|
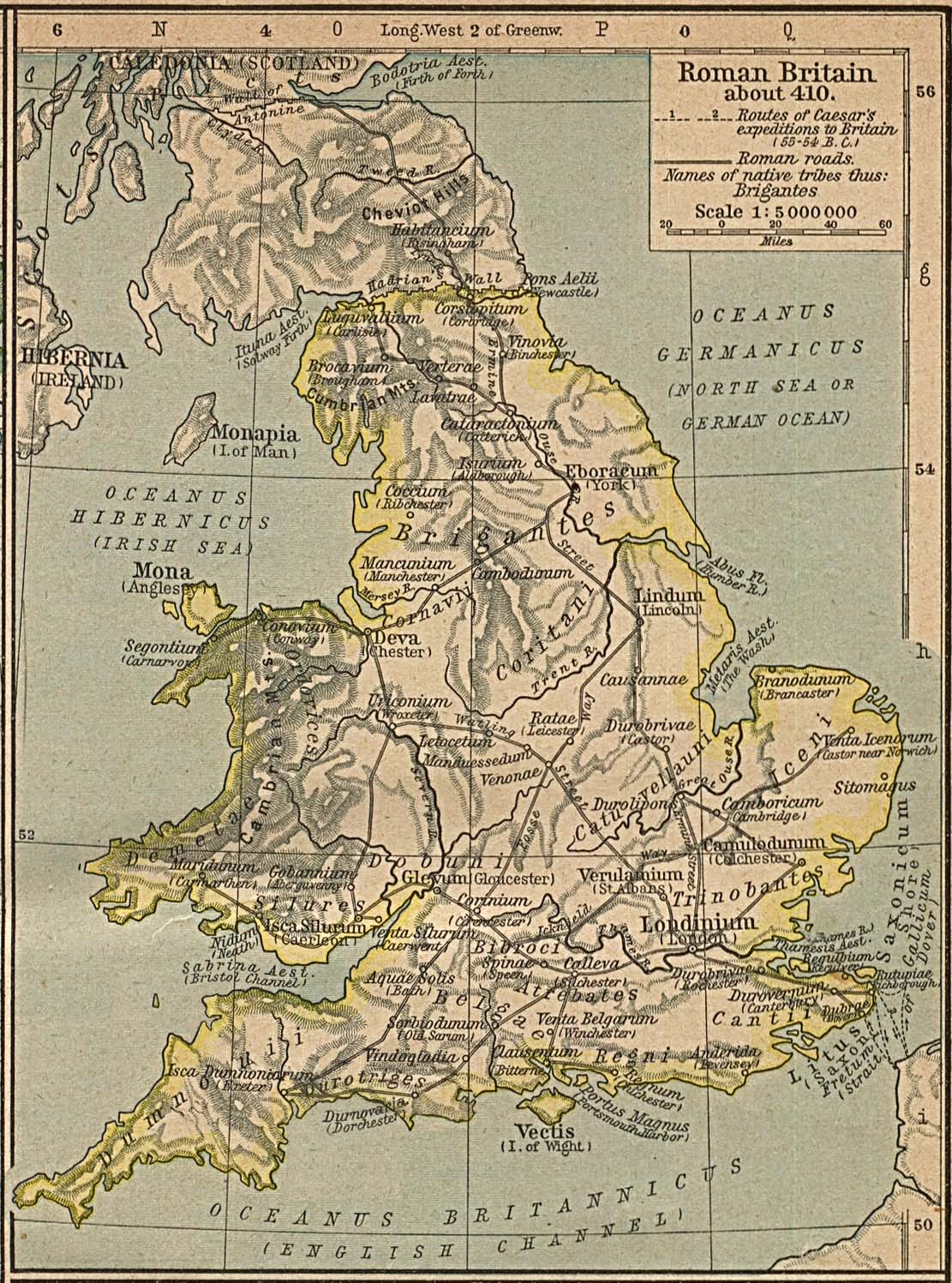
Valentia (Roman Britain)
Valentia (Latin for "Land of Valens") was probably one of the Roman provinces of the Diocese of "the Britains" in late Antiquity. Its position, capital, and even existence remain a matter of scholarly debate. It was not mentioned in the Verona List compiled around AD 312 and so was probably formed out of one or more of the other provinces established during the Diocletian Reforms. Some scholars propose Valentia was a new name for the entire diocese, but the List of Offices names it as a consular-rank province along with Maxima Caesariensis and the other equestrian-ranked provinces. Hypotheses for the placement of Valentia include Wales, with its capital at Deva (Chester); Cumbria south of Hadrian's Wall, with its capital at Luguvalium (Carlisle),S.S. Frere, ''Britannia: a history of Roman Britain'' (3rd edn, Guild Publishing, London 1987), 200. the lands between the Antonine Wall and Hadrian's Wall, possibly with a capital at Habitancum ( Risingham),, although the latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittain 410
Brittain may refer to: * Brittain, West Virginia, United States * Brittain, Ohio, United States * Brittain Creek, a stream in North Carolina * Brittain Dining Hall * Brittain Speaker, a Leslie speaker#History, historical name for the Leslie speaker People * Brittain (surname) * Brittain Alexander, Member group Insight 23 * Brittain Ashford, American actress * Brittain Brown (born 1997), American professional football player * Brittain Gottlieb (born 2003), American professional soccer player See also * Brittian, a Hettinger County, North Dakota#Townships, township in Hettinger County, North Dakota * Britain (other) * Britten (other) * Brittin {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Running from Wallsend on the River Tyne in the east to Bowness-on-Solway in the west of what is now northern England, it was a stone wall with large ditches in front and behind, stretching across the whole width of the island. Soldiers were garrisoned along the line of the wall in large Castra, forts, smaller milecastles, and intervening Turret (Hadrian's Wall), turrets. In addition to the wall's defensive military role, its gates may have been customs posts. Hadrian's Wall Path generally runs close along the wall. Almost all the standing masonry of the wall was removed in early modern times and used for local roads and farmhouses. None of it stands to its original height, but modern work has exposed much of the footings, and some segments d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It included the modern regions western Hungary, western Slovakia, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia, and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. Background In the Early Iron Age, Transdanubia was inhabited by the Pannonians or Pannonii, a collection of Illyrians, Illyrian tribes. The Celts invaded in the Late Iron Age and Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman historian Pompeius Trogus writes that the Celts were met with heavy resistance from the locals and were not able to overrun the southern part of Transdanubia. Some tribes advanced as far as Delphi, with the Scordisci settling in Syrmia (279 BC) upon being forced to withdraw. The arrival of the Celts in Transdanubia disrupted the flow of amber from the Balti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). Written in Latin and known as the '' Res gestae'', his work chronicled the history of Rome from the accession of Emperor Nerva in 96 to the death of Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Only the sections covering the period 353 to 378 survive. Biography Ammianus was born in the East Mediterranean, possibly in Syria or Phoenicia, around 330, into a noble family of Greek origin. Since he calls himself ''Graecus'' ( Greek), he was most likely born in a Greek-speaking area of the empire. His native language was Greek, but he also knew Latin. The surviving books of his history cover the years 353 to 378. Ammianus began his career as a military officer in the Praetorian Guard, where he gained firsthand exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aethicus Ister
Aethicus Ister (Aethicus Donares, Aethicus of Istria or Aethicus Ister) was the protagonist of the 7th/8th-century ''Cosmographia'', purportedly written by a man of church Hieronymus (Jerome, but not the Church Father Jerome), who purportedly censors an even older work for producing the book as its censored version. It is a forgery from the Middle Ages. It describes the travels of Aethicus around the world, and includes descriptions of foreign peoples in usually less than favourable terms. It displays a flat Earth cosmology, maybe for making sport of it. There are also numerous passages which deal directly with the legends of Alexander the Great. Heinz Löwe (1913–1991) found a striking correspondence between and the Old Turkic script. He considers Aethicus to be of late Avar ethnicity from the Carpathian basin. Aethicus is believed by Franz Brunhölzl to have been a Scythian that lived in the region of present day Dobrogea, Romania.Franz Brunhölzl: Zur Kosmographie des Aethicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
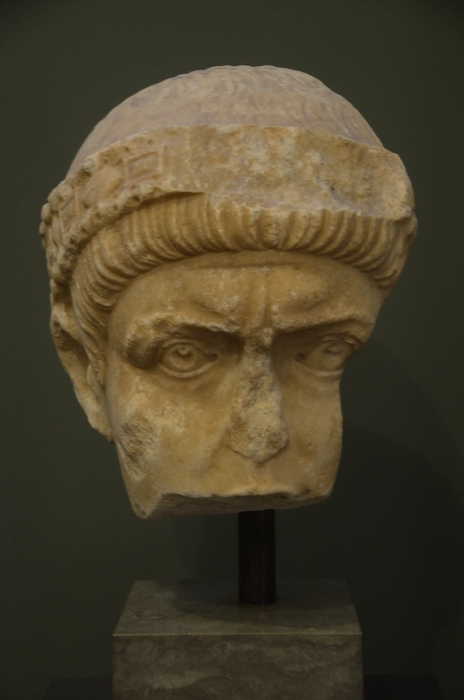
Valentinian I
Valentinian I (; 32117 November 375), also known as Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. He ruled the Western Roman Empire, Western half of the empire, while his brother Valens ruled the Byzantine Empire, East. During his reign, he fought successfully against the Alamanni, Quadi, and Sarmatians, strengthening the border fortifications and conducting campaigns across the Rhine and Danube. His general Count Theodosius, Theodosius defeated a revolt in Africa (Roman province), Africa and the Great Conspiracy, a coordinated assault on Roman Britain by Picts, Scoti, and Saxons. Valentinian founded the Valentinian dynasty, with his sons Gratian and Valentinian II succeeding him in the western half of the empire. Early life Valentinian was born in 321 at Cibalae (now Vinkovci, Croatia) in southern Pannonia into a family of Illyro-Roman origin. Valentinian and his younger brother Valens were the sons of Gratianus Funarius, Gratianus (nicknamed Funarius), a military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain - AD 400
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible *Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risingham
Habitancum was an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Risingham, Northumberland, England. The fort was one of series of built along the extension of Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose, in Scotland. The fort's name is derived from the word ''Habitanci'' inscribed on an altar set up by Marcus Gavius Secundinus, a consular beneficiary on duty there. It is not mentioned in other sources such as the ''Notitia Dignitatum''. Location The fort is situated north of Corbridge ('' Coria'') and south of Rochester (''Bremenium''), the next Roman forts on Dere Street. The fort occupies a low mound overlooking the River Rede. It is about 9 miles north of Hadrian's Wall History The fort was built in the early Antonine period c. 138 AD when the frontier was re-established further north on the Antonine Wall. It was destroyed in c. 197 AD but was rebuilt under Septimius Severus by the First Cohort of Vangiones (nominally one thousand stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |