|
Aurelius Ambrosius
Ambrosius Aurelianus (; Anglicised as Ambrose Aurelian and called Aurelius Ambrosius in the ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' and elsewhere) was a war leader of the Romano-British who won an important battle against the Anglo-Saxons in the 5th century, according to Gildas. He also appeared independently in the legends of the Britons, beginning with the 9th-century ''Historia Brittonum''. Eventually, he was transformed by Geoffrey of Monmouth into the uncle of King Arthur, the brother of Arthur's father Uther Pendragon, as a ruler who precedes and predeceases them both. He also appears as a young prophet who meets the tyrant Vortigern; in this guise, he was later transformed into the wizard Merlin. According to Gildas Ambrosius Aurelianus is one of the few people whom Gildas identifies by name in his sermon ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', and the only one named from the 5th century. ''De Excidio'' is considered the oldest extant British document about the so-called Arthuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Kings (f
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on Primary source, primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrician (Ancient Rome)
The patricians (from ) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom and the early Roman Republic, Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 BC). By the time of the late Republic and Roman Empire, Empire, membership in the patriciate was of only nominal significance. The social structure of ancient Rome revolved around the distinction between the patricians and the plebeians. The status of patricians gave them more political power than the plebeians, but the relationship between the groups eventually caused the Conflict of the Orders. This time period resulted in changing of the social structure of ancient Rome. After the Western Roman Empire, Western Empire fell, the term "patrician" continued as a high Byzantine aristocracy and bureaucracy, honorary title in the Eastern Empire. In many Italian city-states, medieval Italian republics, especially in Republic of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrians
The Illyrians (, ; ) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Ancient Greece, Greeks. The territory the Illyrians inhabited came to be known as Illyria to later Greek and Roman Republic, Roman authors, who identified a territory that corresponds to most of Albania, Montenegro, Kosovo, much of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, western and central Serbia and some parts of Slovenia between the Adriatic Sea in the west, the Drava river in the north, the Great Morava, Morava river in the east and the Ceraunian Mountains in the south. The first account of Illyrian people dates back to the 6th century BC, in the works of the ancient Greek writer Hecataeus of Miletus. The name "Illyrians", as applied by the ancient Greeks to their northern neighbors, may have referred to a broad, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratian (usurper)
Gratian or Gratianus (died c. February 407) was a Roman usurper in Roman Britain from 406 to 407. Career After the murder of the usurper Marcus, Gratian was proclaimed emperor by the army in Britain in late 406, probably around October. His background, as recorded by Orosius, was that of a Romano-Briton and member of the urban aristocracy, possibly a '' curialis''. The promotion of a non-military official by the army suggests that there were issues that the army felt would be better handled by a civilian official, such as pay, or perhaps disagreements between the '' Comes Britanniarum'', the '' Comes Litoris Saxonici'' and the '' Dux Britanniarum''.Anthony Birley disagreed with the assumption that Gratian held a civilian position, arguing that Orosius only meant that he was a native of Britain, and that Gratian was therefore still one of the higher officers of the British army, either a ''Comes'' or a ''Dux''. Gratian's usurpation coincided with a major barbarian invasion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus (usurper)
Marcus (d. 406) was a Roman usurper who was proclaimed Emperor of Roman Britain. He was killed later that same year in a subsequent mutiny. Career Marcus was a high-ranking soldier in Roman Britain who was proclaimed emperor by the local army sometime in 406, possibly during the summer. Possibly one of the army commanders in Britain ('' Comes Britanniarum'', '' Comes Litoris Saxonici'' or '' Dux Britanniarum''), he may have risen to power in response to increasing raids from abroad at a time when the Empire was withdrawing troops from its far-flung provinces, such as Britain, to protect its heartland. While the historian J. B. Bury has suggested that the revolt of the British legions in 406 was primarily directed against Stilicho, the ''magister militum'' of the Emperor Honorius, the ancient sources (Olympiodorus of Thebes, Zosimus and Orosius) generally link the revolt to the barbarian incursions into Gaul and Italy, especially the Vandal and Alanic tribes crossing the Rhine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alex Woolf
Alex Woolf (born 12 July 1963) is a British medieval historian and academic. He specialises in the history of Britain and Ireland and to a lesser extent Scandinavia in the Early Middle Ages, with a particular emphasis on interaction and comparison across traditional ethnic boundaries. He is a senior lecturer at the University of St Andrews. He is author of volume two in the ''New Edinburgh History of Scotland'', covering the period between 789 and 1070. For this he won the 2008 Saltire Society award for "history book of the year". He is the younger brother of the ancient historian Greg Woolf. Education Woolf first went to University to study Scandinavian Studies at University College London, including spending time in Norway, but dropped out before completing the degree and spent four years working in service-sector jobs. He then proceeded to the University of Sheffield, where he completed a degree in Medieval History and Medieval English.Jack Davey,InFocus: Dr Alex Woolf, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentia (Roman Britain)
Valentia (Latin for "Land of Valens") was probably one of the Roman provinces of the Diocese of "the Britains" in late Antiquity. Its position, capital, and even existence remain a matter of scholarly debate. It was not mentioned in the Verona List compiled around AD 312 and so was probably formed out of one or more of the other provinces established during the Diocletian Reforms. Some scholars propose Valentia was a new name for the entire diocese, but the List of Offices names it as a consular-rank province along with Maxima Caesariensis and the other equestrian-ranked provinces. Hypotheses for the placement of Valentia include Wales, with its capital at Deva (Chester); Cumbria south of Hadrian's Wall, with its capital at Luguvalium (Carlisle),S.S. Frere, ''Britannia: a history of Roman Britain'' (3rd edn, Guild Publishing, London 1987), 200. the lands between the Antonine Wall and Hadrian's Wall, possibly with a capital at Habitancum ( Risingham),, although the latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxima Caesariensis
Maxima Caesariensis (Latin for "The Caesarian province of Maximus"), also known as Britannia Maxima, was one of the provinces of the Diocese of " the Britains" created during the Diocletian Reforms at the end of the 3rd century. It was probably created after the defeat of the usurper Allectus by Constantius Chlorus in AD 296 and was mentioned in the Verona List of the Roman provinces. Its position and capital remain uncertain, although it was probably adjacent to Flavia Caesariensis. On the basis of its governor's eventual consular rank, it is now usually considered to have consisted of Augusta or Londinium (London) and southeastern England. __NOTOC__ History Following the Roman conquest of Britain, Britain was administered as a single province from Camulodunum (Colchester) and then Londinium (London) until the Severan Reforms following the revolt of its governor Clodius Albinus. These divided the territory into Upper and Lower Britain (''Britannia Superior'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
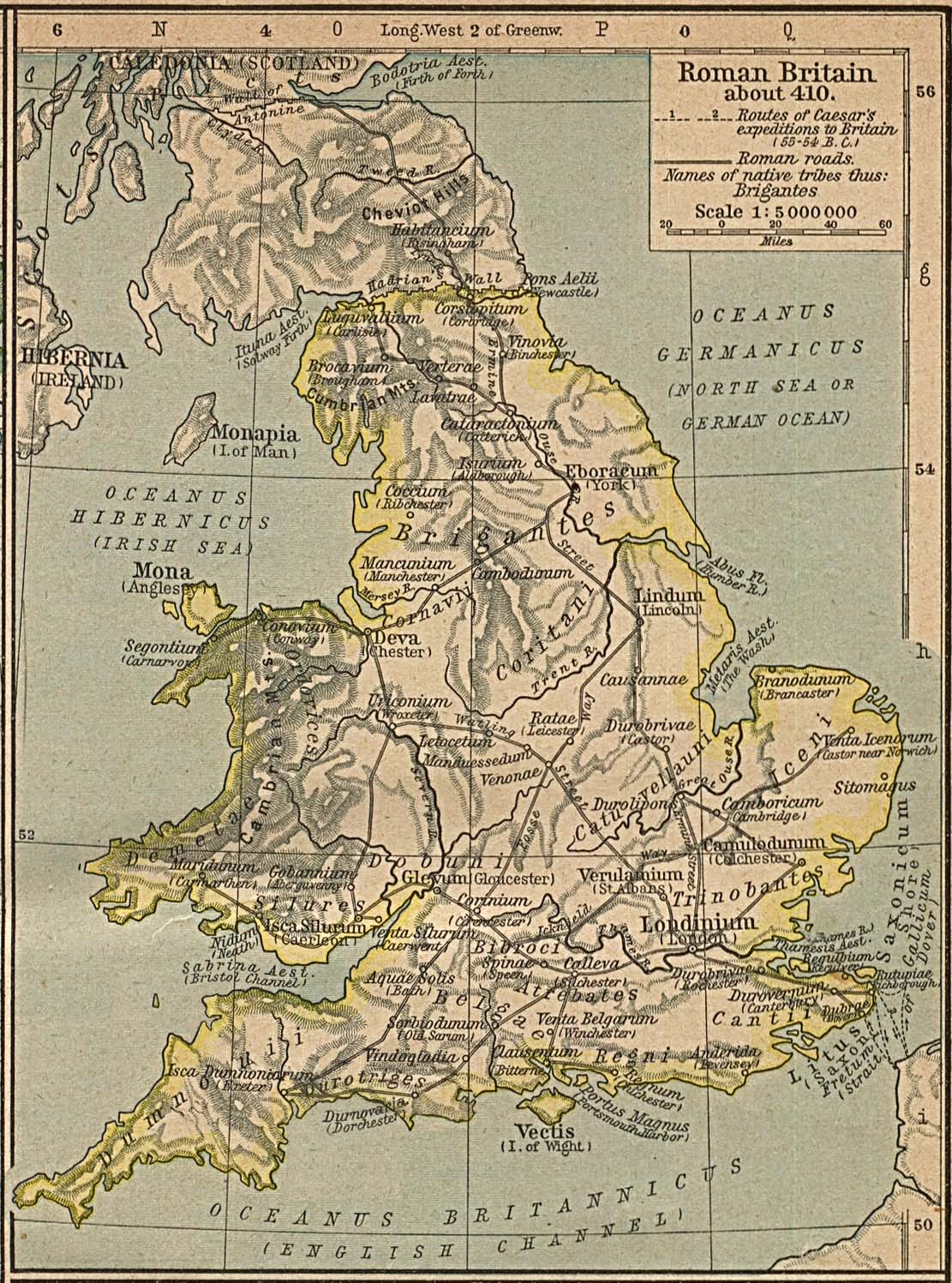
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notitia Dignitatum
The (Latin for 'List of all dignities and administrations both civil and military') is a document of the Late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very few surviving documents of Roman government, and describes several thousand offices from the imperial court to provincial governments, diplomatic missions, and army units. It is usually considered to be accurate for the Western Roman Empire in the 420s AD and for the Eastern or Byzantine Empire in the 390s AD. However, the text itself is not dated (nor is its author named), and omissions complicate ascertaining its date from its content. Copies of the manuscript There are several extant 15th- and 16th-century copies of the document, plus a colour-illuminated iteration of 1542. All the known, extant copies are derived, either directly or indirectly, from ''Codex Spirensis'', a codex known to have existed in the library of the Chapter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the Roman censor, censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding ''fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its Roman provinces, provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former King of Rome, kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |