; Marshall, P.; Pollard, J.; Richards, C.; Thomas, J.; Welham, K. (2013). "Stonehenge", in Fokkens, H.; Harding, A. (eds.) ''The Oxford Handbook of the European Bronze Age''. Oxford University Press.
* Pitts, M., ''Hengeworld'' (Arrow, London, 2001)
* Pitts, M. W., "On the Road to Stonehenge: Report on Investigations beside the A344 in 1968, 1979 and 1980" (''Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society'' 48, 1982)
* Richards, J. C., ''English Heritage Book of Stonehenge'' (B T Batsford Ltd, 1991)
* Julian Richards ''Stonehenge: A History in Photographs'' (English Heritage, London, 2004)
*
* Stone, J. F. S., ''Wessex Before the Celts'' (Frederick A Praeger Publishers, 1958)
* Worthington, A., ''Stonehenge: Celebration and Subversion'' (Alternative Albion, 2004)
* English Heritage: ''Stonehenge: Historical Background''
Videography
* Spencer, Christopher (dir.) "Stonehenge decoded", New York City : National Geographic, 2008
External links
Stonehenge
English Heritage official site: access and visiting information; research; future plans
Skyscape- live webfeed
360° panoramic
English Heritage: interactive view from the centre
Stonehenge Landscape
National Trust – information about the surrounding area.
Stonehenge Today and Yesterday
– Frank Stevens (1916), via Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
.
Stonehenge, a Temple Restor'd to the British Druids
– William Stukeley (1740), via Project Gutenberg.
Stonehenge, and Other British Monuments Astronomically Considered
– Norman Lockyer (1906), via Project Gutenberg.
British Archaeology essay about the bluestones as glacial deposits.
Stonehenge: The Lost Circle Revealed
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stonehenge
4th-millennium BC architecture
Archaeological sites in Wiltshire
Bronze Age sites in Wiltshire
Buildings and structures completed in the 26th century BC
English Heritage sites in Wiltshire
Henges in England
History of Wiltshire
Locations associated with Arthurian legend
Places in Celtic mythology
Megalithic monuments in England
National Trust properties in Wiltshire
Ruins in Wiltshire
Scheduled monuments in Wiltshire
Stone Age sites in Wiltshire
Stone circles in Wiltshire
Tourist attractions in Wiltshire
World Heritage Sites in England
Amesbury
Summer solstice
Wiltshire folklore
Vandalized works of art in the United Kingdom
 The ''
The '' Mike Parker Pearson, leader of the Stonehenge Riverside Project based around Durrington Walls, noted that Stonehenge appears to have been associated with burial from the earliest period of its existence:
Stonehenge evolved in several construction phases spanning at least 1500 years. There is evidence of large-scale construction on and around the monument that perhaps extends the landscape's time frame to 6500 years. Dating and understanding the various phases of activity are complicated by disturbance of the natural chalk by periglacial effects and animal burrowing, poor quality early excavation records, and a lack of accurate, scientifically verified dates. The modern phasing most generally agreed to by archaeologists is detailed below. Features mentioned in the text are numbered and shown on the plan, right.
Mike Parker Pearson, leader of the Stonehenge Riverside Project based around Durrington Walls, noted that Stonehenge appears to have been associated with burial from the earliest period of its existence:
Stonehenge evolved in several construction phases spanning at least 1500 years. There is evidence of large-scale construction on and around the monument that perhaps extends the landscape's time frame to 6500 years. Dating and understanding the various phases of activity are complicated by disturbance of the natural chalk by periglacial effects and animal burrowing, poor quality early excavation records, and a lack of accurate, scientifically verified dates. The modern phasing most generally agreed to by archaeologists is detailed below. Features mentioned in the text are numbered and shown on the plan, right.
 The first monument consisted of a circular bank and ditch
The first monument consisted of a circular bank and ditch  Archaeological excavation has indicated that around 2600 BC, the builders abandoned timber in favour of stone and dug two concentric arrays of holes (the Q and R Holes) in the centre of the site. These stone sockets are only partly known (hence on present evidence are sometimes described as forming 'crescents'); however, they could be the remains of a double ring. Again, there is little firm dating evidence for this phase. The holes held up to 80 standing stones (shown blue on the plan), only 43 of which can be traced today. It is generally accepted that the bluestones (some of which are made of dolerite, an igneous rock), were transported by the builders from the Preseli Hills, away in modern-day
Archaeological excavation has indicated that around 2600 BC, the builders abandoned timber in favour of stone and dug two concentric arrays of holes (the Q and R Holes) in the centre of the site. These stone sockets are only partly known (hence on present evidence are sometimes described as forming 'crescents'); however, they could be the remains of a double ring. Again, there is little firm dating evidence for this phase. The holes held up to 80 standing stones (shown blue on the plan), only 43 of which can be traced today. It is generally accepted that the bluestones (some of which are made of dolerite, an igneous rock), were transported by the builders from the Preseli Hills, away in modern-day 
 During the next major phase of activity, 30 enormous
During the next major phase of activity, 30 enormous 

 In July 2020, a study led by David Nash of the University of Brighton concluded that the large sarsen stones were "a direct chemical match" to those found at West Woods near Marlborough, Wiltshire, some 15 miles (25 km) north of Stonehenge. A core sample, originally extracted in 1958, had recently been returned. First the fifty-two sarsens were analysed using methods including x-ray fluorescence spectrometry to determine their chemical composition which revealed they were mostly similar. Then the core was destructively analysed and compared with stone samples from various locations in southern Britain. Fifty of the fifty-two megaliths were found to match sarsens in West Woods, thereby identifying the probable origin of the stones.
During 2017 and 2018, excavations by professor Parker Pearson's team at Waun Mawn, a large stone circle site in the Preseli Hills, suggested that the site had originally housed a diameter stone circle of the same size as Stonehenge's original bluestone circle, also orientated towards the midsummer solstice.
The circle at Waun Mawn also contained a hole from one stone which had a distinctive pentagonal shape, very closely matching the one pentagonal stone at Stonehenge (stonehole 91 at Waun Mawn / stone 62 at Stonehenge). Soil dating of the sediments within the revealed stone holes, via optically stimulated luminescence (OSL), suggested the absent stones at Waun Mawn had been erected around 3400–3200 BC, and removed around 300–400 years later, a date consistent with theories that the same stones were moved and used at Stonehenge, before later being reorganised into their present locations and supplemented with local sarsens as was already understood. Human activity at Waun Mawn ceased around the same time which has suggested that some people may have migrated to Stonehenge. It has also been suggested that stones from other sources may have been added to Stonehenge, perhaps from other dismantled circles in the region.
Further work in 2021 by Parker Pearson's team concluded that the Waun Mawn circle had never been completed, and of the stones which might once have stood at the site, no more than 13 had been removed in antiquity.
In February 2021, archaeologists announced the discovery of "vast troves of Neolithic and Bronze Age artifacts" while conducting excavations for the proposed highway tunnel near Stonehenge. The find included Bronze Age graves, late neolithic pottery and C-shaped enclosure on the intended site of the Stonehenge road tunnel. Remains also contained a shale object in one of the graves, burnt flint in C-shaped enclosure and the final resting place of a baby.
In January 2022, archaeologists announced the discovery of thousands of prehistoric pits during an electromagnetic induction
In July 2020, a study led by David Nash of the University of Brighton concluded that the large sarsen stones were "a direct chemical match" to those found at West Woods near Marlborough, Wiltshire, some 15 miles (25 km) north of Stonehenge. A core sample, originally extracted in 1958, had recently been returned. First the fifty-two sarsens were analysed using methods including x-ray fluorescence spectrometry to determine their chemical composition which revealed they were mostly similar. Then the core was destructively analysed and compared with stone samples from various locations in southern Britain. Fifty of the fifty-two megaliths were found to match sarsens in West Woods, thereby identifying the probable origin of the stones.
During 2017 and 2018, excavations by professor Parker Pearson's team at Waun Mawn, a large stone circle site in the Preseli Hills, suggested that the site had originally housed a diameter stone circle of the same size as Stonehenge's original bluestone circle, also orientated towards the midsummer solstice.
The circle at Waun Mawn also contained a hole from one stone which had a distinctive pentagonal shape, very closely matching the one pentagonal stone at Stonehenge (stonehole 91 at Waun Mawn / stone 62 at Stonehenge). Soil dating of the sediments within the revealed stone holes, via optically stimulated luminescence (OSL), suggested the absent stones at Waun Mawn had been erected around 3400–3200 BC, and removed around 300–400 years later, a date consistent with theories that the same stones were moved and used at Stonehenge, before later being reorganised into their present locations and supplemented with local sarsens as was already understood. Human activity at Waun Mawn ceased around the same time which has suggested that some people may have migrated to Stonehenge. It has also been suggested that stones from other sources may have been added to Stonehenge, perhaps from other dismantled circles in the region.
Further work in 2021 by Parker Pearson's team concluded that the Waun Mawn circle had never been completed, and of the stones which might once have stood at the site, no more than 13 had been removed in antiquity.
In February 2021, archaeologists announced the discovery of "vast troves of Neolithic and Bronze Age artifacts" while conducting excavations for the proposed highway tunnel near Stonehenge. The find included Bronze Age graves, late neolithic pottery and C-shaped enclosure on the intended site of the Stonehenge road tunnel. Remains also contained a shale object in one of the graves, burnt flint in C-shaped enclosure and the final resting place of a baby.
In January 2022, archaeologists announced the discovery of thousands of prehistoric pits during an electromagnetic induction  The twelfth-century ''
The twelfth-century '' The plot bought by Chubb and gifted to the nation was only in size, and various buildings stood within clear sight of the monument, the most prominent being Stonehenge Aerodrome. Some from the stones, the aerodrome was built during the First World War for the
The plot bought by Chubb and gifted to the nation was only in size, and various buildings stood within clear sight of the monument, the most prominent being Stonehenge Aerodrome. Some from the stones, the aerodrome was built during the First World War for the  In 1927 the land around Stonehenge was put up for auction in three plots. Plot A lay immediately west of the monument and included the (by now disused) Stonehenge Aerodrome, Plot B was to the south on the other side of the main road, and Plot C on the north side included part of the Stonehenge Cursus.
There was interest from developers, and in August 1927 a subscription fund was launched in order to "save the skyline" of the monument. The subscription made rapid progress, with
In 1927 the land around Stonehenge was put up for auction in three plots. Plot A lay immediately west of the monument and included the (by now disused) Stonehenge Aerodrome, Plot B was to the south on the other side of the main road, and Plot C on the north side included part of the Stonehenge Cursus.
There was interest from developers, and in August 1927 a subscription fund was launched in order to "save the skyline" of the monument. The subscription made rapid progress, with  During the twentieth century, Stonehenge began to revive as a place of religious significance, this time by adherents of Neopaganism and
During the twentieth century, Stonehenge began to revive as a place of religious significance, this time by adherents of Neopaganism and  The earlier rituals were complemented by the Stonehenge Free Festival, loosely organised by the Polytantric Circle, held between 1972 and 1984, during which time the number of midsummer visitors had risen to around 30,000. However, in 1985, the site was closed to festivalgoers by a High Court injunction. A consequence of the end of the festival in 1985 was the violent confrontation between the police and New Age travellers that became known as the Battle of the Beanfield, when police blockaded a convoy of travellers to prevent them from approaching Stonehenge. Beginning in 1985, the year of the confrontation, no access was allowed into the stones at Stonehenge for any religious reason. This "exclusion-zone" policy continued for almost fifteen years: until just before the arrival of the twenty-first century, visitors were not allowed to go into the stones at times of religious significance, the
The earlier rituals were complemented by the Stonehenge Free Festival, loosely organised by the Polytantric Circle, held between 1972 and 1984, during which time the number of midsummer visitors had risen to around 30,000. However, in 1985, the site was closed to festivalgoers by a High Court injunction. A consequence of the end of the festival in 1985 was the violent confrontation between the police and New Age travellers that became known as the Battle of the Beanfield, when police blockaded a convoy of travellers to prevent them from approaching Stonehenge. Beginning in 1985, the year of the confrontation, no access was allowed into the stones at Stonehenge for any religious reason. This "exclusion-zone" policy continued for almost fifteen years: until just before the arrival of the twenty-first century, visitors were not allowed to go into the stones at times of religious significance, the  When Stonehenge was first opened to the public it was possible to walk among and even climb on the stones, but the stones were roped off in 1977 as a result of serious erosion. Visitors are no longer permitted to touch the stones but are able to walk around the monument from a short distance away.
When Stonehenge was first opened to the public it was possible to walk among and even climb on the stones, but the stones were roped off in 1977 as a result of serious erosion. Visitors are no longer permitted to touch the stones but are able to walk around the monument from a short distance away.  In 2009, the government gave approval for a £25 million scheme to create a smaller visitors' centre and close the A344, although this was dependent on funding and local authority planning consent. In 2010, Wiltshire Council granted planning permission for a centre to the west, and English Heritage confirmed that funds to build it would be available, supported by a £10m grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund. In June 2013, the A344 was closed to begin the work of removing the section of road and replacing it with grass. The centre, designed by Denton Corker Marshall, opened to the public in December 2013.
An announcement in November 2020 stated that a plan to construct a four-lane tunnel to take traffic below the site had been approved. This was intended to eliminate the section of the A303 that runs close to the circle. The plan had received opposition from a group of "archaeologists, environmentalists and modern-day druids" according to '' National Geographic'' but was supported by others who wanted to "restore the landscape to its original setting and improve the experience for visitors". Opponents of the plan were concerned that artifacts that are underground in the area would be lost, or that excavation in the area could de-stabilize the stones, leading to their sinking, shifting or perhaps falling. In July 2023, the Department for Transport announced that, despite the original planning application having been overturned by the High Court in 2021, the Transport Secretary, Mark Harper, had approved plans for a road tunnel. In February 2024, the High Court in London rejected a fresh bid by campaigners to stop construction of the road tunnel. A further legal challenge was made in the High Court in July 2024. Although this action was dismissed by the High Court in October 2024, the incoming Labour government had already announced in July that the tunnel would 'not move forward'.
In March 2025, English Heritage announced that planning permission had been granted for two buildings to be constructed near the visitor facilities: a 'Learning Centre' to the east of the shuttle bus turning circle and a 'Neolithic classroom' near the existing recreated Neolithic village. These are due to open in the autumn of 2026.
In 2009, the government gave approval for a £25 million scheme to create a smaller visitors' centre and close the A344, although this was dependent on funding and local authority planning consent. In 2010, Wiltshire Council granted planning permission for a centre to the west, and English Heritage confirmed that funds to build it would be available, supported by a £10m grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund. In June 2013, the A344 was closed to begin the work of removing the section of road and replacing it with grass. The centre, designed by Denton Corker Marshall, opened to the public in December 2013.
An announcement in November 2020 stated that a plan to construct a four-lane tunnel to take traffic below the site had been approved. This was intended to eliminate the section of the A303 that runs close to the circle. The plan had received opposition from a group of "archaeologists, environmentalists and modern-day druids" according to '' National Geographic'' but was supported by others who wanted to "restore the landscape to its original setting and improve the experience for visitors". Opponents of the plan were concerned that artifacts that are underground in the area would be lost, or that excavation in the area could de-stabilize the stones, leading to their sinking, shifting or perhaps falling. In July 2023, the Department for Transport announced that, despite the original planning application having been overturned by the High Court in 2021, the Transport Secretary, Mark Harper, had approved plans for a road tunnel. In February 2024, the High Court in London rejected a fresh bid by campaigners to stop construction of the road tunnel. A further legal challenge was made in the High Court in July 2024. Although this action was dismissed by the High Court in October 2024, the incoming Labour government had already announced in July that the tunnel would 'not move forward'.
In March 2025, English Heritage announced that planning permission had been granted for two buildings to be constructed near the visitor facilities: a 'Learning Centre' to the east of the shuttle bus turning circle and a 'Neolithic classroom' near the existing recreated Neolithic village. These are due to open in the autumn of 2026.
 On 19 June 2024, climate protesters from Just Stop Oil vandalised three of the standing stones by spraying orange cornflour powder paint onto them.
On 19 June 2024, climate protesters from Just Stop Oil vandalised three of the standing stones by spraying orange cornflour powder paint onto them.